Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
1/46
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
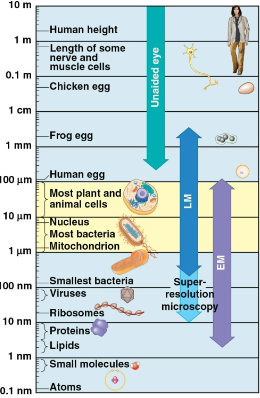
Microscope
An instrument used to magnify objects to small to be seen by the naked eye
Light microscope (LM)
A microscope where visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass lenses, which magnify the image
Magnification
The ratio of an object’s image size to its real size
Resolution
The measure of the clarity of the image
Organelles
The membrane-enclosed structures in eukaryotic cells, such as mitochondria which aids ATP and cellular respiration
Light microscopy cannot study these due to low resolutions despite staining or labeling
Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs)
Electron microscope that focuses a beam of electrons onto the surface of a specimen, providing images that look 3-D
Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs)
Electron microscope that focuses a beam of electrons through a specimen, used to study internal cell structures
Electron microscopes (EMs)
Microscopes that transmit electrons to view closer details, can be cost prohibitive and includes scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes
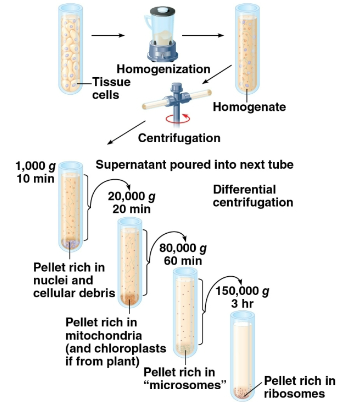
Cell fractionation
The use of centrifuges to fractionate cells into their component parts of organelles, helping determine the functions of organelles based on structure
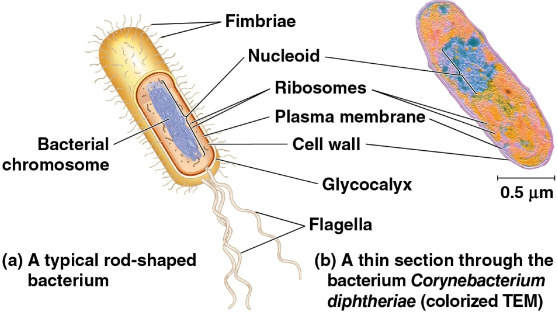
Prokaryotic cells
Cells have no nucleus, consisting of the Bacteria and Archaea domains
DNA is contained in the nucleoid
No membrane-bound organelles
Cytoplasm bound by plasma membrane
Eukaryotic cells
Cells that do have a nucleus, consisting of protists, fungi, and animals
DNA in a nucleus bounded by a double membrane
Membrane-bound organelles
Cytoplasm in between the plasma membrane and nucleus
Larger than prokaryotic cells
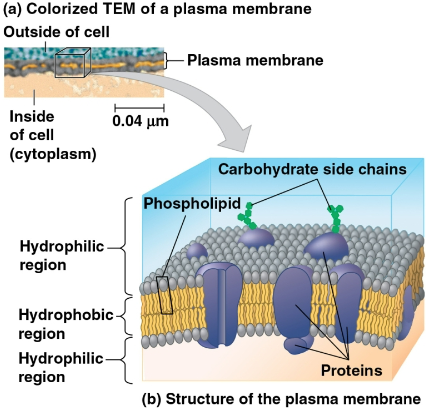
Plasma membrane
A selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service cells
Greater sizes require greater surface areas for sufficient nutrients, limiting size
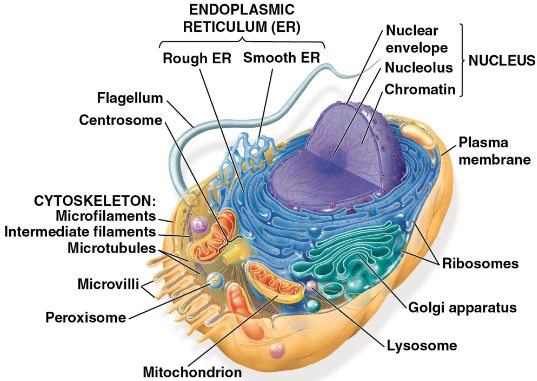
Organelles
Compartments within eukaryotic cells that serve different functions to maintain the overall cell, separated by a membrane of phospholipids and similar between plant and animal cells
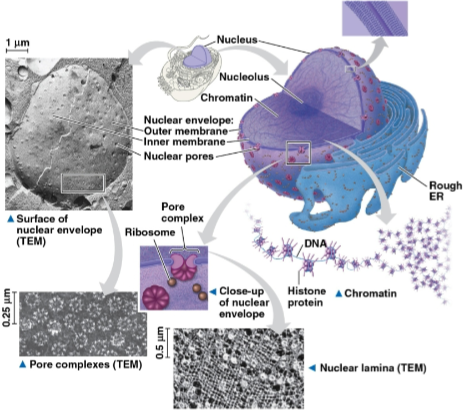
Nucleus
Organelle in eukaryotic cells that contains most of the DNA, which is used by ribosomes to make proteins
One of the most conspicuous organelles
Separated from the cytoplasm by the nuclear envelope
Nuclear envelope
A double membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Nuclear lamina
Proteins within the nuclear envelope that maintain the shape of the nucleus
Nuclear matrix
A framework of protein fibers throughout the interior of the nucleus
Chromosomes
Discrete units of DNA containing one DNA molecule associated with proteins called chromatin that condenses to form chromosomes during cell division preparation
Nucleolus
Site located within the nucleus for ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis
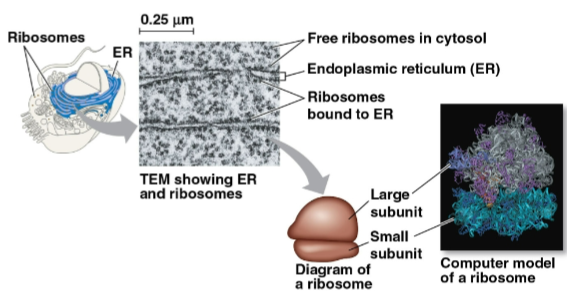
Ribosomes
Complexes of ribosomal RNA and protein that build protein in the cytosol and on the rough endoplasmic reticulum or nuclear envelope
Free ribosomes
Ribosomes that produce proteins in the cytosol
Bound ribosomes
Ribosomes that produce protein on the outside of the endoplasmic reticulum or on the nuclear envelope
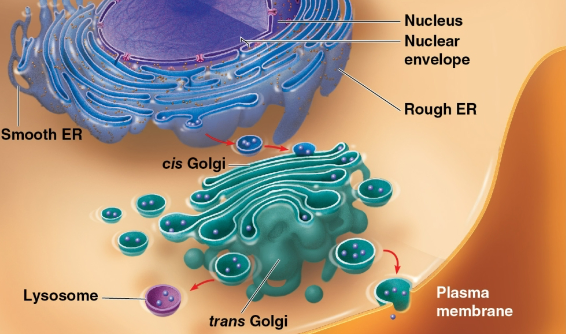
Endomembrane system
System that consists of the:
Nuclear envelope
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
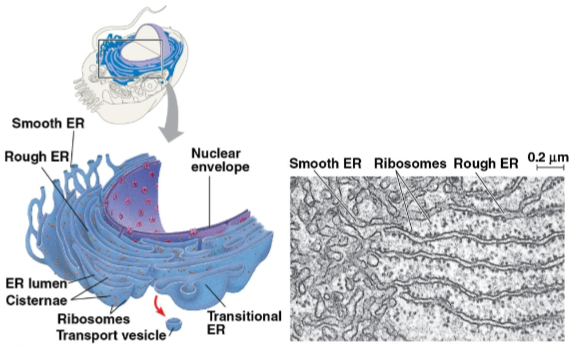
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Organelle that accounts for more than half of the total membrane in many eukaryotic cells
Continuous with the nuclear envelope
Divided into smooth and rough ER based on ribosomal presence
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)
Endoplasmic reticulum section that
does not have ribosomes
synthesizes lipids
detoxifies drugs and poisons
stores calcium ions
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER)
Endoplasmic reticulum section that
has bound ribosomes, secreting glycoproteins
distributes transport vesicles
creates membrane for the cell
Transport vesicles
Secretory proteins surrounded by membranes
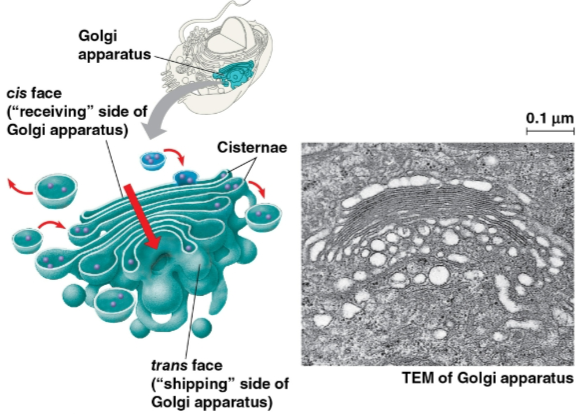
Golgi apparatus
Flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
modifies products of the endoplasmic reticulum
makes certain molecules
sorts and packages materials into transport vesicles
Lysosome
A membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest (break down) macromolecules
Has an acidic environment to support lysosomal enzymes
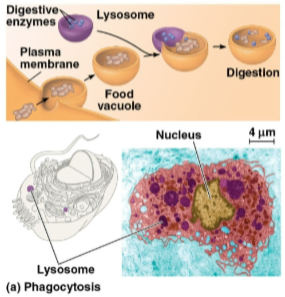
Phagocytosis
Engulfing another cell for food, creating a food vacuole that is digested by lysosomes
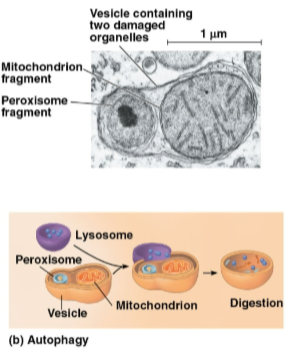
Autophagy
The process in which lysosomes recycle the cell’s own organelles and macromolecules
Vacuoles
Large vesicles derived from the ER and Golgi apparatus
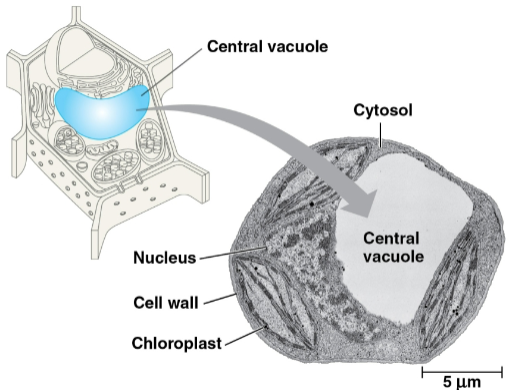
Central vacuoles
Vacuoles found in mature plant cells that contain a solution called sap
Serves as the plant cell’s main repository of inorganic ions, including potassium and chloride
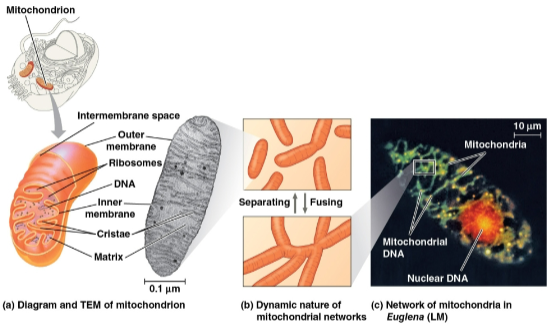
Mitochondria
The sites of cellular respiration, the metabolic process that uses oxygen to generate ATP found in nearly all eukaryotic cells
Contains cristae, creating an intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix with a large surface area
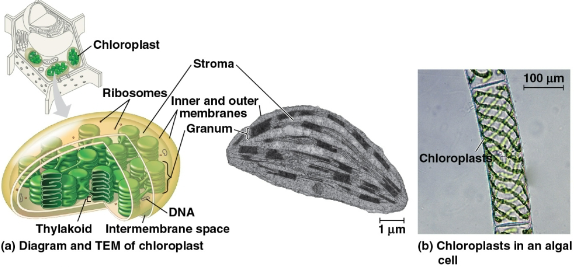
Chloroplasts
The sites of photosynthesis in plants and algae
Contains the green pigment chlorophyll, as well as other enzymes and molecules functioning in photosynthesis
Found in leaves and other green organs of plants and algae
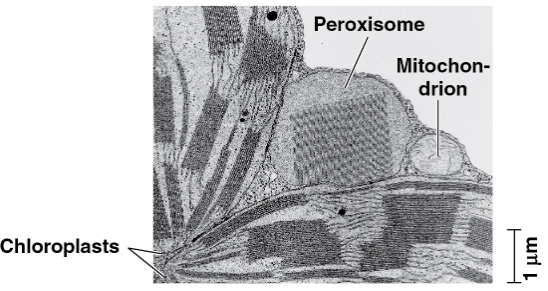
Peroxisomes
Oxidative organelles with an unknown lineage
Bounded by a single membrane
Contains enzymes that remove hydrogen atoms from various substances to be transferred to oxygen, forming hydrogen peroxide
Have been found to break fatty acids down for fuel, detoxify alcohol and other harmful compounds in the liver
Cristae
An inner membrane with folds, creating a large surface area for activity
Mitochondrial matrix
Sites where some steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed, presenting a large surface area for enzymes
Thylakoids
Membranous sacs within a chloroplast stacked to form a granum
Stroma
The internal fluid within a chloroplast
Plastids
A group of plant organelles that inlcudes the chloroplast
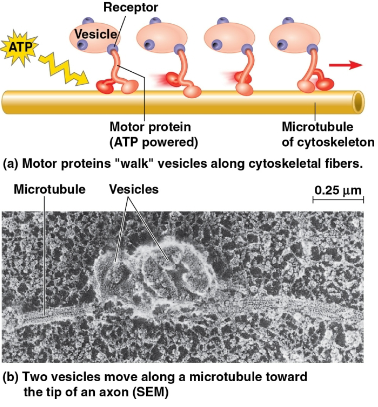
Cytoskeleton
The support of the cell to maintain shape, interacting with motor proteins to produce cell motility for vesicles and other organelles
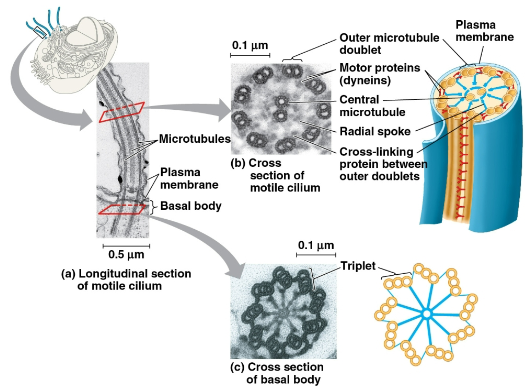
Microtubules
The thickest of the three components of the cytoskeleton that help shape the cell, guide organelle movement, and separate chromosomes during cell division
Also control flagella and cilia beating that project from some cells, where they are sheathed in a plasma membrane extension
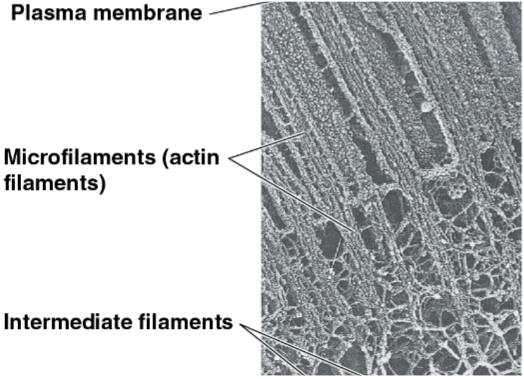
Microfilaments (actin filaments)
The thinnest of the three components of the cytoskeleton, forming a cortex inside the plasma to support the cell’s shape
Makes up the core of microvilli in intestinal cells
Intermediate filaments
Fibers with diameters in a middle range in the cytoskeleton
Pseudopodia
Cellular extensions that allow cells to crawl along a surface
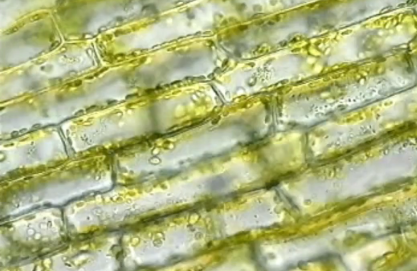
Cytoplasmic streaming
A circular flow of cytoplasm within cells, driven by actin-protein interactions