1.7 clinical uses of abx
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what is the most likely explanation for increasing abx resistance in community-acquired disease?
A. pts not completing Rx therapy
B. Gr - outer membrane permeability
C. generic branding and import medicines
D. overuse of abx in farming and industry
E. Metronidizole resistant spore forming anaerobes
D
(key is community-acquired)
what are the characteristics of ideal abx agents
-bacteriocidal
-long half life
-low binding to plasma proteins
-oral and injected preparations (rather than just inj)
-good tissue distribution
-minimal side effects or interactions
-"narrow spectrum"
define what a "narrow spectrum" abx is
highly targeted
are oral or injected abx preferred
oral
what is one drug example that has a "narrow spectrum"
penicillin V
abx resistance typically occurs within _______ _______
several years
were genes coding for abx resistance present before or after humans began producing abx
before
what was the purpose of Joshua Lederberg's 1952 "Replica Plate" experiment
demonstrate mutations (resistance) in bacteria can occur before they are exposed to selective pressures (ie abx)
carbapenem is a _____-_____ abx with a _____ _____ activity against bacteria resistant
beta-lactam; broad spectrum
in an ideal situation you are able to ID bacteria, _____ __ _____, and then ______. Does this always happen?
test for sensitivity; prescribe; no often you are unable to test for sensitivity
what are some sensitivity tests/categories that might be tested for?
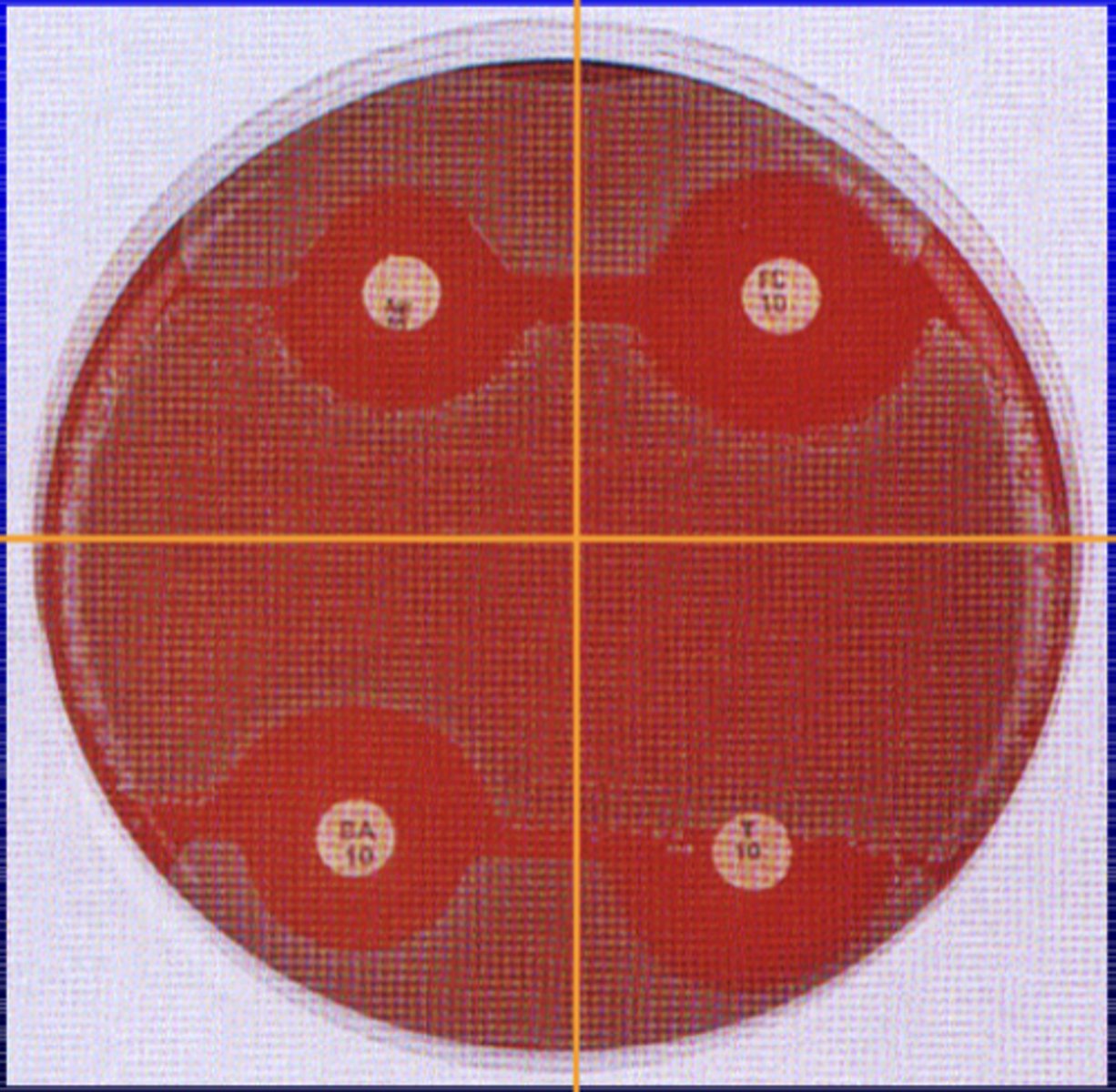
what type of test is used to test for resistance or sensitivity
disc diffusion
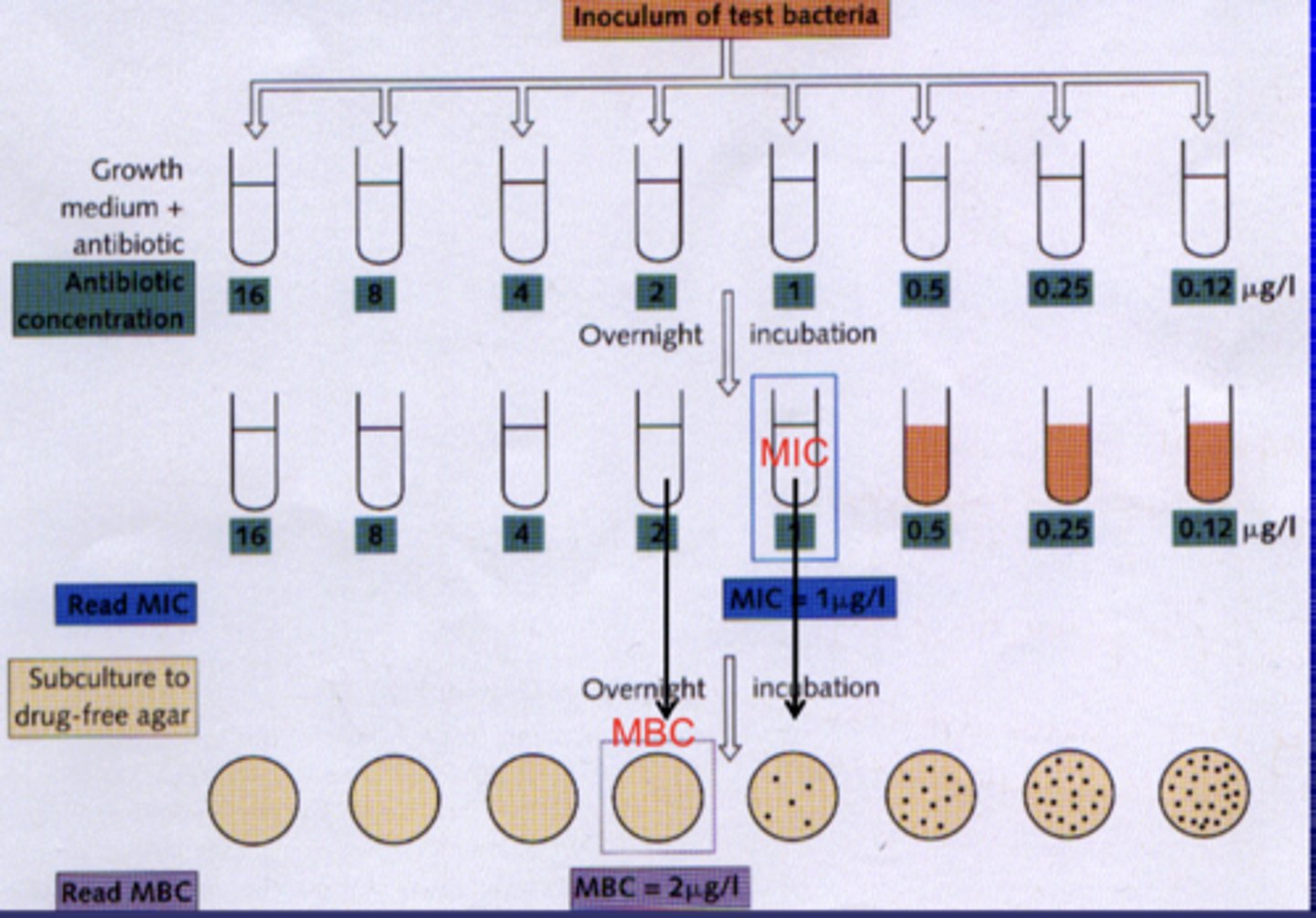
define minimum inhibitory concentration
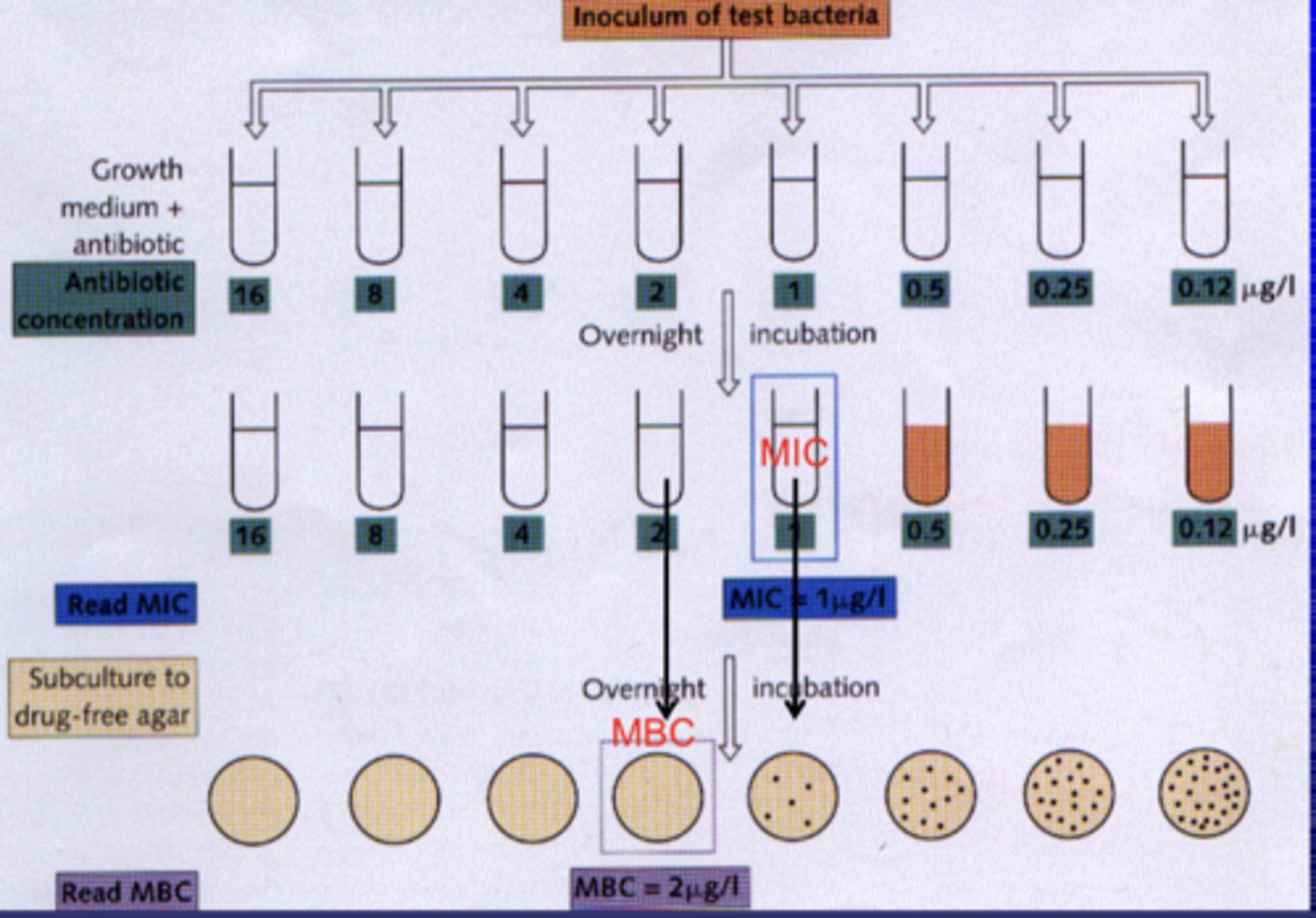
define minimum bactericidal concentration
should abx be rx for upper respiratory tract infections? why or why not?
no; half of these infections could be a viral source
in what cases are upper respiratory tract infections of a bacterial cause?
10+ days and advanced sinusitis
if pt's do not respond or progress within ______ of taking abx, they should be referred to an ID specialist
24hrs
in what cases should pt's always be referred back to their MD or to specialist prior to tx with abx?
pts with hx of prosthetic heart valves or endocarditis
most oral-facial infections are ______ ______ that are not often ____-_____ resistant
mixed anaerobes; beta-lactam
clinical situations that require abx are often accompanied by what other symptoms?
elevated body temp, swelling, restricted jaw movement
what situations automatically require rx of abx
-facial cellulitis
-acute necrotising ulcerative gingivitis
-lateral periodontal abscess
-acute pericoronitis with systemic signs
facial cellulitis may often be associated with?
dysphagia and development of septicemia
specifically in dentistry, antimicrobials are used prior to surgery in what cases/situations?
-risk of post op inf is high
-compromised immune system
-contaminated wounds
-consequence of potential infection is life threatening
what 4 conditions were listed where abx are still recommended prophylactically for dental visits
-artificial heart valves
-prev endocarditis
-congenital heart cond
-heart transplant
are abx still required for pts with joint replacements
no
in what cases/conditions are abx no longer recommended prophylactically for dental visits
-mitral valve prolapse
-rheumatic heart disease
-bicuspid valve disease
______ are prophylactically used when someone is allergic to penicillin
macrolides
(azithromycin or clarithromycin)
which abx are the most commonly used by dentists
beta lactams
penicillin G
penicillin V
in what cases would metronidazole be used
-against anaerobic bacteria
-pts with perio disease
metronidazole is _____ ______ and has _____ ______
well absorbed; low resistance
is drinking recommended when taking metronidazole
no
consider metronidazole if no improvement within _____ after taking penicillin
48 hrs
clinical uses of metronidazole
-acute ulcerative gingivitis
-rapidly progressing periodontal disease
-anaerobic infection around erupted wisdom teeth
why is clindamycin no longer rx as an alternative if someone has a penicillin allergy?
increased risk for C.diff.
after macrolides, what is the 3rd best option as a substitute to penicillins
quinolones
(ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin)
can young children or pregnant women use tetracyclines
no
tetracyclines inhibit ____ _______ ______
30S ribosomal subunits
tetracyclines may still be a drug of choice for some _______ or ______ ______ intracellular bacterial infections
chlamydial; mycoplasma obligate
chlorhexidine can be used for?
gingivitis, periodontitis, dental traumas, oral cysts, post extraction
chlorhexidine primarily used to reduce ______
plaque
fluoride reduces cavities up to ____-_____%
20-60
what is the systemic effect of fluoride
what is the topical effect of fluoride
what is the antimicrobial effect of fluoride
fluoride inhibits ______ of bacterial glycolytic enzymes
enolases
what is recommended for pts to take while on abx to prevent C. diff?
probiotics
(which includes saccharomyces boulardii)