Chapter 7 Skeletal System
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Conyloid Joint
side to side movement and back and forth (knuckle joints)
gliding joint
allows one bone to slide over another; found in wrist and ankles
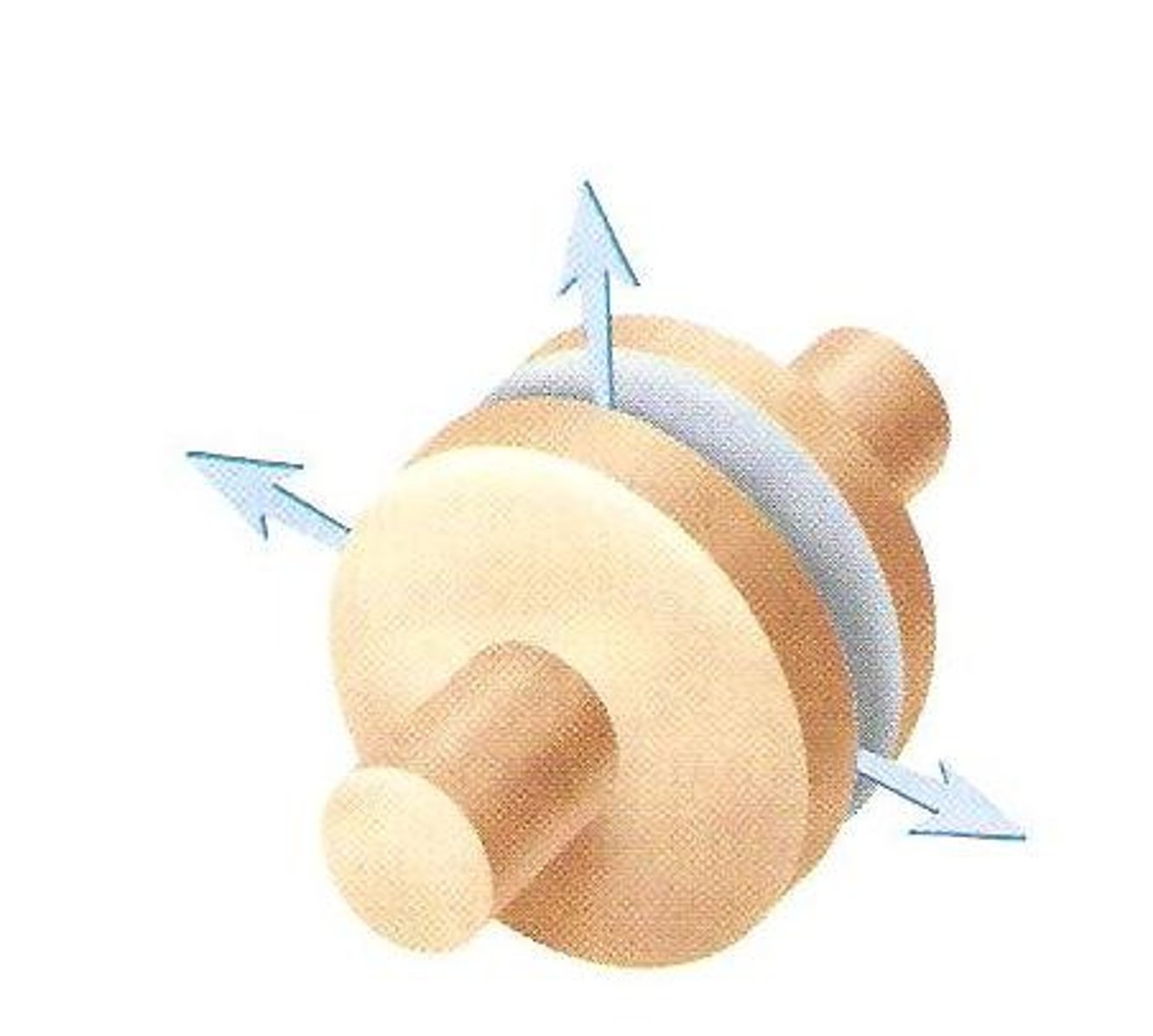
saddle joint
Two concave surfaces fit against a convex surface
Thumbs
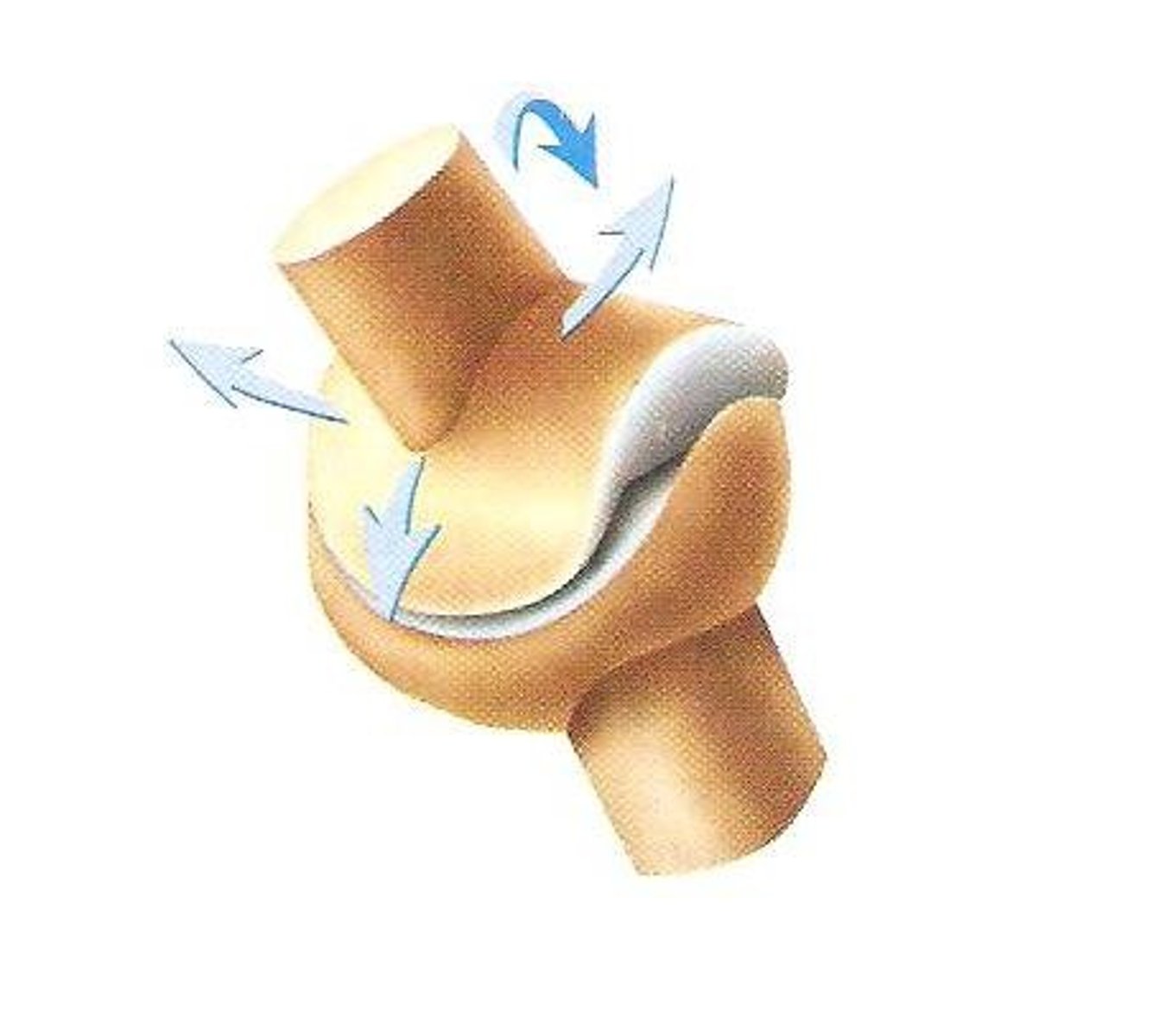
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
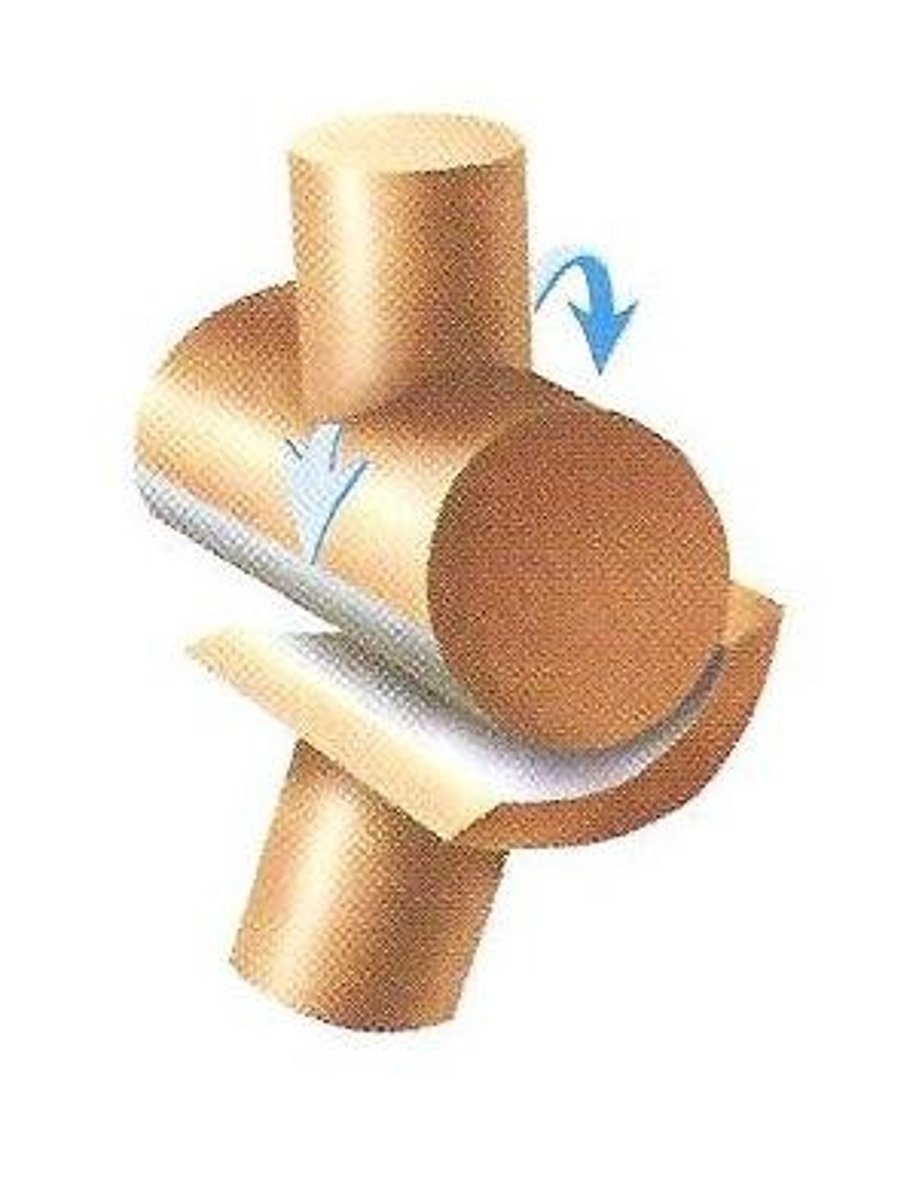
pivot joint
a freely moving joint in which movement is limited to rotation

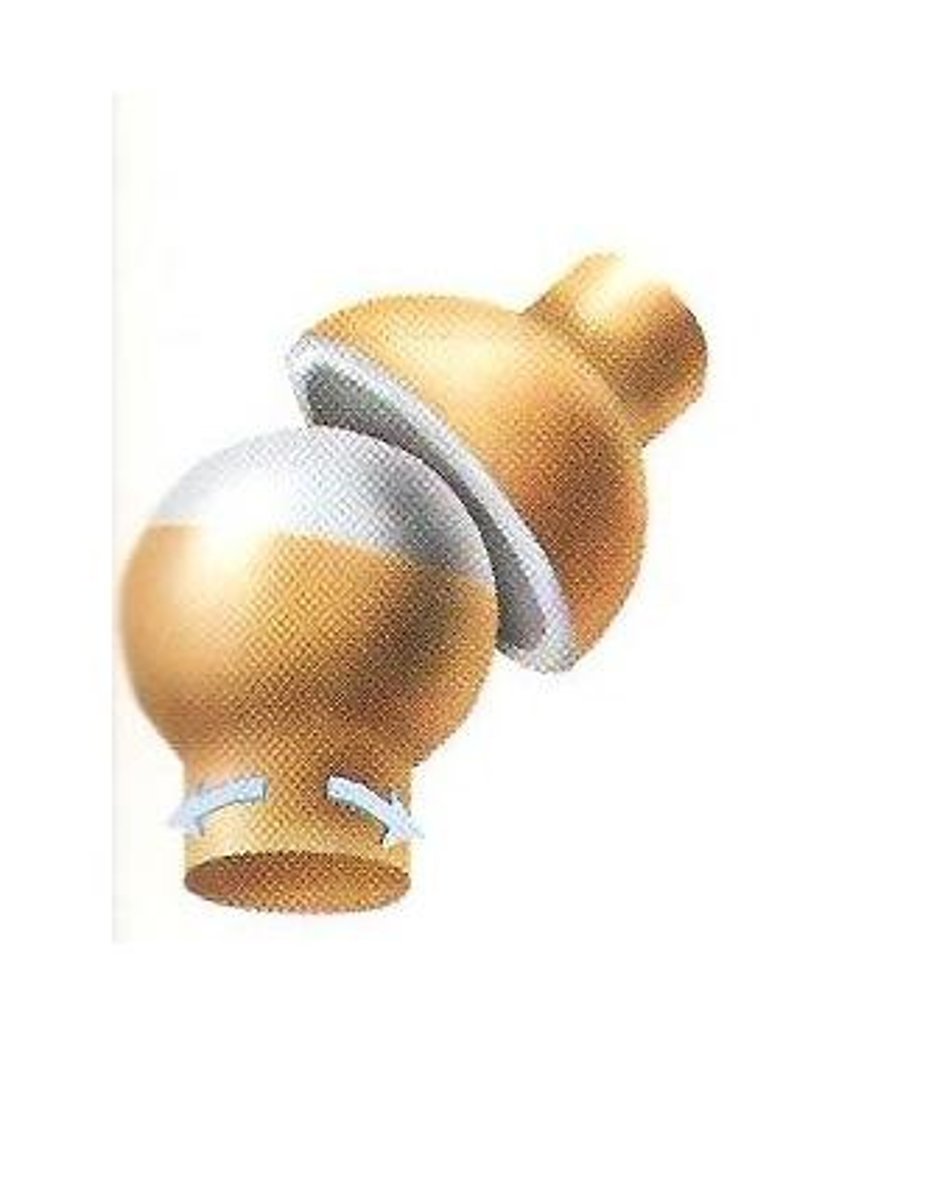
ball and socket joint
allow complete rotation to move in all directions; hips and shoulders

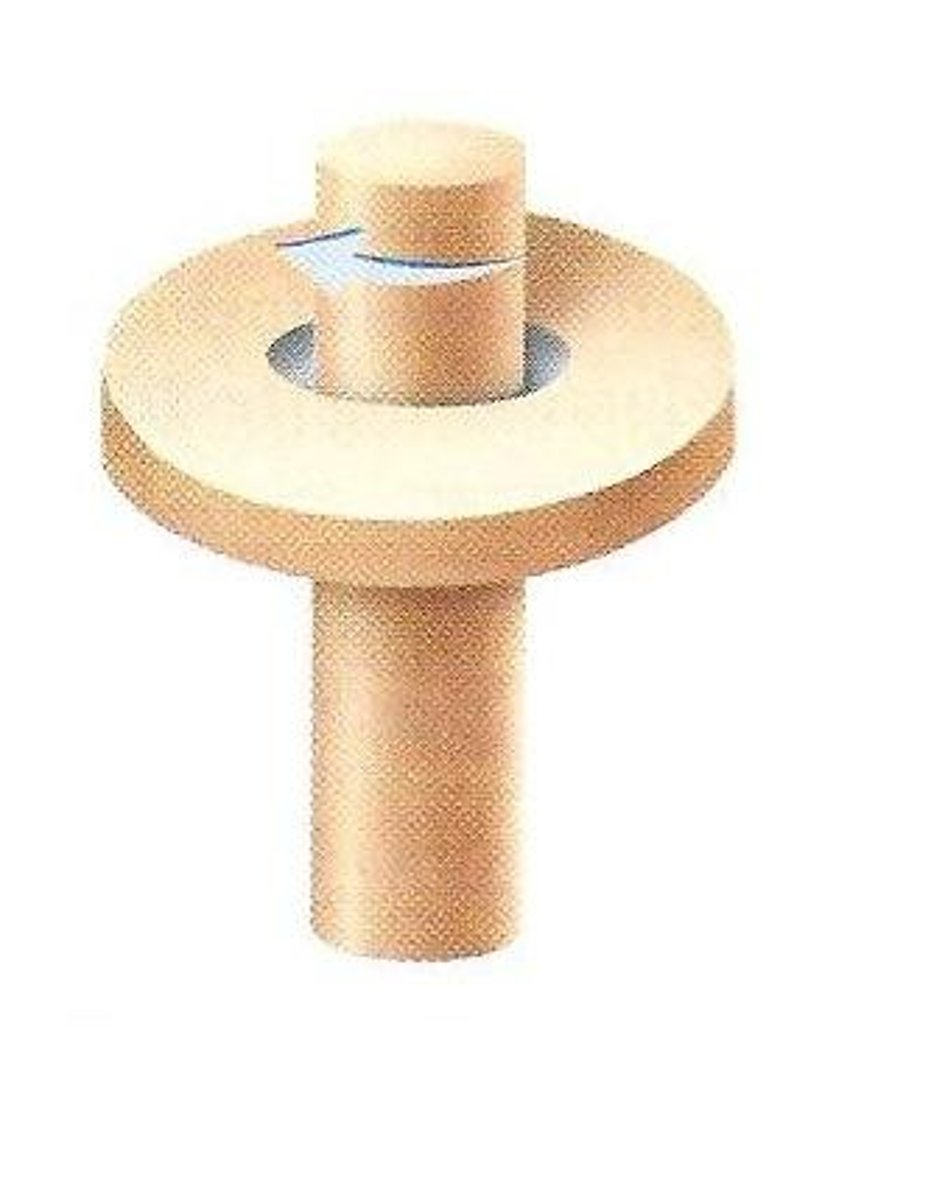
Diaphysis or shaft
a hollow tube made of hard, compact bone, hence a rigid and strong structure light enough in weight to permit easy movement
Medullary cavity
the hollow area inside the diaphysis of a bone; contains soft yellow bone marrow, an inactive, fatty form of marrow found in the adult skeleton
Epiphyses
the ends of a long bone; red bone marrow fills in small spaces in the spongy bone inside the epiphyses; some yellow marrow may appear as a person ages
Articular cartilage
thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering each epiphysis; functions like a thin, smooth rubber cushion would if it were placed over the ends of bones where they form a joint
Periosteum
strong membrane of dense fibrous tissue covering a long bone everywhere except at joint surfaces, where it is covered by articular cartilage
Endosteum
a thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity
Axial Skeleton
Skull
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Cranial bones
Axial Skeleton
Skull
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Ear bones
Axial Skeleton
Skull
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Face bone
Axial Skeleton
Spine
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Vertebrae
Axial Skeleton
Thorax
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Ribs
Axial Skeleton
Thorax
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Sternum
Axial Skeleton
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Hyoid
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper Extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Arm and Forearm bone
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Wrist bones
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Hand Bones
Appendicular Skeleton
Lower extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Pelvic (Hip) girdle
Appendicular Skeleton
Lower extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Thigh and Leg bones
Appendicular Skeleton
lower extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Ankle bones
Appendicular Skeleton
lower extremities
axial or appendicular skeleton? Upper/Lower Extremities, Skull, Spine, Thorax?
Foot Bones
Hyoid Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Hyoid Bone: U-shaped bone in neck; not joined to any other bone (not part of skull); between mandible and upper edge of larynx
Ear Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Stapes: Stapes means “stirrup”—shape of bone (2)
Ear Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Incus: Incus means “anvil”—shape of bone (2)
Ear Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Malleus: Malleus, incus, and stapes are tiny bones in middle ear cavity in temporal bone; malleus means “hammer”—shape of bone (2)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Vomer: Forms posterior, back part of nasal septum (1)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Inferior nasal concha: Form curved “ledge” along inside of side wall of nose, below middle concha (2)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Palatine: Form posterior part of roof of mouth and floor and side walls of nose and part of floor of orbit (2)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Lacrimal: Small bones; help form medial wall of eye socket and side wall of nasal cavity (2)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Mandible: Lower jawbone articulates with temporal bone at condyloid process; only bone of skull that moves freely; mental foramen is hole for blood vessels and nerves (1)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Zygomatic: Cheek bones; also help form orbit (1)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Maxilla: Upper jawbones; also help form roof of mouth, floor, and side walls of nasal cavity and floor of orbit; large cavity in maxillary bone is maxillary sinus (2)
Face Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Nasal: Small bones that form upper part of bridge of nose (2)
Cranial Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Eithmoid: Complicated bone that helps form floor of cranium, side walls and roof of nose and part of its middle partition (nasal septum—made up of the ethmoid’s perpendicular plate and the vomer bone), and part of orbit; contains honeycomblike spaces, the ethmoid sinuses; superior and middle conchae are projections of ethmoid bone; form “ledges” alongside wall of each nasal cavity (1)
Cranial Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Sphenoid: Forms central part of floor of cranium; pituitary gland located in small depression in sphenoid called sella turcica (Turkish saddle); muscles attach to pterygoid process (1)
Cranial Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Occipital: Forms back of skull; spinal cord enters cranium through large hole (foramen magnum) in occipital bone
Cranial Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Temporal: Form posterior sides of cranium; contain middle and inner ear structures; mastoid sinuses are mucosa-lined spaces in mastoid process, the protuberance behind ear; external auditory canal is tube leading into temporal bone; muscles attach to styloid process(2)
Cranial Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Parietal: Form bulging topsides of cranium (2)
Cranial Bone
Cranial, Face, Ear or Hyoid Bone?
Frontal: Forehead bone; also forms front part of floor of cranium and most of upper part of eye sockets; cavity inside bone above upper margins of eye sockets (orbits) called frontal sinus; lined with mucous membrane (1)
12
Next 12 vertebrae; ribs attach to these
How many bone are in the Thoracic vertebrae?
7
Upper seven vertebrae, in neck region; first cervical vertebra called atlas; second, axis
How many bone are in the cervical vertebrae?
5
Next five vertebrae; located in small of back
How many bone are in the Lumbar vertebrae?
1
In child, five separate vertebrae; in adult, fused into one
How many bones are in the Sacrum?
1
In child, three to five separate vertebrae; in adult, fused into one
How many bones are in the coccyx?
14
Upper seven pairs; attached to sternum by costal cartilages
Bones in the Thorax
True ribs
10
Lower five pairs; first three pairs attached to sternum by costal cartilage of seventh ribs; lowest two pairs do not attach to sternum, therefore called floating ribs
Bones in the Thorax
False Ribs
1
Breastbone; shaped like a dagger; piece of cartilage at lower end of bone called xiphoid process; superior portion called the manubrium
Bones in the Thorax
Sternum
no movement
No Movement, Slight Movement and Free Movement
Synarthroses
slight movement
No Movement, Slight Movement and Free Movement
Amphiarthroses
free movement
ball-and-socket: shoulder and hip joint
hinge: elbow
pivot: Head of radius rotating against ulna
saddle: carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
gliding: Articular processes between vertebrae
condyloid joints Alantooccipital Joint
No Movement, Slight Movement and Free Movement
Diarthroses
Reduces the angle of the joint, as in bending the elbow
Flexion (to flex a joint)
Increases the angle of a joint, as in straightening a bent elbow
Extension (to extend a joint)
Increases the angle of a joint to move a part away from the midline, as in moving the arm to the side and away from the body
Abduction (to abduct a joint)
Decreases the angle of a joint to move a part toward the midline, as in moving the arm in and down from the side
Adduction (to adduct a joint)
Spins one bone relative to another, as in rotating the head at the neck joint
Rotation (to rotate a joint)
Moves the distal end of a bone in a circle, while circumducting a joint, keeping the proximal end relatively stable, as in moving the arm in a circle and thus circumducting the shoulder joint
Circumduction (to circumduct a joint)
can flex, extend, abduct, adduct, and circumduct (thumb)
saddle joints