PSY3103 week 4 content
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is extinction?
the nonreinforcement of a previously reinforced response = a decrease in the strength of that response
Explain both the procedure and process for extinction
-procedure of extinction: non-reinforcement of previously reinforced response
-process of extinction: resultant decrease in response strength
What is the difference between complete and incomplete cessation of extinction?
-complete cessation = behaviour is extinguished
-incomplete cessation = behaviour is partially extinguished
What is the importance of identifying the reinforcer when applying an extinction procedure?
-determining the effective reinforcer that is maintaining a behaviour is a critical first step in extinguishing a behaviour
What are some of the side effects of extinction?
-extinction burst
-increase in variability
-emotional behaviour
-aggression
-resurgence
-depression
What is an extinction burst?
a temporary increase in the frequency and intensity of responding when extinction is first implemented
What is emotional behaviour?
-we typically refer to these behaviours as frustration
-aggression is also common
What is resurgence?
the reappearance during extinction of other behaviors that had once been effective in obtaining reinforcement
What are the problems with these side effects?
-can impede successful implementation of extinction
-can be inadvertently strengthened if one suddenly gives in and provides the subject with the sought-after reinforcer
What is resistance to extinction?
the extent to which responding persists after an extinction procedure has been implemented
What do the responses look like for high and low resistance?
very persistent response = high resistance to extinction
response that disappears quickly = low resistance to extinction
What are the factors that affect resistance to extinction?
-schedule of reinforcement*
-history of reinforcement
-magnitude of the reinforcer
-degree of deprivation
-previous experience with extinction
-distinctive signal for extinction
How does schedule of reinforcement and extinction connect?
resistance to extinction is particularly strong when behavior has been maintained on a variable ratio schedule
What is the partial reinforcement effect and how does it connect to schedules?
behaviour maintained on an intermittent schedule will extinguish more slowly than behaviour on a continuous schedule
What is unwanted behaviour and how does it connect to extinction?
-partial reinforcement effect accounts for unwanted behaviours that are hard to eliminate.
-behaviour that has been continuously reinforced is less resistant to extinction, you should spend several days reinforcing each instance of the unwanted behaviour.
How does someone’s history of reinforcement affect extinction?
the more reinforcers an individual has received for a behaviour, the greater the resistance to extinction (easier to get rid of early on)
How does magnitude of the reinforcer affect extinction?
-large-magnitude reinforcers sometimes result in greater resistance to extinction
-it may take longer to extinguish a behaviour which resulted in a highly preferred reinforcer
How does degree of deprivation affect extinction?
greater the level of deprivation, the greater the resistance to extinction
How does previous experience connect to extinction?
greater the number of prior exposures to extinction, the quicker the behaviour will extinguish during later exposures
What is spontaneous recovery after extinction?
-reappearance of an extinguished response following a rest period after extinction
-behaviour will likely be weaker than it was at the start of the extinction phase the day before
-persistence pays off**
What is stimulus control?
-presence of a discriminative stimulus reliably affects the probability of the behaviour
↳some behaviours feel like autopilot
What is stimulus generalization?
-tendency for an operant response to be emitted in the presence of a stimulus that is similar to an SD
-the more similar the stimulus, the stronger the response (ex. you have a bad teacher that has brown hair and glasses and you get another teacher who looks similar you might also initially think she is bad)
What is the generalization gradient?
-steep gradient = less generalization
-flat gradient = more generalization
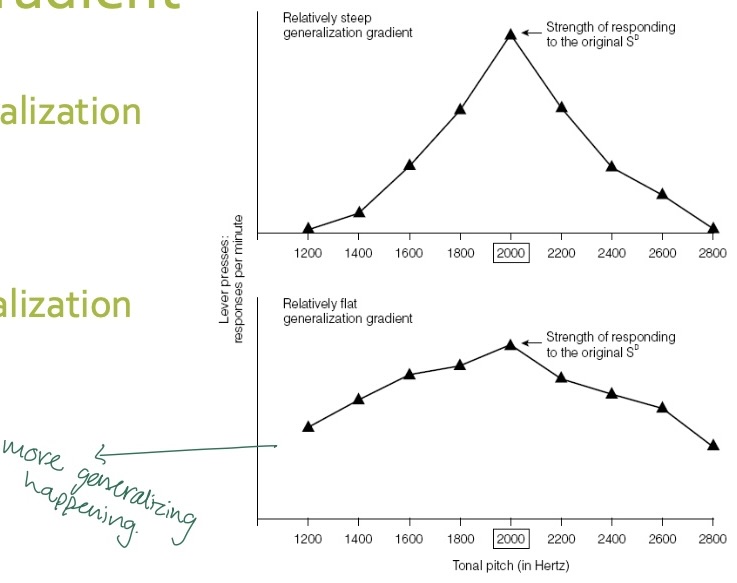
How does the gradient relate to stimulus discrimination?
-steep gradient = weak generalization and strong discrimination
-flat gradient = strong generalization and weak discrimination
What is discrimination training?
-reinforcement of responding in the presence of one stimulus (the SD) and not another stimulus (an SΔ)
-a discriminative stimulus for extinction (SΔ) signals the absence of reinforcement
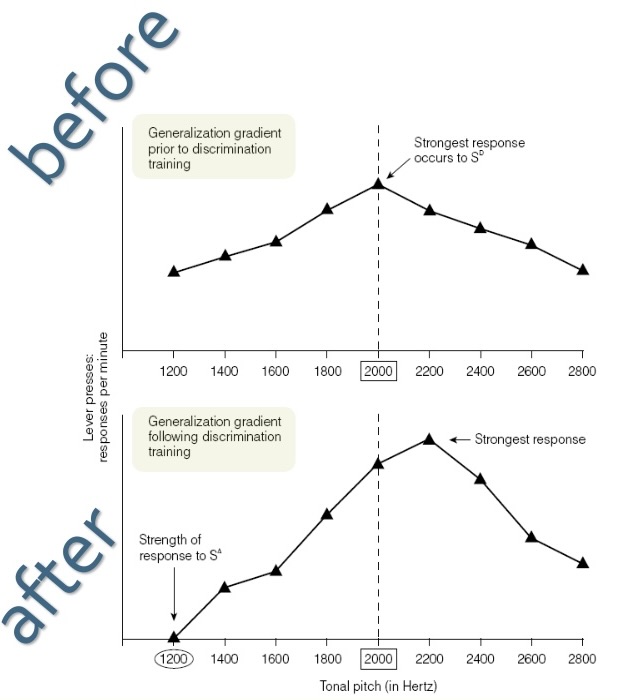
What is the peak shift effect?
the peak of a generalization gradient following discrimination training will shift from the SD to a stimulus that is further removed from the SΔ
What are multiple schedules?
-consist of two or more independent schedules
-presented in sequence (can be presented in random or alternating order or for set periods of time)
-each resulting in reinforcement and each having a distinctive SD
What is behavioural contrast?
occurs when a change in the rate of reinforcement on one component of a multiple schedule produces an opposite change in the rate of response on another component
What is positive contrast effect?
a decrease in rate of reinforcement on one component results in an increase in rate of response on the other component
What is negative contrast effect?
an increase in the rate of reinforcement on one component produces a decrease in the rate of response on the other component
What is anticipatory contrast?
-the rate of response varies inversely with an upcoming change in the rate of reinforcement
-consequences for behaviour in one setting can affect the strength of it another setting
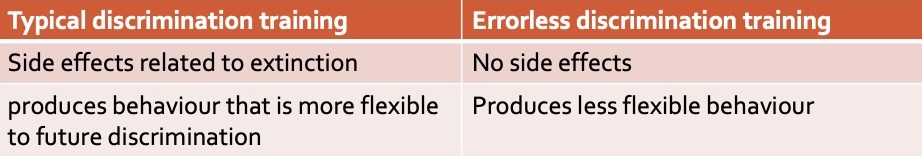
What is errorless discrimination training?
a procedure that minimizes the number of errors and reduces many of the adverse effects associated with discrimination training
What are the 2 aspects of errorless discrimination training?
1. The SΔ is introduced early in training, soon after the animal has learned to respond appropriately to the SD
2. the SΔ is presented in weak form to begin with and then gradually strengthened
What is fading? (relates to errorless discrimination training)
the process of gradually altering the intensity of a stimulus
What are the differences between typical discrimination and errorless discrimination?
What is delayed matching-to-sample?
at one time the animal is shown a certain stimulus and is then required to identify that stimulus at a later time in order to receive a reinforcer
What is directed forgetting?
-occurs when you have been told to forget something
O = remember cue
X = forget cue
What is the process of targeting?
involves training an animal to approach and touch a particular object