Final Review - BIOL 1306 Cheek
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
Hypothesis
an idea about something that can be tested
Prediction
statement about what will happen in an experiment if the hypothesis is true
Ionic Bond
- formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another
- stronger than covalent bonds
-cation = positive charged ions
- anions = negatively charged ions
Nonpolar Covalent
- formed when atoms share valence electrons equally
- weaker than ionic bond
Polar Covalent
- formed when atoms share valence electrons unequally
- weaker than ionic bonds
Hydrogen Bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule
much weaker than covalent and true ionic bonds
What properties of water are caused by hydrogen bonds?
Cohesion
Adhesion
Surface Tension
Specific Heat
Heat of Vaporization
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
Surface Tension
the force that acts on the surface of a liquid and that tends to minimize the area of the surface; hydrogen bonds form a lattice of water molecules which is strong and flexible
Specific Heat
the heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass of a given substance by a given amount (usually one degree). Takes LOTS OF ENERGY
Heat of Vaporization
The amount of energy required for the liquid at its boiling point to become a gas; takes LOTS OF ENERGY
Why is water considered polar?
the polar covalent bonds (unequal sharing of electrons between atoms) and the unsymmetrical shape of the molecule means that water molecules have two poles - a positive charge at the hydrogen pole and a negative charge on the oxygen pole
Hydrophilic
"water-loving";soluble in water
Polar molecules dissolve easily in water and are hydrophilic
Hydrophobic
"Water-fearing"; pertaining to non-polar molecules (or parts of molecules) that do not dissolve in water.
Hydroxyl Group
- hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond
- hydrophilic
-forming chains of sugar or fatty acids
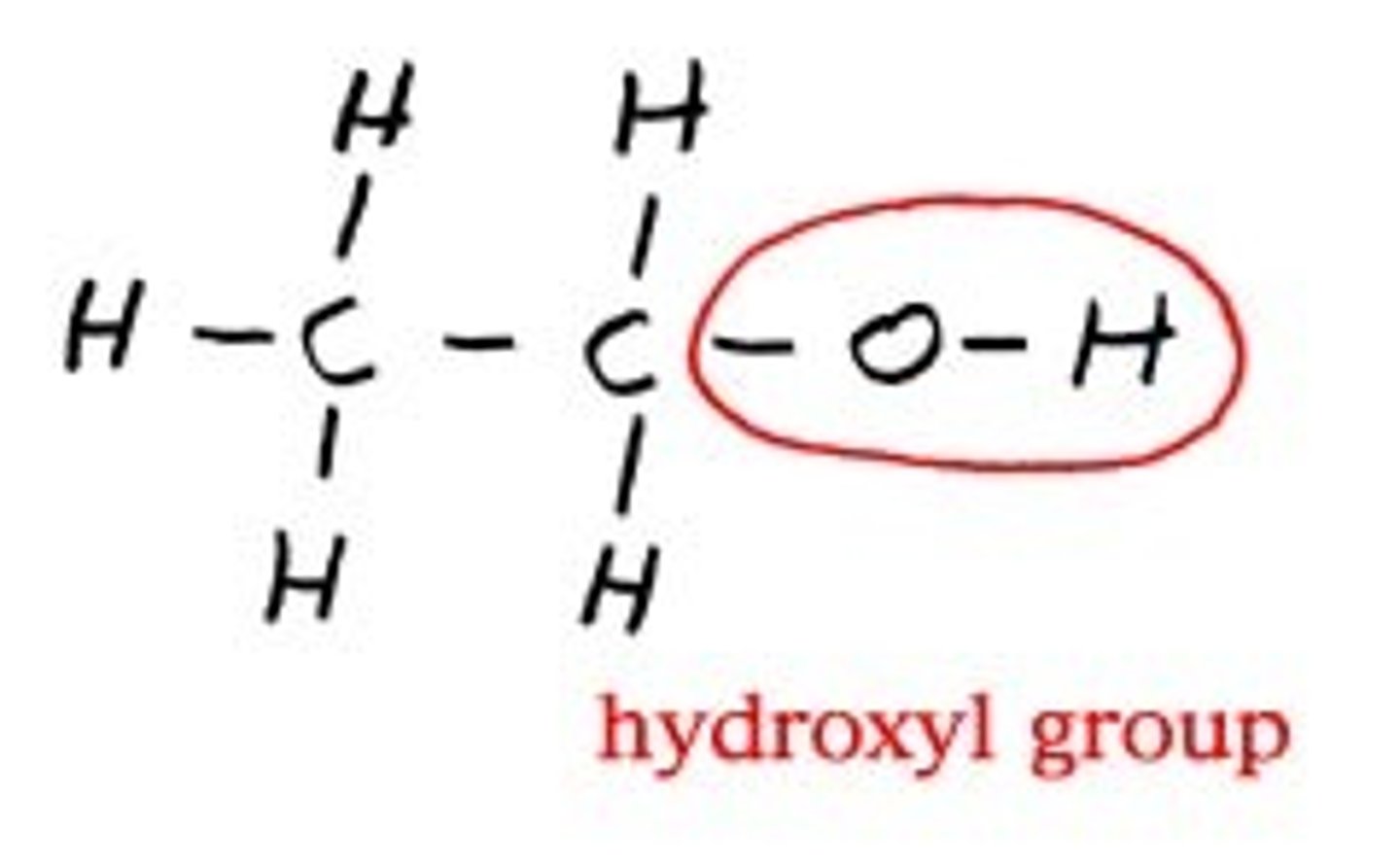
Carbonyl Group
- a carbon atom linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom
-polar
- Hydrophilic
-Aldehydes and Ketones
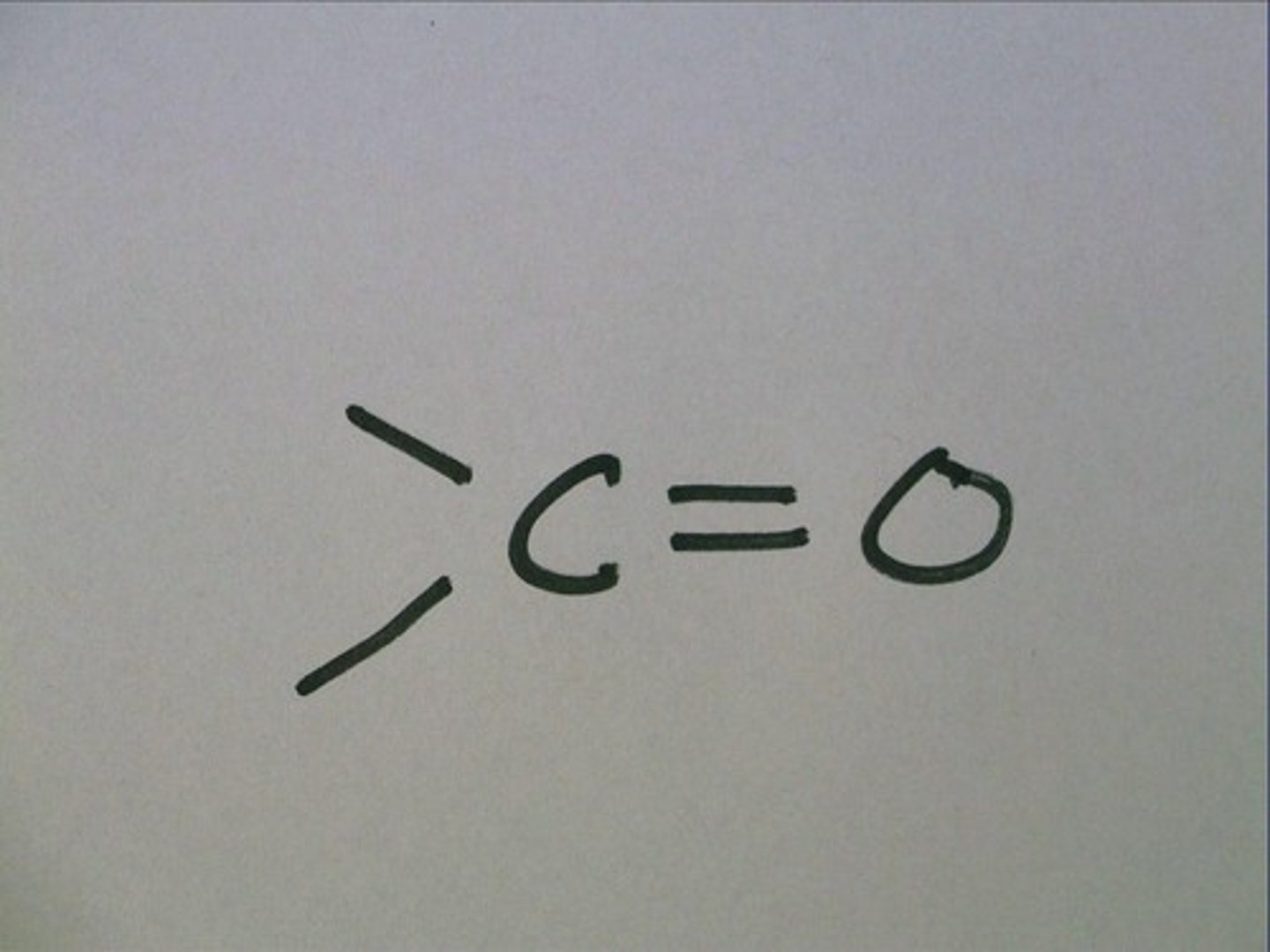
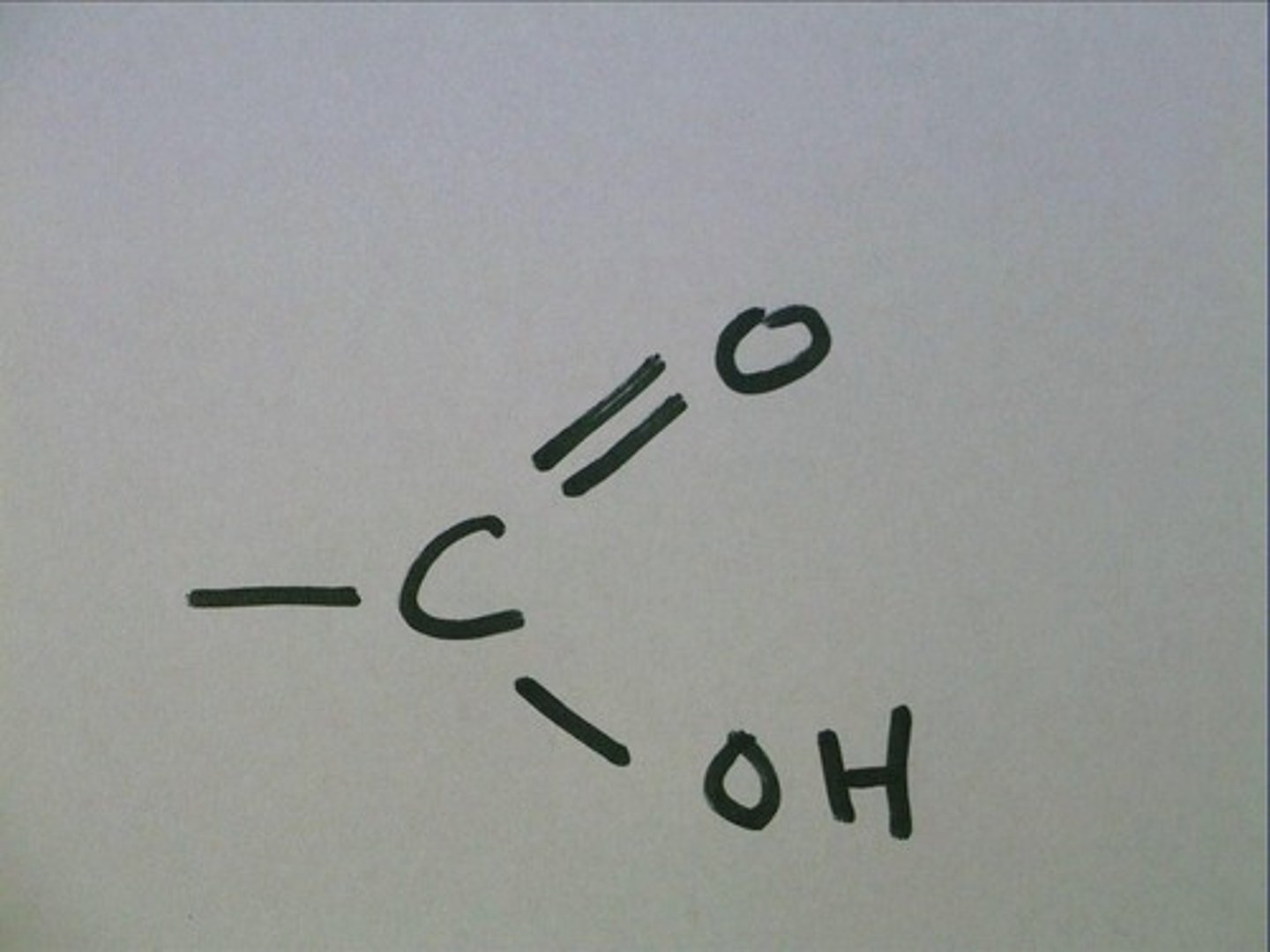
Carboxyl Group
- a single carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group
- acidic
-polar
- hydrophilic
- components of fatty acids and amino acids
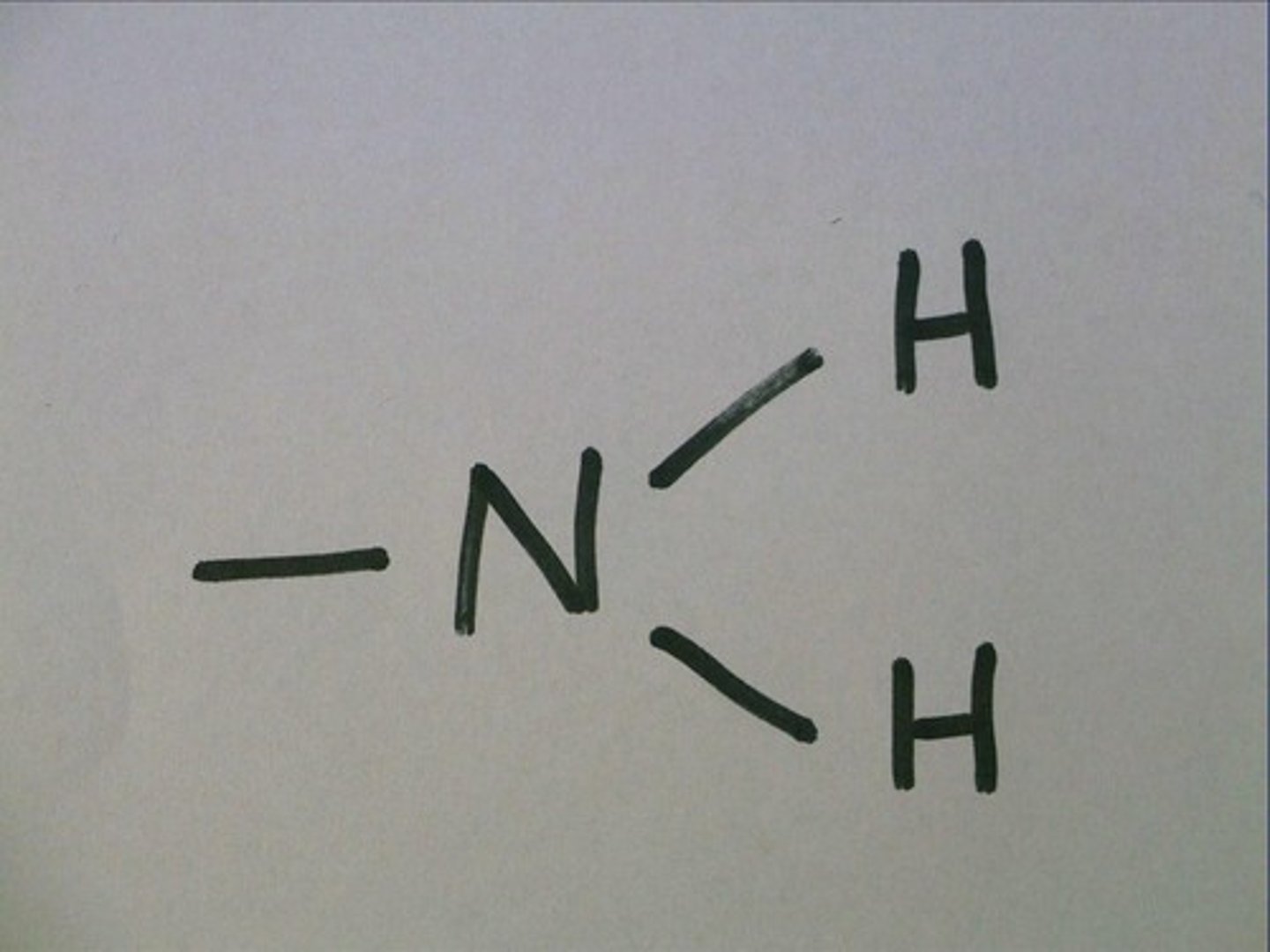
Amino Group
A functional group that consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms
- basic
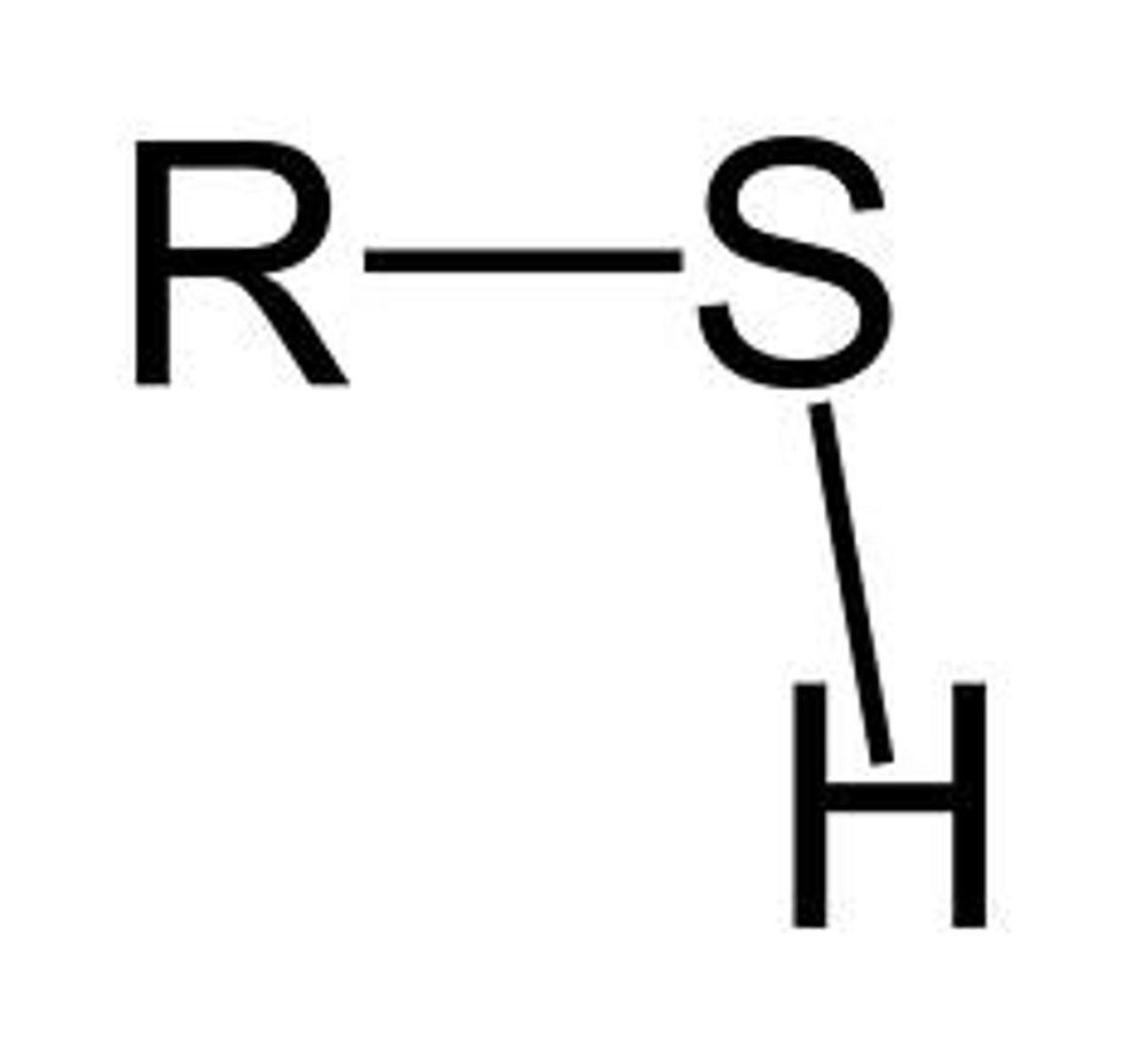
Sulfhydryl Group
A functional group consisting of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (—SH).
- polar
- Hydrophilic
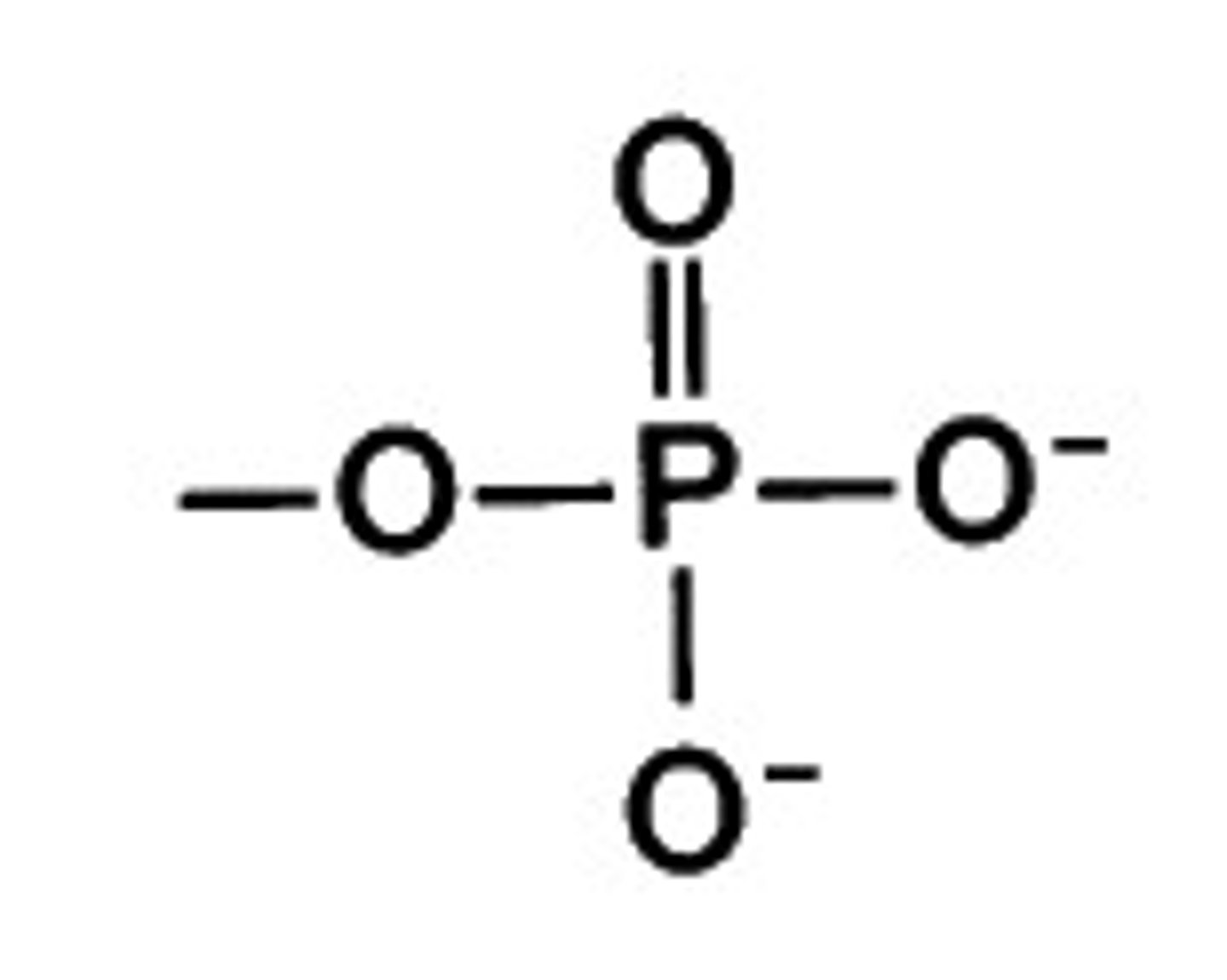
Phosphate Group
A functional group consisting of a phosphorus atom covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms
- acidic
- polar
-hydrophilic
Primary Protein Structure
sequence of amino acids
Secondary Protein Strucutre
Folding of the structure into alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
A-helix is coiled
B-Pleated is accordion/folded sheet
forms due to hydrogen bonding between carbonyl ) of 1 aa with amino H of another aa in another part the protein
Tertiary Protein Structure
three-dimensional folding pattern of a protein due to side chain interactions
side chain interactions caused by
- hydrogen bonds
-ionic bonds
- Van Der Waal's Interactions
-Disulfide Bridges
Quaternary Protein Structure
association between two or more polypeptide chains within one protein
Ex: insulin, collagen, hemoglobin
Prokaryotic Cells
cells without a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles
DNA stored in the cytoplasm
Eukaryotic Cells
have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
much more complex than prokaryotic cells and are multicellular
DNA stored in nucleus
Nucleus
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Mitochondrion
bean-shaped organelle that supplies energy to the cell and has its own ribosomes and DNA.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins production occurs - mainly transport proteins
Golgi Apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell; protein modification and export
Peroxisome
Lipid Destruction; contains oxidative enzymes
Lysosome
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down proteins
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs; produces energy and oxygen releasing processes
How are proteins transported through the endomembrane system?
1. Begins in cytosol
2. Proteins are fed into the ER if they have an amino sequence called signal peptide; if they don't they stay in cytosol for rest of translation
3. The signal peptide (a series of hydrophobic amino acids) send proteins into the ER
4. in the ER, protein fold into their correct shapes and may attach to sugar groups. Most are then transported to golgi apparatus in vesicles. In the golgi, protein undergo modificiations. The final destinations includes lysosome, plasma membrane, and cell exterior
How do polar molecules cross membrane?
through active and passive transport
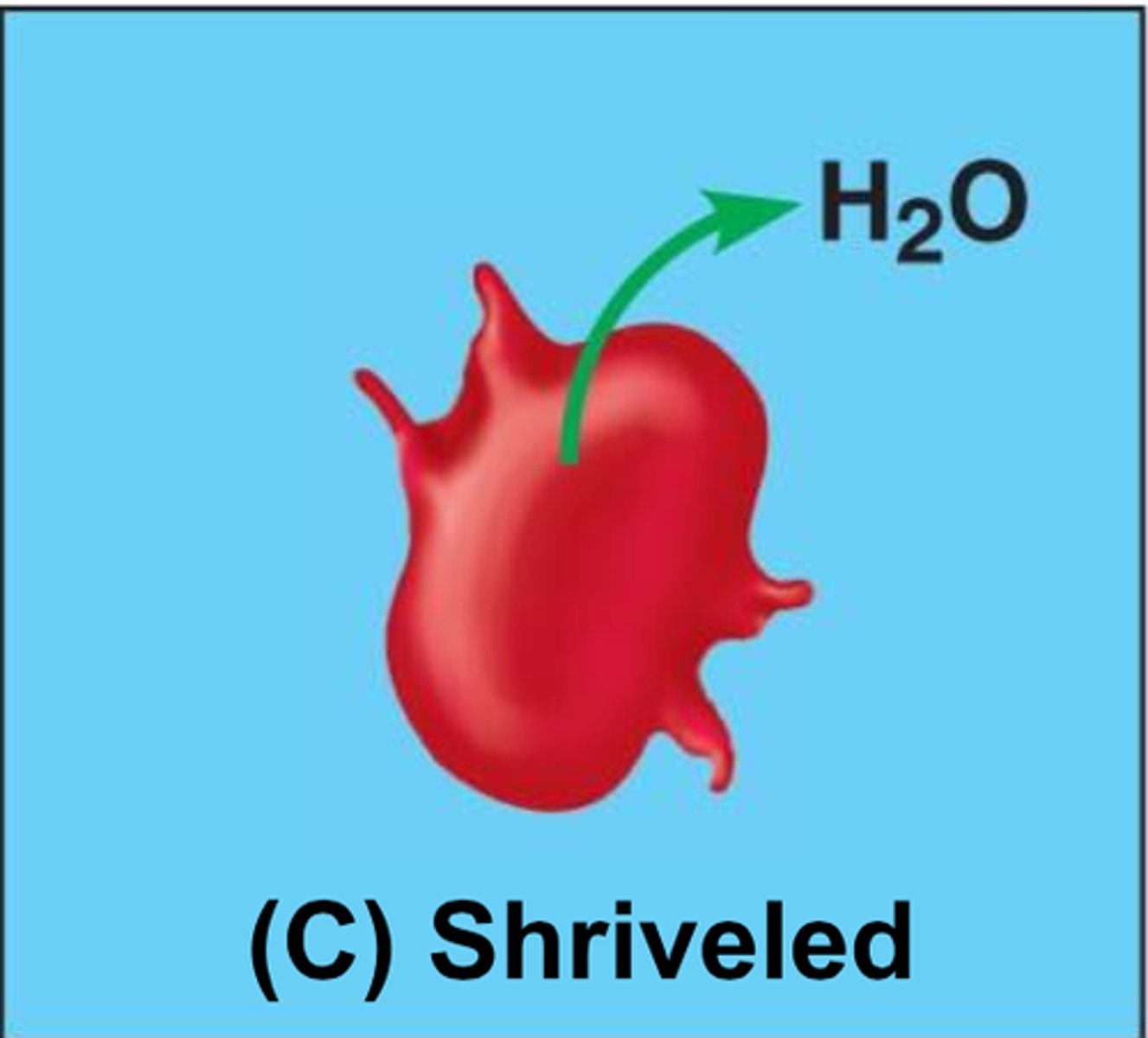
Hypertonic Solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution
water will leave cell
cell will shrink
Hypotonic Solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution
- water will enter cell
- cell will swell
Isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
- no net water movement
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane AGAINST a concentration difference
REQ ATP
Cotransport
The carrier transports two substances in the same direction simultaneously, either in or out of the cell
Simple Diffusion
movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels
Passive Transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
H to L
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
How does ATP couple exergonic and endergonic reactions?
AtP provides energy for both energy consuming ender rxns and energy releasing exer rxns
When the chemical bonds within ATP are broken, energy is released and can be used
ATP transfers energy to ender rxns by phosphorylating other molecules while exer rxns phosphorylate ADP to regenerate ATP
Activation Energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
Catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
Enzyme
a biological catalyst, usually a protein, that speeds up the rate of specific biological reactions
Substrate
- the molecule upon which an enzyme acts
Enzymes catalyze the rxns involving the substrates
Active Site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
Induced Fit
the binding of a substrate or some other molecule to an enzyme causes a change in the shape of the enzyme so as to enhance or inhibit its activity.
Competitive Inhibitor
competes with substrate for active site
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
A substance that impedes the activity of an enzyme without entering an active site. By binding elsewhere on the enzyme, a noncompetitive inhibitor changes the shape of the enzyme so that the active site no longer functions.
Allosteric Regulation
The binding of a molecule to a protein that affects the function of the protein at a different site.
Cooperativity
oxgyen binding to hemoglobin. after first oxygen molecle is bound to one heme unit, Oxygen affinity of the heme units increases to facilitate complete loading of hemoglobin with four oxygen molcules
Feedback Inhibition
A method of metabolic control in which the end product of a metabolic pathway acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme within that pathway.
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
conversion of NAD from NAD+ (oxidized) to NADH (reduced) and back provides the cell with a mechanism fro accepting and donating electrons
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
Oxidized form: FAD
Reduced form: FADH2
Glycolysis
- Cytoplasm
- Reactants: 1 glucose and 2 ATP
- product: 2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate
- G3P, NAD+, and Pi are used in later rxns
- without O2, glycolysis would still occur as it is anaerobic
- if inhibited ATP production would cease
Fermentation
- occurs in cytoplasm
- reactants: pyruvate, NADH, proton
- Products: lactate and NAD+
- fermentation replenishes NAD+ from NADH, H+ produced in glycolysis
- without O2, fermentation occurs (anaerobic)
- if inhibited, you have no method of ATP production
Pyruvate Oxidation
- occurs in mitochondrial matrix
- reactants: pyruvate, NAD+ , coenzyme A
- Products: CO2, NADH, and acetyl CoA
- pyruvate can be converted into carbohydrates, fatty acids, energy, amino acid alanine, and ethanol
- without O2, pyruvate will undergo fermentation
- if inhibited, citric acid decreases as oxaloacetate increases
Citric Acid Cycle
- occurs in Mitochondria matrix
- reactants: acetyl Coa
- products: 2 CO2, 1 ATP, NADH, FADH2 (reduced forms)
- without O2, respiratory cycle cannot function shutting down critic acid cycle (aerobic)
- if inhibited, ETC cannot occur
Electron Transport Chain
- occurs in mitochondria
- reactants: NADH, FADH2, protons, ADP, and O2
- Products: NAD+, FAD, water, protons
- without O2, electrons can't be accepted so ETC will stop and ATP will not be produced by chemiosmosis. The electrons will become backed up and eventually stop ETC. Causing products of glycolysis to go through fermentation instead of CCA
- if inhibited, there is no glycolysis so no ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation
- occurs in mitochondria
- reactants: 8 NADH, 4FADH2, 6 O2
- products: 8 NAD+, 4 FAD+, 32 ATP, 6 H2O
- without O2, ETC does not occur so there is no proton gradient formed by electron flow. Water will not form and NAD cannot be reformed
- if inhibited, ATP cannot be produced.
Chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
Light Reactions
Input:
- water
- light
- Pi
- NADP
- ADP
Output:
- NADPH
- ATP
- Oxygen
Location: Thylkoid
Calvin Cycle
Input:
- CO2
- ATP NADH
Output:
- Pi
- ADP
- NADP+
- Sugars
Location: Stroma
How are calvin cycle and light reactions linked?
light reactions supply Calvin Cycle with CO2 to produce sugars. The Calvin Cycle supplies the light reactions with sugars to produce ATP.
Light reactions provide ATP and NADPH to Calvin Cycle and ADP, Pi, and NADP+ is returned to light reactions
Chemiosmosis in Cellular Respiration
- during ETC of cellular respiration
- in mitochondrial inner membrane
- H+ is pumped from matrix into inter-membrane space using energy derived from electron flow
- ATP synthesis occurs towards the matrix side as ATP synthase is oriented towards matrix side
chemiosmosis in photosynthesis
- occurs during light dependent reactions
- in thylakoid membrane of chloroplast
- H+ is pumped from stroma into thylakoid lumen or thylakoid space using energy derived from electron flow
- ATP synthesis occurs towards stromal side as ATP synthase is oriented towards stromal side
role of NADP+ in photosynthesis
Light rxns use energy from photons to generate high-energy electrons. These electrons are used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH - usuallly stable and can pass its H atom to other molecules
in 2nd stage of calvin cycle, AtP and NADPH are used to convert 3PGA molecules into a 3C sugar (G3P). NADPH donates electrons to a 3C intermediate to make the G3P.
Water-Soluble Hormone
-hydrophilic OR TOO large to cross membrane
- bind to extracellular membrane receptor changing the receptor intracellular domain.
Lipid Soluble Hormone
- hydrophobic
- occurs in cytoplasm
- cross membrane and bind to receptor to form hormone-receptor complex
- moves into the nuclues to bind to specific DNA sequence and begin transcription
Interphase
cell grows and makes copy of its DNA
Includes
- G1 phase
- S phase
- G2 Phase
G1 Phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
S phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated. also duplicated the centrosome
G2 phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
Mitosis (M phase)
cell division; produces 2 identical daughter cells (each with exact same content)
Ploidy Level
number of sets of chromosomes in a cell
Somatic Cells
are diploid meaning that that cell doubles its chromosomes to 4N during mitosis before dividing and resulting in daughtor cells that are 2 N
Prophase
- chromatin condenses into chromosome; each replicated chromosome appears as chromatids joined by centromeres
- mitotic spindles begin to form
- centrosomes begin to move to opposite poles (propelled by lengthening of microtubules)
Prometaphase
- nuclear envelope falls apart
- microtubules invade the nuclear and are bound to some of the chromosomes
- microtubules bind at the kinetochores
Metaphase
- centrosomes have migrated to opposite poles of the cell
- chromosomes have all lined up at the metaphase plate in middle of cell
Anaphase
- sister chromatids break apart and chromosomes begin moving to opposite ends of cell
- by end of anaphase, the 2 halves of the cell have equal # of chromosomes
Telophase
- 2 daughter nuclei form
- nuclear envelope begins to reform
- DNA begins to recondense and spindle microtubules begin to depolymerize
Cytokinesis
- division of cytoplasm
- in animals: Cleavage furrow
- in plants: cell plate
Conduction
transfer of heat from one object to another through physical contact
Convection
The transfer of thermal energy by the circulation or movement of a liquid or gas
Radiation
transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves
Evaporation
transfer of heat energy when a liquid is changed to a gas
Endotherms
-warm blooded
- use internal heat to maintain body temperatures
Ecotherms
- cold blooded
- allows body temperatures to be influenced by external environment temperatures
counter current exchange
the exchange of a substance or heat between two fluids flowing in opposite directions
Ammonia
does not required energy
but causes lots of water loss
Urea
does not lose as much water but require enzyme catalyzed reactions to convert ammonia to urea and excrete it through urination
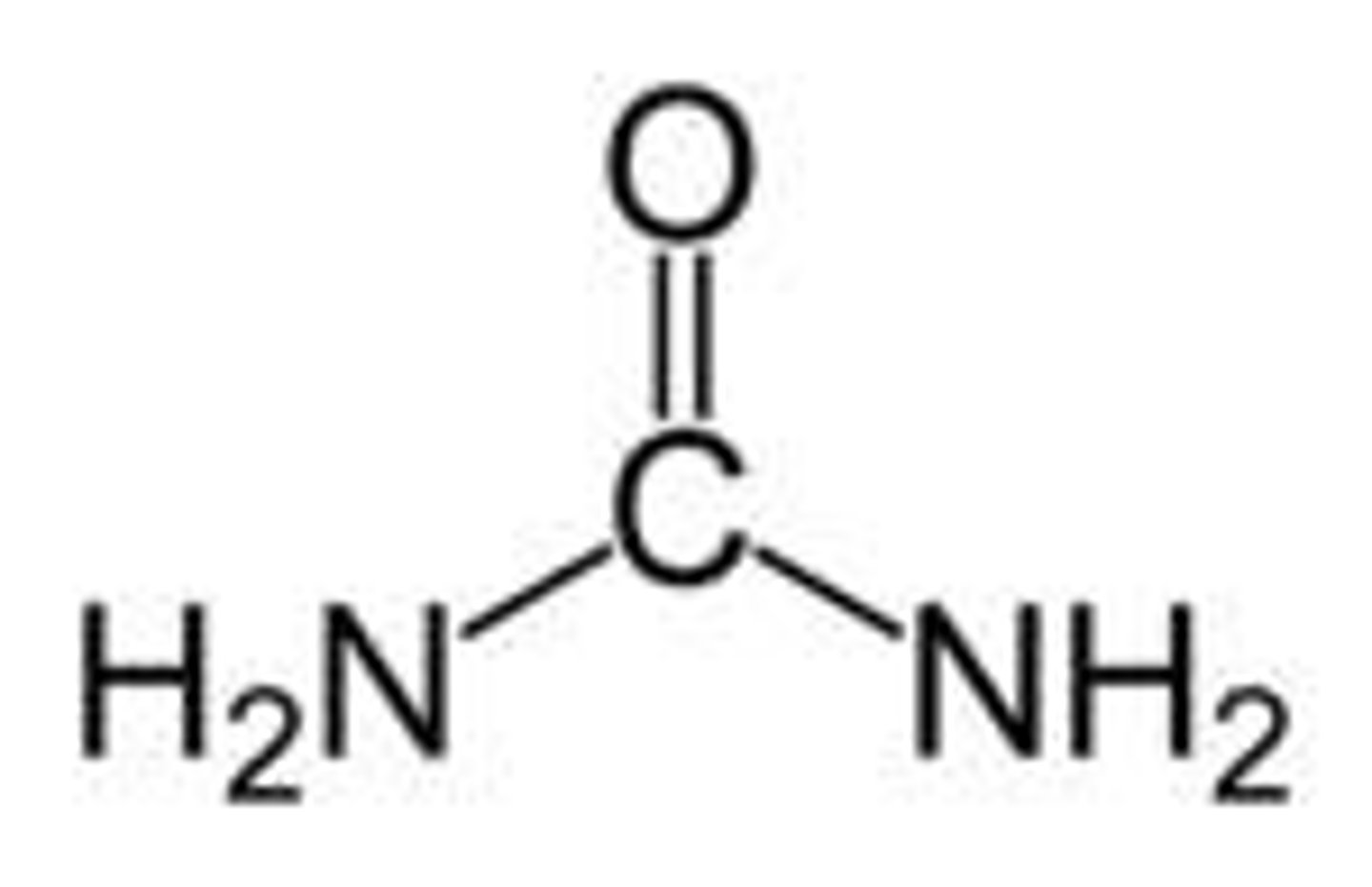
Uric Acid
lose almost no water upon excretion but does require ATP to convert ammonia to uric acid
Tight Junctions
adjacent intestinal epithelia form tight junctions that act as a physical intestinal barrier, regulating movement of various substances across the intestinal epithelium
How does the structure of intestinal lining enhance surface area?
lining is highly folded to form microscopic finger like projections called villi which increase surface area to help with abosrption