Unit 5: Energy Resources and Use
1/249
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
250 Terms
Thermodynamics
The study of energy transfer
System
Matter relevant to a particular case of energy transfer
Open system
Energy is exchanged with its surroundings
Examples of open systems
Pot, stove, water, biological organisms
Closed system
Energy is not exchanged with its surroundings
Surroundings
Everything outside the matter of a system
Energy
The ability to do work or change
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred
Example of radiant energy
Light energy from the sun can be transformed by solar panels into electricity
Example of chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds in food are broken during digestion and the energy is released and can be used as mechanical enerrgy, allowing people to run, play, and move
Example of mechanical energy
Cars use chemical energy from gas to power engines, transforming it into mechanical energy
Mechanical energy
A form of kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
Energy of motion
Nuclear energy
Released when nuclei split or combine, can be used for electrical energy
Electrical energy example
Light bulb uses electrical energy to create radiant energy
Thermal energy
Heat energy can be transferred by conduction, convection, or radiation
Heat
The transfer of energy, but it cannot always be used to do work
Entropy/Disorder
Energy that is lost as heat and is unuseable. Higher entropy = greater disorder. Determines the efficiency of a system
How many Joules in 1 calorie?
4.184 J
How many calories in 1 kcal?
1000 calories
How many joules in 1 British Thermal Unit (BTU)
1,055 Joules
How many joules in 1 kcal
4,184 j
Formula for mechanical energy
work energy = force x distance
Formula for rate of energy flow
Watt = joules/second
Why do electric bills report energy usage in kilowatt hours?
Power = Energy / Time
Energy = Power x Time
Joules = Watts x Seconds
What does 1 kWh (kilowatt hour) equal in kilojoules
3600 kj
What source of energy has been used since the United States was founded in 1775?
Wood
What source of energy was increasingly utilized after the Industrial Revolution which ended in the 1840s?
Coal
How has the consumption of coal changed in the last fifty years?
It has declined
How has the energy consumption from petroleum changed over time?
Drastically increased during early 1900s
Industrial Revolution
Occurred from 1760 to 1840. Shift from small-scale production of goods to large-scale production using machines occurred
When was oil/petroleum discovered in the US
1859
When did strip-mining begin
1866 in Illinois
When did the mass production of autmobiles begin?
1890
When did Coal consumption see an increase?
Following conflicts with OPEC nations
First commercial hydropower plant that utilized alternating current
The Redlands Power Plant in California (1893)
Monongah Mining Disaster
The worst mining accident in U.S. history when 360 men were killed in an explosion in West Virginia in 1907
Enrico Fermi
Produced the first self-sustaining nuclear reaction in 1942, proved that neutrons could split the nucleus of atoms, releasing energy, He thought that if he had a critical mass of nuclear materials, he could trigger a chain reaction which would produce a self-sustaining continuous release of energy
Why was nuclear energy not used until the 1960’s
Research and development of nuclear material was focused on building nuclear weapons
When did the world's first nuclear power plant begins operations?
1957 in Pennsylvania
What event happened in 1973 that was basd for oil prices in the U.S?
Arab members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) placed an embargo that banned petroleum exports to the U.S.
When was the US Department of Energy established
1977
The Iranian Revolution of 1978
Reduced petroleum production
Three Mile Island
A loss of coolant from the reactor core causes an accident at Three Mile Island nuclear power station in Pennsylvania in 1979 —> caused public fear
Hurricanes Katrina and Rita of 2005
Caused major damage to several oil rigs in the Gulf of Mexico
The Energy Policy Act of 2005
Provided tax incentives for different types of energy production, such as natural gas, biofuels, and wind
What increased the demand for gasoline in the U.S.
1980’s; production of automobiles.
What happened as population grew?
Number of automobiles did which led to petroleum replacing coal as the largest source of energy in the later part of the 20th century.
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, (OPEC)
Formed in 1960. Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela coordinated policies involving petroleum production and export
OPEC now includes 14 countries that account for 73% of the world's oil reserves.
What did the reliance on OPEC nations for petroleum lead to?
An increase in coal consumption, as well as natural gas due to countries wanting to be oil-independent
What else allowed americans to be even more oil-independent?
Advancements in science leading to nuclear energy consumption and hydroelectric power plants gradually became more prevalent
What percent of US energy use is renewable
10%
What percent of the world’s energy comes from oil?
40%.
Oil prices
Depend on discoveries and also political events
World energy consumption
Rising, especially in developing countries
Global demand for energy
Tripled in the past 50 years, and may again in the next 30
Much of the growth comes from booming economies of china and india
Renewable energy
Growing fast, Germany plans to meet 20% of its electricity and 10% of its overall energy needs w/ renewable resources by 2020
China
Second largest consumer of oil in 2003
Over ⅓ of oil is imported
Coal dominates the commercial energy resources of China, accounting for ⅔ of its energy consumption
Largest generator of CO2 in 2009
Largest consumer of oil
United States
India
main energy resources are biomass (wood and dung) and coal
½ of India’s oil is imported. About 70% of India’s electricity is generated by highly polluting coal
Renewables: rapidly growing wind energy base, and it has the largest solar cooking program in the world
What percent of global energy comes from the nonrenewable resources petroleum, coal, and natural gas (fossil fuels)
87%
GDP vs Energy
Countries with higher GDPs consume more energy
(japan is different; has a higher GDP, but consumes about half as much energy)
Energy use graph
118% increase since 1990
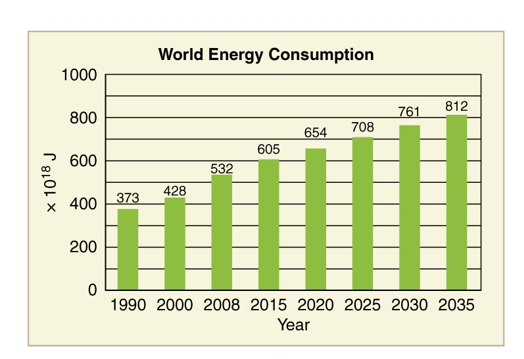
What is the projected world energy consumption in the year 2035?
812 x 1018 Joules
Fossil fuels
Materials created through the compression of prehistoric organic plant and animal matter in the Earth's crust → this compression converts into carbon-rich material that can be burned to release enormous amounts of energy
The formation of fossil fuels occurred over millions of year
The three main types of fossil fuels
coal, oil, and natural gas.
What is the largest source of human-produced air pollution?
Fossil fuels
How is petroleum produced?
Refining crude oil
What does fuel efficiency mean?
How far could a car travel on one gallon of gas, typically in miles per gallon (mpg)
Most abundant fossil fuel on Earth
Coal, formed over millions of years
How large is Earth’s total coal reserve
1 trillion metric tons.
Where is majority of Earth’s total coal reserve found?
Eastern Europe and Asia, large reserves in U.S.
How is coal formed
carbon-filled matter in these ancient swamps compressed into peat, a near-solid soil-like material
What determines what type of coal is formed?
Temperature and pressure differences
Ignite coal
50% carbon & 50% water, produces the lowest energy output, produces relatively low amounts of smog-causing sulfur
Bituminous coal
85% carbon and 3% water, Majority found in U.S., Produces most sulfur dioxide when burned
Anthracite
~100% carbon, Hardest coal, Produced most energy when burned
How is coal mined?
Strip mining and sub-surface mining.
Cons of coal mining
Causes a lot of environmental damage like erosion and habitat destruction. sub- surface causes less environmental damage but is dangerous for miners like if a tunnel collapses or explodes
What percent of electricity in US comes from coal burning plants?
50%
Where is coal used?
Used for heating and cooling in developing countries and rural areas of developed countries
How long are coal reserves estimated to last?
200 years
What does burning coal produce?
Sulfur dioxide and other harmful pollutants; Ex: nitrogen oxides, heavy metals, and carbon dioxide, waste in the form of toxic ash
How can harmful pollutants produced during coal burning be reduced?
Installing scrubbers and electrostatic precipitator in the smokestacks of coal burning power plants
Oil
Relatively inexpensive, preferred over coal because an equal amount of oil produces more kilowatts of energy than coal, burns cleaner; producing about 50% less sulfur dioxide.
What is oil used for
Gasoline, diesel fuel, jet fuel, and heating oil, used in petrochemical industry to produce chemicals, plastics, and fertilizers.
Where is more than ½ of the World’s oil found?
the Middle East
Where are other oil reserves found?
North America, including Texas, the largest oil-producing state in the U.S.
Rate of oil use
Oil is being used at a rate that exceeds the rate of discovery of new sources; If consumption rate continues to increase and no significant new sources are found, oil supplies may be exhausted in another 30 years or so.
How is oil formed?
Deep below Earth’s oceans: Remains of seaplants and animals sank to the bottom of the ocean and were buried under thousands of feet of sand sediment, forming sedimentary rock. As the rock was forced deeper and deeper into the Earth’s crust, increasing heat and pressure turned the organic matter into petroleum and gas deposits.
Shale
Oil forms underground in rock that is rich in organic matter
What happens once oil is formed?
It moves upward into porous reservoir rock such as sandstone or limestone, where it can become trapped by an overlying impermeable cap rock → Geologists drill wells into these oil reservoirs to remove the gas and oil
Where are over 70% of oil fields found?
Near tectonic plate boundaries, because the conditions there are conducive to oil formation.
Oil recovery stages
Pump oil from reservoirs under the normal reservoir pressure
This removes about 25% of the oil in a reservoir.
Injecting hot water into the reservoir around the well
Water pushes the remaining oil toward the area of the well from which it can be recovered
**Sometimes a third method of recovery is used in order to remove as much of the remaining oil as possible
involves pumping steam, carbon dioxide gas, or nitrogen gas into the reservoir to force the remaining oil toward the well
very expensive and can cost up to half of the value of oil removed.
Fractional distillation
boiling crude and separating the gases
Natural gas
Considered the cleanest burning fossil fuel; does not contain sulfur, easy and inexpensive to transport once pipelines are in place
Where are most of the world's natural gas reserves found?
Eastern Europe and the Middle East
What is natural gas used for?
Heating, cooking, and powering vehicles in developed countries, or for making ammonia fertilizer.
How many natural gas reserves are there?
Around 100 million metric tons
How long will natural gas reserves last us?
~ 100 years