Lab 7: Protostomes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
triploblastic animals 2 types
deuterostomes
protostomes
deuterostomes ex.
Echinodermata, Chordata, and one other phylum
protostomes ex.
2 major groups of phyla
ecdysozoa: arthropoda, nematoda, and others
lophotrochozoa: mollusca, annelida, bracihopoda, platyhelminthes, and many more
protostome: fate of the blastopore
embryonic blastopore becomes the mouth
deuterostome: fate of the blastopore
embryonic blastopore becomes the anus
protostome: coelem formation
coelom formation is schizocoelous
the body cavity forms when the mesodermal tissue "splits”
deuterostome
coelom formation is enterocoelous
the body cavity forms when pockets of the primitive gut (archenteron) bud off
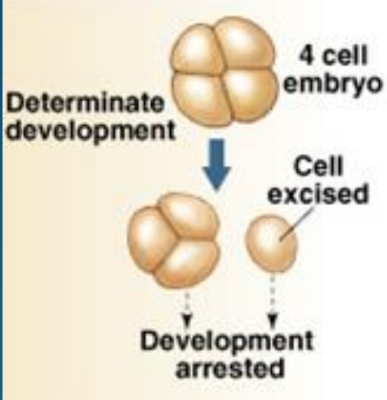
protostome: cell fate
determinate: cells are pre-programmed
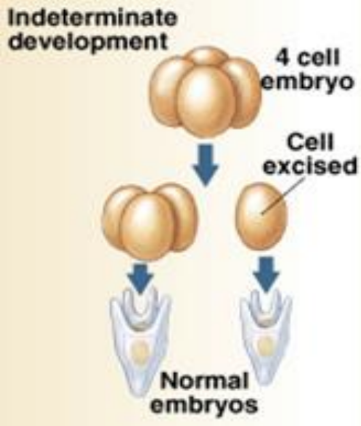
deuterostome
indeterminate: cells are stem cells
ecdysozoa
one of the two major branches of the protostomes
ecdysis = molting
triploblastic
bilaterally symmetrical
more ecydsozoan species than all other animals combined
true or false. ecydysozoa are triploblastic
true
true or false. ecdysozoa are asymmetrical
false. ecdysozoa are bilaterally symmetrical
phylum nematoda
nemata or roundworms
pseudocoelomate
complete digestive tract
longitudinal muscles only (whiplike movement)
dioecious (separate sexes usually)
phylum nematoda
Ascaris, Trichinella, vinegar eel
phylum nematoda: vinegar eels
turbatrix aceti
free living
feed on bacteria & yeast
phylum arthropoda
jointed appendages
segmented body
exoskeleton composed of chitin
open circulatory system
3 major groups: myriapoda, chelicerata, and pancrustacea
phylum arthropoda: subphylum myriapoda
single pair of antennae
single pair simple ocelli (“eyes”)
3 pairs of modified appendages for mouthparts
breathe w/ spiracles and tracheae
centipedes
millipedes
phylum arthropoda: subphylum myriapoda: centipedes
carnivorous
1 pair of legs per segment
possess poison fangs
phylum arthropoda: subphylum myriapoda: millipedes
herbivorous
2 pair of legs per segment: each segment is 2 segments fused together
phylum arthropoda: subphylum chelicerata
possess chelicerae
used as pincers or fangs
2 body regions
cephalothroax & abdomens
6 pairs of appendages
4 pairs of legs, 1 set of chelicerae, 1 set of pedipalps
breathe using gills or book lungs
phylum arthropoda: subphylum chelicerata: 2 body regions
cephalothorax and abdomen
phylum arthropoda: subphylum chelicerata: possess chelicerae
used as pincers or fangs
phylum arthropoda: subphylum chelicerata: 6 pairs of appendages
4 pairs of legs, 1 set of chelicerae, 1 set of pedipalps
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea
hexapoda and crustacea are more closely related than any other two groups within the arthropoda
molecular studies suggest this is a monophyletic clade
many synapomorphies between hexapods and crustaceans
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea: synapomorphies between hexapods and crustaceans
heavily segmented
compound eyes
well-developed mandibles
3 clearly distinguished body regions: head, thorax, and abdomen
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea: subphylum hexapoda
insects and related taxa
3 pairs of walking legs
wings
usually 2 pairs
the only invertebrates to have evolved true flight
also have special feeding appendages and sensory organs
breathe using well-developed spiracles and tracheae
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea: subphylum crustacea
most marine, some freshwater, a few terrestrial
2 pairs of sensory antennae
each body segment has 2 appendages: antennae, mouth parts, cheliped, legs, swimmerets, and tail fins
>3 pairs walking legs
biramous (branched) appendages
gills or “branchiostegal lungs” for respiration
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea: subphylum crustacea: how many sensory atennae
2
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea: subphylum crustacea: body segments
each body segments has 2 appendages
antennae, mouth parts, cheliped, legs, swimmerets, and tail fins
phylum arhthropoda: pancrustacea: subphylum crustacea: what is used for respiration?
gills or “branchiostegal lungs”
phylum arhthropoda: lophotrochozoans
aka spiralia: the other major branch of protostomes
triploblastic & bilaterally symmetrical
very diverse clade w/ around 10-15 phyla
3 defining features found in many, but not in all
phylum arhthropoda: lophotrochozoans: 3 defining features found in many, but not in all
many have spiral cell division
lophophore (lophophorates) crown of ciliated tentacles that surround the mouth used for feeding
trochophore (trochozoans) the larval stage of annelids and mollusks, some others
phylum platyhelminthes: flatworms
flat bodies
aceoelomate
hermaphroditic
ladder-like (simple) nervous system, exhibit primitive organ systems
first example of cephalization (development of a head) in the fossil record
phylum platyhelminthes: planarians
have protonephridia (flame cells) for osmoregulation
incomplete digestive tract
phylum platyhelminthes: rhabditophora
planarians
free-living predators or scavengers
have protonephridia (flame cells) used for osmoregulation
“eyespots” - photoreceptive neurons (aka ocelli)
protrusible pharyx used for eating and voiding feces
incomplete digestive tract
phylum platyhelminthes: rhabditophora: protrusible pharyx
used for eating and voiding feces
incomplete digestive tract
phylum platyhelminthes: rhabditophora: eyespots
photoreceptive neurons (aka ocelli)
phylum platyhelminthes: rhabditophora: class cestoda
tapeworms
internal parasites
definitive host is a vertebrate
no digestive system
attachment organ called scolex
no its head, doesn’t have one :(
proglottids
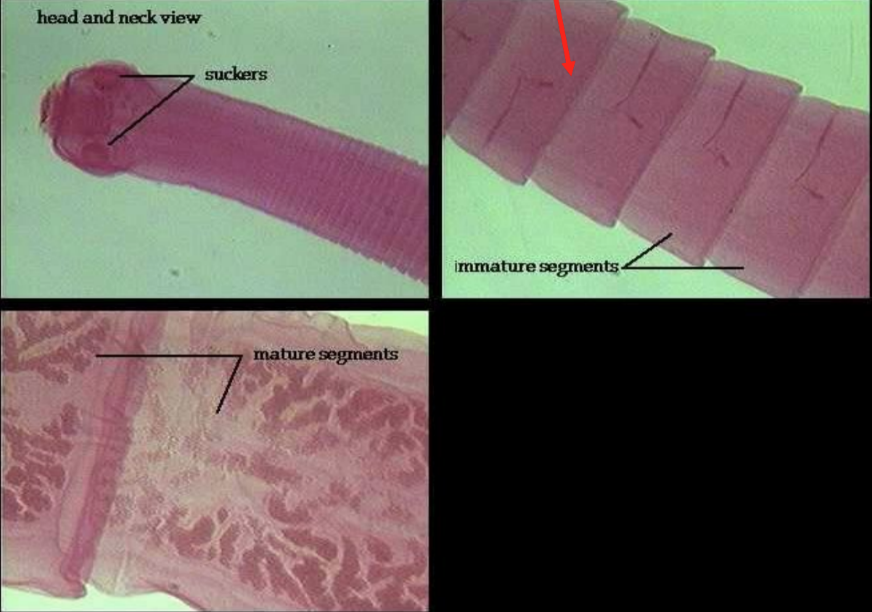
phylum platyhelminthes: rhabditophora: class cestoda: proglottids
reproductive segments, break off end of worm when fully mature
phylum platyhelminthes: rhabditophora: class cestoda: attachment organ
called a scolex (not its head)
phylum mollusca
chiton, snails, clams, and cephalopods
mostly marine
have a trochophore larval stage
4 major clades: Polyplacophora, Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda
phylum mollusca: characteristics
foot: movement and food capture
visceral mass: contains the organs
mantle: secretes shell (usually)
radula: scrapes food, found in 2 of the major clades
open circulatory system: no blood vessels except heart, found in 3 of major clades
phylum mollusca: class polyplacophora
chitons
segmented shell (8 plates) does NOT represent true segmentation
scrapes algae off rocks w/ a radula
phylum mollusca: class polyplacophora: how many plats does the segmented shell have?
8 plates, does NOT represent
phylum mollusca: class gastropoda
slugs, snails, and nudibranchs
some exhibit torsion: 180 degree rotation of the visceral mass
some have shells many snails have radulas
phylum mollusca: class gastropoda: torsion
180 degree rotation of the visceral mass
phylum mollusca: class bivalvia
clams, oysters, scallops, and mussels
animals contained within 2 hinged valves
incurrent and excurrent siphons
4 oversized gills for filter feeding
phylum mollusca: class bivalvia: how many oversized gills?
4, for filter feeding
phylum mollusca: class cephalopoda
chambered nautilus, squid, and octopi
all are predators
the most advanced invertebrates
chromatophores
octopi have 8 arms; squid also have 8 arms AND 2 longer tentacles
notice hooks on tentacles used for grabbing prey
pen is remnant of shell, is internal - found in squid
octopi have no pen
all octopi have venomous bites
phylum mollusca: class cephalopoda: the most advanced invertebrates
closed circulatory system w/ 3 hearts - dual circuit circulation
well-developed eyes
most intelligent invertebrates
phylum mollusca: class cephalopoda: chromatophores
pigmented cells that help these animals change color: communication and camouflage
phylum mollusca: class cephalopoda: pen
remnant of shell, is internal - found in squid
phylum brachiopoda: lophophorates
sessile
coelomate
lophophore and pedicle present
very abundant in fossil record (paleozoic era), now only about 350 species remain
are NOT mollusks
shells of calcite (CaCO3) & proteins, around body
2 classes: articulata & inarticulata
phylum brachiopoda: lophophorates: true or false. lophophore and pedicle are present.
true
phylum brachiopoda: lophophorates: true or false, they are mollusks
false. not mollusks
phylum brachiopoda: lophophorates: shells
shells of calcite (CaCO2) & protein, around body
phylum brachiopoda: lophophorates: 2 classes
articulata & inarticulata
phylum annelida: segmented worms characteristics
truly segmented body (divded by septa)
closed circulatory system
convergent w/ vertebrates & cephalopods
have a trochophore larval stage
shared w/ Mollusca and a few other phyla
phylum annelida: segmented worms: 2 major clades
errantia: free-living marine sand worms
sedentaria: mostly sessile marine worms, earthworm and fres
phylum annelida: class errantia: well-developed sense organs
antennae and eyes
phylum annelida: class errantia: true or false. class errantia are free-living mobile marine worms
true
phylum annelida: class errantia: possess fleshy _______ with tiny, chitinous ______ aka ____ (bristles) on each segment
parapodia, chaetae, setae
phylum annelida: class sedentaria
sedentary marine tubeworms, earthworms, and leeches
posses few to no setae (bristles) and (often) a clitellum
gives them together while mating
secretes cocoon around eggs
phylum annelida: class sedentaria: function of the few to no setae (bristles) and clitellum
glues them together while mating
secretes cocoons around eggs
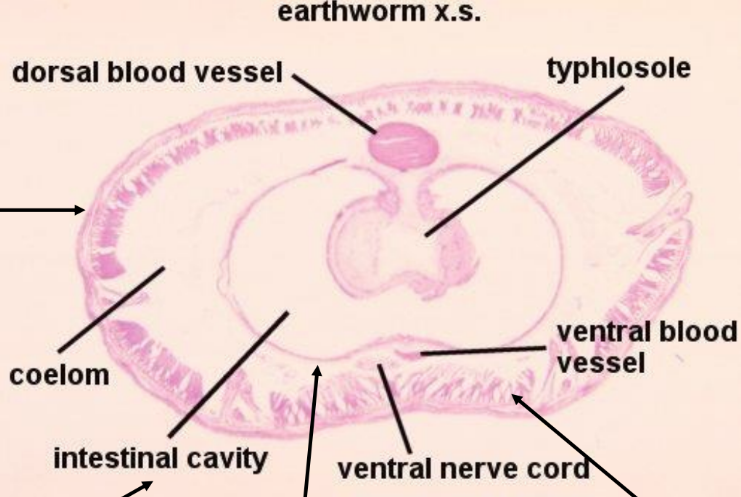
earthworm cross section
body wall
intestinal lumen
intestinal wall
longitudinal muscle layer
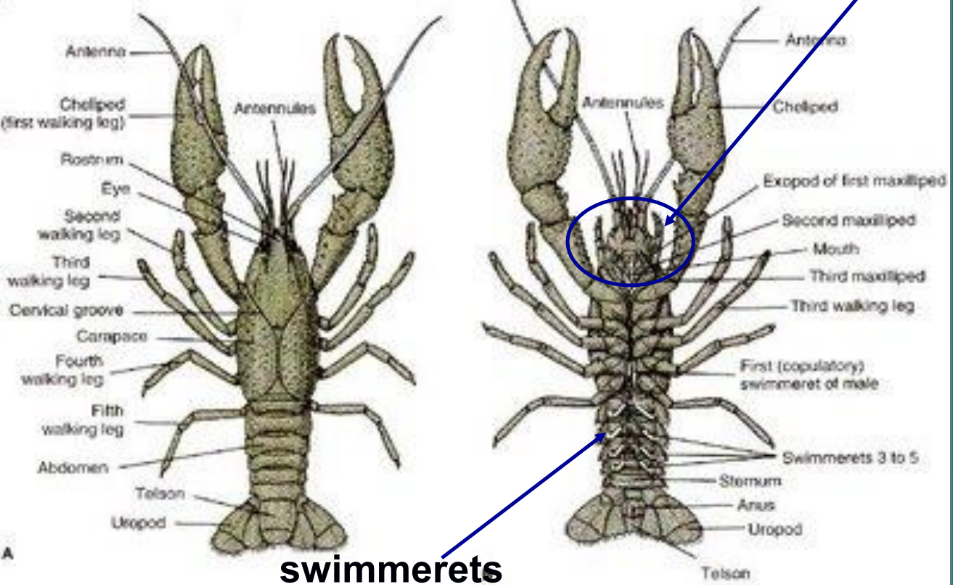
crayfish anatomy
antennae, antennules, compound eyes, chelipeds, rostrum, swimmerets, head, thorax, abdomen, tail, walking legs, carapace, inner and outer jaws
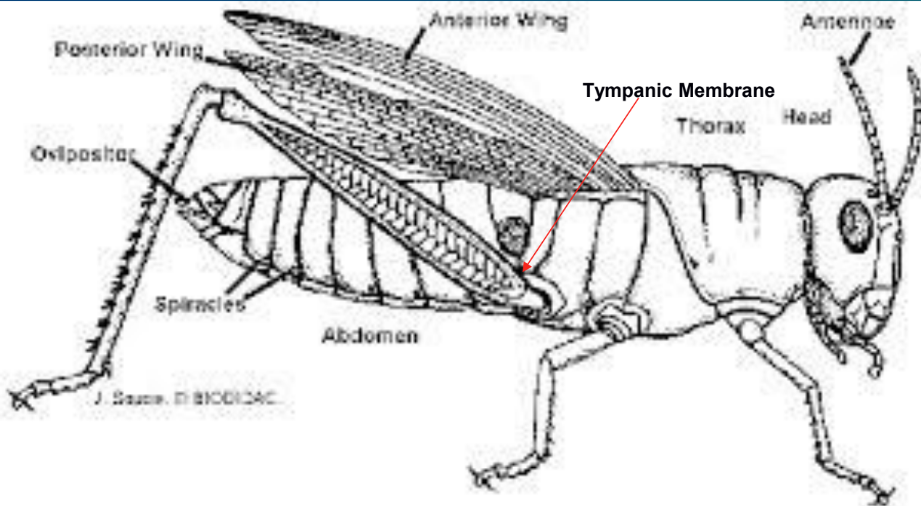
insect anatomy
compound eyes, antennae, head, thorax, abdomen, tympanic membrane, spiracles, wings, walking legs
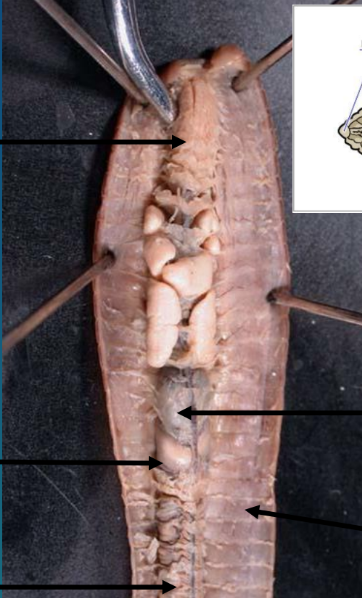
earthworm dissection
pharynx, gizzard, intestine, dorsal blood vessel, crop, septum
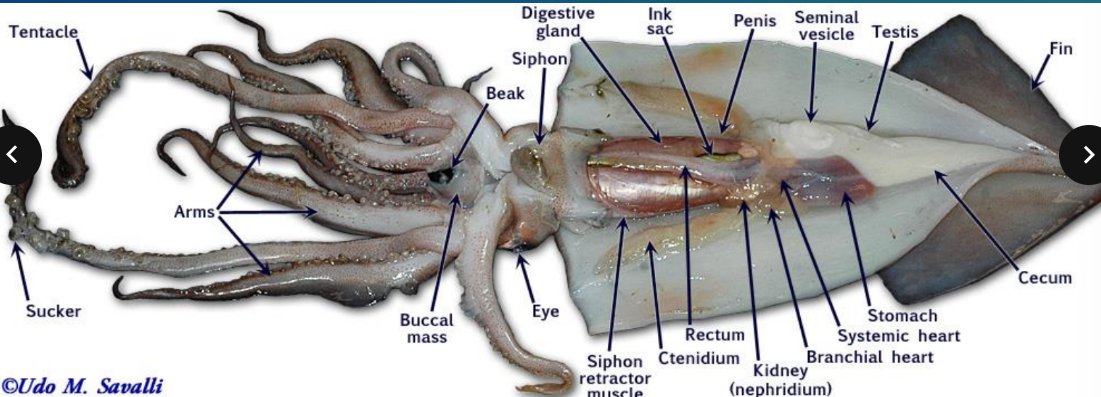
squid dissection
suckers, arms, tentacles, mouth, eyes, siphon, gills, mantle, pen and ink sac