Articulations and Synovial Joints: Structure, Function, and Movements
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are joints (articulations)?
Points of contact between two bones, bone and cartilage, or bone and teeth.
What is the functional classification of joints based on movement?
Immovable = synarthrosis, Slightly movable = amphiarthrosis, Freely movable = diarthrosis.
What is the structural classification of joints based on?
Presence of a synovial cavity and the type of connective tissue binding the bones together.
What are fibrous joints?
Joints connected by dense regular connective tissue with no synovial cavity.
What are cartilaginous joints?
Joints connected by cartilage, which can be either hyaline or fibrocartilage, and lack a synovial cavity.
What characterizes synovial joints?
Presence of a synovial cavity, articular capsule, synovial fluid, and articular cartilage.
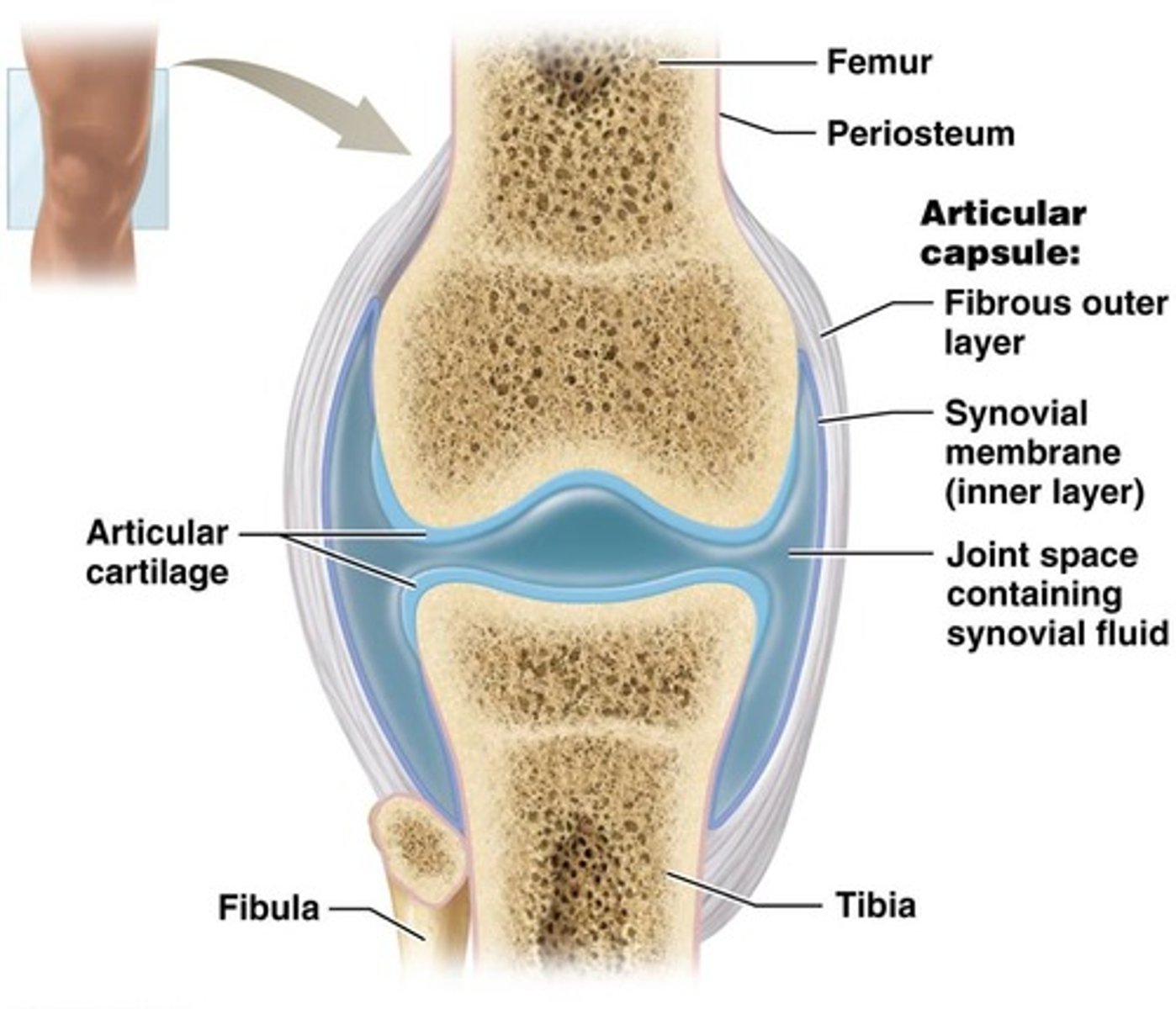
What is the function of the articular capsule in synovial joints?
Surrounds the synovial joint, encloses the synovial cavity, and unites articulating bones.
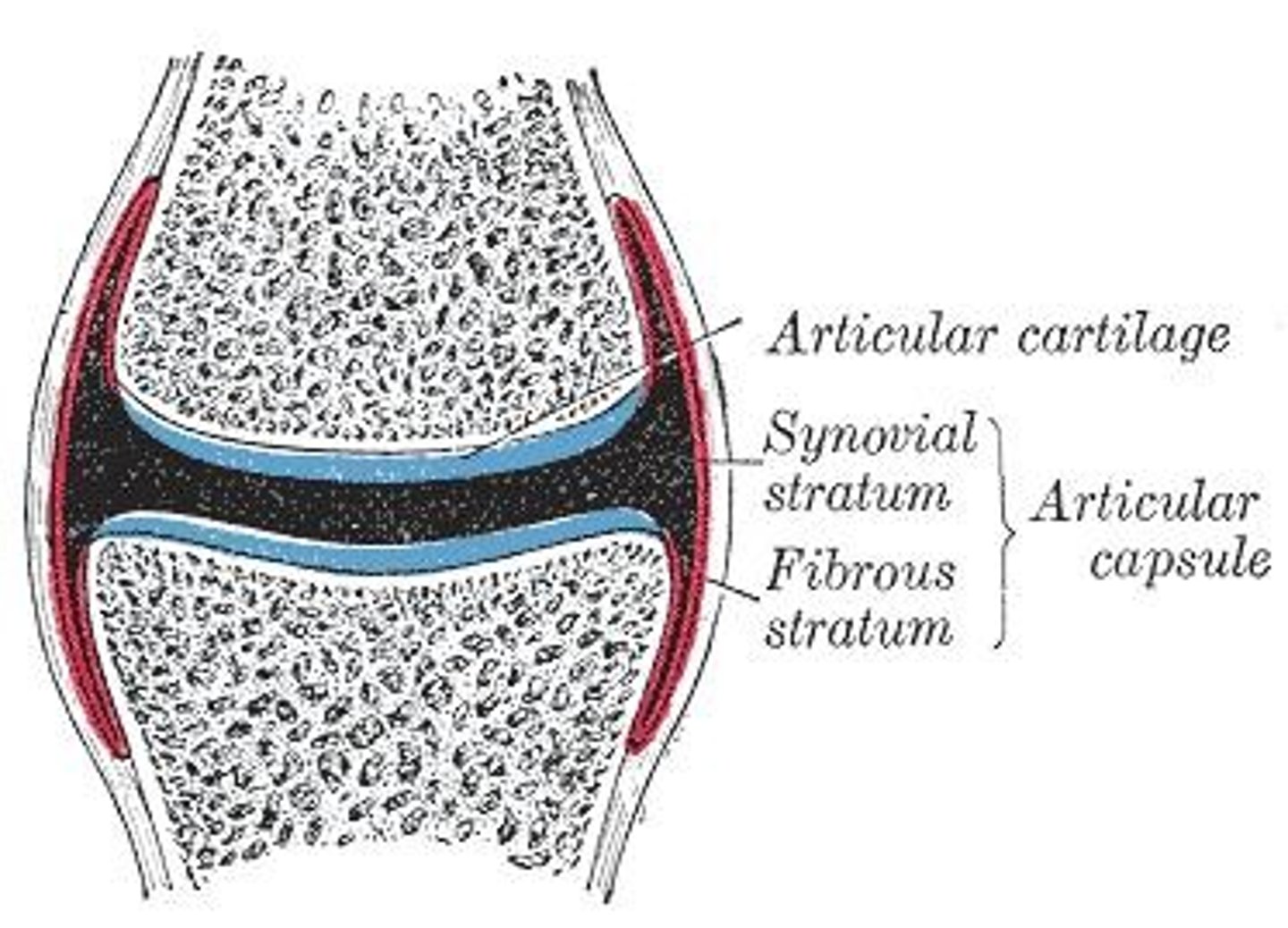
What are the two layers of the articular capsule?
Outer fibrous layer (dense irregular connective tissue) and inner synovial membrane (loose connective tissue).
What is synovial fluid and its major functions?
A thick, colorless liquid that lubricates joints, supplies nutrients, and absorbs shock.
What is articular cartilage?
A layer of hyaline cartilage covering the bones at a synovial joint that reduces friction and absorbs shock.
What are accessory ligaments in synovial joints?
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue that connects bones and reinforces the joint.
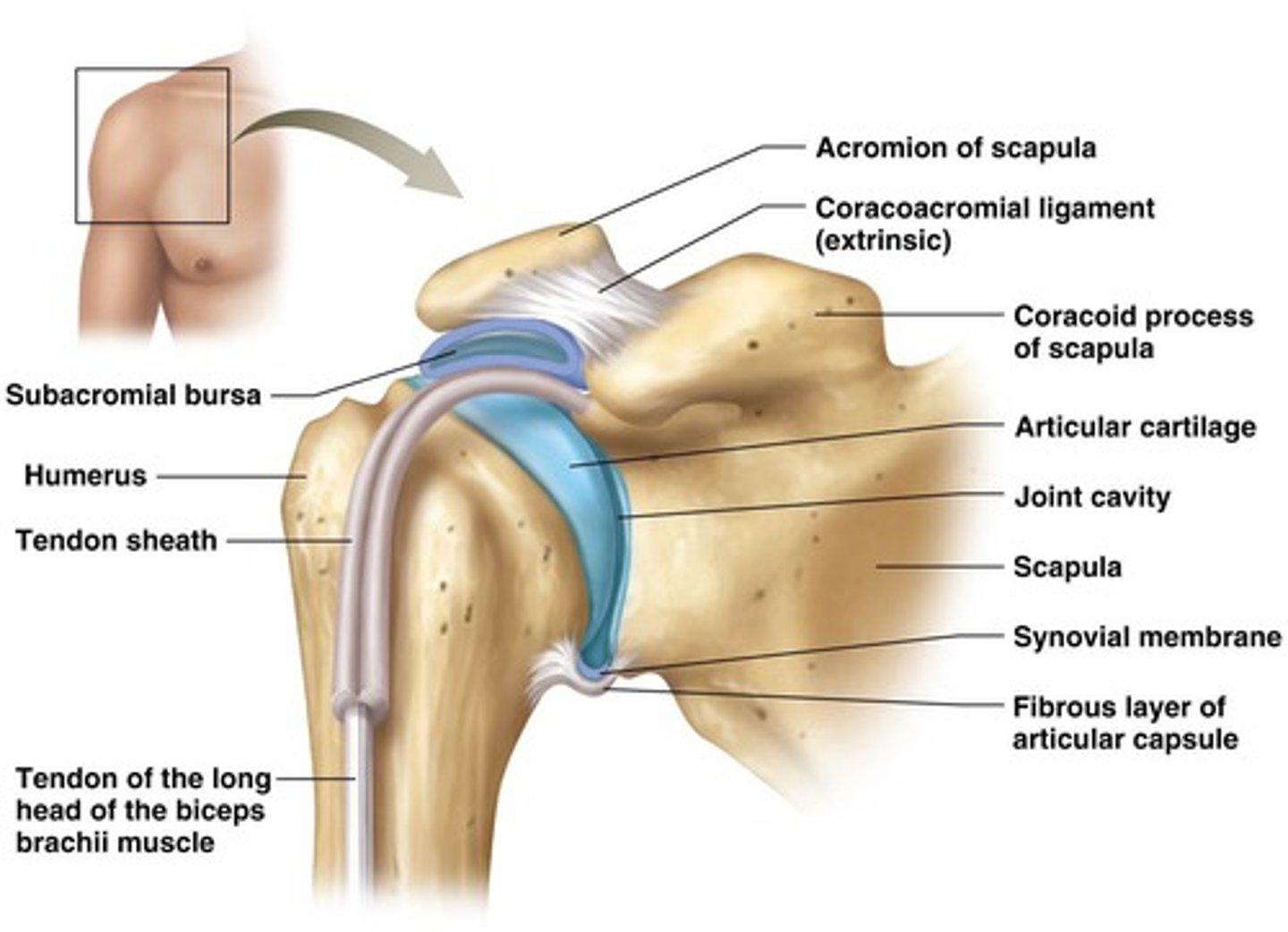
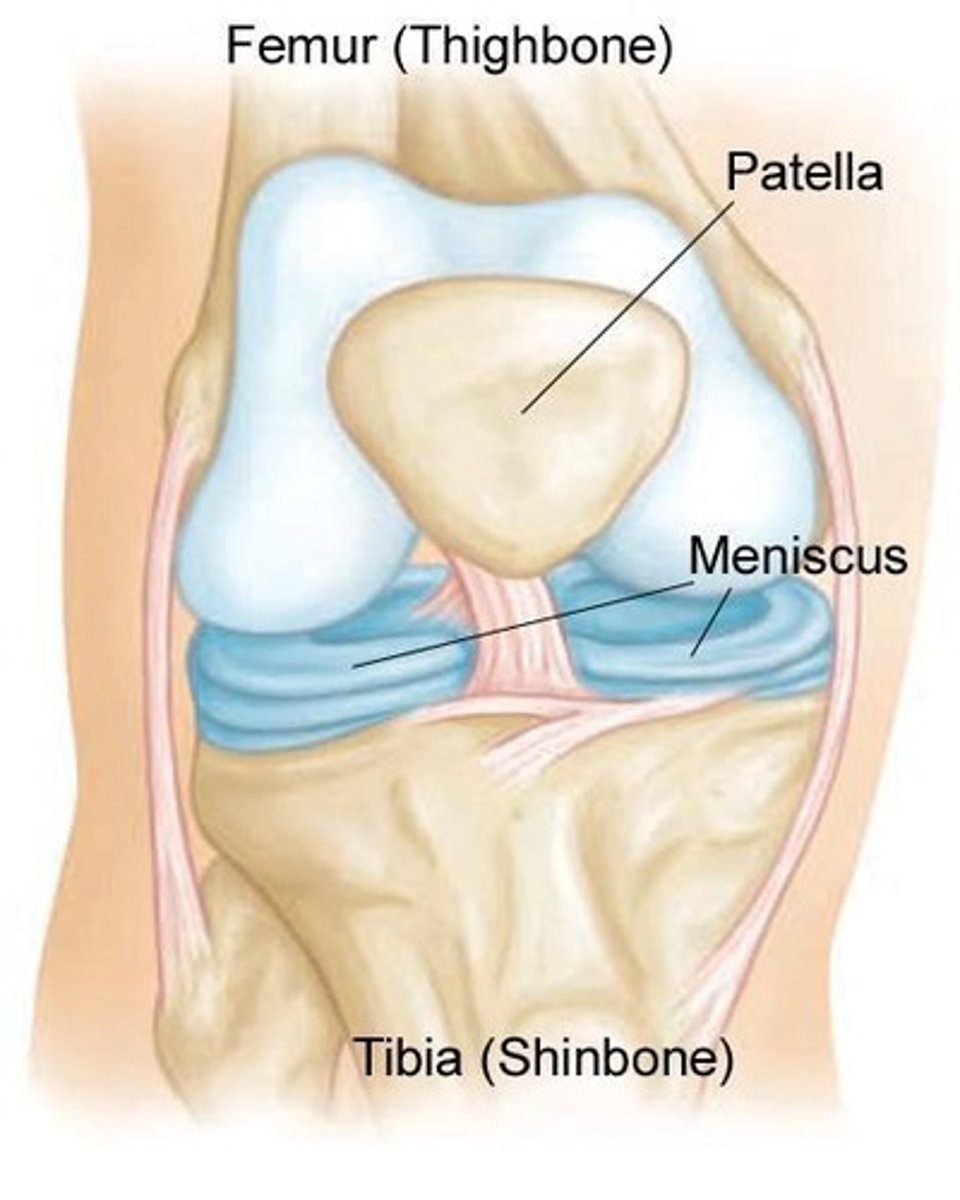
What are menisci or articular discs?
Crescent-shaped pads of fibrocartilage that provide shock absorption and improve fit between articulating surfaces.
What are bursae?
Sac-like structures that cushion and reduce friction in areas of high stress around joints.
What are tendons?
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone and stabilizes joints.
What are tendon sheaths?
Tube-like bursae that wrap around tendons experiencing high friction.
What is the largest diarthrosis in the human body?
The knee joint.
How does the stability of the shoulder joint compare to the hip joint?
The shoulder joint is less stable than the hip joint due to its greater range of motion.
What are the three key features of a synovial cavity?
Articular capsule, synovial fluid, and articular cartilage.
What is the relationship between joint stability and mobility?
There is a tradeoff; increased stability often results in decreased mobility and vice versa.
What type of joint is characterized by having a synovial cavity?
Synovial joints, which are also classified as diarthroses.
What is the role of the synovial membrane?
Lines the joint cavity and secretes synovial fluid.
What are synovial joints classified by?
Classified by movements and shapes of joint surfaces.

What is a nonaxial joint?
A joint that allows motion in one or more planes but does not move around an axis.
Define a uniaxial joint.
A joint where bone moves in just one plane or axis.
What characterizes a biaxial joint?
A joint where bone moves in two planes or axes.
What is a multiaxial joint?
A joint where bone moves in multiple planes or axes.
What type of movement is gliding?
A sliding motion between articulating surfaces of bones in a joint.
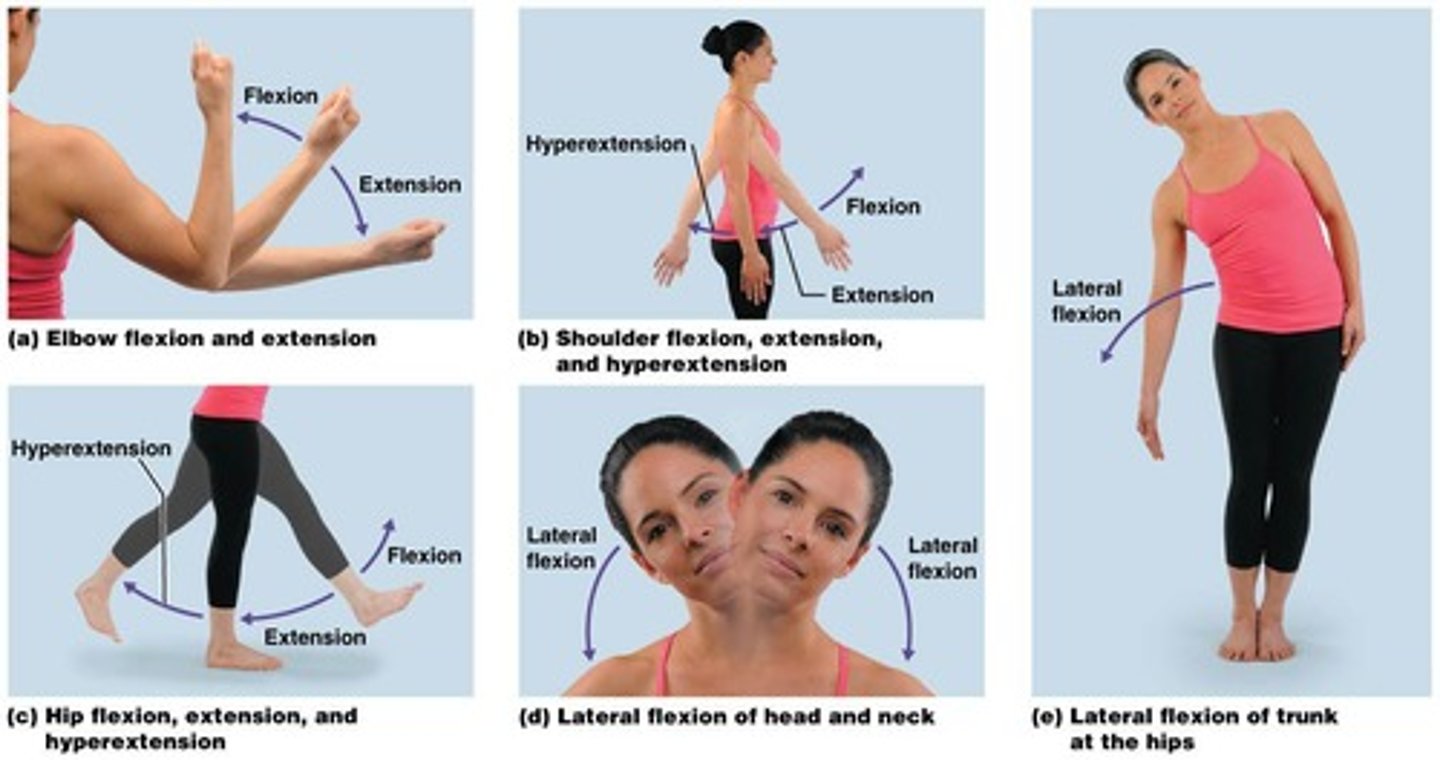
What are angular movements?
Movements that increase or decrease the angle between articulating bones.
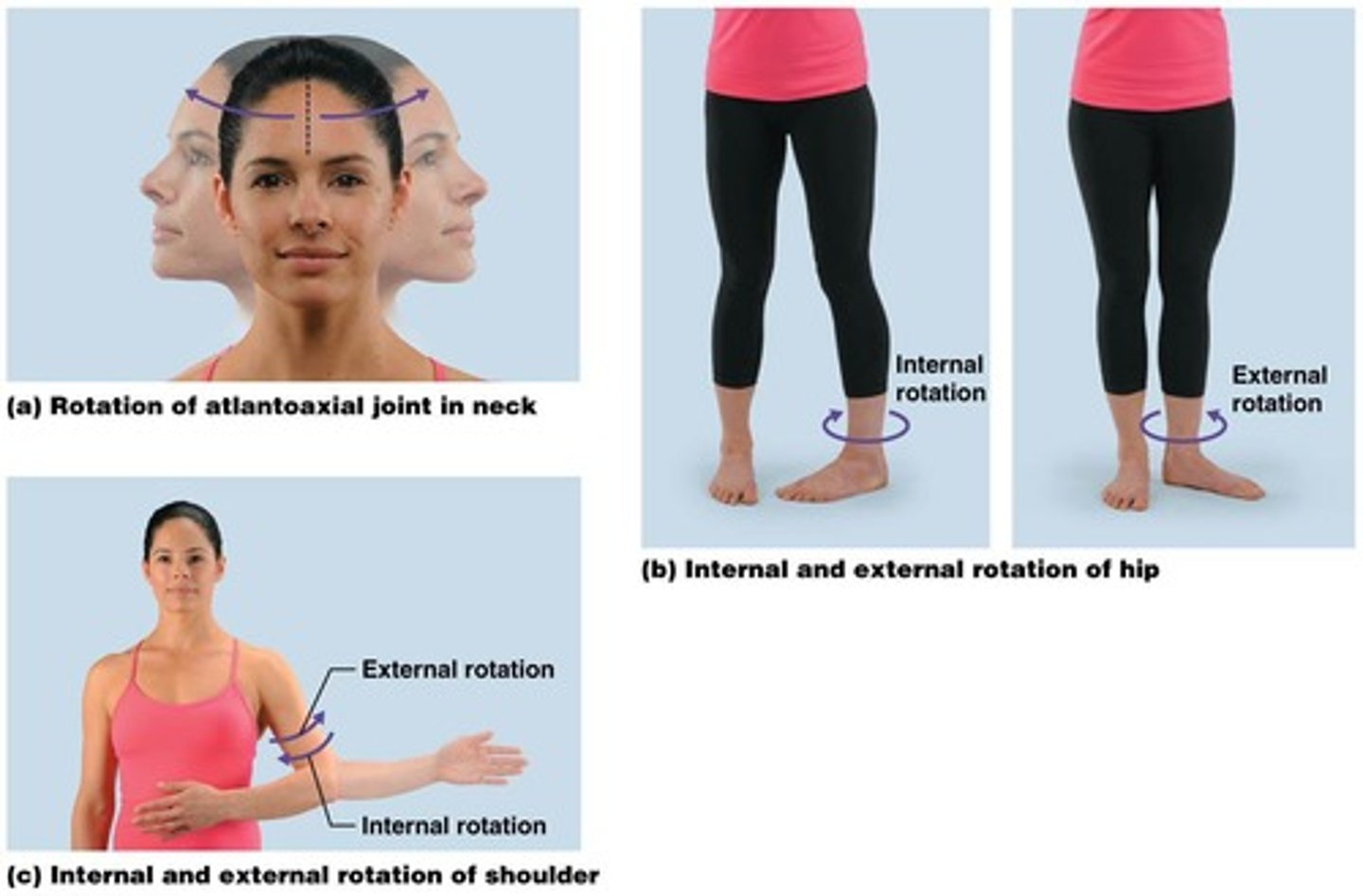
Describe rotational motion.
A non-angular, pivoting motion where one bone rotates along its longitudinal axis.
What is flexion?
Movement that decreases the angle between bones, bringing them closer together.
What is extension?
Movement that increases the angle between articulating bones.
Define hyperextension.
Joint extension beyond 180 degrees.
What is abduction?
Lateral movement of a body part away from the midline.
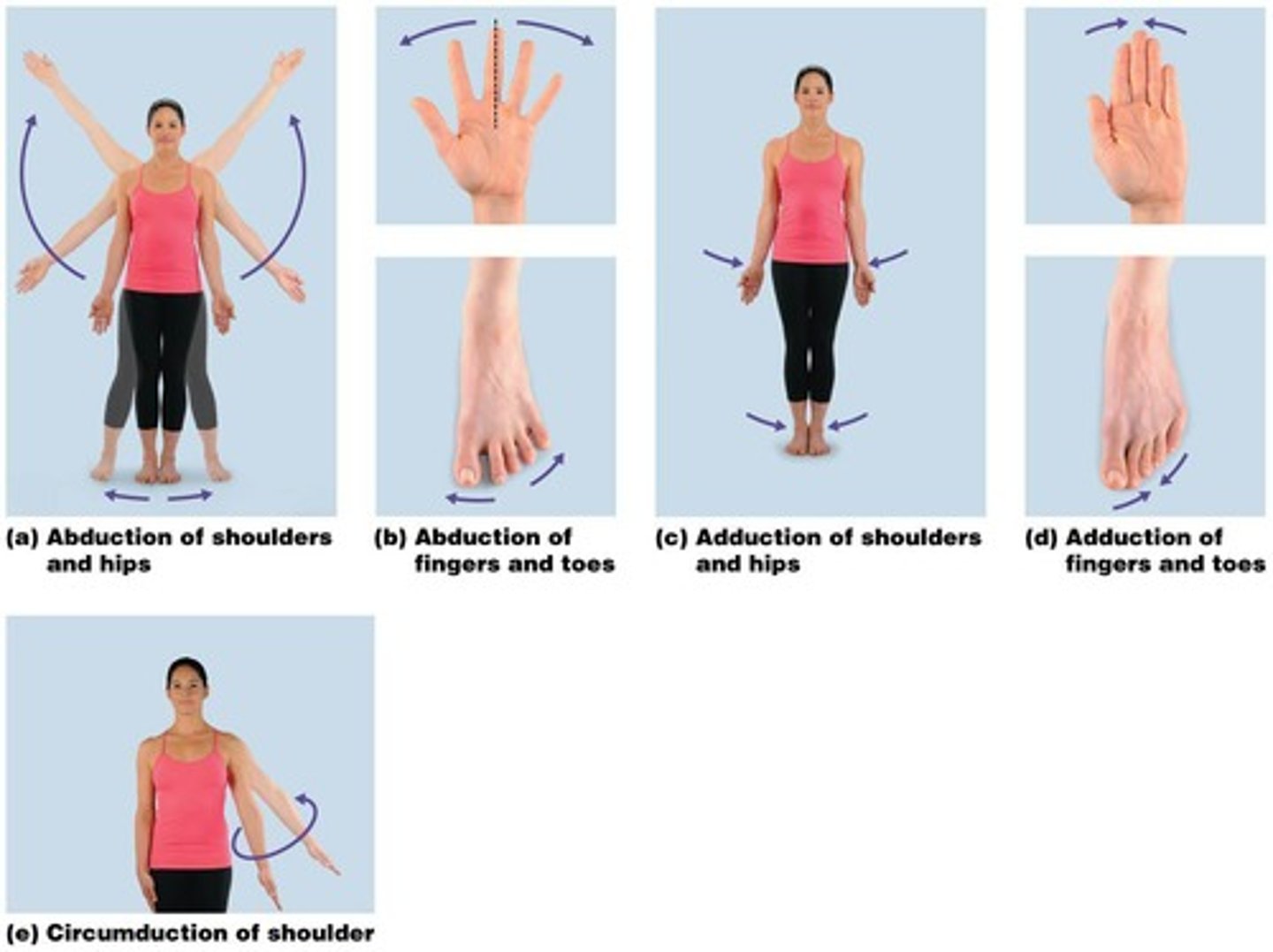
What is adduction?
Medial movement of a body part toward the midline.
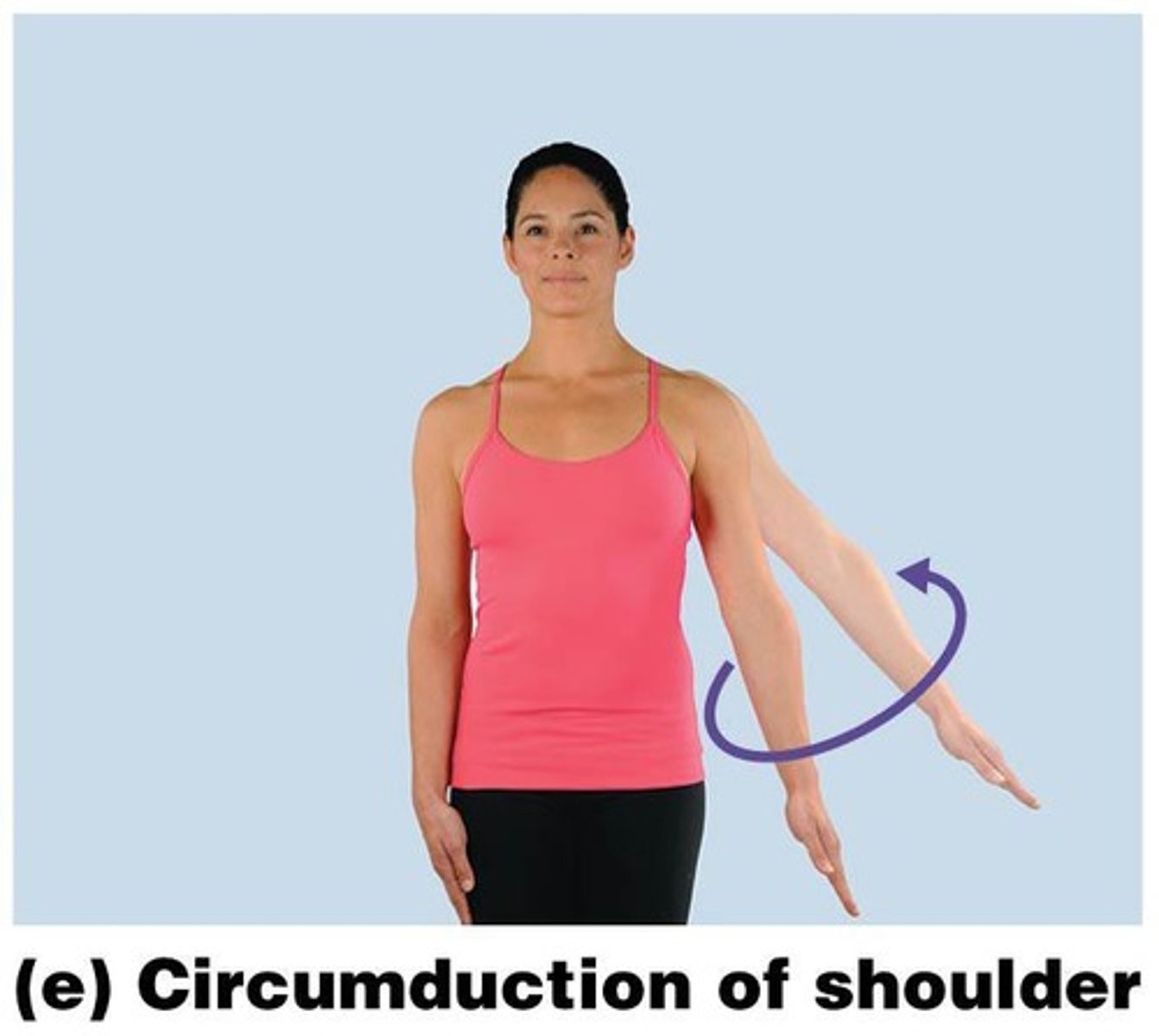
What is circumduction?
A circular motion where the proximal end remains stationary while the distal end moves in a circular path.
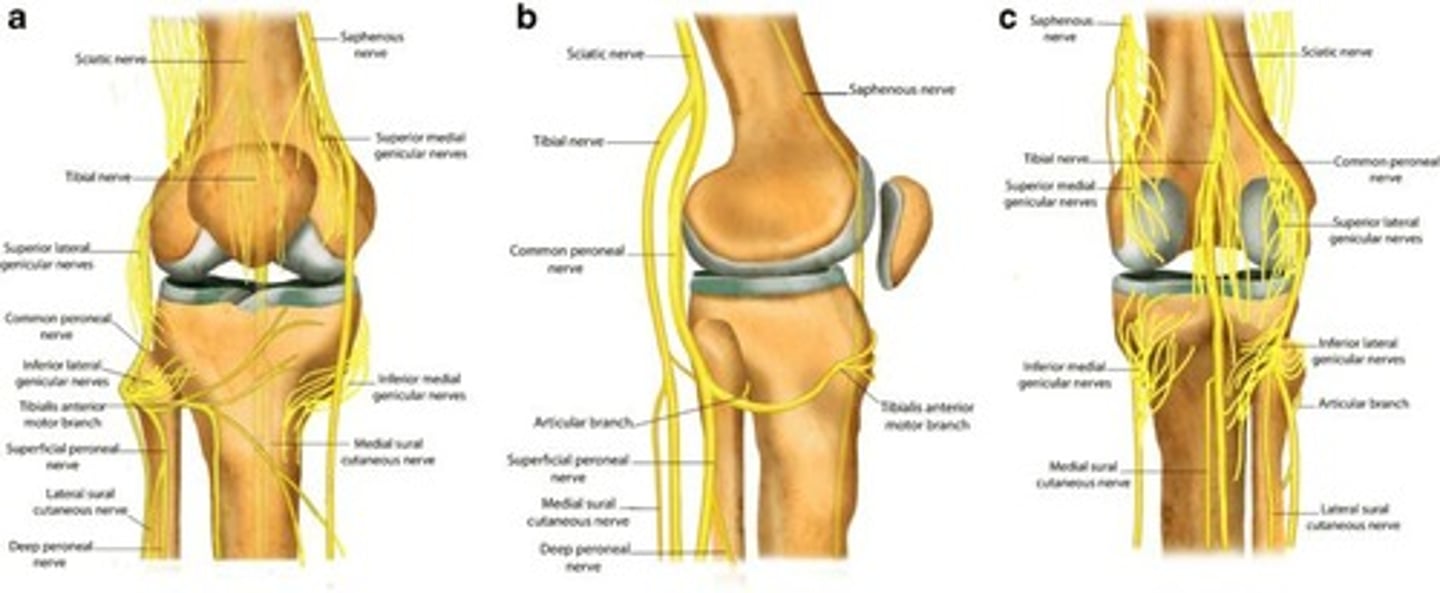
What is the knee joint classified as?
The largest diarthrosis in the body and a complex hinge joint.
What stabilizes the knee joint?
Stabilized by ligaments including the ACL, tibial collateral ligament, and menisci.
What is the shoulder joint also known as?
The glenohumeral joint, which is the most freely moving joint in the body.
What stabilizes the shoulder joint?
Stabilized by five major ligaments and reinforced by the rotator cuff muscles.
What is the hip joint also called?
The coxal joint, which is a ball and socket joint with greater stability than the shoulder.
What is the role of adipose tissue in synovial joints?
Fills spaces surrounding the joint and provides protection and padding.
What are the two types of rotation in joints?
External (lateral) rotation and internal (medial) rotation.
What are common knee injuries related to?
Strains or tears in the ACL or tibial collateral ligament.
What is the function of sensory nerves in synovial joints?
To monitor position, stretch, and painful stimuli.