Allied Strategies and Tensions in World War II
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Totalitarianism
A political system where the state recognizes no limits to its authority and seeks to regulate every aspect of public and private life.
Fascism
A far-right, authoritarian ultranationalist political ideology characterized by dictatorial power, forcible suppression of opposition, and strong regimentation of society and the economy.
Appeasement
A diplomatic policy aimed at avoiding war by making concessions to an aggressor, often seen as a failure when it emboldens the aggressor.
Axis Powers
The coalition of nations led by Germany, Italy, and Japan during World War II, opposing the Allies.
Allied Powers
The coalition of nations, including the United States, the Soviet Union, and the United Kingdom, that opposed the Axis Powers in World War II.
Munich Agreement
A settlement reached in 1938 allowing Nazi Germany to annex parts of Czechoslovakia, seen as a failed act of appeasement.
Cold War
A period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States and their respective allies, following World War II.
Spanish Civil War
A conflict from 1936 to 1939 in which the Republicans fought against the Nationalists led by Francisco Franco, with significant international involvement.
Manchuria
A region in Northeast Asia that was invaded by Japan in 1931, marking the beginning of Japanese expansionism in the 1930s.
Treaty of Versailles
The peace treaty that ended World War I, imposing heavy reparations and territorial losses on Germany, which contributed to the conditions leading to World War II.
Invasion of Poland
The military action by Germany on September 1, 1939, that marked the beginning of World War II in Europe.
Allies
The coalition of countries, including Great Britain, France, the Soviet Union, and the United States, that opposed the Axis powers during World War II.
Pearl Harbor
The U.S. naval base in Hawaii that was attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941, leading to the United States' entry into World War II.
Franklin D. Roosevelt
The 32nd President of the United States who led the country during the Great Depression and most of World War II.
Winston Churchill
The Prime Minister of Great Britain during World War II, known for his leadership and speeches that rallied the British people.
Joseph Stalin
The leader of the Soviet Union during World War II, who played a crucial role in the defeat of Nazi Germany.
Atlantic Charter
A pivotal policy statement issued in August 1941 by Roosevelt and Churchill outlining the goals for the post-war world.
Great Depression
A severe worldwide economic downturn that lasted from 1929 to the late 1930s, affecting many countries, including the United States.
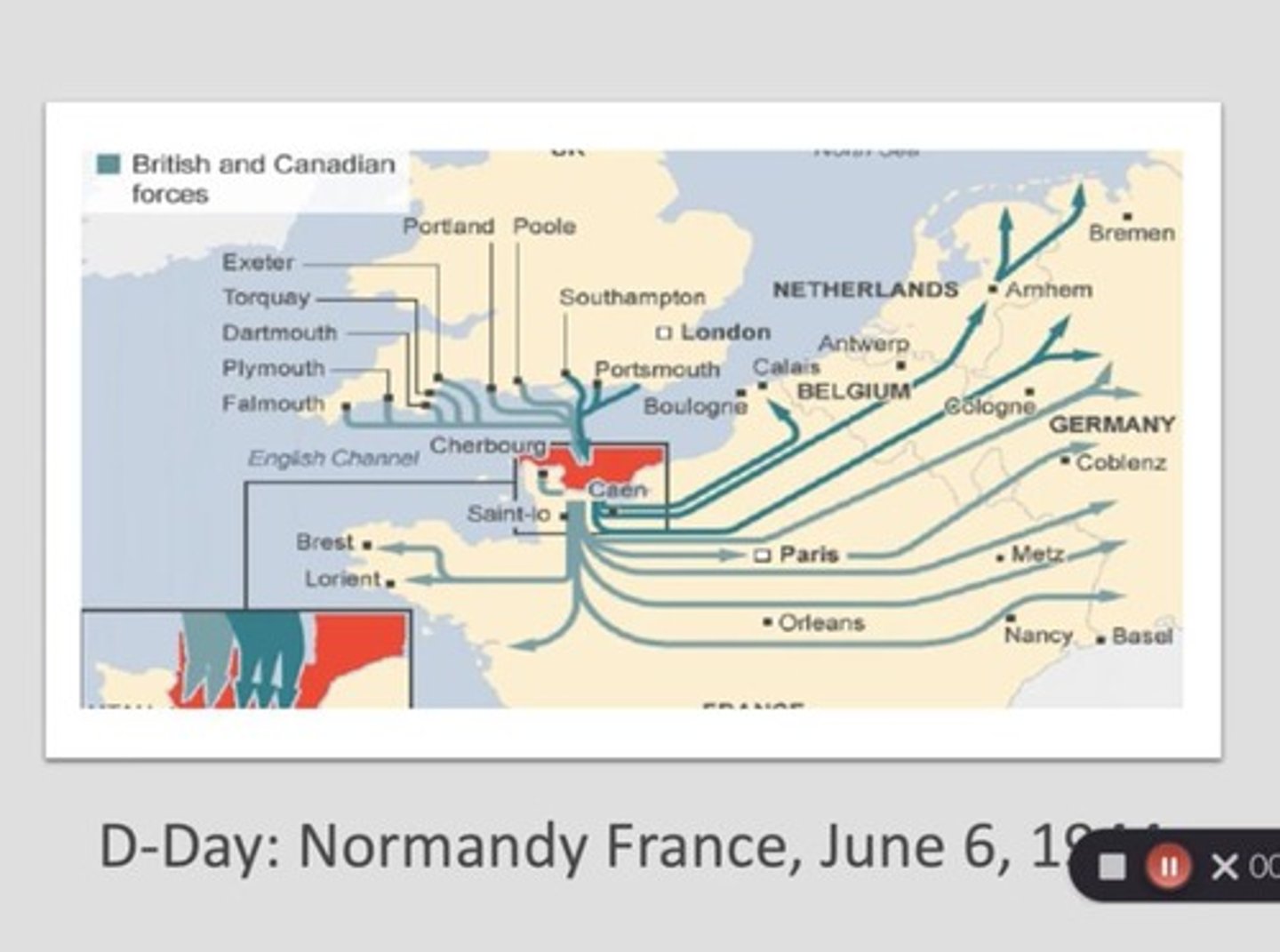
D-Day
The Allied invasion of Normandy on June 6, 1944, which marked a significant turning point in the war against Nazi Germany.
Holocaust
The systematic, state-sponsored persecution and murder of six million Jews and millions of others by the Nazi regime during World War II.
War Bonds
Debt securities issued by a government to finance military operations during wartime, encouraging citizens to support the war effort.
Rationing
The controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, or services, often implemented during wartime to ensure equitable distribution.
Self-determination
The principle that nations have the right to choose their own government and political future without external interference.
Free Trade
An economic policy that allows goods and services to be traded across borders with minimal government restrictions or tariffs.
Buffer Zone
A region created to separate two or more entities, often established for security purposes to prevent conflict.
Imperialism
A policy or ideology where a country extends its power and influence through colonization, military force, or other means.
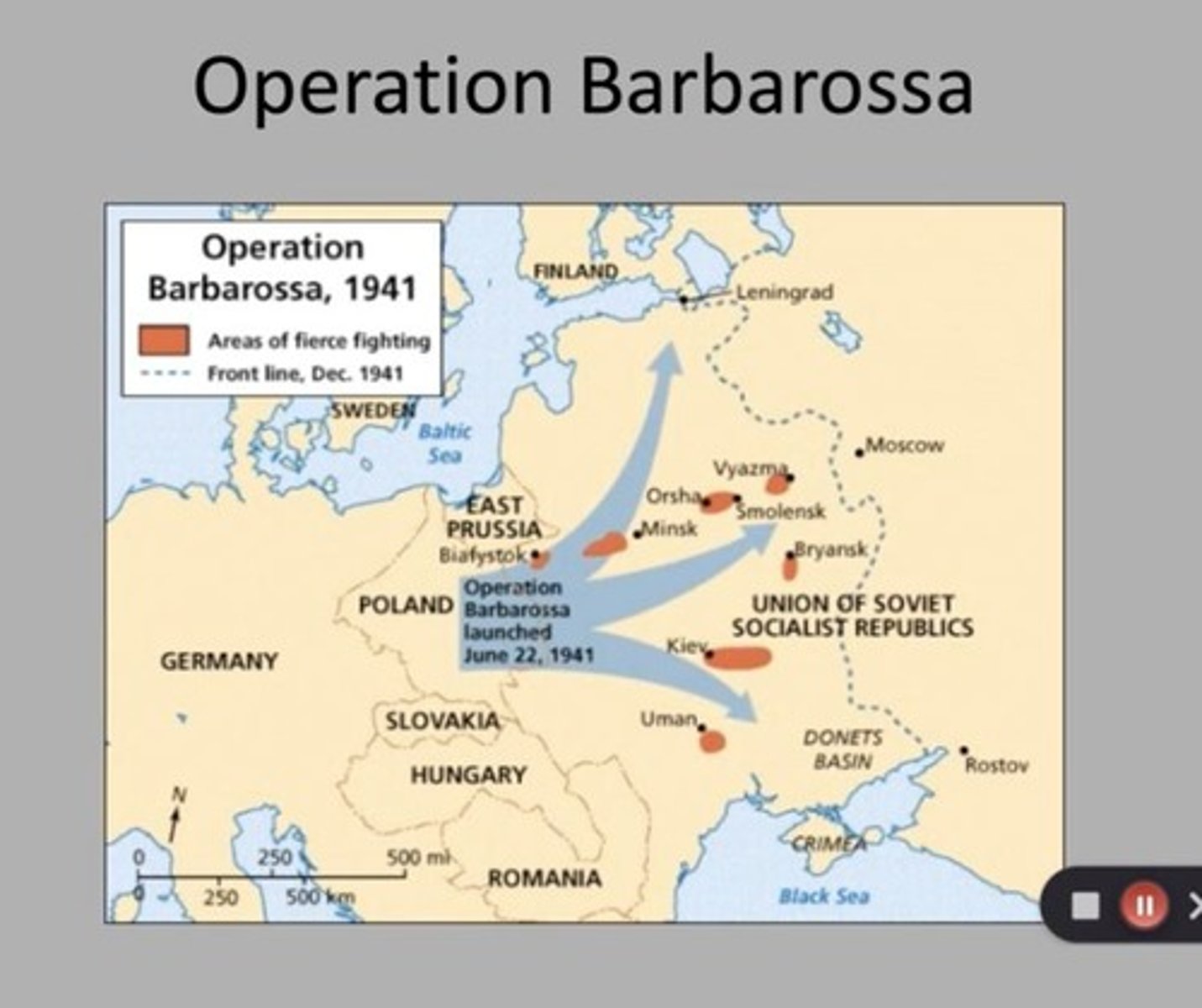
Operation Barbarossa
The code name for Nazi Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II, which resulted in massive casualties.
Post-war World
The period following the conclusion of a war, often characterized by efforts to rebuild, establish peace, and create new political and economic systems.
Bargaining Position
The relative strength or leverage of a party in negotiations, influenced by their military, economic, and political power.
Second Front
A military strategy aimed at opening a new front against the Axis powers in Europe, primarily to relieve pressure on Soviet forces fighting Germany.
Pacific Theater
The area of military operations in the Pacific Ocean during World War II, where the United States focused its efforts against Japan after the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Suez Canal
A crucial waterway in Egypt that connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, vital for trade and military logistics during the war.
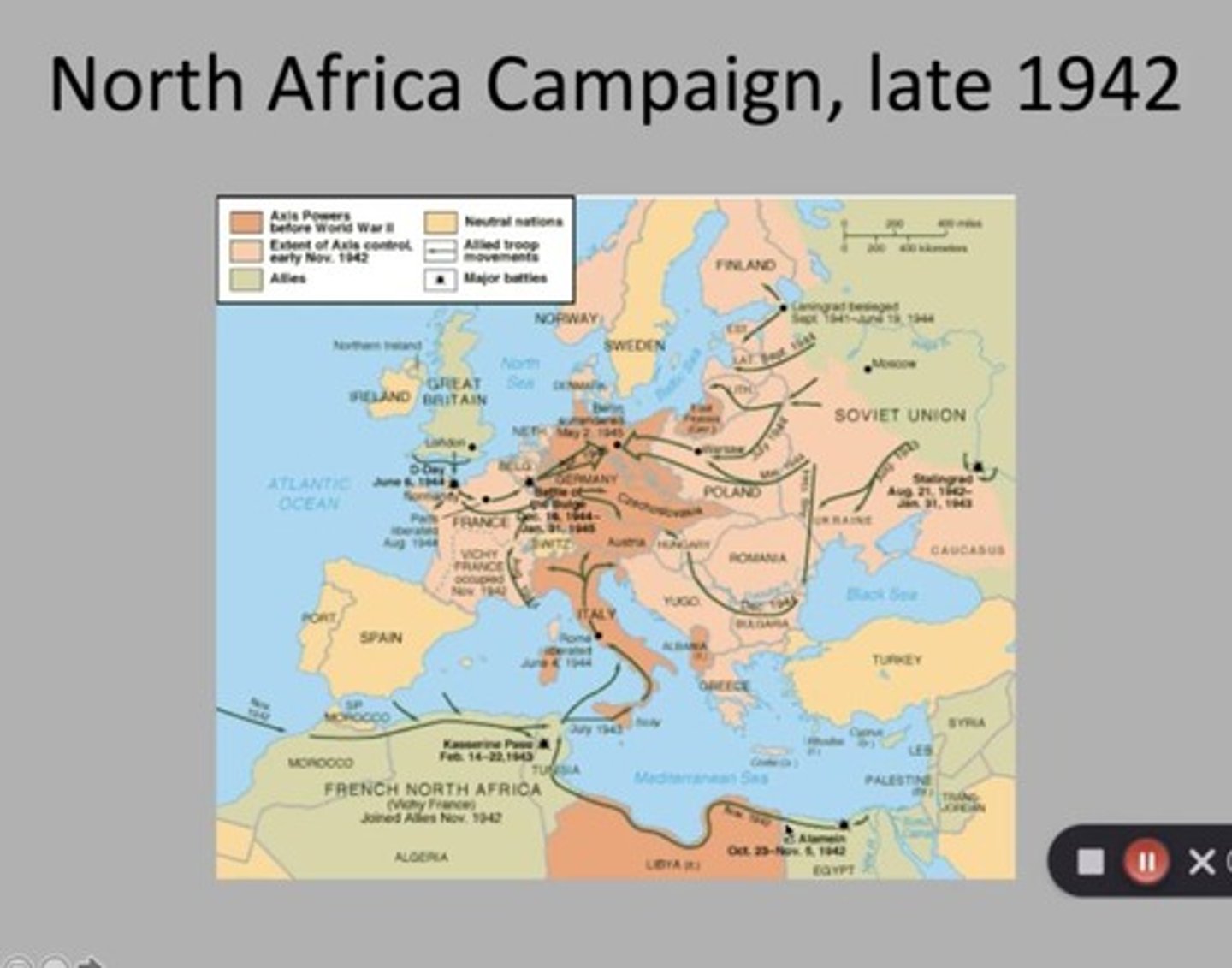
Operation Torch
The code name for the Allied invasion of North Africa in late 1942, aimed at gaining control of the Suez Canal and pushing Axis forces out of the region.
Eastern Front
The theater of conflict between the Axis powers and the Soviet Union during World War II, marked by significant battles and heavy casualties.
Stalin's Requests
Demands made by the Soviet leader for immediate support from the United States and Great Britain to open a second front against Germany.
Military Divisions
Units of soldiers organized for combat, with the German army deploying a significant number against the Soviet Union during the war.
Allied Strategy
The coordinated military approach taken by the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union to defeat the Axis powers, involving various campaigns across multiple theaters.
Casablanca Conference
A meeting held in January 1943 where Allied leaders discussed military strategy, including the decision to focus on Italy before aiding the Soviet Union.
Unconditional Surrender
A principle declared by Roosevelt stating that the Allies would only accept total surrender from Germany, ensuring no negotiated peace.
Stalingrad
A major battle during World War II where the Soviet Union successfully defended the city against a prolonged German siege, marking a turning point in the war.
Soviet Counteroffensive
A military strategy employed by the Soviet forces to push back German troops after their initial advances, particularly successful during the Battle of Stalingrad.
Sixth Army
The German army division that was encircled and defeated in Stalingrad, suffering significant losses that weakened German forces on the Eastern Front.
Mussolini
The Italian dictator whose forces were targeted by the Allies in the Mediterranean campaign, as part of their strategy to weaken Axis powers.
Big Three
The alliance of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union during World War II, which coordinated military strategies and post-war plans.
Tehran Conference
A meeting held in late 1943 where the leaders of the Big Three discussed military strategies and post-war arrangements.
Eastern Europe
The region that Stalin aimed to influence and control after the war, seeking to secure Soviet borders.
Negotiating Power
The influence and leverage that a nation possesses in diplomatic discussions, particularly after significant military victories.
Yalta Conference
A meeting in February 1945 where the Allied leaders discussed the reorganization of post-war Europe and agreed on the division of Germany.
FDR
The 32nd President of the United States who led the country during the Great Depression and most of World War II.
Potsdam Conference
A meeting held in July-August 1945 where Allied leaders discussed the administration of Germany and the post-war order.
Eastern Poland
A region that became a point of contention during World War II, particularly regarding Soviet influence and control.
Civil War in China
A conflict between the Nationalists and Communists in China that affected the country's ability to support the Allies during World War II.
Adolf Hitler
The leader of Nazi Germany who initiated World War II and ultimately committed suicide in 1945 as Allied forces closed in.
Japanese Navy
The naval force of Japan that posed significant challenges to Allied forces in the Pacific during World War II.
Chen Kaishiek
The leader of the Nationalist government in China during World War II, who was preoccupied with a civil war against the Communists.
Surrender of Germany
The formal capitulation of Nazi Germany in May 1945, marking the end of the war in Europe.
Military Leaders Surrender
The act of German military officials capitulating to Allied forces, leading to the conclusion of hostilities in Europe.
Island Hopping
A military strategy used by the United States in the Pacific Theater to capture specific islands and use them as bases for further attacks.
Post-war Order
The political and territorial arrangements established after World War II to maintain peace and prevent future conflicts.
Atomic Bomb
A powerful weapon that uses nuclear reactions to release massive amounts of energy, first used in warfare during World War II.
Harry Truman
The 33rd President of the United States who succeeded Franklin D. Roosevelt and made the decision to use atomic bombs against Japan.
Clinton Atlee
The British Prime Minister who succeeded Winston Churchill after the 1945 elections, representing the Labour Party.
Emperor Hirohito
The Emperor of Japan during World War II, who was allowed to remain on the throne after Japan's surrender.
Military-Industrial Complex
A concept referring to the close relationship between a country's military and the defense industry that supplies it, often influencing national policy.
Ideological Conflict
A disagreement based on differing beliefs and values, particularly between capitalism and communism during the Cold War.
Soviet Expansionism
The policy of the Soviet Union to expand its influence and control over other nations, particularly in Eastern Europe after World War II.
Containment Policy
A United States strategy aimed at preventing the spread of communism during the Cold War.
Nuclear Deterrence
A military strategy that uses the threat of nuclear retaliation to deter an adversary from attacking.
Proxy Wars
Conflicts where two opposing countries or parties support combatants that serve their interests instead of waging war directly.
Détente
A period of improved relations between the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War, characterized by arms control agreements and diplomatic negotiations.