High to Late Renaissance
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms

Madonna and Child with Angels
Date: c.1455
Artist: Fra Filippo Lippi
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Playful, humanized version of Madonna and child
Findspot shows renaissance perspective
Tempura on wood
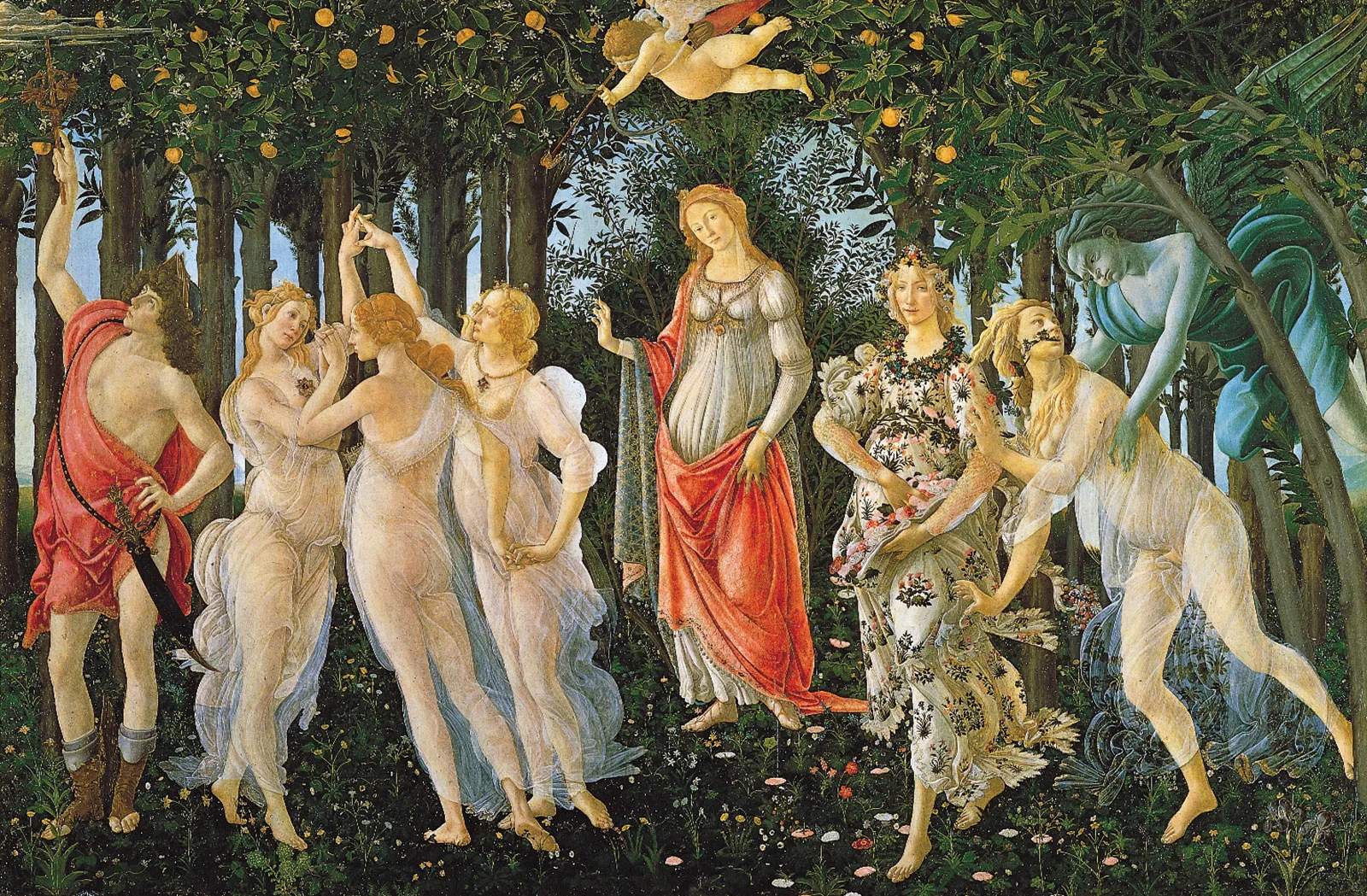

Primavera
Date: c.1478
Artist: Sandro Botticelli
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Spring, venus in the middle
Gods and goddesses of paganism, ancient greek influence
Intricate floral details
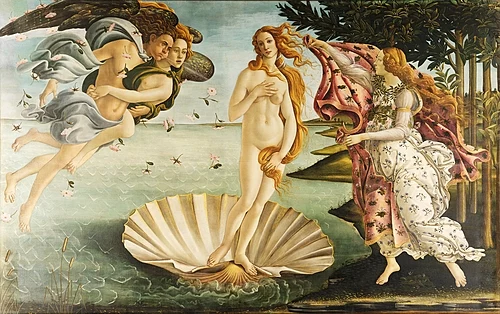
The Birth of Venus
Date: c.1482
Artist: Sandro Botticelli
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Depicts mythological birth of Venus.
First large-scale canvas painting of Renaissance.
Emphasis on decorative line and idealized beauty.
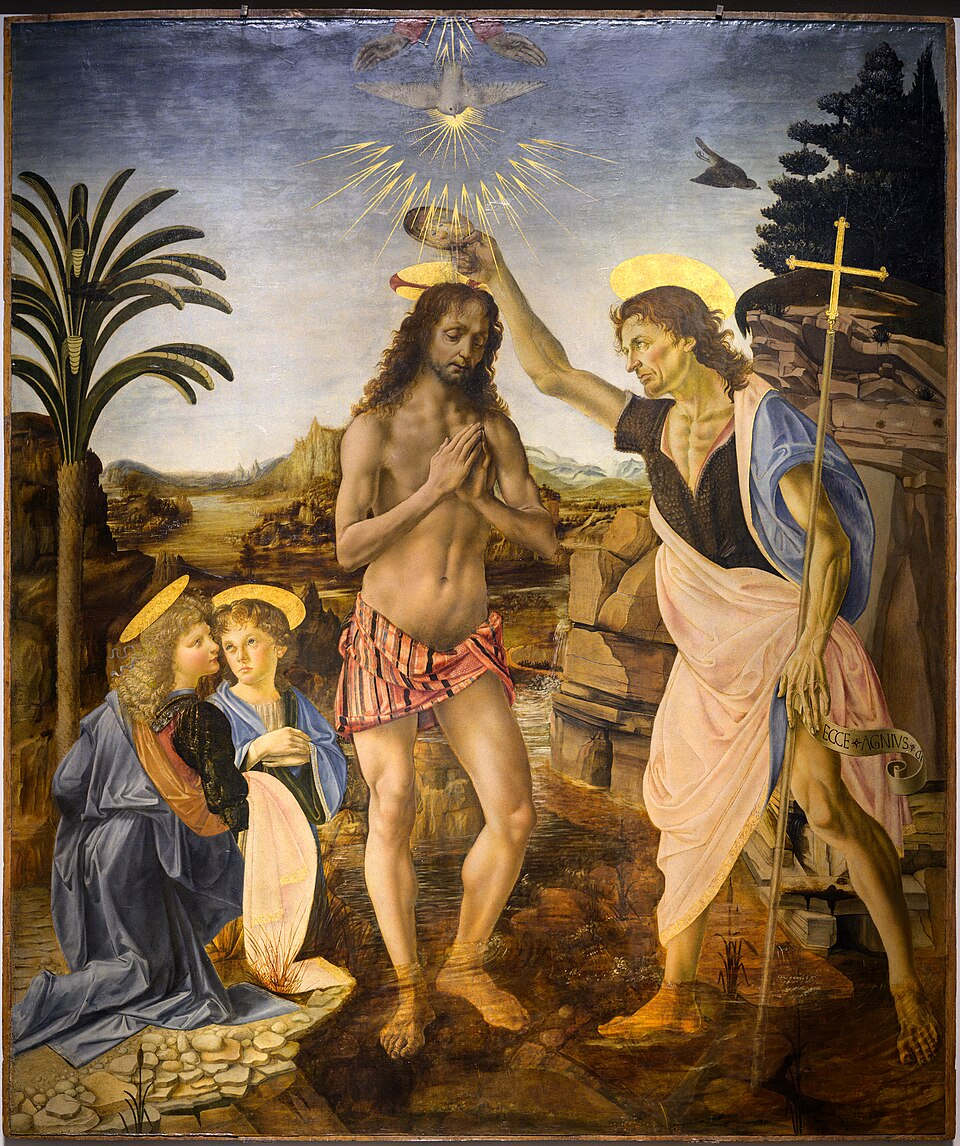

Baptism of Christ
Date: c.1475
Artist: Andrea Verrocchio
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Leonardo da Vinci painted one of the angels. Demonstrates the disciple-mentor relationship of Verrocchio and Leonardo
The holy Dove symbolizes that the holy spirit is present
Depicts the baptism of christ as a biblical scene in the new testament
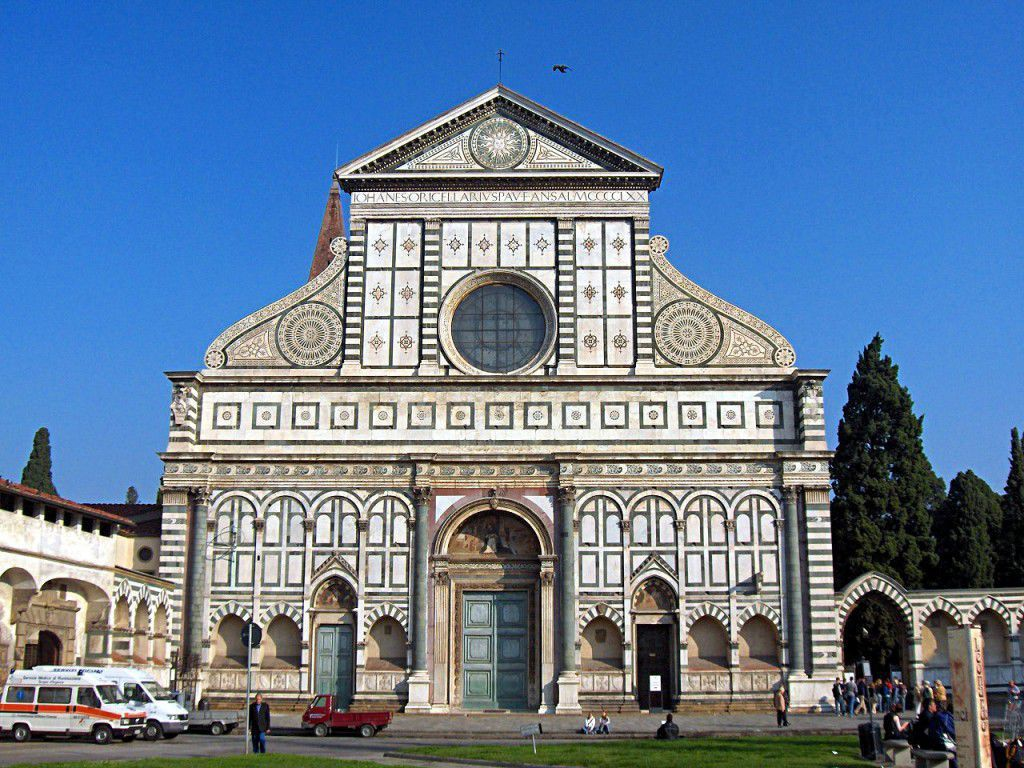

Sta. Maria Novella
Date: c.1456
Artist: Leon Battista Alberti
Culture: Florentine
Location: Florence, Italy
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Classical and Gothic architecture technique mixed, use of winged consoles
Use of symmetric geometric proportion.
First example of a Renaissance church façade in Florence.
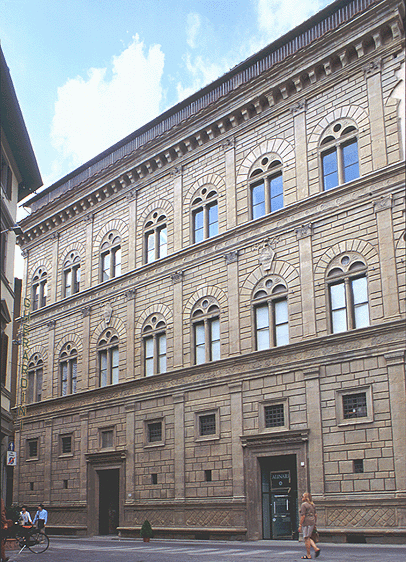

Palazzo Rucellai
Date: c.1455
Artist: Leon Battista Alberti
Culture: Florentine
Location: Florence, Italy
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
All 3 types of columns
Facade-focused, mathematical harmony and perfection
purposely made to look rusticated
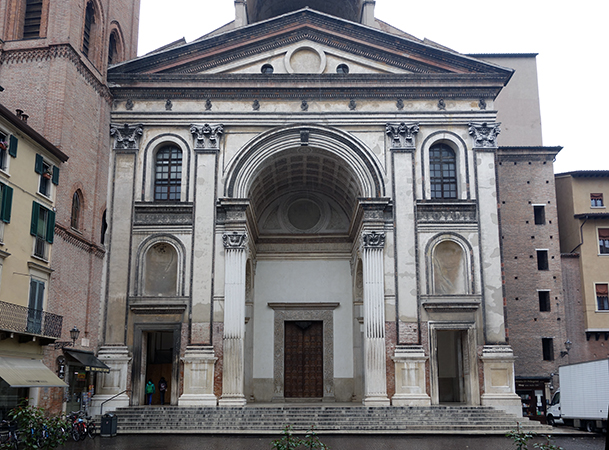

Sant Andrea
Date: c.1470
Artist: Leon Battista Alberti
Culture: Florentine
Location: Mantua, Italy
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Use of Ancient Greek and Roman architectural designs
Use of the pediment and Corinthian style columns
Creates a sense of engulfment
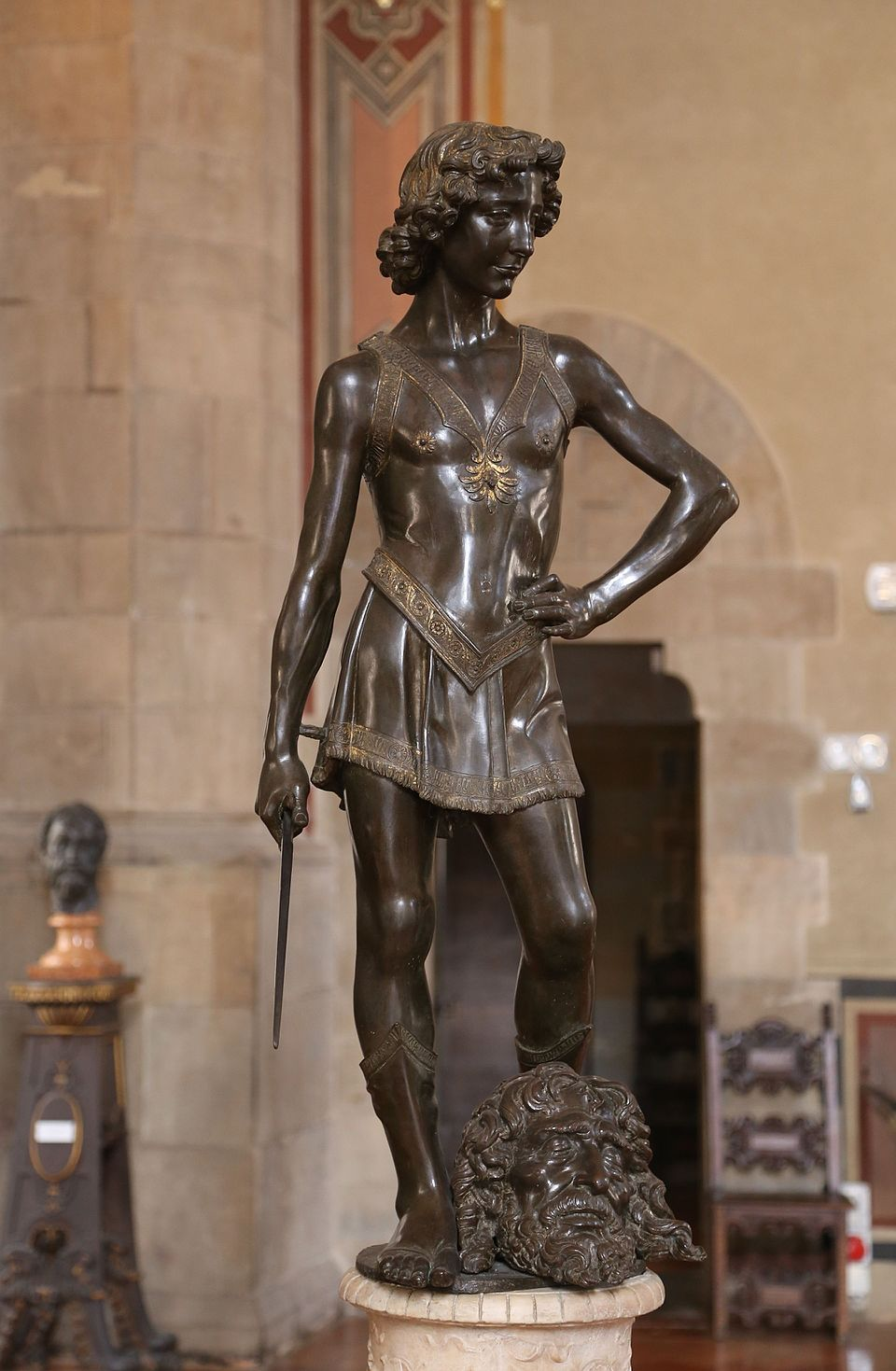

David
Date: c.1475
Artist: Andrea Verrocchio
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
- Used young Leonardo as a model
- cire perdu, contrapossto pose
- depicts David as victorious, as symbolized by the head of Goliath
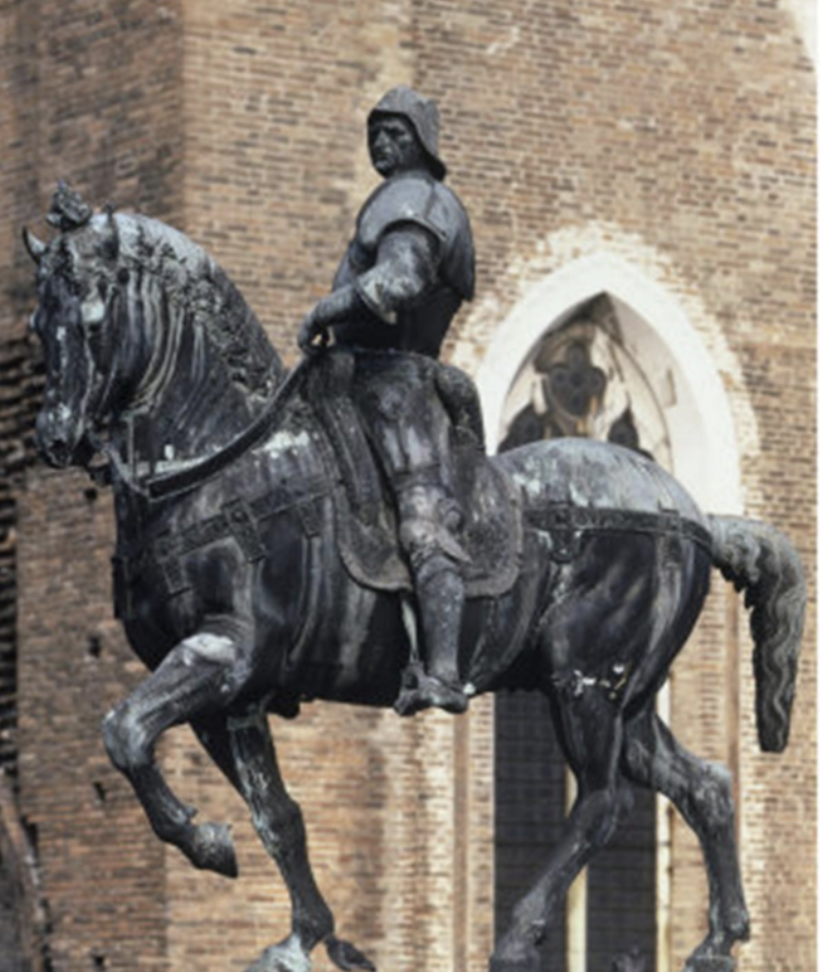

The Condotierre (Bartolomeo Colleoni)
Date: c.1475
Artist: Andrea Verrocchio
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Equestrian statue of an Italian military leader. (Condotierre meaning)
Tried to beat the gatamallatta, didn’t need cannonball to balance
Demonstrates forcefulness, very brute, contrasted with the elegance of Erasmo Da Narni (Gattamelata)

Putto with Dolphin
Date: c.1467
Artist: Andrea Verrocchio
Culture: Florentine
Period: Late Renaissance
3 facts:
Small fountain figure depicting
Demonstrates that the putto is being blown by the wind
Very playful, lively putto.
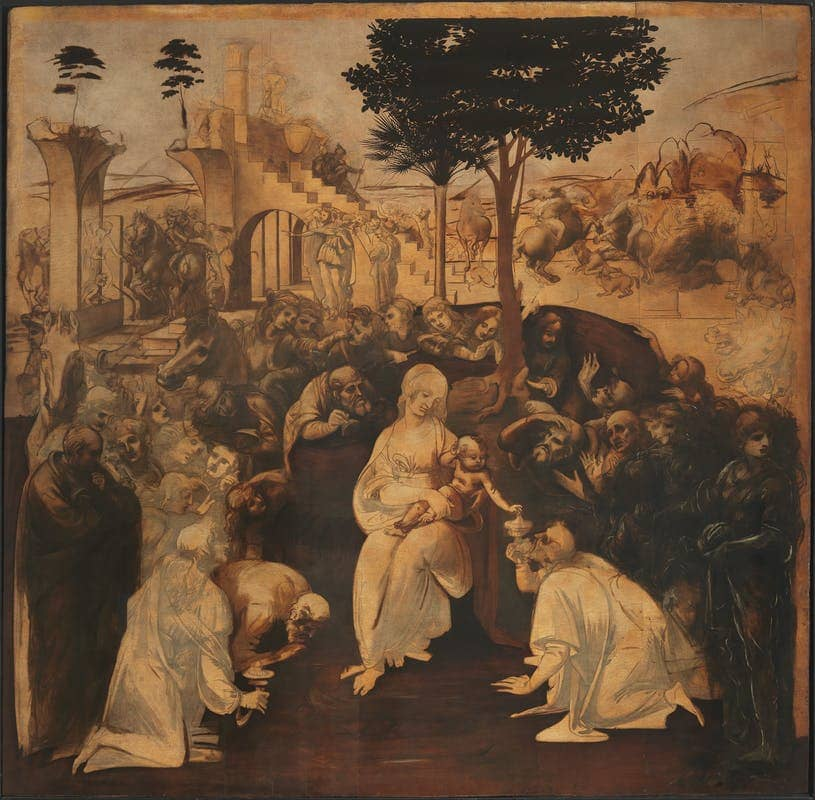

Adoration of the Magi
Date: c.1482
Artist: Leonardo da Vinci
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Unfinished; only done underpainting
Skeletal look at the bodies, Leonardo studied the structure of a dead person
Experimental painting
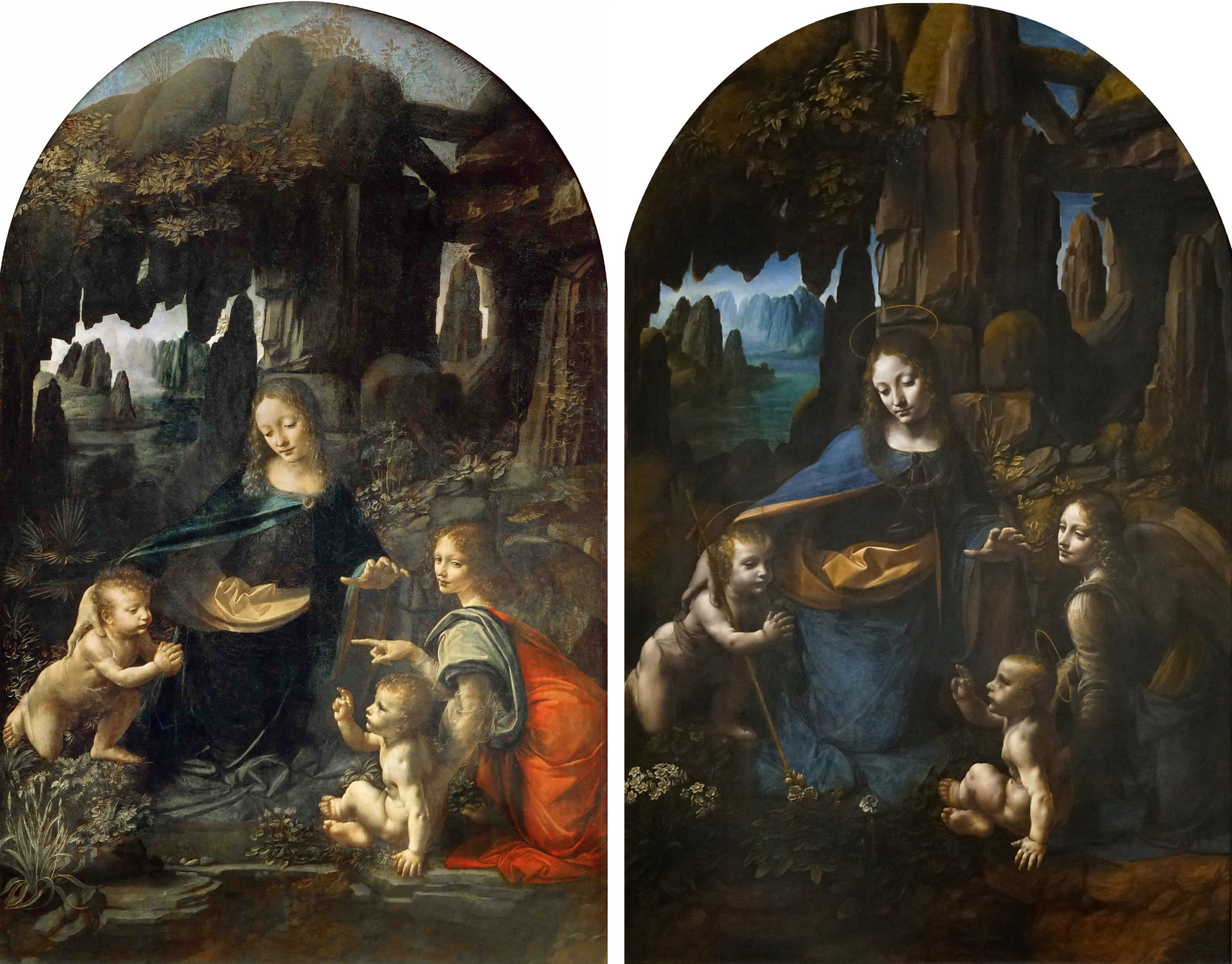

Madonna of the Rocks (Louvre and London)
Date: c.1485
Artist: Leonardo da Vinci
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Use of the sfumato technique.
No halos, couldn’t tell apart which is Jesus and John the Baptist in the first version; had to redraw the composition
Figures arranged in pyramidal composition. Not a real biblical event

Last Supper
Date: c.1495-98
Artist: Leonardo da Vinci
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Use of the window to create a halo for Christ
Sfumato technique, very dramatic scene
Linear perspective directs focus to Christ.
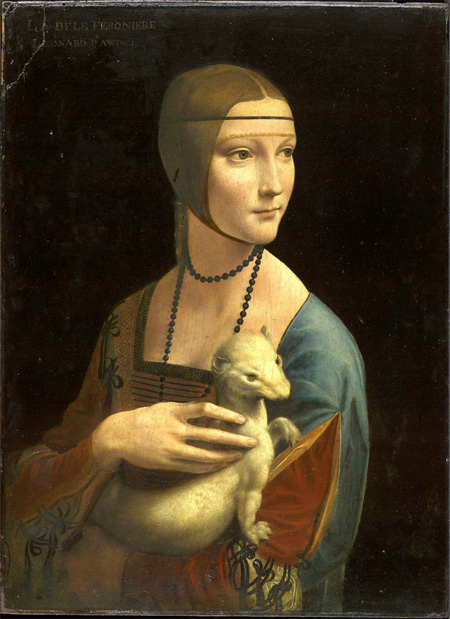

Lady with an Ermine
Date: c.1489–91
Artist: Leonardo da Vinci
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Use of Sfumato with chiaroscuro
One of the 4 female portraits Leonardo has done in his lifetime
Themes of tranquility and composure, the ermine symbolizes purity
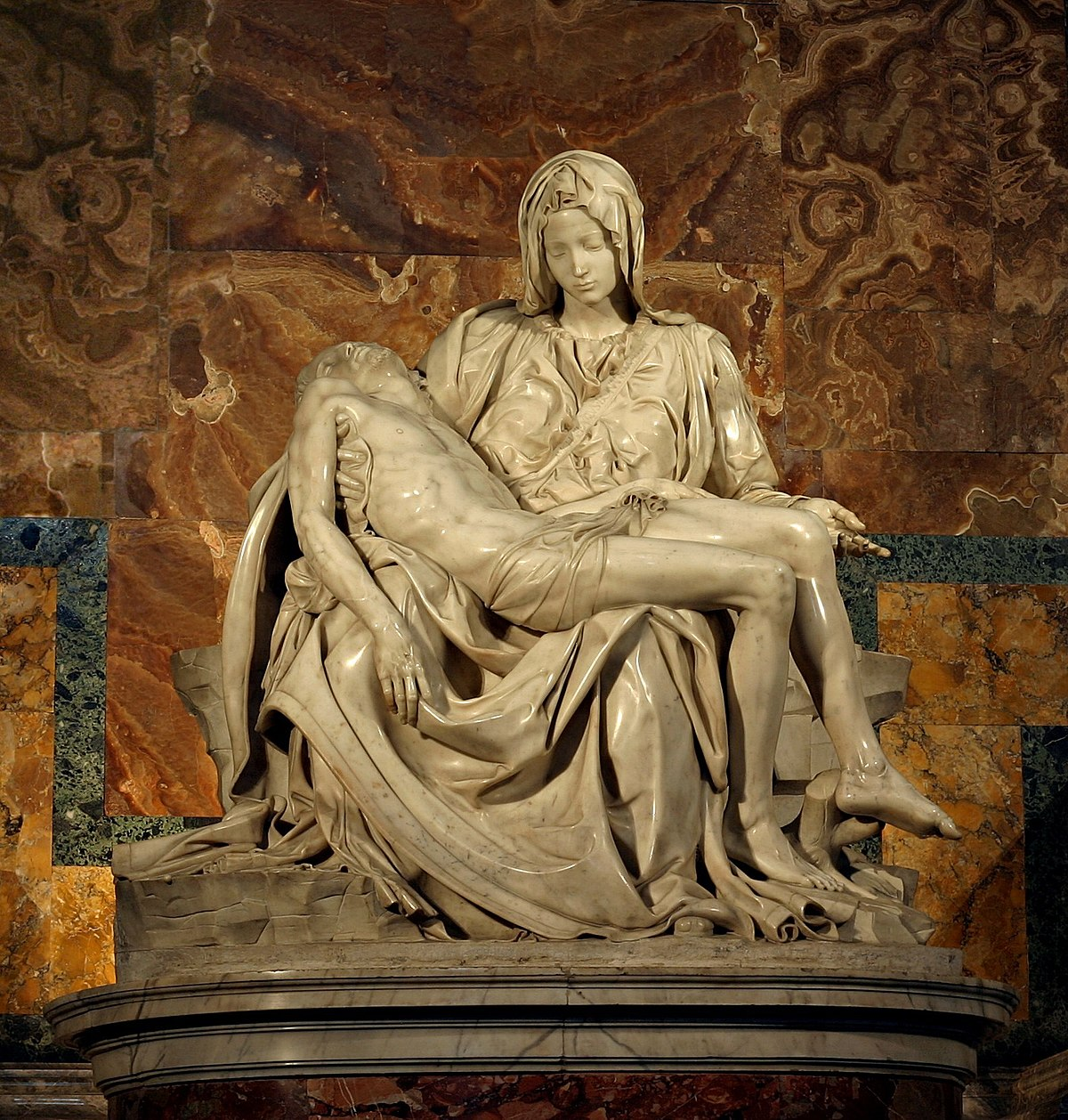

Pieta
Date: c.1498
Artist: Michelangelo Buonarroti
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Depicts Virgin Mary holding dead Christ.
Commercial to stray women away from prostitution (young virgin Mary)
Depicts the scene with precise details, very realistic drapery and other features
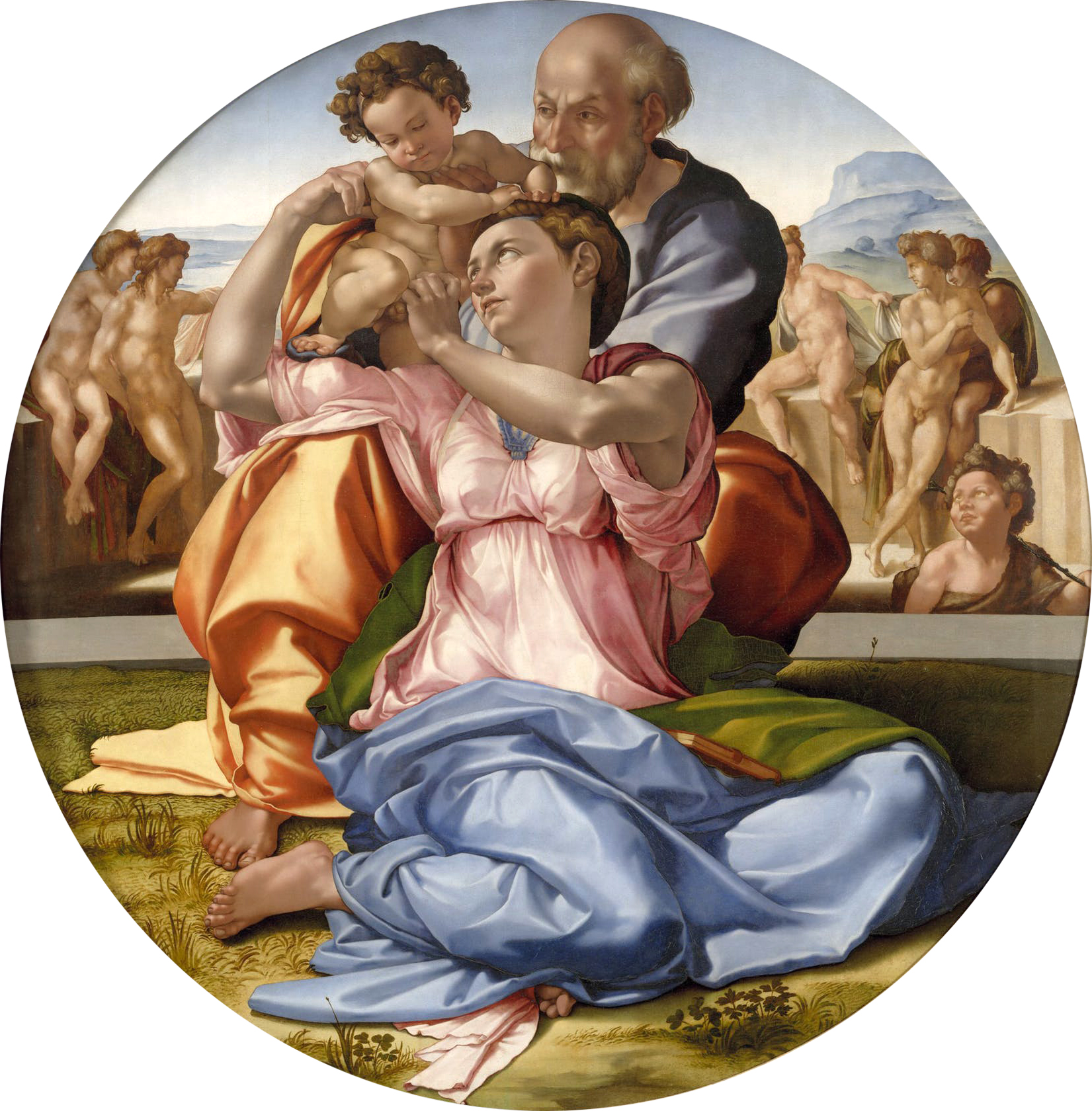

Doni Tondo
Date: c.1504
Artist: Michelangelo Buonarroti
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Circular panel painting (tondo).
Dynamic figures and sculptural forms.
The idea of carrying Jesus from the Old Testament in prophecies to the New Testament in a physical form

David
Date: c.1501
Artist: Michelangelo Buonarroti
Culture: Florentine
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Marble statue meant to be viewed from below (worm’s eye view)
Represents youthful David before the battle; shows signs of nervousness
Contrapossto pose

Sistine Chapel
Date: c.1508-12
Artist: Michelangelo Buonarroti
Culture: Florentine
Location: Vatican, Rome
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Michelangelo had to create his own scaffolding
Tight security during the time of painting prevented Raphael from seeing
Anatomically accurate characters with a bold, muscular anatomy
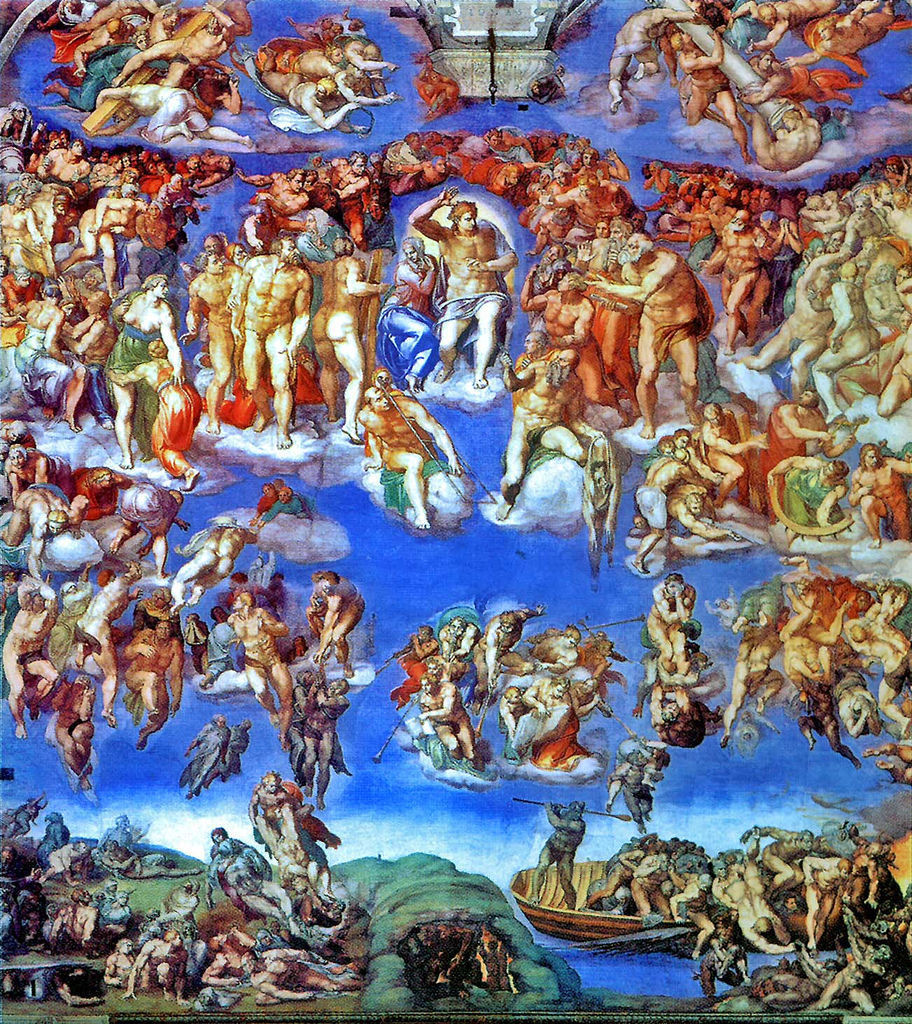

The Last Judgement
Date: c.1508-12
Artist: Michelangelo Buonarroti
Culture: Florentine
Location: Vatican, Rome
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
Massive fresco on Sistine Chapel altar wall.
Structural, muscular look to the figures
The church didn’t approve of nude figures, so Michelangelo had to cover phalluses
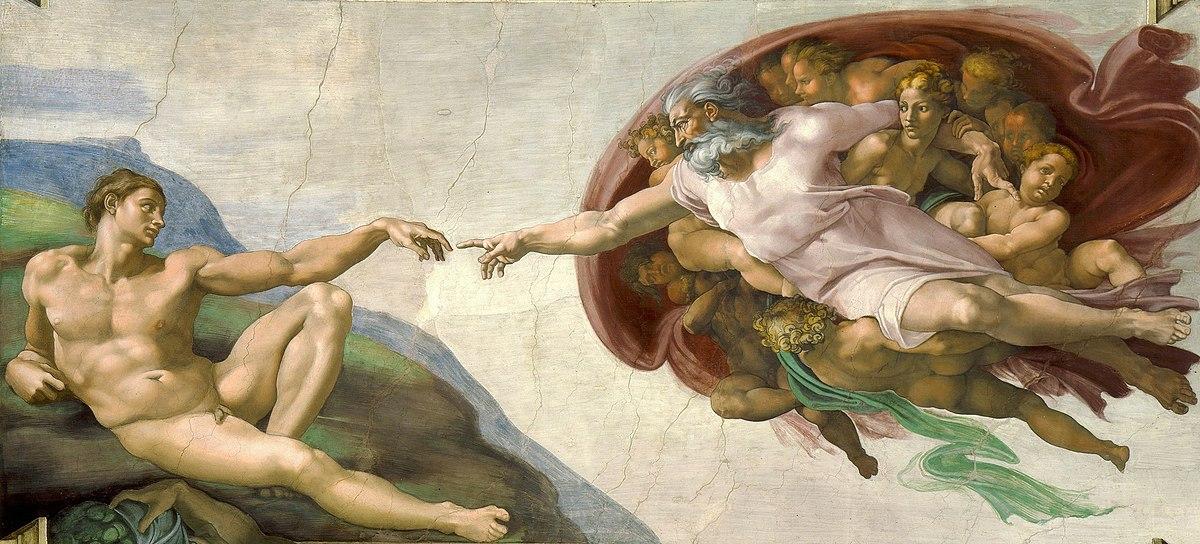

Creation of Man
Date: c.1508-12
Artist: Michelangelo Buonarroti
Culture: Florentine
Location: Vatican, Rome
Period: High Renaissance
3 facts:
One of the fresco panels at the Sistine Chapel ceiling
Very anatomically accurate, a structural look to the figures
God is giving Adam the option to have Eve and be the predecessor of mankind, but Adam is unsure
Horae
Goddess of the seasons
Aura
Minor Wind Goddess
Nymph Chloris
Goddess who was associated with spring, flowers and new
growth.
Zephyrus
God of the west wind and the messenger of spring.
Flora
Goddess of flowers
Cupid
God of love, desire, and attraction. He is the son of Venus and Mars.
The Graces
Aglaia (Brightness), Euphrosyne (Joyfulness), and
Thalia (Bloom)
Mercury
God of commerce, eloquence, travellers, communication, messengers, and trickery.
Sfumato
painting technique which involves blending the edge
between colors so that there is a soft transition. The term
"sfumato" is Italian which translates to soft, vague or blurred.