BT 3 FINALS - PART 2 FRAMING & ROOF SYSTEMS
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Floor systems
The horizontal planes that must support both live loads— people, furnishings, and movable equipment—and dead loads—the weight of the floor construction itself.
Concrete
Cast-in-place concrete floor slabs are classified according to their span and cast form.
Precast concrete planks may be supported by beams or loadbearingwalls.
Steel
Closely spaced light-gauge or open-web joists may be supported by beams or loadbearing walls.
Steel beams support steel decking or precast concrete planks
Wood
Support structural planking or decking.
Beams may be supported by girders,posts, or loadbearing walls.
Relatively small, closely spaced joists may be supported by beams or loadbearing walls.
Suspended slab
One-way joist slab or Ribbed slab- are cast integrally with a series of closely spaced joists, which in turn are supported by a parallel set of beams.
Designed as a series of T-beams joist slabs are more suitable for longer spans and heavier loads than one-way slabs.
Two-way waffle slab
Reinforced by ribs in two directions. They can carry heavier loads and span longer distances than flat slabs.
Two-way flat plate
Are concrete slabs of uniform thickness reinforced in two or more directions and supported directly by columns without beams or girders.
Two-way flat slab
Are flat plates thickened at their column supports to increase their shear strength and moment-resisting capacity
One-way slabs
The most used type or reinforced concrete construction consists of a solid slab supported by two parallel beams, the beams framing into girders, and the girders in turn framing into columns.
Beam-and-girder floor
The number of beams in a panel depends upon the column spacing and the live load to be supported. The beams are spaced uniformly and generally frame into the girders at the center, third or quarter points.
5th points
One-way slabs The main tensile reinforcement (running along the short direction) in fully continuous slabs are alternately bent up, usually at an angle of 30 to 45 degrees, at the )_______ of the span and extend over the supports to the quarter points of the adjoining span.
20mm (¾”)
One Way Slabs - Minimum protective covering for slab reinforcement is ______.
irregular grid patterns
One Way Slabs - Beams may be placed in ________ to accommodate varying bay sizes, changing load conditions, and slab penetrations.
20' to 30' (6 to 9m)
One Way Slabs - Column spacing varies from _______ but is limited only by the size of the girders required to span between the columns.
Two-way slabs
When a floor panel is square or nearly so, having beams or walls on four sides, it is generally economical to use two sets of reinforcing bars placed at right angles to each other. These bars in two directions transfer the loads to the four supporting beams or walls. Slabs thus reinforced.
span/16, including the slab depth
Two-way slabs - Rule of thumb for estimating beam depth: __________.
Reinforced concrete beams
A beam may be defined as a structural member, resting on supports usually at its ends, which supports transverse loads.
Simple beams
These are beams having a single span with a support at each end, there being no restraint at the supports.
Cantilever beams
These are beams that are supported at one end only, or they may be that portion of beams projecting beyond one of its supports
Continuous beams
These are beams resting on more than two supports. It refers to a beam having two spans with little or no restraint at the two extreme ends of the beam.
compression
Reinforced concrete floor systems -The lower part of the beam is said to be in tension, while the upper part is in _________.
Point of inflection
The section of a beam at which the bending moment changes from positive to negative is called the ______.
web reinforcement
Reinforcement used to resist shearing stresses is known as_________. Ties are frequently used for web reinforcement in place of stirrups
Roof Structures
Are horizontal spanning systems. Also control the passage of moisture vapor, the infiltration of air, and the flow of heat and solar radiation.
Flat Roofs
Analogous to floor structures in how they are structured and constructed.
Their structure may consist of:
• Steel or timber beams and decking
• Flat timber or steel trusses
• Steel or wood joists and sheathing
• Reinforced concrete slabs
Require a continuous membrane roofing material, such as built-up or single-ply roofing.
1/4" per foot (1:50).
Flat Roofs - The minimum recommended slope for draining rainwater is _________.
Sloping Roofs
Affects the choice of roofing material, the requirements for underlayment and eave flashing, and design wind loads.
3:12 pitches
Low-slope roofs require roll or continuous membrane roofing; some shingles and sheet materials may be used on _______.
Roof Beams Parallel with Slope
The steel or timber roof beams may be spaced 4’ to 8' (1220 to 2440) o.c. and spanned with steel or wood decking. The beams may be supported by girders, columns, or a reinforced concrete or masonry bearing wall.
Roof Beams Perpendicular to Slope
The roof beams may be spaced close enough to be spanned with roof decking. Spaced farther apart, the beams can support a series of secondary beams parallel with the slope.
Multiple-Slope Roofs
Sloping roof planes can be combined to create a variety of roof forms. One of the most common is the gable roof, consisting of two roof planes that slope downward from a central ridge.
Multiple-Slope Roofs
It is useful to think of any roof composition as several sloping planes that meet or intersect at either ridges, hips, or valleys, keeping in mind the resulting drainage pattern for shedding rainwater and melting snow
Vaulted Roofs
Curved roof surfaces may be structured by using spanning elements, such as built-up or custom-rolled steel beams, glue-laminated timber beams, or trusses that are shaped to match the desired profile of the form or space.
Steel Trusses
A truss is a structural frame based on the geometric rigidity of the triangle and composed of linear members subject only to axial tension or compression.
Saw tooth
In factory buildings where considerably more light is desirable the saw tooth truss is used. In this type the steep sides of the trusses will be glazed.
North light
The glazed panels are usually faced towards North to avoid the direct glare of the sun
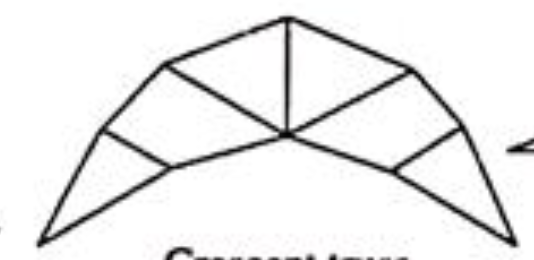
Crescent truss
For long spans and where more head room is required the crescent truss is adopted. For such conditions the scissors truss, the curb truss, the shed truss, the three hinged arched truss, the Hammer beam truss are also used.
Quadrangular
Segments are arranged in such an order that they form a ‘W’ shape
Span of trusses
The distance between the supporting end joints of a truss
Pitch of trusses
Is the distance between the centers of the supports and its rise is the distance between the apex of the truss and the line joining the points of support.
12” run
Pitch of trusses -The slope of an inclined member is the tangent of the angle of inclination with
the horizontal, usually specified in inches rise per _______.
Span of trusses
When the rise is not more than 1 vertical to 6 horizontal the roof is called a flat roof. If the rise exceeds the above limit the roof
1/3 to 1/5 of the span
Spacing of trusses is may be about _______.
Roof Slabs
Formed and site cast in the same manner as the concrete floor systems.
Are normally covered with a type of membrane roofing.
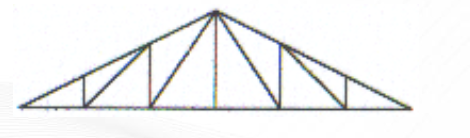
Fink Truss
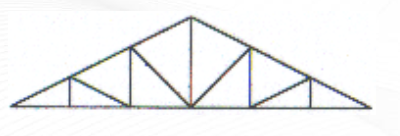
Howe Truss
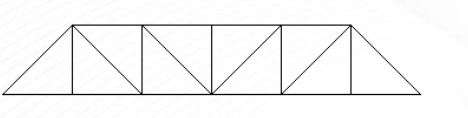
Pratt Truss
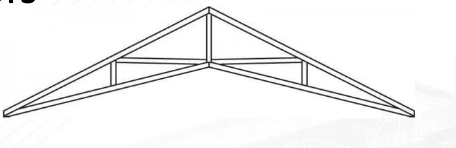
Scissors Truss
Hammer-Beam Truss
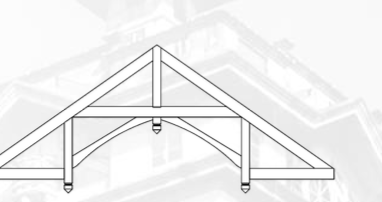
Saw Tooth Truss
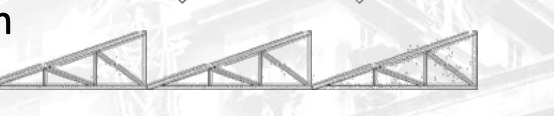
Warren Truss
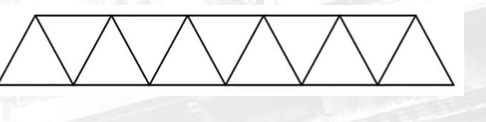
Pettit Truss
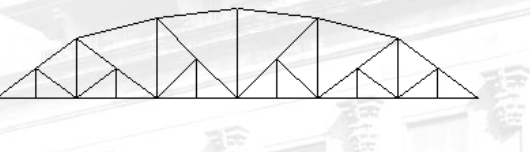
Deck Warren
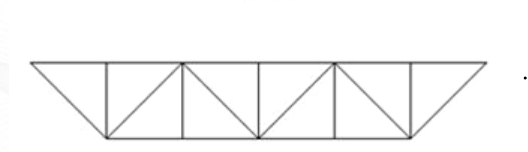
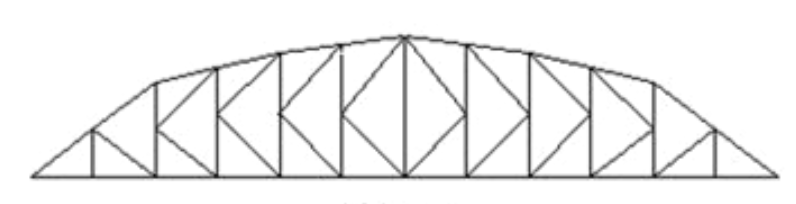
Parker or Camel-Back
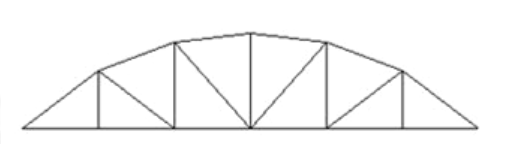
Baltimore
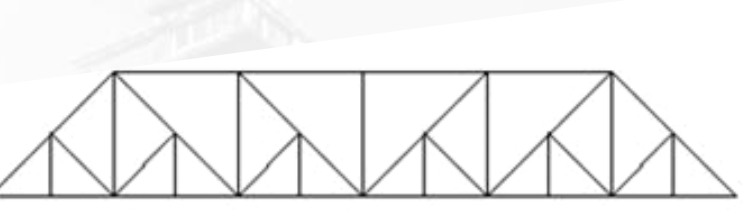
Pennsylvania or Petit
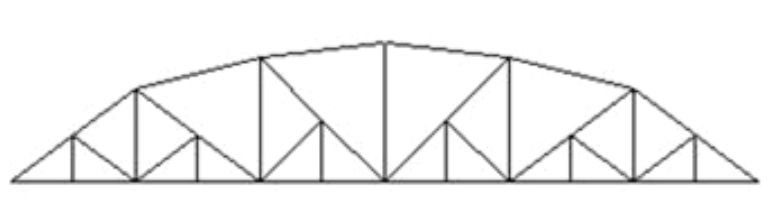
K Truss
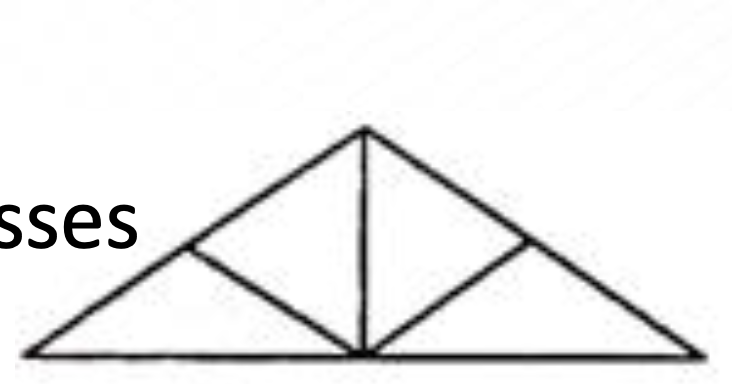
King Post Truss
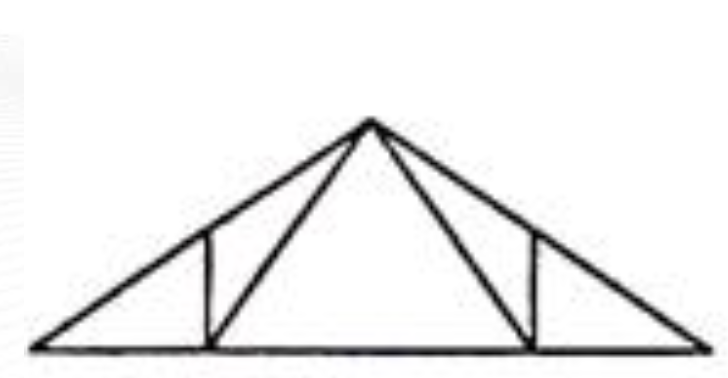
4 Panel Pratt Truss
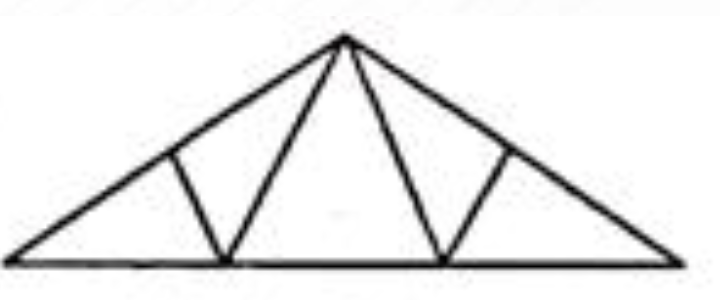
Simple Fink Truss
English Truss
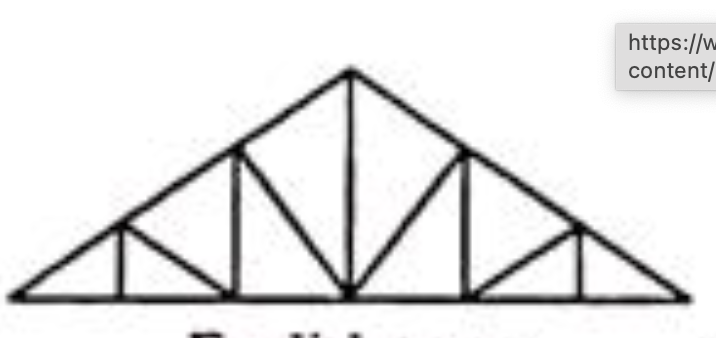
Belgian Trusses
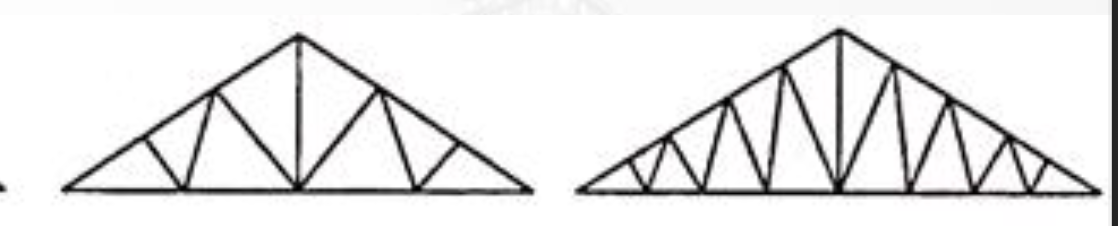
Modified Truss
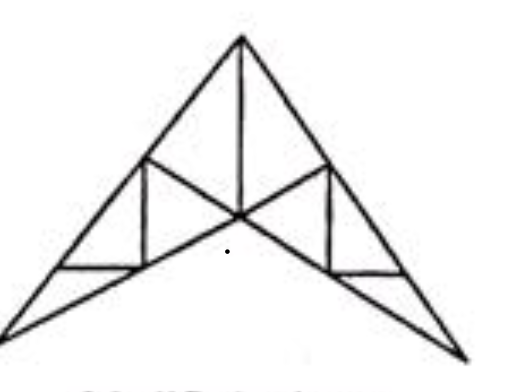
Crescent Truss
Shed Truss
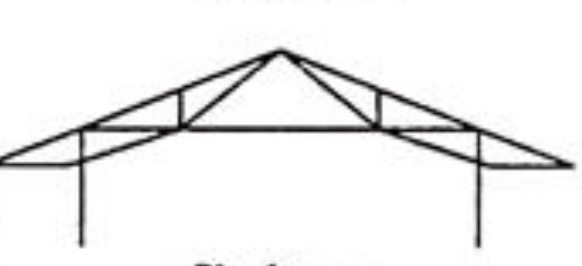
3-Hinged Arch
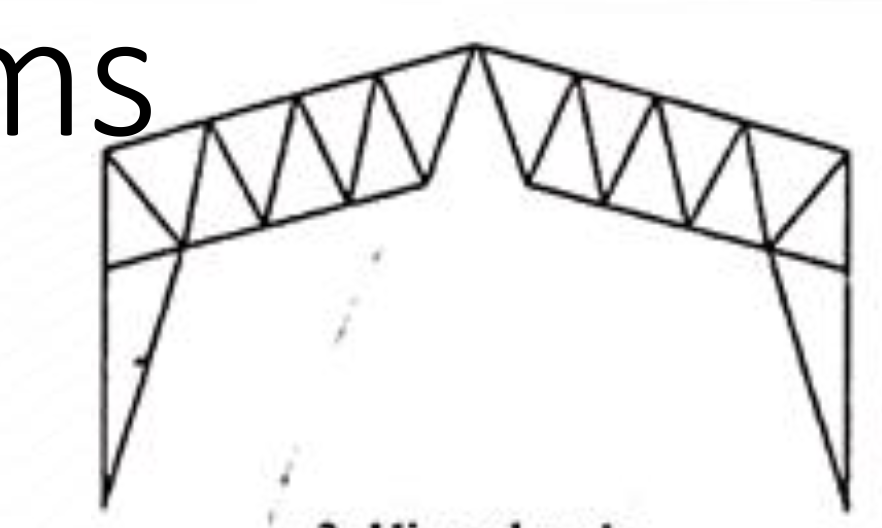
One Way Slab

Two Way Slab
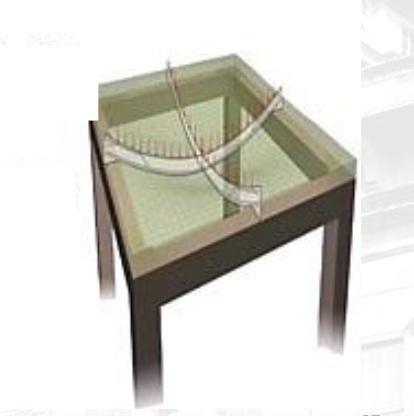
Cantilever

Simply Supported

Overhanging

Continuous
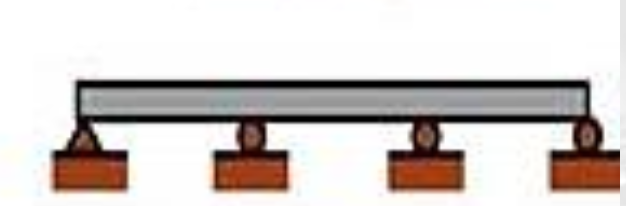
Fixed Ended

Cantilever, Simply Supports
