Comprehensive Guide to South African Law of Persons: Birth, Death, Status, and Capacity with 100% expert curated questions and answers (Guaranteed Pass)
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
What is the purpose of the Law of Persons module?
To provide insight into the basic concepts, terminology, and principles of the Law of Persons.
What should the study guide be read in conjunction with?
The study material contained on the module course site accessed via the Learning Management System (LMS), Canvas.
What is the significance of the STADIO study guides?
They are part of tuition and constitute an integral part of the learning experience.
What should students do to confirm textbook requirements?
Consult Canvas to confirm whether a prescribed textbook must be purchased.
How can students find answers to administrative questions?
By contacting the South African or Namibian office via phone or email.
Where can students access academic questions and updated learning materials?
On CANVAS@mySTADIO, the Learning Management System.
What is the ISBN for the 2nd edition of 'The Law of Persons in South Africa'?
ISBN:
What is the ISBN for the 3rd edition of 'The Law of Persons in South Africa'?
ISBN:
What does the term 'legal subjectivity' refer to?
The status of being recognized as a legal entity with rights and obligations.
What marks the beginning of legal subjectivity?
Birth is recognized as the moment when legal subjectivity begins.
What is the focus of Topic 4 in the study guide?
The end of legal subjectivity, including proof and consequences of death.
What are the different kinds of legal subjects mentioned?
Natural persons and juristic persons.
What is the significance of domicile in the Law of Persons?
Domicile determines a person's legal residence and jurisdiction.
What does the term 'minority' refer to in legal terms?
The status of being under the age of majority, which affects legal capacity.
What is curatorship?
A legal arrangement where a person is appointed to manage the affairs of another who is unable to do so.
What is the role of customary law in the Law of Persons?
Customary law influences legal status and rights within certain communities.
What are self-assessment questions used for in the study guide?
To help students evaluate their understanding of the material covered.
What is the importance of registration of births and deaths?
It provides legal recognition of a person's existence and status after death.
What does the term 'prodigality' refer to?
The condition of being wasteful or extravagant, often leading to financial difficulties.
How does mental illness affect legal capacity?
It can limit a person's ability to make legal decisions and enter contracts.
What is the influence of race on legal status?
Race can affect an individual's rights and legal recognition under certain laws.
What is the significance of the 'duty to bury the deceased'?
It is a legal obligation to ensure that the deceased is buried according to the law.
What are the consultation times for academic questions?
Monday to Friday, between 08:00 - 16:30.
What is the purpose of the glossary of terms in the study guide?
To provide definitions and explanations of key terms used throughout the material.
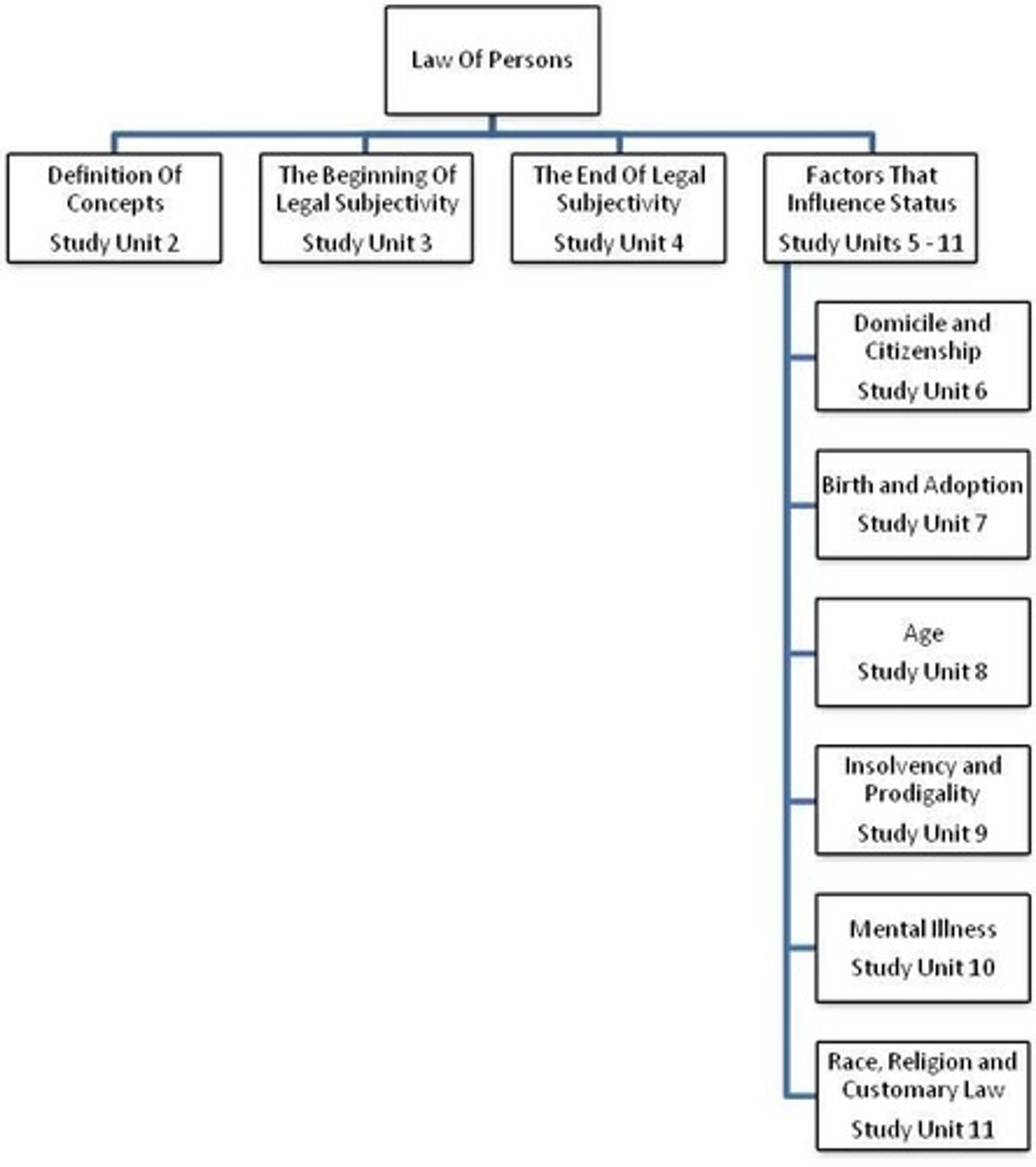
What is the focus of the Law of Persons?
It focuses on legal personality, including how it begins and ends, and the associated rights and duties.
What is meant by 'legal subject' in the context of the Law of Persons?
All human beings are recognized as legal subjects, having rights, duties, and capacities regardless of age or capacity to act.
What significant change did the Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1996 bring to the Law of Persons?
It profoundly affected common law and legislation, ensuring equal treatment of children regardless of their birth circumstances.
What landmark case allowed a child born from artificial fertilization of a lesbian partner to be treated equally to a child born from a married woman?
J v Director-General, Department of Home Affairs 2003 (5) SA 621 (CC).
What did the case Du Toit v Minister of Welfare and Population Development 2003 (2) SA 198 (CC) establish?
It allowed same-sex partners to adopt jointly, granting legal recognition to both adoptive parents.
What was found unconstitutional in Bhe v Magistrate, Khayelitsha (2005)?
The customary law rule of primogeniture, which favored male heirs.
What does section 28(2) of the Constitution state regarding children's rights?
A child's best interests are of paramount importance in every matter concerning the child.
What is the significance of the Children's Act 38 of 2005?
It fundamentally changed traditional law by emphasizing the best interests of the child and redefining parental authority.
What did the Children's Act 38 of 2005 replace 'parental authority' with?
The concept of 'parental responsibilities and rights'.
What age was the age of majority lowered to by the Children's Act 38 of 2005?
From 21 to 18 years.
What rights do unmarried fathers have under the Children's Act 38 of 2005?
They can acquire full parental responsibilities and rights under specified circumstances.
What is the legal distinction regarding children born in and outside of marriage according to the Children's Act?
The distinction is significantly reduced, promoting equality for all children.
What does the Children's Act state about minors consenting to medical treatment?
Minors over the age of 12 may consent to medical treatment if they are mature enough to understand the implications.
What does the Children's Act regulate for the first time in South African law?
Surrogacy.
What is the focus of the Child Justice Act 75 of 2008?
It addresses the criminal capacity of children, particularly those below the age of seven.
What is one of the learning outcomes of the Law of Persons module?
To analyze and solve well-defined problems related to the Law of Persons.
How does the Law of Persons module relate to the Constitution?
It explores the influence of constitutional principles on the rights and duties associated with legal personality.
What is the aim of studying the sources of the Law of Persons?
To extract principles from these sources and apply them to factual situations.
What recent development in the Law of Persons involves the registration of births?
Unmarried fathers were allowed to register their children's births under certain conditions.
What does the term 'legal personality' entail?
It encompasses the recognition of individuals as bearers of rights and duties under the law.
What is the significance of the Bill of Rights in the context of the Law of Persons?
It ensures fundamental rights are upheld, influencing legal interpretations and applications.
What does the term 'paramountcy principle' refer to in child law?
It refers to the principle that a child's best interests are the primary consideration in legal matters involving children.
What is one of the primary objectives of the Law of Persons module?
To demonstrate an in-depth understanding of the basic concepts and principles of the Law of Persons.
What is the law of persons?
It regulates the coming into being and the end of a person (legal subject) and their private-law status.
What is the minimum age of criminal accountability according to the Child Justice Act 75 of 2008?
The minimum age is ten years.
What presumption exists for children aged 10 to 14 under the Child Justice Act?
They are rebuttably presumed to lack criminal capacity.
What change will the Child Justice Amendment Act 28 of 2019 introduce regarding criminal capacity?
It will raise the minimum age of criminal capacity to 12 years.
What is the nasciturus fiction?
A legal concept that protects the interests of unborn children by treating them as if they are born for certain legal purposes.
What are the two categories of legal subjects?
Natural persons and juristic persons.
What distinguishes a juristic person from a natural person?
A juristic person has a legal existence independent from its members and acts through functionaries.
What are the three types of juristic persons recognized in South African law?
1. Associations established in separate legislation, 2. Associations incorporated under enabling legislation, 3. Associations complying with common requirements.
What is the difference between objective law and subjective law?
Objective law refers to the system of laws and rules, while subjective law deals with the rights and relationships between legal subjects.
What are the four categories of legal objects?
1. Corporeal things, 2. Immaterial property, 3. Personality property, 4. Performance.
What is a legal subject?
An entity that can have rights, duties, and capacities.
What is a legal object?
Objects upon which the law has not conferred the capacity to have rights, duties, and capacities.
What is the significance of the Road Accident Fund v Mtati case?
It settled the debate on the necessity of extending the nasciturus fiction to the law of delict.
What is the role of medical practitioners regarding contraceptives for children aged 12 and older?
Medical practitioners must be involved for contraceptives other than condoms.
What is the legal status of children below the age of ten in terms of criminal accountability?
They are completely unaccountable for their crimes.
What does the law of persons address regarding legal subjects?
It addresses who qualifies as a legal subject and what they are legally able to do.
How does the law of persons relate to private law?
It includes rules that apply to legal relationships between legal subjects, such as family law and contracts.
What is the objective law also known as?
Positive law.
What is the significance of the age of 12 years in the context of the Child Justice Amendment Act?
It will establish a presumption of unaccountability for children between 12 and 14 years.
What is meant by 'subject-subject' and 'subject-object' relationships in subjective law?
Subject-subject refers to the relationship between rights bearers, while subject-object refers to the relationship between a rights bearer and the object of their rights.
What is the relationship between legal subjects and legal objects?
A legal subject has claims over legal objects, which are typically things with economic value.
What is the moment when legal subjectivity begins?
At birth, when the foetus is completely separate from the mother's body.
What are the two requirements for birth to be recognized as the beginning of legal subjectivity?
1. The birth must be fully completed, meaning the foetus is separate from the mother. 2. The foetus must have lived independently after separation.
What is the significance of signs of life in determining legal subjectivity?
Any sign of life, such as breathing or a heartbeat, can serve as evidence that the child lived independently.
What does the term 'nasciturus fiction' refer to?
A legal principle that allows an unborn child to be considered as already born for the protection of their interests.
How does the nasciturus fiction apply in the law of succession?
It allows unborn children to be considered for inheritance rights, ensuring their interests are protected.
What is the difference between intestate and testate succession?
Intestate succession applies when a person dies without a valid will, while testate succession applies when there is a valid will.
What statutory obligation exists regarding the registration of birth?
The Births and Deaths Registration Act requires the registration of any child born alive, regardless of specific signs of life.
What is the role of medical evidence in establishing legal subjectivity?
Medical evidence is crucial to prove whether a child lived independently after birth.
What does the Sterilisation Act 44 of 1998 allow?
It allows voluntary sterilisation of individuals aged 18 and older who can consent.
What must be explained to a person before they consent to sterilisation?
The proposed procedure, its consequences, risks, and whether it is reversible or irreversible.
Under what condition can a person under 18 be sterilised?
If failure to perform the sterilisation would endanger their life or seriously impair their health, with consent from a guardian.
What is the legal status of an unborn child in terms of protection?
An unborn child is granted legal protection in certain situations, even though they do not have full legal subjectivity.
What is the relevance of the case Road Accident Fund v Mtati 2005?
It clarified that the nasciturus fiction is unnecessary in the law of delict, affirming the use of ordinary delict rules.
What is the significance of the Criminal Procedure Act 51 of 1977 regarding birth?
It defines the evidence required to prove a child was born alive for legal purposes, focusing on signs of life.
What does the term 'legal subject' refer to?
An entity that has legal rights and obligations, typically a person or organization.
What does the term 'legal object' refer to?
The subject matter of legal rights and obligations, which can include property, contracts, and other interests.
What are the different kinds of legal subjects?
Legal subjects can include natural persons (individuals), legal persons (companies, organizations), and in some cases, unborn children.
What is the purpose of protecting the interests of unborn children?
To ensure that their rights and interests are considered in legal matters, particularly in succession and private law.
How does the law of delict relate to the nasciturus fiction?
The application of the nasciturus fiction in delict was debated and ultimately deemed unnecessary by the Supreme Court.
What is the importance of the registration of births?
It creates a legal record of a child's existence and is essential for establishing legal rights and identity.
What is the main focus of the study unit on legal subjectivity?
To understand the beginning of legal subjectivity, the protection of unborn children's interests, and related legal principles.
Who must consent for sterilization to take place?
The consent must be obtained from the person's parent, spouse, civil union partner, guardian, or curator.
What is required from an independent medical practitioner before sterilization?
They must consult the person and provide a written report indicating that the sterilization is in the person's best interests.
What professionals are included in the panel evaluating sterilization?
The panel must include a psychiatrist (or medical practitioner), psychologist or social worker, and a nurse.
Under what conditions can a person incapable of consenting be sterilized?
If they are mentally disabled to the extent that they cannot make decisions about contraception or sterilization, develop the capacity to make informed decisions, or fulfill parental responsibilities.
What factors must the panel consider when deciding on sterilization?
Factors include the person's age, availability of alternatives, mental and physical health, potential effects of the procedure, nature of the sterilization, likelihood of future consent, and overall best interests.
What is the requirement for the method of sterilization performed?
The method posing the smallest risk to the patient's health must be used.
What does the Choice on Termination of Pregnancy Act regulate?
It regulates the circumstances under which pregnancy may be terminated.
Who is responsible for registering a child's birth?
The child's parents are responsible for registering the birth within 30 days.
What happens if the child's parents are deceased?
Notice of the birth must be given by the child's next-of-kin or legal guardian.
What is required for a birth to be registered?
A forename (first name) and a surname must be assigned to the child.
How is the surname determined for children born to married parents?
The surname can be either parent's surname or both names joined as a double-barrel surname.