lec 5 (mcbride) - one carbon metabolism
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
folic acid
folic acid (vitamin b9) = critical for reactions with one-carbon units
typical reaction type
transfer of one carbon components; thymine synthesis
consequences of deficiency
anemia
neural-tube defects in development
sources of folic acid
naturally found in many foods
beans
peas
asparagus
eggs
leafy greens
beets
citrus fruits
brussel sprouts
broccoli
nuts and seeds
also added to foods and sold as supplement
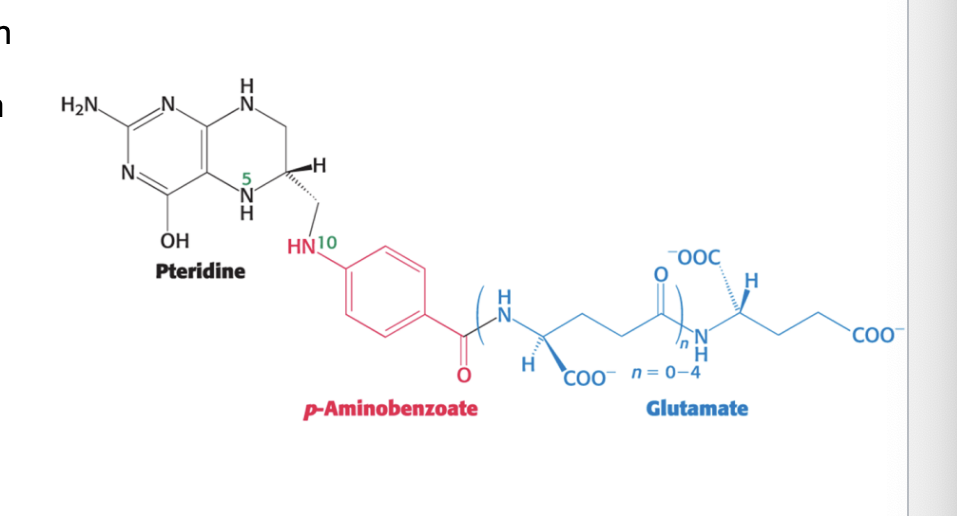
folic acid is made up of 3 components
pteridine ring
p-aminobenzoate (PABA)
glutamate
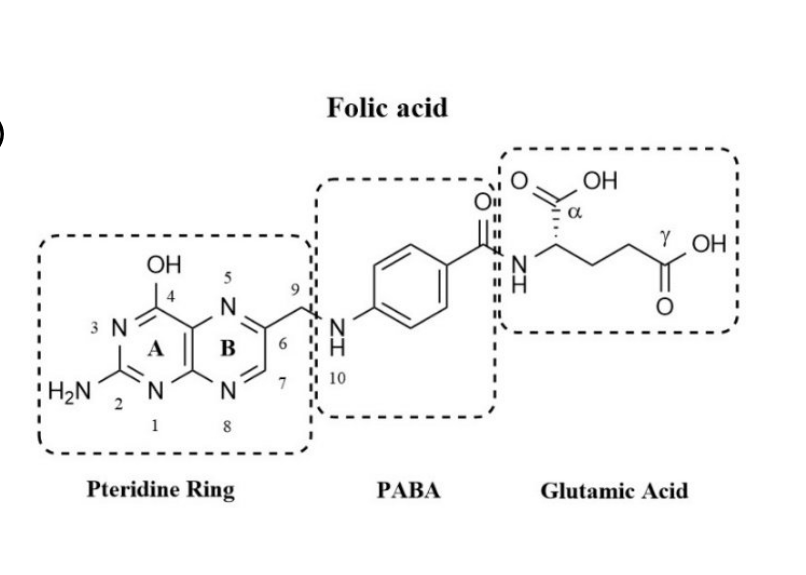
folic acid becomes…
polyglutamated
variable chain length polyglutamate tail serves to localize the molecule within cell
monoglutamates = actively transported across the cell membrane
for retention within the cell, folates are polyglutamates which redcues their affinity for the transporter and enhances their affinity for folate enzymes
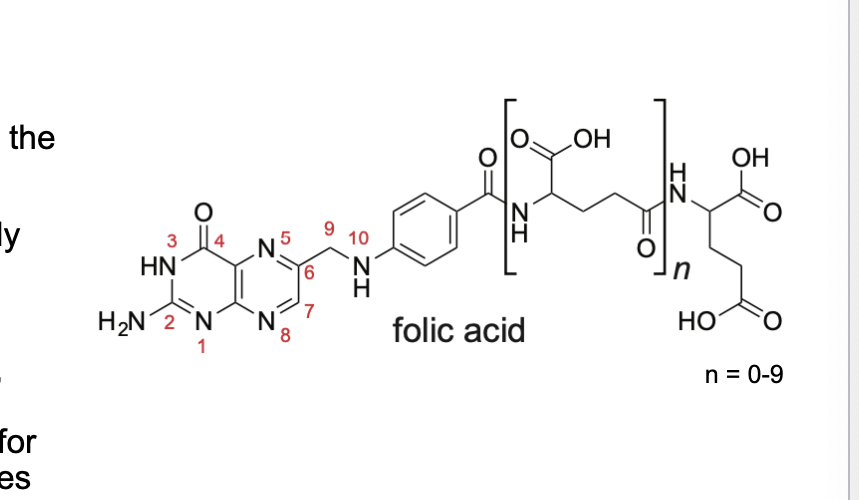
folic acid deficiency during pregnancy…
increases risk of neural tube defects
MRC vitamin study → showed that about 80% of neural tube defects could be prevented by taking 4 mg folic acid immediately BEFORE pregnancy
defects result when the neural tubes fail to close properly
rapidly dividing cells of the developing neural tube requires the synthesis of large amounts of nucleotides to facilitate DNA replication
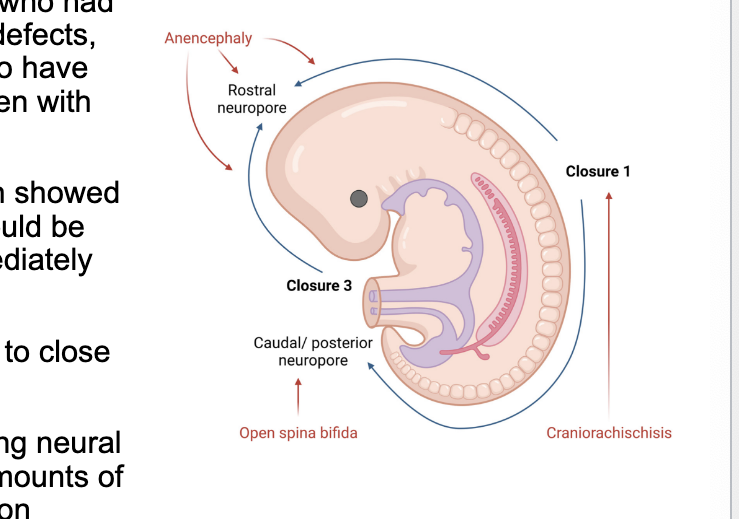
folic acid must be converted to …
tetrahydrofolate (THF)
folic acid is sequentically reduced → DHF → THF
enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) carries out both steps
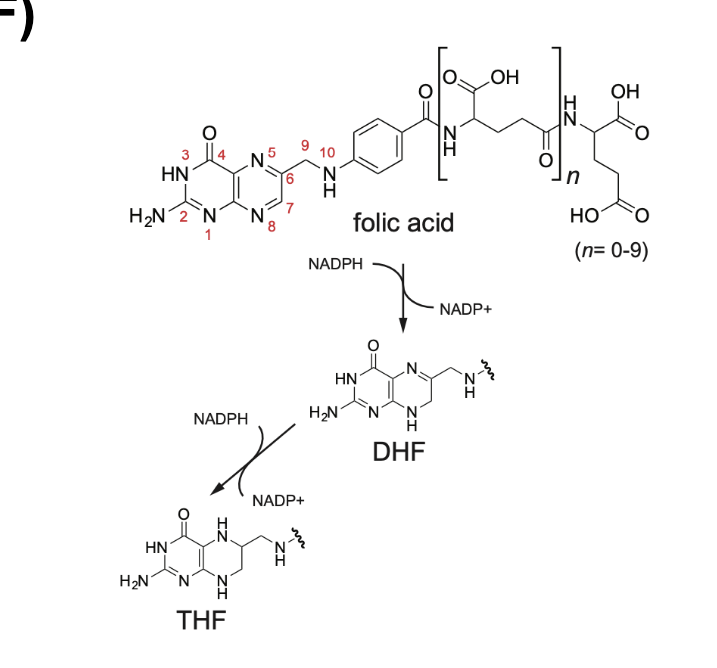
tetrahydrofolate (THF)
is the coenzyme form
THF = important carrier of activated one carbon units
the one-carbon group carried by THF is bonded to its N-5 or N-10 nitrogen atom or to BOTH
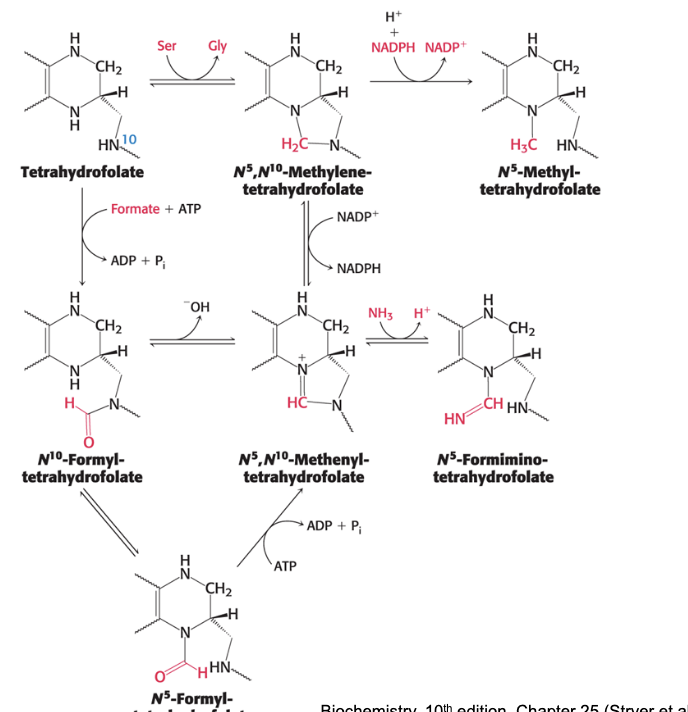
tetrahydrofolate is the carrier for one-carbon units in different oxidative states
one carbon groups carried by tetrahydrofolate
most reduced = methanol → -CH3 → methyl (group name)
intermediate = formaldehyde → -CH2- → methylene (group name)
most oxidized = formic acid → -CHO/-CHNH/-CH= → formyl/formimino/methenyl (group name)
one carbon units attach to THF in an…
interconvertible manner
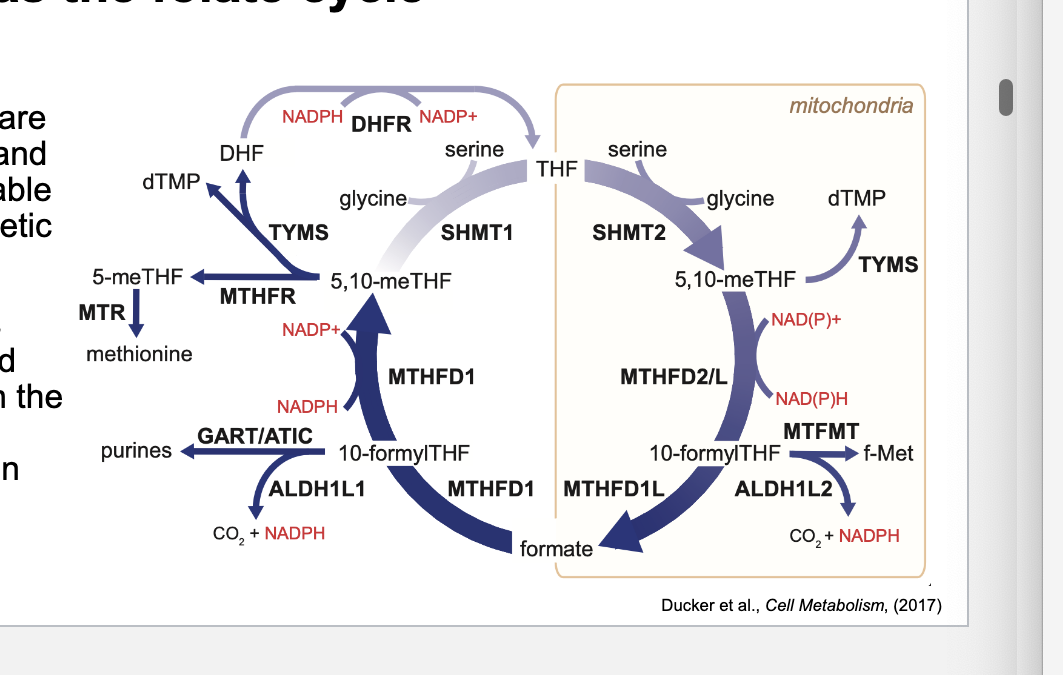
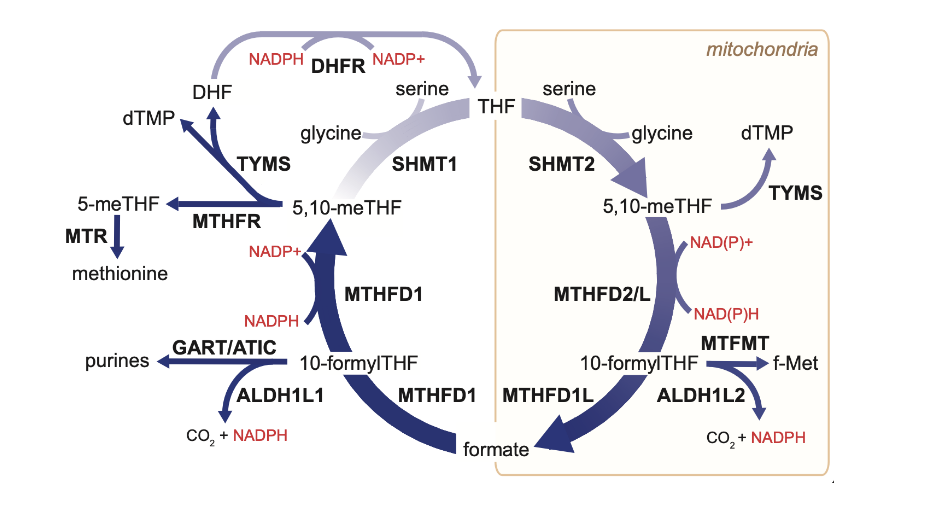
folate cycle
the processing of modifying THF = folate cycle
1C units are loaded onto THF and converted into usable forms for biosynthetic processes
folate cycle is compartmentalized and occurs in both the cytoplasm and mitochondria within cells
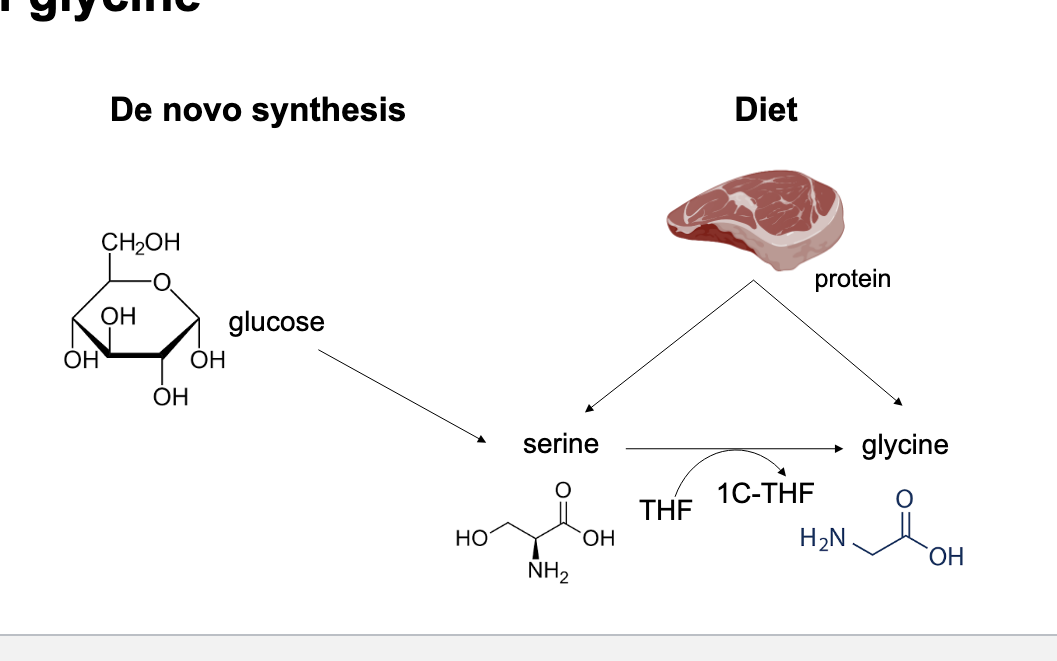
THF is critical in…
de novo synthesis of glycine
de novo synthesis
glucose → serine → through THF glycine made
diet (protein)
creates both serines and glycine
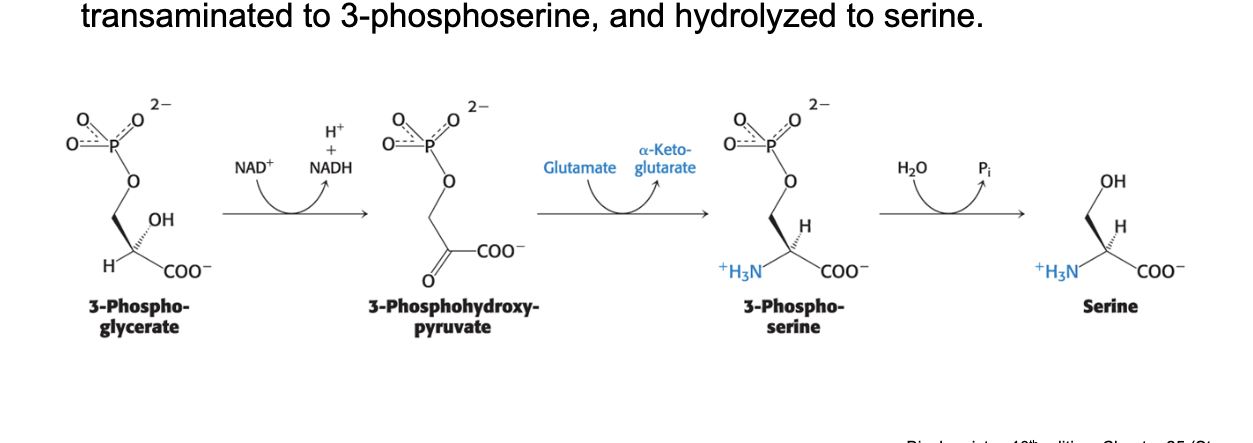
precursor of serine synthesis
3-phosphoglycerate is the precursor of serine synthesis
serine is synthesized from the glycolytic intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate
3-phosphoglycerate is oxidized to 3-phosphohydroxypyrvuate → transaminated to 3-phosphoserine → hydrolyzed to serine
precursor of glycine
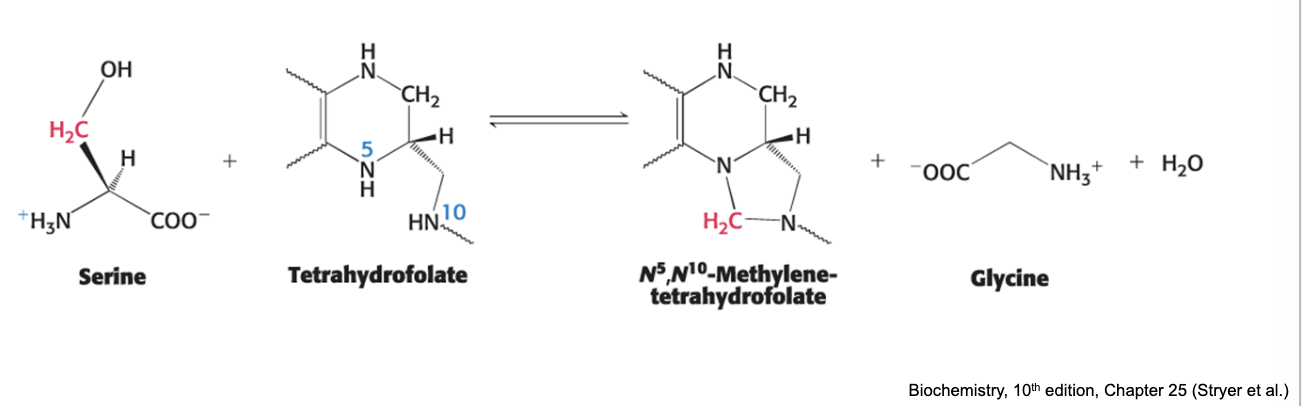
serine is the precursor of glycine
in the formation of glycine, the side-chain methylene group of serine is transferred to THF
catalyzed by PLP enzyme serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT1 or SHMT2)
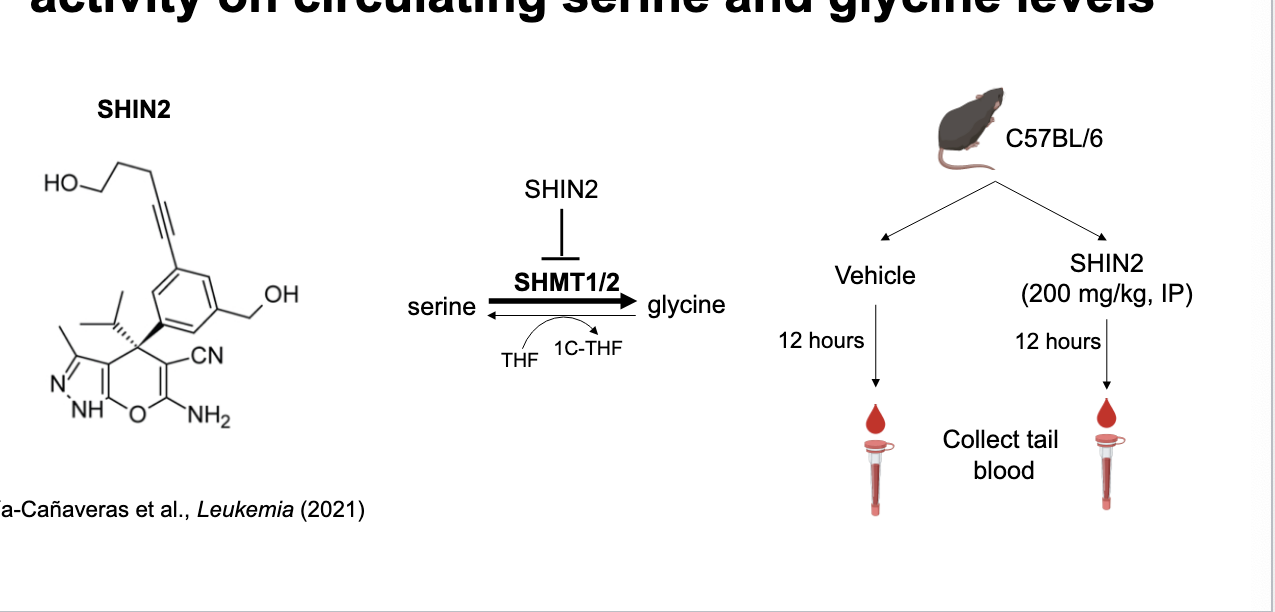
experiment to understand the role of SHMT activity on circulating serine and glycine levels
LOK AT HIS VIDEO
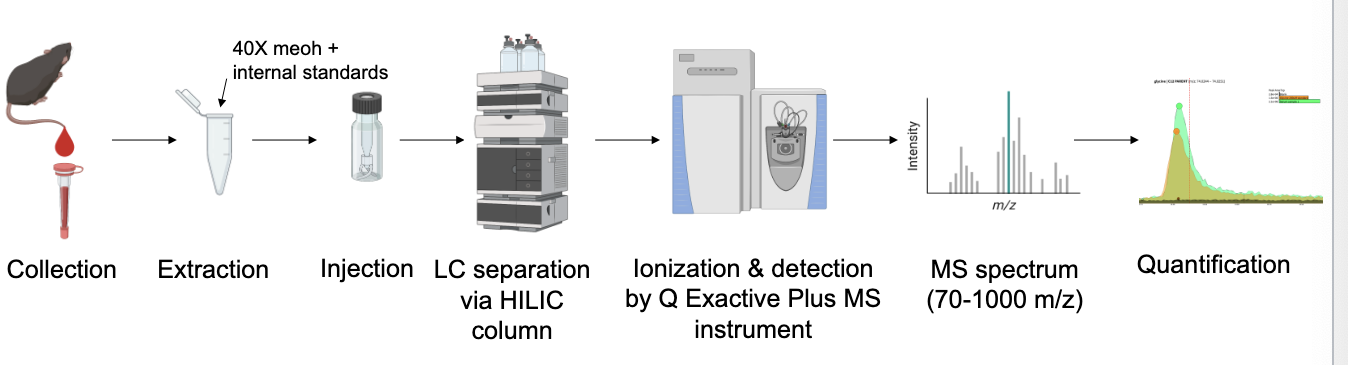
quantifying metabolite levels using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)
collection → extraction → injection → LC separation via HILIC column → ionization & detection by Q exactive plus MS instrument → MS spectrum → quantification
separate and detect up to 400 water soluble metabolites with a single 25 minute method
inhibiting SHMT 1/2 elevates glycine levels
SHIN inhibits SHMT1/2
SHMT1/2 converts serine → glycine while also transferring a 1C unit to THF; when inhibited, reaction is blocked, leading to buildup of glycine as in order for glycine → serine it needs the 1C-THF
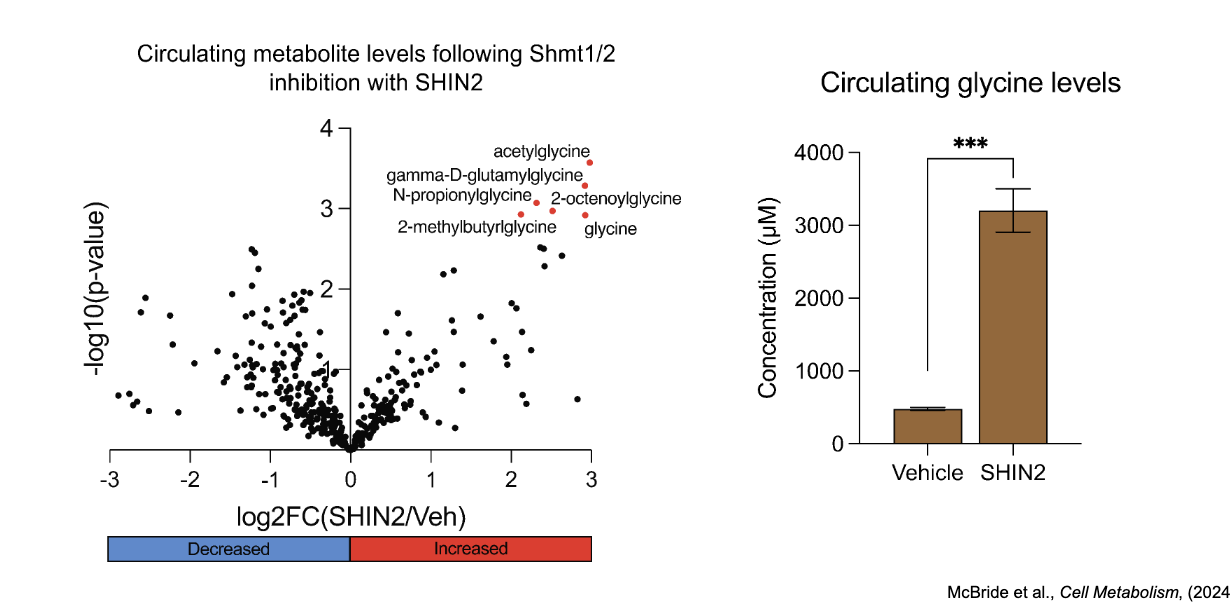
whole body glycine clearance
reverse SHMT flux in the liver is required for whole body glycine clearance
most tissues and proliferating cells have forward SHMT FLUX where serine → glycine
highlights the highly reservable nature of reactions with exchange of a 1C unit via the coenzyme THF
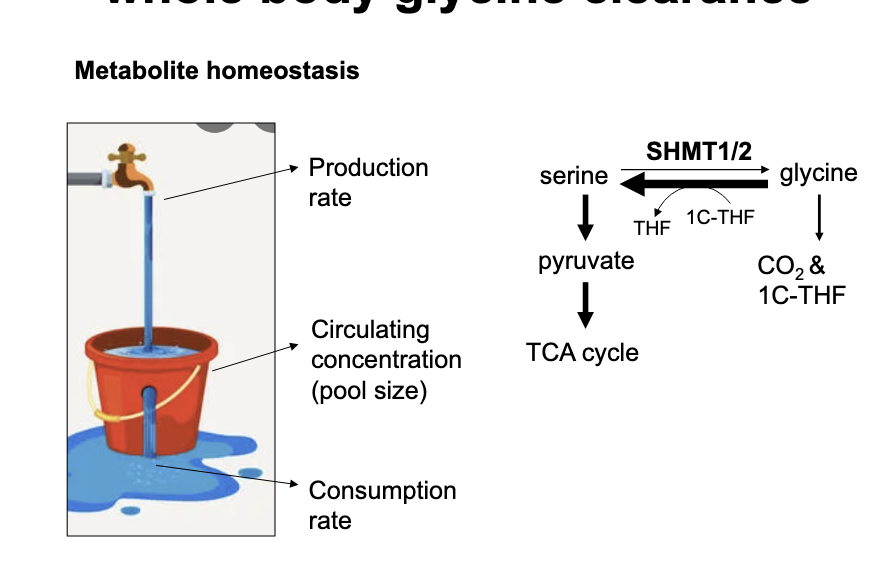
glycine is also cleared by glycine cleavage system
glycine cleavage system is a series of 4 enzymes that convert glycine → CO2 and 5,10-methyleneTHF
predominately active in liver
critical source of 1C units in early development
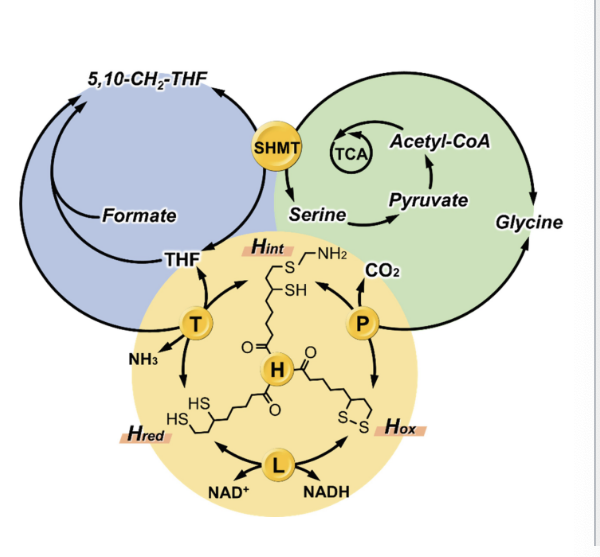
SHMT and glycine cleavage system = major contributors to glycine clearance
historically, glycine cleavage system was thought to be major pathway of glycine clearance in mammals
however, liver knockout of either SHMT2 or major enzyme of the glycine cleavage system (GLDC) dramatically elevate glycine levels in mouse models
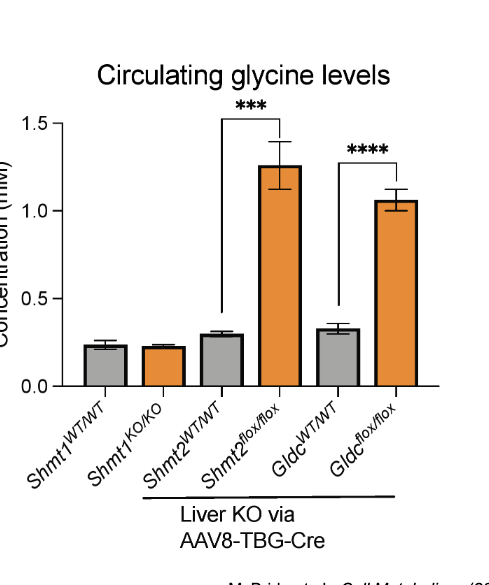
synthesis of methionine
1C unit, as 5-methylTHF, is required for the synthesis of methionine
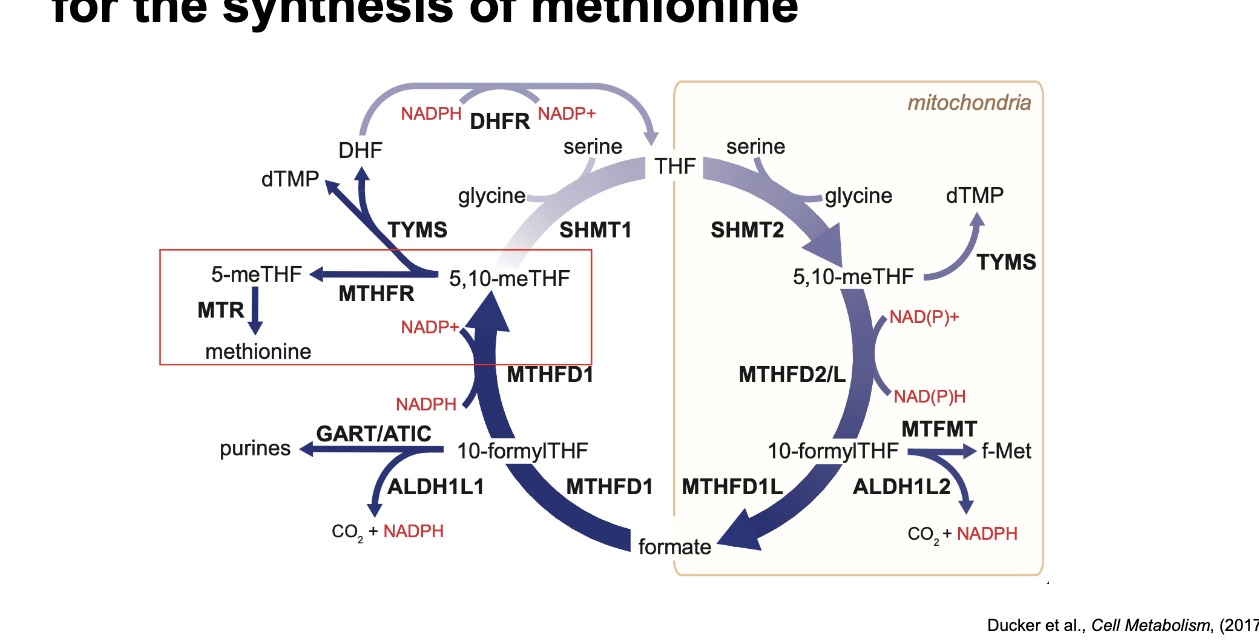
methionine cycle
is coupled to folate cycle
methionine = essential amino acid b/c the full carbon backbone CANNOT be synthesized so must be obtained from diet
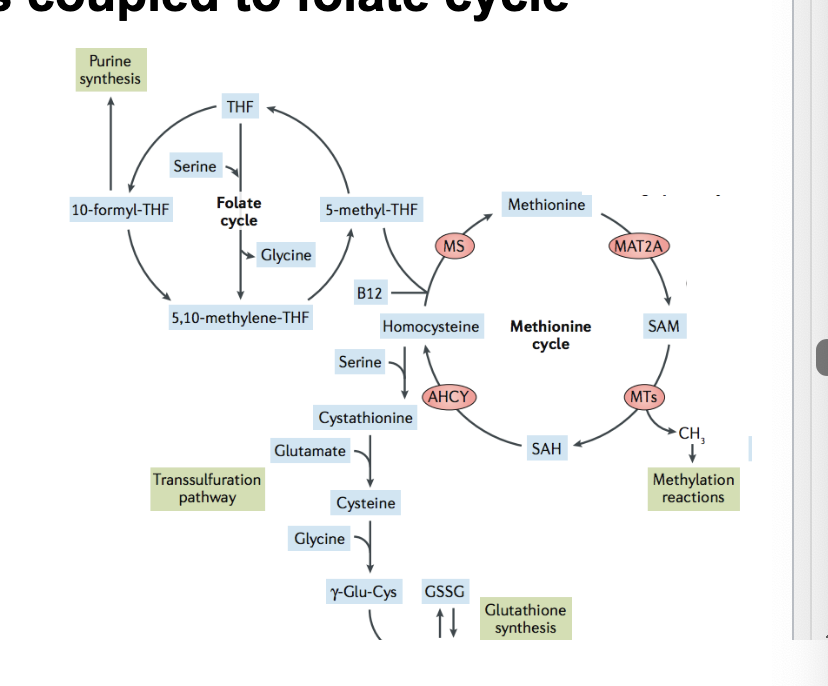
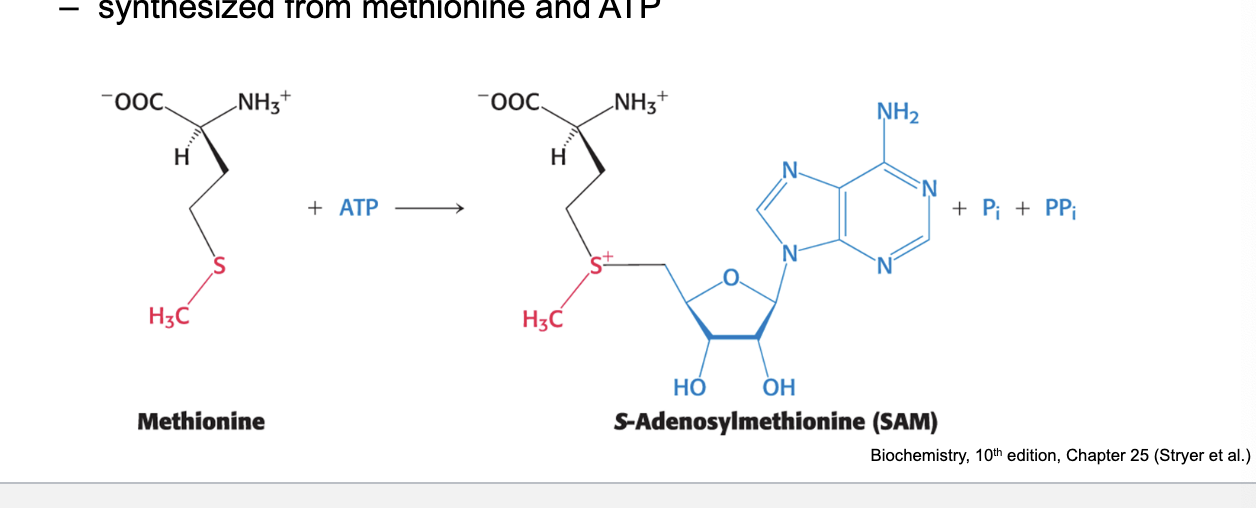
major donor of methyl groups
s-adenosylmethionine = major donor of methyl groups
SAM = activated methyl donor with higher transfer potential than THF
synthesized from methionine and ATP
methylation by SAM is…
critical modification for numerous biological functions
methylation of DNA, typically on cytosine ring, is generally repressive of gene expression
methylation of histone proteins, typically on lysine or arginine residues, can either promote or repress gene expression depending on the chromatin structure and recruitment of other proteins
methylation of RNA, typically on adenine, can influence splicing, stability, nuclear export, translation and other properties
methylation of proteins can play important regulatory roles by influencing structure
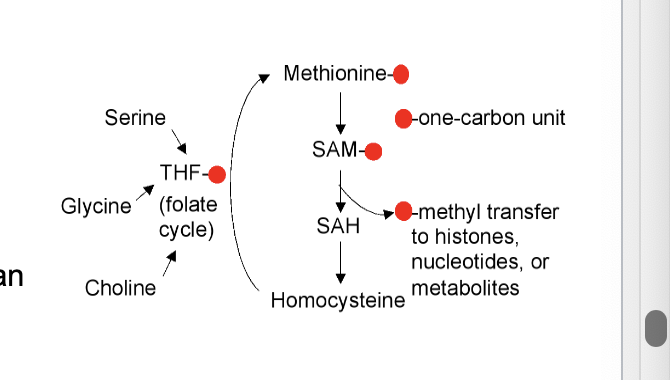
SAM is converted to…
homocysteine
after donation of methyl group by SAM, resulting s-adenosylhomocysteine is hydrolyzed, yielding adenosine and homocysteine
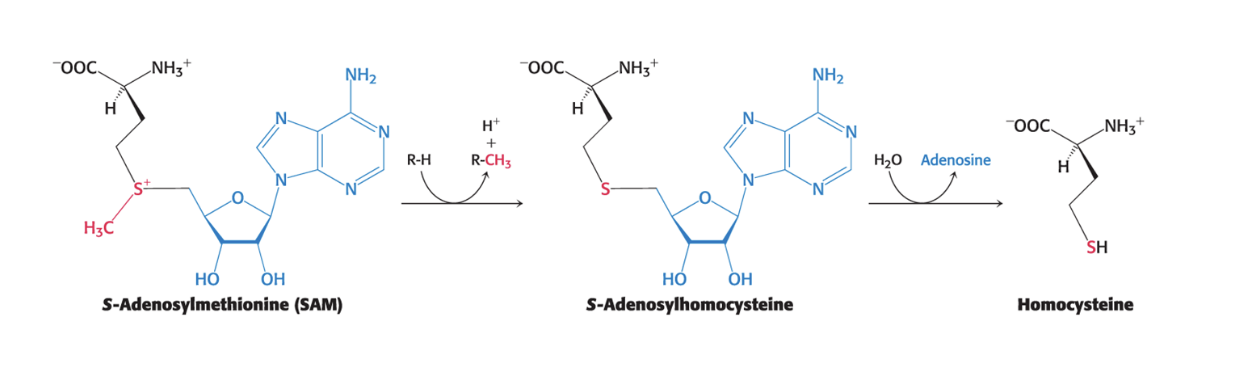
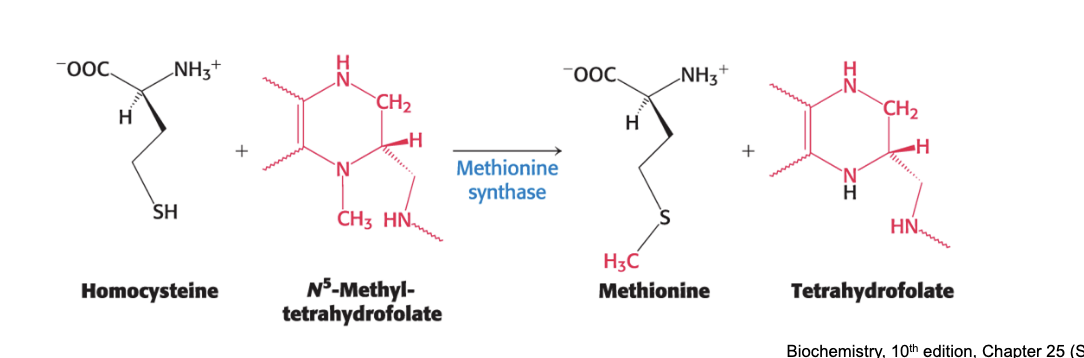
regeneration of methionine
methionine is regenerated by transfer of methyl group to homocysteine from N5-methyltetrahydrofolate
catalyzed by methionine synthase
mediated by the coenzyme methylcobalamin which is derived from vitamin B12
deficiency of vitamin b12 or folic acid can lead to…
increased homocysteine levels
regularly homocysteine is converted back to methionine via methionine synthase which requires 5-methyl-THF (provides methyl curve), vit. B12 (acts as cofactor), methionine synthase (catalyzes the rxn)
WITHOUT folic acid, NO 5-methyl-THF so homocysteine CANNOT be converted into methionine
even if folate is present, B12 is required as cofactor and without it
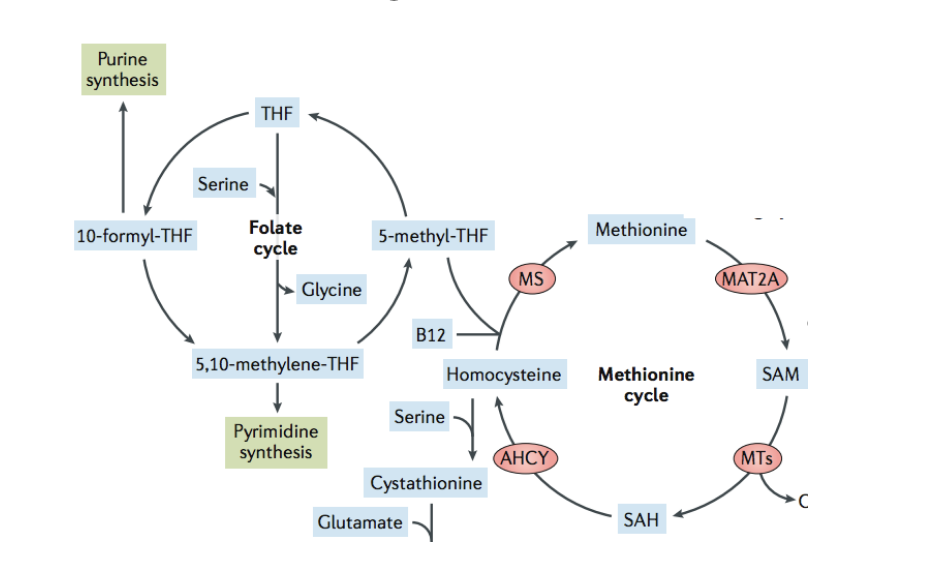
high homocysteine levels…
correlate with vascular disease
elevated serum levels of homocysteine or the disulfide-linked dimer homocysteine = predisposing factor for coronary heart disease and arteriosclerosis
elevated homocysteine levels can also result from mutations in the gene encoding cystathionine β-synthase
high levels of homocysteine:
damage cells lining blood vessels
increase the growth of vascular smooth muscle
raise oxidative stress
implicated in the development of type 2 diabetes
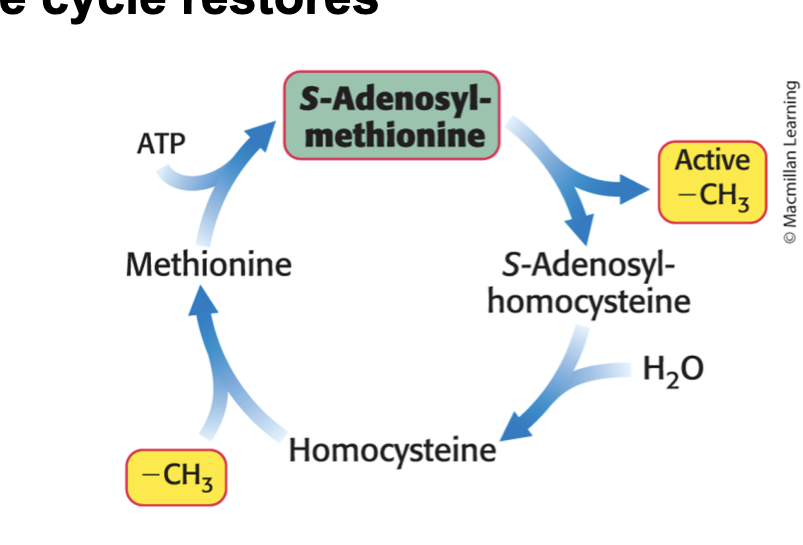
formation of SAM activates…
methyl group of methonine which the folate cycle restores
SAM loses active -CH3 → s-adenosylhomocysteine → hydrolyzed to homocysteine → gains -CH3 group (from folate cycle) to become methionine → ATP to become SAM
nucleotides can be synthesized by de novo or salvage pathways
nucleotides are key biomolecules
activated precursors of nucleic acids
ATP = universal currency of energy
GTP = energy source
nucleotide derivatives participate in biosynthetic processes
cAMP and cGMP = essential components of signal-transduction pathways
ATP = acts as donor of phosphoryl groups transferred by protein kinases
de novo pathway
activate ribose (PRPP) + amino acids + ATP + CO2 + … → nucleotide
salvage pathway
activated (PRPP) + base → nucleotide
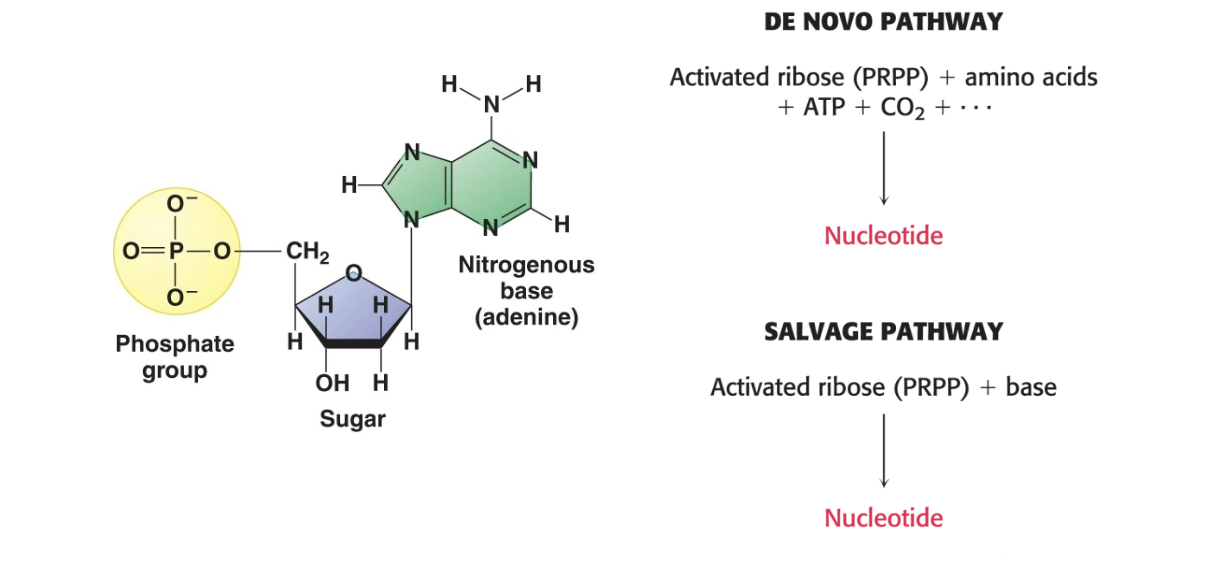
de novo and salvage pathways use different starting material for nucleotide synthesis
de novo pathways = pathways in which nucleobases are assembled from scratch
for pyrimidines, framework for the base is assembled first and then attached to ribose
for purines, base is synthesized piece by piece directly onto a ribose-based structure
salvage pathays = pathways in which preformed bases are recovered and reconnected to a ribose unit
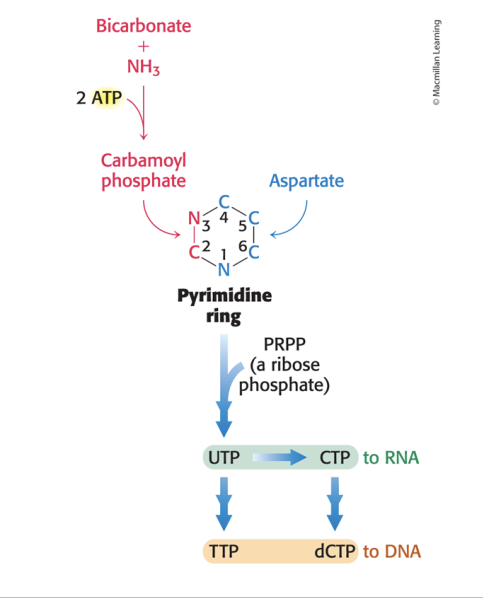
pyrimidine ring
assembled de novo from CO2, ammonia, aspartate
pyrimidine rings are assembled from bicarbonate, aspartate and ammonia
glutamate often serves as ammonia donor
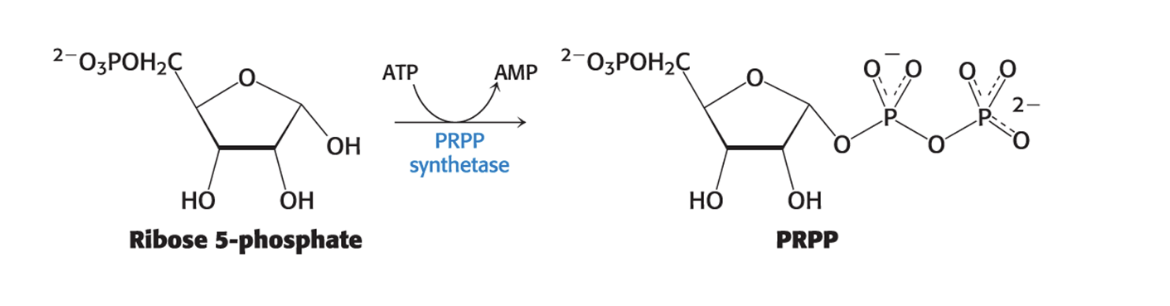
formation of PRPP
5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyroposphate (PRPP) = form of ribose activated to accept nucleobases
synthesized by 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate synthetase
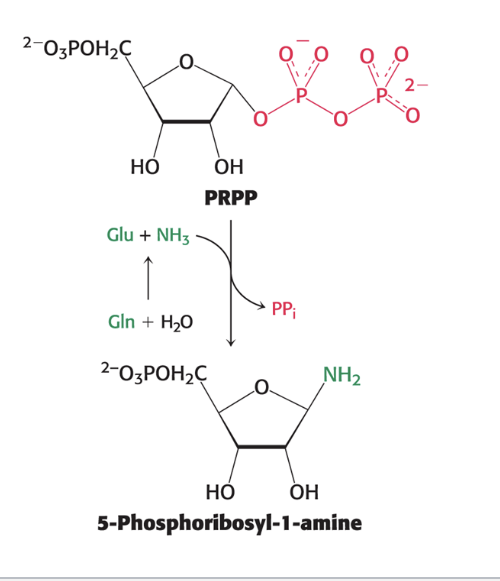
glutamine and purine synthesis
glutamine provides the nitrogen via ammonia for the committed step in purine synthesis
purine bases are assembled already attached to the ribose ring
committed step in purine biosynthesis forms 5-phosphoribosyl-1-amien from PRPP and glutamine
catalyzed by glutamine phosphoribosyl amidotransferase
purine nucleotide synthesis
requires 1C units as 10-formylTHF from folate cycle
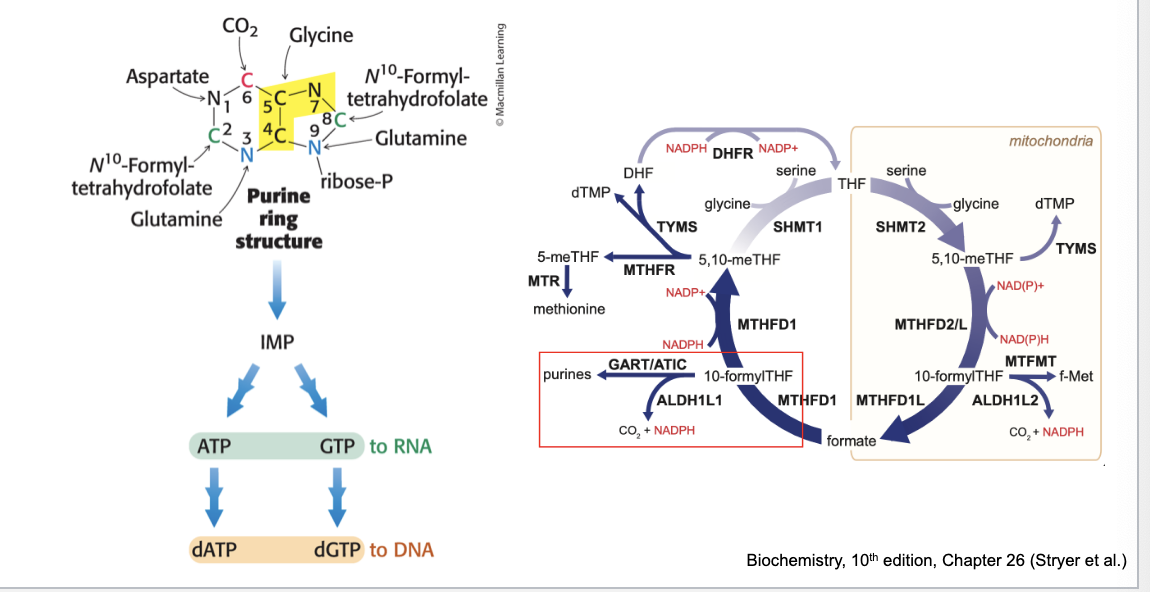
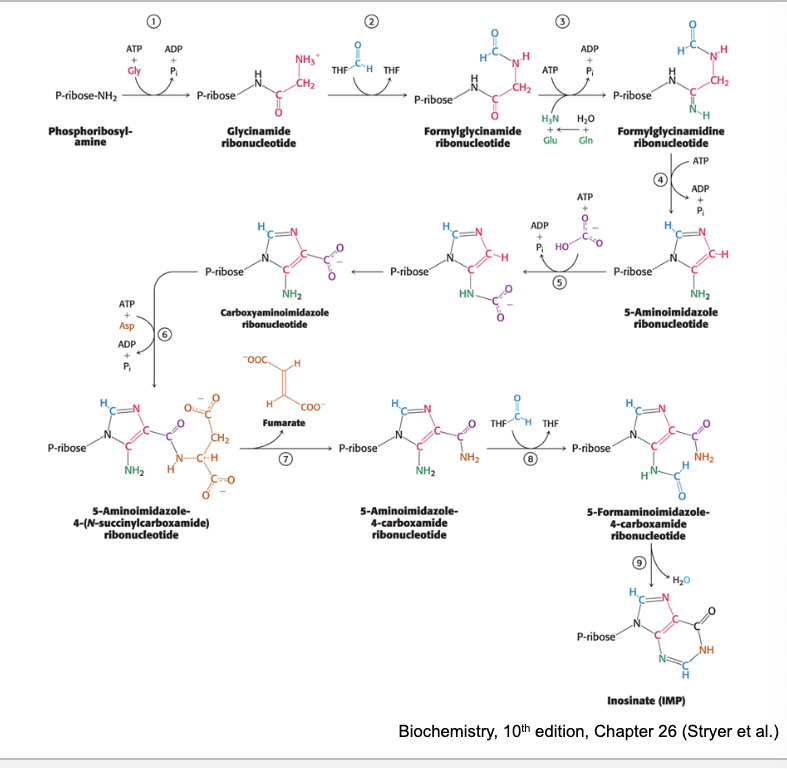
de novo purine biosynthesis pathway
2 of the enzymes in the de novo purine biosynthesis pathway require 10-formyl-THF
glycinamide ribonucleotide → formylglycinamide ribonucleotide
3-aminoidazole-4-carboxyamide ribonucleotide → 5-formaminoimidazole-4-carboxyamide ribonucleotide
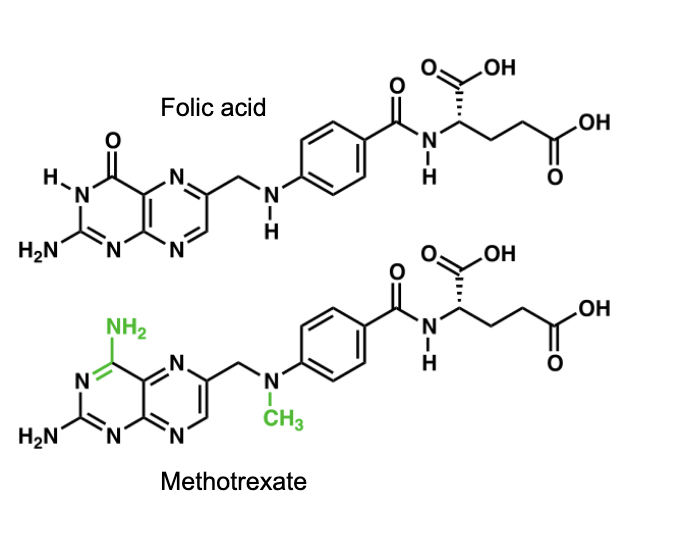
first chemotherapeutic agents
the first chemotherapeutic agents were antifolates
Dr. Sydney Farber treated 16 children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (AML) with aminopterin, amino derivative of folic acid
10 of the pts → temporary remission
trial = first ever succesful remission of leukaemia and foundation of modern chemotherapy
aminopterin → developed to methotrexate; less toxic and commonly used in chemotherapy treatment
methotrexate
is a folic acid derivative
chemotherapeutic agent in many types of cancer
immunosuppressant used to treat inflammatory conditions including rheumatoid arthritis
methotrexate is a DHFR inhibitor
inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR)
prevents generation of THF to carry 1C units for purine synthesis
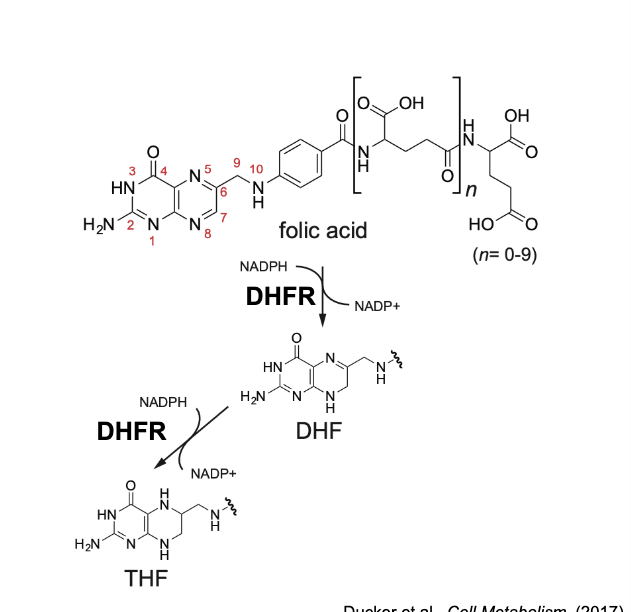
methotrexate and other antifolate therapies mechanism
block cell division by depleting 10-formylTHF levels and inhibiting purine synthesis
in a patient with folic acid deficiency, what synthetic form of folic acid is optimal for this person to receive?
A. no glutamate tail
B. monoglutamated
C. di-glutamated
D. highly polyglutamated
answer = monoglutamated
polyglutamated would be stuck in circulation b/c it has poor affinity for transporter the tissues that need the folic acid won’t be able to take it up
monoglutamated lets it enter different tissues → polyglutamated to stay in cell
how is 5,10-meTHF generated in the mitochondria transported to the cytoplasm for biosynthetic processes in the cellular compartment that require this form of a 1C unit?
A. passive diffusion
B. active transport
C. broken-down and re-synthesized
answer = broken down and re-synthesized
5,10-meTHF → 10-formylTHF via MTHFD2/L → formate via MTHFD1L → formate diffuses out of mitochondria and enters the cytoplasm → formate reconverted into 10-formylTHF via MTHFD1 → 5,10-meTHF via MTHFD1
if a cancer cell line is growing in folic acid-supplemented culture media and then is suddenly switched into folic acid-free culture media, how would you predict the levels of serine and glycine would change?
A. serine increases and glycine decreases
B. serine decreases and glycine increases
C. serine and glycine both increase
D. serine and glycine both decrease
answer = serine increases and glycine decreases
removing vitamin precursor of folic acid → reduce THF → THF is substrate for SHMT rxn → less conversion of serine into glycine
a patient consumes 100 mols of glycine supplement and all of the glycine is cleared in the liver; 25 moles is cleared by SHMT to make serine and 75 mols is cleared by glycine cleavage system to make CO2. what is the predicted change to 5,10-methyleneTHF levels in the liver?
A. increase by 10 mols
B. increase by 50 mols
C. decrease by 100 mols
D. decrease by 50 mols
answer = increase by 50 mols
through the SHMT rxn 25 mols of glycine is converted to serine which consumes 25 mols of 5,10-meTHF → THF
through glycine cleavage system, 75 mols of glycine make 75 mols of CO2 and also 5,10-meTHF
75-25 = +50 mols