Chapter 4 - Psychological Theories
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Psychodynamic theory - Freud
Unconscious mental processes that develop in early childhood control personality
True or False: According to Freud, when the 3 parts of the personality are in conflict children can become maladjusted which ultimately leads to delinquency
True
Id
- Basic biological and psychological drives
- No distinction between reality and imagination
- Antisocial, knows no rules, limits, or limitations
Ego
- Grows from the Id
- Problem-solving dimension of personality
- Differentiates reality from fantasy
- Teaches delayed gratification
Superego
- Develops from the ego
- Comprises moral code, norms, and values acquired through life
- Responsible for guilt and shame (conscience)
Sigmund Freud - What makes up the personalituy
Id, Ego, Superego
Sublimation (psychodynamic theory)
The channeling of energy from the negative to the positive
- a defense mechanism
Attachment theory
The bond between a child and a caregiver significantly relates to child development
- buffers and protects against development of antisocial behavior
- morally socializes children
- helps to regulate emotions and conduct
- instills self-esteem, self-efficacy, and self-concept
Oedipus Complex
An unconscious desire of a child to have the exclusive love of the parent of the opposite sex
Behavioral theory
Behavior reflects interactions with others throughout life
Skinner - behavioral theory
Children repeat rewarded behavior and stop punished behavior
Alber Bandura - social learning theory
Children learn by modeling and imitating others
Social Cognition
how people perceive, think, learn and behave in particular ways as a result of their interactions in the social world
Moral disengagement
An individual's tendency to use mechanisms that are conducive to a selective disengagement of moral censure
- self-serving behaviors that limit negative emotions such as guilt
Morality of constraint
Children think rigidly about moral concepts and believe that breaking the rules should be punished
Morality of cooperation
Children employ moral flexibility and learn that behavior has no absolute moral standard
LL Thurstone - Five Factor model of personality
A structural model of personality measured by the NEO personality inventory
- 5 factors and 6 facets make up the human personality
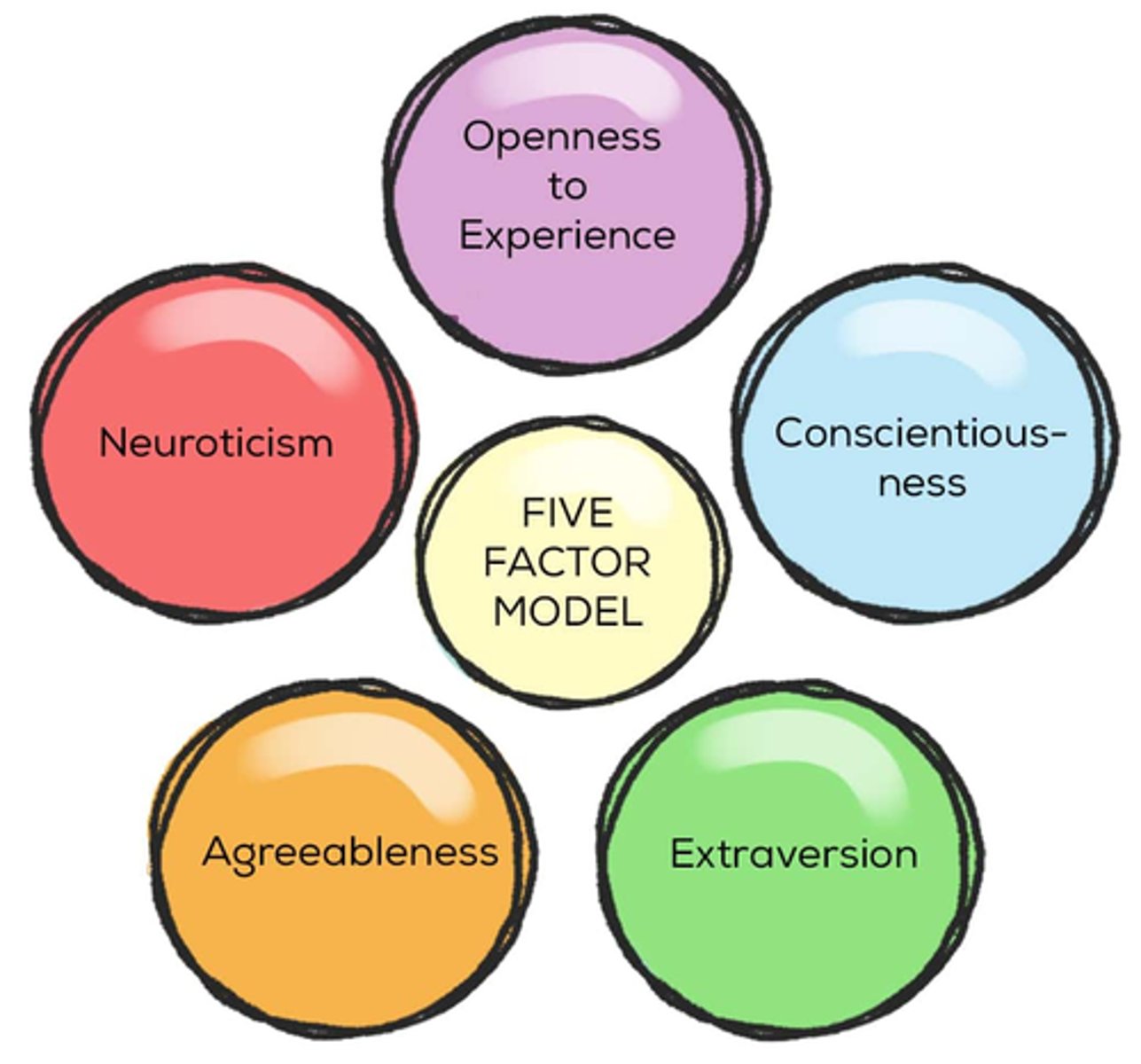
Neuroticism
Assessed by anxiety, hostility, depression, self-consciousness, impulsiveness, and vulnerability to stress
Extraversion
Assessed by warmth, gregariousness, assertiveness, activity, excitement seeking, and positive emotion
Openness to experiences
Assessed by fantasy, aesthetic, feelings, actions, ideas and values
Aggreeableness
Assessed based on trust, straightforwardness, altruism, compliance, modesty, and tendermindedness
Conscientiousness
Assessed by competence, order, dutifulness, achievement striving, self-discipline, and deliberation
Egocentric bias
Delay in moral development and immaturity that becomes an almost child-like self-centeredness
Reactive aggression
Impulsive, thoughtless, and unplanned
- driven by anger
- occurs as a reaction to a perceived provocation
Proactive aggression
Premeditated means of obtaining a goal in addition to harming the victim
Indirect aggression
Verbal
- not as easily visible
- gossip, ostracism, etc.
Direct aggression
Physical
- easy to be seen
- hitting, kicking, punching, biting, etc.
Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)
Pattern of anger, irritability, argumentativeness, defiant behavior, or vindictiveness
- Lasts over 6 months
- symptoms exhibit during interaction with at least 1 non-sibling individual
Prodrome
An early, nonspecific symptom (or set of symptoms) that indicates the start of a disease before the disease symptoms appear
- ODD is seen as a prodrome for conduct disorders
Comorbidity
Children who have both ODD and conduct disorder at the same time
Conduct disorder
repetitive and persistent pattern of behavior in which the basic rights of others or major age-appropriate social norms/rules are violated
Psychopathy
Personality disorder that impairs interpersonal, affective, and behavioral functions
- closely linked to antisocial behavior
Etiological
Sociopath
Antisocial personality
the set of characteristics that describe someone's deviant beliefs and deviant ways of thinking, and antisocial behaviors
Psychopathology
A set of behaviors and attitudes that show clinical evidence of psychological impairment