DMI 108 Upper Extremity
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
how many phalanges are there?
five
which digit is the first phalange?
thumb
how many metacarpals are there?
five
how many carpals are there?
eight
what is type of joint are the interphalangeal (IP) joints?
hinge or ginglymus, provides flexion and extension
what type of joint are the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints?
ellipsoidal/condyloid joint: flexion, extension, adduction, abduction movements
what type of joint is the first carpometacarpal (CMC) joint?
saddle/sellar joint: all types of movement
what type of joints are the second to fifth CMC joints?
plane/gliding joints
what are the intercarpal joints?
plane, gliding
what type of joint is the wrist joint? (radiocarpal)
ellipsoidal, condyloid
what type of joint is the proximal radioulnar joint?
pivot, trochoidal
what type of joint is the elbow joint?
ginglymus, hinge, also classified as synovial and is diarthrodial
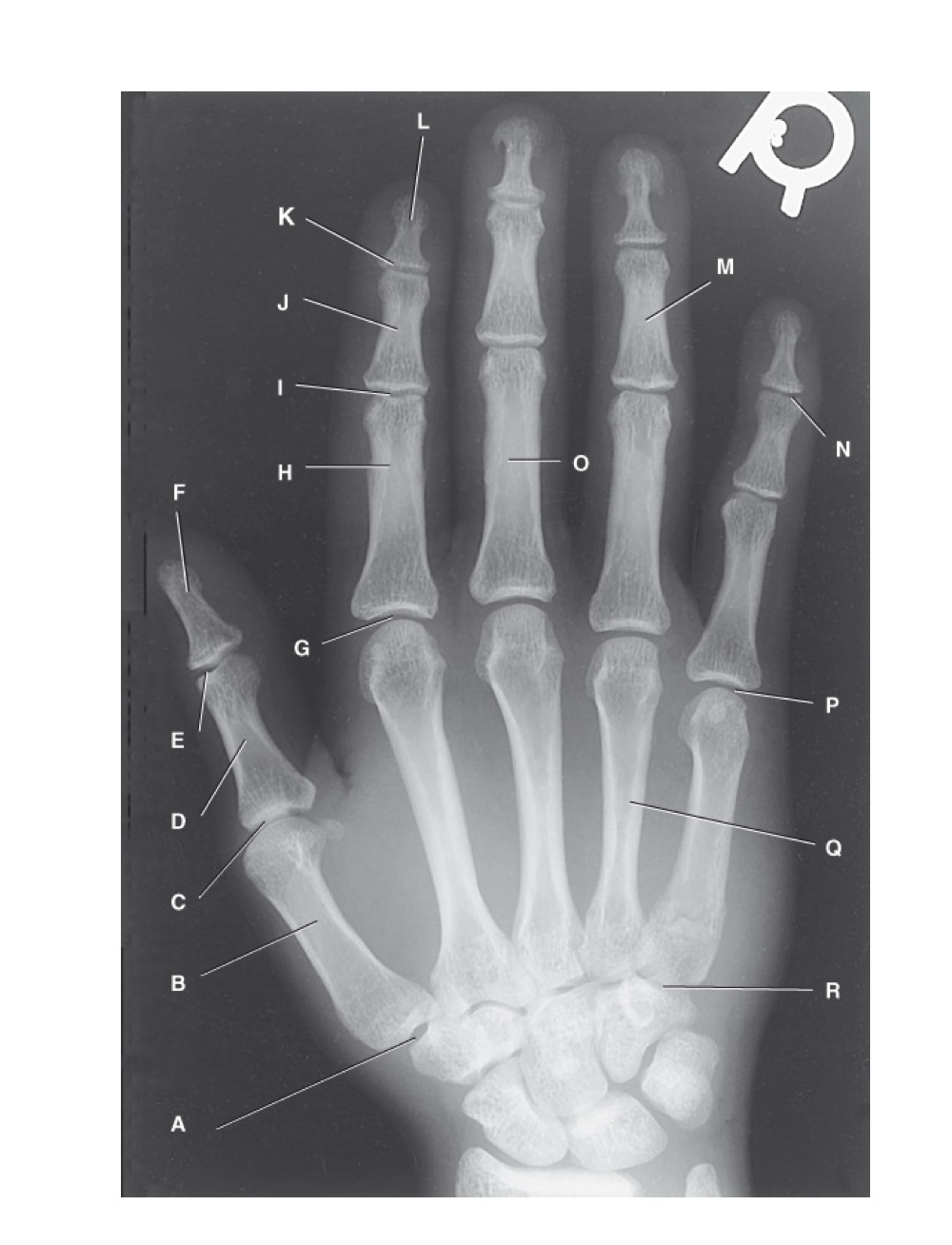
identify A
first carpometacarpal
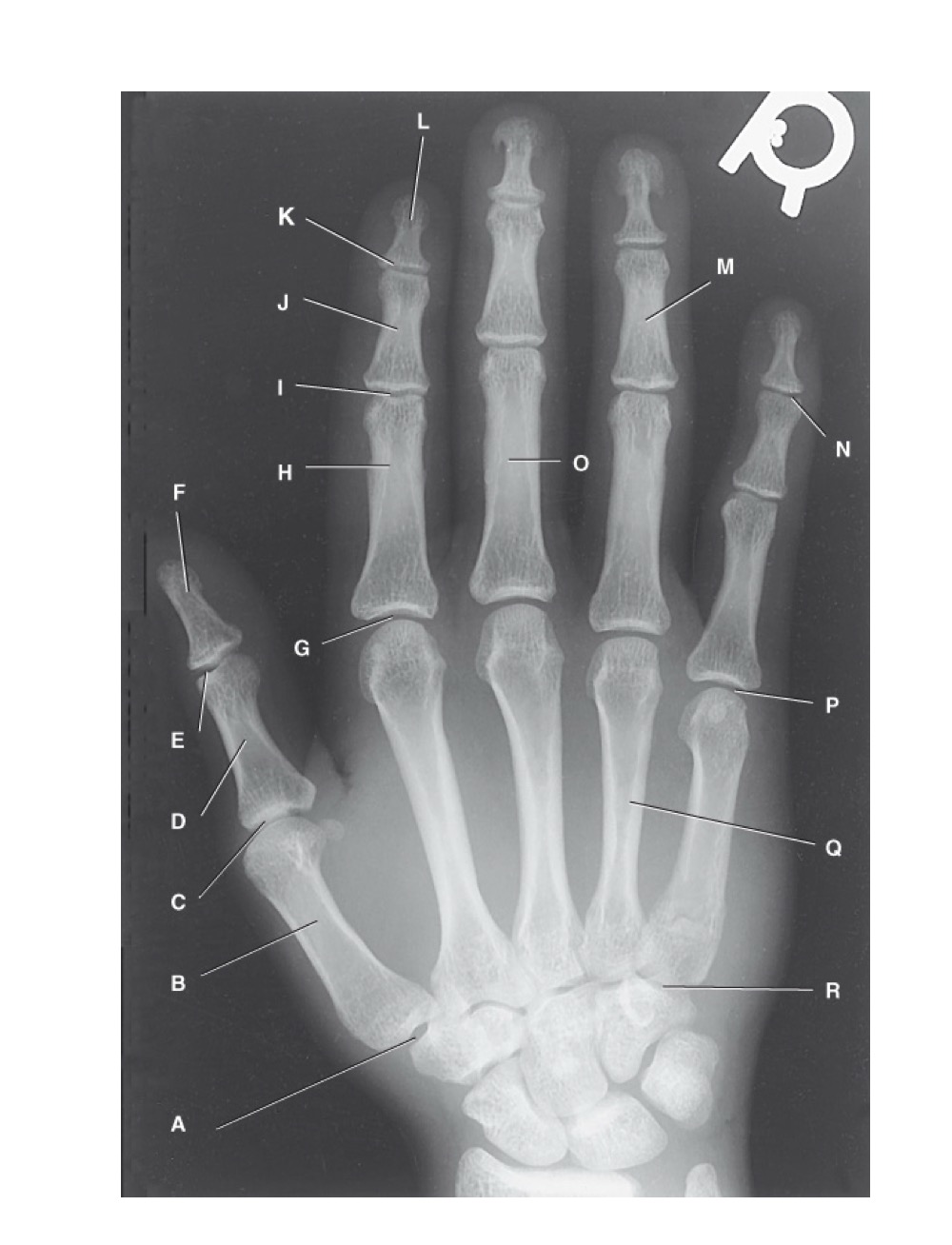
B?
first metacarpal
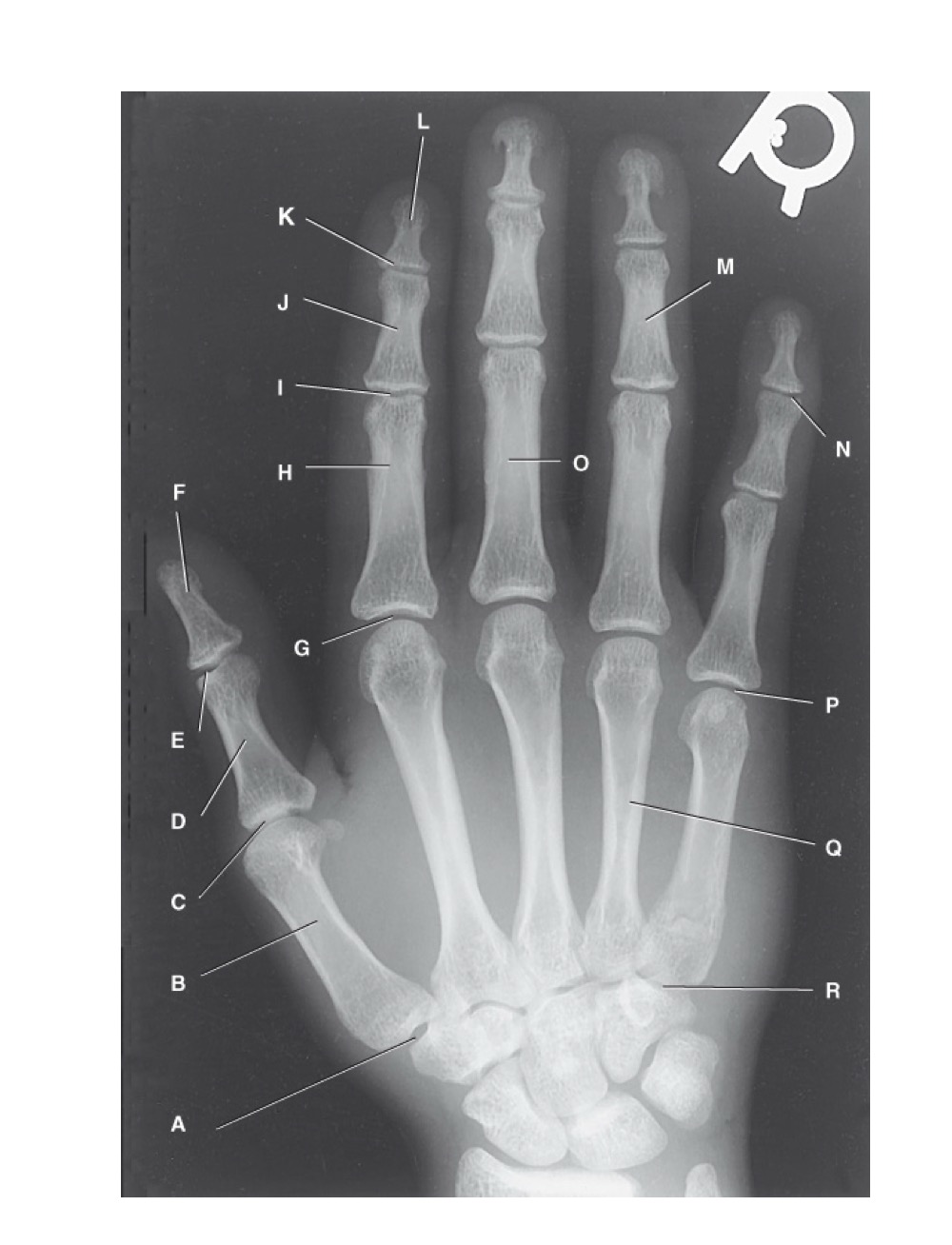
C?
first metacarpophalangeal joint
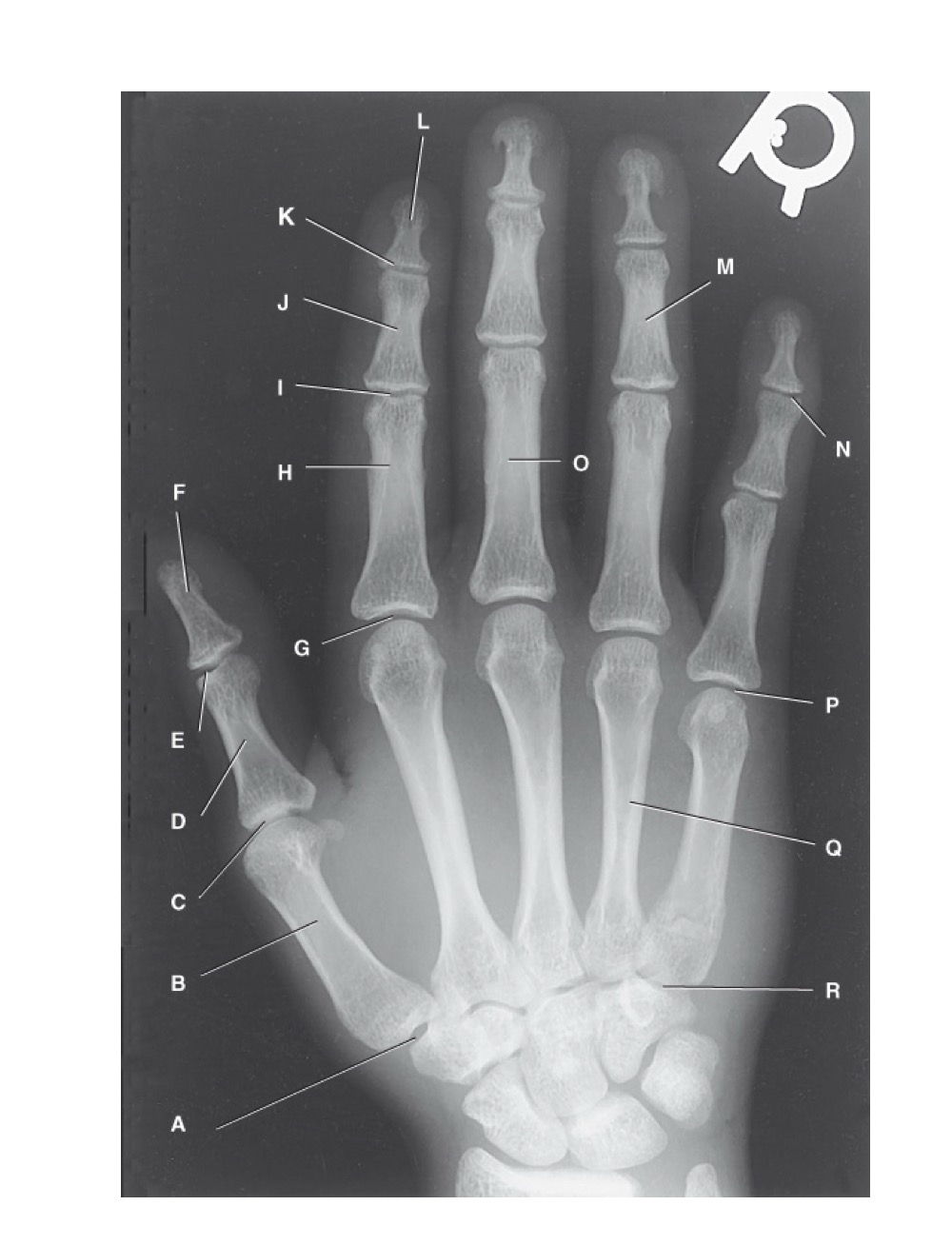
D?
proximal phalanx of the first digit
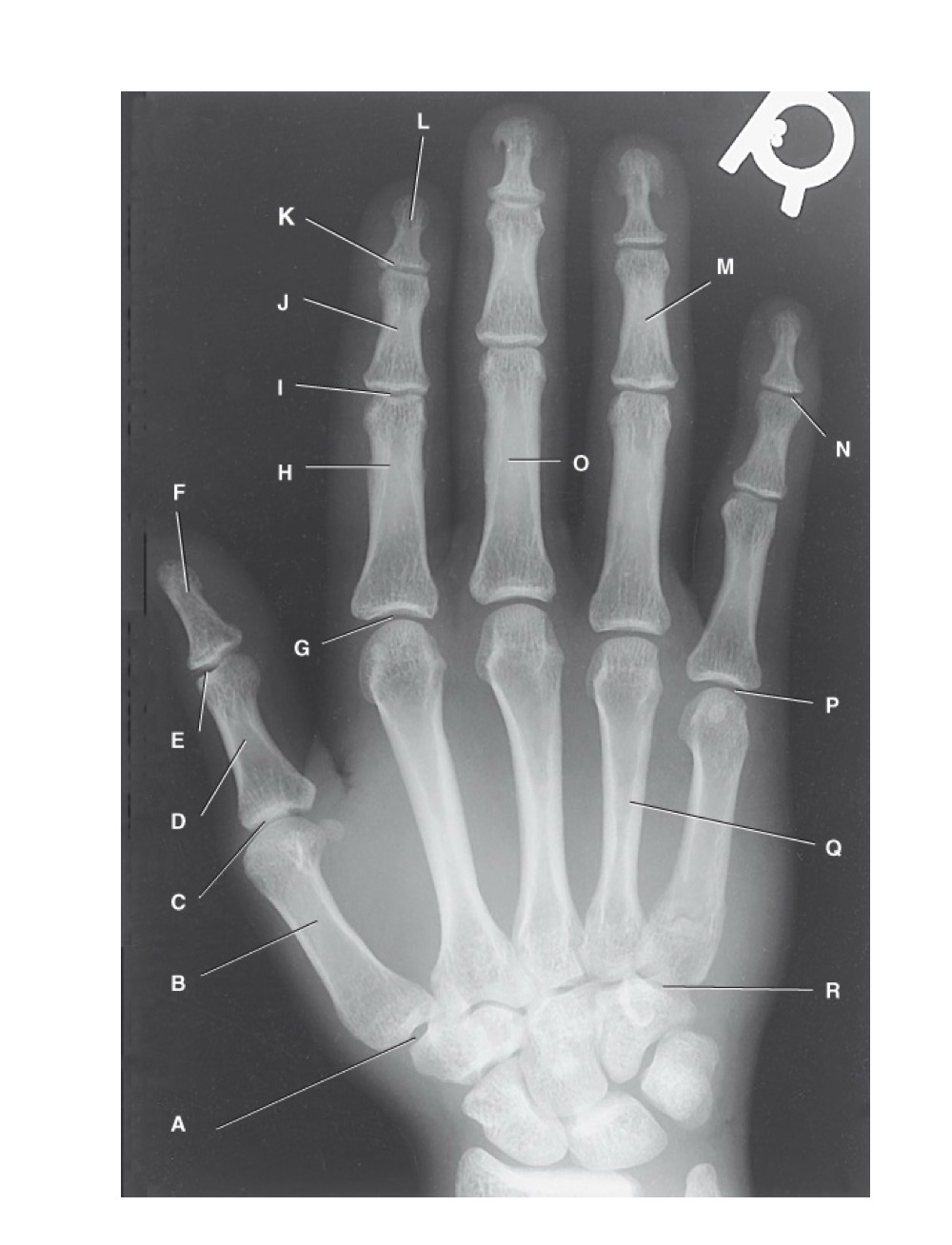
E?
interphalangeal joint of the first digit
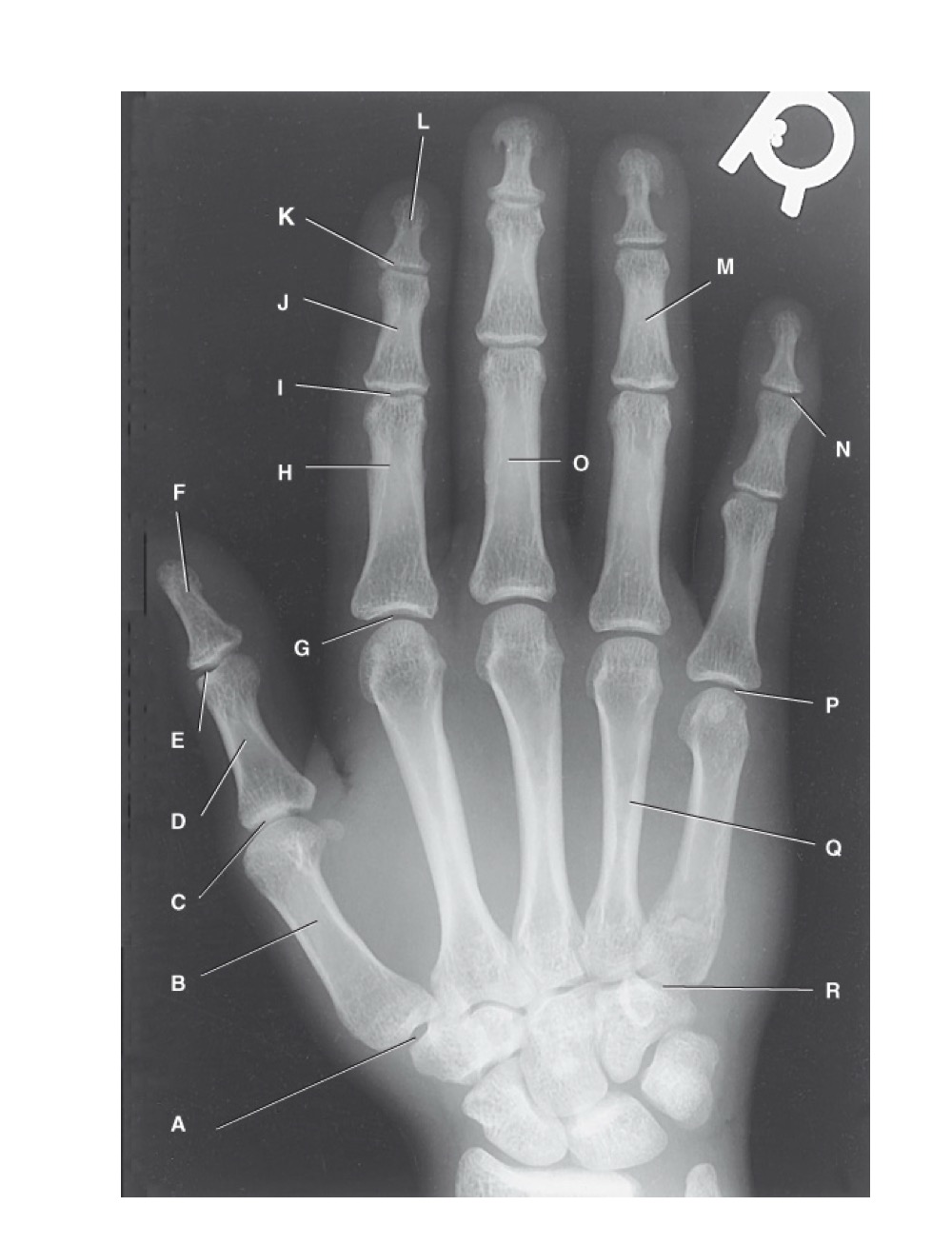
F?
distal phalanx of the first digit
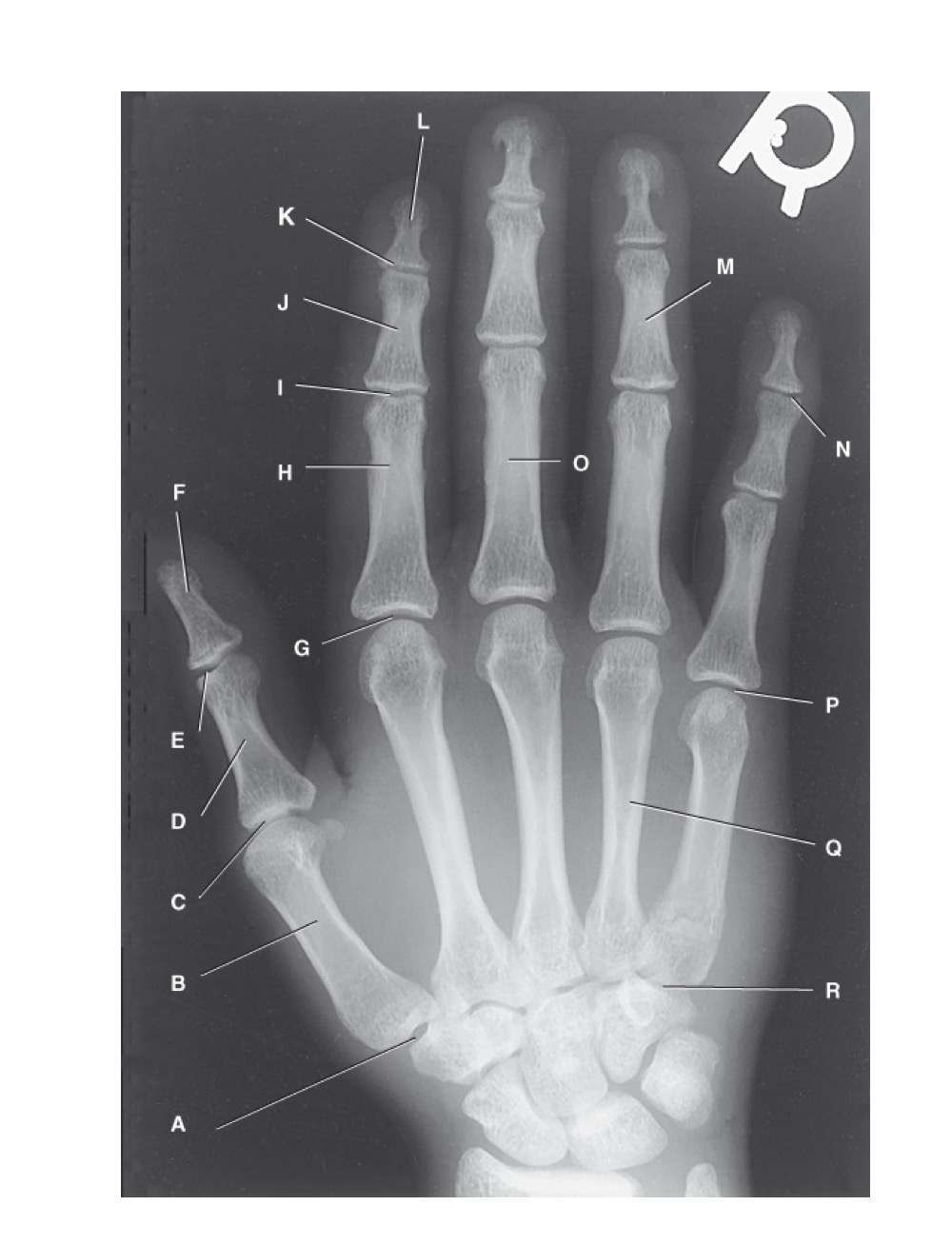
G?
second metacarpophalangeal joint
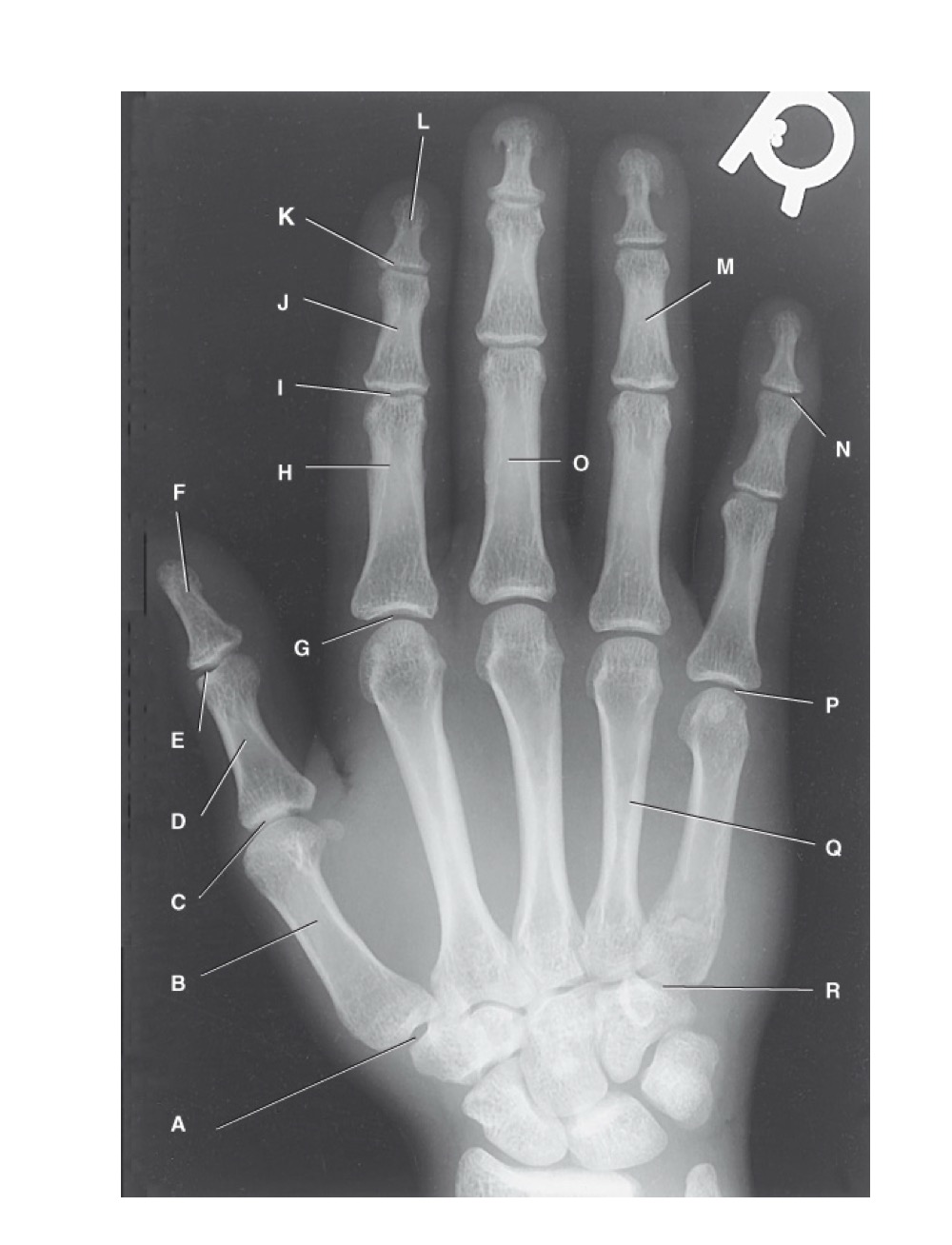
H?
proximal phalanx of the second digit
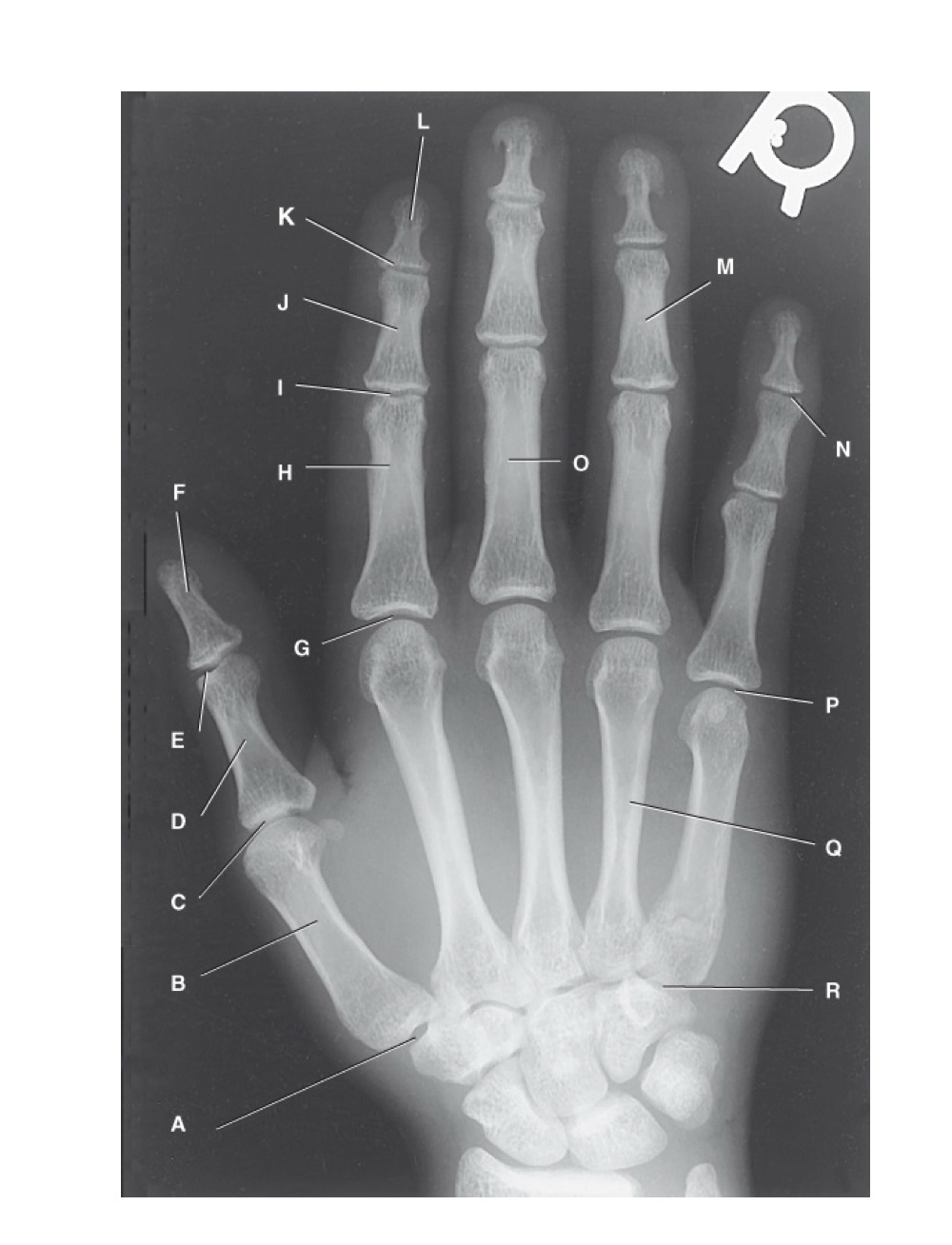
I?
proximal interphalangeal joint of the second digit
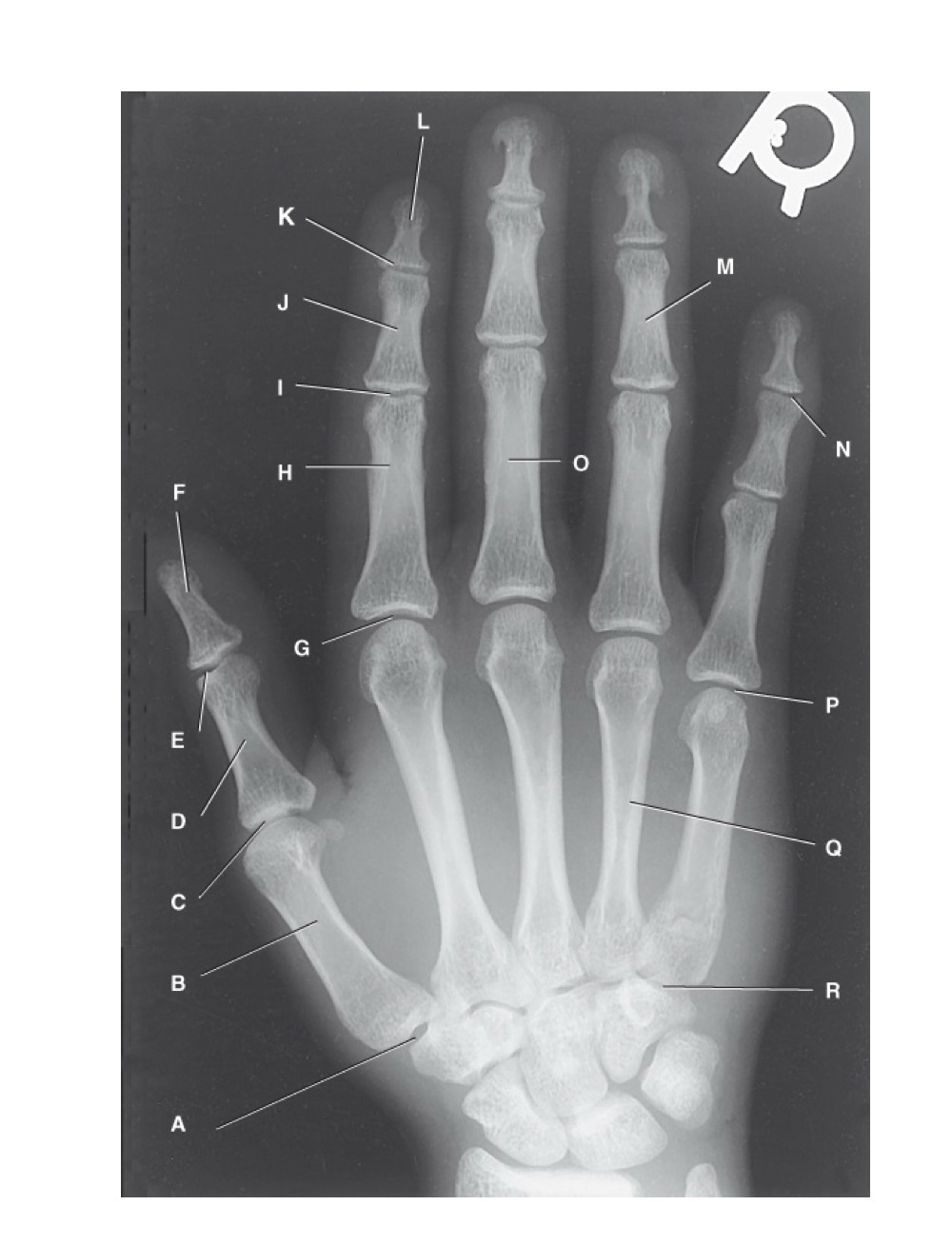
J?
middle phalanx of second digit
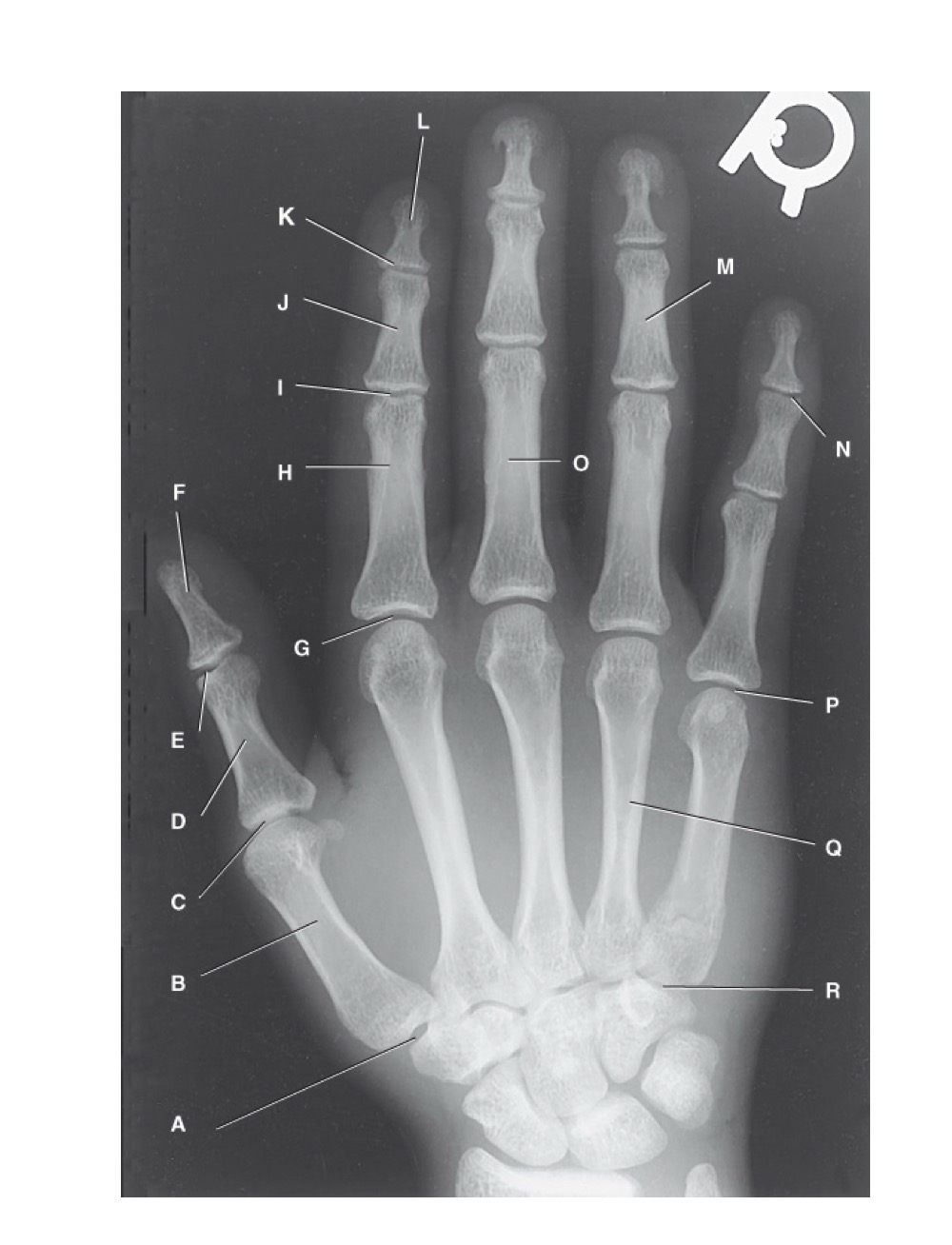
K?
distal interphalangeal joint of second digit
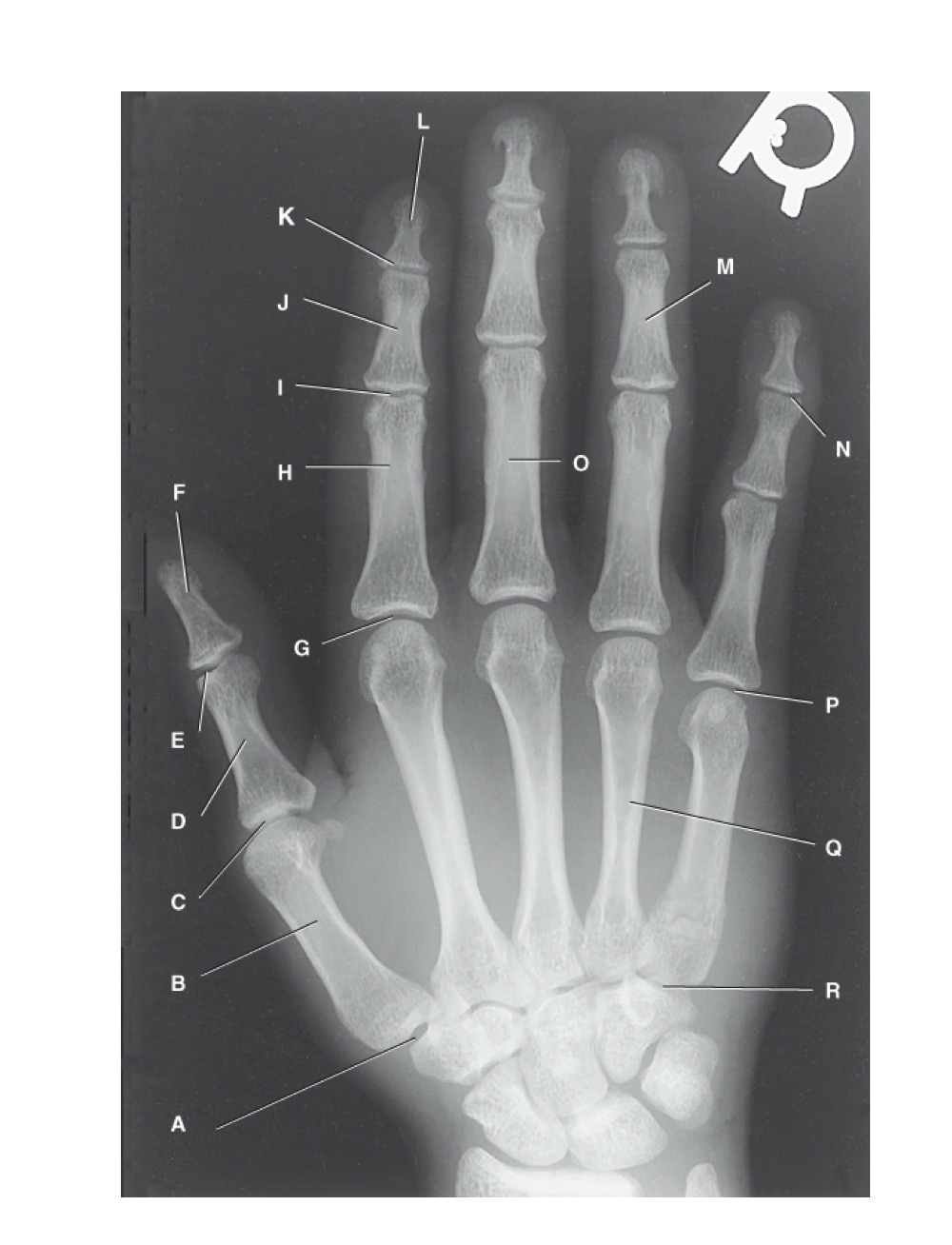
L?
distal phalanx of second digit
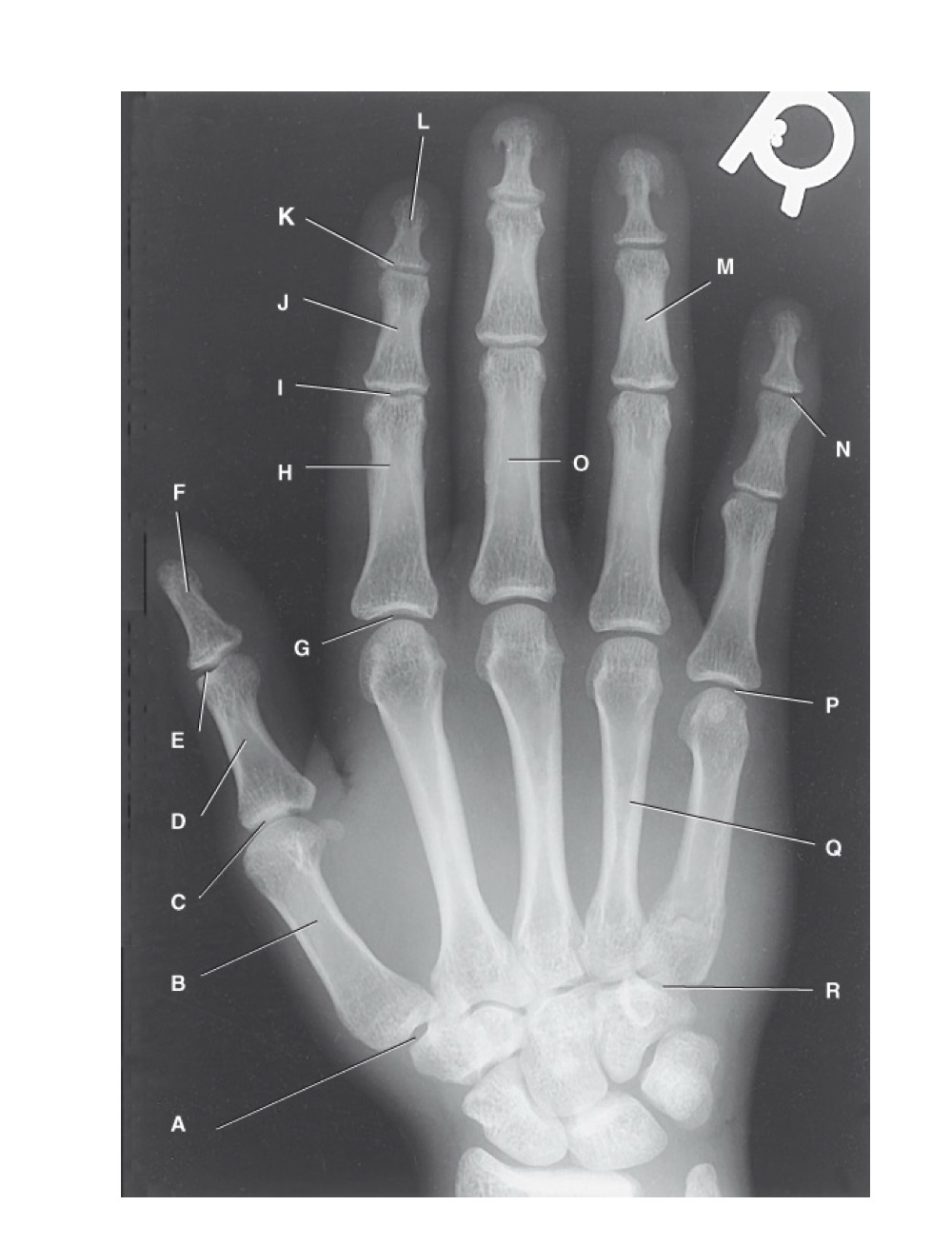
M?
middle phalanx of the fourth digit
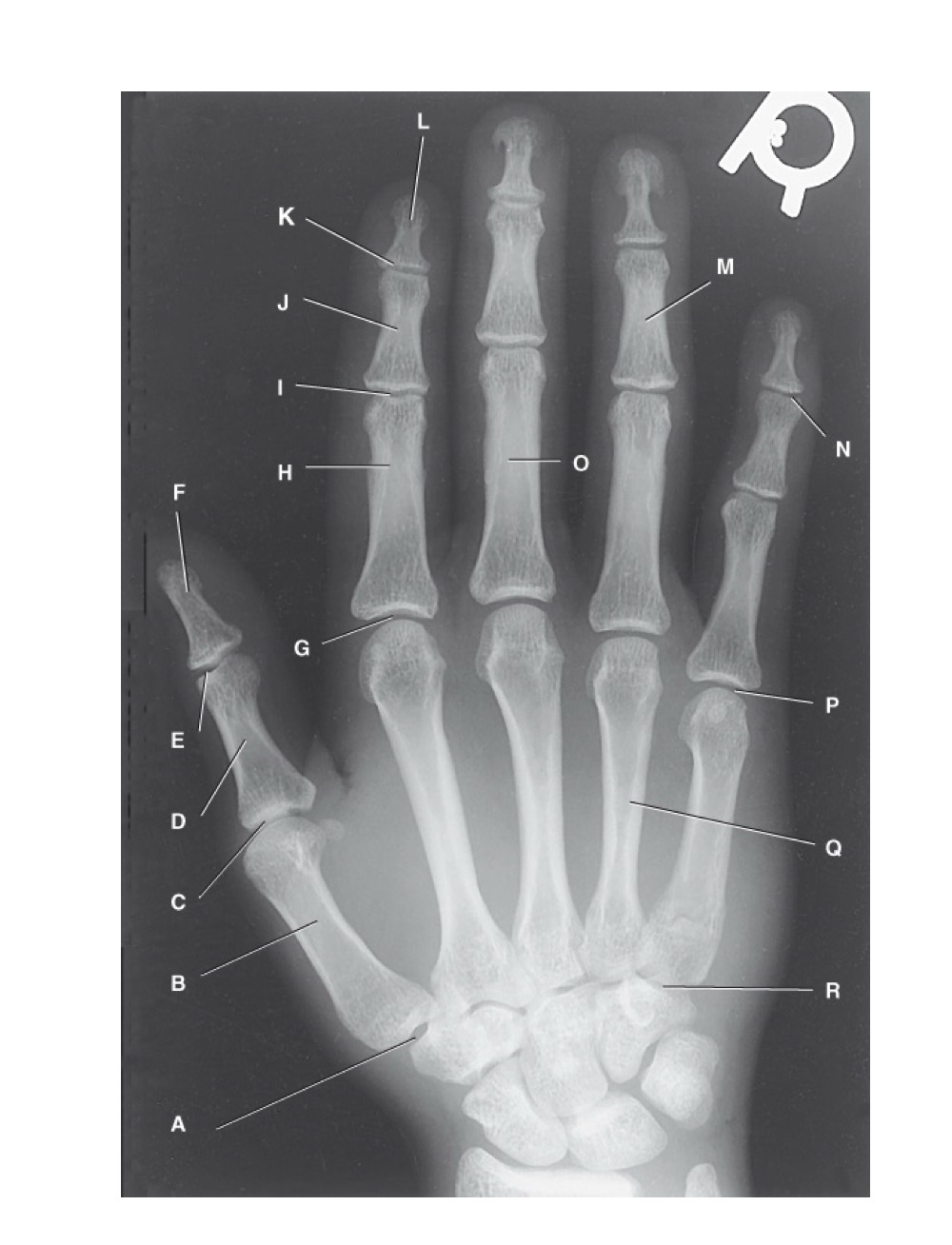
N?
distal interphalangeal joint of fifth digit
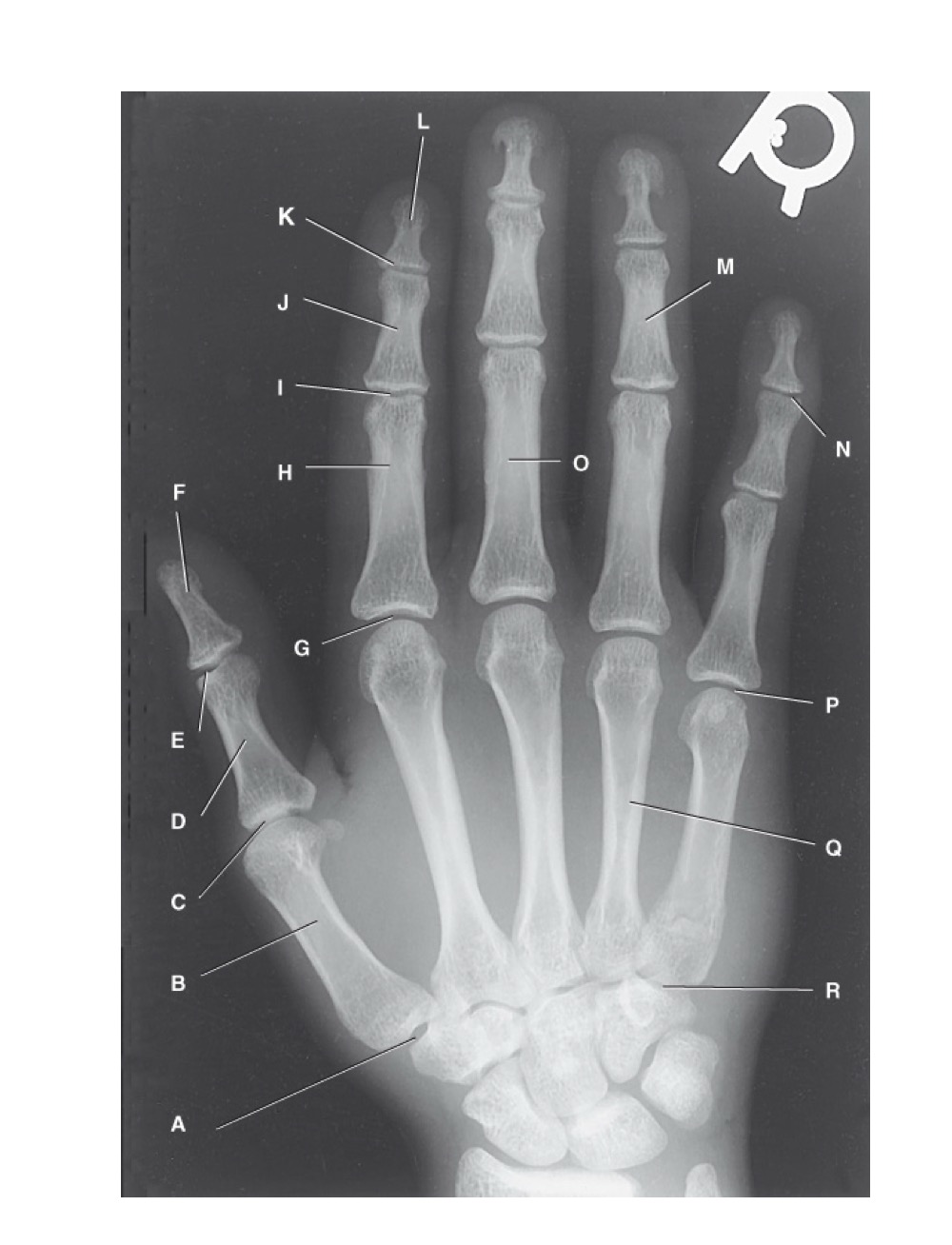
O?
proximal phalanx of third digit
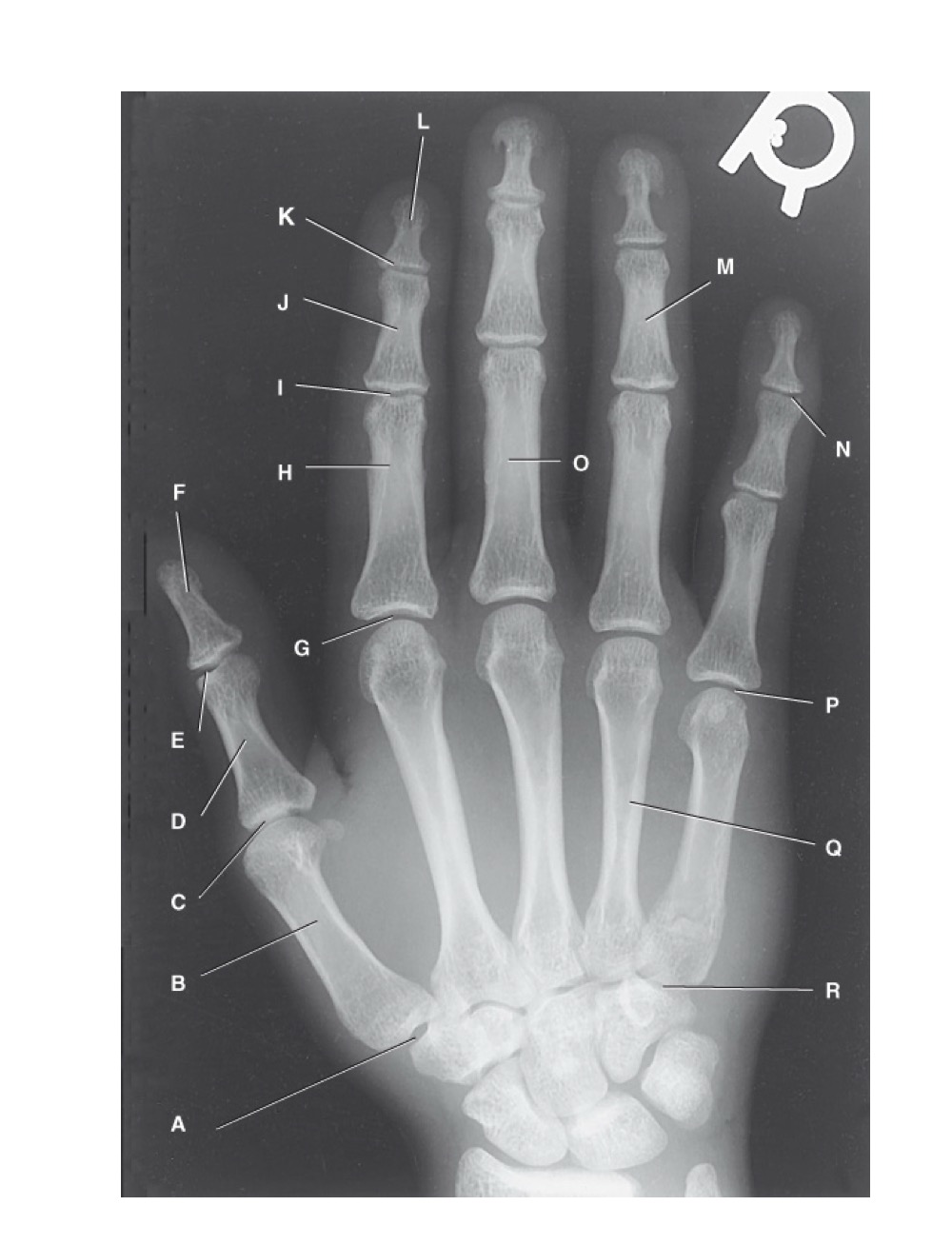
P?
fifth metacarpophalangeal joint
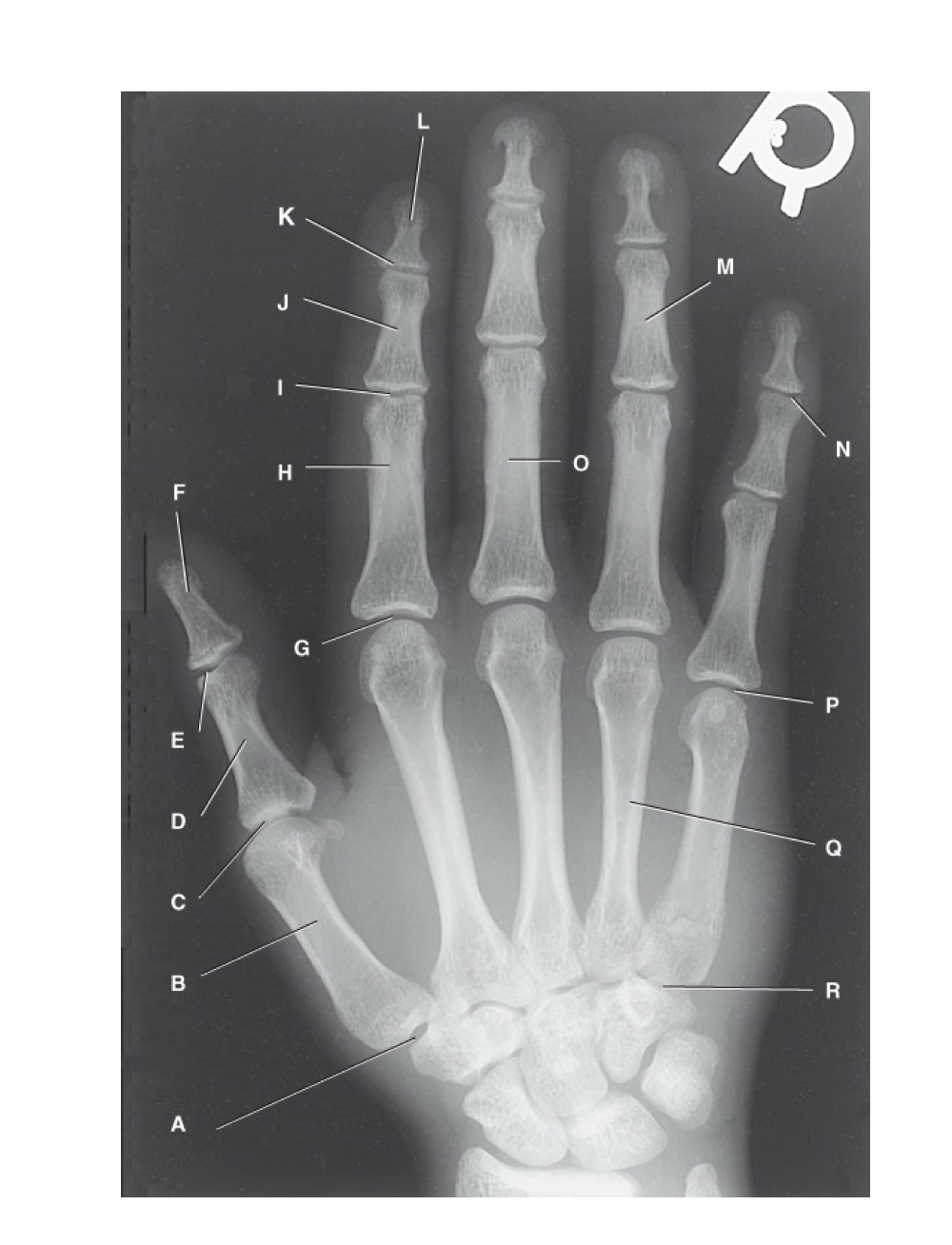
Q?
fourth metacarpal
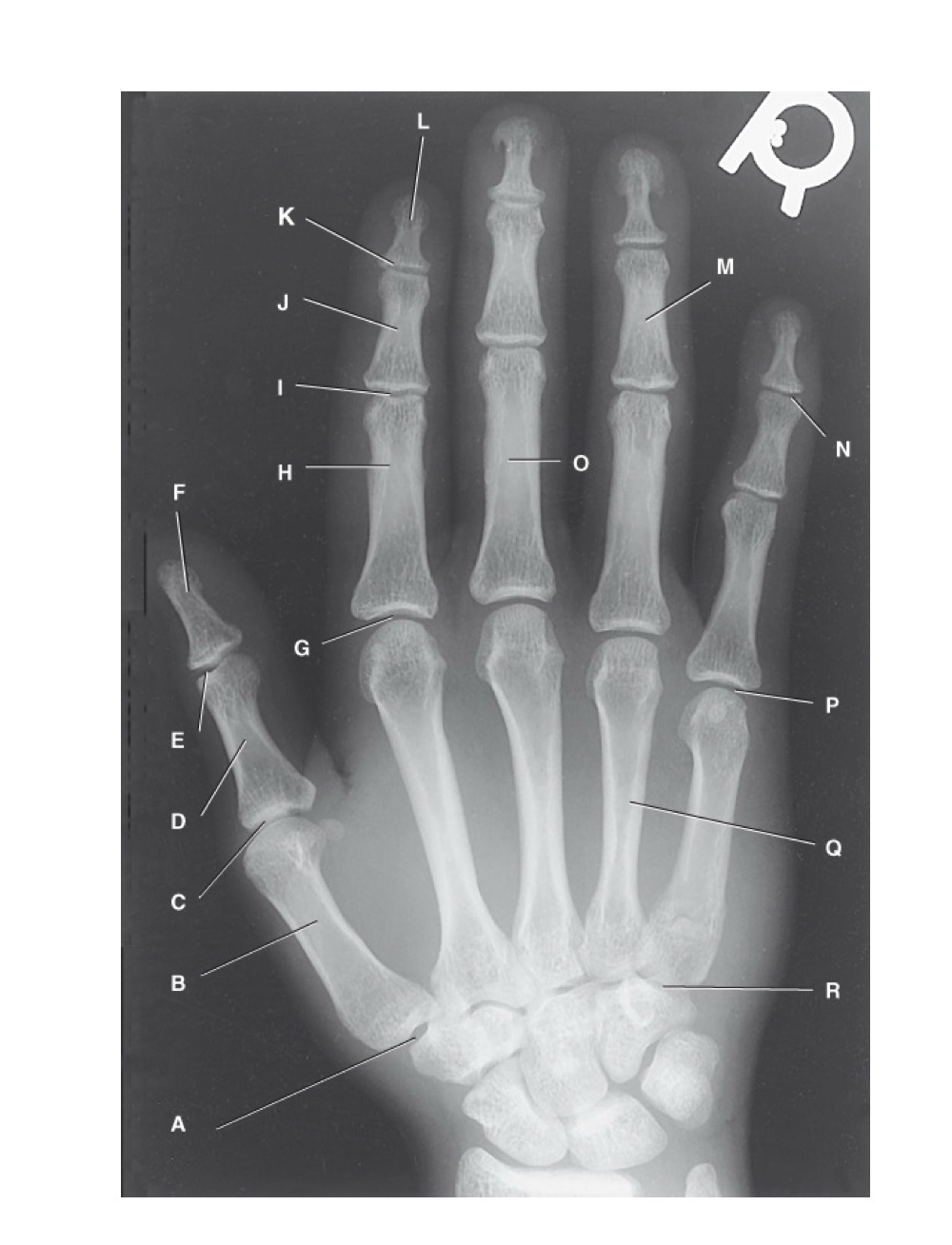
R?
fifth carpometacarpal joint
what are the carpals of the distal row
trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
what are the carpals of the proximal row?
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
radial deviation
deviated towards radius
ulnar deviation
deviated toward ulnar, for scaphoid view
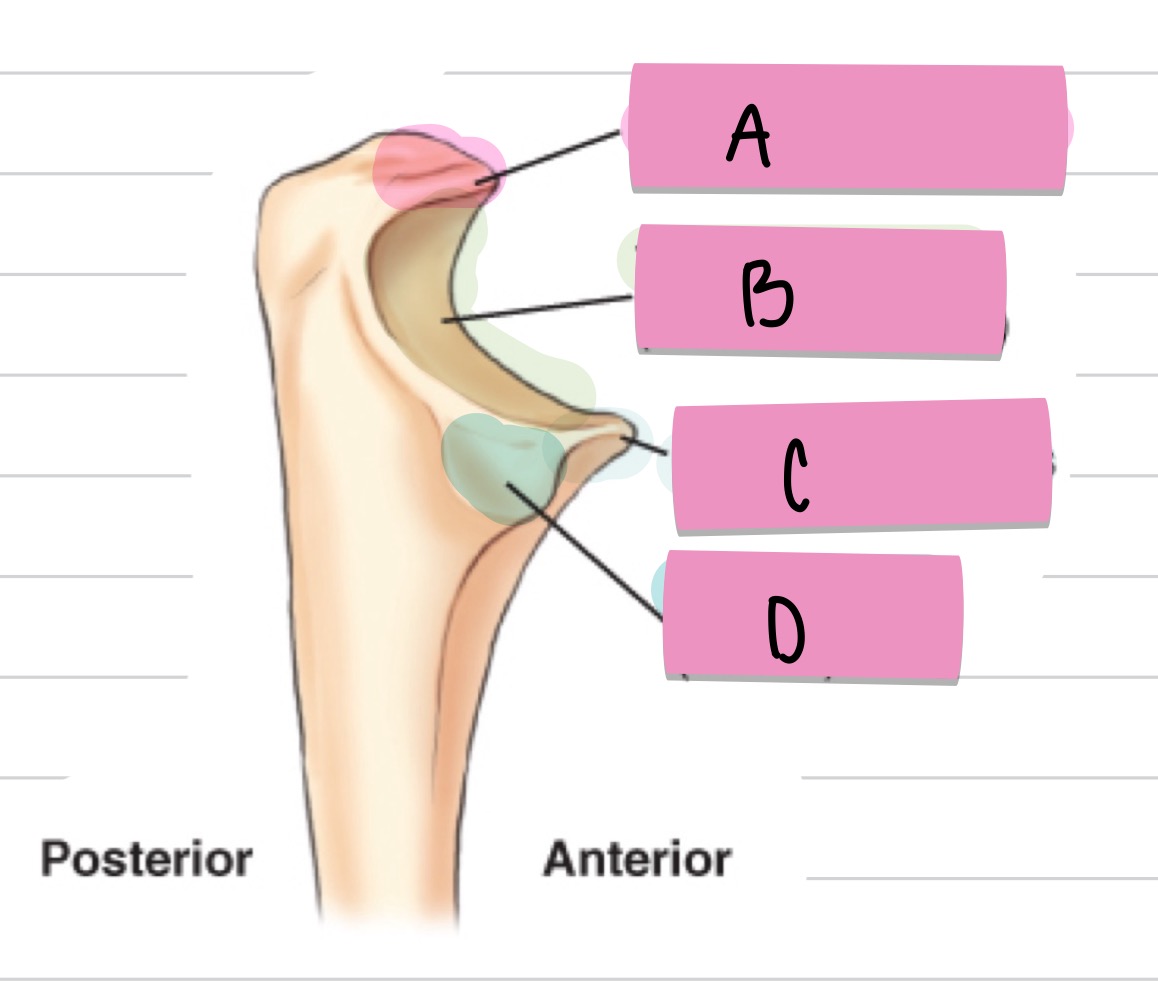
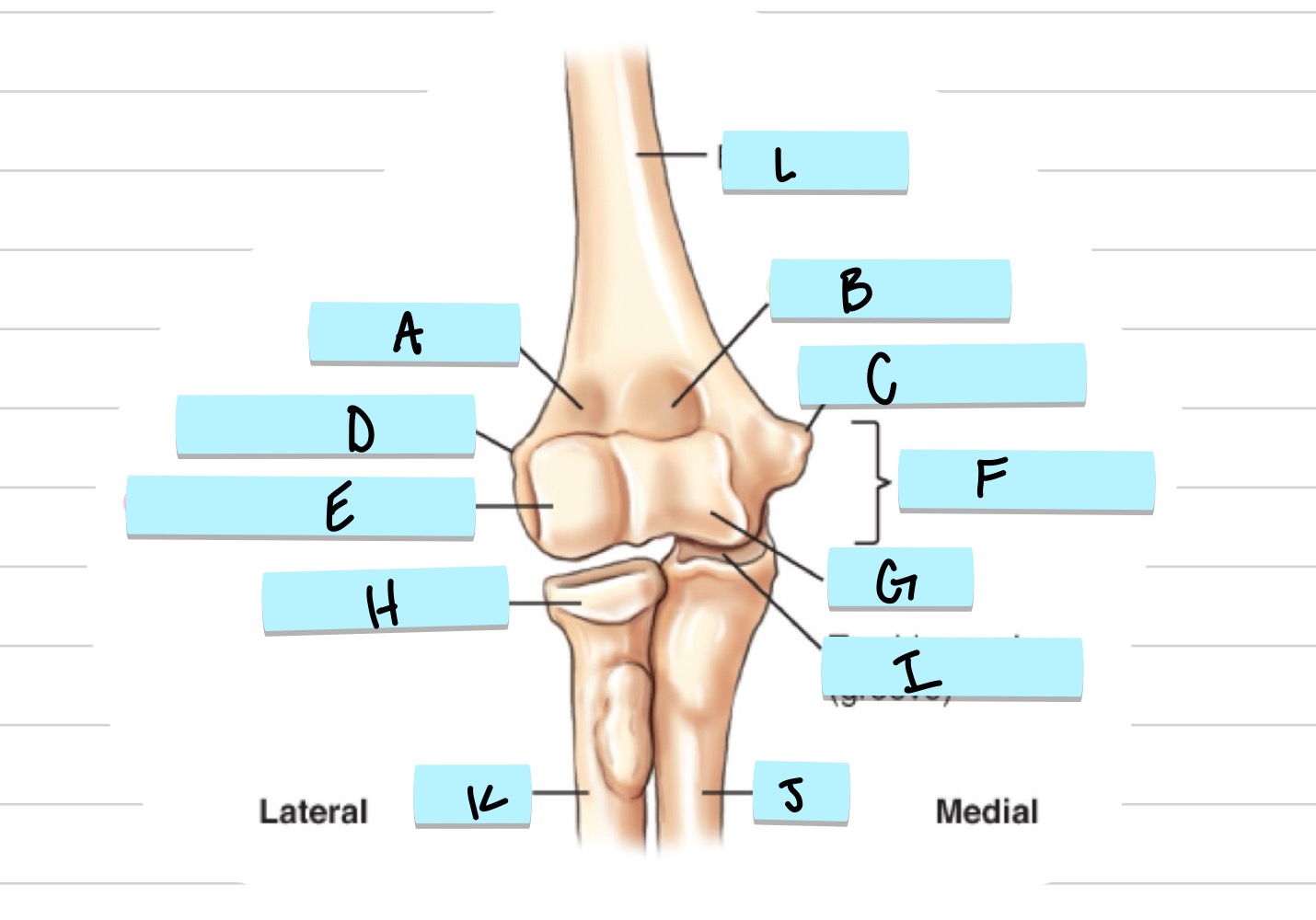
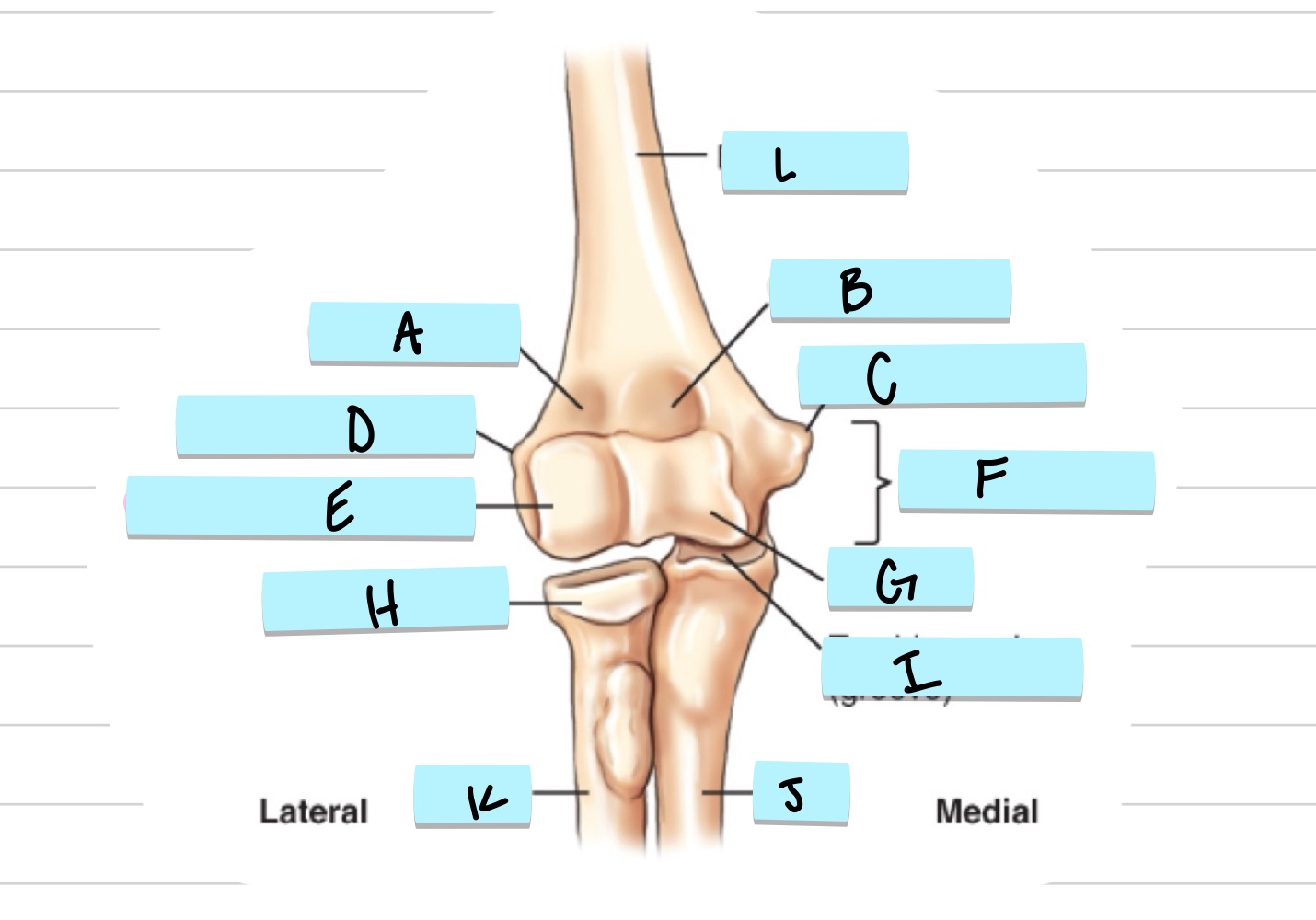
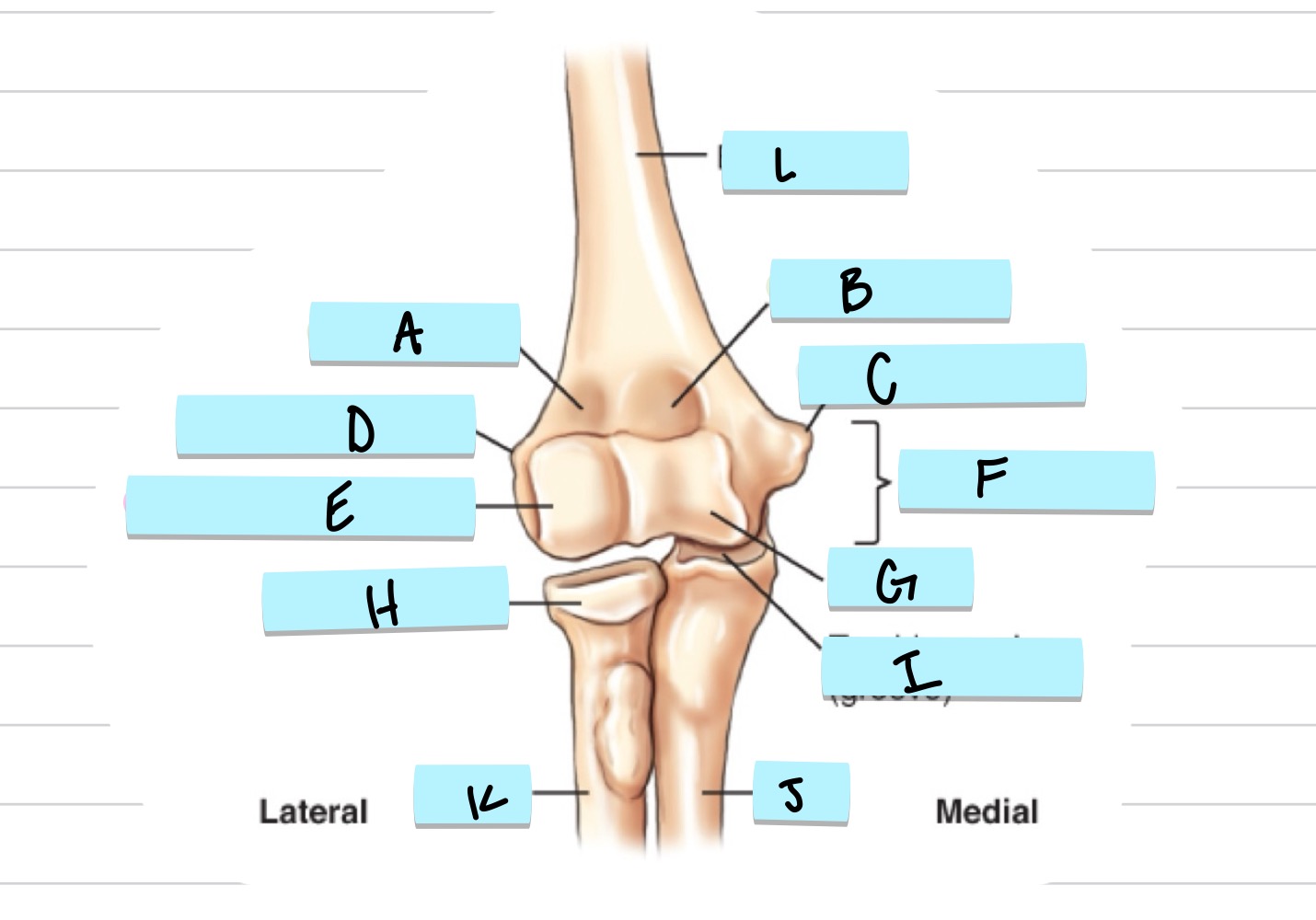
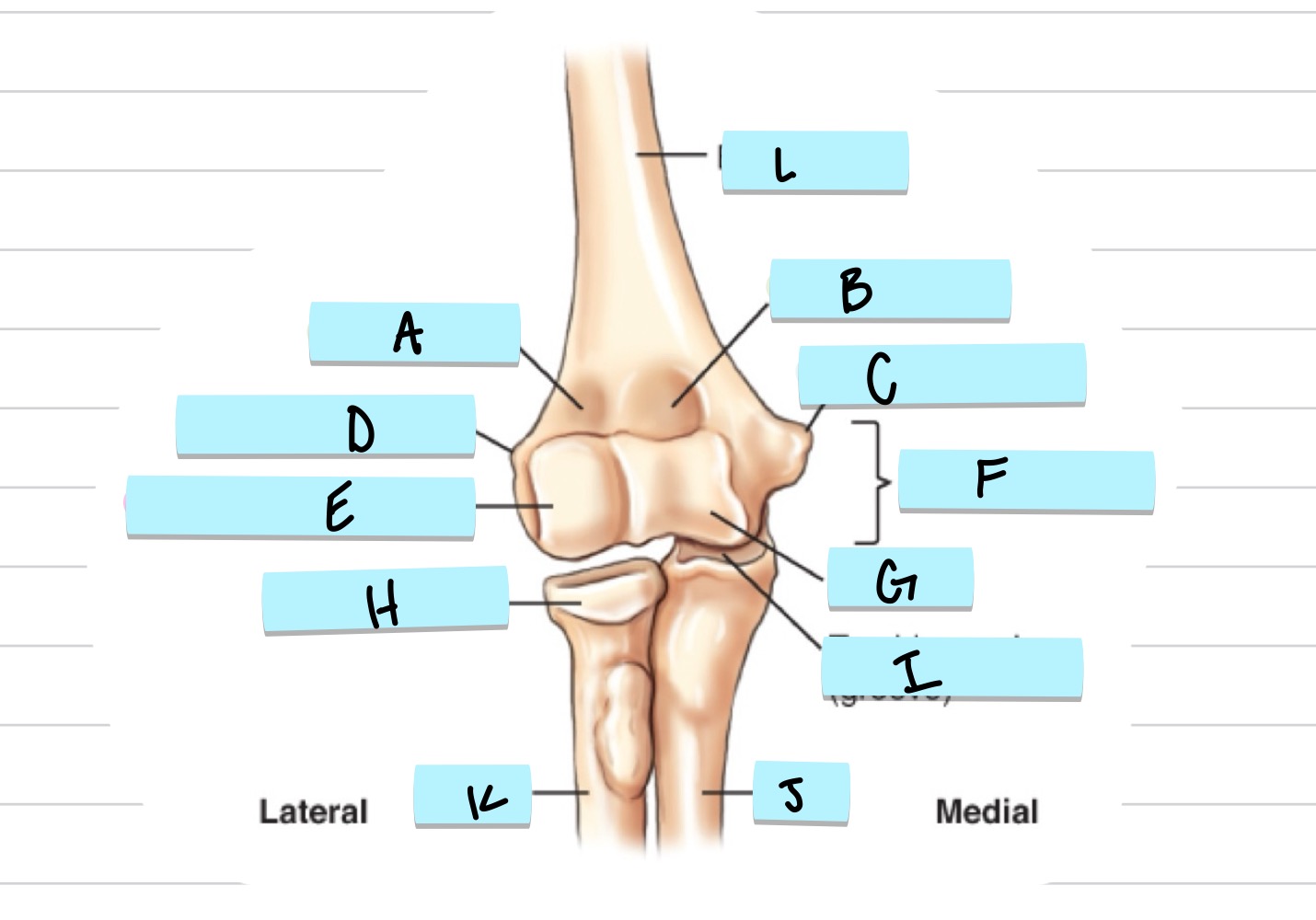
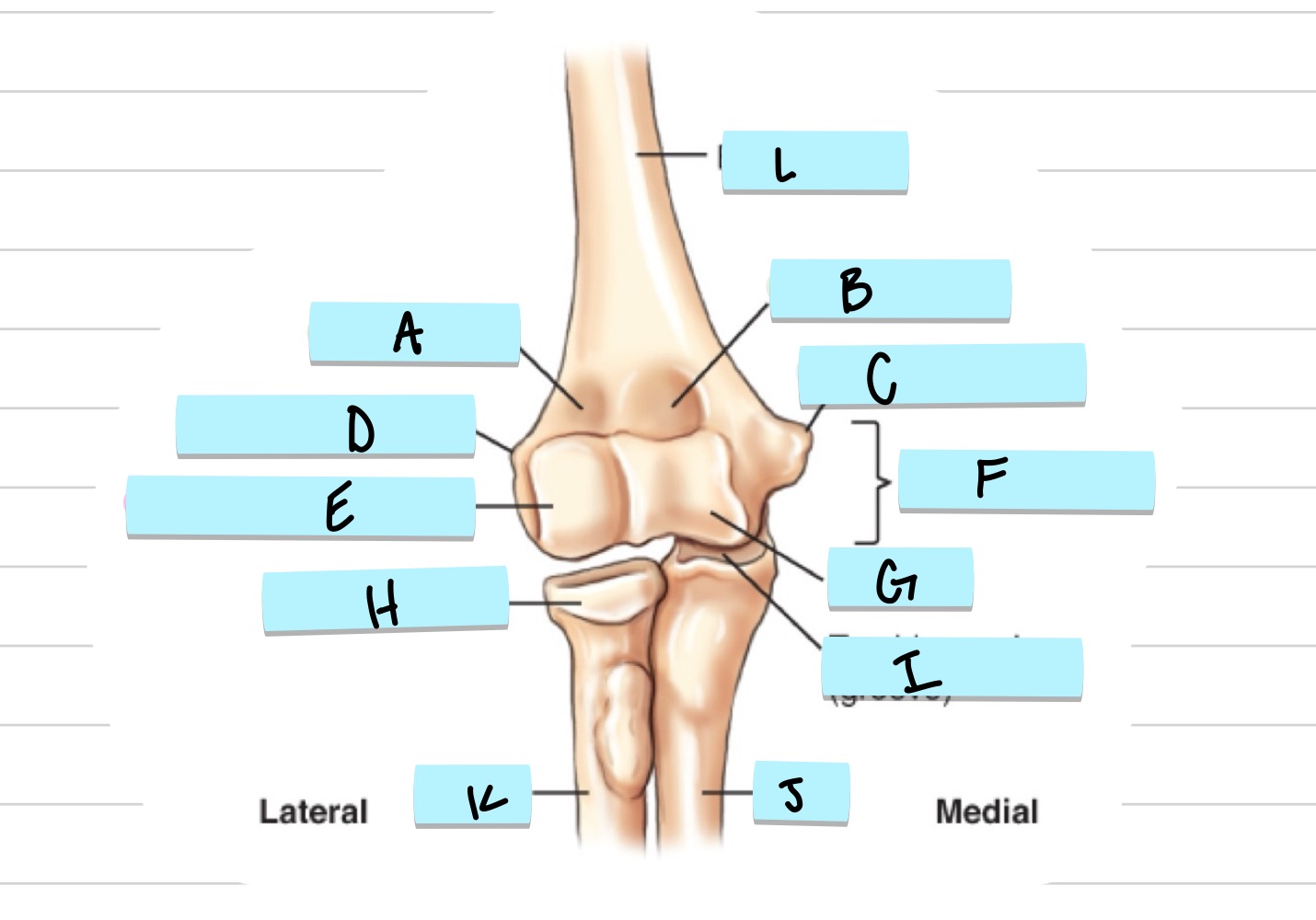
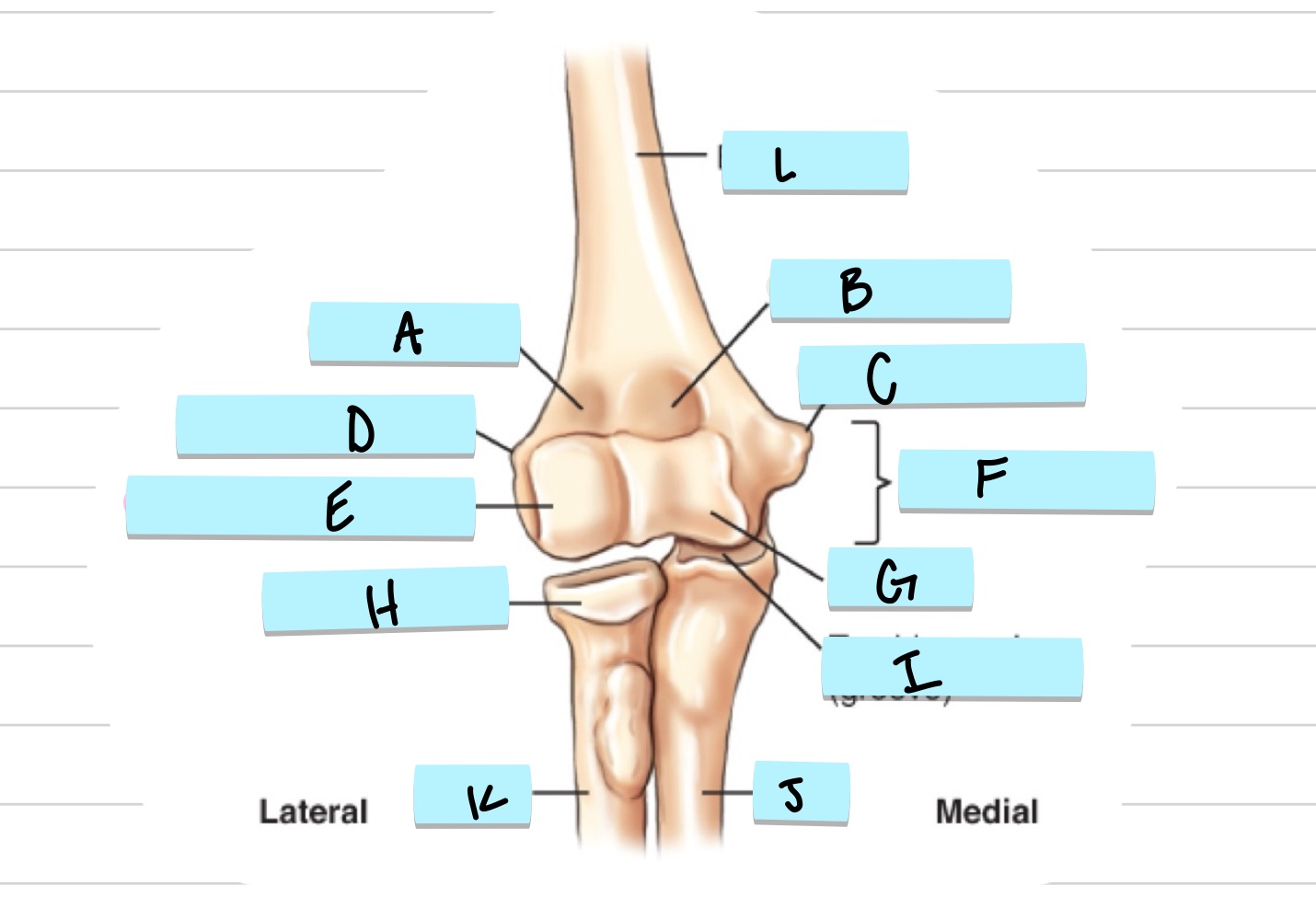
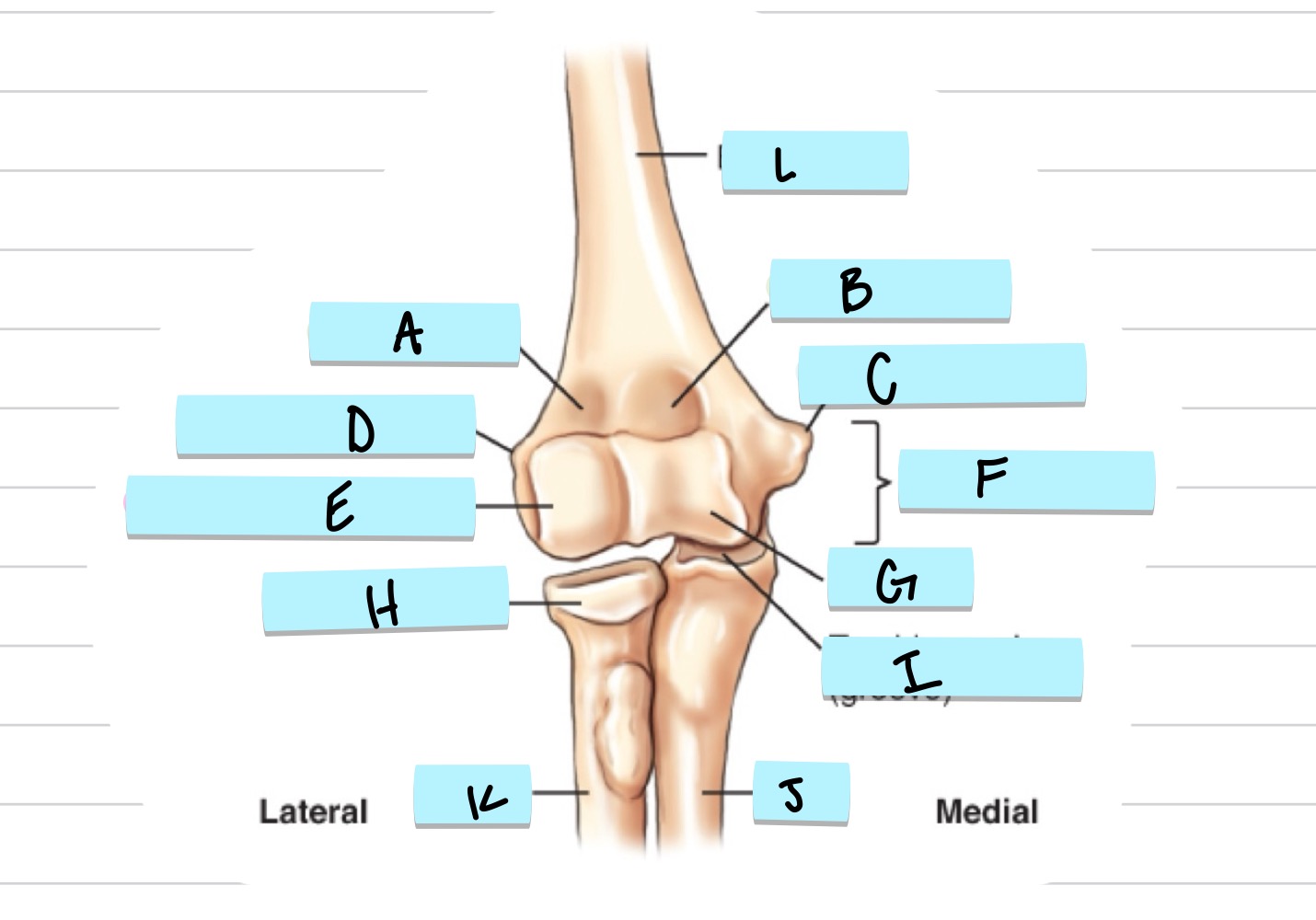
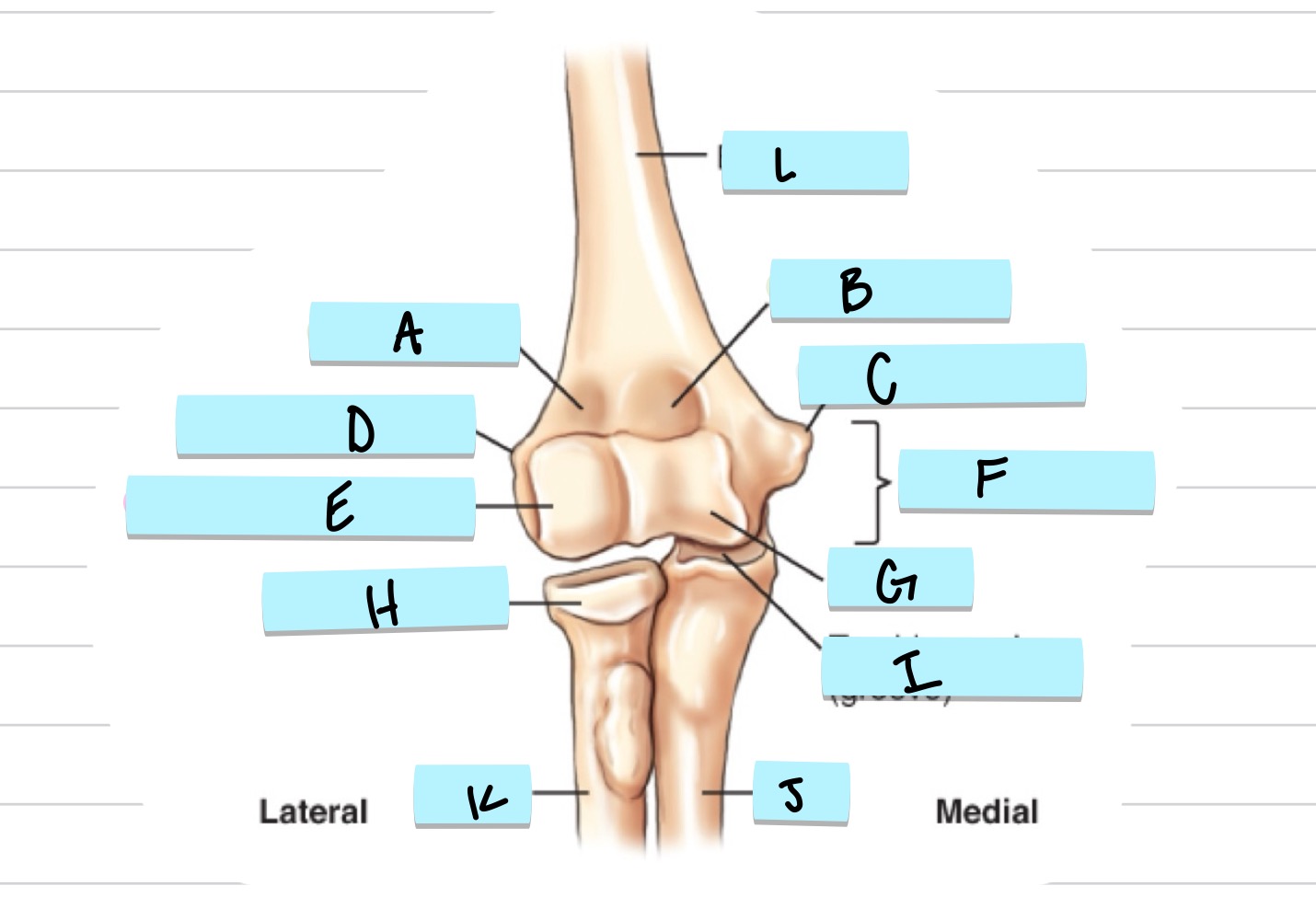
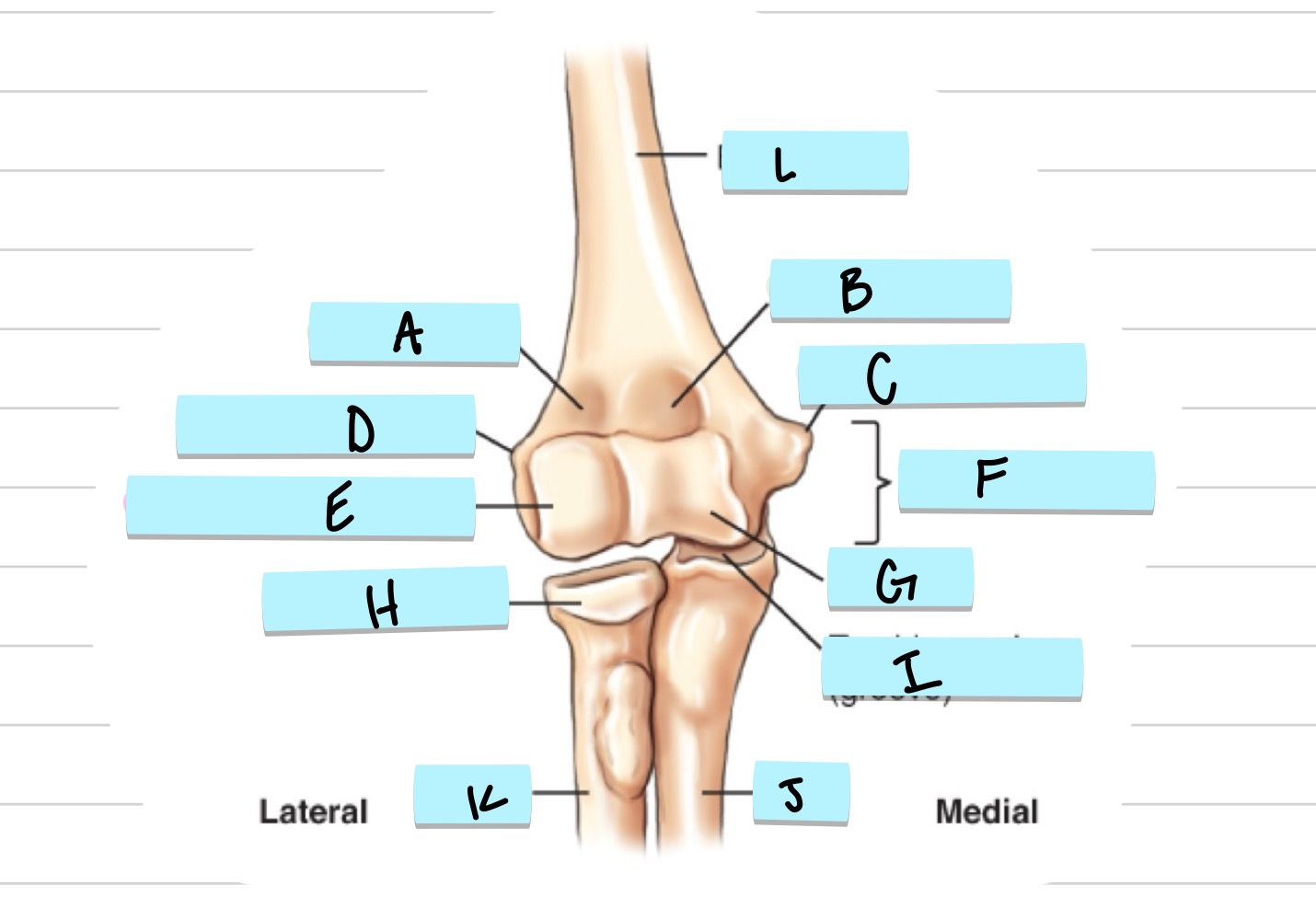
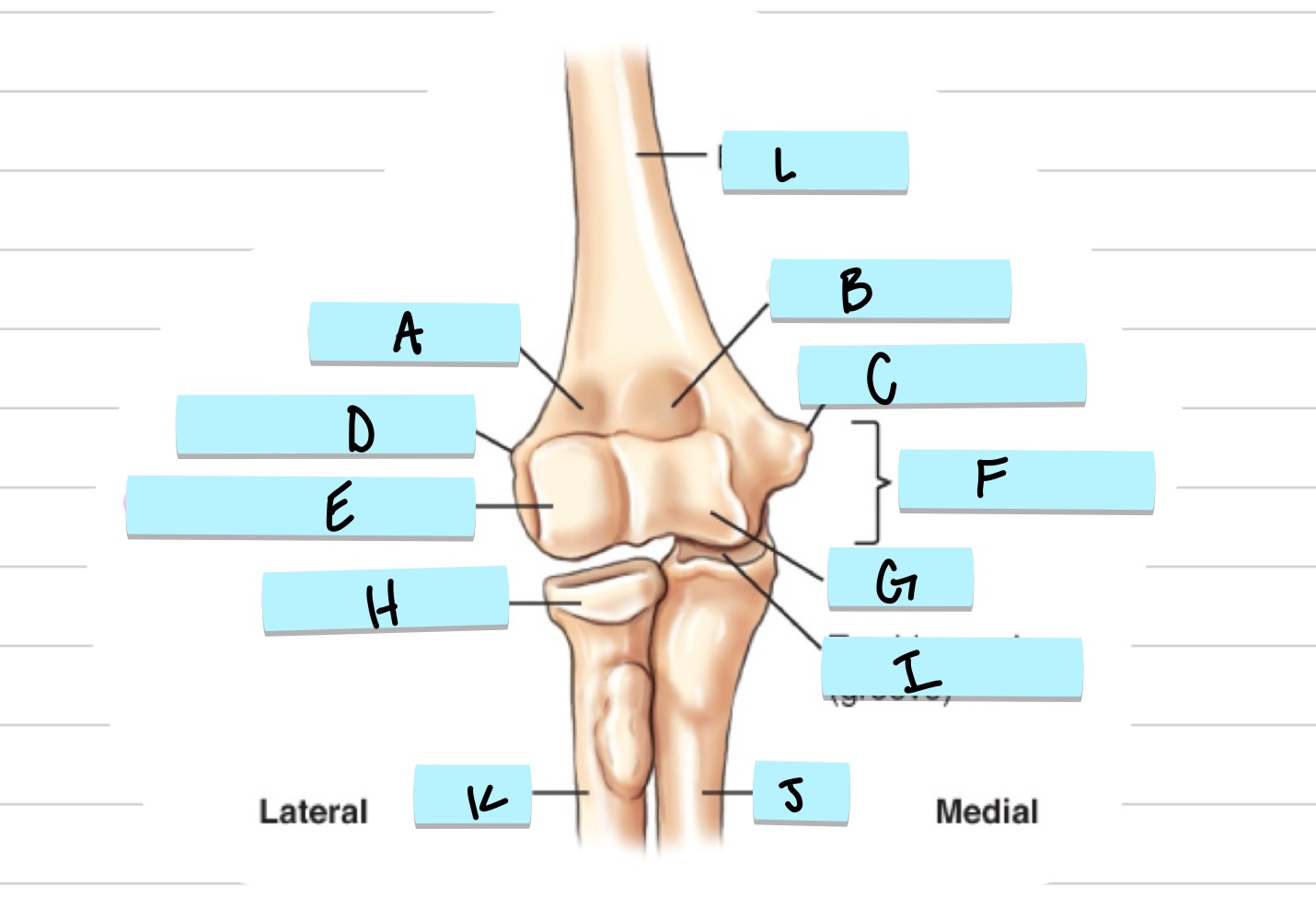
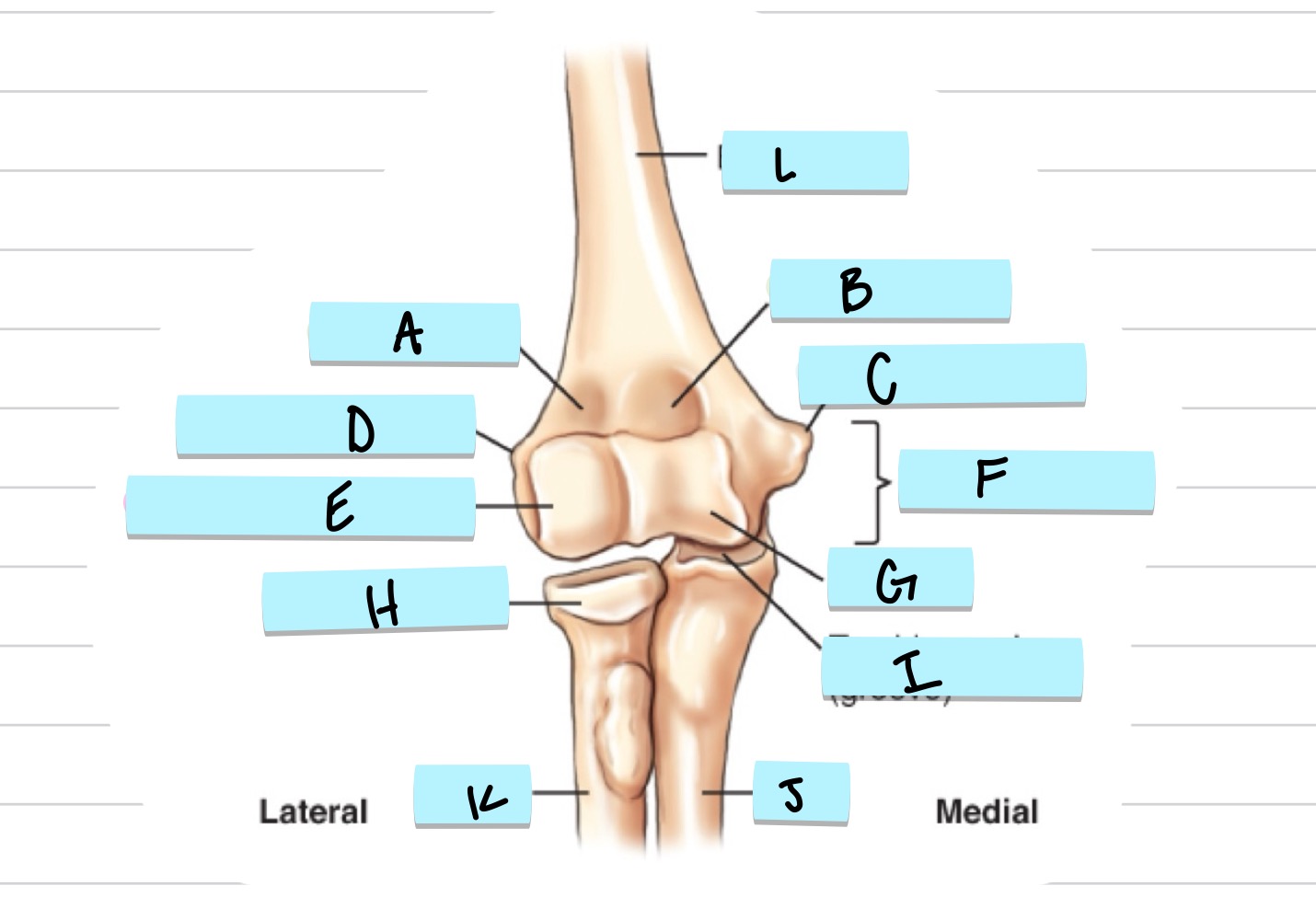
What is A?
olecranon process
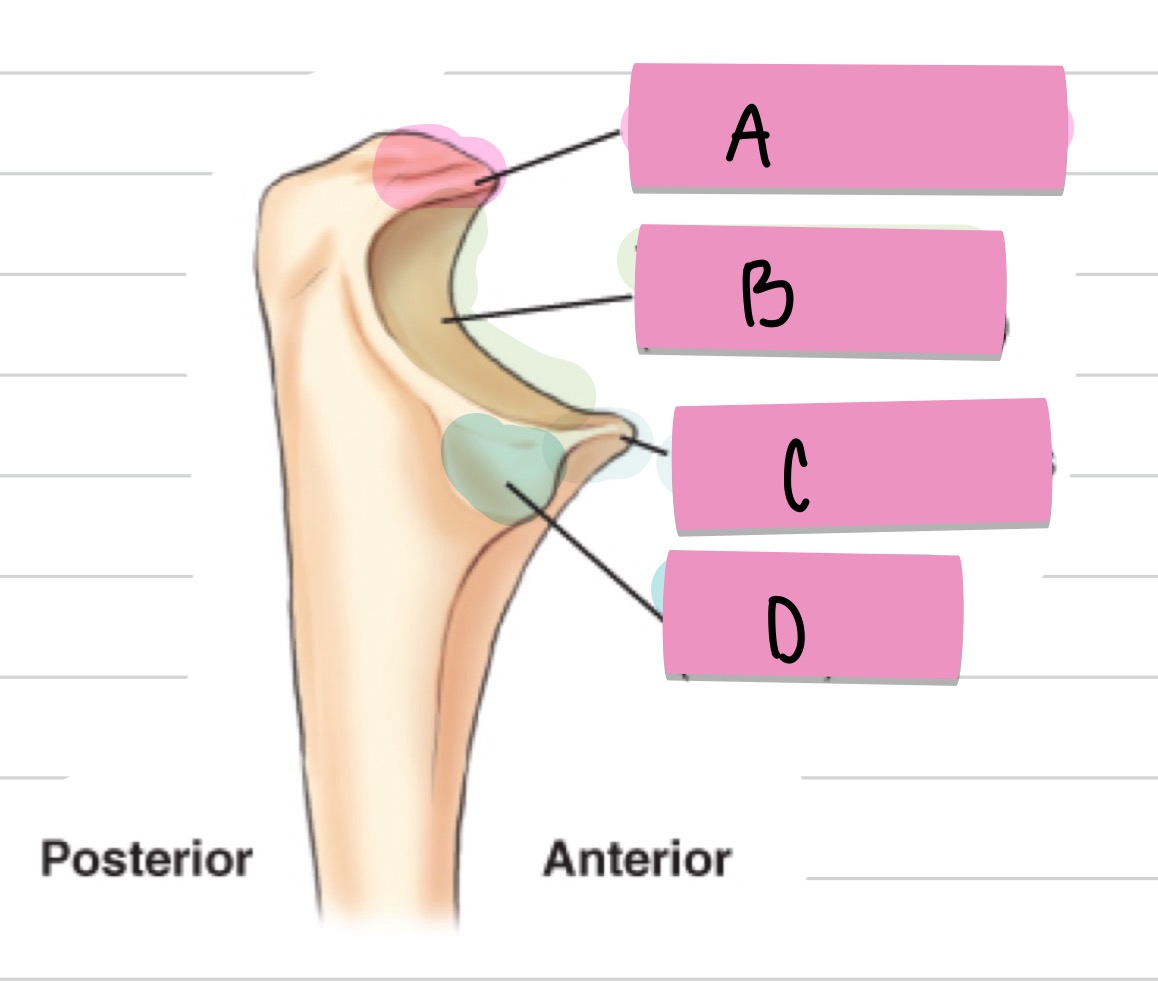
what is B?
trochlear notch
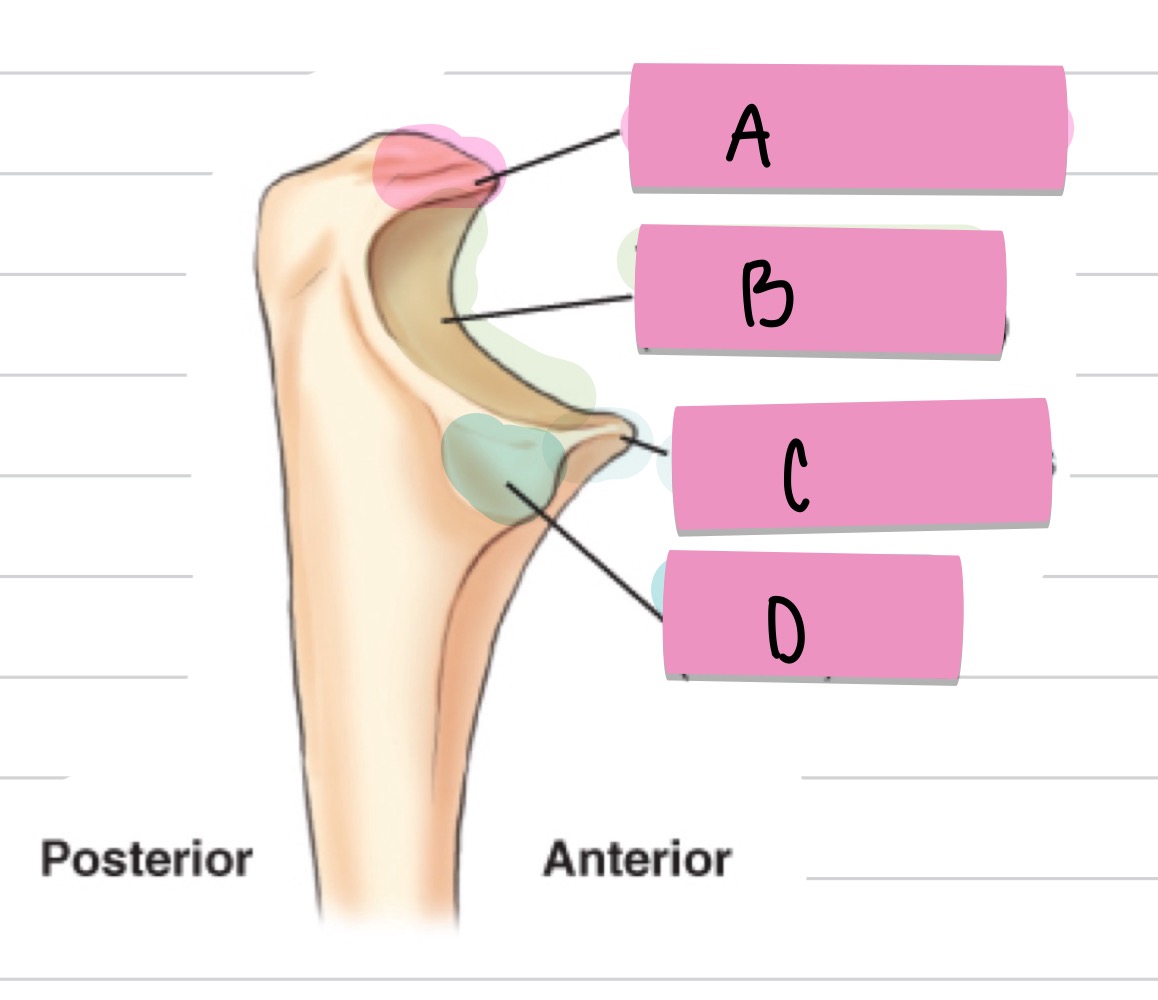
what is C?
coronoid process
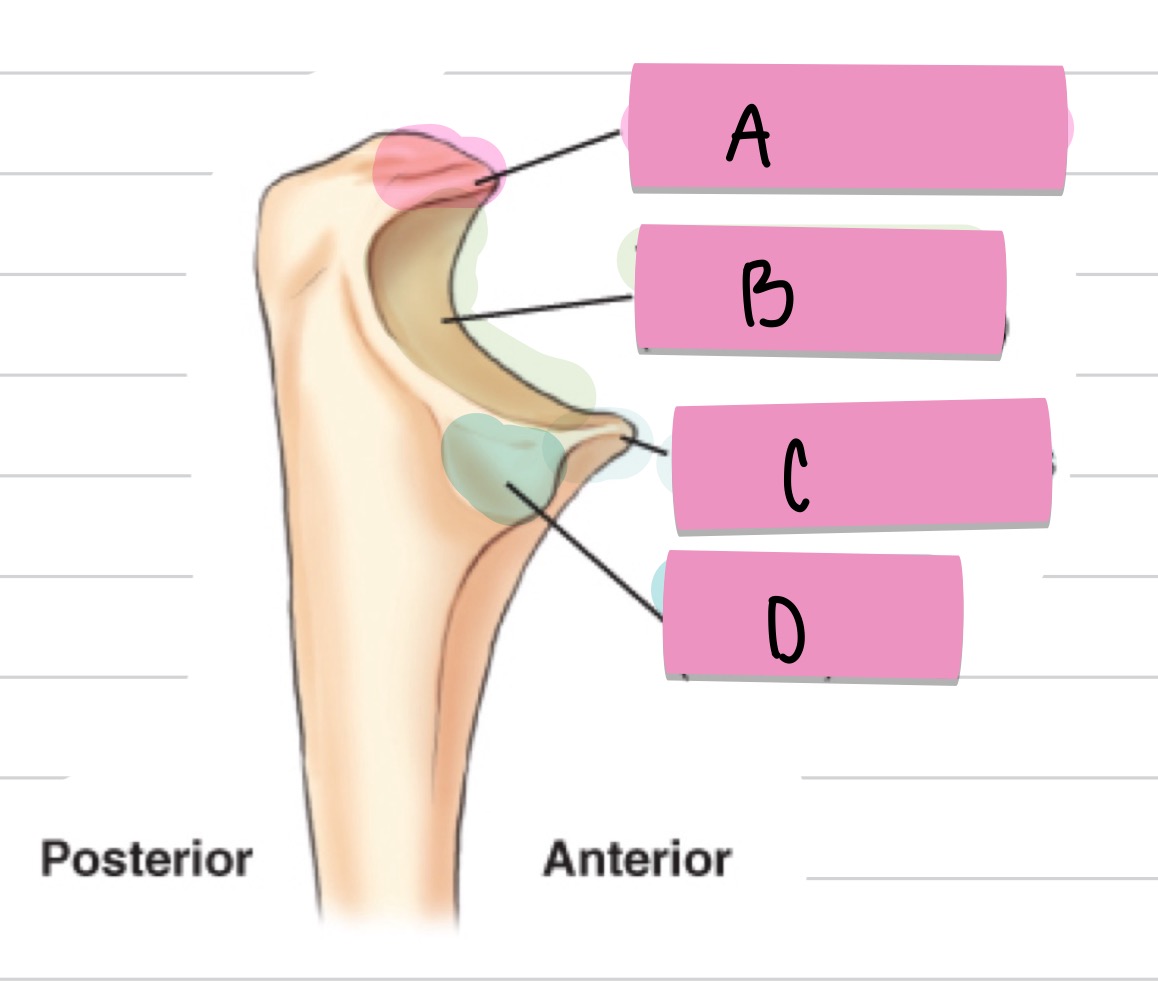
what is D?
radial notch
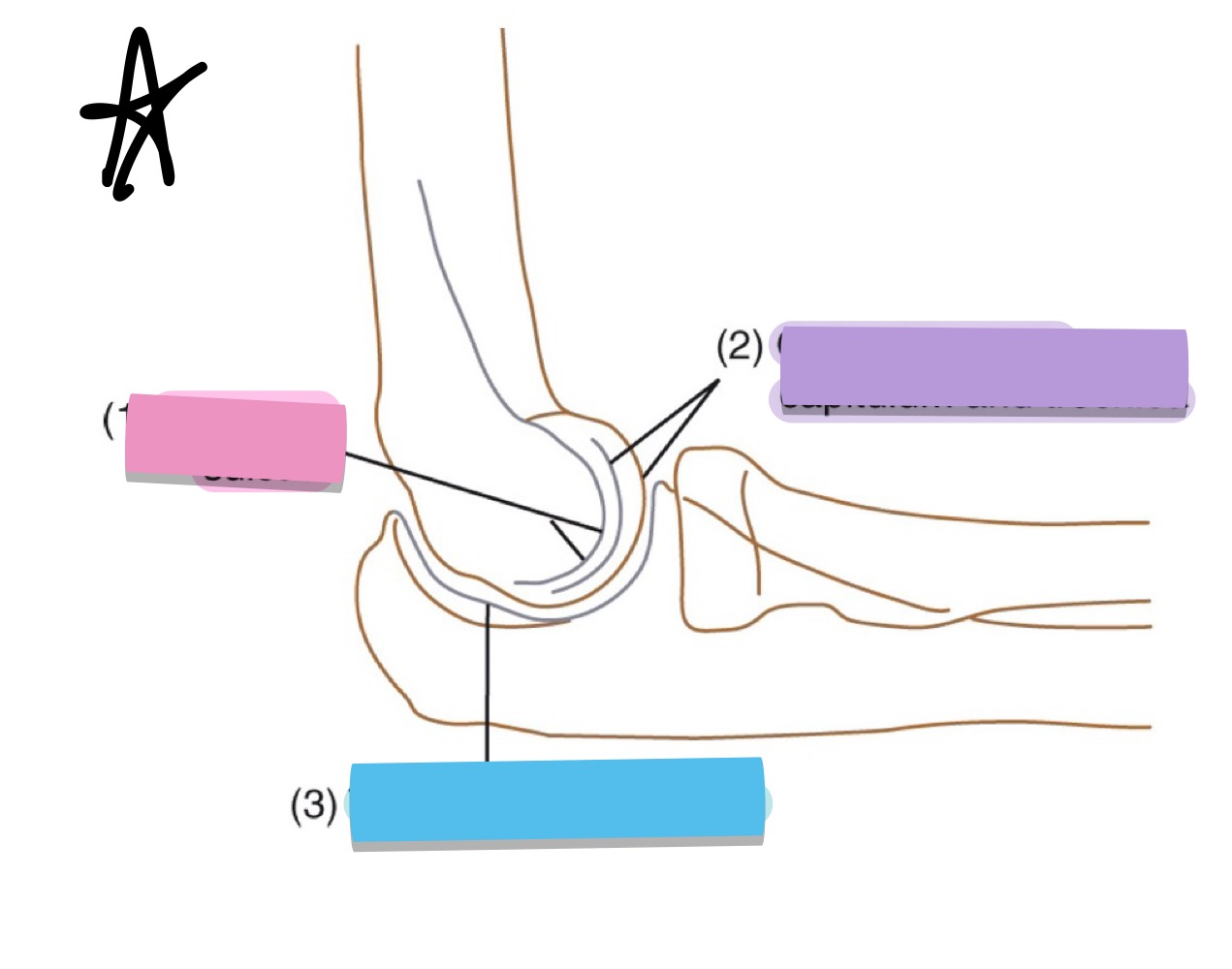
what is the purple pointing to?
outer ridges of capitulum and trochlea
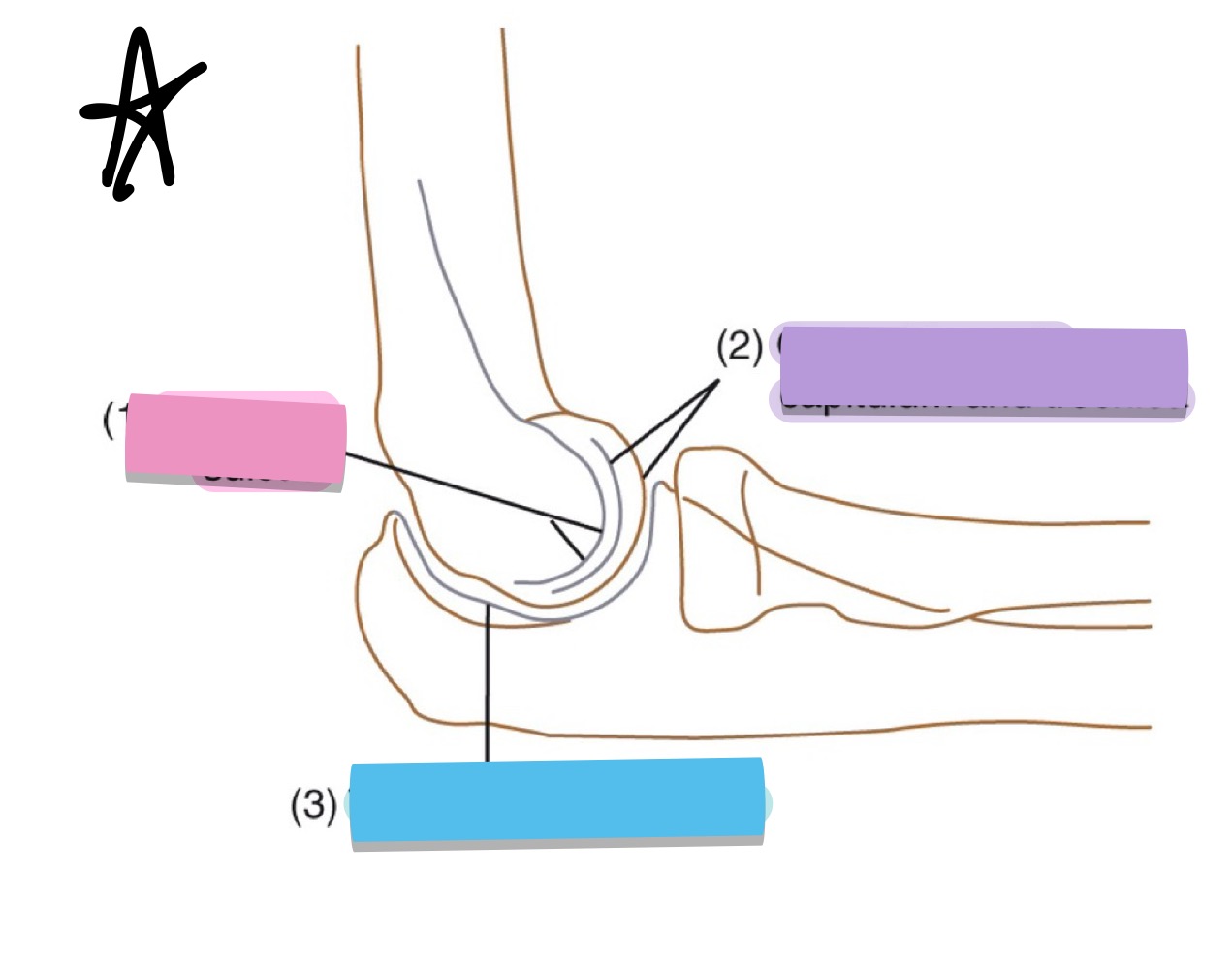
what is the blue pointing to?
trochlear notch of ulna
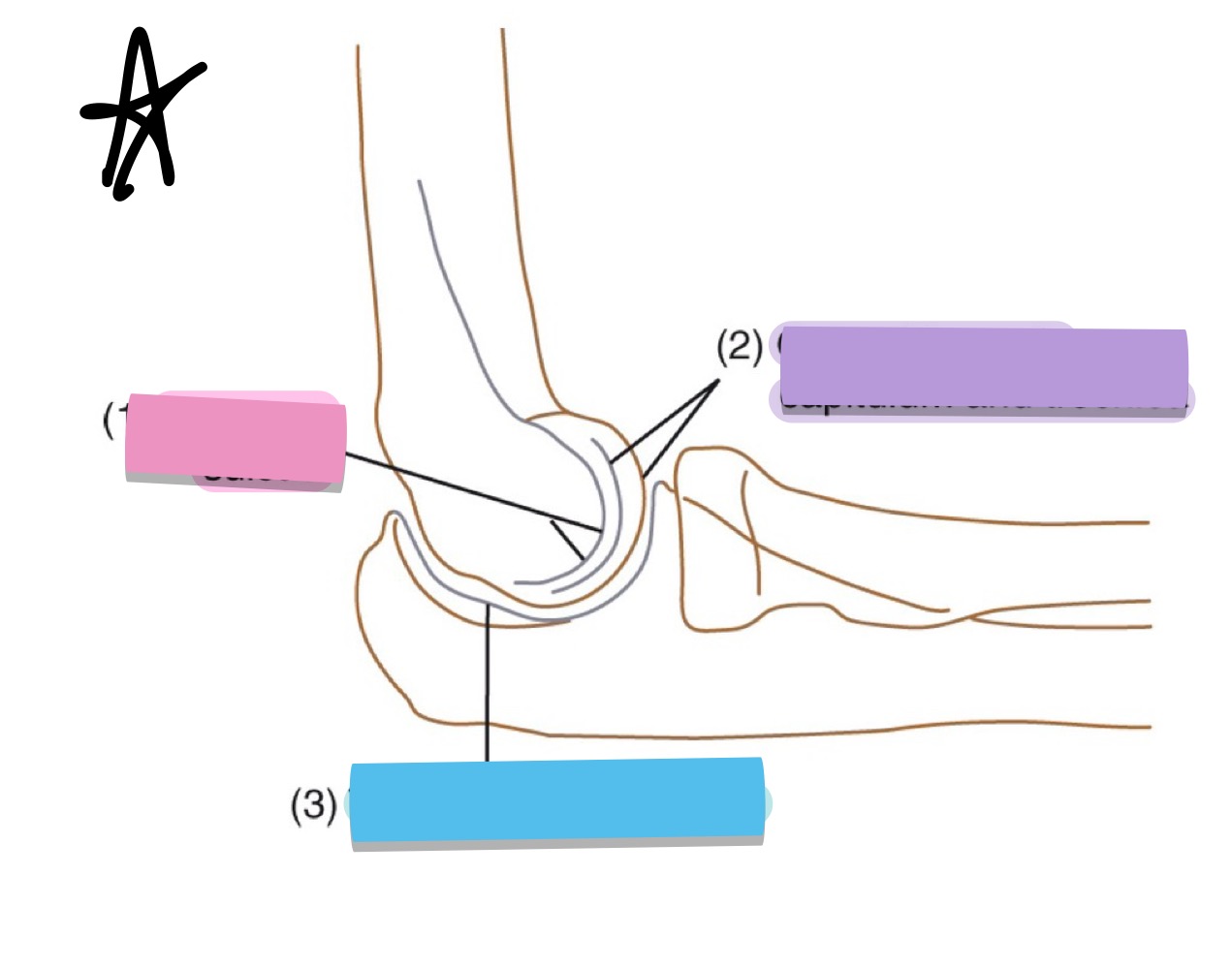
what is the pink pointing to?
trochlear sulcus
what are the carpal bones?
scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate
what is DIP?
distal interphalangeal joint
what is PIP?
proximal interphalangeal joint
what is MCP?
metacarpophalangeal joint
what is CMC?
carpometacarpal
what is IP?
interphalangeal joint
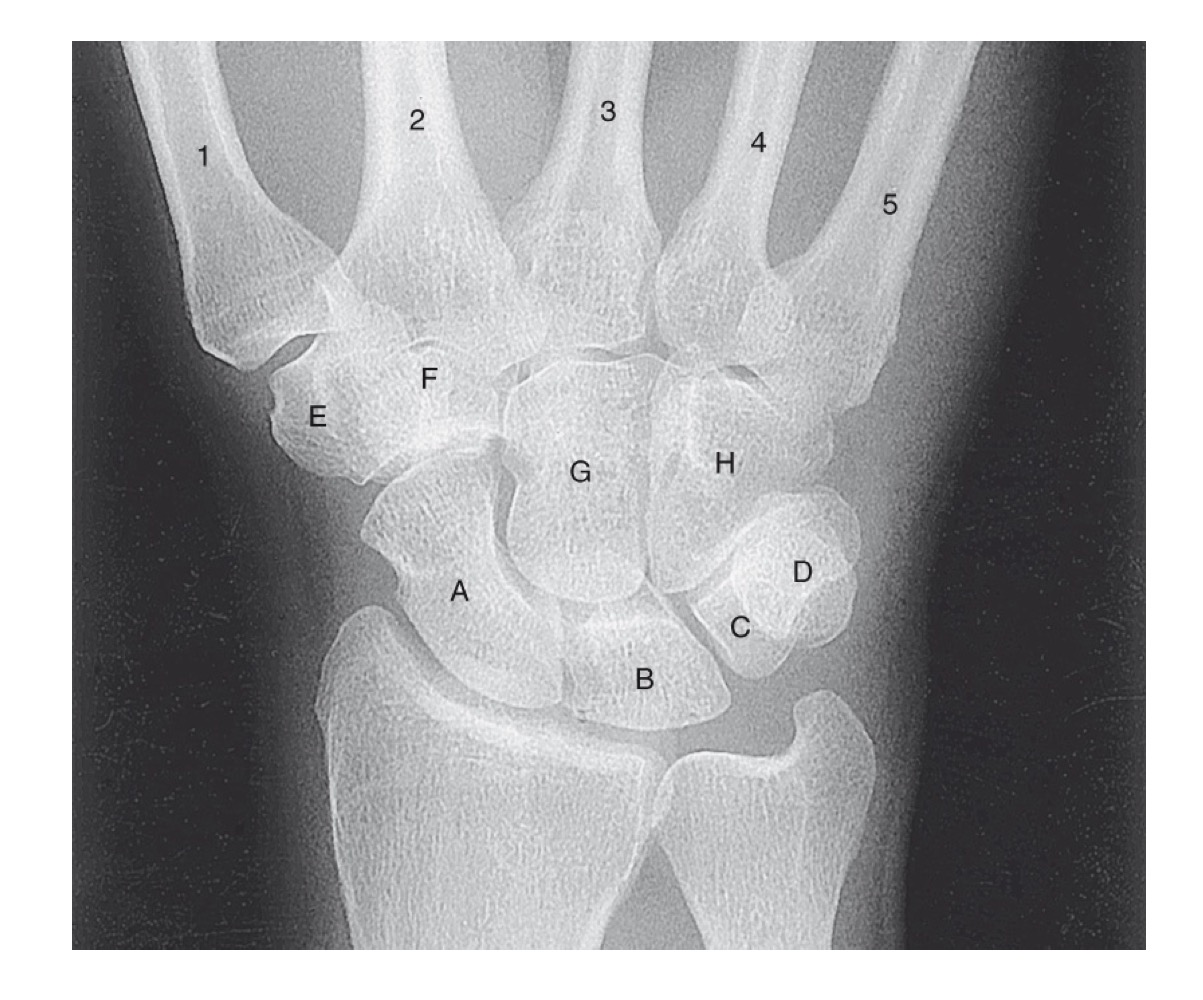
what is A
scaphoid
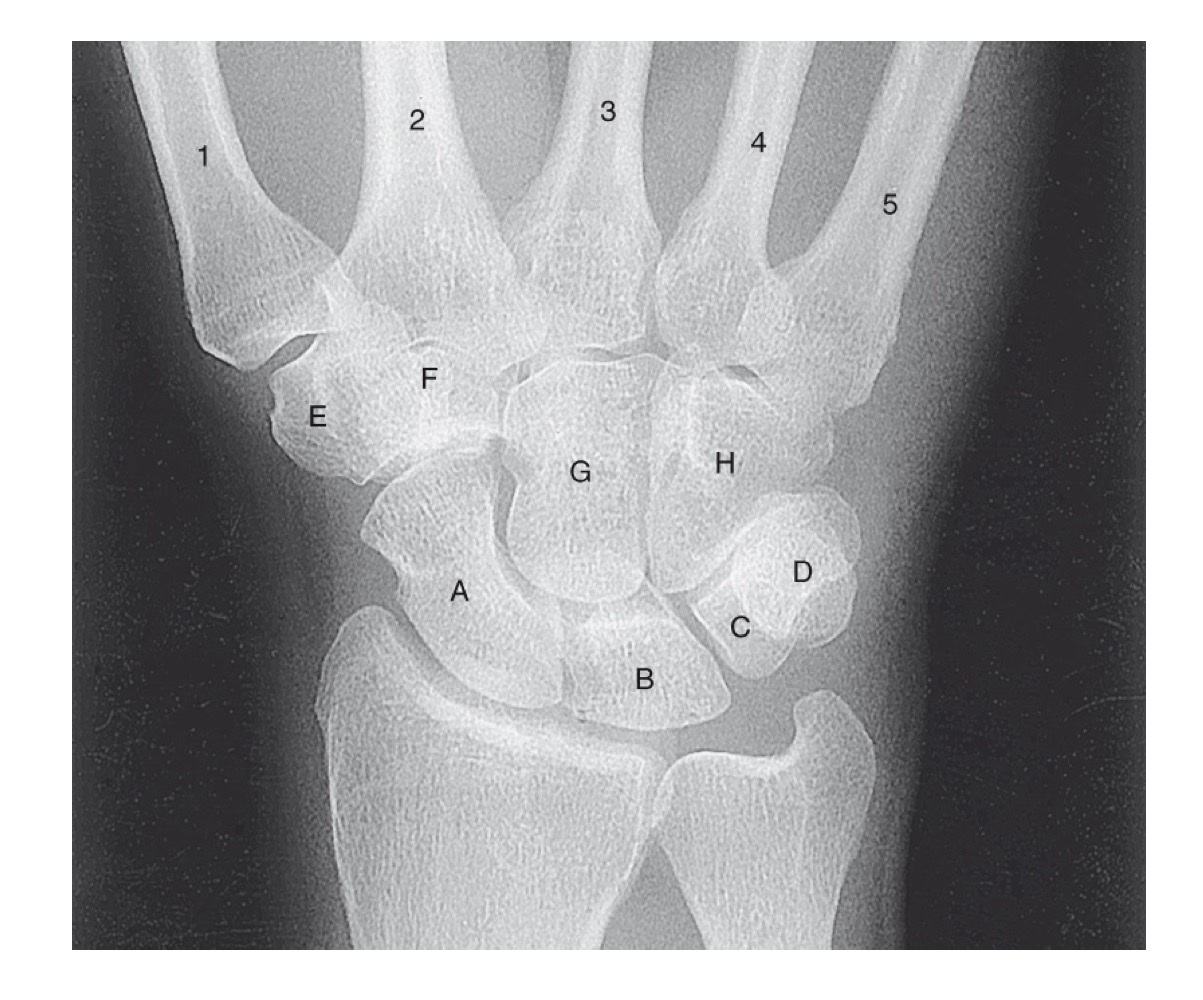
what is B
lunate
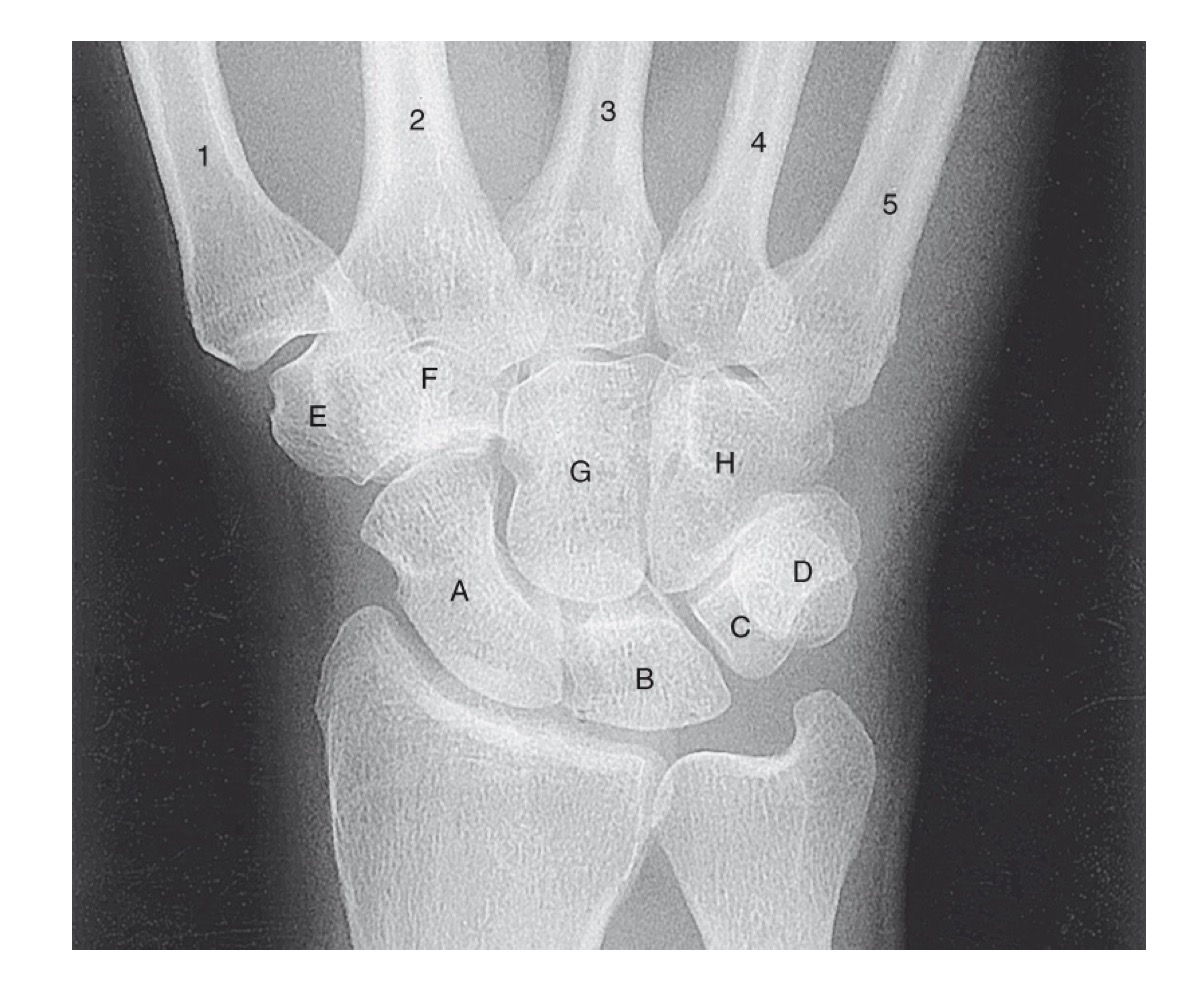
what is C
triquetrom
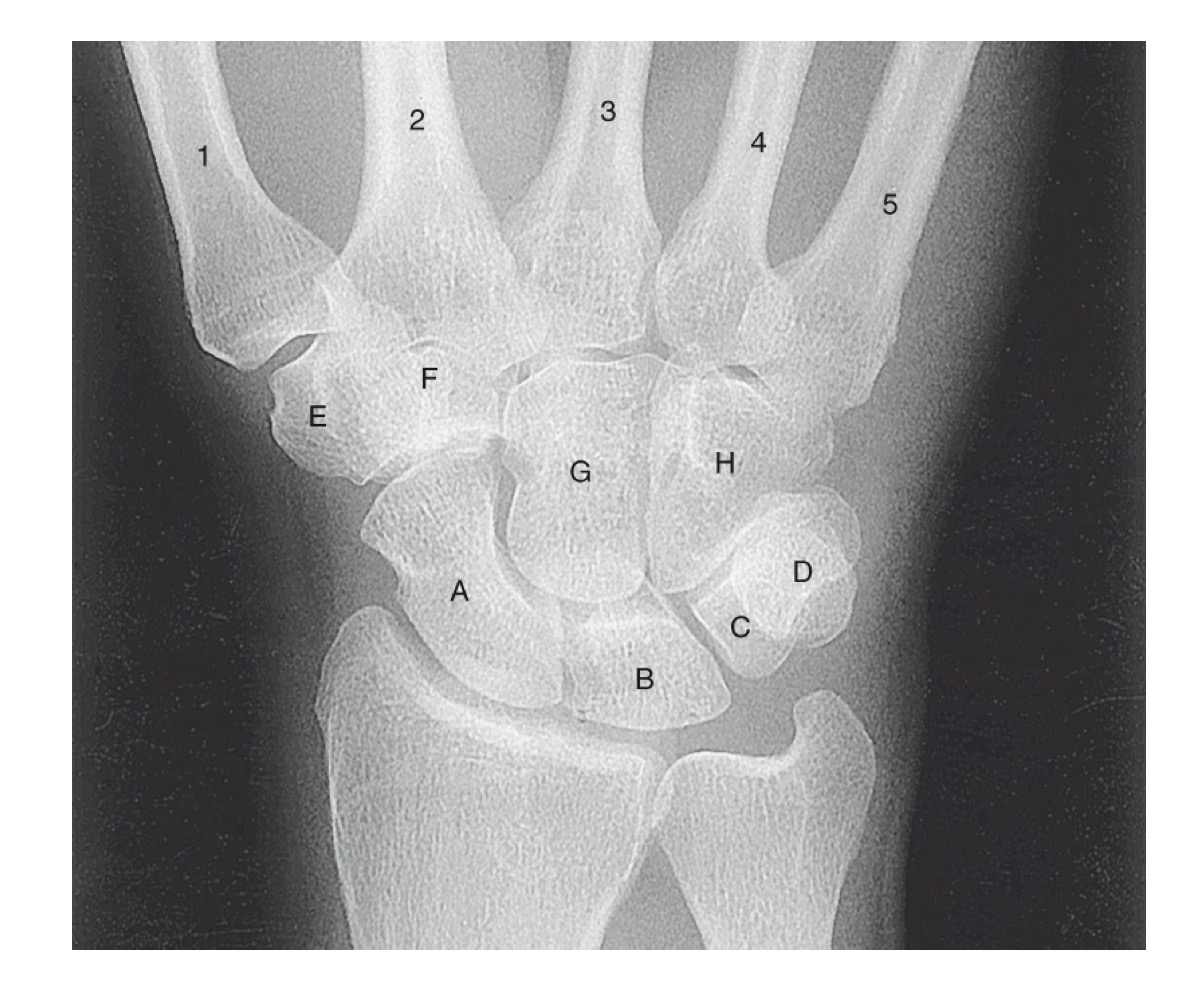
what is D
pisiform
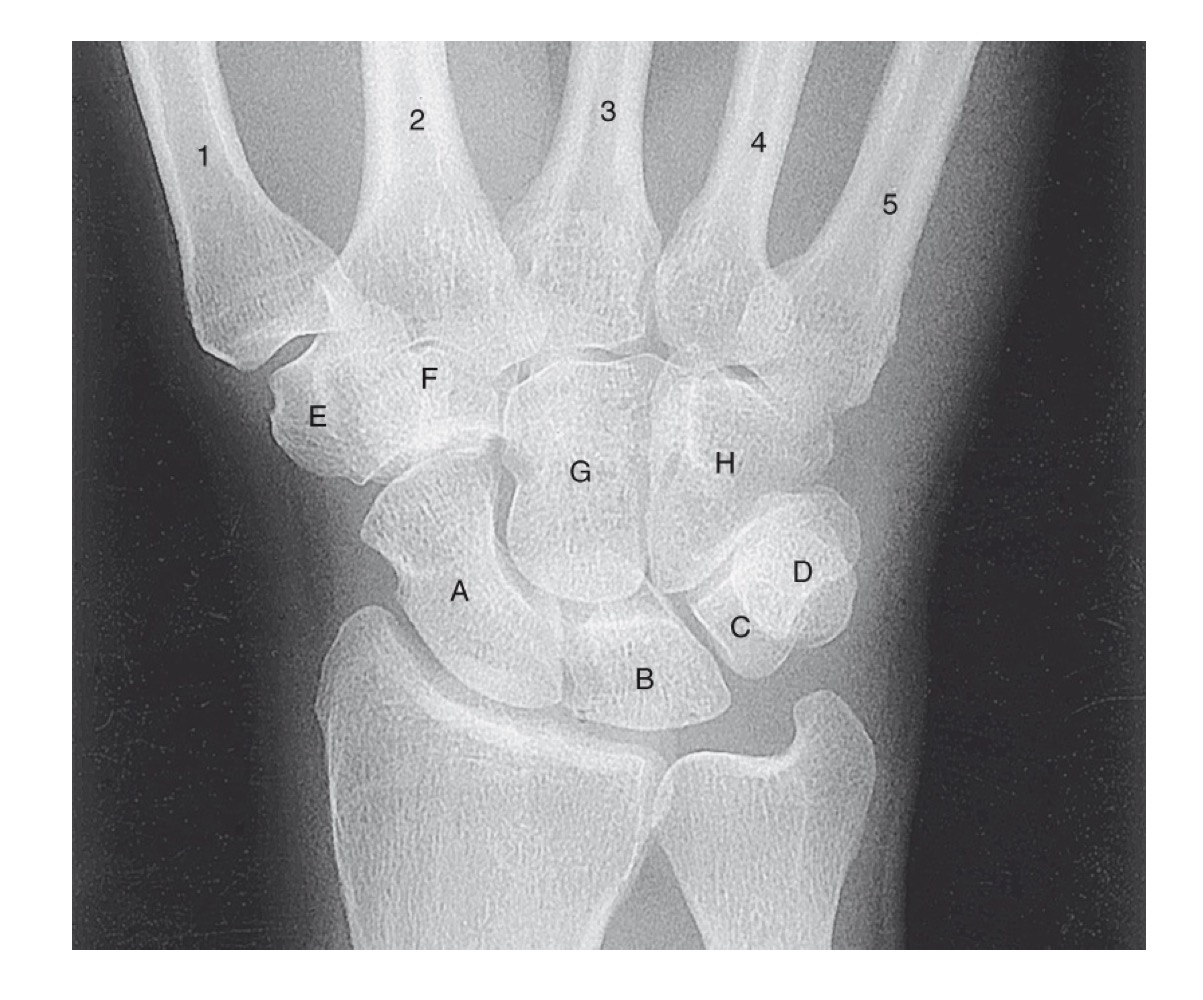
what is E
trapezium
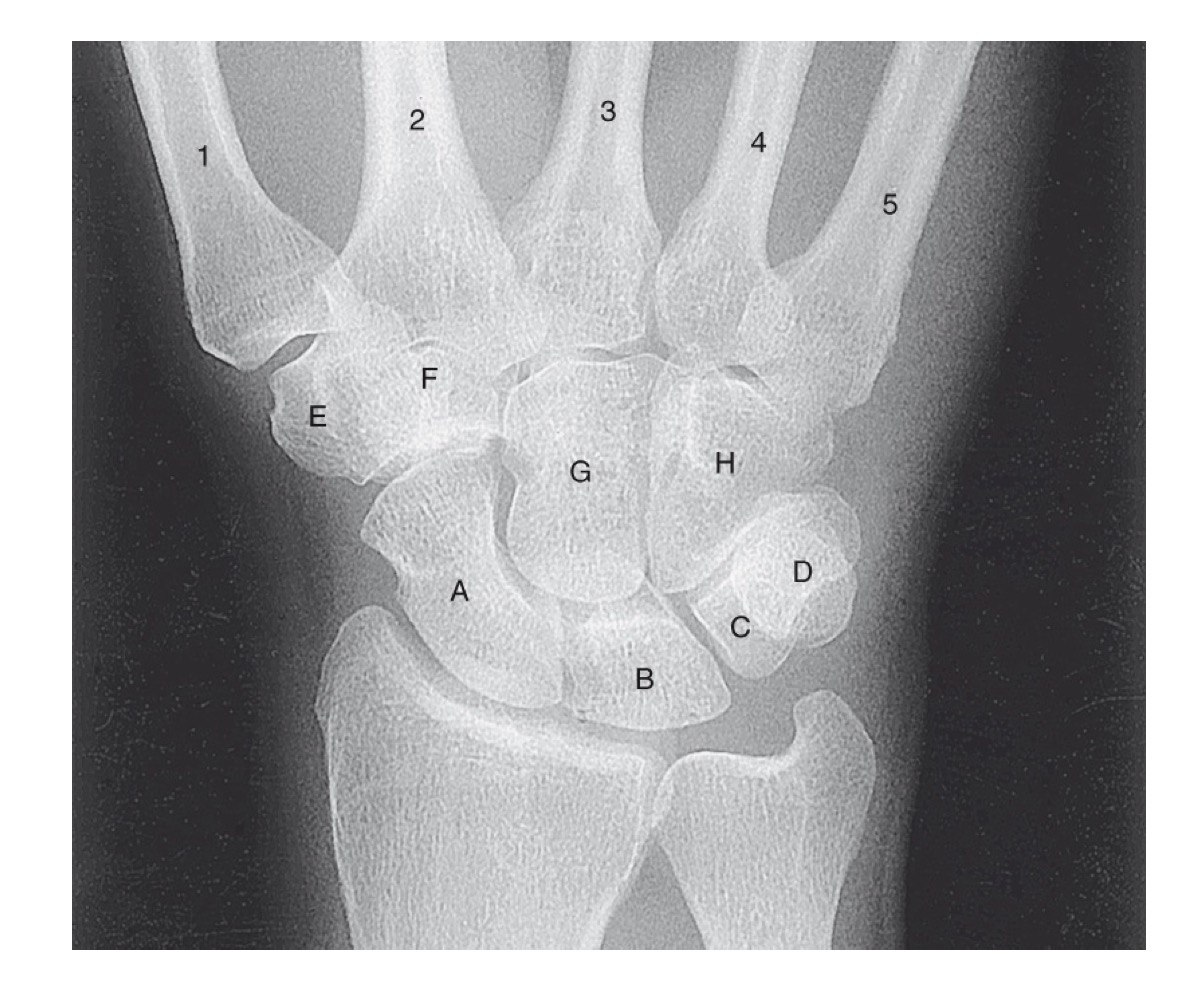
what is F
trapezoid
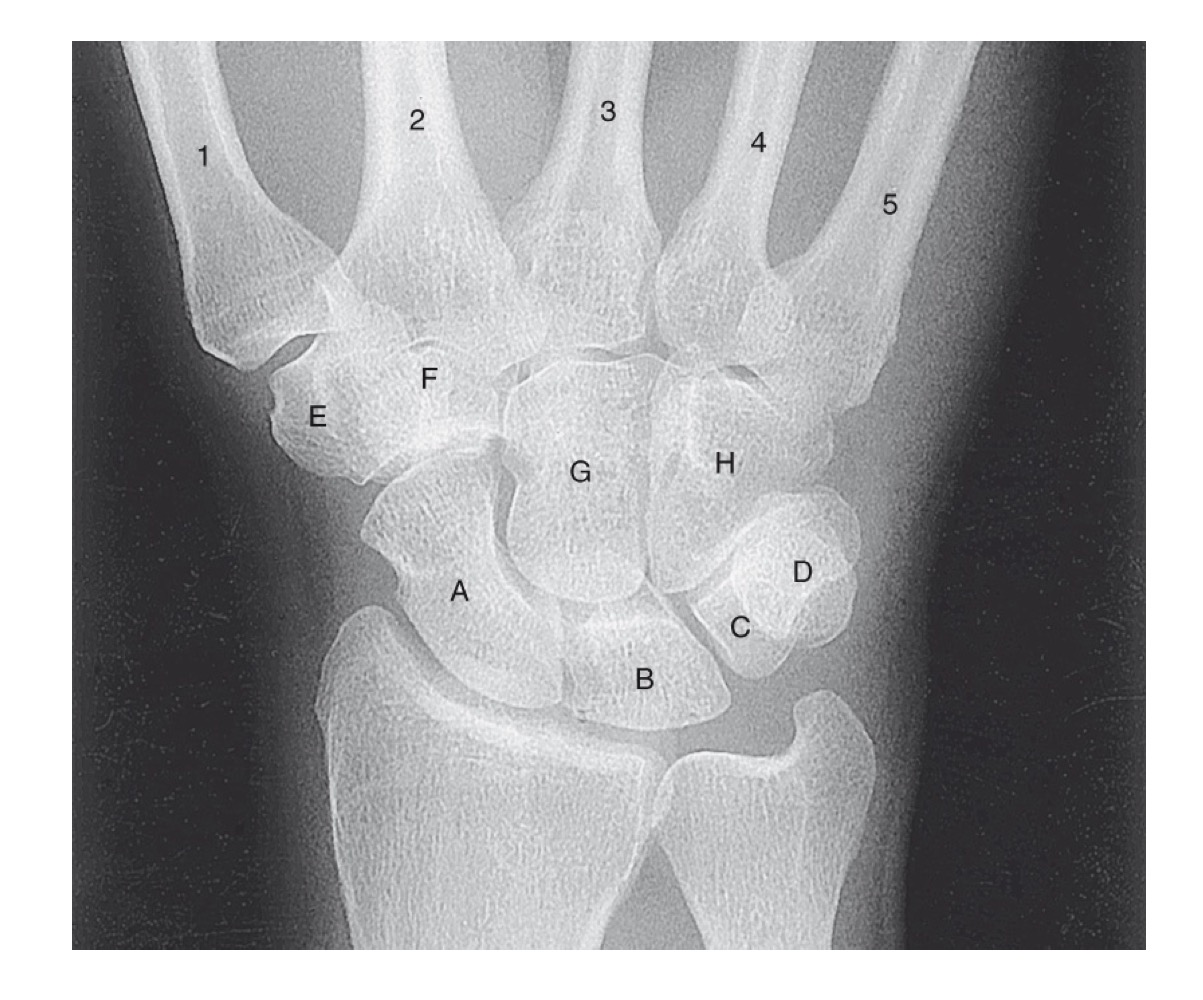
what is G
capitate
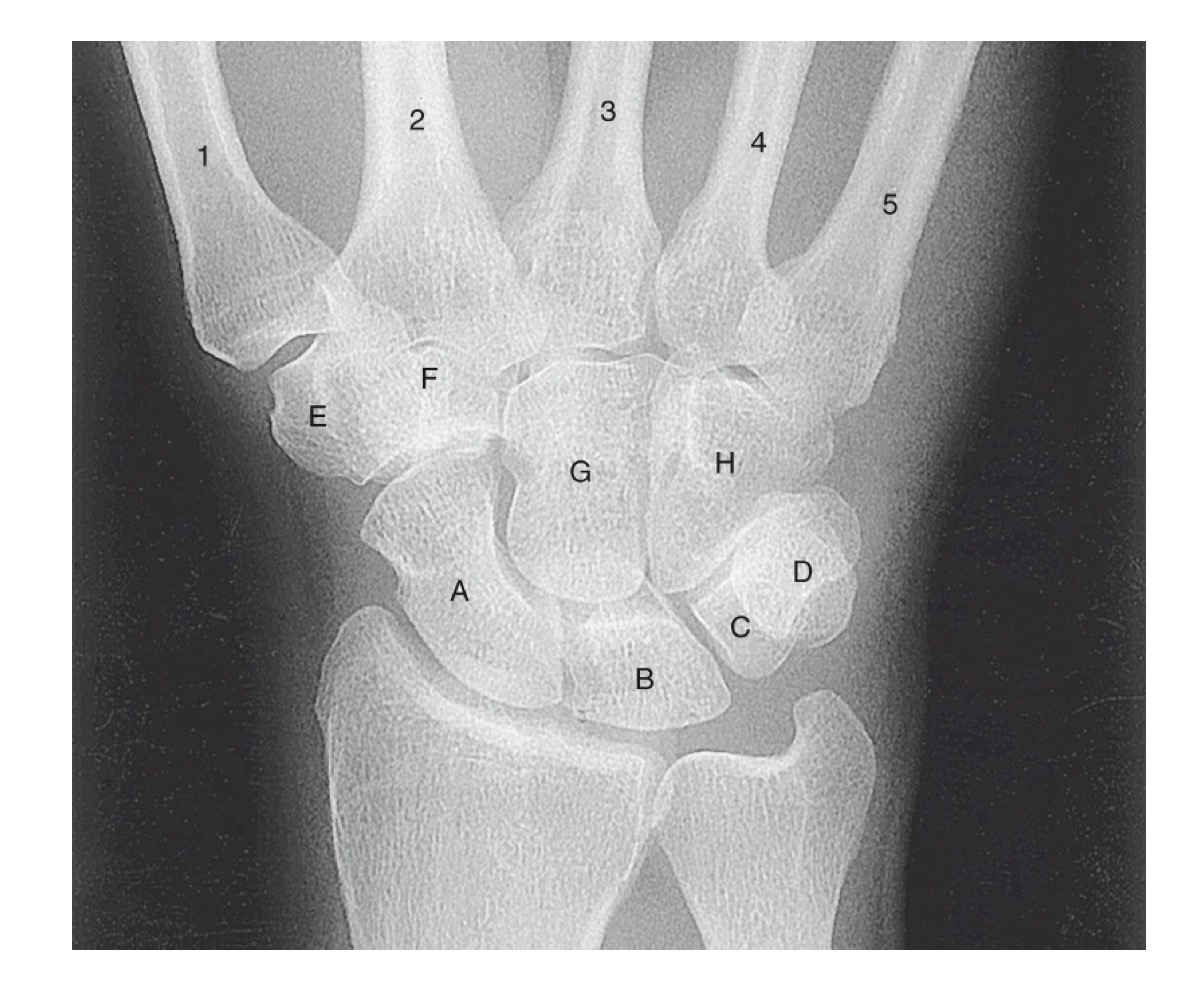
what is H
hamate
bone metasases
transfer of disease or cancerous lesions from one organ or part that may not be directly connected
bursitis
inflammation of the bursae or fluid-filled sacs that enclose the joints, usually involves formation of calcification in associated tendons
carpal tunnel syndrome
common painful disorder if the wrist and hand resulting from compression of the median nerve as it passes through the center of the wrist, most commonly found in middle aged women
fracture
a break in the structure of bone caused by a force
how many types of fractures are there?
5 we have to know
barton fracture
fracture and dislocation of the posterior lip of the distal radius
bennett fracture
fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone
boxer fracture
transverse fracture that extends through the metacarpal neck most commonly in the fifth metcarpal
colles fracture
transverse fracture of the distal radius where distal fragment is displaced posteriorly, most commonly also seen with an ulnar styloid fracture
smith fracture
reverse of colles fracture, transverse fracture of distal radius with distal fragment displaced anteriorly
joint effusion
accumulated fluid in the joint cavity, sign of underlying condition
osteoarthritis
aka degenerative joint disease (DJD), non inflammatory joint disease characterized by gradual deterioration of the articular cartilage with hypertrophic bone formation
osteomyelitis
local or generalized infection of bone or bone marrow that may be caused by bacteria introduced by trauma or surgery
osteopetrosis
hereditary disease marked by abnormally dense bone
osteoporosis
reduction in the quantity of bone or atrophy of skeletal tissue
paget disease
a common chronic skeletal disease, characterized by bone destruction followed by a reparative process of overproduction of dense yet soft bones that tend to fracture easily
rheumatoid arthritis
chronic systemic disease with inflammatory changes throughout the connective tissues
scapholunate ligament injuries
involve the ligament that connects the scaphoid to the lunate bone
skier’a thumb
sprain or tear of the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb near the MCP joint of the hyperextended thumb
tumors
neoplasms, bone neoplasia; most often benign sometimes cancerous
multiple myeloma
malignant, most common primary cancerous bone tumor, usually fatal within a few years
osteogenic sarcoma
malignant, second most common primary cancerous bone tumor, may develop in older persons with paget disease
ewing sarcoma
common primary malignant bone tumor in children and young adults that arises from bone marrow
chondrosarcoma
slow growing malignant tumor of the cartilage, radiographic appearance is similar to other malignant tumors but desne calcifications are often seen within the cartilaginous mass
endochondroma
slow growing benign cartilaginous tumor most often found in small bones of the hands and feet of adolescent and young adults, usually well defined radiolucent appearing tumors with a thin cortex often lead to pathologic fracture with only minimal trauma
osteochondroma
aka exostosis, most common type of benign bone tumor, arise from the outer cortex with the tumor growing parallel to the bone, pointing away from the adjacent joint, most common at the knee
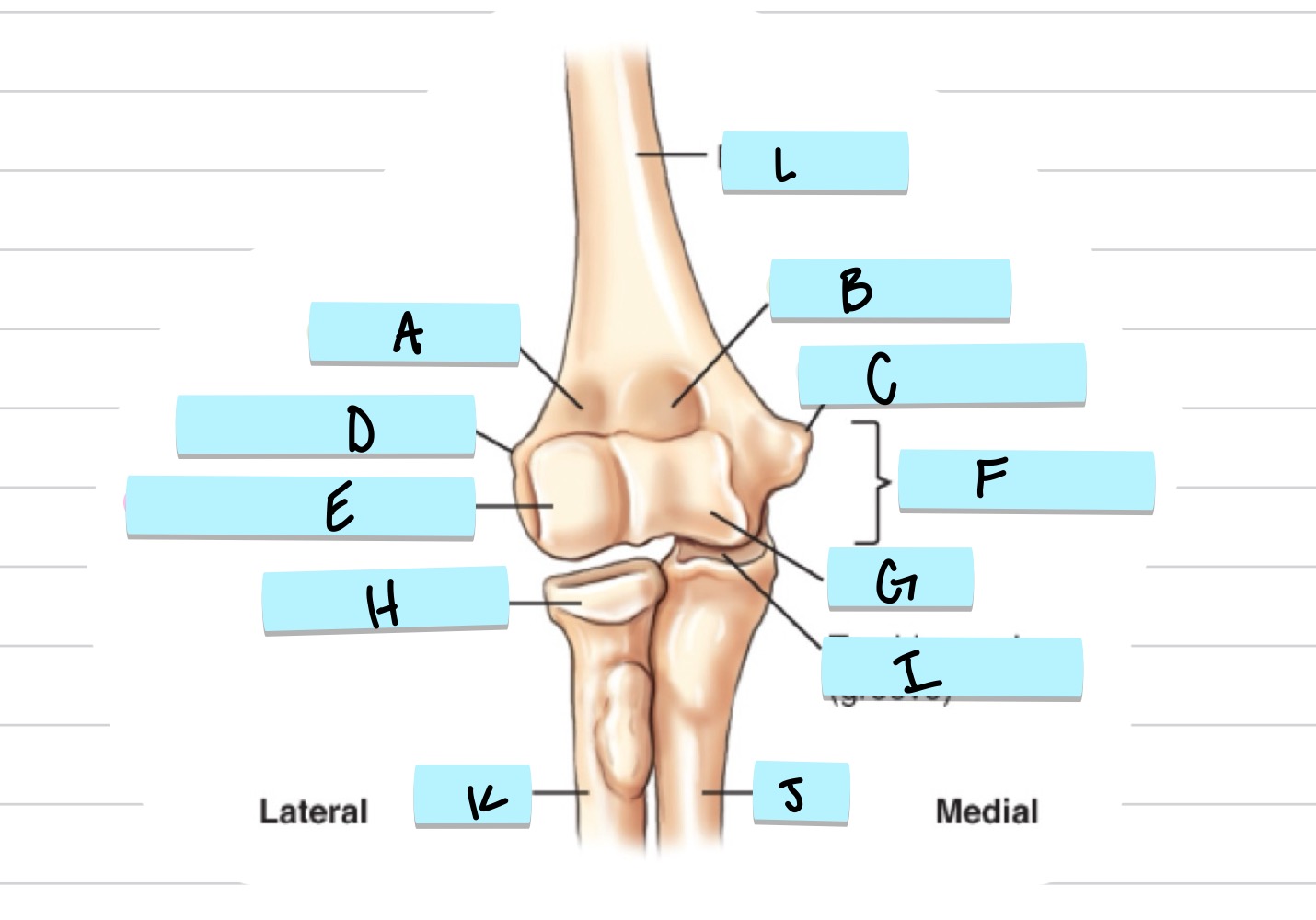
what is A?
radial fossa
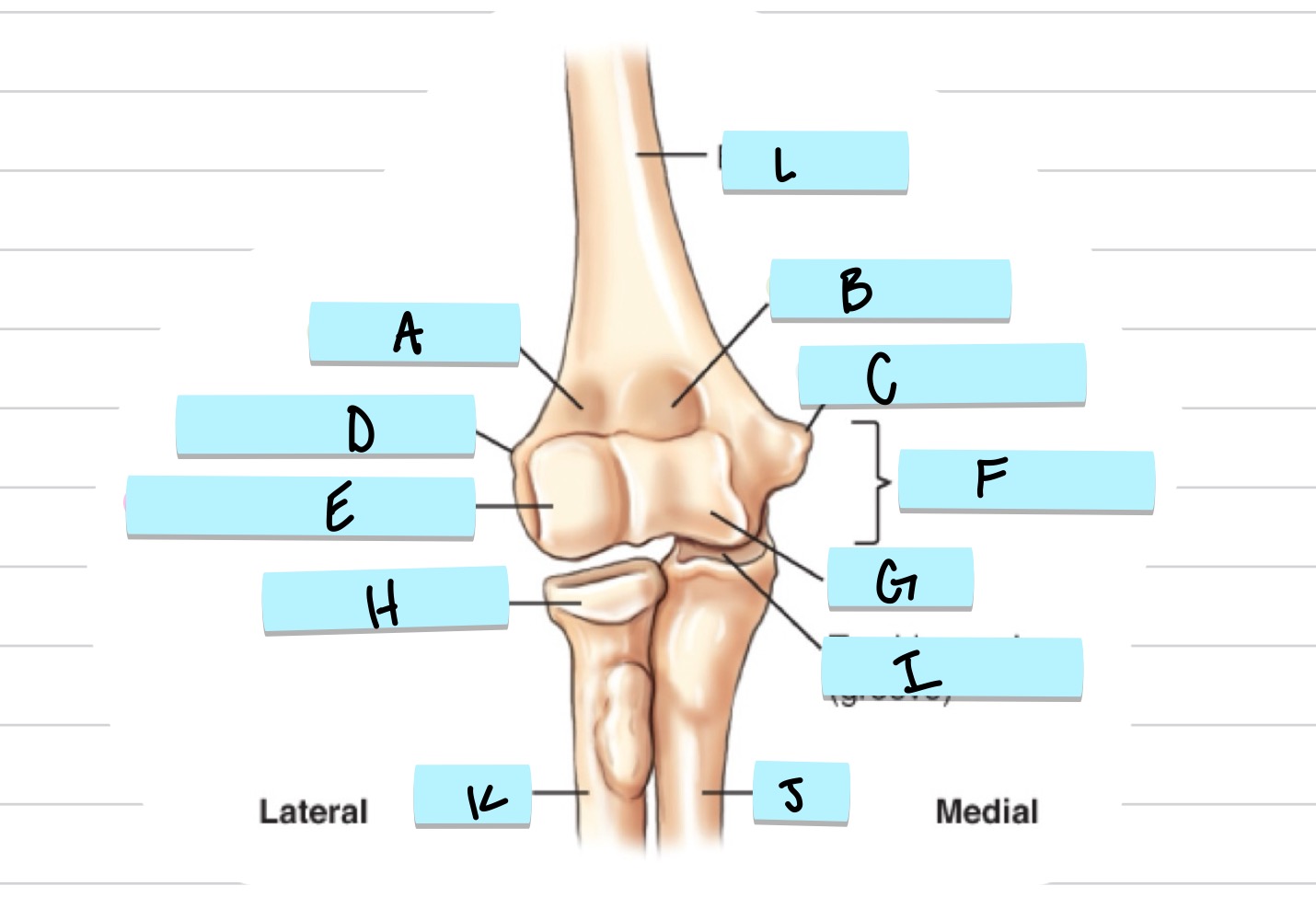
what is B?
coronoid fossa