Anatomy of the Thorax: Pleura & Mediastinum, Pericardium & Trachea, and Lungs
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
cavity housing lungs and heart
Thoracic cavity
1.) muscles
2.) bones
3.) ligaments
The walls of the thoracic cavity are formed by (3):
pleural
The thoracic cavity is bound to the _________ membrane
endothoracic fascia
What binds the thoracic cavity to the pleural membrane?
areolar tissue that attaches the costal and diaphragmatic pleurae to the underlying muscles, ligaments, and bones of the thoracic wall
endothoracic fascia
two pleural sacs, thoracic viscera, blood vessels, nerves, lymph nodes, and lymphatics
Thoracic cavity contains (6):
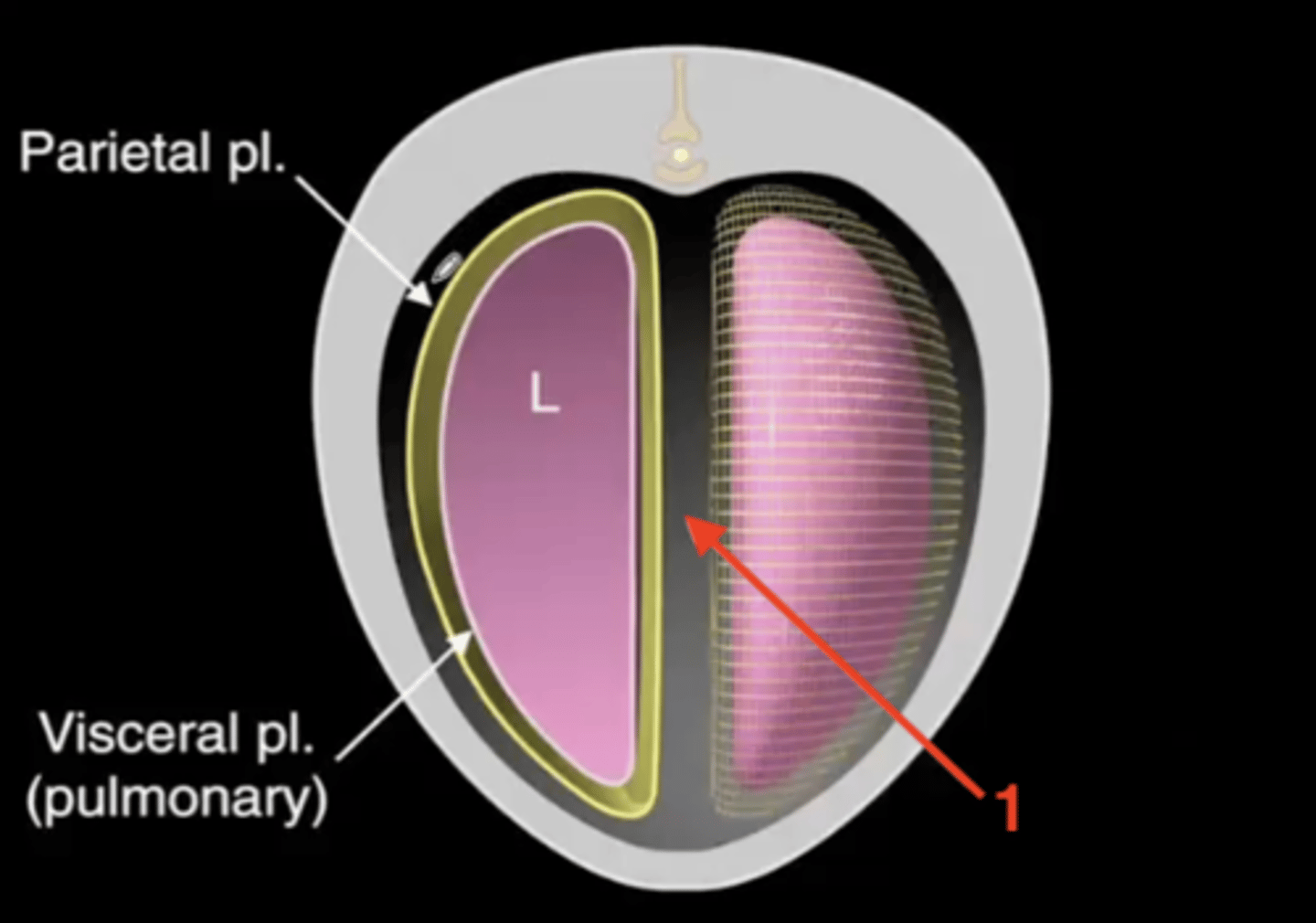
serous membrane that lines the wall of the thoracic cavity and covers the lungs
Pleura
a potential space between the parietal and visceral pleura, contains a small amount of fluid
Pleural cavity
pleura that immediately surrounds the thoracic wall
Parietal pleura
1.) costal pleura
2.) mediastinal pleura
3.) diaphragmatic pleura
The parietal pleura is divided into three parts:
pleura that lines the ribs
costal pleura
pleura that lines the mediastinum
mediastinal pleura
pleura that lines the diaphragm
diaphragmatic pleura
pleura that immediately surrounds the lungs
Visceral pleura
space between the left and right pleural sacs, occupied by most of the thoracic organs
Mediastinum
the lungs and sympathetic trunk
The mediastinum contains most thoracic organs except...
spaces where regions of parietal pleura are directly applied to each other
Pleural recesses
because the pleural sac is more extensive/larger than the space the lungs occupy
Why does the pleural recess take place?
enclose the lungs
Pleural sacs
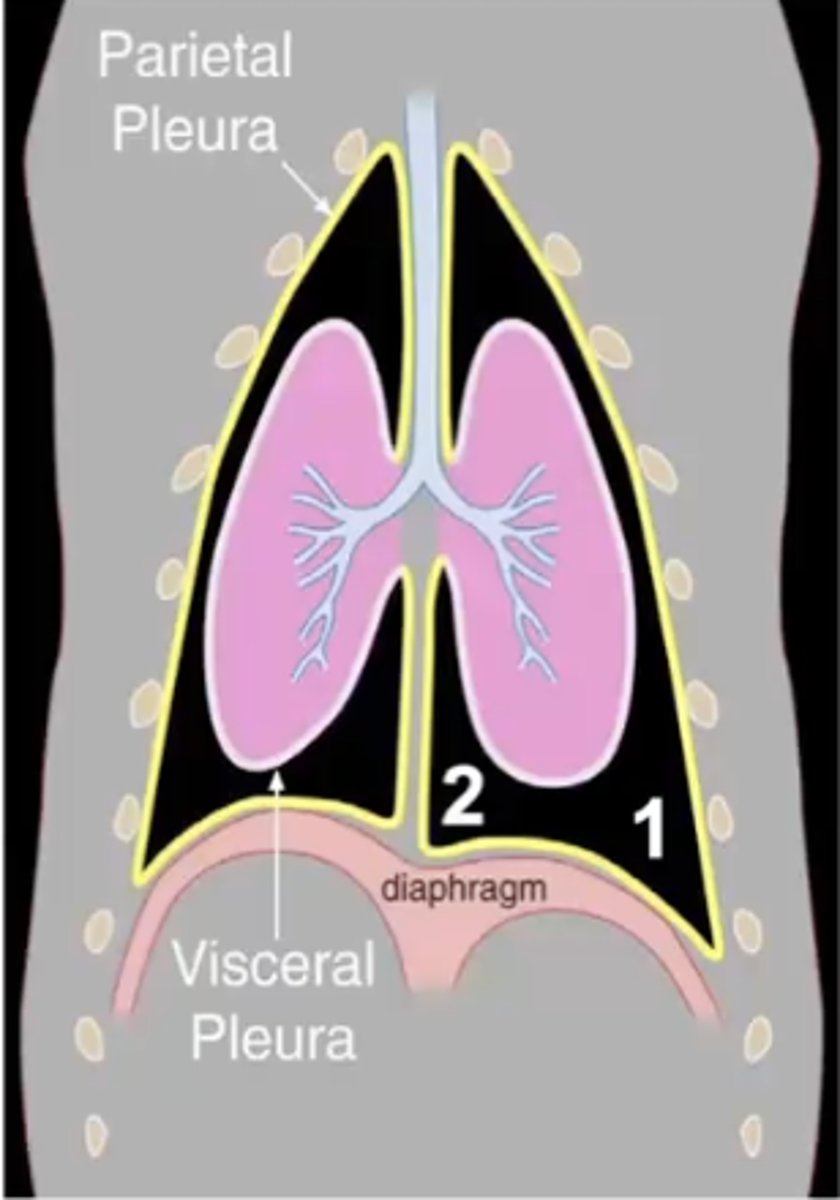
1.) costodiaphragmatic recess
2.) costomediastinal recess
Two pleural recesses:
where the costal and diaphragmatic pleura meet
costodiaphragmatic recess
where the costal and mediastinal pleura meet
costomediastinal recess
needle insertion into the costodiaphragmatic recess; at the 6th, 7th, or 8th intercostal space ventral to the costochondral junction
Thoracocentesis
cranial extend of the parietal pleura in the pleural cavity extending through the thoracic inlet
Cupula pleurae (pleural cupula)
pneumothorax
The cupula pleurae can be mistakenly opened during caudal neck surgery/neck injury and cause...
air in the plerual cavity
pneumothorax
space between the left and right pleural sacs/lungs
Mediastinum
1.) cranial mediastinum
2.) middle mediastinum
3.) caudal mediastinum
The mediastinum is divided into three parts by the heart:
space between the lungs that is cranial to the heart
cranial mediastinum
occupied by the heart
middle mediastinum
space between the lungs that is caudal to the heart
caudal mediastinum
1.) dorsal mediastinum
2.) ventral mediastinum
The mediastinum is further divided into two parts by the roots of the lungs:
where the lungs end and bifurcate into the primary bronchi
root of the lungs
space dorsal to the root of the lungs
dorsal mediastinum
space ventral to the root of the lungs
ventral mediastinum
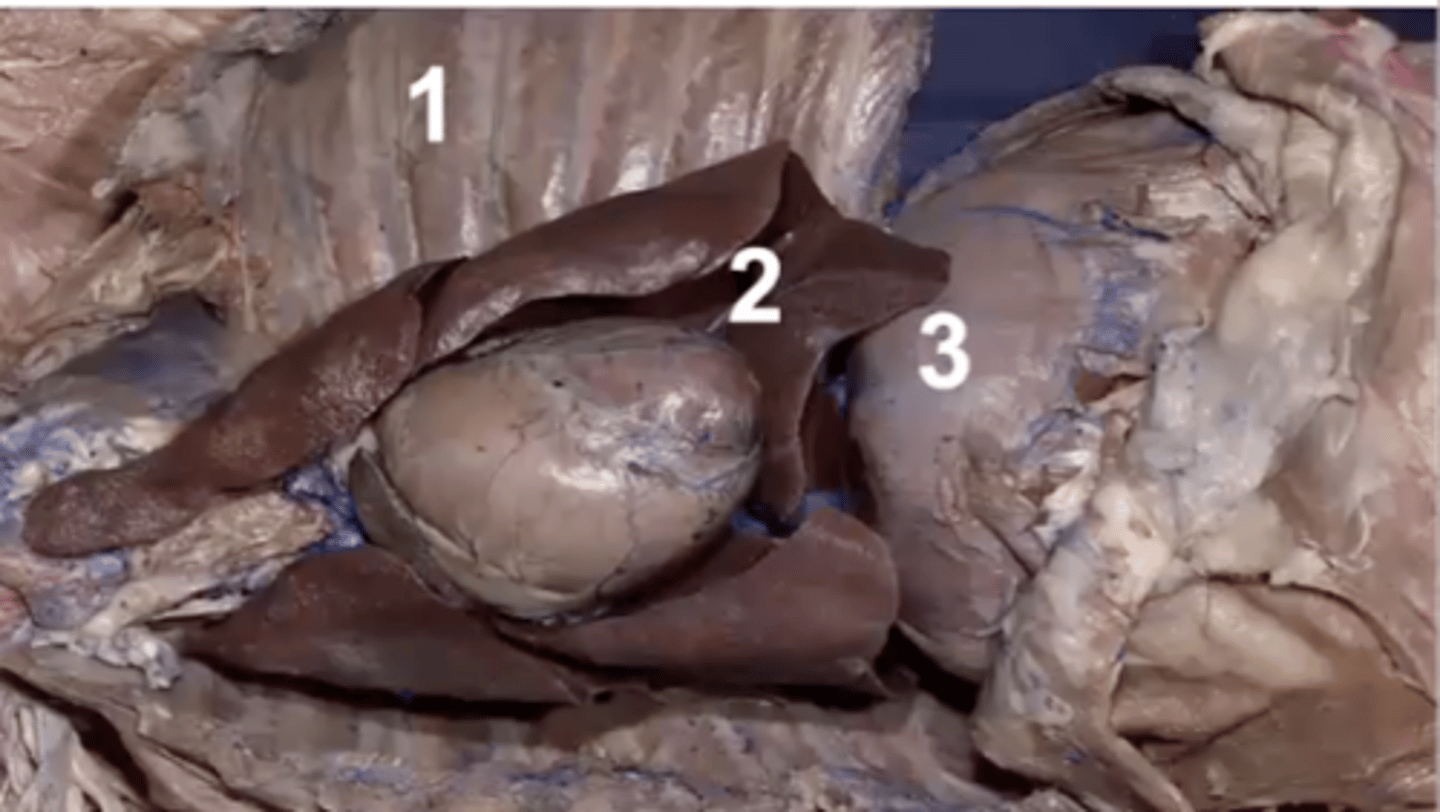
parietal pleura
1
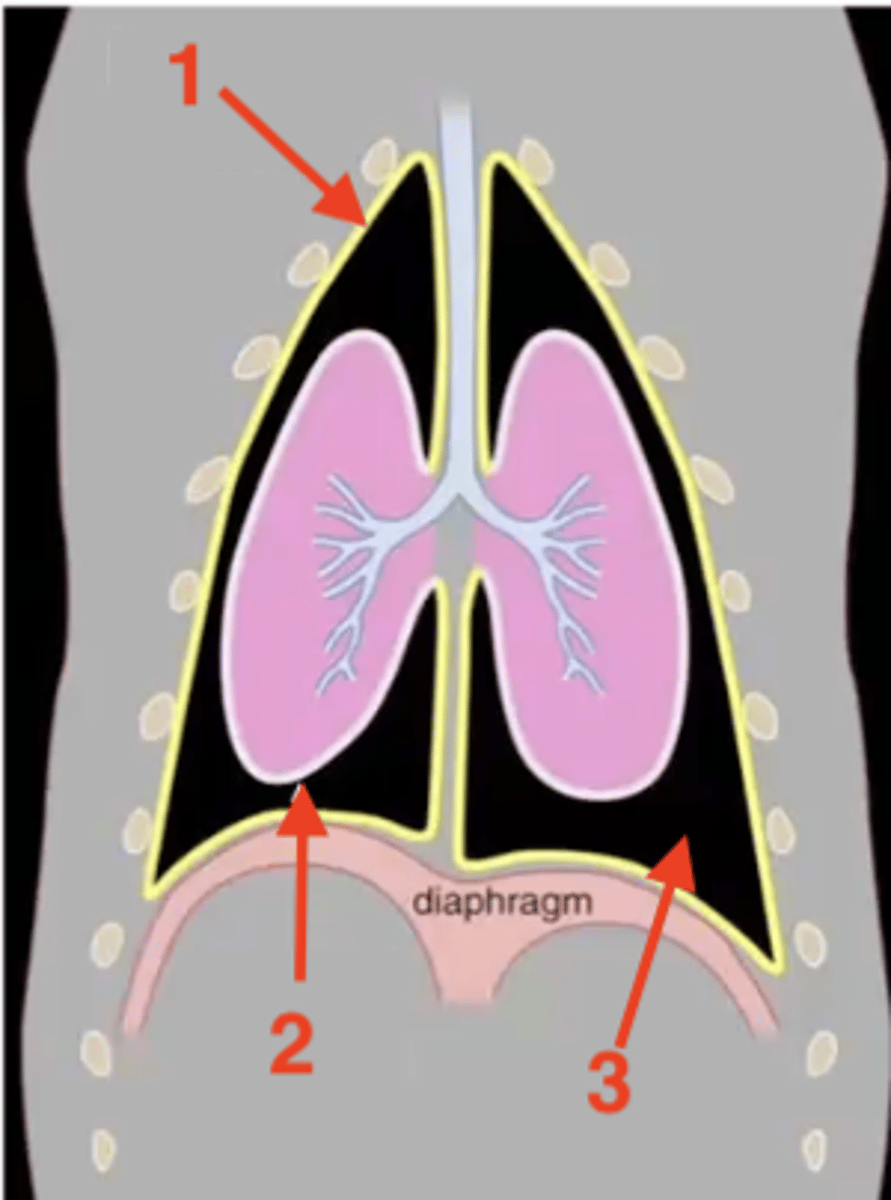
visceral pleura
2
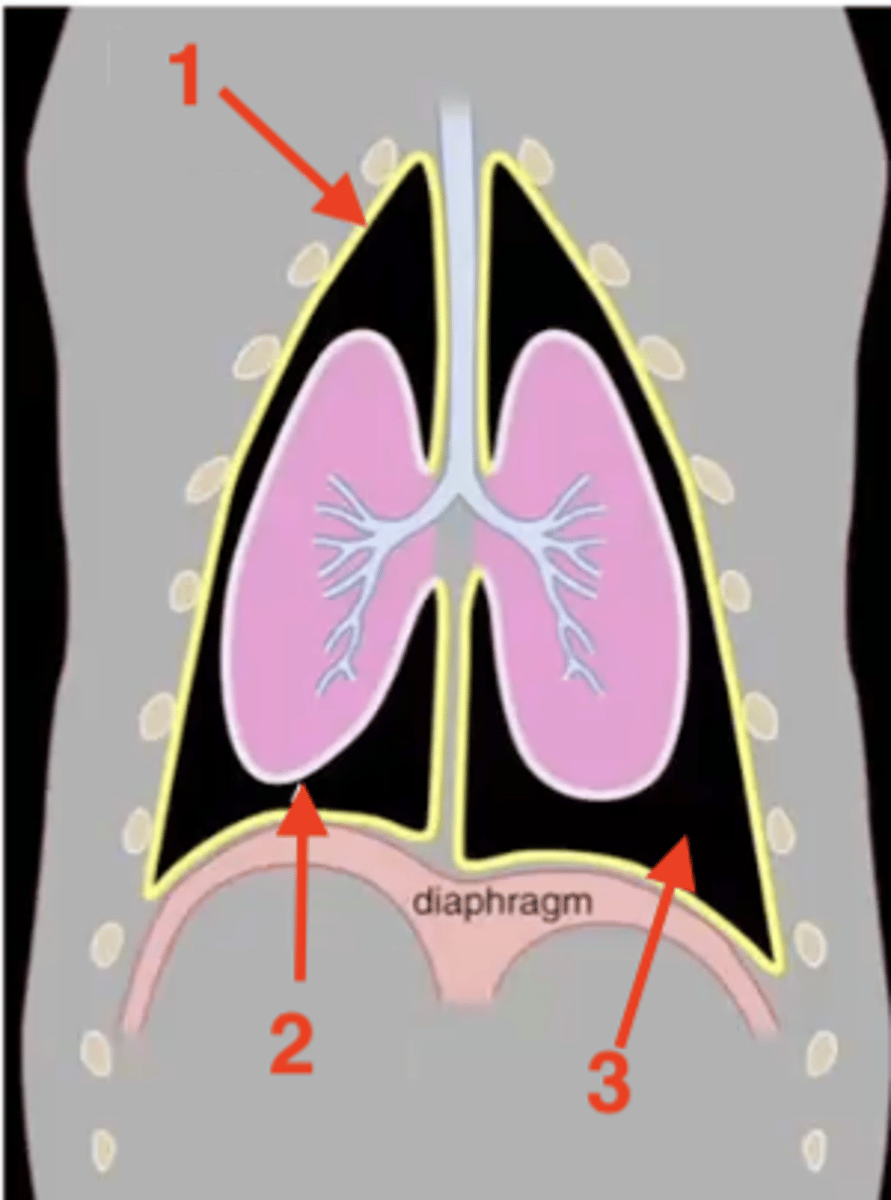
pleural cavity
3
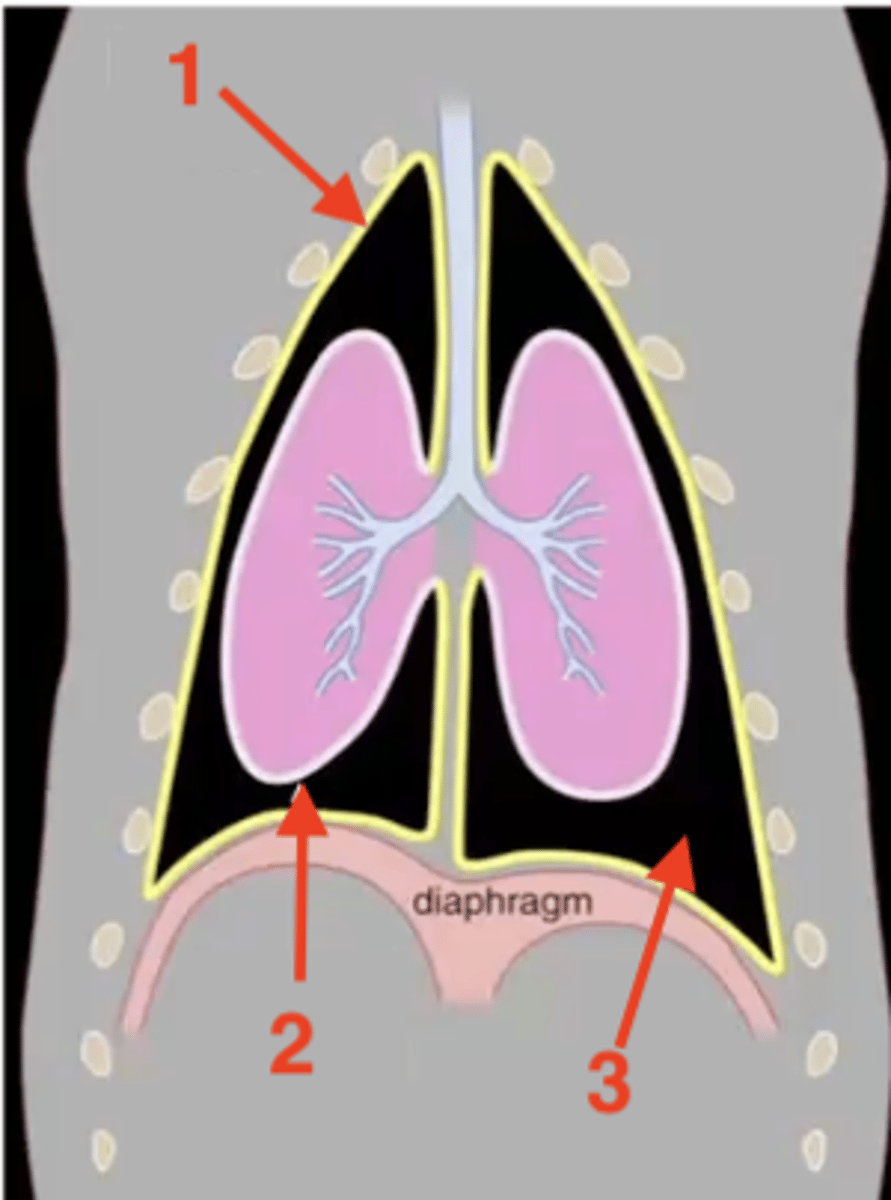
mediastinum
1
costal pleura
What type of pleura is 1?
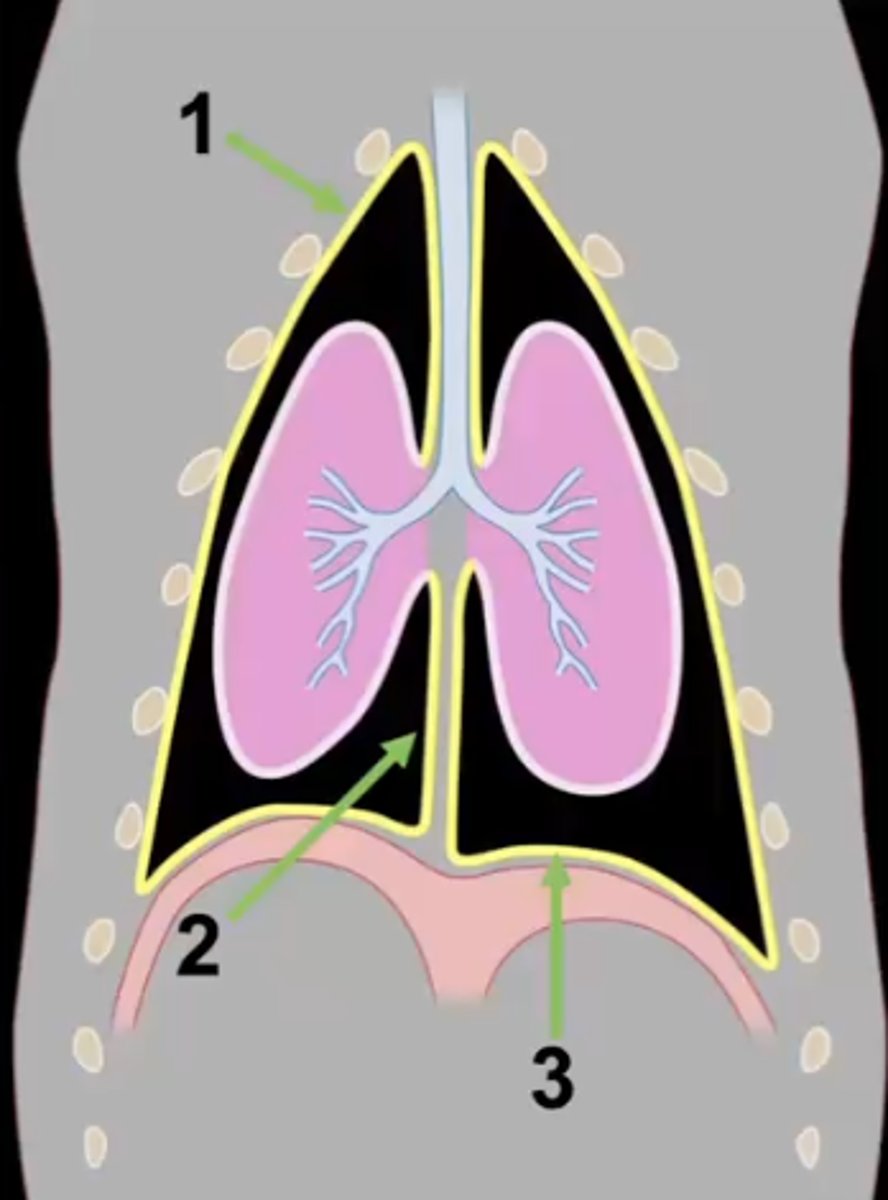
mediastinal pleura
What type of pleura is 2?
diaphragmatic pleura
What type of pleura is 3?
costal pleura
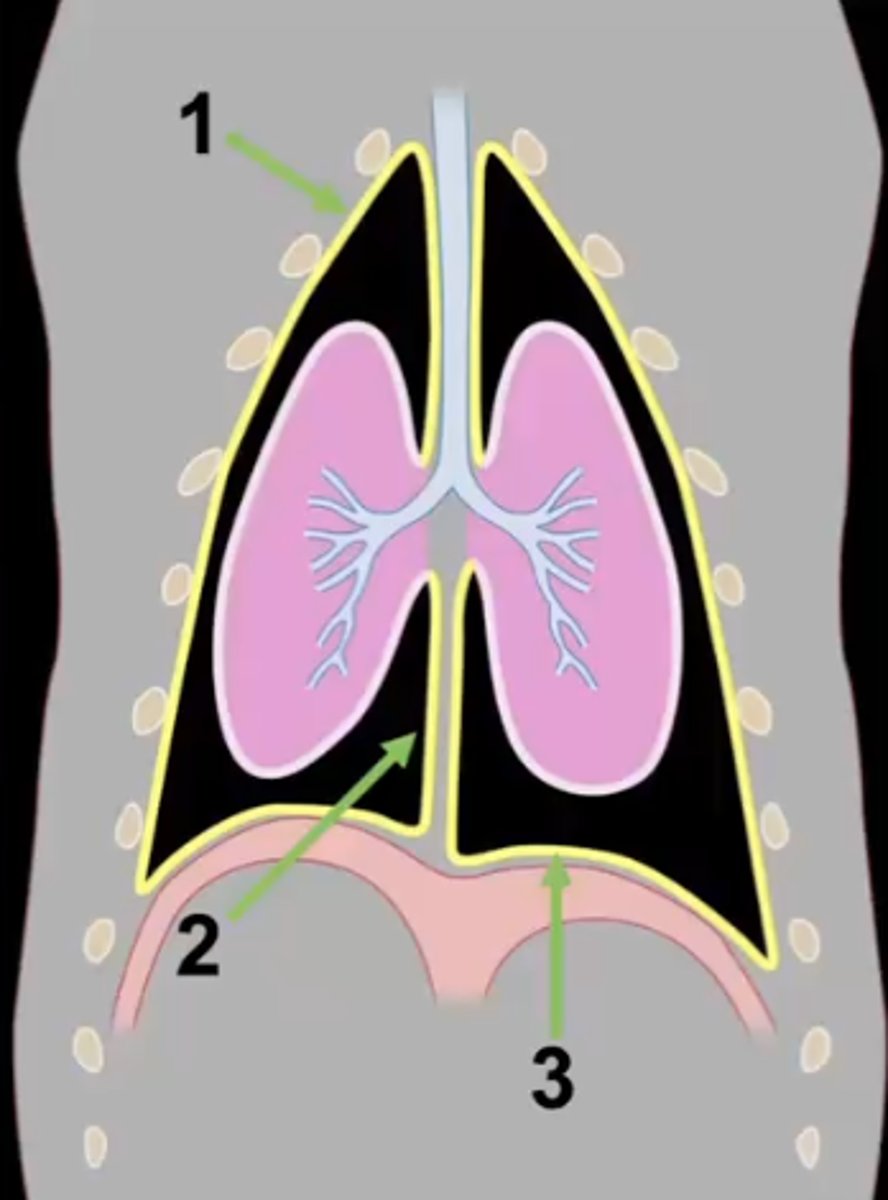
What type of pleura is 1?
mediastinal pleura
What type of pleura is 2?
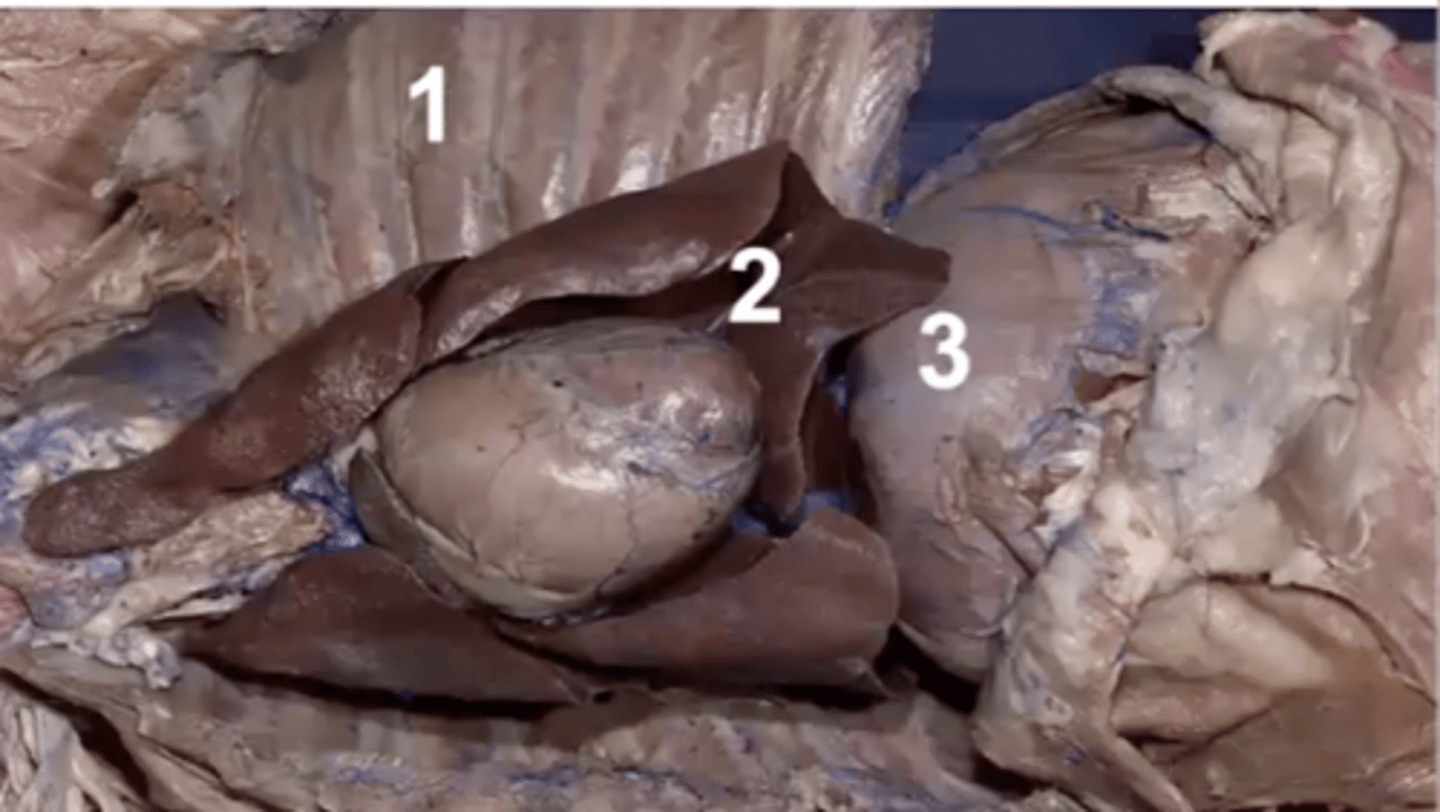
diaphragmatic pleura
What type of pleura is 3?
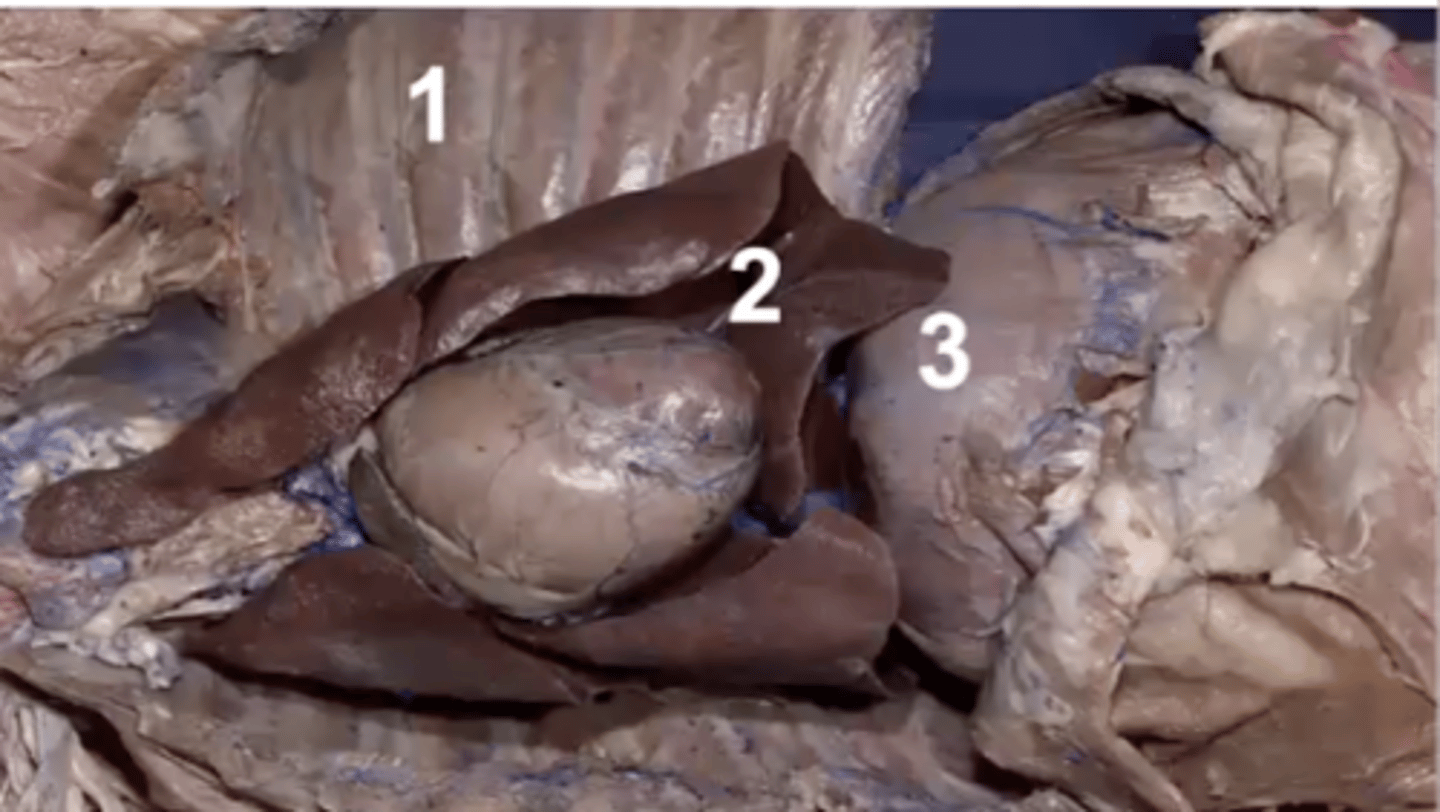
costodiaphragmatic recess
Which pleural recess is 1?
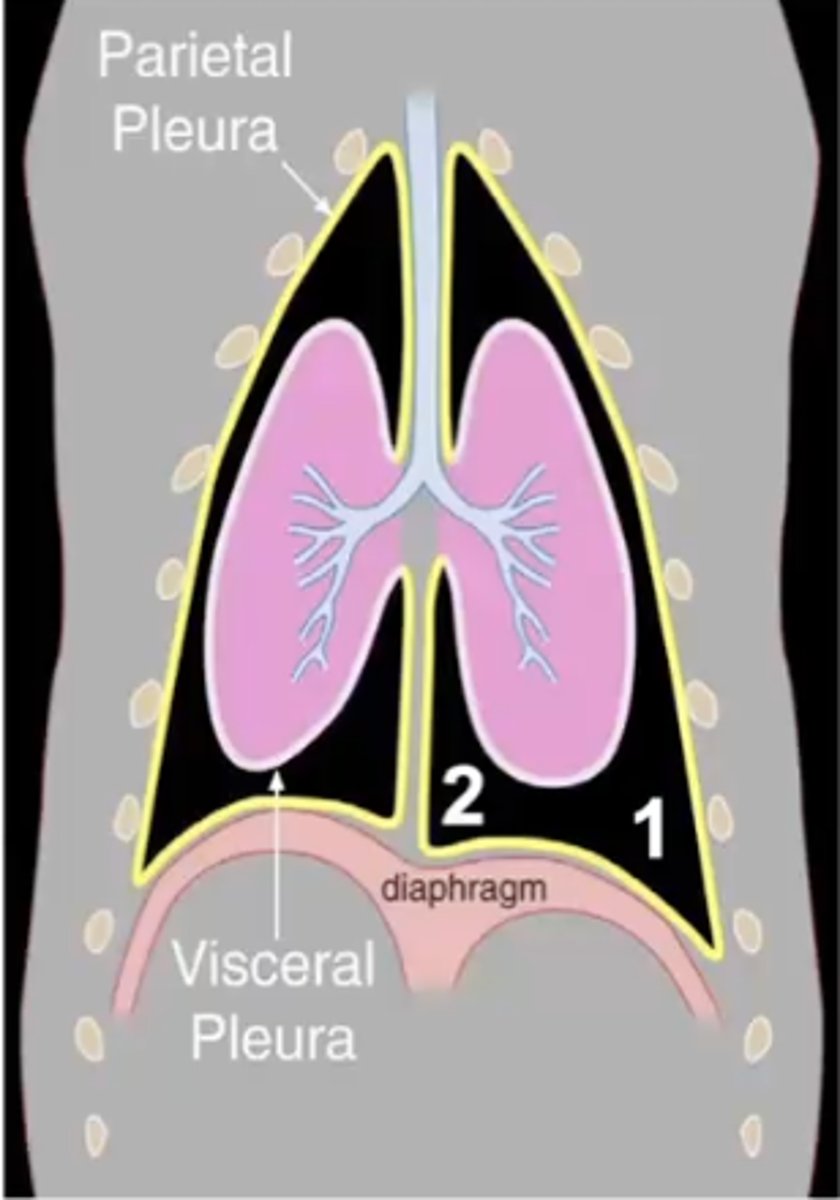
costomediastinal recess
Which pleural recess is 2?
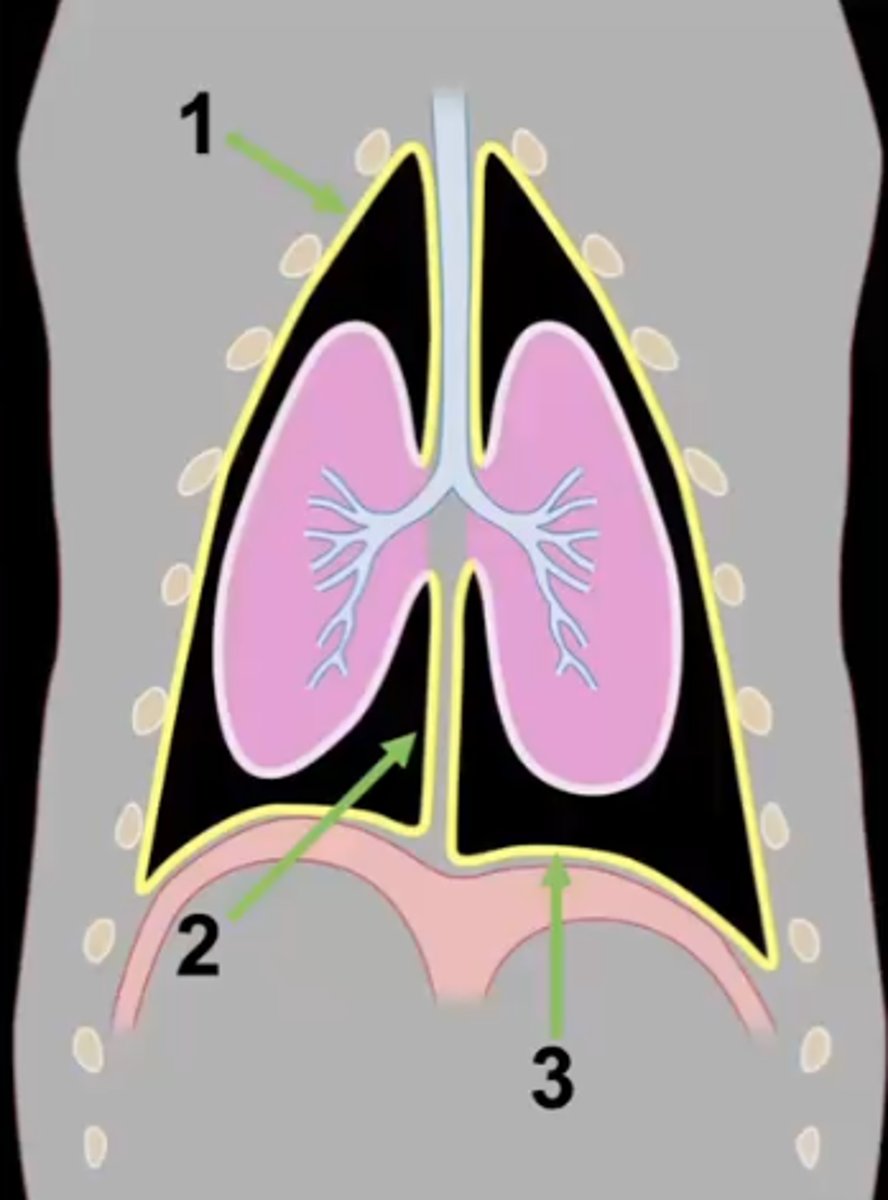
cranial mediastinum
Which section of mediastinum is 1?
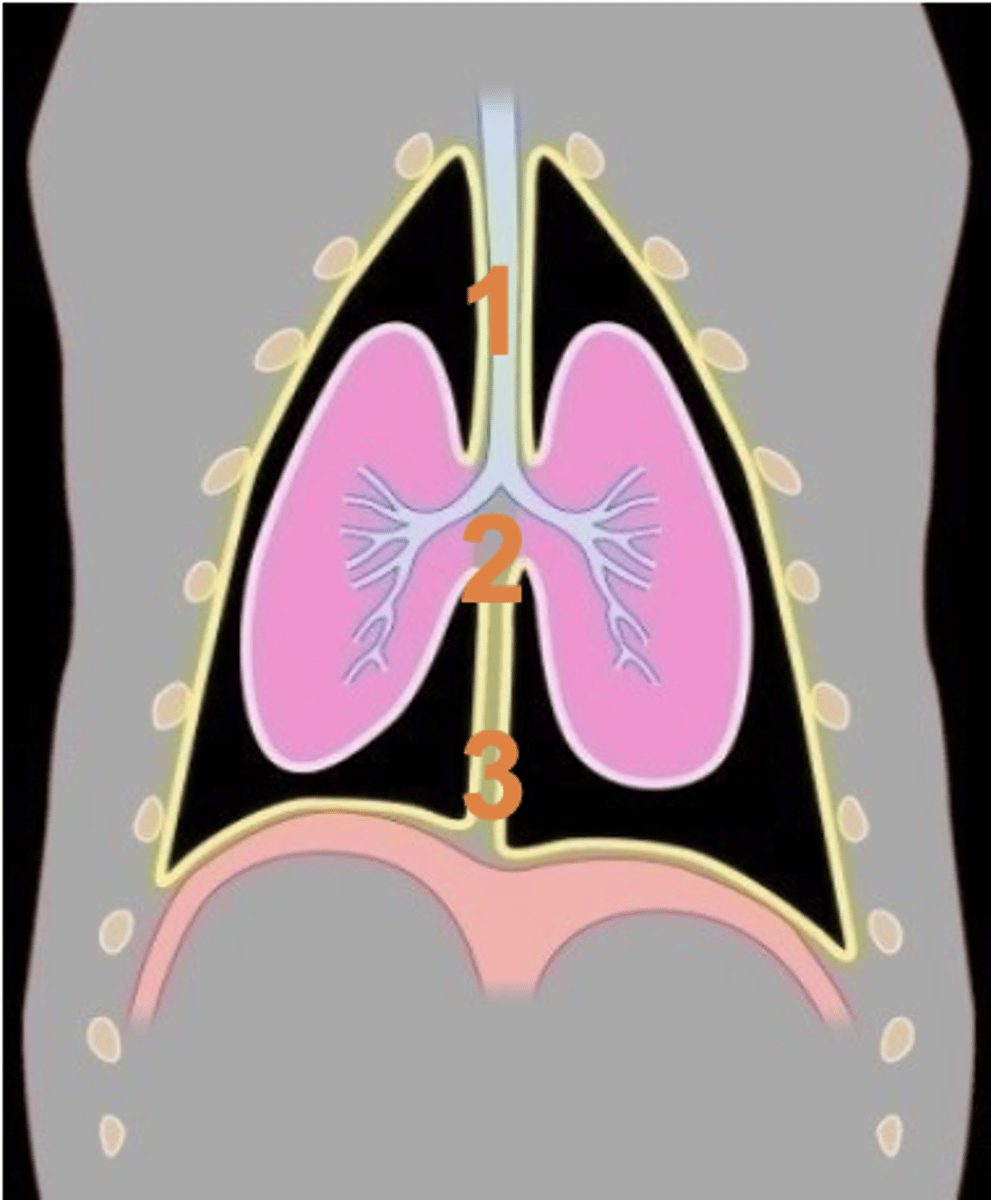
middle mediastinum
Which section of mediastinum is 2?
caudal mediastinum
Which section of mediastinum is 3?
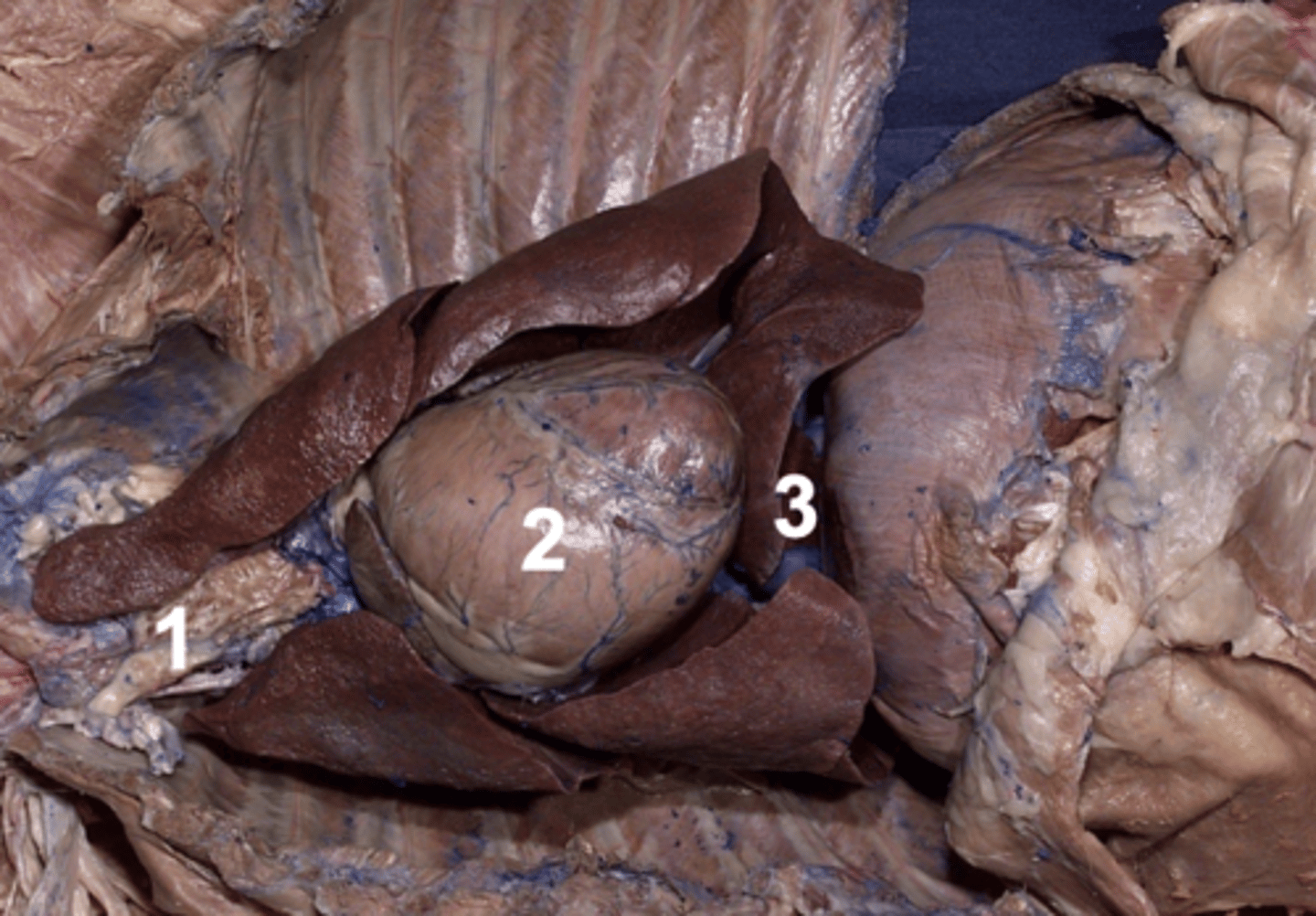
cranial mediastinum
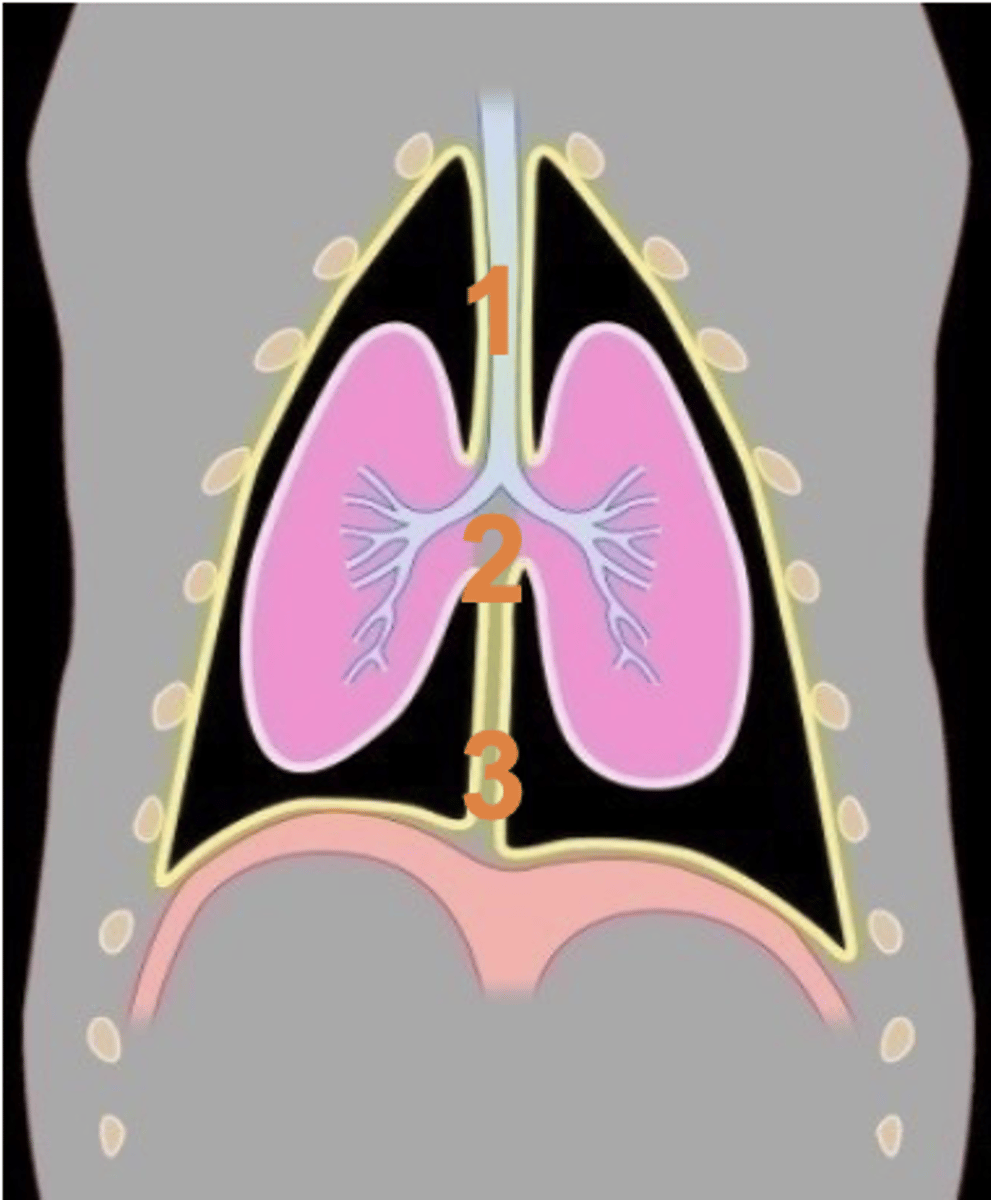
Which section of mediastinum is 1?
middle mediastinum
Which section of mediastinum is 2?
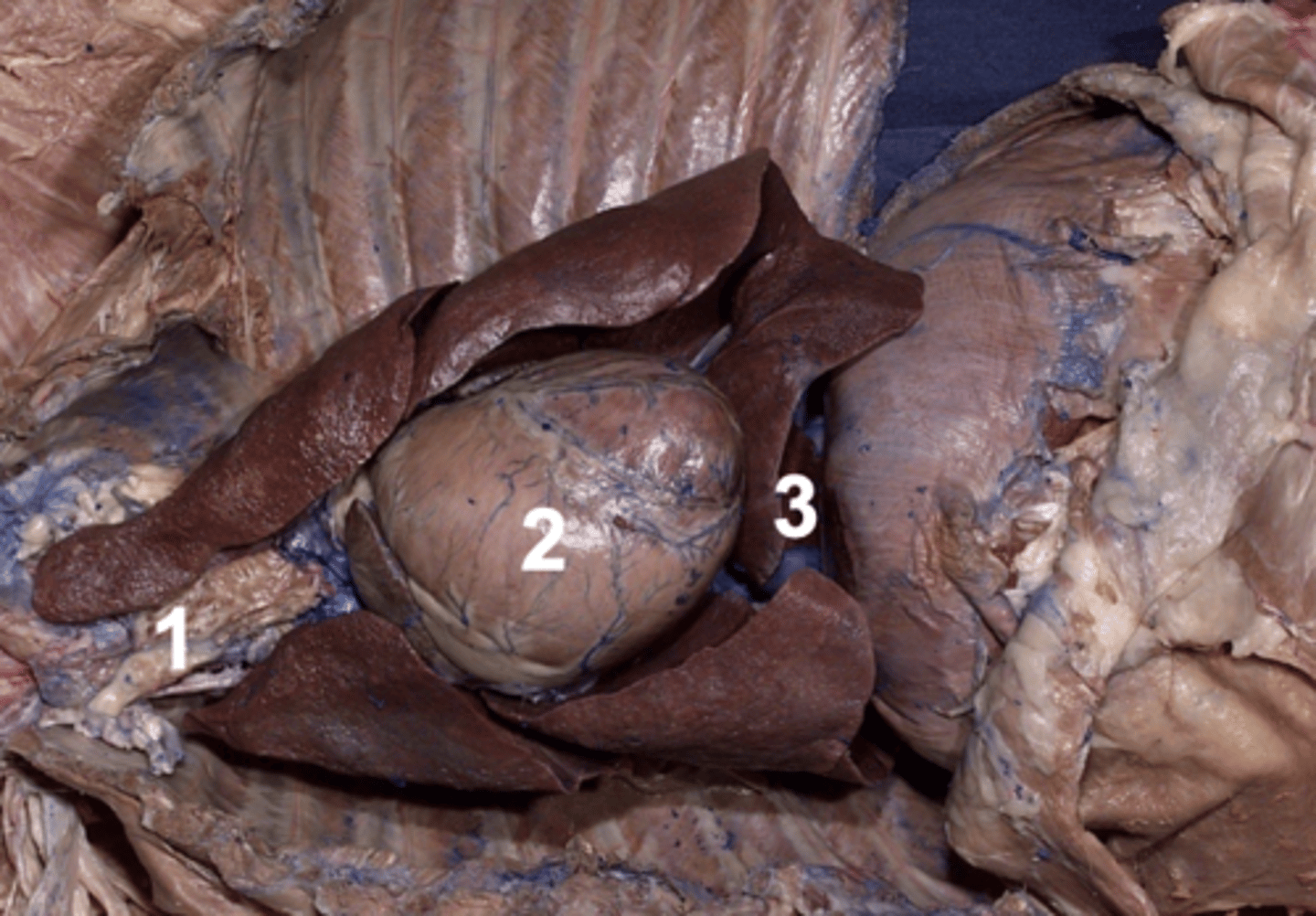
caudal mediastinum
Which section of mediastinum is 3?
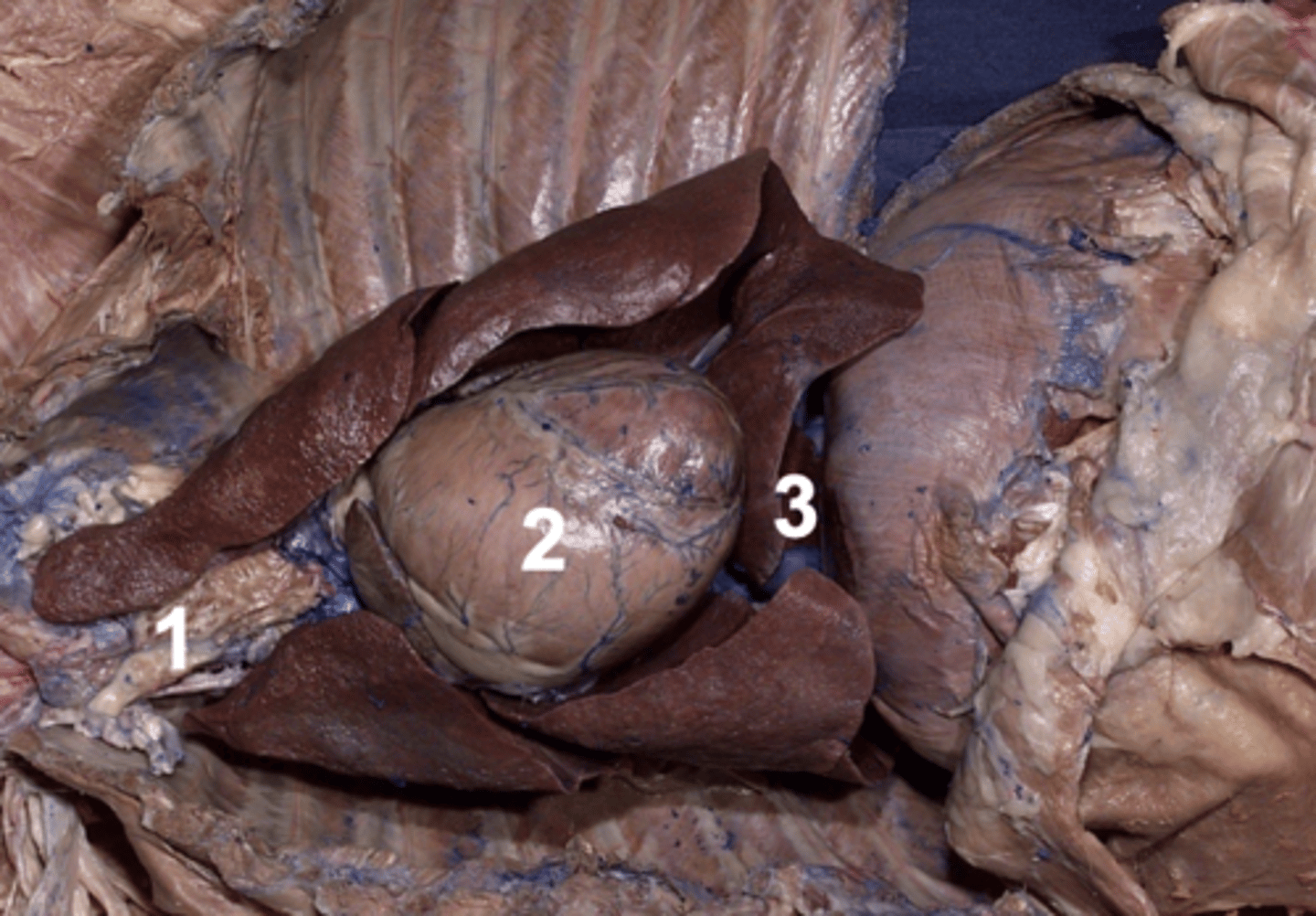
the fibroserous envelope of the heart
Pericardium
1.) fibrous pericardium
2.) serous pericardium
The pericardium has two layers
outer layer that adheres tightly to the pericardial mediastinal pleura
fibrous pericardium
1.) phrenicopericardial ligament
2.) sternopericardiac ligament
The fibrous pericardium contains two ligaments
connects the fibrous pericardium to the diaphragm
phrenicopericardial ligament
connects the fibrous pericardium to the sternum
sternopericardiac ligament
inner layer that
serous pericardium
1.) parietal serous pericardium
2.) visceral serous pericardium
The serous pericardium is further divided into two layers:
adheres to the fibrous pericardium
parietal serous pericardium
adheres to the heart
visceral serous pericardium
space between the parietal and visceral serous pericardium
Pericardial cavity
-pericardial mediastinal pleura
-fibrous pericardium
-parietal serous pericardium
------pericardial cavity----------
-visceral serous pericardium
Layers surrounding the heart from outside to inside
excess fluid in the pericardial cavity; most are not harmful, but they sometimes can make the heart work poorly
Pericardial effusion
surgical removal of a portion or all of the pericardium
Pericardiectomy
inflammation of the pericardium
Pericarditis
pericardial mediastinal pleura
1
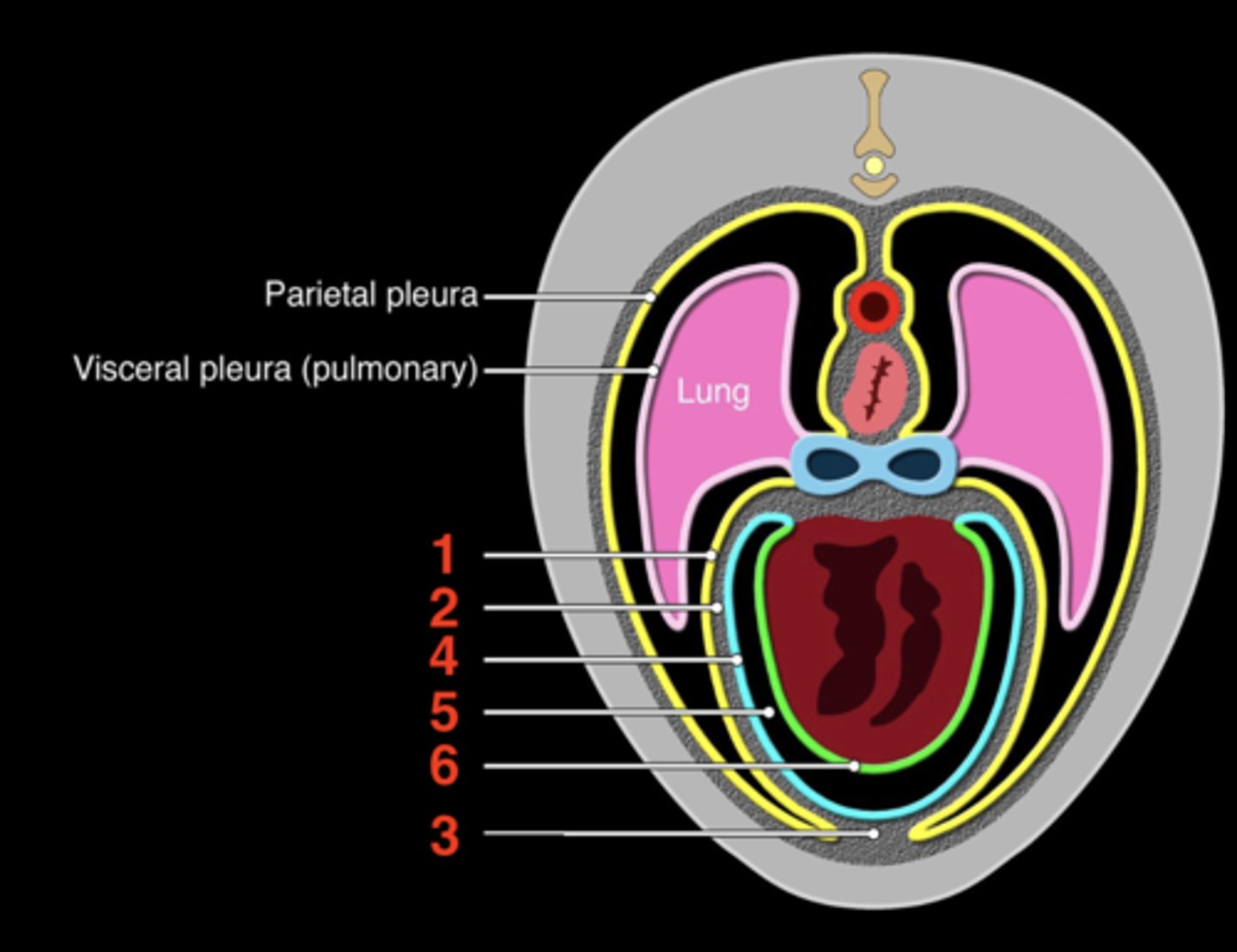
fibrous pericardium
2
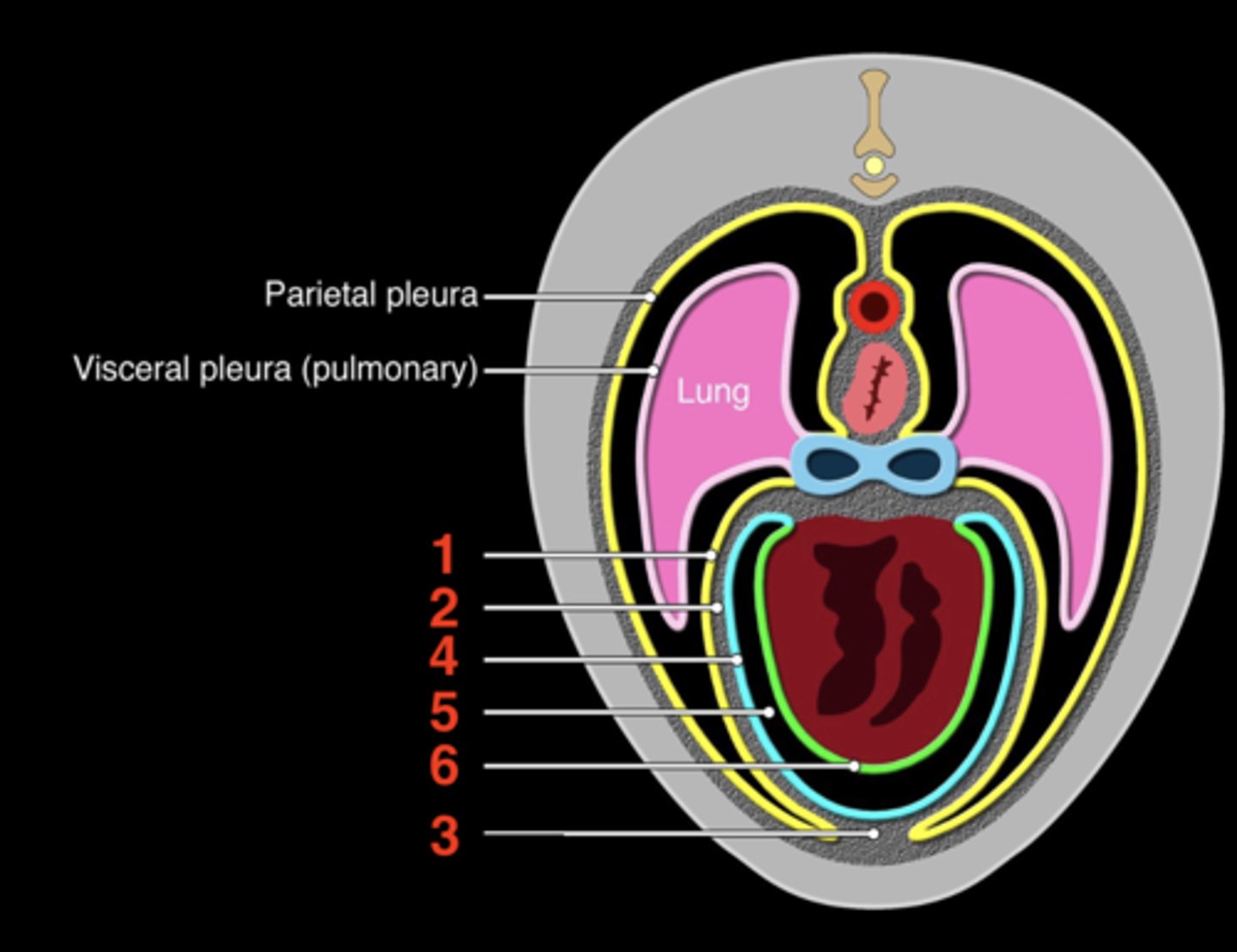
sternopericardiac ligament
3
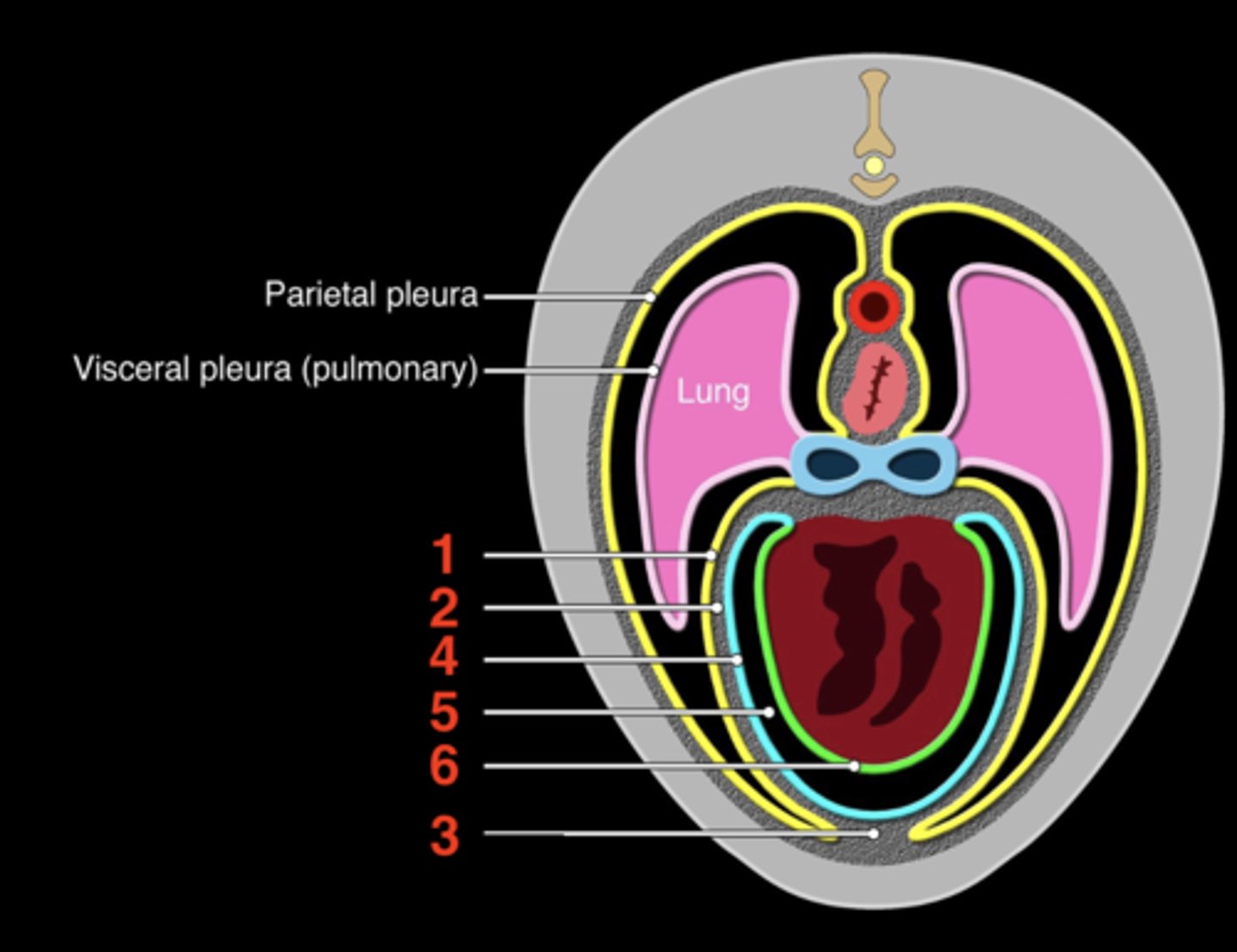
parietal serous pericardium
4
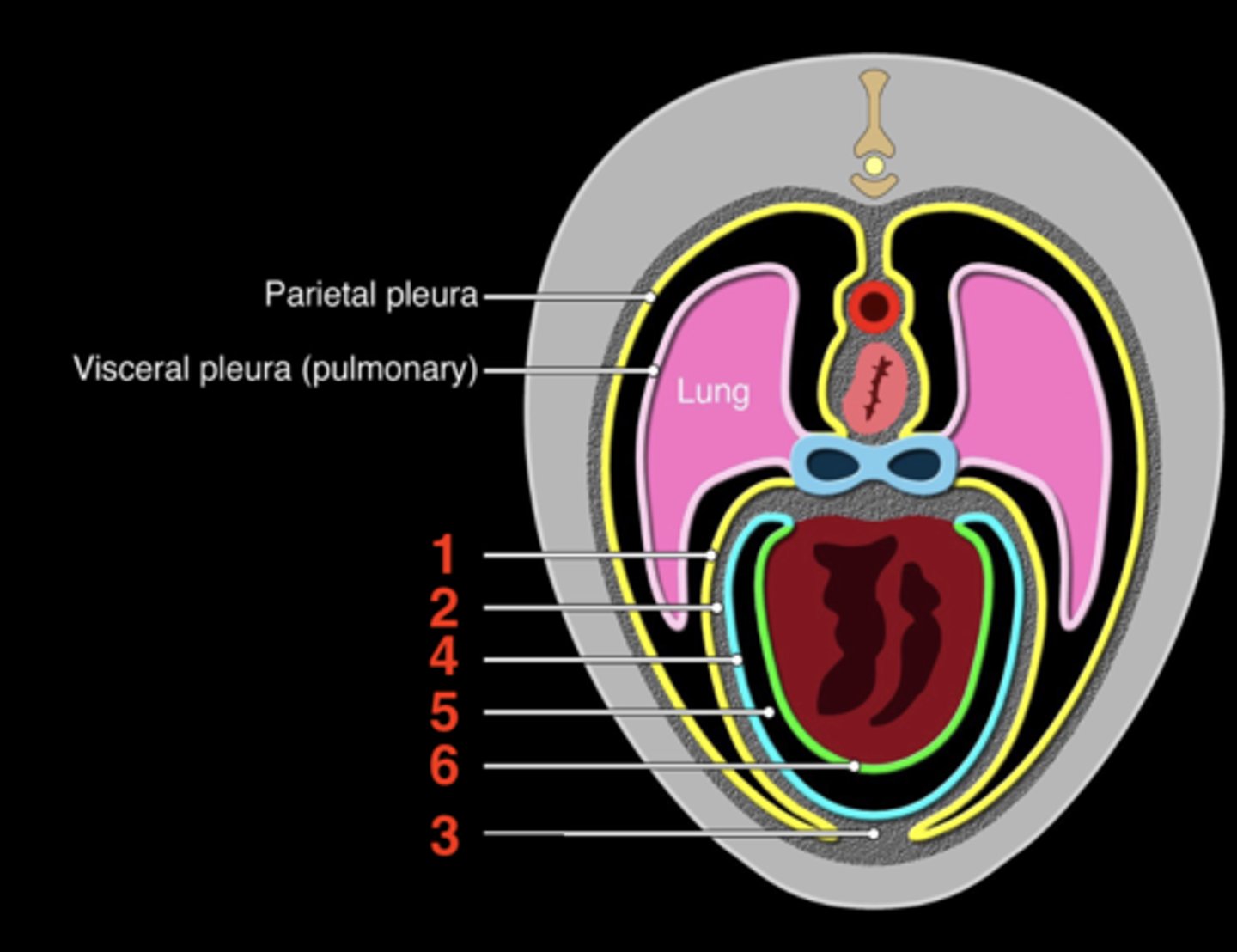
pericardial cavity
5
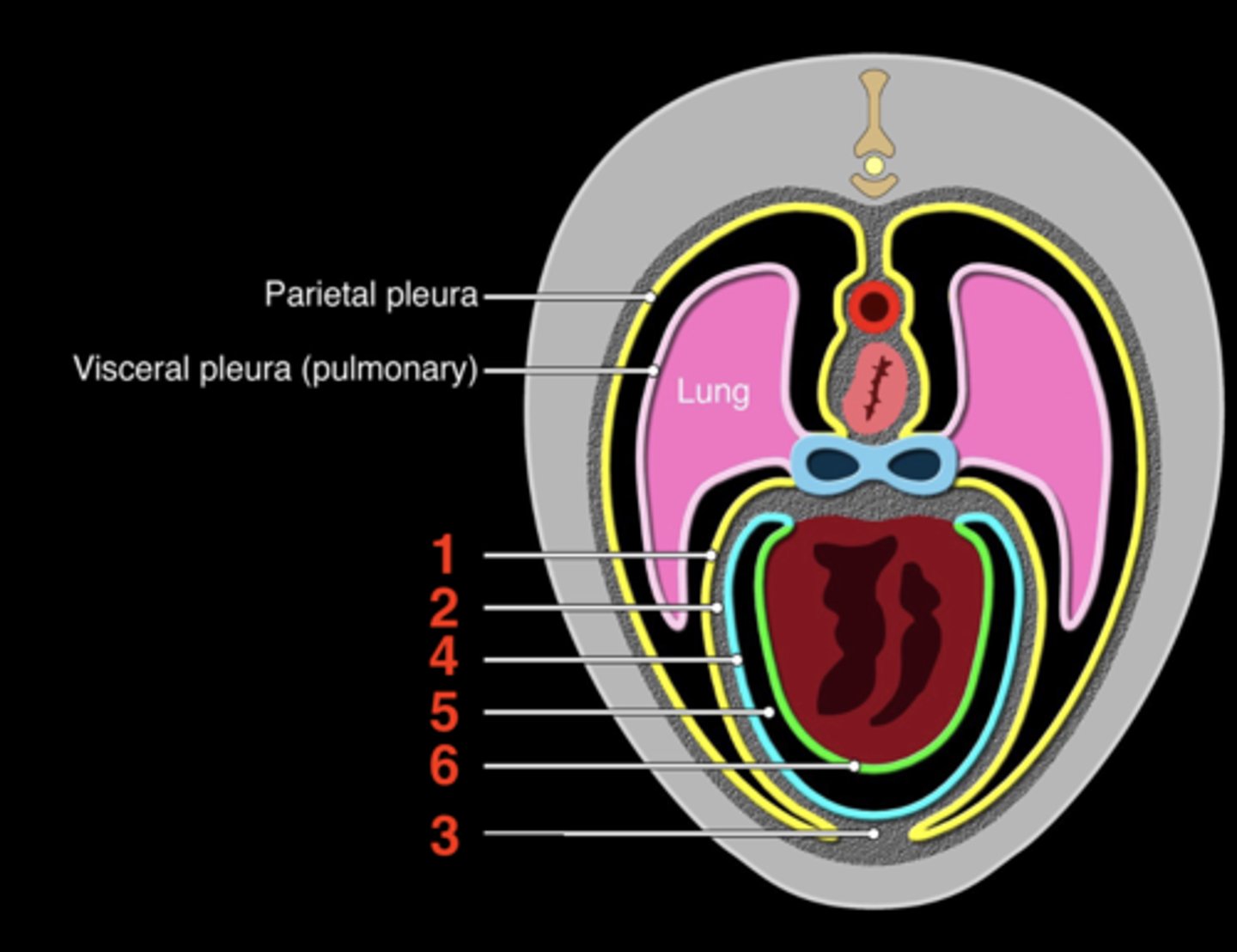
visceral serous pericardium
6
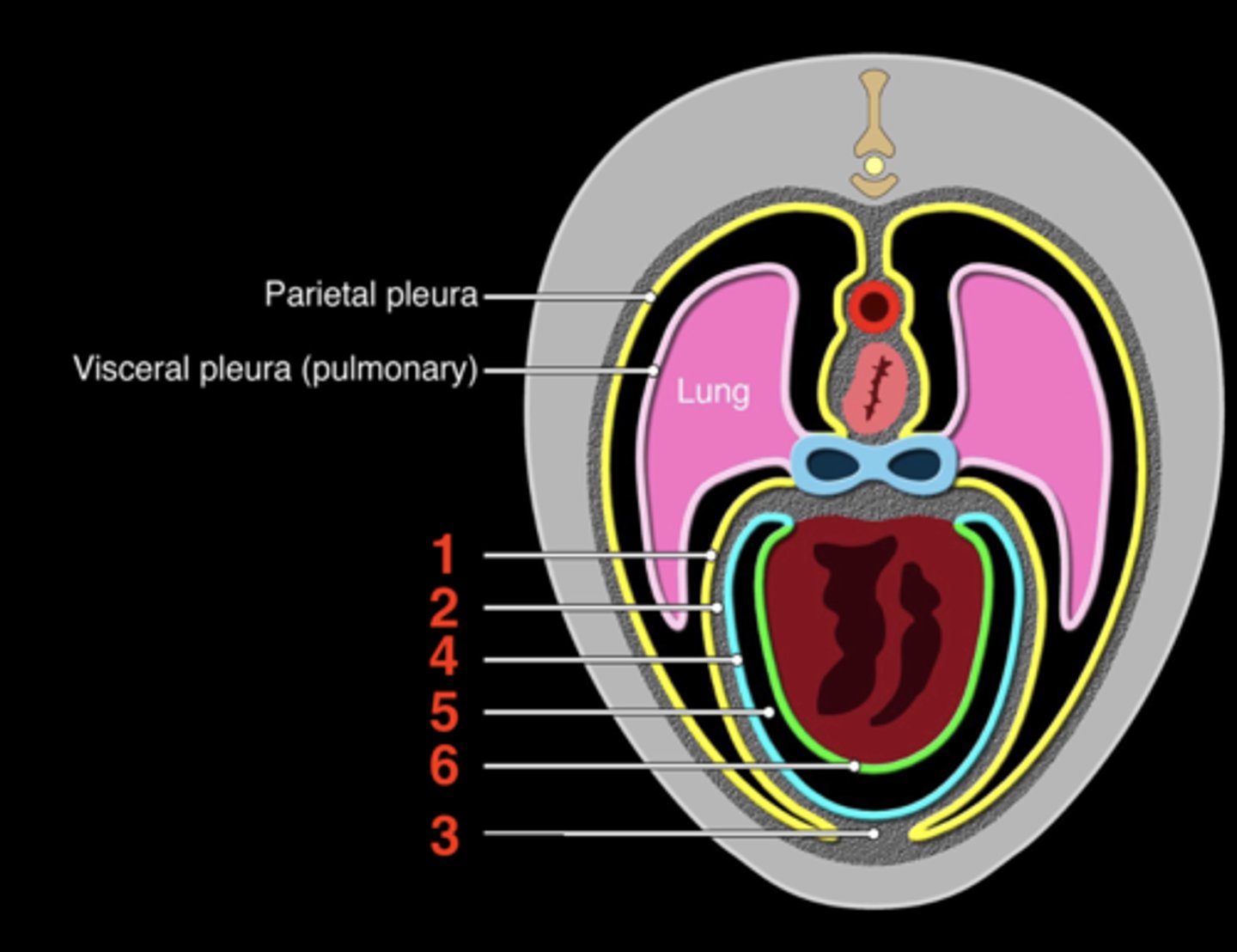
upper; lower
The respiratory system is divided into _______ and ________ respiratory tracts
the nares and the lungs
upper respiratory tract includes structures between....
1.) nasal cavity
2.) pharynx
3.) larynx
4.) trachea
Four structures of the upper respiratory tract:
to conduct air to and from the lungs
Main function of upper respiratory system
1.) modification of inspired air
2.) thermoregulation
3.) defense against harmful substances
4.) olfaction
Four other functions of the upper respiratory system:
the lungs
Lower respiratory tract
gas exchange of oxygen from the atmosphere and carbon dioxide from the blood
Function of the lower respiratory tract
1.) respiratory bronchioles
2.) alveolar ducts
3.) alveoli
Where does gas exchange take place (3)?
cervical and thoracic parts
The trachea is divided into two parts:
starts from cricoid cartilage to the thoracic inlet
Cervical part of trachea
goes from thoracic inlet to the bronchi
Thoracic part of trachea
where the trachea bifurcates into a left and right primary bronchi
Tracheal bifurcation
at T4 to T5
Where does the tracheal bifurcation take place?
crest into the bifurcation of the trachea
tracheal carina
right; ventral
The trachea enters the thoracic cavity to the _________ of the esophagus, then turns ________ to the esophagus
base
The trachea ends at the _______ of the heart
1.) tracheal cartilage
2.) tracheal muscle
3.) annular ligaments of the trachea
Three components of the trachea:
hyaline cartilage
What is tracheal cartilage made of?
makes up 35 incomplete tracheal rings
Tracheal cartilage function
smooth muscle
What are the tracheal muscles made of?
connects the tracheal cartilage dorsally
Tracheal muscles function
fibroelastic tissue
What are the annular ligaments of the trachea made of?
connects consecutive tracheal rings
Function of the annular ligaments of the trachea
narrowing of tracheal lumen as a result of flattening tracheal cartilages, a redundant dorsal tracheal membrane, or both
Tracheal collapse
involves creating an opening in the neck in order to place a tube into the windpipe; tube is inserted through a cut in the neck below the vocal cords to allow air to enter the lungs
Tracheostomy
technique for collecting airway samples
Tracheal wash