1 Biopharmaceutics & pharmacokinetics - LADMER & biopharmaceutics
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Biopharmaceutics
study of the relationship between drugs physico-chemical properties and the pharmacology or clinical response observed after its administration
LADMER System
Liberation
Absorption
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Response
There are several steps a dosage form/delivery system has to undergo before it produces a therapeutic response. This can be explained by the ____ system
Liberation
First step process
Drug release from the drug product
Aqueous
in the Liberation process, the drug must be in ____ solution before absorption
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Drugs are mostly weak electrolytes/unionized
Drug factors
Excipient Factors
Dosage form factors
What are the three factors affecting the oral absorption?
pH rules
Dissolution
Crystal Forms
Drug Stability
Adsorption
6 Drug Factors that affect the oral absorption
ALL
Strong acids or bases = ionized at ____ pHs
CERTAIN
Weak acids or bases = only ionized at ______ pHs
Polar (Excretable)
An ionized drug means what?
pKa
Solubility depends on ____
Dependent
% ionization is pH ___
High
Weak acids are highly ionized at _____ pH
Low
Weak bases are highly ionized at _____ pH
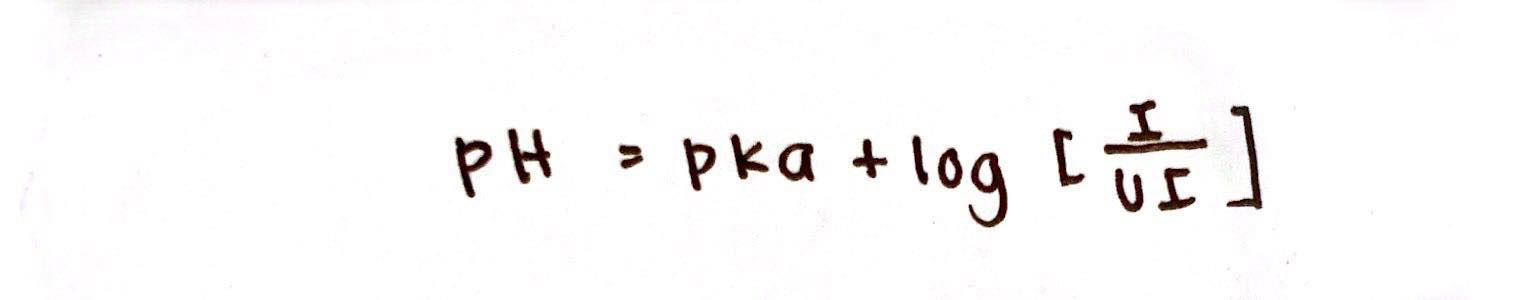
Henderson-Hasselbach Equation for Weak Acids
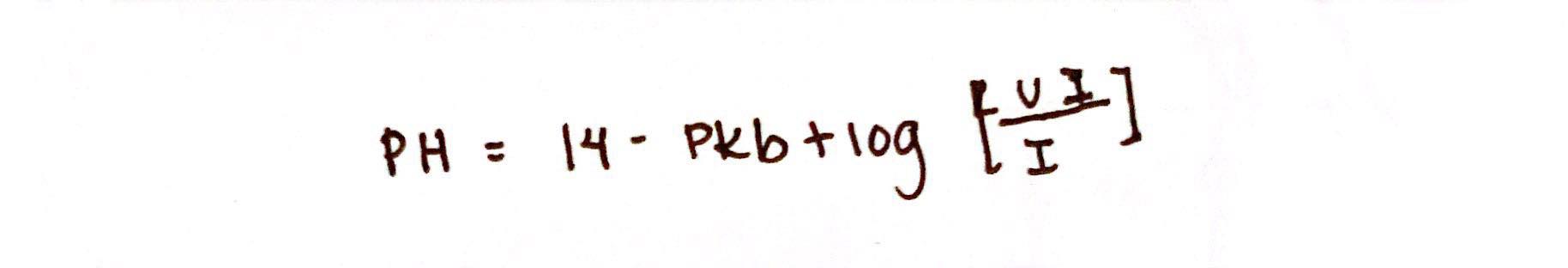
Henderson-Hasselbach Equation for Weak Base
Ionizable
if the pH > pka, the weak acid is __
Unionizable
if the pH < pka, the weak acid is __
50% ionized & 50% unionized
if the pH = pka, the weak acid is __
pH-Partition Theory
“states that ionizable compounds penetrate biological membranes primarily in the unionized forms”
Low
Acidic drugs are best absorbed at _________ pH
High
Basic drugs are best absorbed at _________ pH
↑ contact time of drugs in the small intestine
↑ Surface Area
Despite their high degree of ionization (pH < pKa), weak acids are highly absorbed in small intestine. Why?
Dissolution
process by which a solid drug substance is dissolved in a solvent over time
Noyes-Whitney
dissolution rate is governed by ___________________ equation
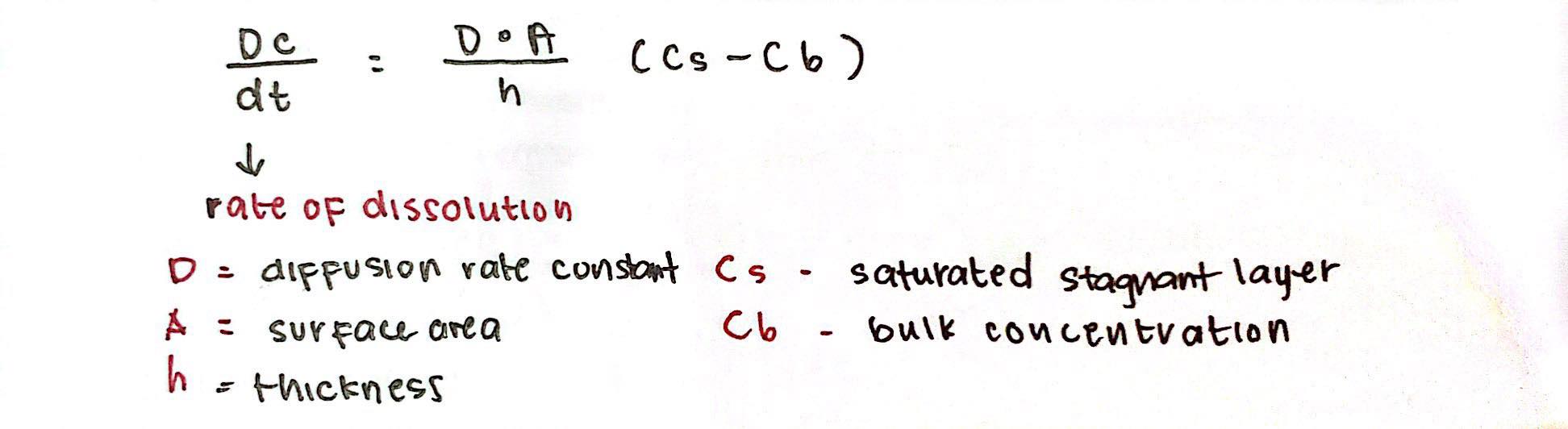
Noyes-Whitney Formula:
↑rate of dissolution
↑Cs-Cb - __ rate of dissolution
Sink Condition
Cb«««Cs
C~0
↑rate of dissolution
↑Surface Area = ____ rate of dissolution
↓Particle Size
↑Surface Area = ____ Particle Size
↑rate of dissolution
↓Particle Size = _____ rate of dissolution
↓rate of dissolution
↑Thickness = ____ rate of dissolution
Amorphous
Non-crystalline solids
Irregular
Crystalline
Crystal forms that have regular shape
Less stable & Faster Dissolution rate
Irregular shapes tend to be __ stable, thus, they have _ dissolution rate
More stable & Slow Dissolution rate
Regular shapes tend to be __ stable, thus, they have _ dissolution rate
Polymorphism
arrangement of a drug substance in various molecular packing (crystal forms)
affects the stability, solubility, dissolution rate etc
Pseudopolymorphs
Hydrates or solvates of a drug substance
FALSE
Ampicillin (Anhydrous) has a faster dissolution rate
TRUE or FALSE
Ampicillin (trihydrate) has a FASTER dissolution rate compared to Ampicillin (Anhydrous)
Delays the dissolution
erythromycin (Acid unstable) + enteric coat = _____ dissolutions
pH
basis for optimum stability & solubility of the final product
↑solubility
acidic drug + basic solvent = __ solubility
↑solubility
basic drug + acidic solvent = __ solubility
poorly absorbed
streptomycin + mucin = ___ absorbed
well absorbed
Tetracycline + Calcium ions = ___ absorbed
well absorbed
Lipophilic drug + water soluble complexing agent = __ absorbed
decrease in absorbent of drug
Drug + Adsorbent (activated charcoal) = ____ absorbent of drug
Excipient factors
They are also known as the inactive ingredients that enhance the property of dosage forms
Lubricant
Disintegrants
Coatings
Three Excipient factors
↓rate of dissolution
↑lubricant = ___ rate of dissolution rate
↓rate of dissolution
↓disintegrant = ___ rate of dissolution rate
↓rate of dissolution
↑coating = ___ rate of dissolution rate
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Liquid Dosage Forms have a FASTER dissolution rate compared to Solid Dosage Forms
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Liquid Dosage Forms does NOT go through Liberation, they right away go through the systemic circulation
TRUE
TRUE OR FALSE
Aspirin is more absorbable in Small Intestine
Novobiocin
Chloramphenicol palmitate
examples of Amorphous drugs
FALSE
Their amorphous form is active and have a better absorption compared to their crystalline form, which is inactive & have a less absorption
TRUE OR FALSE
The crystalline nature of Novobiocin & Chloramphenicol palmitate have a BETTER absorption compared to its amorphous form.
Intermediate acting; Lente
Semi Lente is an amorphous short acting agent
Ultra Lente is a crystalline long acting agent
The combination of Semi Lente + Ultra Lente have a ____ acting
Beta Chloramphenicol
Alpha Chloramphenicol - stable
Gamma Chloramphenicol - unstable
Which drug has a high rate of dissolution and is meta stable?
Alpha Chloramphenicol
Beta Chloramphenicol
Gamma Chloramphenicol
A. Liberation
Which of the following is purely a biopharmaceutics parameter?
A. Liberation
B. Response
C. Absorption
D. Metabolism
B. Stomach
An acidic drug is mostly unionized in the
A. Duodenum
B. Stomach
C. Small Intestine
D. Blood
Hydrate
A drug that is united to water molecule forming a crystal is called:
B. The surface area of drug particle
The rate of drug dissolution from a tablet dosage form will increase with:
A. The particle size of the drug
B. The surface area of drug particle
C. The disintegration time
D. The amount of excipients to dilute the drug
Pharmacokinetics
it answers the question “what the body does to the drug?”
Handerson-Hasselbach Equation
This describes the relationship between pH and pKa