Thẻ ghi nhớ: Motor Neurons (focus on nervous system organization) | Quizlet
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
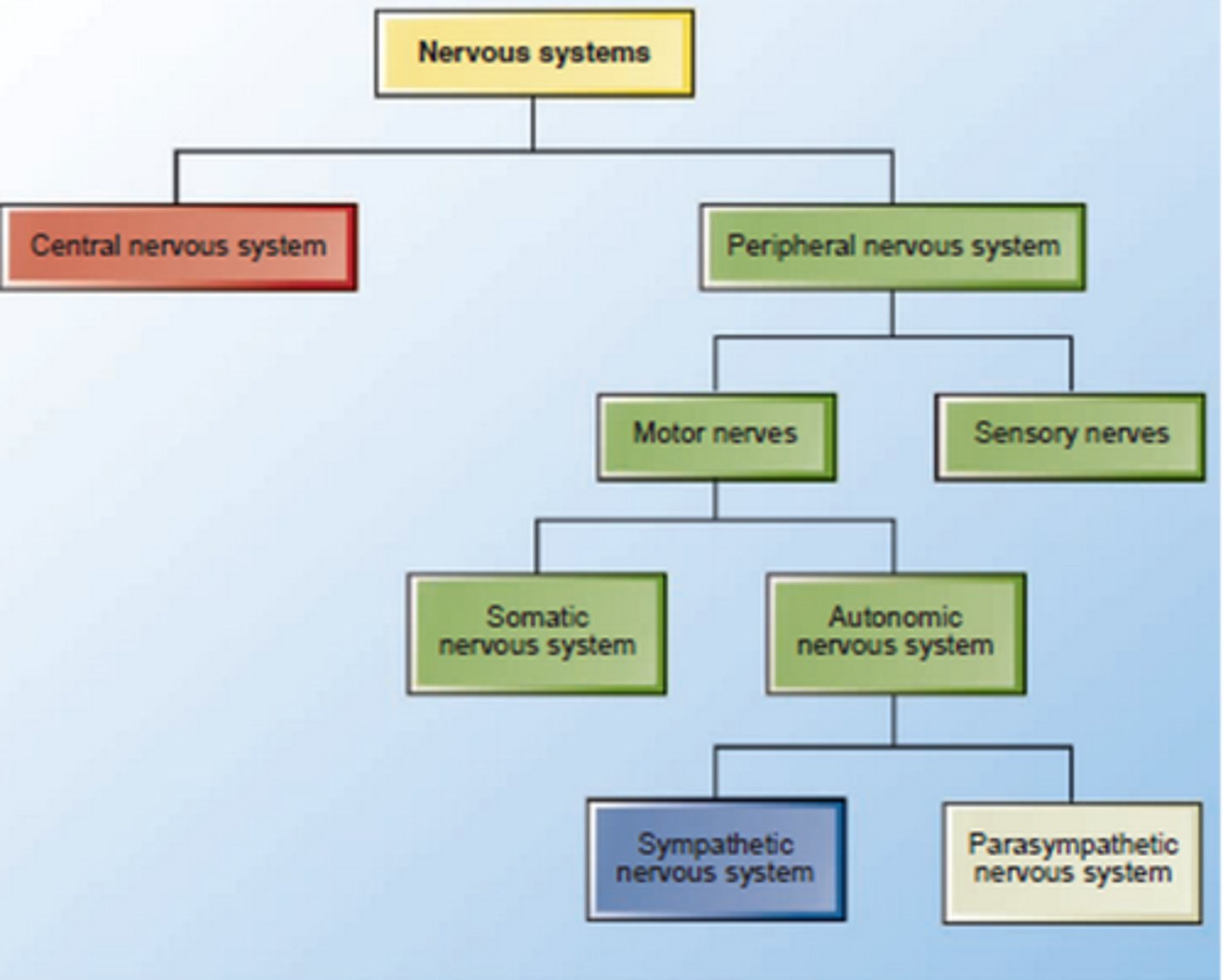
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain and spinal cord
Integration and command center
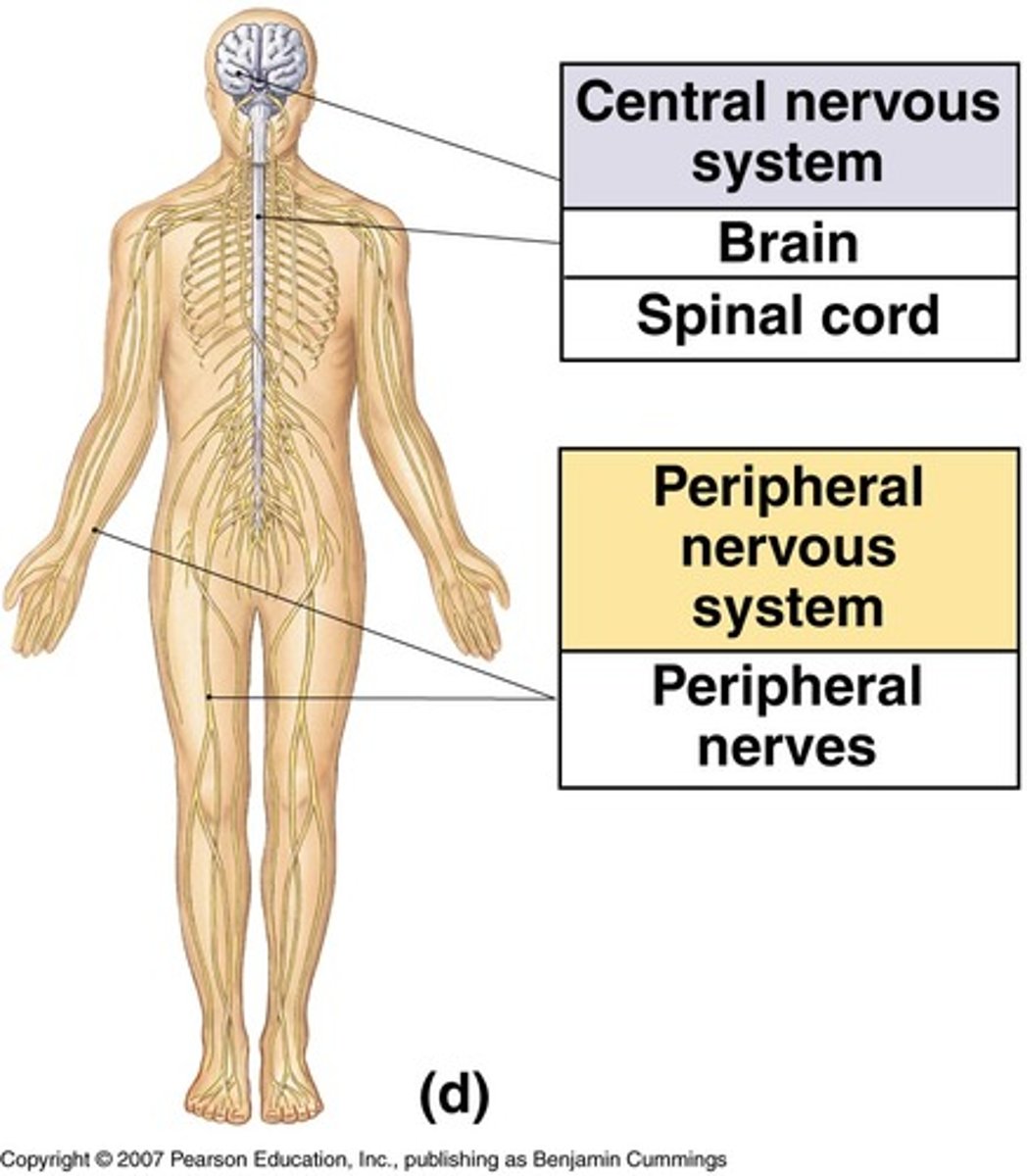
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
the sensory and motor neurons (found in cranial nerves and spinal nerves) that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves that carry impulses to and from the spinal cord
motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands
somatic motor neuron
Neuron that stimulates contraction of skeletal muscles (voluntary muscles)
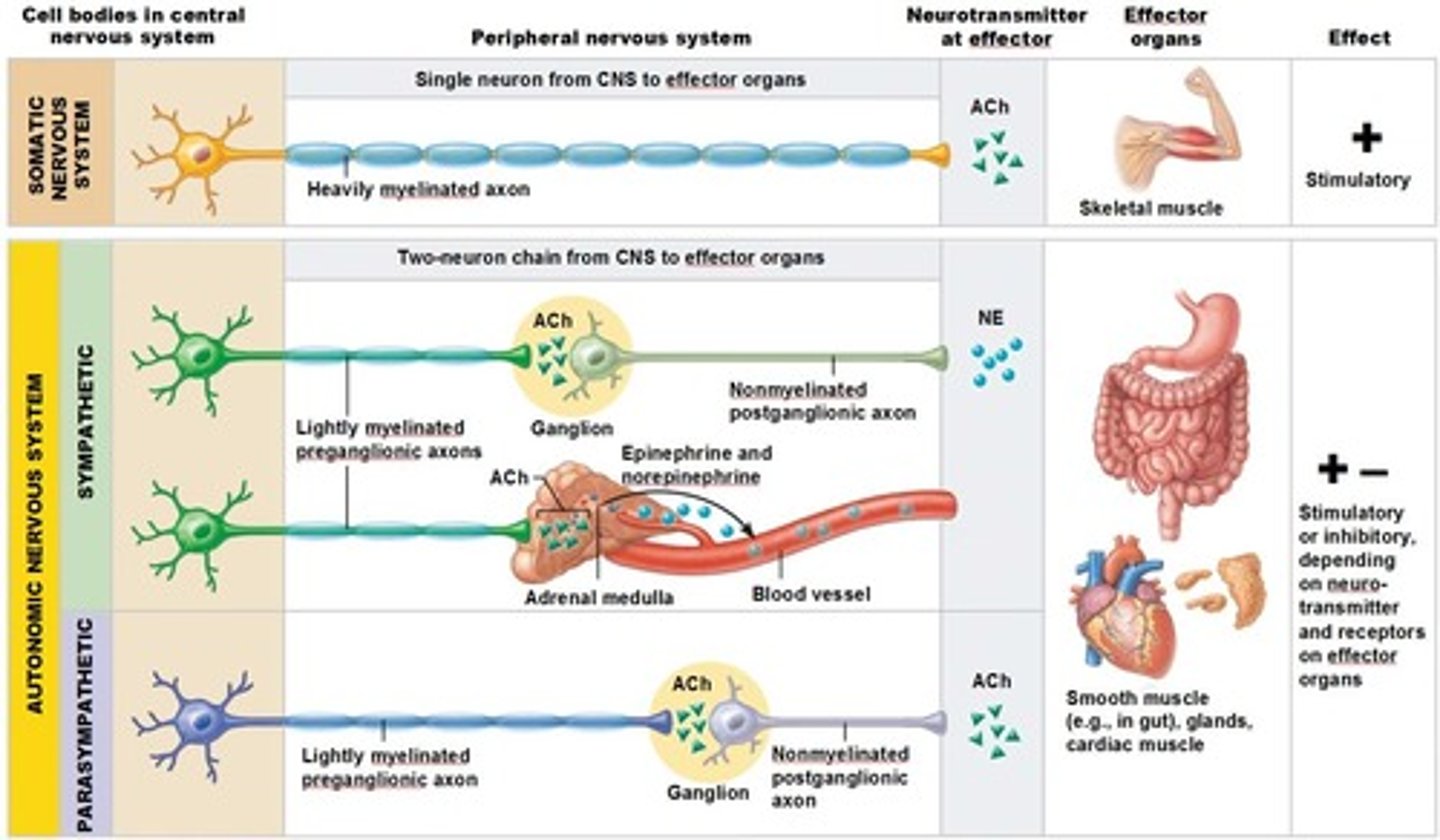
Acetylcholine in the PNS
*Stimulates skeletal muscle contraction at neuromuscular junctions.
*Mediates parasympathetic effects in the autonomic nervous system
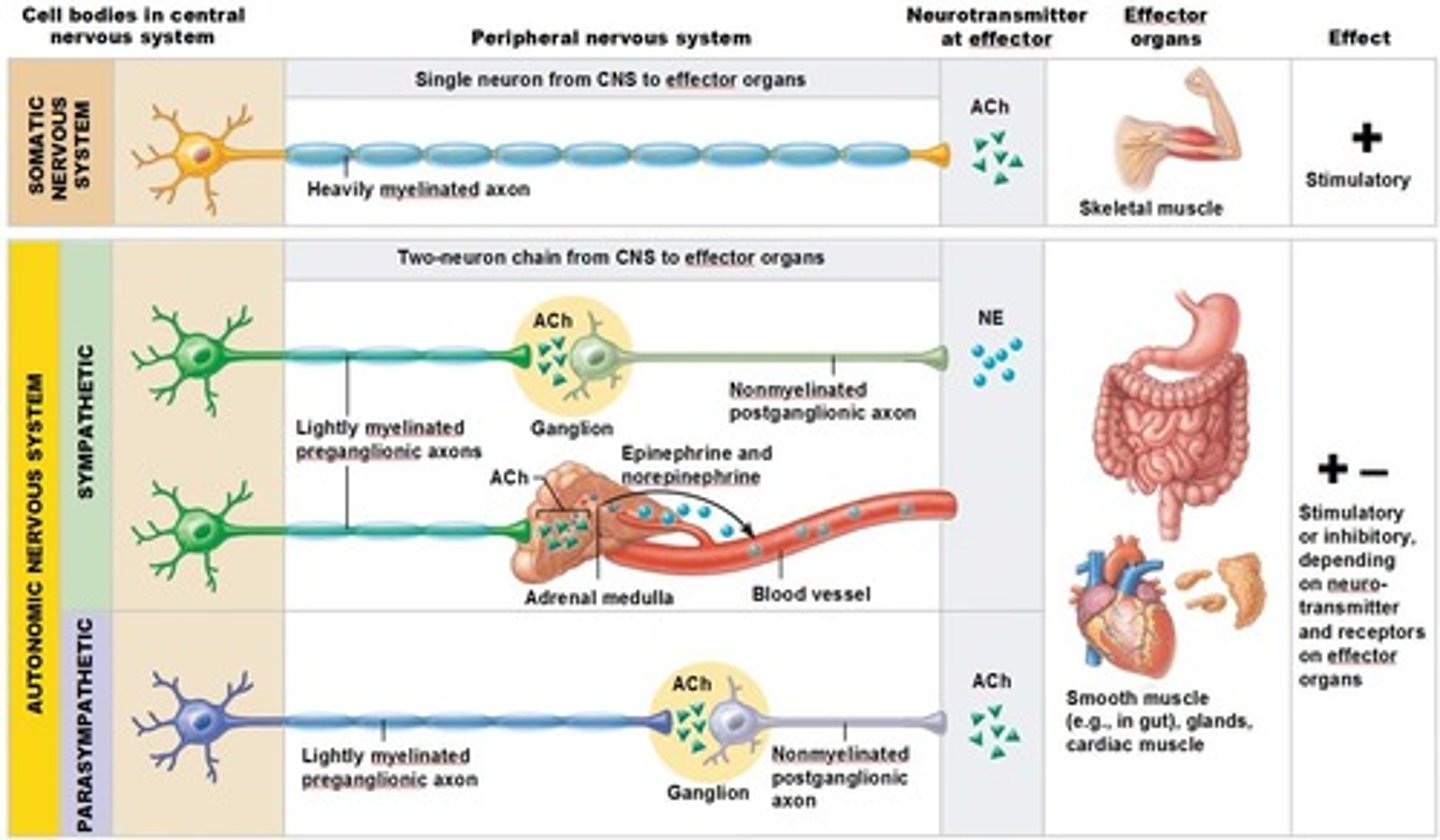
NE in the PNS
*mediates sympathetic effects in the autonomic nervous system
Autonomic neuron myelination
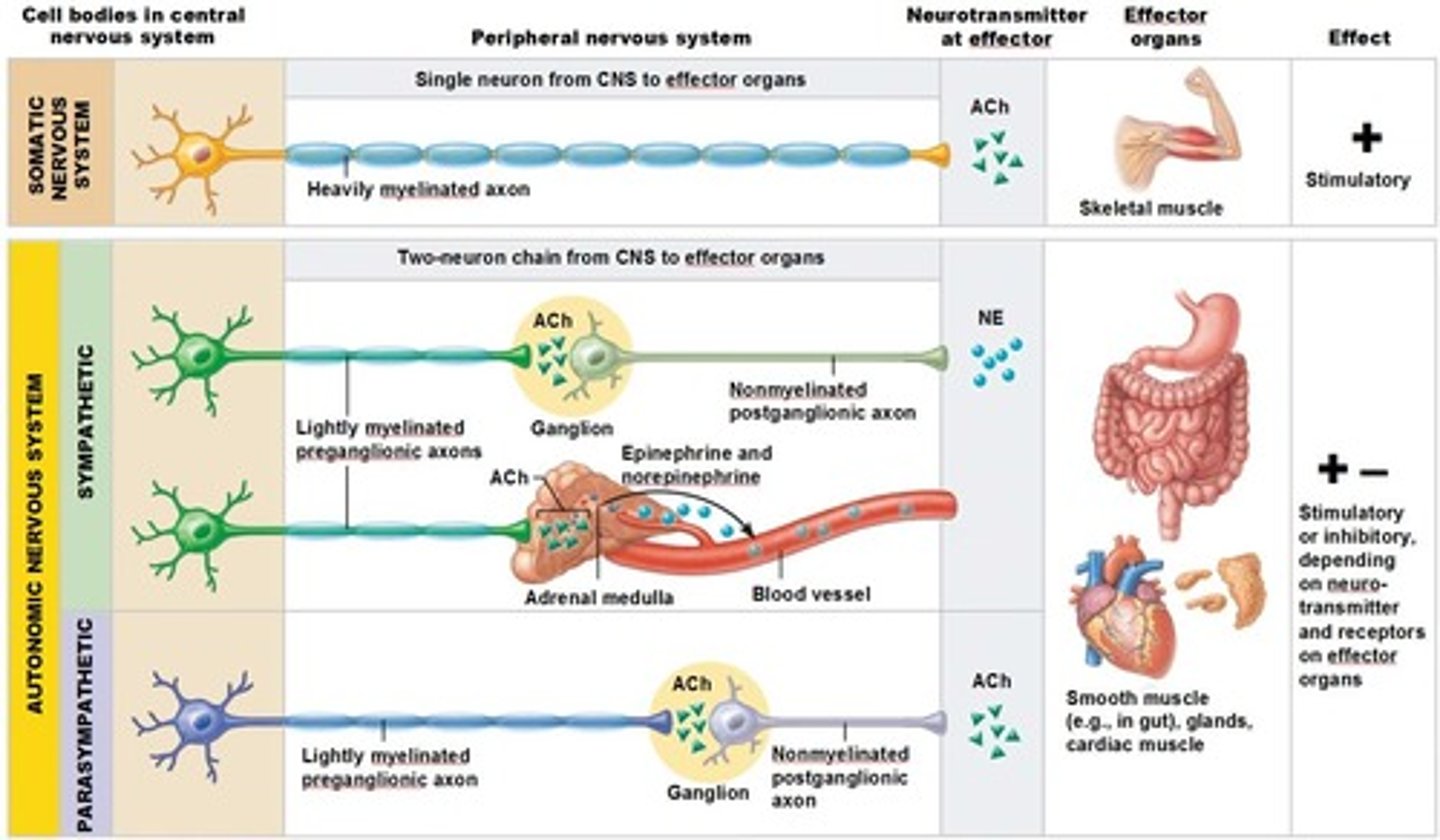
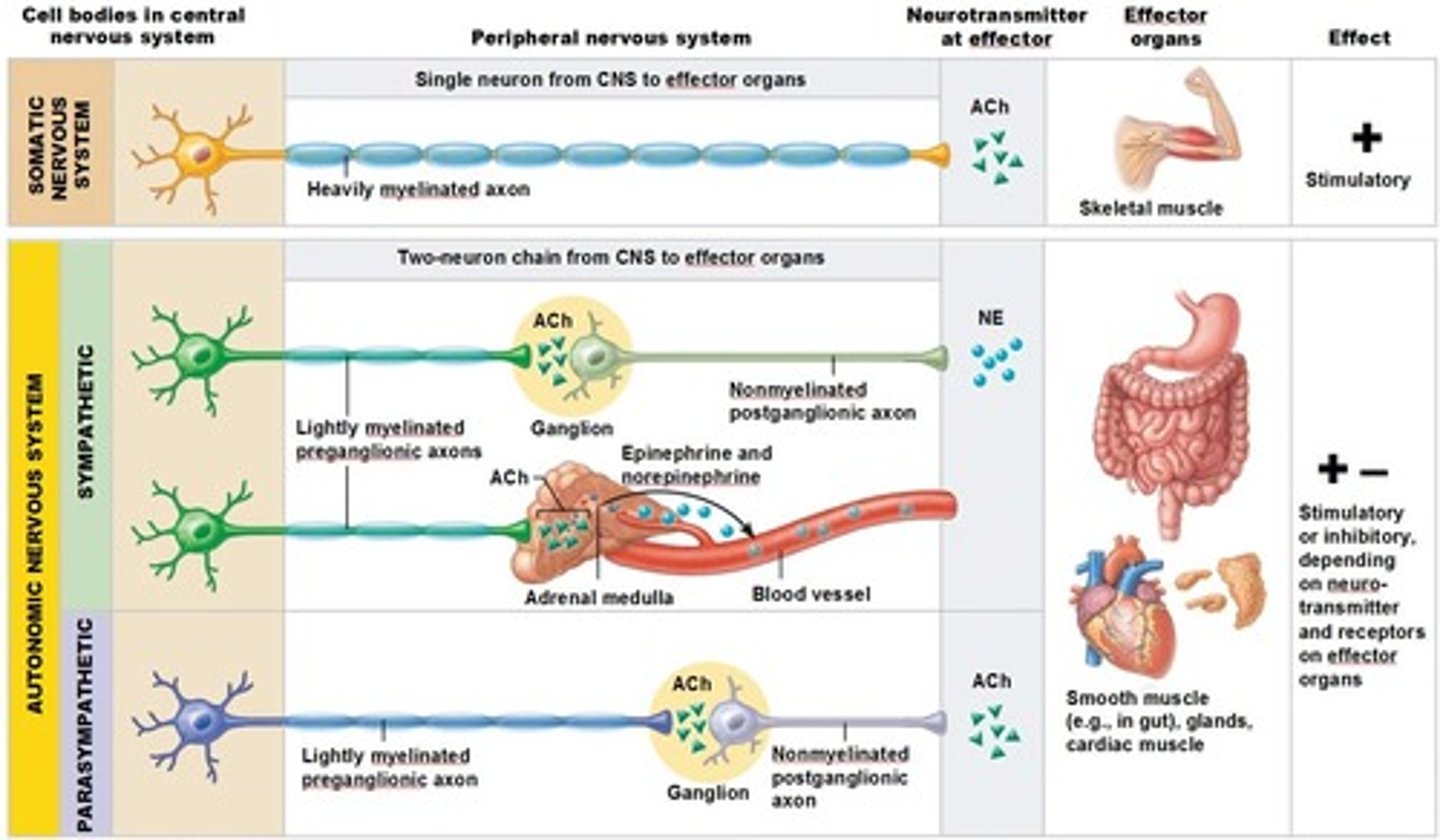
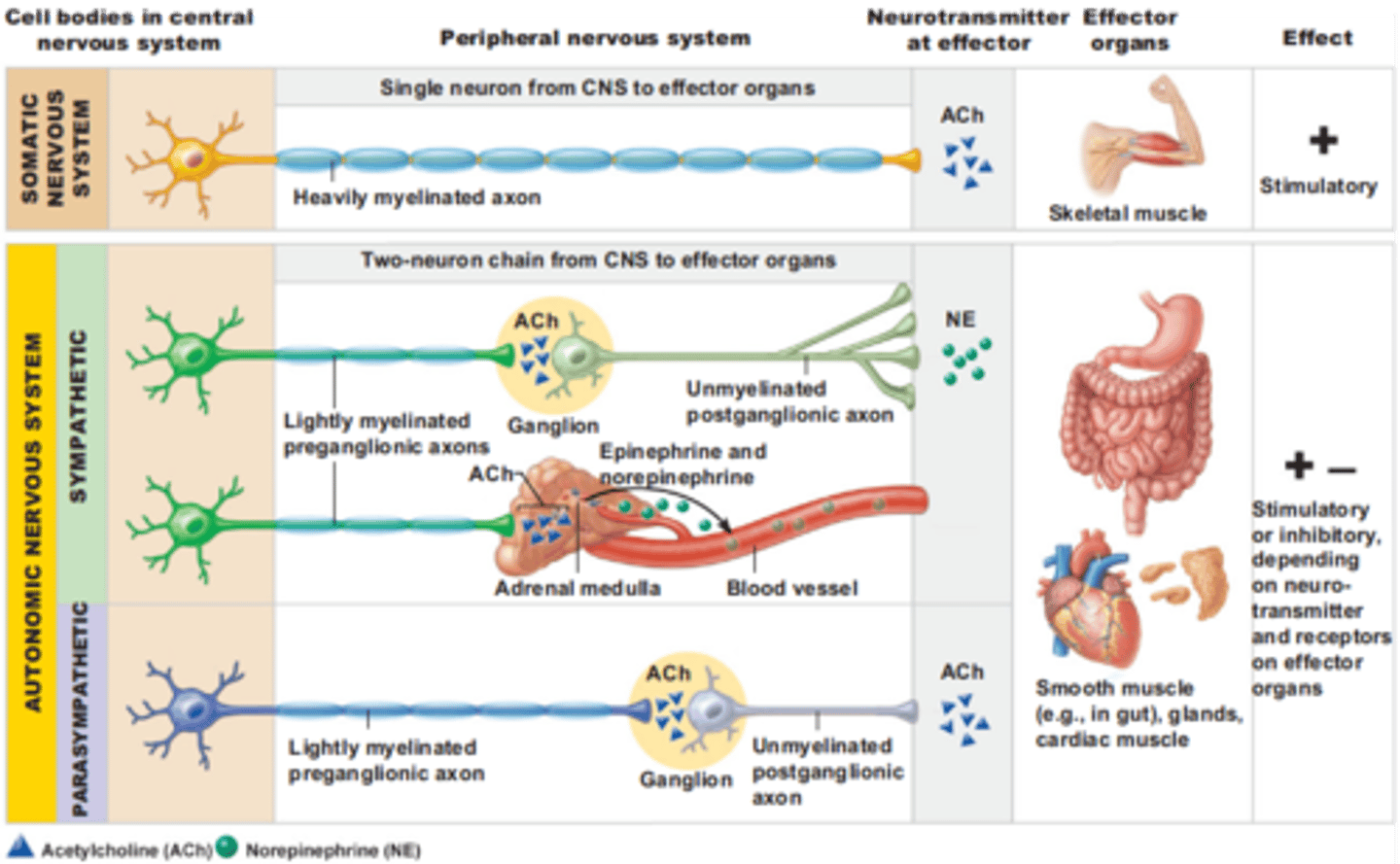
generally these type of motor neurons have limited myelination and don't send signals as fast
Somatic motor neuron myelination
Generally these types of neurons are heavily myelinated and travel extremely fast
Somatic Motor Neurons Neurotransmitter
ACh - released onto these voluntary muscle targets
Picture A here
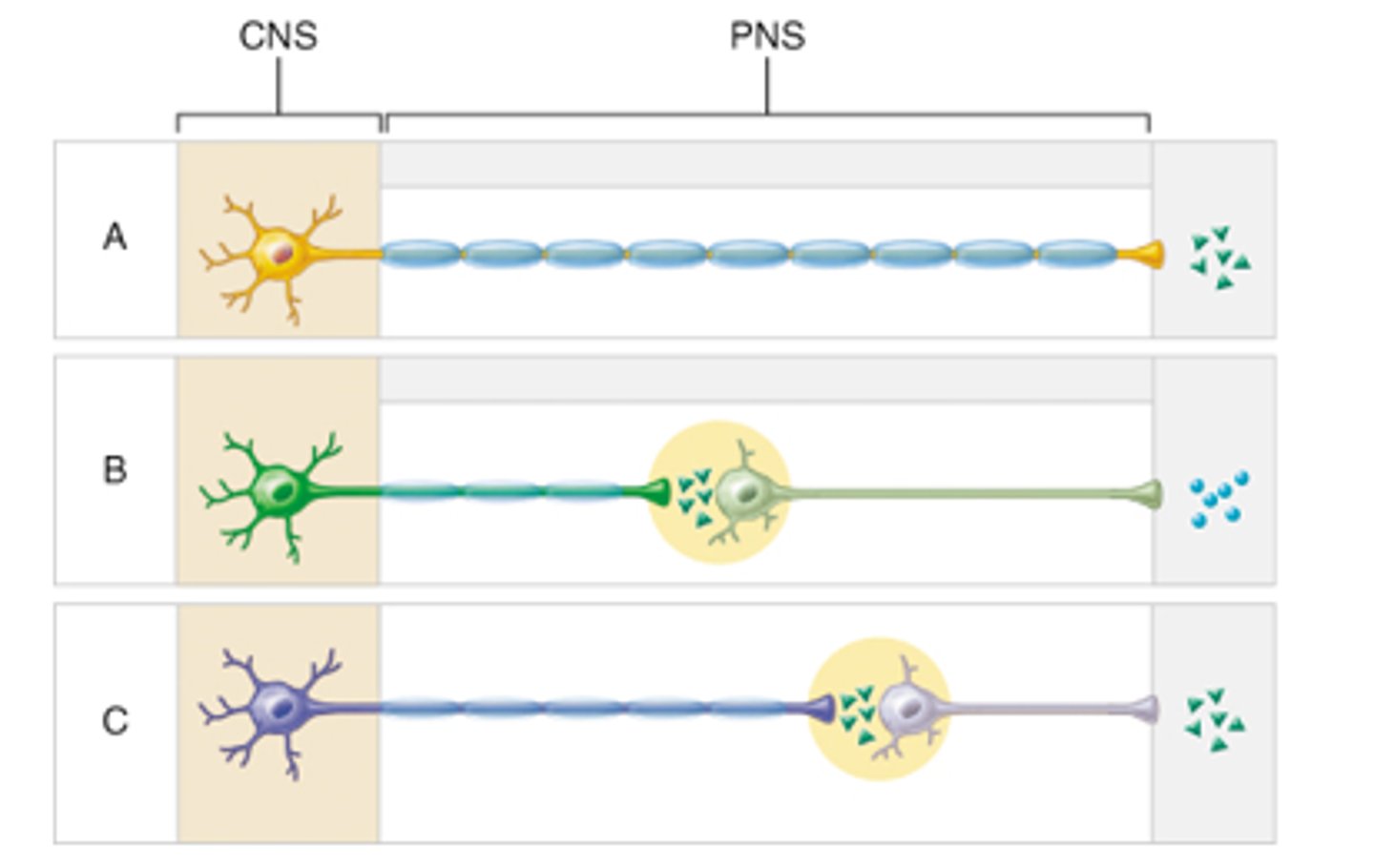
Sympathetic Neurons Neurotransmitter
NE - released on these autonomic targets
Parasympathetic Neurons Neurotransmitter
ACh - released onto these autonomic targets
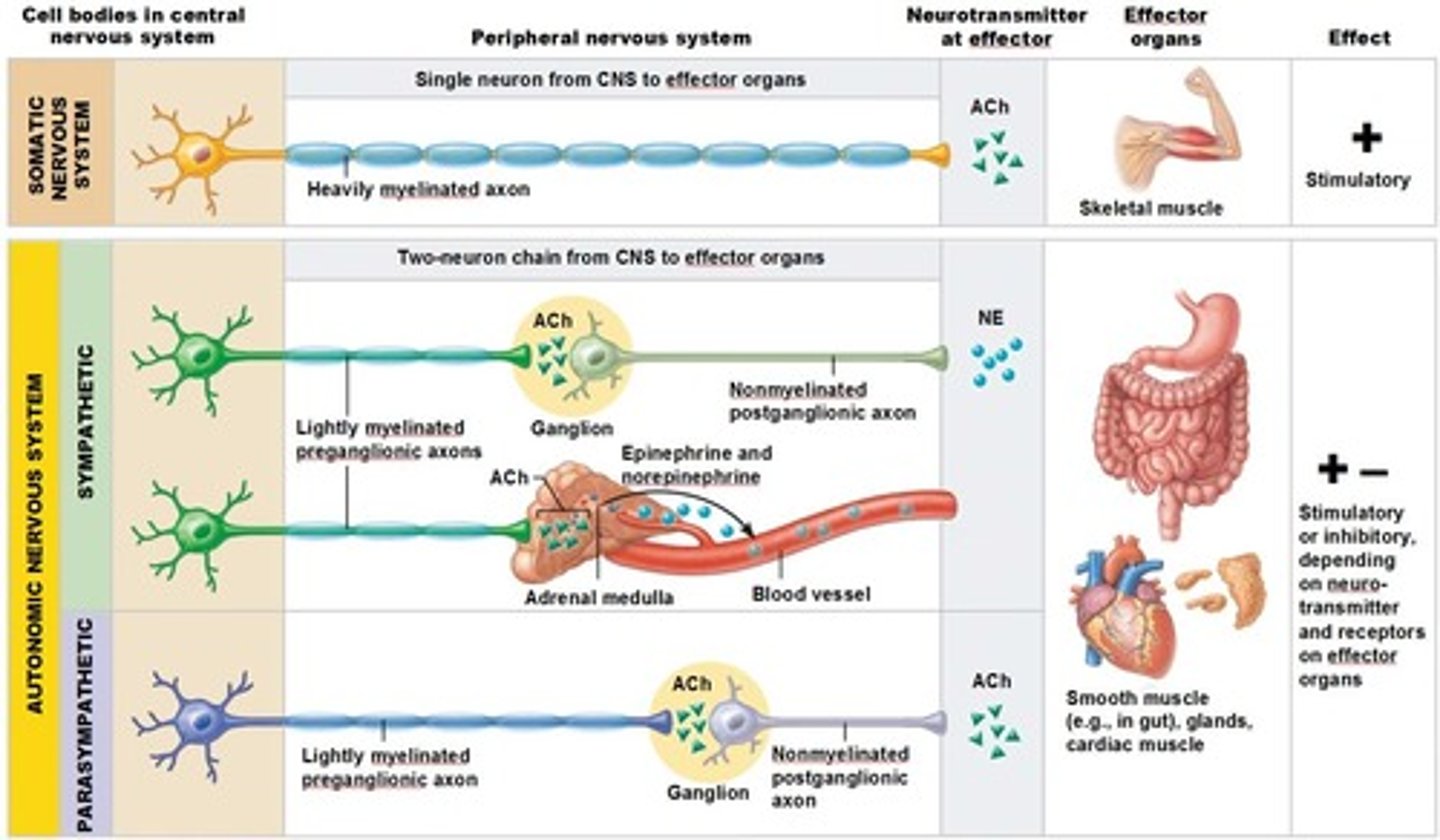
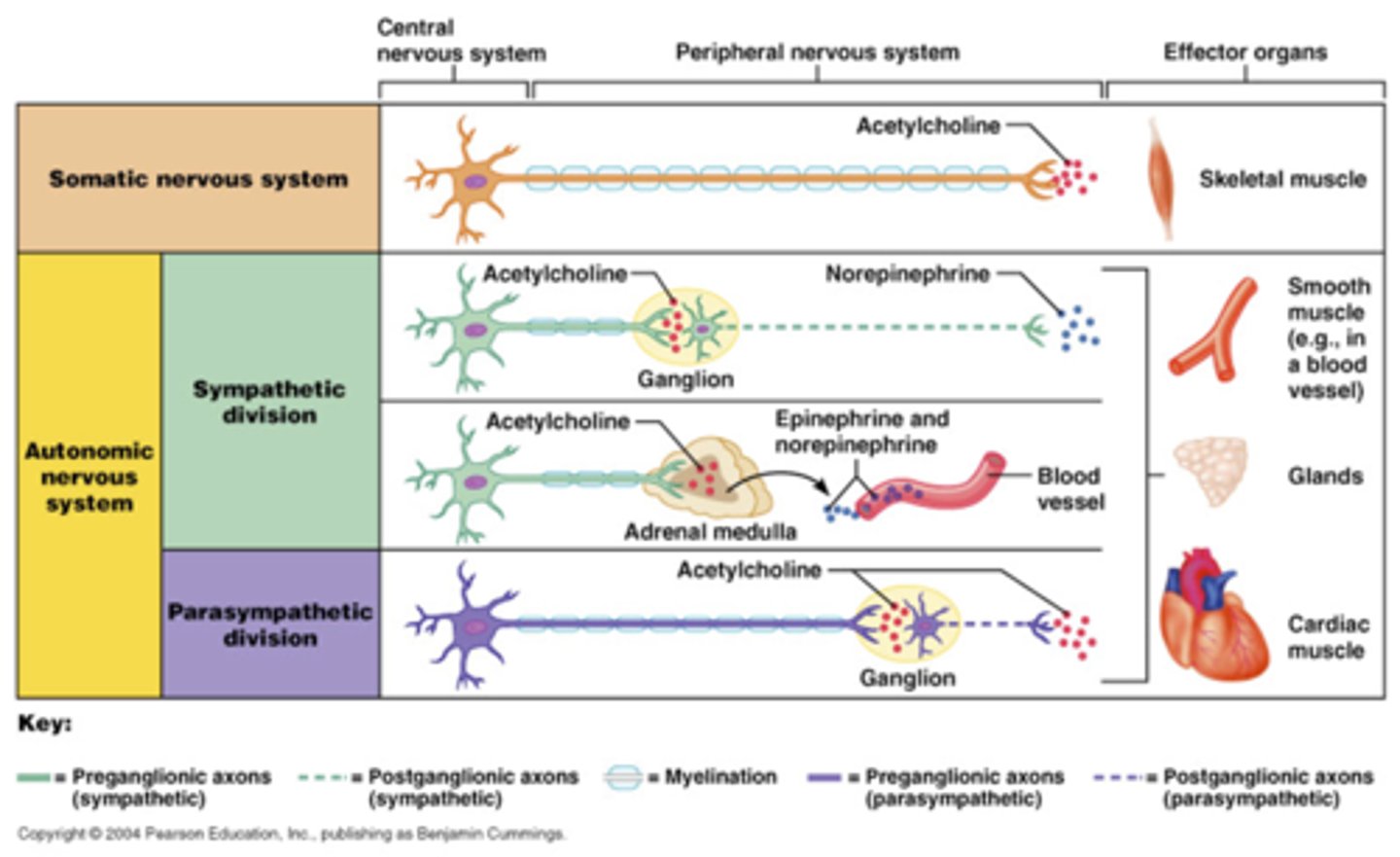
Autonomic targets include
cardiac muscle
smooth muscle - around blood vessels, glands, GI organs, bladder, etc
The PNS has these two divisions
sensory (afferent)
motor (efferent)
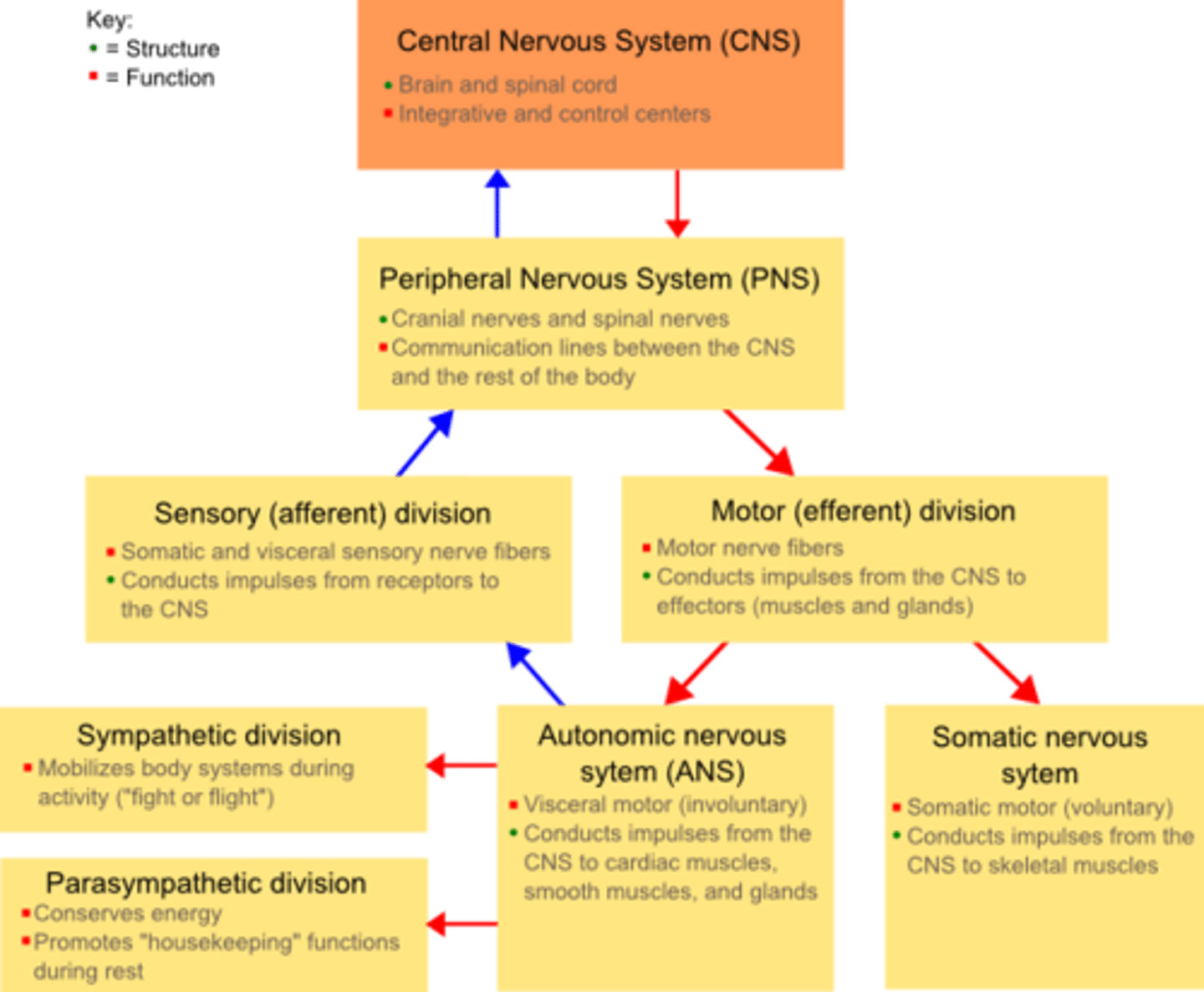
The motor division of the PNS has these 2 branches
voluntary (somatic) - skeletal muscles
involuntary (autonomic) - cardiac muscle, smooth muscles and glands
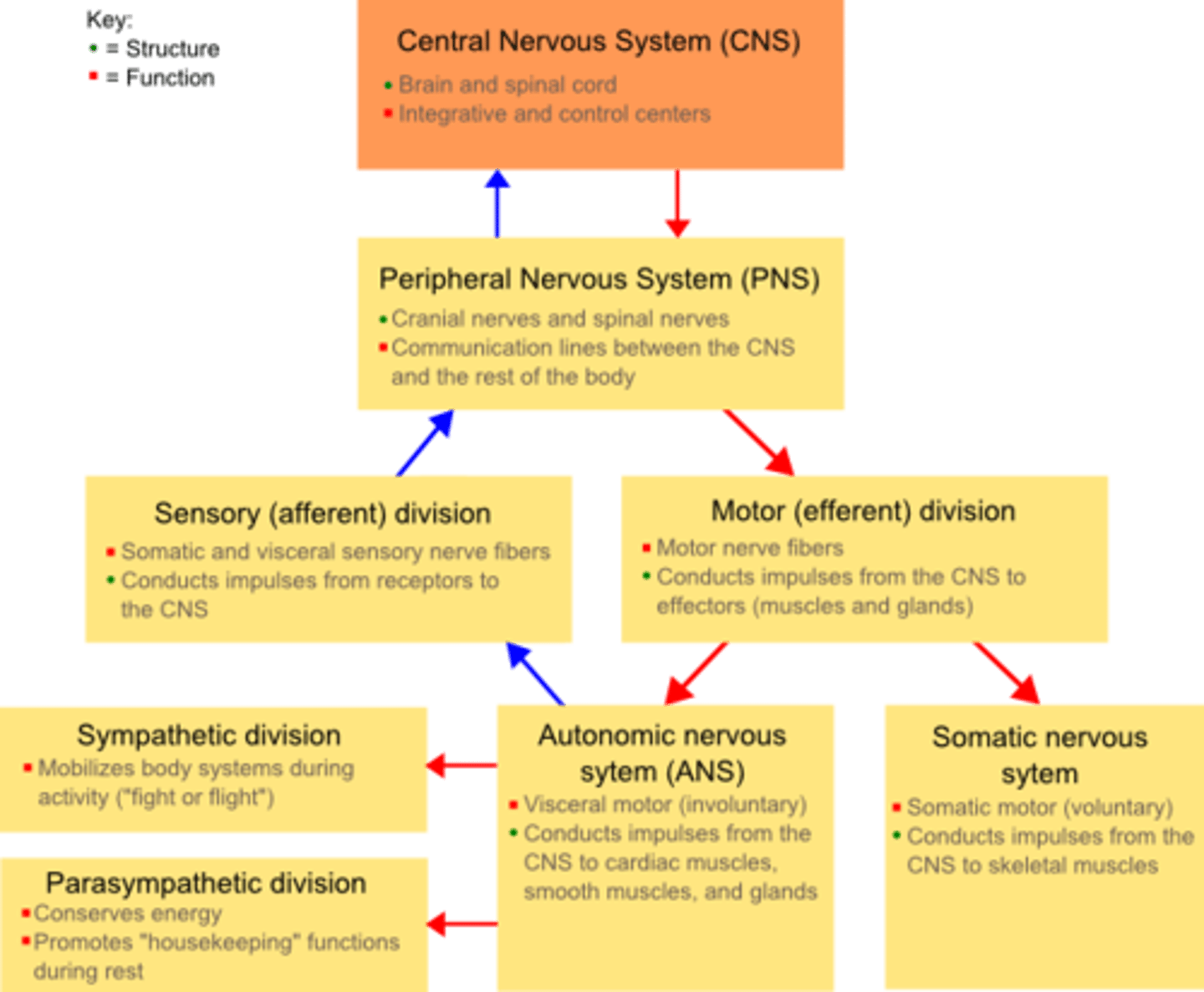
The autonomic nervous system has these 2 branches
sympathetic
parasympathetic