102 sea eggs ham one
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
How has the view of abnormal behavior changed over time?
It was originally thought to be specifically about mental disorders, but now reflects the growing frequency of mental disorders, which are no longer considered abnormal.
What are the problems with referring to psychopathology as 'abnormal'?
The term 'abnormal' is linked to stigma and undermines hope for forward-thinking approaches to mental health.
What are the seven indicators of abnormality?
1. Subjective distress; 2. Maladaptiveness; 3. Statistical deviancy; 4. Violation of societal standards; 5. Social discomfort; 6. Irrationality and unpredictability; 7. Dangerousness.
What is the DSM and why is it revised?
The DSM, or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, is an unfinished project that is revised as new scientific developments and cultural understandings occur.
What are the pros and cons of classification and diagnosis in mental health?
Pros: Structures information, allows a common language, facilitates research. Cons: Can facilitate stigma, stereotyping, labeling, bullying, and discrimination.
How do cultural influences affect perceptions and diagnosis of mental illness?
Cultural influences can affect the expression of disorders and the willingness to seek treatment, with some cultures focusing more on physical symptoms than emotional ones.
What are cultural-bound syndromes?
Cultural-bound syndromes are specific mental health conditions that are recognized within certain cultures, such as Ataque de nervios (panic attacks) in Hispanic cultures and Ghost Sickness (depression) in Native American cultures.
What is the difference between reliability and validity in psychological measurement?
Reliability refers to the consistency of a measurement, while validity refers to the accuracy and relevance of a measurement.
What is the difference between incidence and prevalence?
Incidence is the number of new cases of a disorder in a given period, while prevalence is the total number of cases in a population during that period.
What are the most common and least common mental disorders?
Most common: Major depressive disorder, alcohol abuse, specific phobias, social phobia, conduct disorder. Least common: Schizophrenia, Alice in Wonderland Syndrome (AIWS).
What is the case study method in psychopathology research?
An in-depth analysis of a single individual or small group to gain detailed insights into rare or complex conditions, though it lacks generalizability.
What are the strengths and limitations of self-report data in research?
Strengths: Efficient for large samples. Limitations: Possible social desirability bias or inaccurate reporting.
What is the purpose of observational research in psychopathology?
To observe and record behavior in a lab or natural environment, providing real behavioral data, but it can be time-consuming and subject to observer bias.
What is the significance of correlational design in research?
It examines relationships between variables without manipulation, but correlation does not imply causation.
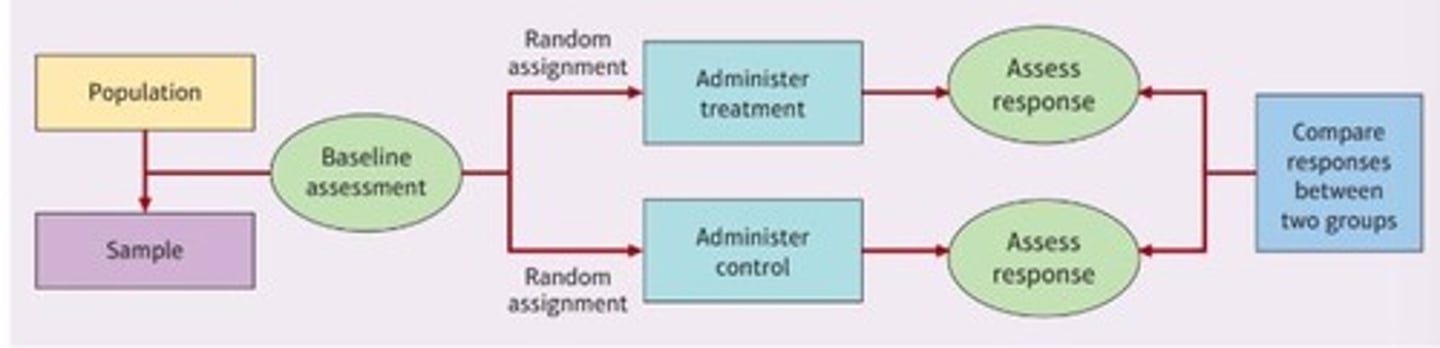
What is experimental design in psychopathology research?
It determines causal relationships by manipulating variables, allowing for inferences about causality and high internal validity.
What are the different types of prevalence in epidemiology?
1. Point-prevalence: active cases at a specific time. 2. 1-year prevalence: cases throughout the year. 3. Lifetime prevalence: cases at any time in life.
What are the criteria for demonstrating causality?
There must be correlation, effects must not be explained by time, and no spurious correlation should exist.
What are the key components of experimental design?
Independent variable (manipulated factor), dependent variable (outcome studied), random assignment (equal chance for participants), double-blind study (neither researchers nor participants know group assignments), placebo treatment (ineffective treatment to control for belief effects).
What was the humanitarian reform in mental health treatment?
A movement advocating for more humane treatment of patients after 200 years of inhumane practices in asylums, focusing on social, individual, and occupational needs.
What is deinstitutionalization in mental health?
The movement to close psychiatric hospitals and integrate patients into communities which aimed to provide humane treatment but often lacked sufficient resources. Spike in homelessness and low quality of living
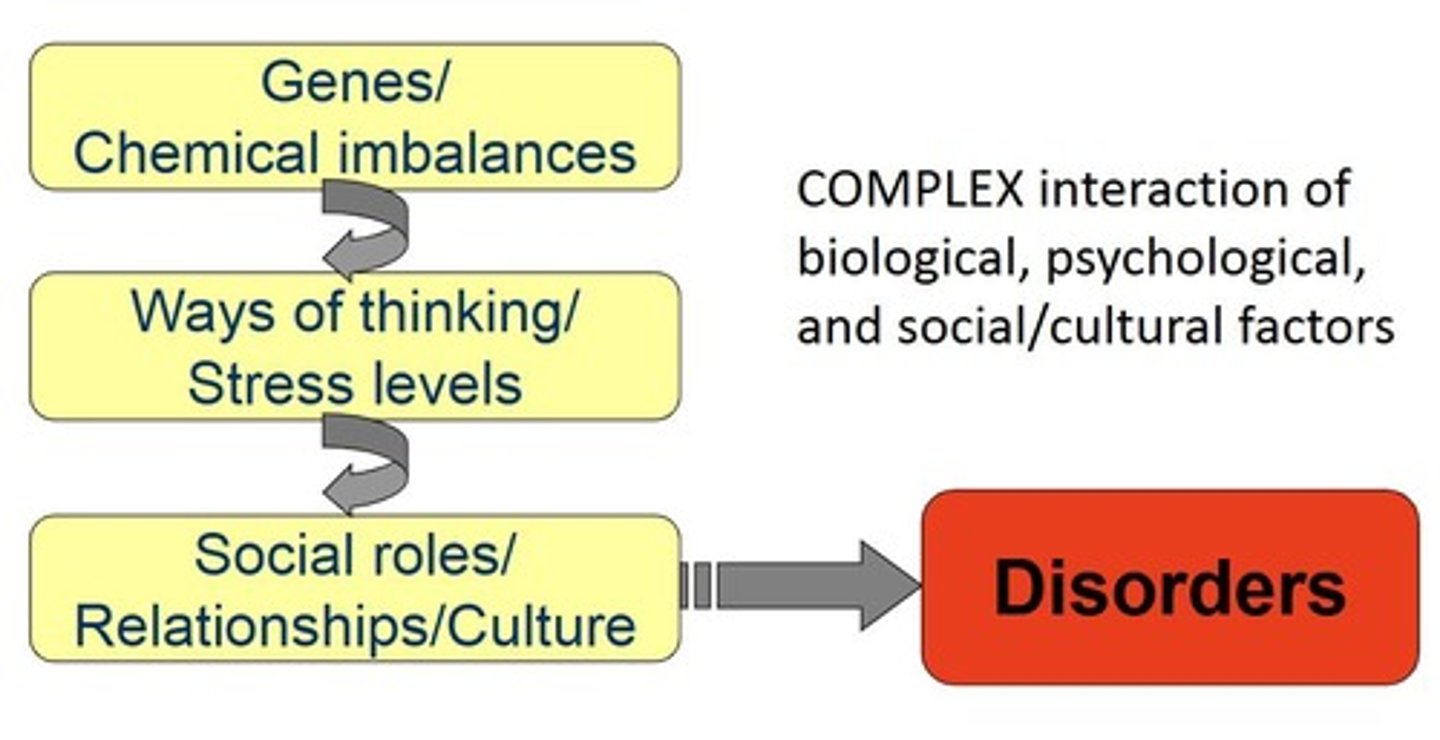
What is the biopsychosocial model of abnormal behavior?
It emphasizes the interaction between biological, psychological, and social aspects that affect overall well-being.
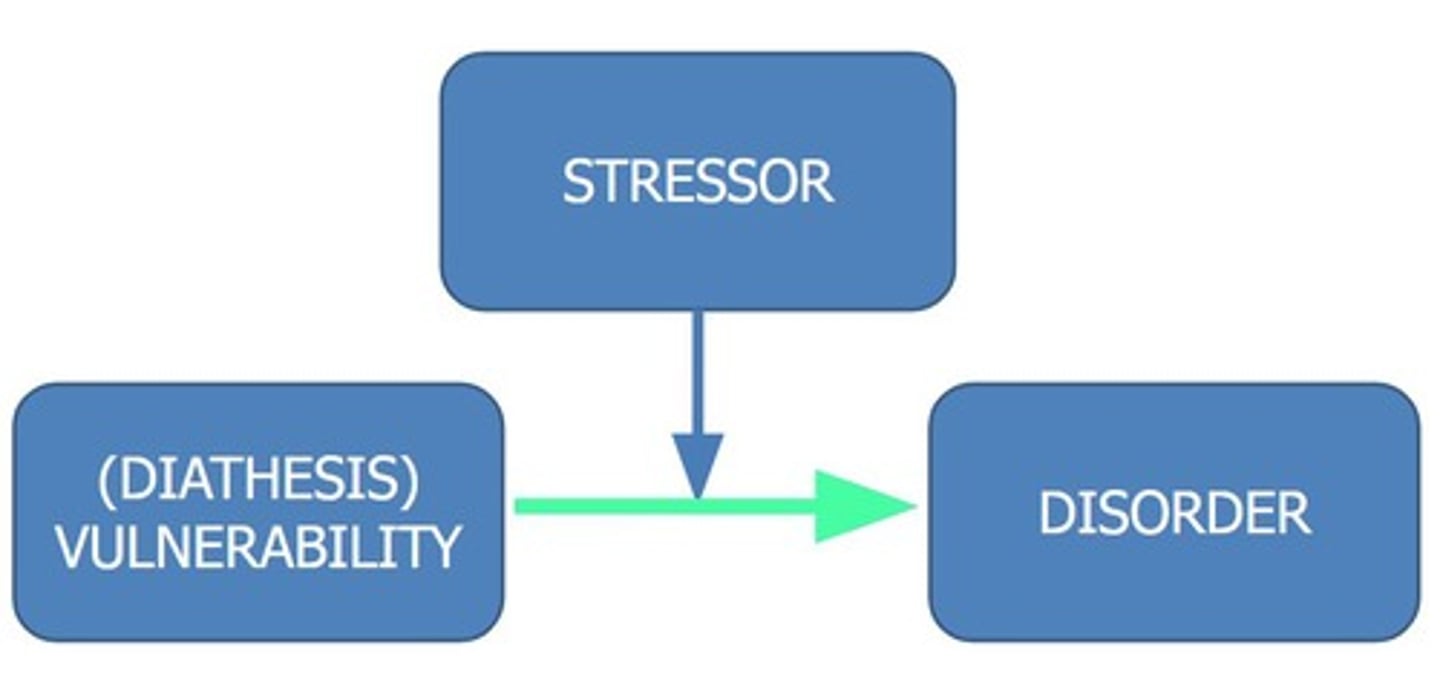
What is the Diathesis-Stress Model?
It posits that a predisposition/vulnerability to a disorder (diathesis) combined with a stressor leads to the development of the disorder.
What does the term 'etiology' refer to in psychology?
Etiology refers to the cause or origin of a disease.
What are the main goals of etiological research?
To understand what is necessary and sufficient for a disease, distinguishing between necessary and sufficient conditions.
Define 'necessary' in the context of psychopathology.
A necessary condition must be present for a disorder to occur.
Define 'sufficient' in the context of psychopathology.
A sufficient condition will produce the disorder but is not the only way to do so.
What are 'contributory' factors in psychopathology?
Factors that increase the probability of a disorder but are neither necessary nor sufficient.
What are 'distal' factors in psychopathology?
Factors that occur early before the onset of the disorder.
What are 'proximal' factors in psychopathology?
Factors that occur shortly before the onset of the disorder.
How did syphilis influence the understanding of abnormal behavior?
The discovery that syphilis caused general paresis linked biological infection to mental illness, leading to medical treatments for mental disorders.
What is the significance of Freud's work in psychoanalysis?
Freud's work emphasized the role of unconscious processes and early childhood experiences in the development of disorders.
What is the role of neurotransmitters in abnormal behavior?
Neurotransmitters are chemical substances that influence mood and behavior, and imbalances can lead to mental disorders.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype refers to the expressed traits.
What is behavior genetics?
A field that studies the genetic influences on behavior, often using methods like twin studies and adoption studies.
What is the focus of the behavioral perspective on abnormal behavior?
It emphasizes observable behavior and the idea that abnormal behavior is learned, similar to normal behavior.
What is classical conditioning?
A learning process where a neutral stimulus is paired with an unconditioned stimulus to elicit a conditioned response.
What is the difference between generalization and discrimination in classical conditioning?
Generalization is responding similarly to different stimuli, while discrimination is learning to respond differently to distinct stimuli.
What is operant conditioning?
A learning process where behavior is modified by its consequences, such as reinforcement or punishment.
What is the purpose of systematic desensitization in behavior therapy?
It gradually exposes individuals to feared stimuli while practicing relaxation techniques to reduce anxiety.
What is the Bobo Doll study and its significance?
A study demonstrating observational learning, where children imitated aggressive behavior towards a Bobo doll after seeing adults do the same.
What is the role of hormones in abnormal behavior?
Hormones are chemical messengers that can influence mood and behavior, and imbalances may contribute to mental disorders.
What is the criticism of early psychoanalytic theories?
Critiques include lack of scientific validation, overemphasis on sexual drive, and failure to consider growth and fulfillment.
What is attachment theory?
A theory emphasizing the importance of early relationships and environments on later psychological development.
What is the significance of the biopsychosocial model?
It integrates biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors in understanding mental disorders.
What is the role of temperament in abnormal behavior?
Temperament refers to an individual's biologically-based emotional and behavioral style, influencing their reactions to the environment.
What is the core idea of the cognitive-behavioral perspective on abnormal behavior?
Abnormal behavior results from failure to learn and/or learning ineffective/dysfunctional responses to the environment, which influence emotions and actions.
What influenced the emergence of the cognitive-behavioral perspective?
It emerged in the 1960-70s as psychologists integrated learning theory with cognitive psychology, influenced by Albert Bandura's Social Learning Theory and Aaron Beck's ideas on depression (depression thought to result from negative automatic thoughts and distortions about the self, world, and future).
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)?
CBT is a treatment that focuses on changing maladaptive and irrational thoughts and behaviors through structured, goal-oriented methods.
What are schemas in the context of cognitive behavioral theory (CBT)?
Schemas are cognitive frameworks that guide how we think and live. Different schemas influence distortions of thinking that are characteristic of certain disorders (i.e depression, anxiety, personality disorders)
What is the difference between assimilation and accommodation?
Assimilation is the process of integrating new experiences into existing cognitive frameworks, while accommodation involves changing those frameworks to incorporate new information.
What does attribution theory involve?
Attribution theory is the process of assigning causes to events, with attributional styles reflecting how individuals typically assign causes to good or bad events (i.e someone depressed might attribute bad events to internal causes like "I failed a test because I was stupid")
How do sociocultural factors influence psychopathology?
Cultural values, family structures, and community environments shape the development, expression, and treatment of disorders.
What impact does early deprivation or trauma have on children?
Children lacking resources for proper development may suffer psychological scars, leading to emotional, behavioral, and learning problems. Causes come from a lack of food, love, shelter, or attention. Commonly seen in orphans.
What is an authoritative parenting style?
Parents have high warmth, moderate control, set clear limits and restrictions on certain behaviors. Children tend to be friendly and are competent in dealing with others and environments.
What is the authoritarian parenting style?
Parents with low warmth, high control, and cold/demanding. Children are conflicted, irritable/moody, and have poor social & cognitive skills in adolescence.
What is the permissive/indulgent parenting style?
Parents with high warmth, low control & discipline. Children are impulsive/aggressive and be spoiled, selfish, impatient, inconsiderate.
What is the neglectful/uninvolved parenting style?
Parents with low warmth, low control. Children tend to be moody, have low self-esteem and have other problems in childhood, like peer relationships and academic performance.
How does marital discord and divorce affect children?
Children from high-conflict homes may exhibit aggression, while divorce can lead to feelings of insecurity and psychological issues, although it may also relieve them from a toxic environment.
What is the relationship between socioeconomic status and mental health?
Lower socioeconomic status is associated with a higher incidence of mental disorders, and unemployment can lead to financial hardship and emotional distress.
How do maladaptive peer relationships contribute to mental health issues?
Peer rejection and bullying are strong predictors of future mental health problems, including depression and suicidal thoughts/behaviors.
What effects do prejudice and discrimination have on mental health?
They can lead to anxiety, depression, low self-worth, and chronic anger, often resulting in minorities receiving misdiagnoses or inadequate treatment.
How do cultural differences influence perceptions of psychopathology?
While mental health disorders are universal, their forms and prevalence can vary across cultures, affecting symptom expression and treatment approaches.
Why are formal comprehensive assessment procedures important? (pg 17-32)
They help summarize a client's symptoms, issues, and strengths. Helps understand treatment needs and provide necessary information to insurance companies.
What is the significance of assessing social and behavioral histories?
It provides context for symptoms, identifies stressors, improves diagnosis, and guides culturally specific treatments.
What do reliability and validity mean in psychological assessment?
Reliability refers to consistency of measurement, while validity refers to the accuracy of measurement, both crucial for preventing misdiagnosis. Reliability is necessary, but not sufficient for validity.
What are neuropsychological assessments?
They are structured tests of brain function, assessing memory, language, attention, and reasoning to detect brain damage or cognitive impairment.
What are the types of psychological assessments?
They include clinical interviews (structured, unstructured, semi-structured), direct observation, projective personality tests, and objective personality tests.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of projective measures?
Advantages include revealing unconscious material; disadvantages involve low reliability and validity due to subjective interpretations.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of objective measures?
Advantages include high reliability and ease of interpretation; disadvantages include potential influence from social desirability and limited insight into unconscious factors.
Why should we care about stress and physical health?
Stress can significantly impact physical health, leading to various health issues and exacerbating mental health conditions.
What are the disadvantages of self-reported responses in psychological assessments?
Responses can be influenced by social desirability or lack of insight and may not capture deep unconscious factors.
How does stress affect physical health?
Stress affects the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to cardiovascular diseases.
What is stress?
Biological and psychological responses to demands.
When does stress occur?
When challenges to physical and emotional well-being exceed coping mechanisms.
What are the characteristics of stressors?
Severity, chronicity (how frequently it occurs), timing, proximity (not distance, think family, friend, loved one, etc.), expectedness, and controllability.
What are some effects of stress on physical health?
Immune system suppression, cardiovascular disease, brain cell damage, and premature aging.
What is cortisol and what are its benefits?
Cortisol is a hormone produced by adrenal glands that prepares the body for fight or flight in emergencies.
What negative impacts can cortisol have on health?
It can damage cells, especially in the hippocampus, and suppress the immune system.
What is an Adjustment Disorder?
A psychological response to a common stressor resulting in clinically significant behavioral/emotional symptoms.
What are the DSM criteria for Adjustment Disorder?
-Does not meet criteria for another disorder,
-isn't just bereavement,
-symptoms within 3 months of stressor onset,
-more distress than expected.
What characterizes Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Intrusive memories of a traumatic event, emotional withdrawal, and heightened autonomic arousal (body always ready for action).
What is the prevalence of PTSD?
6.8% lifetime prevalence according to DSM-5.
What is the gender ratio for PTSD prevalence?
3:1 female to male.
What are common comorbidities with PTSD?
Depression, anxiety disorders, and substance use disorders.
What biological factors are associated with PTSD?
Smaller hippocampus and higher cortisol levels in affected individuals.
What psychological factors contribute to PTSD?
Severity and duration of trauma exposure, maladaptive thoughts, and lack of social support.
What are the individual risk factors for developing PTSD?
Higher neuroticism, family history of depression/anxiety, substance abuse, low social support, and minority status.
What are common treatments for PTSD?
Cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBT), relaxation techniques, psychological debriefing, exposure therapy, and medications.
What is Acute Stress Disorder (ASD) and how does it differ from PTSD?
ASD occurs within 4 weeks of trauma, lasting 2-30 days; PTSD is a long-term response.
Note: ASD symptoms lasting over 30 days qualify as a PTSD diagnosis.
What defines an anxiety disorder?
Characterized by unrealistic, irrational fears or anxieties causing significant distress or impairment.
What is fear?
Fear is a basic emotion that involves activation of the fight or flight response of the autonomic nervous system.
What are the three parts of fear and panic?
Cognitive/subjective components, physiological components, and behavioral components.
What is an example of a cognitive component of fear?
"I'm in danger"
What are some physiological components of fear?
Increased heart rate and sweating.
What is an example of the behavioral component of fear?
Desire to escape or run.
How does anxiety differ from fear?
Anxiety is a complex blend of unpleasant emotions and cognitions that is more oriented to the future and more diffuse than fear. Not accompanied by fight or flight, instead, fear in the moment.
What are common features of anxiety disorders?
Excessive fear and anxiety, avoidance behavior, cognitive distortion, genetic vulnerability, and comorbidity.
What is a specific phobia?
Marked fear or anxiety about a specific object or situation, leading to avoidance or distress.
What are the DSM criteria for specific phobia?
Fear or anxiety about a specific object/situation, immediate response, avoidance, and persistence for 6 months or more.
What is the lifetime prevalence of specific phobia?
12%