Chapter 25: Phylogenies and the History of Life
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
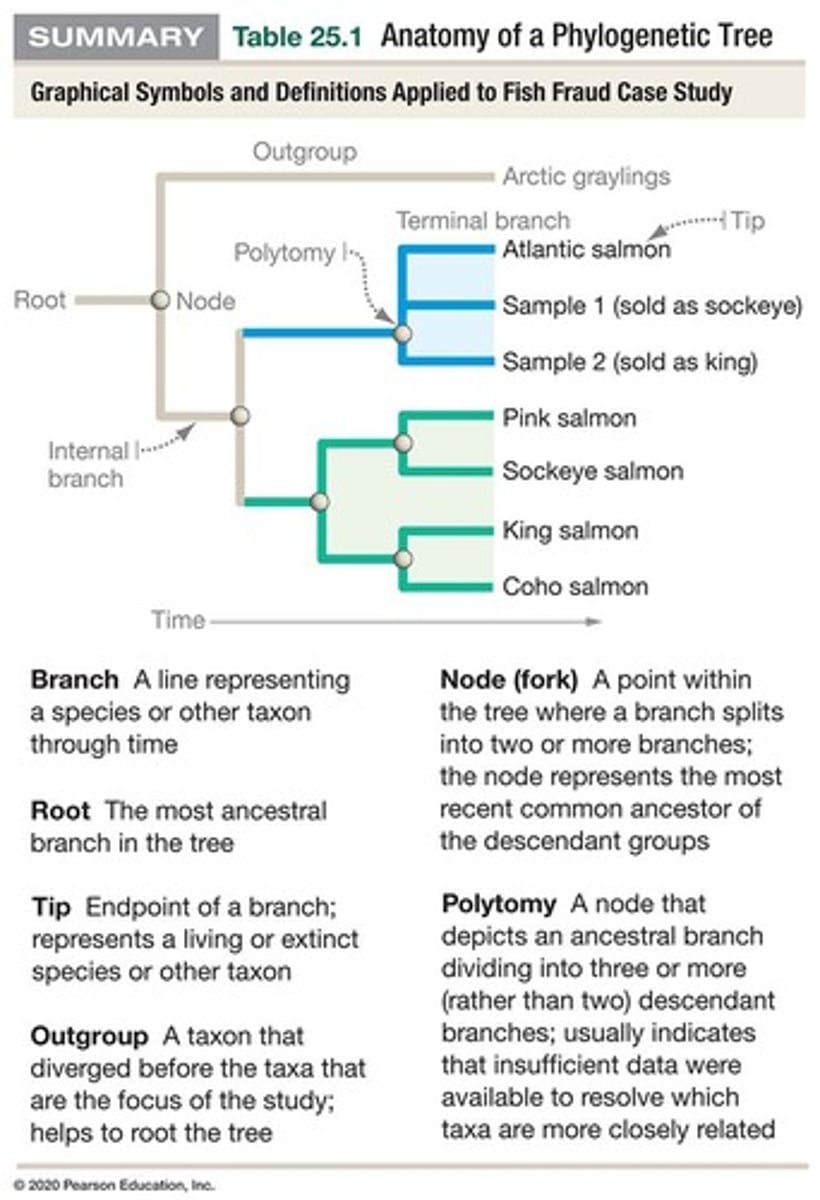
Phylogeny
Branching evolutionary history of organisms.
Phylogenetic tree
Simplified diagram representing evolutionary history.
Systematics
Study of classifying relationships among organisms.
Tree of life
Most universal phylogenetic tree depicting all life.
Taxonomy
Science of naming and classifying organisms.
Taxa
Groups of organisms classified at any level.
Sister groups
Closely related taxa sharing a recent ancestor.
Nodes
Points representing speciation events in trees.
Branches
Lines connecting nodes and taxa in trees.
Conservation priority
Species identified as needing urgent protection.
Fossil record
Historical evidence of past life forms.
Analytical tools
Methods used to reconstruct life's history.
Speciation event
Occurrence when one species diverges into two.
Branch tips
Ends of branches where taxa are located.
Common ancestor
An ancestor shared by two or more taxa.
Proximity of labels
Not indicative of relationships in phylogenetic trees.
Taxa location
Always at branch tips, not within trees.
Rotation of branches
Branches can rotate without altering relationships.
Phylogenetic trees
Hypotheses estimating relationships among taxa.
Data Matrix
Framework for comparing organisms' traits.
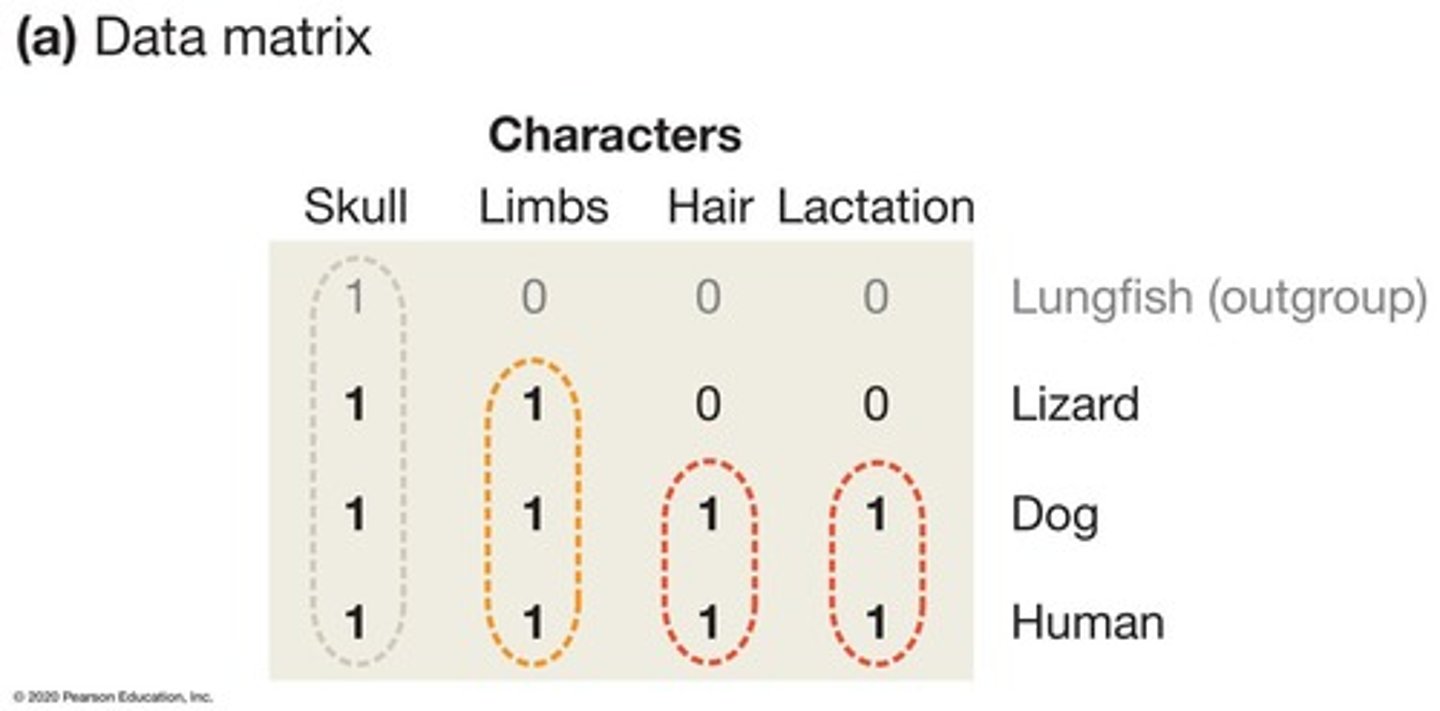
Character or trait
Genetic, morphological, or behavioral feature studied.
Character states
Presence (1) or absence (0) of traits.
Outgroup
Related group used to identify ancestral traits.
Ancestral trait
Character existing in a common ancestor.
Derived trait
Modified form of an ancestral trait.
Homoplasy
Similar traits due to independent evolution.
Homology
Similar traits due to common ancestry.
Synapomorphies
Shared derived traits identifying monophyletic groups.
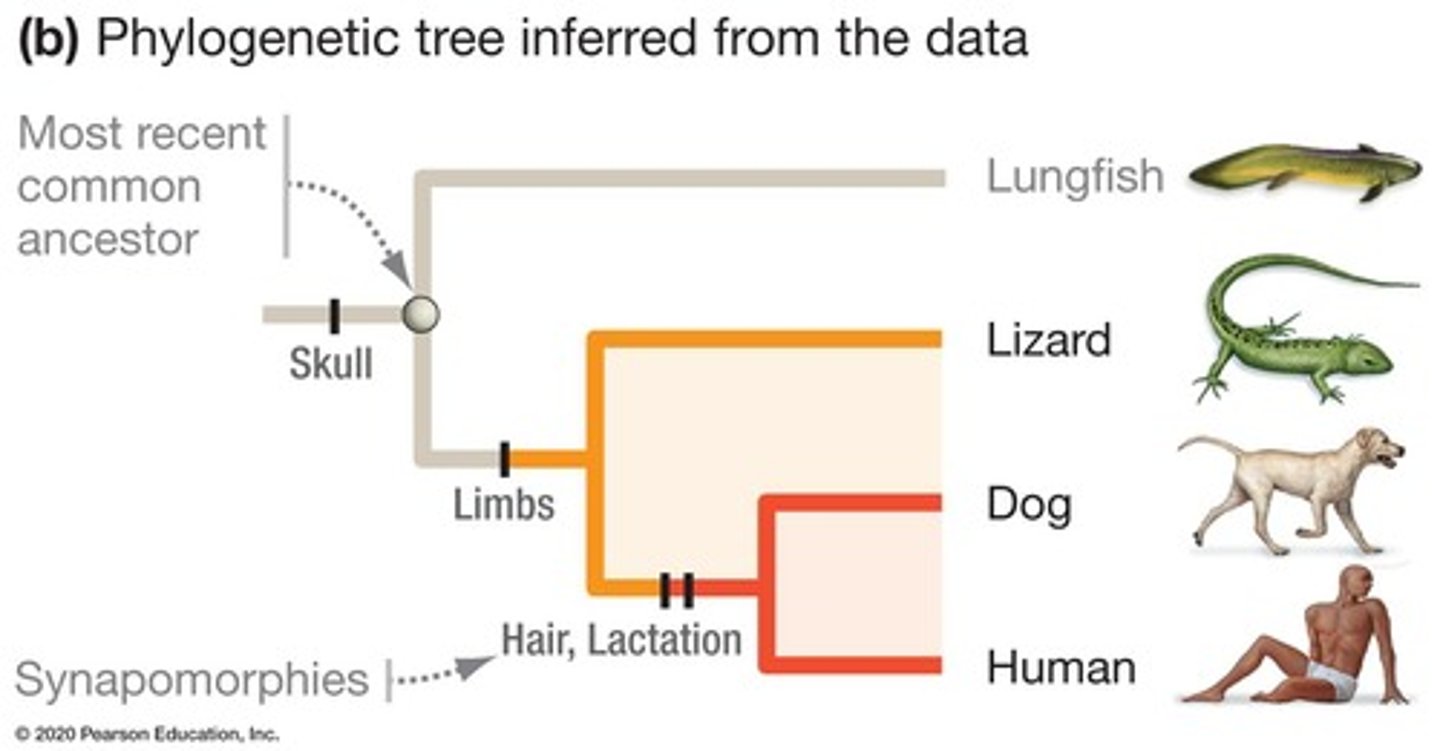
Monophyletic group
Ancestral species and all its descendants.
Clades
Another term for monophyletic groups.
Parsimony
Method minimizing changes to infer relationships.
Evolutionary distance
Average frequency of character changes between taxa.
Maximum likelihood
Statistical method estimating tree based on data.
Bayesian analysis
Probabilistic method using prior information and data.
Convergent evolution
Independent evolution of similar traits in unrelated taxa.
Homologous traits
Similar traits inherited from a common ancestor.
Convergent traits
Similar traits evolved independently in different lineages.
Streamlined bodies
Similar body shapes in dolphins and ichthyosaurs.
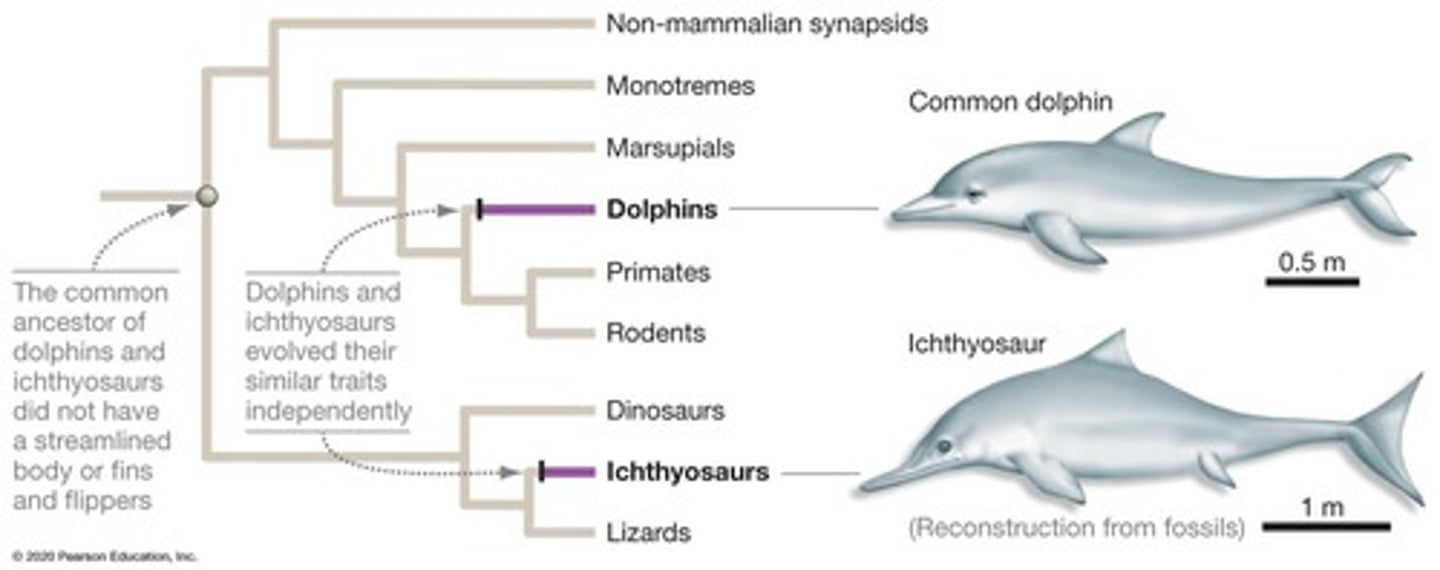
Whale evolution
Study of whales' phylogenetic placement in life.
Branch lengths
Represent evolutionary distance in phylogenetic trees.
Reversal in character state
Change back to an ancestral trait state.
Multiple outgroups
Used to better estimate phylogenetic relationships.
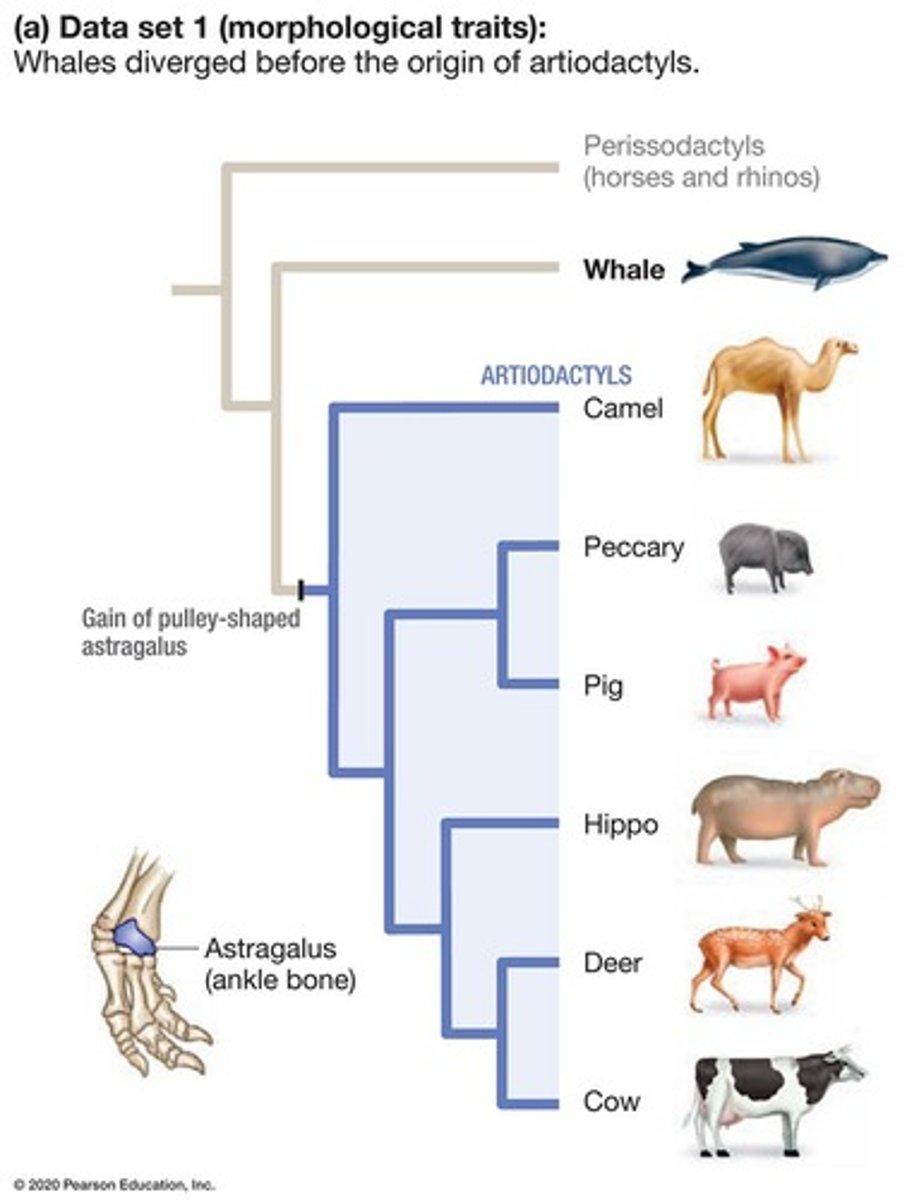
Artiodactyls
Even-toed ungulates including hippos and cows.
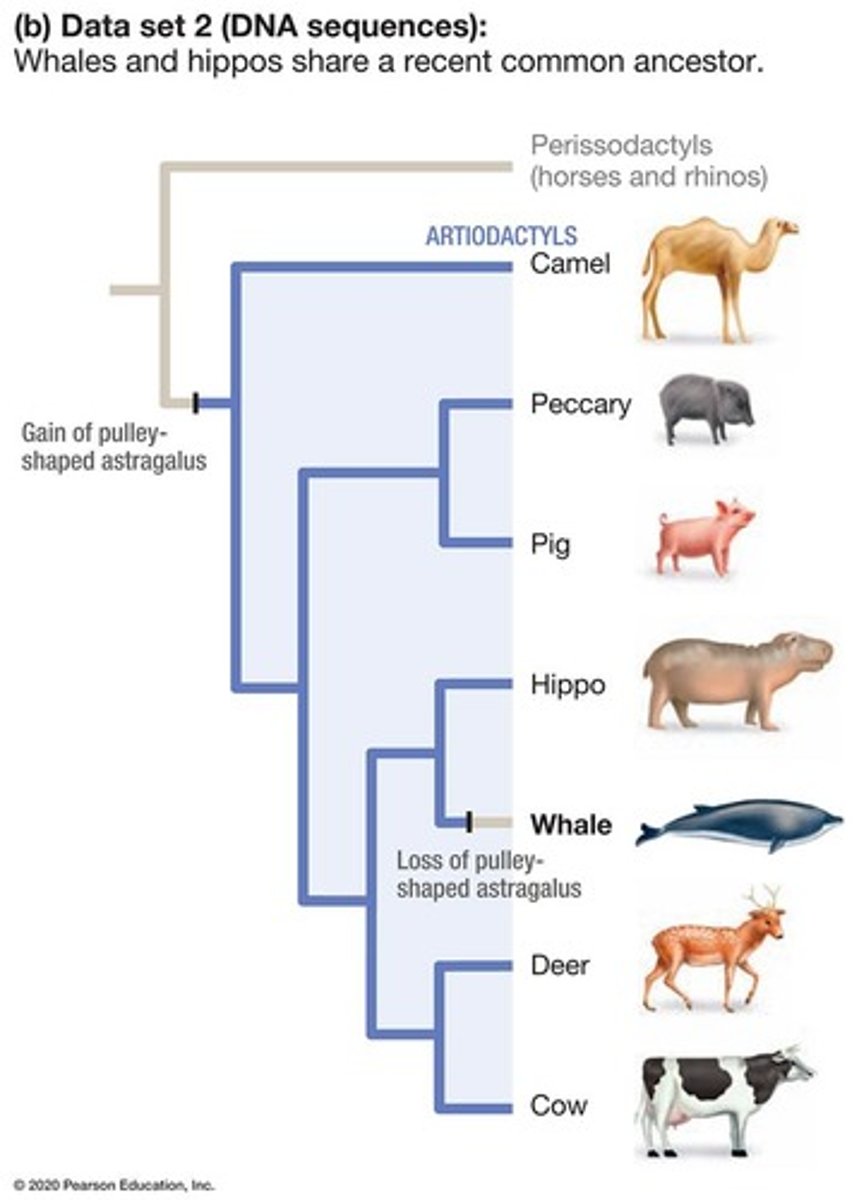
Astragalus
Pulley-shaped ankle bone in artiodactyls.
Outgroup
A taxon outside the group being studied.
SINEs
Short interspersed nuclear elements in genomes.
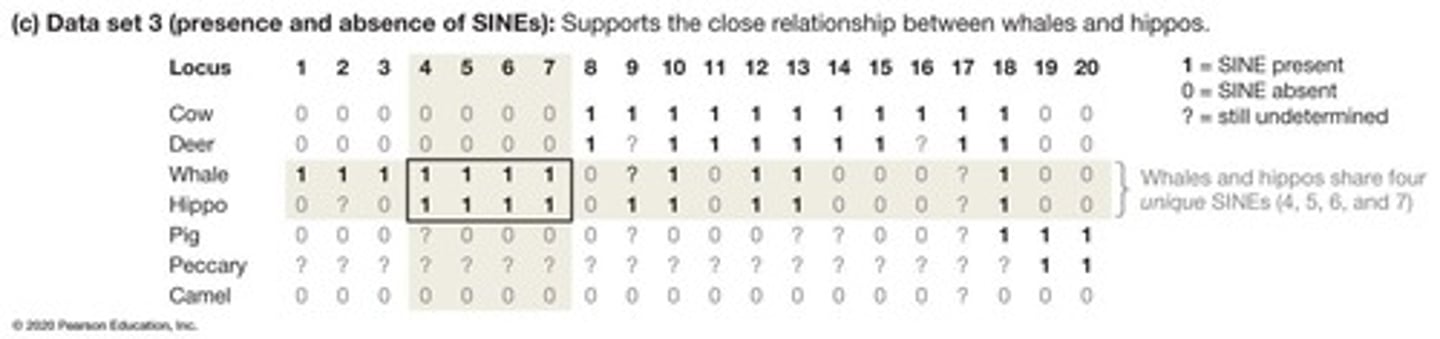
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of species based on traits.
Sister group
Closest relative in evolutionary tree.
Gain event
Evolutionary occurrence of a new trait.
Loss event
Evolutionary disappearance of a trait.
Derived characters
Traits that evolved from a common ancestor.
Fossil record
Total collection of discovered fossils globally.
Fossil
Physical evidence of past organisms.
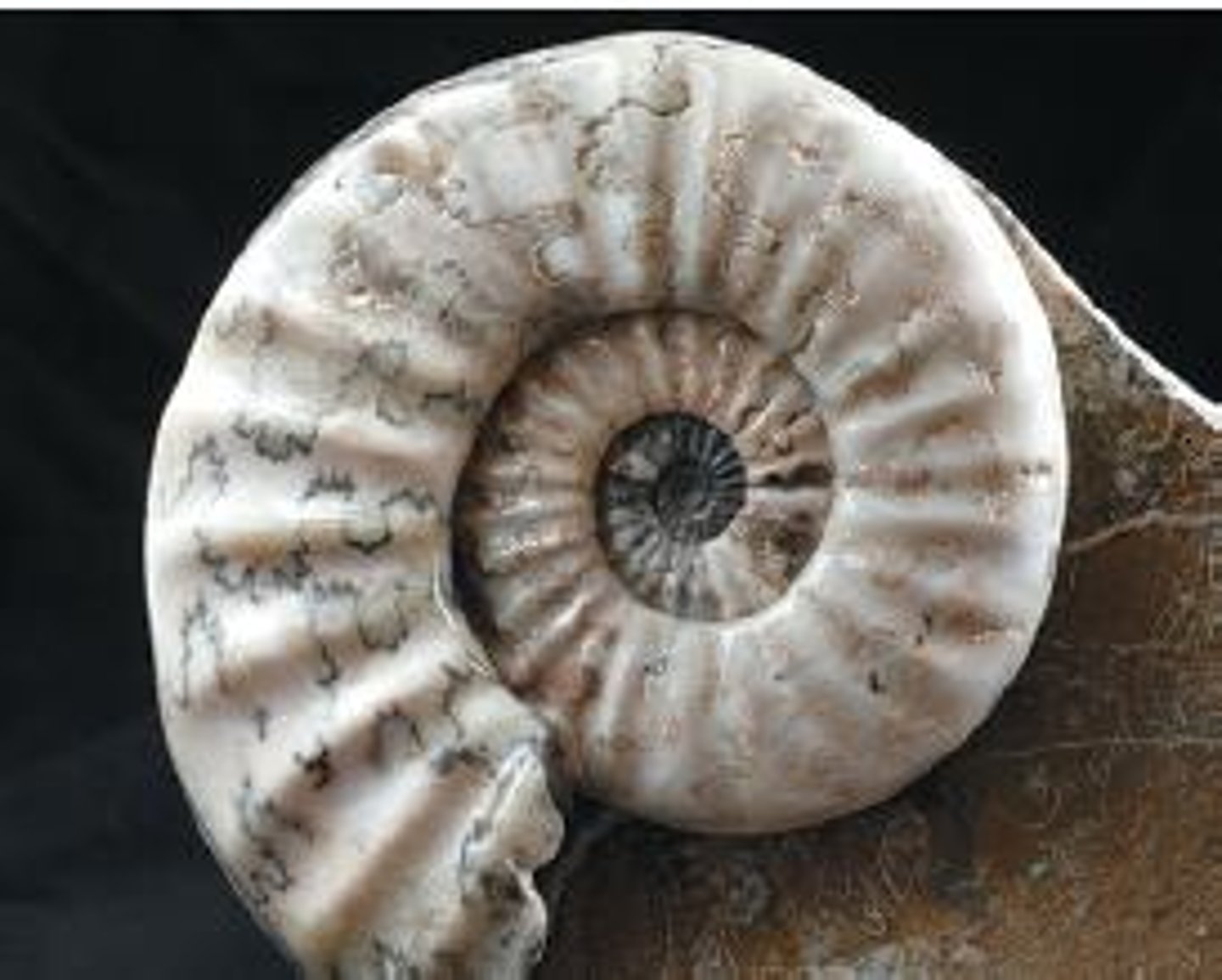

Intact fossils
Complete remains of an organism.
Compression fossils
Organism remains flattened in sediment.
Cast fossils
Mineral-filled molds of organisms.
Permineralized fossils
Fossils with minerals replacing organic material.
Trace fossils
Evidence of organism activity, like footprints.
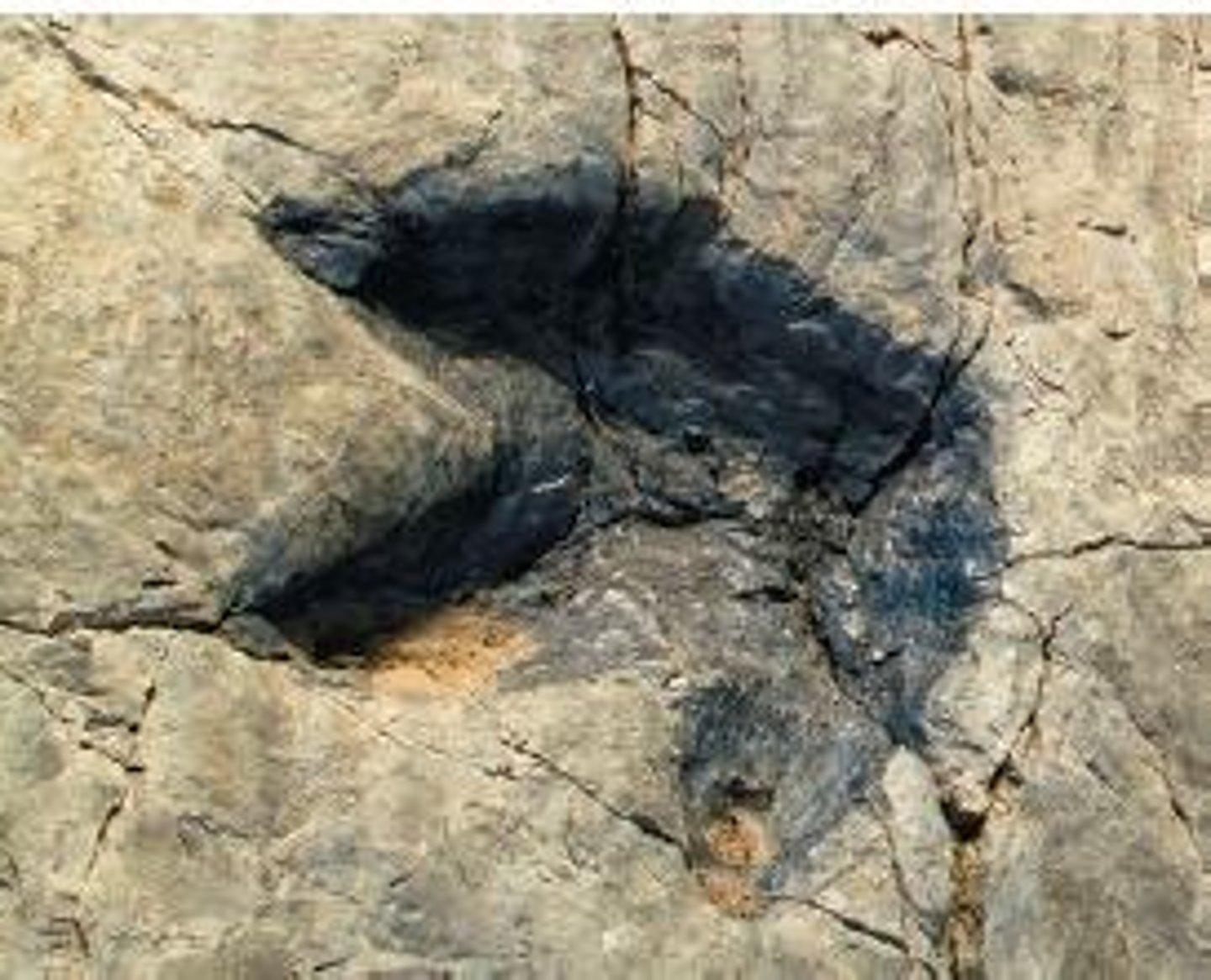

Habitat bias
Fossilization likelihood based on organism habitat.
Taxonomic bias
Fossilization favoring organisms with hard parts.
Temporal bias
Recent fossils more common than ancient ones.
Abundance bias
Common species more likely to fossilize.
Radiometric dating
Method for assigning absolute dates to fossils.
Earth's formation
Estimated to have begun ~4.6 billion years ago.
Life's beginning
Estimated to have started ~3.5 billion years ago.
Archaeopteryx
First birdlike dinosaur in the fossil record.

Evolutionary firsts
Indicate appearance of new lineages or innovations.
Precambrian
Interval from 4.5 billion to 541 million years ago.
Hadean Eon
Earliest eon, before life existed on Earth.
Archaean Eon
Eon characterized by the emergence of unicellular life.
Proterozoic Eon
Eon before the Cambrian explosion of multicellular life.
Phanerozoic Eon
Interval from 541 million years ago to present.
Paleozoic Era
Era of ancient life, major animal lineages appeared.
Mesozoic Era
Era known for dinosaurs and gymnosperms dominance.
Cenozoic Era
Era of recent life, mammals and birds dominate.
Holocene Epoch
Current epoch, following the last Ice Age.
Anthropocene Epoch
Proposed epoch reflecting human impact on Earth.
Adaptive Radiation
Rapid production of diverse species from one lineage.
Hawaiian Silverswords
Example of adaptive radiation from tarweed species.
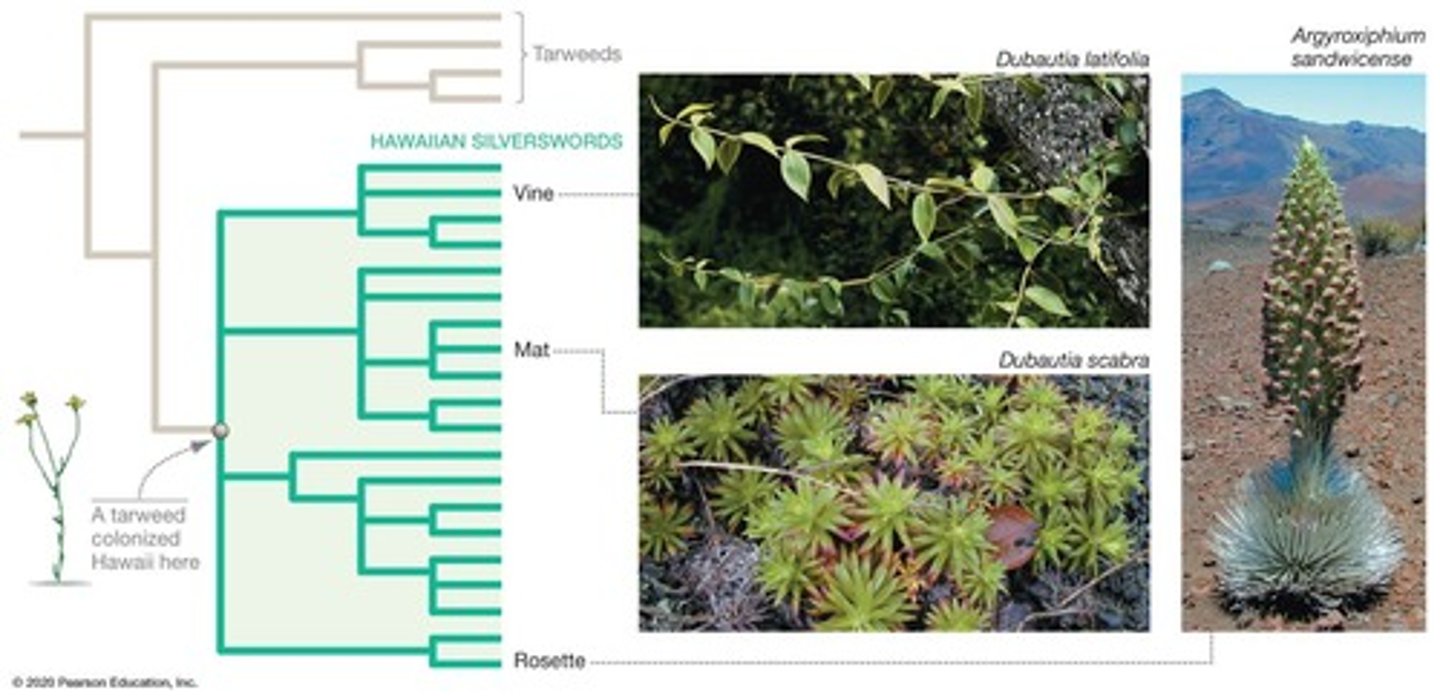
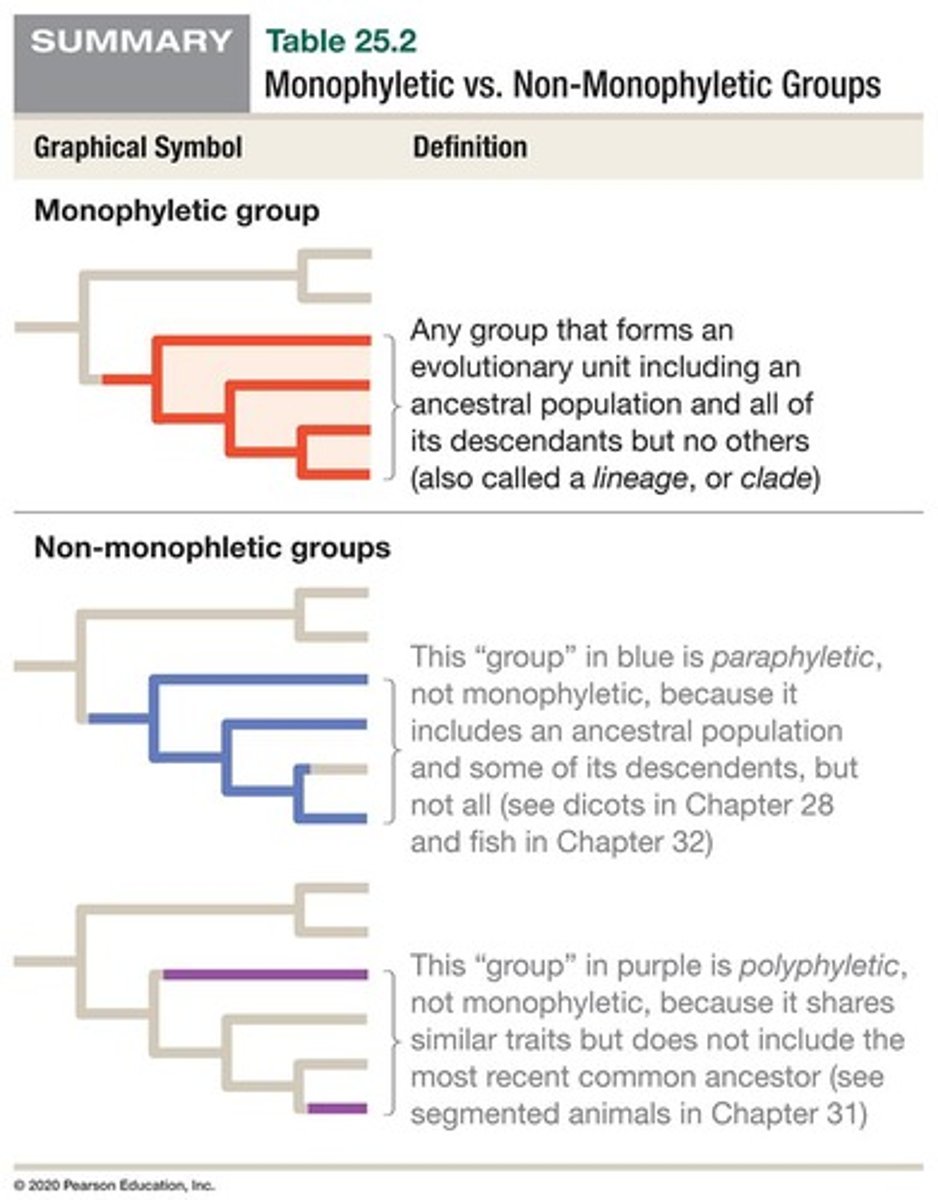
Monophyletic Group
Group consisting of an ancestor and all descendants.
Speciation
Process by which new species arise.
Ecological Diversification
Adaptation of species to various ecological niches.
Niche
Range of resources and conditions a species tolerates.
Permian Period
Last period of the Paleozoic era, major extinction event.
Cretaceous Period
Last period of the Mesozoic era, dinosaurs existed.
Paleogene Period
First period of the Cenozoic era, mammals diversified.
Extrinsic factors
Environmental changes triggering adaptive radiations.
Intrinsic factors
Key trait evolution driving diversification.
Ecological Opportunity
Availability of new resources promoting diversification.
Silverswords
Hawaiian plants diversifying into vacant niches.
Morphological Innovation
Key trait evolution leading to diversification events.
Physiological Innovation
Adaptations in function driving species diversification.
Behavioral Innovation
Changes in behavior leading to evolutionary advantages.
Angiosperms
Flowering plants with over 250,000 known species.
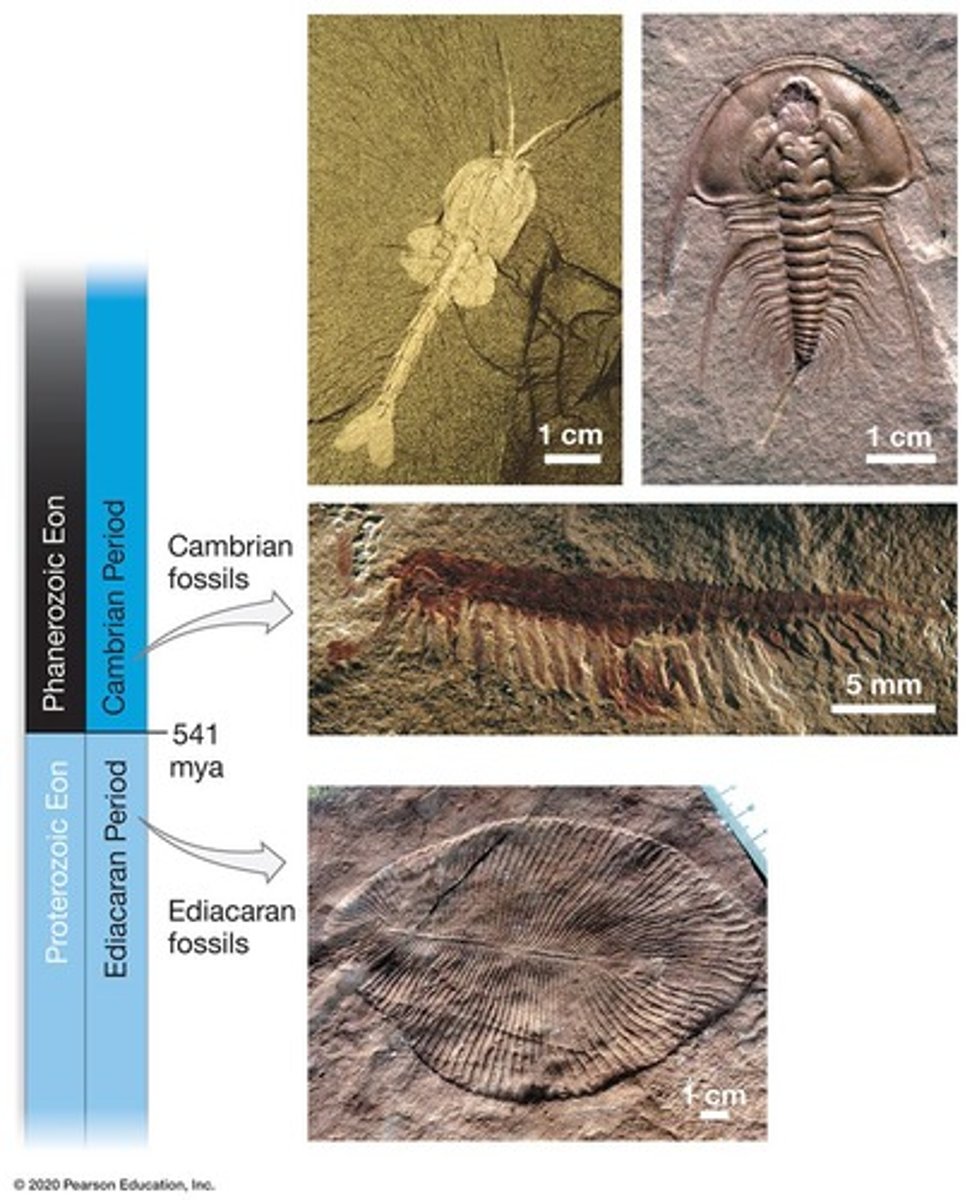
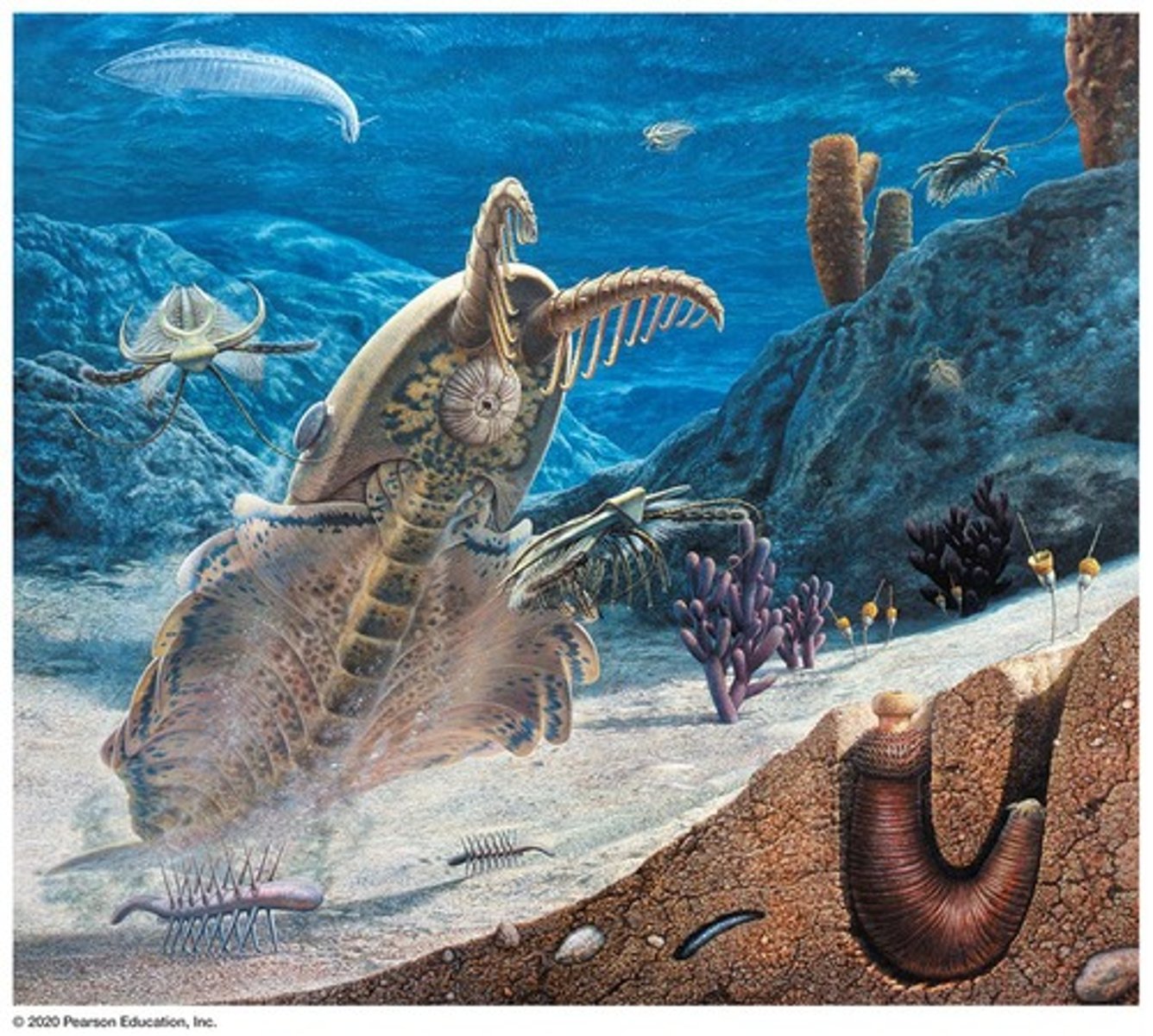
Cambrian Explosion
Rapid diversification of life ~541 million years ago.

Ediacaran period
Time before Cambrian with first multicellular life.
Microfossils
Tiny fossils from early life, less than 1 mm.
Macroscopic fossils
Larger fossils appearing during the Cambrian period.
Filter feeders
Organisms that obtain food by filtering water.
Ecological niches
Roles species play in their environments.