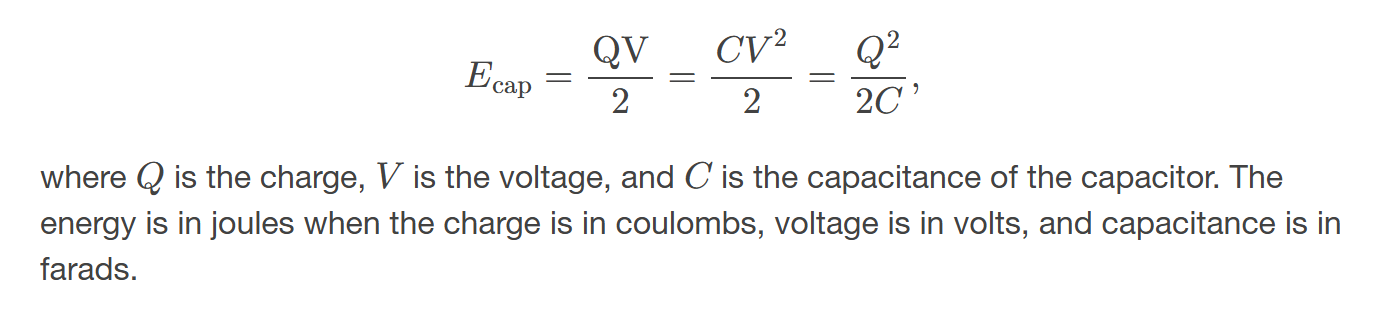Chapter 19: Electric Potential and Electric Field
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
capacitance
amount of charge stored per unit volt
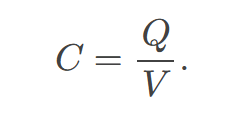
capacitor
a device that stores electric charge
defibrillator
a machine used to provide an electrical shock to a heart attack victim's heart in order to restore the heart's normal rhythmic pattern
dielectric
an insulating material
dielectric strength
the maximum electric field above which an insulating material begins to break down and conduct
electric potential
potential energy per unit charge
electron volt
the energy given to a fundamental charge accelerated through a potential difference of one volt
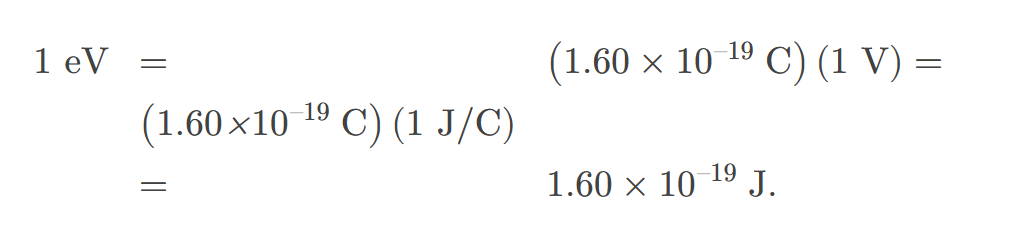
equipotential line
a line along which the electric potential is constant
grounding
fixing a conductor at zero volts by connecting it to the earth or ground
mechanical energy
sum of the kinetic energy and potential energy of a system; this sum is a constant
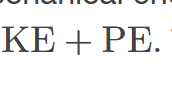
parallel plate capacitor
two identical conducting plates separated by a distance
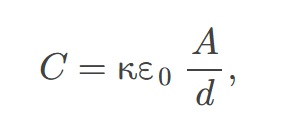
polar molecule
a molecule with inherent separation of charge
potential difference (or voltage)
change in potential energy of a charge moved from one point to another, divided by the charge; units of potential difference are joules per coulomb, known as volt
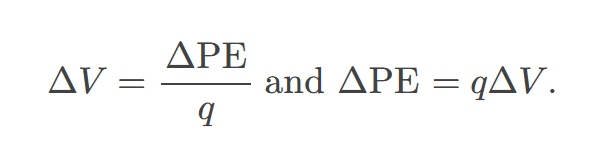
scalar
physical quantity with magnitude but no direction
vector
physical quantity with both magnitude and direction
voltage between points A and B
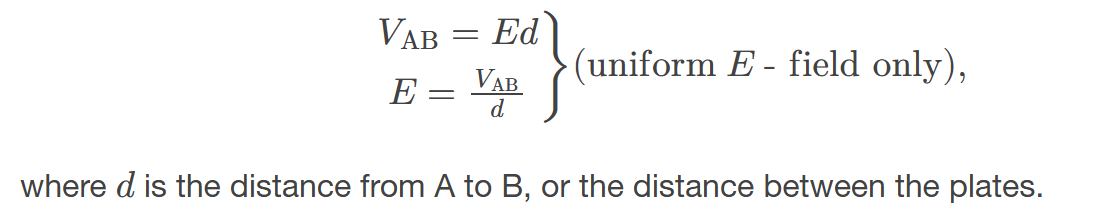
general relationship between voltage and electric field
The voltage between points A and B is determined by the electric field along the path connecting the two points, representing the work done per unit charge to move a charge from A to B.
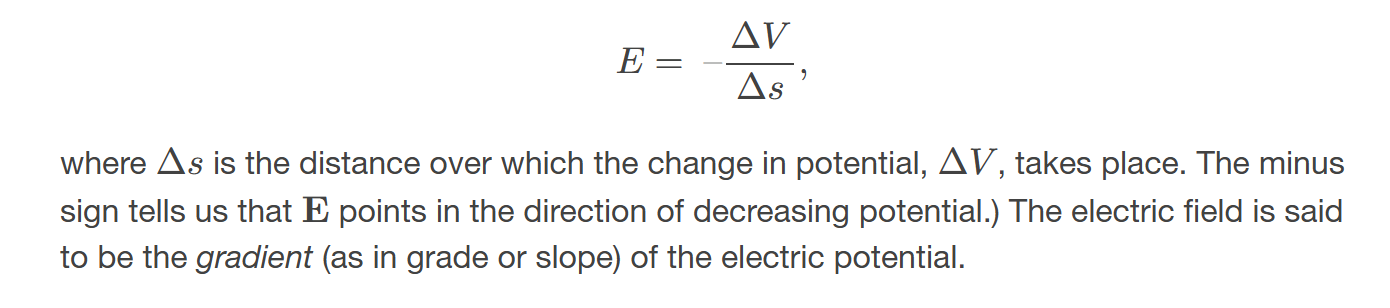
Electric potential of a point charge
is the amount of electric potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in space due to a charge distribution. It is given by the equation V = kQ/r, where V is the electric potential, k is Coulomb's constant, Q is the charge, and r is the distance from the charge to the point.
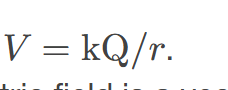
Total Capacitance in Series
is the equivalent capacitance of capacitors connected in series, calculated using the formula 1/Ctotal = 1/C1 + 1/C2 + … + 1/Cn, where C represents the capacitance of each individual capacitor.
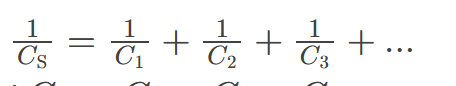
Total Capacitance in Parallel
is the sum of the capacitances of capacitors connected in parallel, calculated using the formula Ctotal = C1 + C2 + … + Cn, where C represents the capacitance of each capacitor.
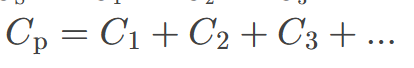
Energy stored in a capacitor
is the work done to charge it, given by the formula U = \frac{1}{2}CV^2, where U is the energy, C is the capacitance, and V is the voltage across the capacitor.