PCB3713C - Midterm
1/378
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
379 Terms
Superior
Top
Inferior
Below
Anterior
Front
Posterior
Back
Ventral
Front/Belly Side
Dorsal
Back/Spine Side
Medial
Middle of body
Lateral
Side of the body, away from the middle
Proximal
Pointing towards the center of the body
Distal
Away from the body
Visceral
Organ lining side
Parietal
Cavity lining
Inter-
Between
Intra-
Within/Inside
Cis-
Same
Trans-
Opposite
Apical
Lumen of the tube
Basolateral
Outside of the tube
Cell Theory
Organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells make up the basic unit of life
Cells come from Pre-existing cells
Cell Membrane
Phospholipid bilayer composed of proteins
Phospholipid Tails
Hydrophobic and lipophilic area of the cell membrane/phospholipid
Phospholipid Heads
Hydrophilic part of the cell membrane/phospholipid
Micelle
Organized phospholipid in a single layer
Liposome
Organized phospholipids in a bilayer
Selective Permeability
A feature of the cell membrane preventing large molecules and charged molecules from crossing
Transmembrane Protein
Protein that crosses over both sides of the bilayer
Embedded Protein
Protein that attaches to a single layer of the bilayer without crossing
Lipid-Anchored Protein
Protein that attaches to the lipid tails of the bilayer
Peripheral Membrane Protein
Protein that attaches to the bilayer without covalently attaching to it
Integral Proteins
Permanent structural components of cell membranes that extend through the entire lipid bilayer
Communication Proteins
Proteins used for signaling across the membrane
Ligand-Binding Protein
Transmembrane protein that has specific ligands that bind to it, causing a conformal change and result in events
Adhesion Molecules
Protein that binds to physical contacts in the extracellular matrix or other cells
Channels
Allows specific molecules or proteins to pass through the membrane
Carries
Actively transports molecules across the membrane
Pump
Carrier protein that actively transports molecules over a membrane
Nucleus
Houses a cell’s genetic information
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Site of protein and lipid synthesis, also acts as a Ca2+ reservoir
Rough ER
Synthesizes membrane-associated proteins and secreted protein
Smooth ER
Lipid synthesis and Ca2+ ion reservoir
Golgi Complex
Process proteins into a saccule and relaxes them into their subcellular destination
Lysosomes
Site of old cell organelle breakdown
Mitochondria
Site of ATP generation
Signal Transduction
Use of a chemical or physical signal to stimulate a cell protein to elicit a cellular response
Receptor
Protein that gets stimulated by a signal
Endocrine Mechanism
Uses hormones to act on distant tissue
Paracrine
Use of chemicals to act on neighboring cells
Autocrine
Use of chemicals to stimulate itself
Juxtacrine
Physical contact with other cells to send signals
Ligands
Chemical that binds to a receptor on the cell surface
Second Messengers
Aids in sending the extracellular signals to downstream proteins
Regulation of Second Messengers
Activation produces 2nd messengers, Deactivation destroys 2nd messengers
Ligand-Gated Receptors
Channels that open or close based on the attachment of a ligand
Ion-Gated Receptor
Channels that open or closed based on the attachment of an ion
Kinases
Integral protein that adds a phosphate group, typically increases enzyme activity
Phosphatases
Integral protein that removes phosphate groups, typically decreases enzyme activity
Nuclear Receptors
Stimulates or inhibits gene transcription; Transcription regulator
G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCRs)
Use of G-Proteins to induce downstream effects in a cell
G-Protein
Protein that is attached to GPCR and activates 2nd messenger systems
GTP/GDP
Activation system for G-Proteins; Acts as a toggle
Transcription
Production of mRNA from DNA. Made in the nucleus
Translation
Production of amino acid sequence from mRNA. Made in the ribosomes
Genes
Segment of DNA transcribed into RNA
Regulatory Elements
DNA sequences that control gene transcription
Transcription Factors
Binds to regulatory elements in DNA to control transcription
Intracellular Fluid
Fluid in the cells, making up 60% of TBW
Extracellular Fluid
Fluid outside the cells, making up 40% of TBW. Consists of Blood Plasma, Interstitial Fluid, and Transcellular Fluid
Electrolytes
Solutes in a liquid to aid in electroneutrality
ECF Electrolytes
Na+, Cl-
ICF Electrolytes
K+, Negatively Charged Proteins
Flux
Movement of solutes across a membrane
Noncoupled Transport
Movement of solute without being affected by other solutes
Permeability
Ability for a solute to move through a membrane
Driving Force
Energy of a solute to move through a membrane
Downhill Transport
Moving the solute concentration from high to low
Uphill Transport
Moving the solute concentration from low to high
Passive Transport
Downhill transport of a solute across a membrane
Facilitated Diffusion
Downhill transport of a solute using a channel
Active Transport
Uphill transport of a solute across a membrane
Net Flux
Inward flux subtracted by the outward flux
Steady-State
Conditions of a solute concentration do not change with time
Equilibrium
The driving force is zero. There is no net transport
Nonequilibrium Steady State
A constant flux that requires energy to maintain
Electrochemical Potential Energy
Energy of a solute based on voltage and concentration
Nernst Equation
Describes the equilibrium voltage of an ion
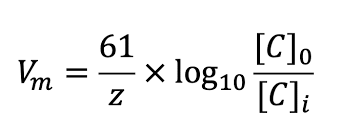
Simple Diffiusion
Movement of an uncharged solute through a membrane
Fick’s Law
Flux rate based on the membrane and concentration
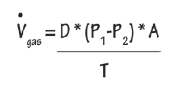
Permeability Coefficient (Px)
Solute’s ability to move through a membrane
Pores
Channel allowing for any solute to freely move through
Channel
Conduit that is gated open or closed
Carrier
Double gated channel, moving certain solutes in exchange for others
Gated-Ion Channel
Channel that open/closes based on the signal
Transmembrane Carrier
Solute binds to a protein to enter, and unbinds to exit
Na-K Pump
Movement of 3 Na+ out, in exchange for moving 2 K+ in using one ATP. Net +1 charge out of the cell
Contransporter
Moves a solute uphill and another downhill in the same direction
Exchanger
Moves a driving solute and driven solute in opposite directions
Aquaporins (AQPs)
Water pores that allow for increased water permeability
Oncotic Pressure
Pressure of water due to water following solutes
Ultrafiltration
High oncotic pressure moving water through a capillary, filtrating it
Membrane Potential
Difference of cytoplasmic electric potential and the extracellular electric potential