End of Year Flashcard ( the real one )
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Convection currents drive… based on … and … . explain how this works
movement of tectonic plates based on density differences and magma . Magma in asthenosphere rises as its heated up. then as it reaches surface it cools down, expands, and then falls. This cycle continues. Hot cold, warm cool is what drives movement of convection.
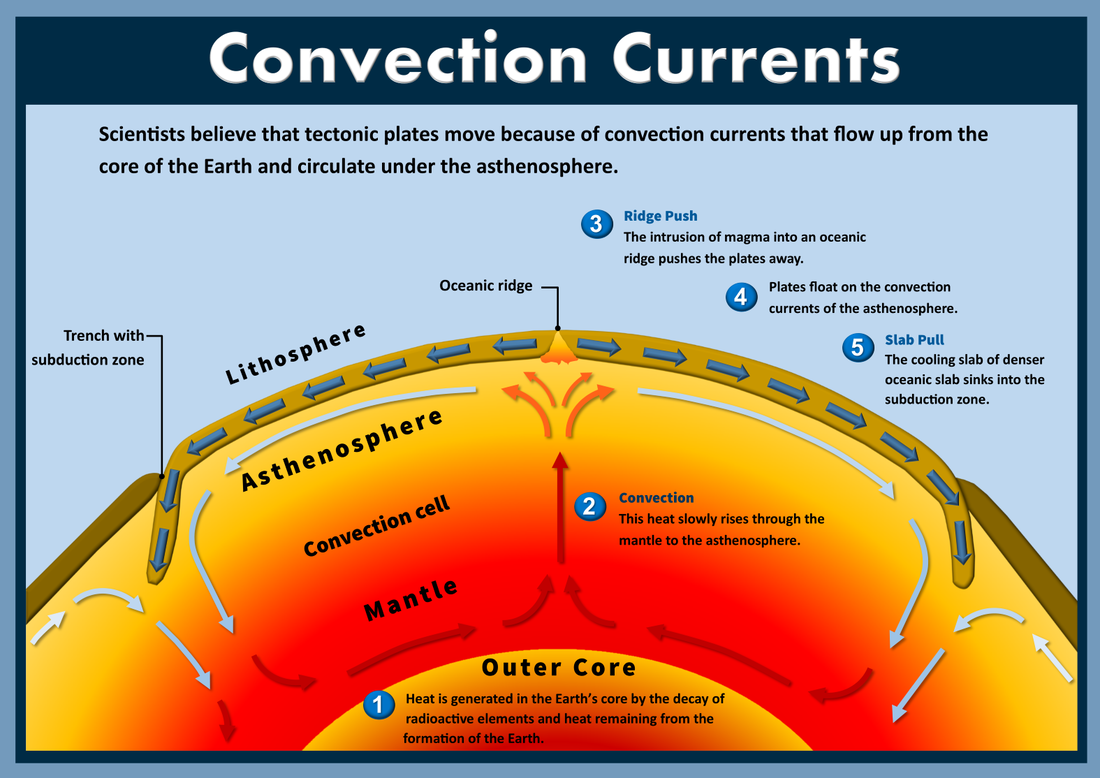
describe how hawaii was formed
liquid in asthenosphere got hot in certain places → burn a hole in the lithosphere → magma seeps through so plate moves over as islands go away from a hotspot . As volcanoes move, the new piece of land over the hotspot will form more volcanoes
Types of rocks and definitions of each
Igneous = formed from the solidification of magma on the earth’s surface ( extrusive ) or within a plate ( intrusive )
Metamorphic = formed from an intense heat or pressure usually deep within a crust
Sedimentary = formed from compaction or cementation, usually on earth’s surface
Label parts of the plate boundaries shown in the diagram.
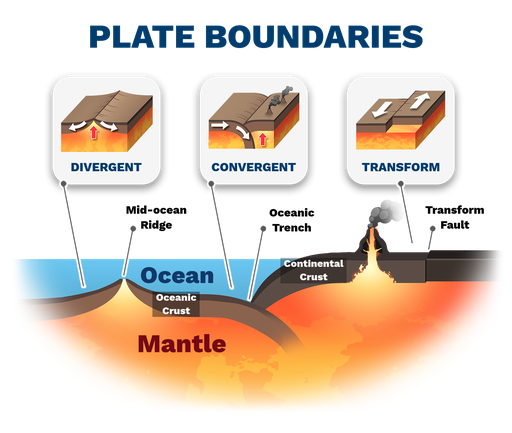
In the red circles area describe what is happening. What crust is being made and being destroyed. How. And at what boundary. Plate motion is due to ____ ___ in the asthenosphere , draw in the arrows
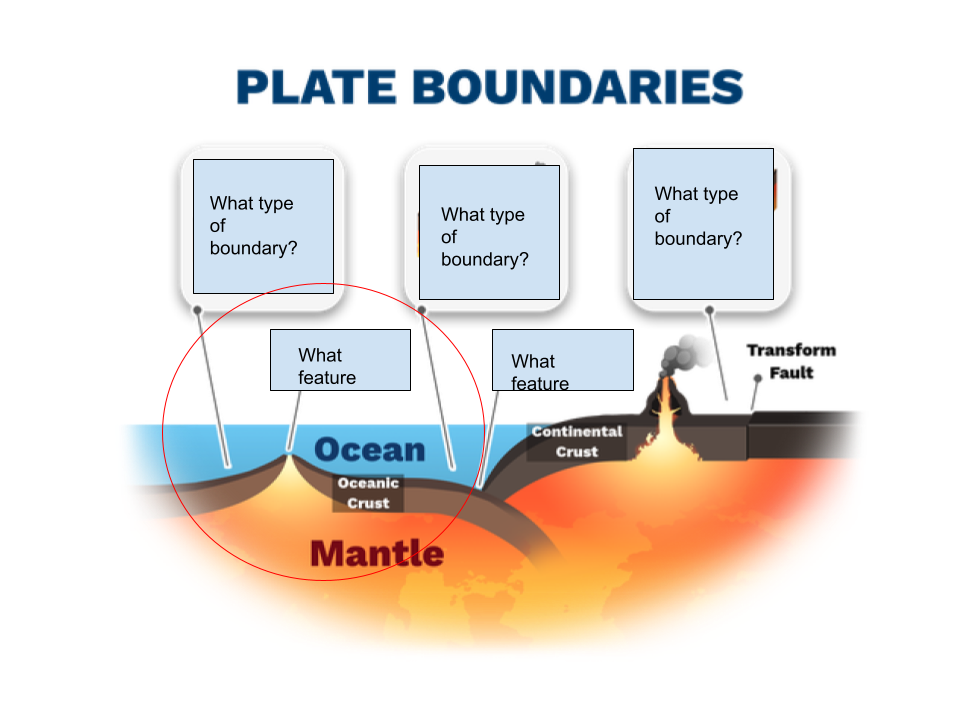
Plate motion is due to convection currents in the asthenosphere.
Magma is rising up as divergent plates in ocean to ocean creates a mid atlantic ridge which expands the sea floor. New oceanic crust is being created at the divergent boundary. Old oceanic crust is being destroyed in the convergent boundary for continent to land → volcanic Mountains because magma rises up because of subduction .
when convection currents are going down together → what boundary
when convection currents are going up together → what boundary
down → convergent
up → divergent

What types of geological activities are common in the ring of fire that make the ring of fire an appropriate description. What type of plate boundaries surround the ring of fire.
oceanic to continent - convergent = subduction zone and volcanic Mountains
oceanic to oceanic - convergent = volcanic islands
the ring of fire follows the boundary of what major tectonic plate
pacific plate
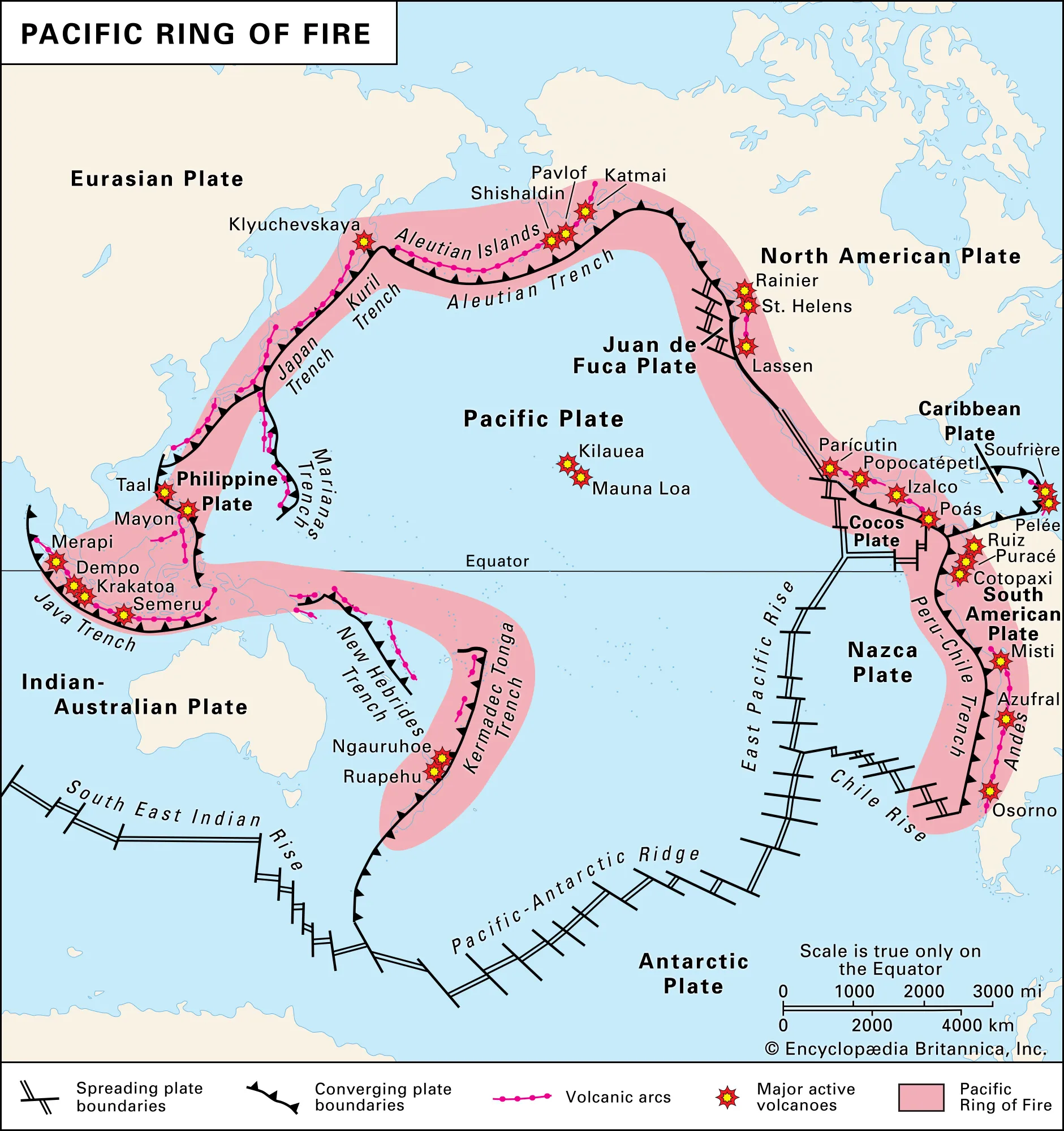
why doesn’t the ring of fire stretch along the equator across the Pacific ocean
because the plate boundary near the bottom are divergent so no subduction so volcanic islands or mountains cannot emerge

3 faults in the US
san andreas
new Madrid
Wasatch

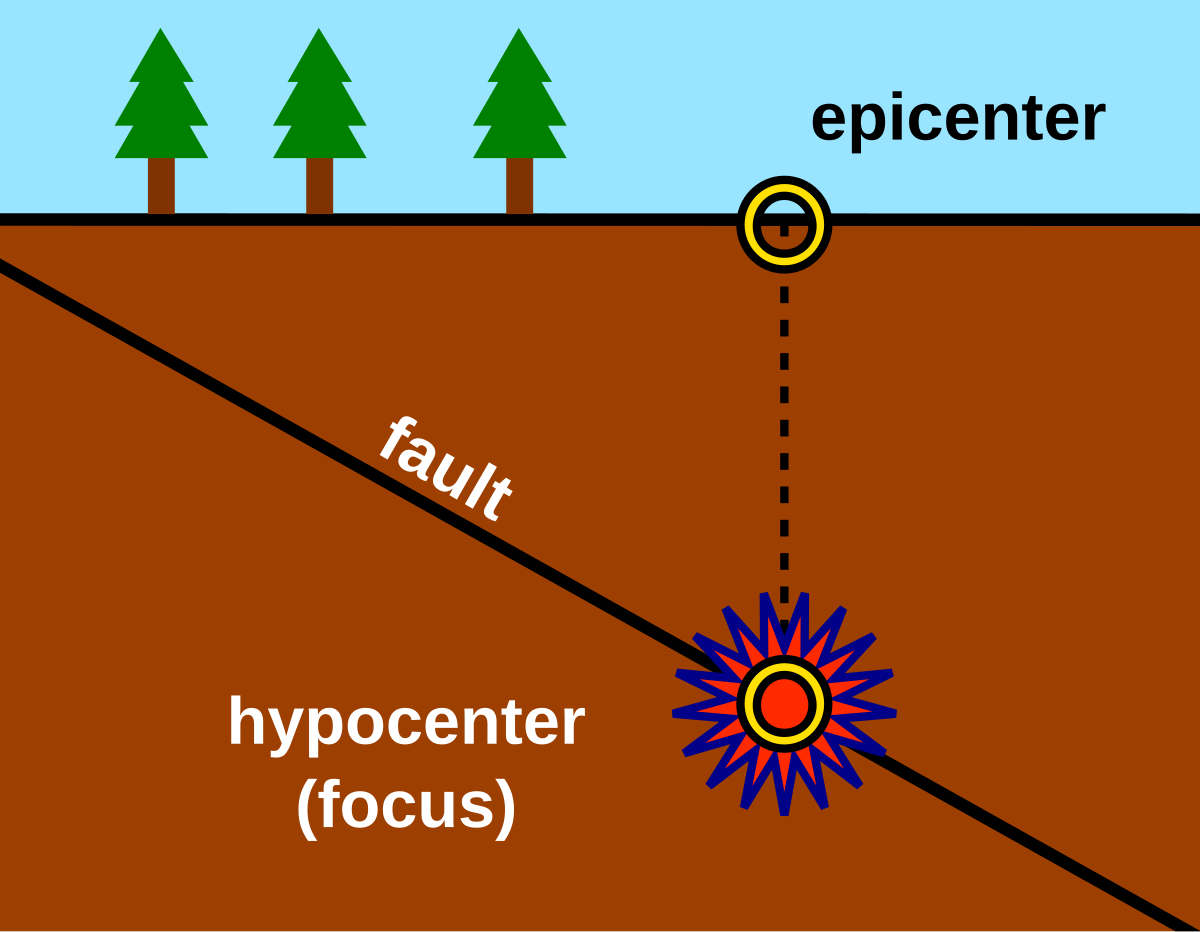
epicenter of an earthquake is
exact point on the surface of the earth directly above the location where the rock ruptures
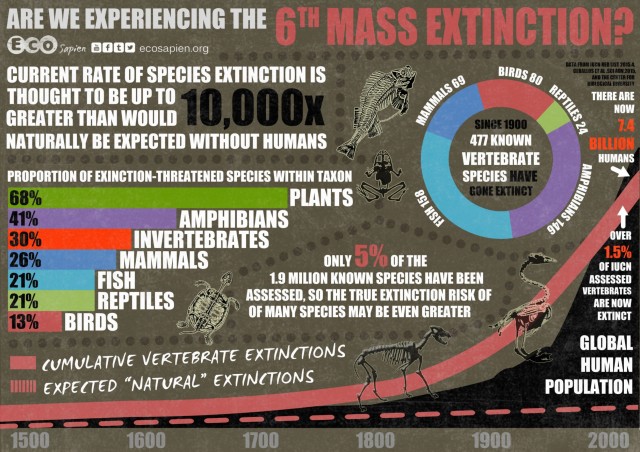
Mass extinction , what must occur
What are the 5 mass extinctions in earth’s history
relatively sudden, global decrease in diversity of life forms.
extinctions occur over the world
a large number of species go extinct
many types of species go extinct
5 Mass Extinctions : Ordovician , Devonian, Permian, Triassic, Cretaceous-Tertiary(K-T boundary )
During the KT boundary : half of all life forms died out
Scientists predict we are in the 6th Mass extinction, what Is this called and why
holocene / anthropocene extinction
caused by human actions
decrease in wild life
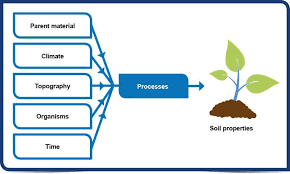
Factors that impact the formation of soil ( and definition )
Climate = over long period of time and , different biomes have different soil types
Topography = slope and elevation of the land
parent material
organisms - types of decomposers and microorganisms present within the soil
time
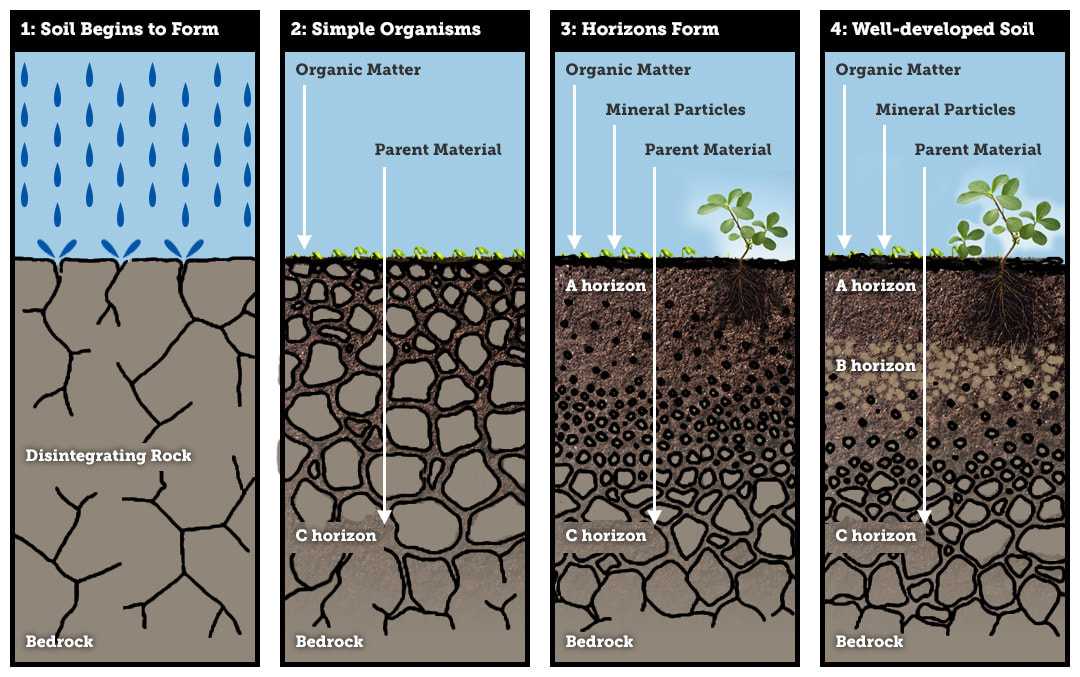
soil is formed by
chemical and physical weathering of rocks over time
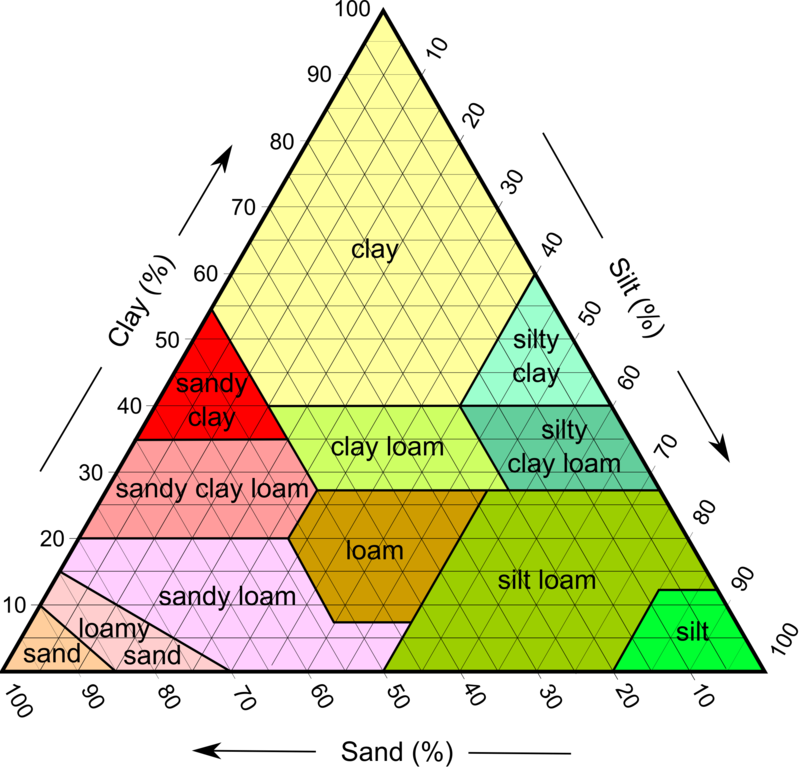
particles of soil in order from largest to smallest
sand, silt, clay

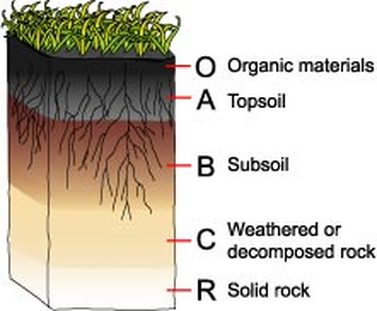
soil horizon
O - Humus
most susceptible to weathering
surface litter like leaves and other decaying matter
A - top soil
phosphorus and nitrogen are examples of some of the limiting nutrients that are found
non renewable
mineral soil with most organic material accumulation and soil life(worms)
E - eluviation layer
sand and silt
infiltration
mostly containing of silicates
zone of leaching ( nutrients from upper horizons seep into lower horizons)
minerals are washed away by leaching so lack of minerals like clay or iron
B - subsoil
zone of accumulation = minerals like iron, clay, aluminum and organic material and other nutrients accumulate a process referred to as eluviation
little to no organic matter
C - parent material
gives soil rest of its characteristics
large layer of unbroken rocks
materials that is broken down to give soil
least weathered
R - Bed rock
Solid rock
not weathered at all
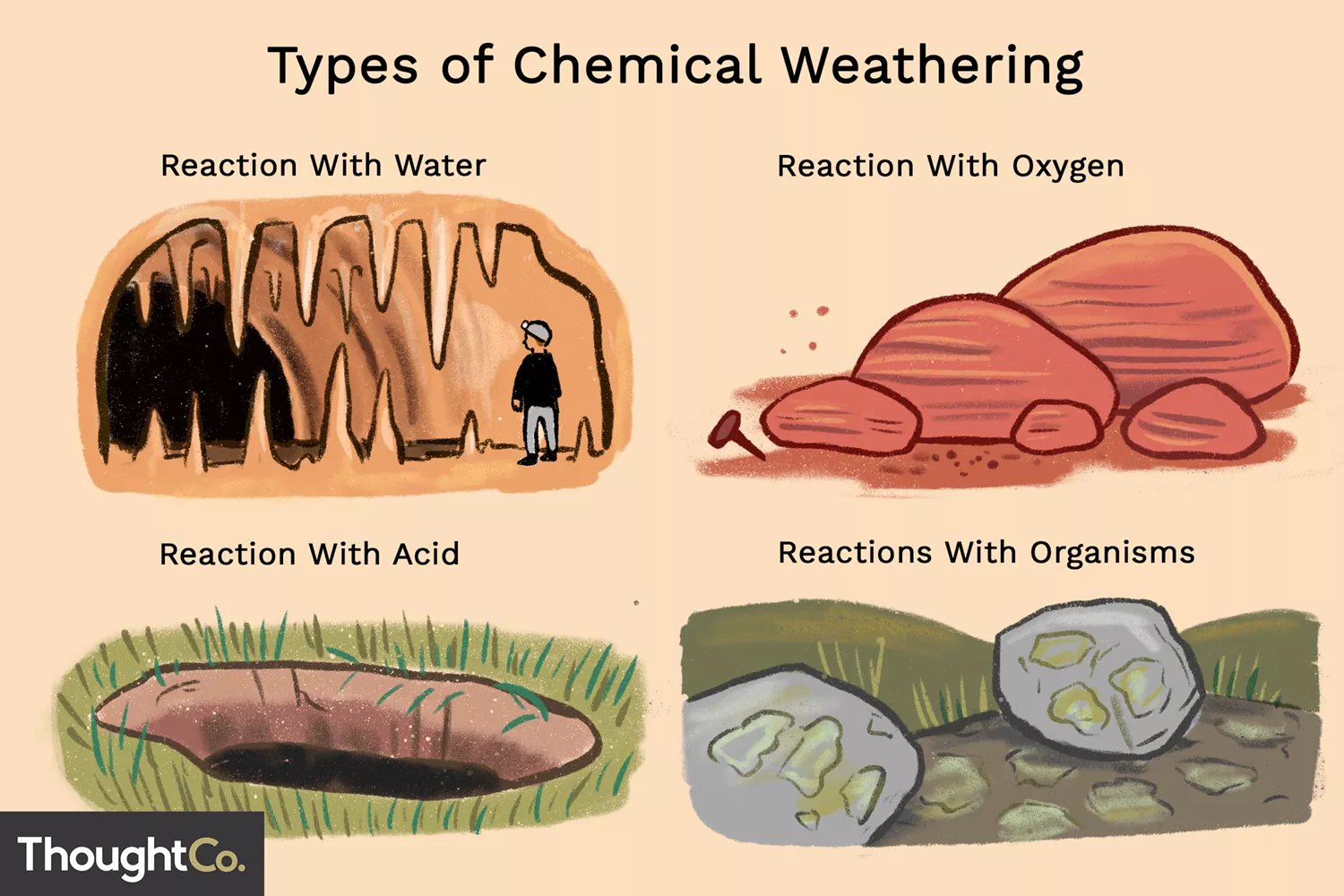
Weathering ( biological and chemical ) Include examples
Breakdown of rock to form soil
ex: lichen and moss can breakdown / primary successores
ex: wind and water, ice, animals , growing plants
chemical weathering =acid rain, rust on rocks
Biological weathering = plants growing in rocks, human activity, animal burrowing
Deposition
The dropping of sediment in a new place
ex: sand dunes , formation of an island
soil particle characteristics
Sand - largest
highest permeability and porosity
water passes through this the most
Silt - medium
Clay - smallest
Lowest permeability and porosity
Highest fertility / nutrient level
negative charge and nutrients are positive so clay attracts nutrients
high water holding capacity
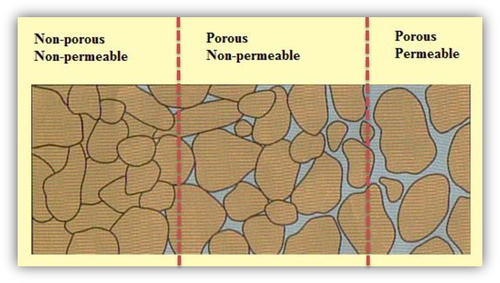
Permeability =
porosity =
fertility =
permeability = ability of air/liquid to go through
porosity = pores /spaces between particles
fertility = how much nutrients ( fertile ) the soil has
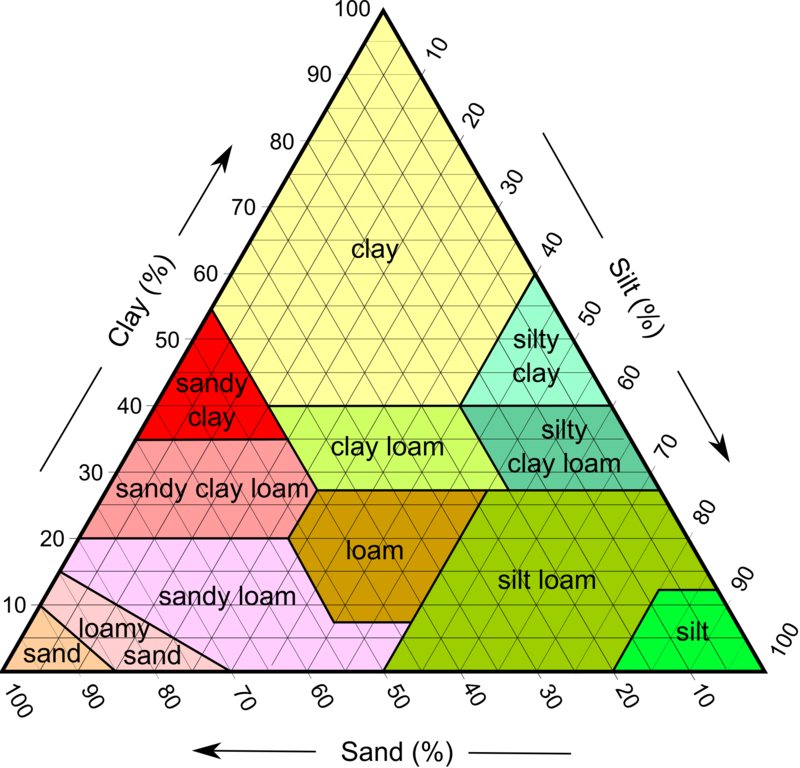
farmers want soil to be ___ because …
loam
loam because its a mixture of sand, silt, and clay so it has the best of each component
watershed characteristics and these characteristics influence what
Area
Length
Slope
soil
vegetation
divides ( boundary with other watershed )
Watershed characteristics influence rainwater flow through the watershed
watershed characteristics and classifications are influenced by
runoff(water that is unable to infiltrate into the ground, so it is carried someplace else and often causes erosion and carries pollutants with it ) and infiltration(Water that seeps into the ground )
water table
the ground below which the ground is saturated with water, usually below infiltration
Aquifer
a body of porous rock and sediment saturated with groundwater, usually below water table
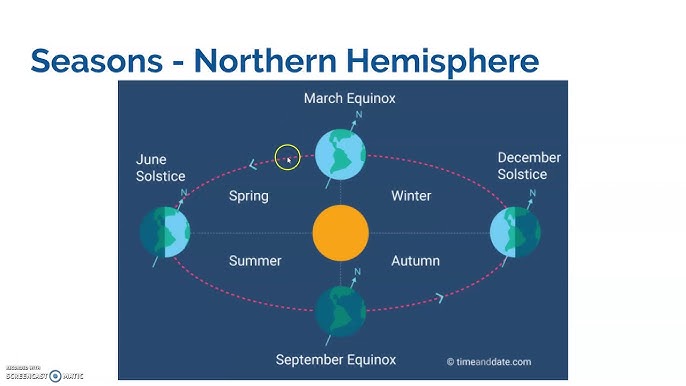
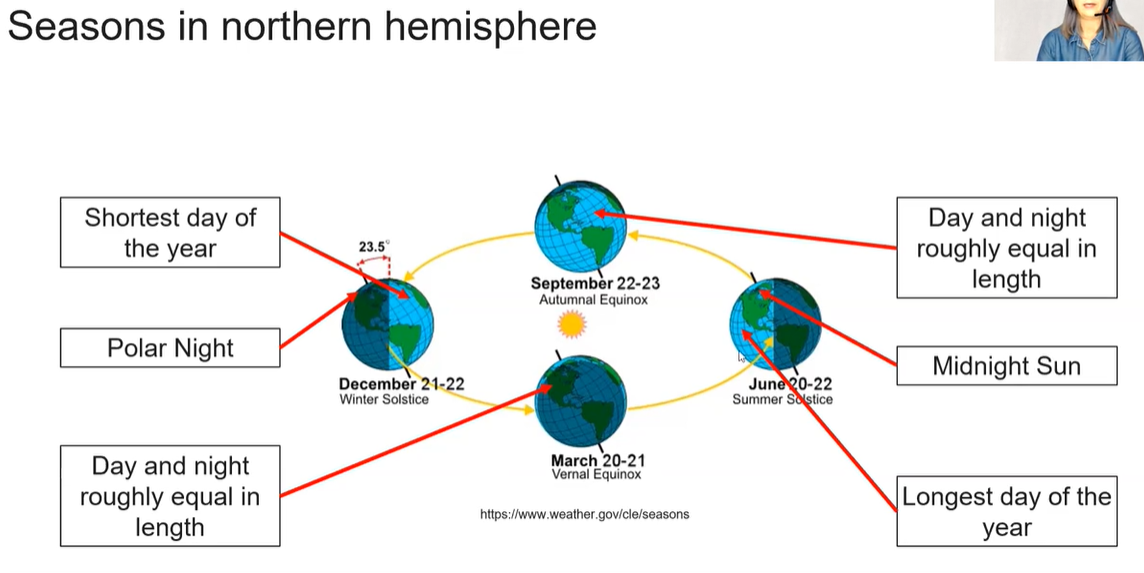
What causes seasons
summer happens in the northern hemisphere when it is tilted towards the sun so that it gets the most direct rays. Sun rises higher and stays above the horizon longer and its rays strike the ground most directly.
7
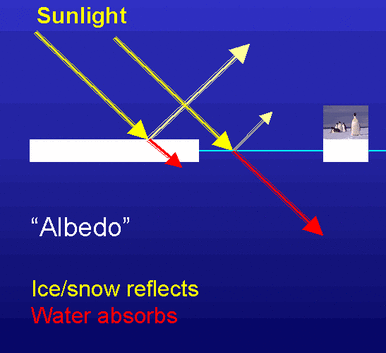
albedo
Proportion of light that is reflected by a surface, mostly determined by a color
surfaces with a high albedo reflect more light and thus gain less heat
like ice snow
surfaces with low albedo absorb light and heat
pavement
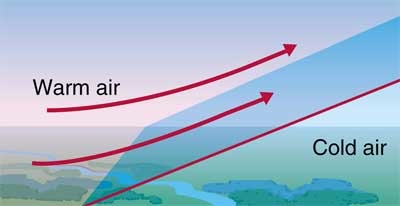
Cold front ___ warm fronts by creating a ___ , how does this work
displaces, wedge, cold air is denser than warm air so the warm air is pushed upwards
usually the higher the altitude the lower the temperature of the air. temperature inversion is when ____ air is trapped at the ground under a layer of ___ air
cool, warm
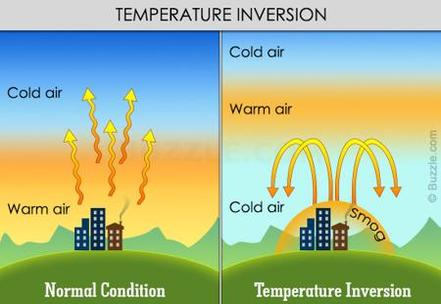
in normal conditions what happens to warm air
in temperature inversion why cant air rise to a higher altitude
what happens to air pollutants during a temperature inversion
temperature inversions are common in valleys why?
rises and then cools down
dense cold air cant rise above warm air
pollutants become trapped near the ground because the cold air cant rise and the same layer of air is staying in the same place → smog
less radiation In valley from sun so cold air under that is denser than warm air so it pulls under. cold air on top because high altitude like valleys mean colder air
global wind patterns primary result from the most intense ___ ___ arriving at the equator resulting in ____ ___ and ___ ___
solar radiation, coriolis effect, density differences

adiabatic heating and cooling
response to pressure changes ( air rises → lower pressure → volume expands → cools )
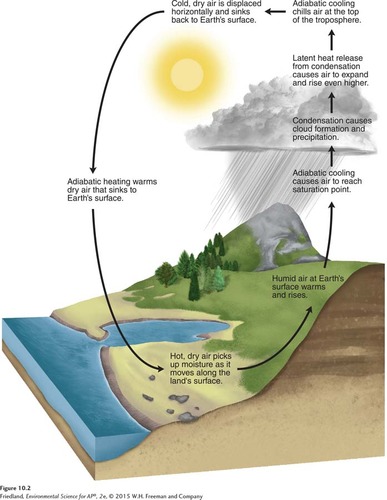
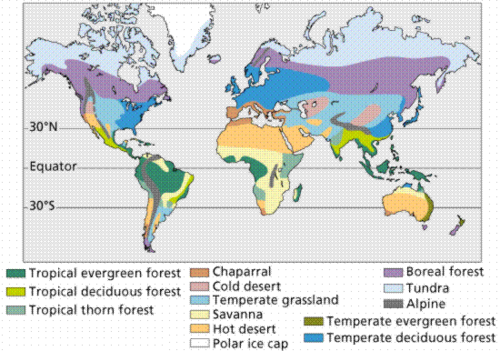
biome at 30 degrees where cold dry air is sinking
biome at equator where warm air is and precipitation
biome at 60 degrees where warm moist air and precipitation
biome at poles where dry cold air is falling
subtropical desert
tropical rainforest
temperate forest / taiga ( small taiga in 60 degrees south )
tundra/cold desert
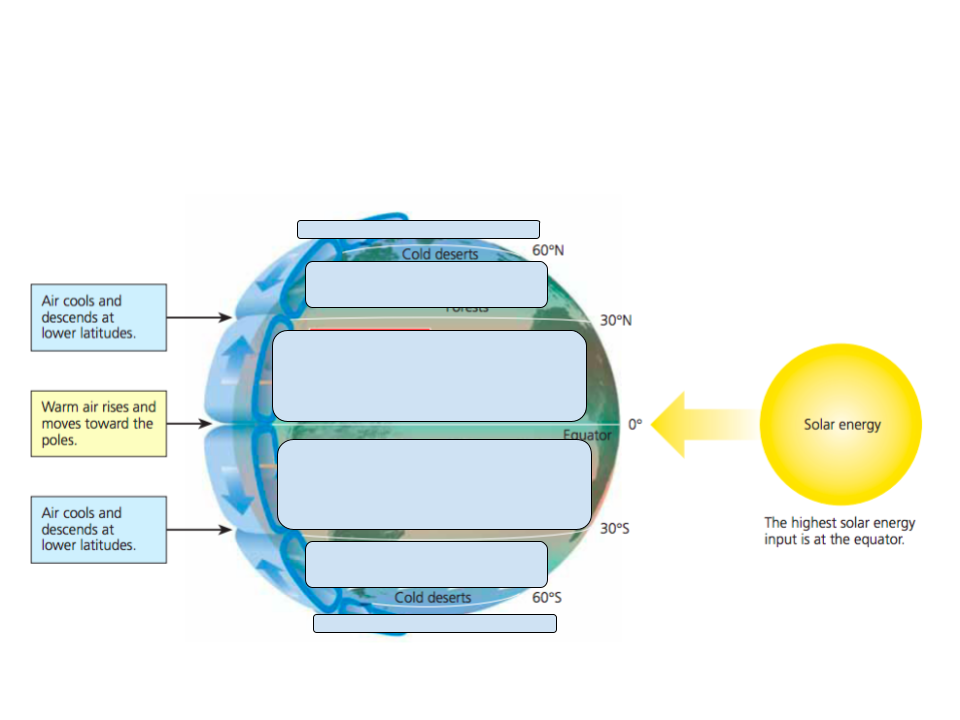
draw arrows and wind names
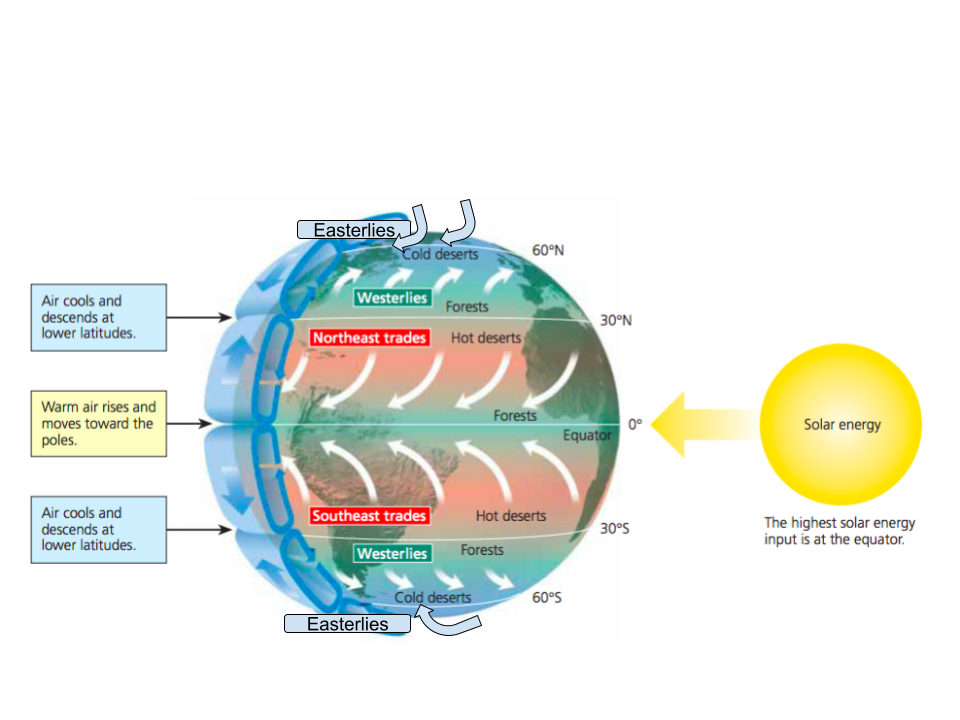
In the northern hemisphere does the coriolis effect cause winds to move in a clockwise or counter clockwise direction
counterclockwise direction

southern hemisphere air deflect ___ when it hits low pressure, due to the earths rotation
left

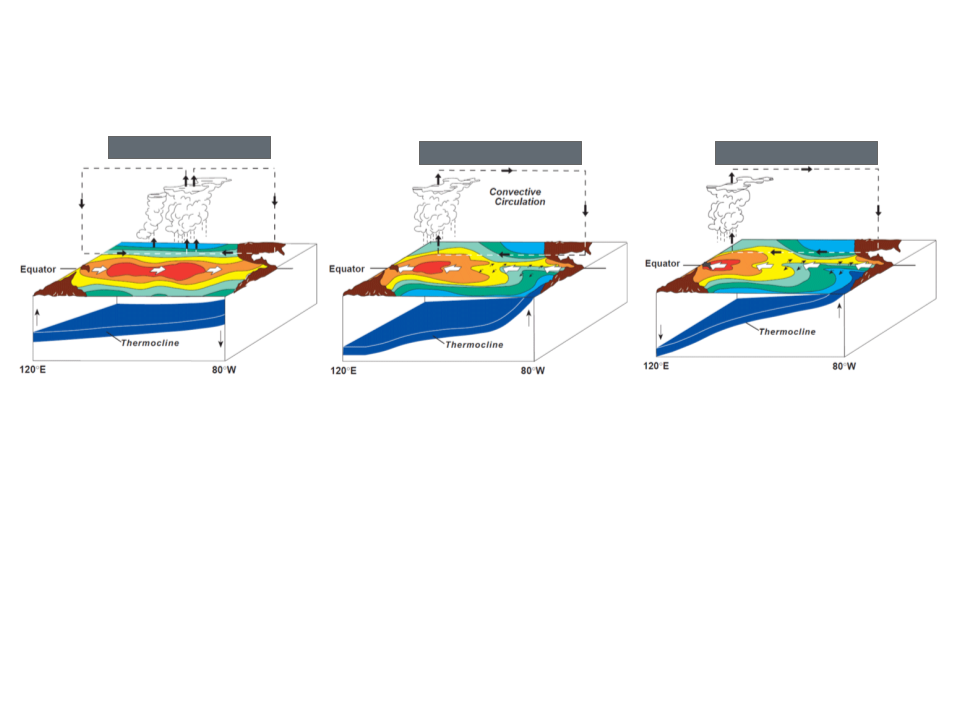
along equator el nino , Nina, normal