Week 6: Cell Culture and Cell Growth
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:09 PM on 4/9/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Division
The process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.
2
New cards
Bacterial Cell Division
Involves DNA replication, cell elongation, cross wall formation, and separation into daughter cells.
3
New cards
Yeast Cell Division
Involves budding, nuclear division, and formation of a new yeast cell from a parent cell.
4
New cards
Mold Cell Division
Involves conidiophores, hyphae, and formation of conidia for reproduction.
5
New cards
Plant Cell Division
Involves interphase, preprophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cell plate formation.
6
New cards
Animal Cell Division
Involves prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis.
7
New cards
Mitotic Differences in Eukaryotic Organisms
Differences in centrosomes, nuclear envelope, cytokinesis, cell shape, mitosis duration, checkpoints, and regulation.
8
New cards
Cell Culture
The process of growing cells under controlled conditions outside their natural environment.
9
New cards
Suspension Cultures
Cells grow freely in the culture medium without requiring attachment.
10
New cards
Adherent Cultures
Cells require attachment to a surface to grow and proliferate.
11
New cards
Cell Passaging
The process of transferring cells to fresh growth medium to maintain healthy populations.
12
New cards
Cell Culture Media
Nutrient-rich gel or solution used to support cell growth, survival, and proliferation.
13
New cards
Solid Medium
Contains gelling agents like agar for colony formation or adherent cells.
14
New cards
Liquid Medium
Supports suspension cultures like bacteria, yeast, and some mammalian cells.
15
New cards
Undefined Medium
Contains complex ingredients like yeast extract or serum, making composition variable.
16
New cards
Defined Medium
A culture medium with an exact, known composition, used for controlled experiments and GMP applications.
17
New cards
18
New cards
Specialized Medium
Contains specific constituents for cell differentiation or produced under strict quality control.
19
New cards
Cell Culture Contaminants
Unwanted agents that compromise cell or microbial cultures.
20
New cards
Biological Contaminants
Bacteria, fungi, mycoplasma, viruses, or mixed cell lines.
21
New cards
Chemical Contaminants
Endotoxins, heavy metals, or other harmful chemicals.
22
New cards
Physical Contaminants
Dust, fibers, glass shards, or metal particles.
23
New cards
Antibiotics
Used to prevent microbial contamination and maintain plasmid-bearing cultures.
24
New cards
Aseptic Techniques
Procedures designed to maintain sterility and prevent contamination during culture work.
25
New cards
Microbial Cell Culture
Growing bacteria, yeast, or fungi in a controlled environment using nutrient-rich media.
26
New cards
Streak Plate Method
Used to isolate individual colonies of a microorganism from a culture.
27
New cards
Spread Plate Method
Used to distribute microorganisms evenly across an agar plate for quantification.
28
New cards
Bacterial Cells for Industrial Biotechnology
Examples include Escherichia coli for recombinant proteins and biofuels.
29
New cards
Fungal Cells for Industrial Biotechnology
Examples include Saccharomyces cerevisiae for ethanol and recombinant proteins.
30
New cards
Plant Suspension Culture
Growth of free-floating plant cells in a liquid nutrient medium.
31
New cards
Plant Cells for Industrial Biotechnology
Examples include Taxus chinensis for paclitaxel production.
32
New cards
Animal Cell Culture
Growth of mammalian cells under controlled conditions for research and therapy.
33
New cards
Animal Cells for Industrial Biotechnology
Examples include CHO cells for monoclonal antibodies.
34
New cards
Cell Preservation
Methods to maintain cell viability and consistency for industrial bioprocesses.
35
New cards
Cell Growth
Increase in cell population number through cell division.
36
New cards
Factors Affecting Cell Growth
Temperature, pH, osmolarity, and oxygen levels.
37
New cards
Effect of Temperature on Cell Growth
Influences enzyme activity, metabolism, and biomolecule stability.
38
New cards
Effects of pH
Influences protein structure, enzyme activity, DNA/RNA integrity, and membrane stability.
39
New cards
Effects of Osmolarity
Influences cell shape, volume, and physiological processes.
40
New cards
Effects of Oxygen
Varies by cell type, crucial for optimizing growth conditions
41
New cards
42
New cards
Oxygen Toxicity
Results from reactive oxygen species like superoxide and hydrogen peroxide.
43
New cards
Batch Growth
Cell culture in a closed system with no additional nutrients added during the process.
44
New cards
Growth Rate
Absolute increase in biomass or cell number over time.
45
New cards
Specific Growth Rate
Rate of biomass increase per unit of biomass concentration.
46
New cards
Continuous Exponential Growth
Assumes cell division and biomass accumulation occur continuously.
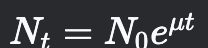
47
New cards
Discrete Exponential Growth
Models cell division at specific intervals, not continuously.
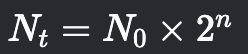
48
New cards
Monod Model
Describes microbial growth kinetics in relation to substrate concentration.
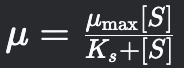
49
New cards
Ks Values
Half-saturation constant for various organisms and substrates.
50
New cards
Multi-Substrate Monod Kinetics
Describes growth when multiple substrates are present.
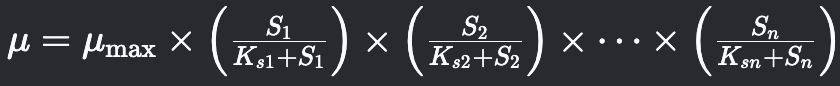
51
New cards
Alternative Models for Complex Systems
Includes Contois, Cybernetic, Pitt's Equation, and Andrews models.
52
New cards
Zero-Growth Bioprocesses
Systems where cell populations are maintained without net biomass increase.
53
New cards
Yield
Efficiency of converting substrates into biomass or desired products.
54
New cards
Biomass Yield
Grams of biomass produced per gram of substrate consumed.
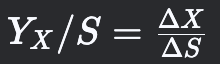
55
New cards
Product Yield
Grams of product formed per gram of substrate consumed.
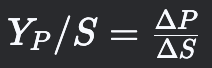
56
New cards
Inoculum
Population of cells introduced into a culture medium to initiate growth or fermentation.
57
New cards
Monitoring Cell Growth
Essential for biological, medical, and industrial applications.
58
New cards
Direct Methods for Monitoring Cell Growth
Includes hemocytometer, automated cell counters, plate counting, and flow cytometry.
59
New cards
Indirect Methods for Monitoring Cell Growth
Includes spectrophotometry, metabolic activity, and dry weight.
60
New cards
Microscope Counting
Manual cell counting using a hemocytometer.
61
New cards
Plate Counting
Estimating viable bacteria or fungi by counting colonies on agar plates.
62
New cards
UV-Vis Spectrometry
Estimating cell density by measuring optical density at specific wavelengths.
63
New cards
Cell Immobilization
Trapping or attaching cells to a solid support or within a matrix.
64
New cards
Types of Cell Immobilization
Adsorption, ionic binding, covalent binding, cross-linking, and encapsulation.
65
New cards
Advantages of Cell Immobilization
Process simplification, reusability, protection, and continuous processing.
66
New cards
Disadvantages of Cell Immobilization
Mass transfer limitations, activity loss, cost, and stability issues
67
New cards
Ludeking-Piret Equation

68
New cards
Obligate Aerobes
Require oxygen for survival
69
New cards
Obligate Anaerobes
Cannot survive in the presence of oxygen
70
New cards
Facultative Anaerobes
Can grow with or without oxygen but prefer oxygenated environments
71
New cards
Microaerophiles
Require oxygen but at lower concentrations than atmospheric levels
72
New cards
Aerotolerant Anaerobes
Do not use oxygen but can tolerate its presence