A&P Skeletal System
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
slide 33-34 bonus on test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
what are the 5 functions of the skeletal system?
support, protection, storage, manufacturing, movement
how does the skeletal system provide support?
bearing the weight of the body
How does the skeletal system provide protection?
encasing essential organs
what is an example of how the skeletal system provides protection?
ribcage protects the heart and lungs from injury
how does the skeletal system provide storage?
stores minerals to be released into the bloodstream, stores fat in yellow bone marrow
how does the skeletal system provide manufacturing?
hematopoiesis
what is hematopoiesis?
production of red and white blood cells from red bone marrow
how does the skeletal system provide movement?
joints provide movement for bones
what structures do the bones provide shape for?
head, face, thorax, limbs
what do the skull bones protect?
brain, ears, eyes
what do the bones of rib cage and shoulder girdle protect?
heart and lungs
what do the bones of the pelvic girdle protect?
internal reproductive organs and lower abdominal organs
what provides movement
bones and muscles
what are bones made of?
a solid matrix of living cells and fibers surrounded by calcium deposits
how are bones classified?
by their shape
what are the 5 shapes of bones?
flat bones, irregular bones, long bones, short bones, sesamoid bones
what is an example of a flat bone?
scapula
what is an example of an irregular bone?
vertebrae
what is an example of a long bone?
femur
what is an example of a short bone?
wrist
what is an example of a sesamoid bone?
patella
what is the shape of long bones?
long and narrow
long bones have _______ ends
expanded
how are short bones shaped?
cubelike: length=width
how are sesamoid (round) bones classified?
included as short bones
where are sesamoid bones found?
embedded in tendons
how are flat bones shaped?
platelike with broad surfaces
how are irregular bones shaped?
variety of shapes
where are irregular bones found?
connected to other bones
what are the 2 basic regions of a long bone?
diaphysis, epiphyses
what is the diaphysis region of a long bone?
shaft, long part of bone
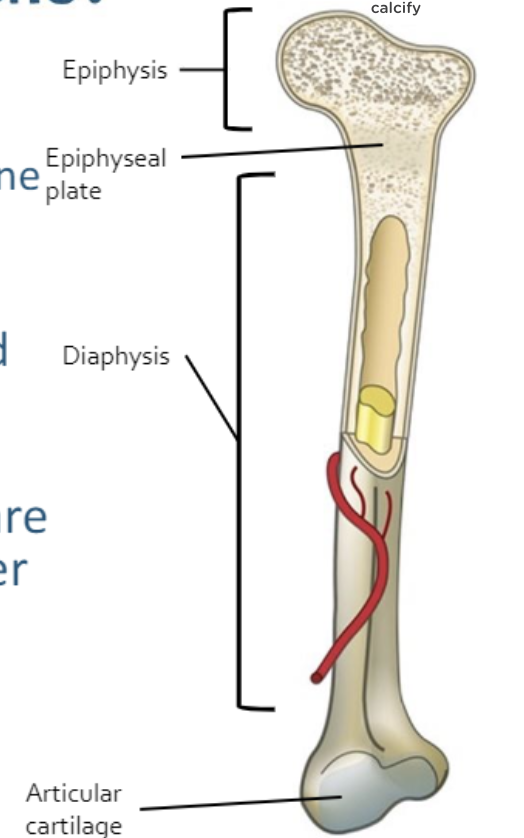
what is the epiphyses region of a long bone?
ends of bone
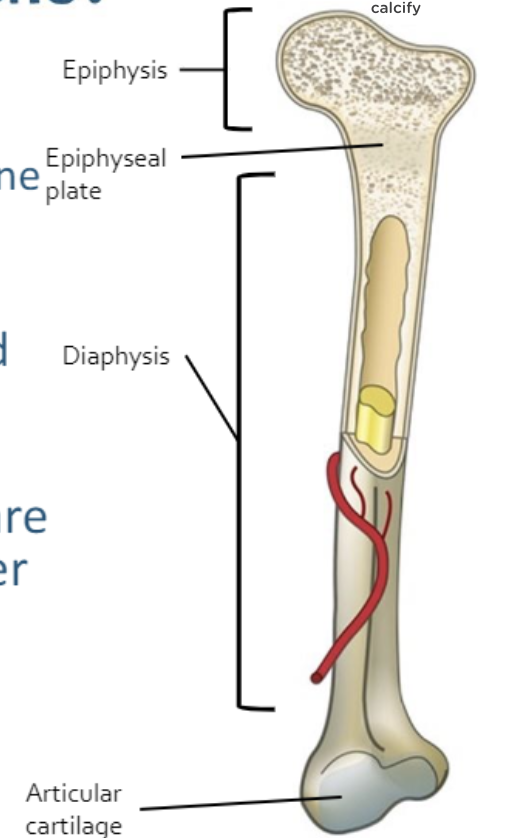
what is the layer of internal cartilage between the diaphysis and epiphysis regions of a long bone?
epiphyseal plate (growth plate)
what are the ends if the epiphyses covered with in a long bone?
articular cartilage
what is the function of articular cartilage?
provides smooth movement of joints and cushion from shock
what is the periosteum of the long bone?
encloses bone; dense connective tissue
where is the compact (cortical) bone found?
wall of diaphysis
what does the spongy (cancellous) bone make up?
epiphyses
what is trabeculae in long bone?
branching bony plates that make up spongy bone
what is the medullary cavity of long bone?
hollow chamber in diaphysis
what does the medullary cavity of long bone contain?
marrow
what is endosteum of long bone?
lines spaces, cavity
what are the kinds of bone marrow?
red or yellow marrow
where is bone marrow found?
lines of medullary cavity, spongy bone spaces
what causes red bone marrow to be replaced with fatty yellow marrow?
age
where are new blood cells produced through hematopoiesis?
within bone marrow
what is the outer layer of bone made of?
periosteum- tough connective tissue
where does muscle attachment and bone repair occur?
periosteum
What layer is underneath the periosteum?
compact bone
spongy bone is found at the _____ of long bone and beneath ______ bone
ends; compact
what is spongy bone made of?
a lattice of trabeculae
where is trabeculae found?
along lines of stress
what is the function of spongy bone?
perfect resistance from compression
what fills the spaces between the spaces of trabeculae?
marrow or blood vessels
how is compact bone arranged?
cylinders called osteons
how are osteons arranged?
in concentric circles called lamellae
what do the lamellae surround?
central/Haversian canal
what does the haversion canal contain?
blood vessels and nerves
how are haversion canals connected?
perforating (volkmann’s) canals running perpendicularly
where are osteocytes found?
in lacunae
what do blood vessels provide to bone tissue?
nutrients
how do osteocytes pass nutrients?
through canaliculi
what are osteocytes?
mature bone cells that make up the majority of bone structure
what is the function of canaliculi?
connect all bone cells, receive nutrients, remove waste
what lines the haversion canals and surfaces of compact and spongy bone?
osteoclasts and osteoblasts
what is the function of osteoclasts?
break down bone
what is the function of osteoblasts?
produce new bone
what is an embryo’s skeleton made of?
cartilage
what do osteoblasts do in the third month of embryo development?
osteoblasts secrete mineral deposits that replace cartilage. The osteoblasts mature into osteocytes.
what is ossification?
The process of incorporating calcium and minerals into cartilage to become bone
when does primary ossification occur?
during fetal development
when does secondary ossification occur?
during childhood and adolescence
what happens during intramembranous ossification?
flat skull bones are forming between sheets of primitive connective tissue
what happens during endochondral ossification?
long bones and most of skeleton are forming from hyaline cartilage models.
what happens to chondrocytes at the epiphyseal plate when a child grows?
tall columns of chondrocytes divide and then deteriorate as the matrix around them calcifies.
what are the cells called after chondrocytes are deteriorated and calcified?
osteoblasts
what do osteoblasts form?
spongy bone
what is the function of acid secreted by osteoclasts?
enlarge the medullary cavity as bone grows so that more marrow is available for cells.
what percent composition is organic in bone?
35% osteiod
what is osteoid made of?
made of ground substance and collagen
what is the function of organic bone composition?
provides the flexability and tensile strength required to keep bones from breaking
what does a lack of collagen cause?
brittle bone disease
what percent composition of bone is inorganic?
65% mineral salts
what are inorganic crystalline salts made of?
hyrdoxyapatites Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2
what is the function of inorganic bone composition?
provides bone strength and hardness
what does a lack of hydrocyapatites cause?
rickets
what other inorganic salts make up the bone matrix?
magnesium ions, sodium ions, potassium ions, carbonate ions
what condition occurs at the loss of bone mineralization
osteoporosis
what regulates blood calcium levels
parathyroid hormone and calcitonin
what is a fragility fracture?
fracture that occurs from less than standing height; a sign of low bone density
how does the body maintain an ideal blood calcium level?
bone is created or dissolved
what gland is activated due to low calcium in the blood?
parathyroid gland produces PTH
what gland is activated due to high calcium in the blood?
thyroid gland produces calcitonin
when does bone remodeling occur?
throughout life
what is bone resorption, and what causes it?
removal of bone, action of osteoclasts
what is bone deposition, and what causes it?
formation of bone, action of osteoblats
what approximate percentage of the skeleton is replaced each year?
10%-20%
what are the 4 steps of repairing a broken bone?
hematoma forms
callus forms
callus ossifies
compact bone forms
what factors affect bone development, growth, and repair?
nutrition, sunlight exposure, hormone levels, and physical exercise
bone is formed as _________ calcifies
cartilage