Chapter 23: Messengers and Receptors
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Slower, widespread, longer, env, growth, development, homeostasis, endocrine, organs, cells, bloodstream
Chemical Signaling:
Is ___ than electrical signaling but more ___ and ___ lasting effects
Functions:
Response to the ___
___ and ___
Maintaining ___
Primarily through the ___ system with ___ and ___ that secrete chemicals to the ___
Autocrine, paracrine, endocrine, neural, neuroendocrine
5 Types of Chemical Signalling:
___ signals that act on the same cell
___ signals that act locally on nearby cells
___ signals that are hormones that are carried by blood
___ signals that are between neurons
___ signals that are hormones secreted by neurons
Ligand-receptor binding, behavior, gene expression, signal reception, signal processing, signal response, signal deactivation
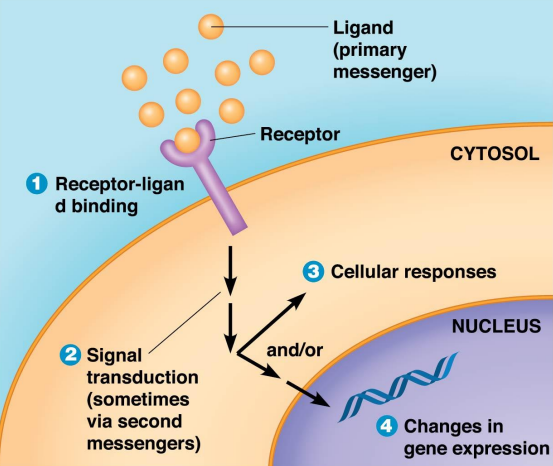
Signal Transduction:
Is the ability of a cell to respond to ___-___ ___ by altering ___ or ___ ___
5 Steps:
___ ___: messenger binds to its receptors in the plasma membrane or inside the cell
___ ___: ligand-receptor
interaction starts signaling process
___ ___: final result is a change cellular function or gene expression
___ ___: signal and transduction pathway is turned off
Dynamic, sensitivity, blocked, surface, intracellularly, cognate, occupied, affinity, dissociation constant, Kd, low, agonists, antagonists
Signal Reception:
Receptors:
Are ___
Can change ___
Can be ___
Found on cell ___ or ___
Receptor-Ligand Binding:
Receptor for a specific ligand is a ___ receptor
Receptor with bound ligand is ___
Relationship of [ligand] and occupied receptor number is ___
___ ___ or ___ is the [free ligand] to occupy half of the receptors
Receptors with high affinity have ___ Kd
___ are drugs that activate receptors
___ are drugs that prevent a change and prevent natural ligands from binding
![<p>Signal Reception: </p><p>Receptors:</p><ul><li><p>Are ___</p></li><li><p>Can change ___</p></li><li><p>Can be ___</p></li><li><p>Found on cell ___ or ___</p></li></ul><p>Receptor-Ligand Binding:</p><ul><li><p>Receptor for a specific ligand is a ___ receptor</p></li><li><p>Receptor with bound ligand is ___</p></li><li><p>Relationship of [ligand] and occupied receptor number is ___</p></li><li><p>___ ___ or ___ is the [free ligand] to occupy half of the receptors</p></li><li><p>Receptors with high affinity have ___ Kd</p></li><li><p>___ are drugs that activate receptors</p></li><li><p>___ are drugs that prevent a change and prevent natural ligands from binding</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7015eeaf-275c-4d35-bfdf-ec403a8d3943.png)
Membrane, second, amplification, hydrophilic, intracellular, direct, hydrophobic
Signal Reception:
Receptor Location:
___ receptors usually involve ___ messaging with signal ___
For ___ chemical signals
___ receptors usually have a ___ signal response
For ___ chemical signals
GPCR, cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP, diacylglycerol, DAG, inositol triphosphate, IP3, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP, calcium ions, Ca2+
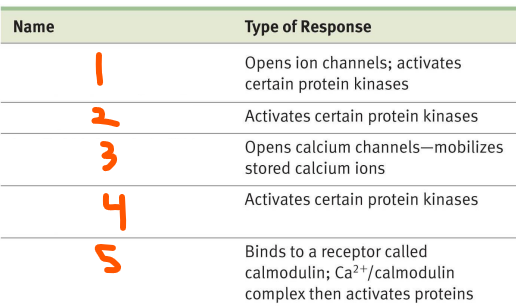
Signal Processing:
2nd Messengers:
All involved in ___ receptors
___ ___ ___ (___) that opens ion channels and activates some protein kinases
___ (___) that activates some protein kinases
___ ___ (___) that opens Ca2+ channels and mobilizes stored Ca
___ ___ ___ (___) that activates some protein kinases
___ ___ (___) that binds to calmodulin and the complex then activates some proteins
Membrane, hydrophilic, 10^6, 1, multiple, different, same, different, different, change
Signal Processing:
Signal Amplification:
Usually occurs with ___ receptors and ___ ligands
1 ligand can illicit a response from ___^___ (#) molecules
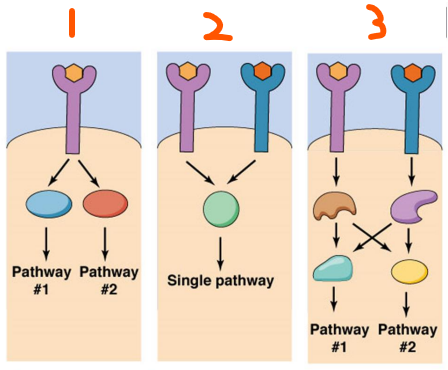
Integration:
Cells must integrate all signals for the right response
3 Types of Integration:
___ (#) receptor activates ___ pathway(s)
___ receptors activate ___ pathway(s)
___ receptors activate ___ pathway(s) that can ___ the other
Mitogenesis, gene expression, apoptosis, migration, cell-cell interactions, sensory, metabolism, protein transport, secretion, contraction, protein synthesis, differentiation
Signal Response:
12 Examples:
___
___ ___
___
___
___-___ ___
___
___
___ ___
___
___
___ ___
___
Automatic, rapid, free ligand [], receptor sensitivity, number, down-regulation, signal [], receptor numbers, activity
Signal Deactivation:
This mechanism is ___ and ___
2 Methods:
Reducing ___ ___ ___
Reducing ___ ___ or ___ (also called ___-___)
This allows cells to stay sensitive to ___ ___ and ___ ___ and ___
Receptor-mediated endocytosis, desensitization
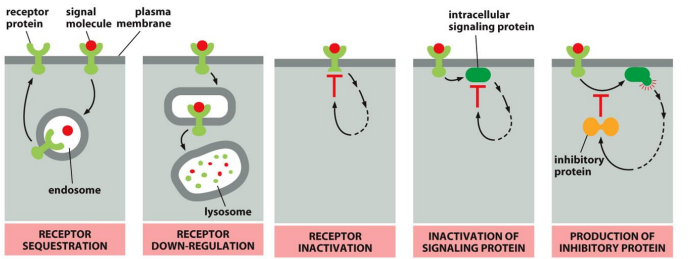
Signal Deactivation:
Down-Regulation:
2 Mechanisms:
___-___ ___ that reduce the receptor number
___ that alters receptors to lower affinity or prevent changes in cellular function
Ligand-gated ion channels, membrane, ionotropic, G protein-coupled receptors, GPCR, membrane, metabotropic, receptor kinase, membrane, metabotropic, nuclear, intracellular
4 Types of Receptors:
___-___ ___ ___ that are ___ and ___ receptors
___ ___-___ ___ (___) that are ___ and ___ receptors
___ ___ that are ___ and ___ receptors
___ receptors that are ___ receptors
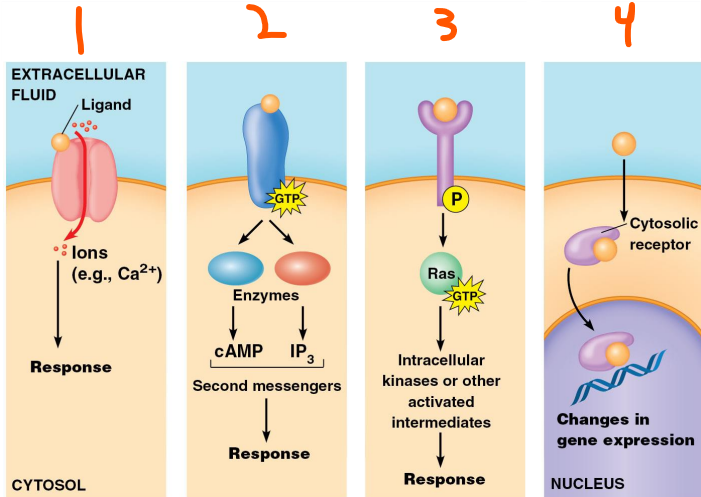
Guanine-nucleotide binding protein, G protein, 7-membrane, 7-transmembrane alpha helices, alternating, loops, N, C, phosphorylation, cytosolic AA, G protein-coupled receptor kinases, GRK, protein kinase A, PKA
G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCR):
Receptors change conformation when ligands bind which activates ___-___ ___ ___ or ___ ___
G proteins are used by many ___-___ spanning receptors
Receptors have ___-___ ___ ___ connected by ___ extracellular and cytosolic ___
___-terminus is exposed to ECF
___-terminus is exposed to cytosol
Regulated by ___ of specific ___ ___
EX: ___ ___-___ ___ ___ (___) and ___ ___ ___ (___)
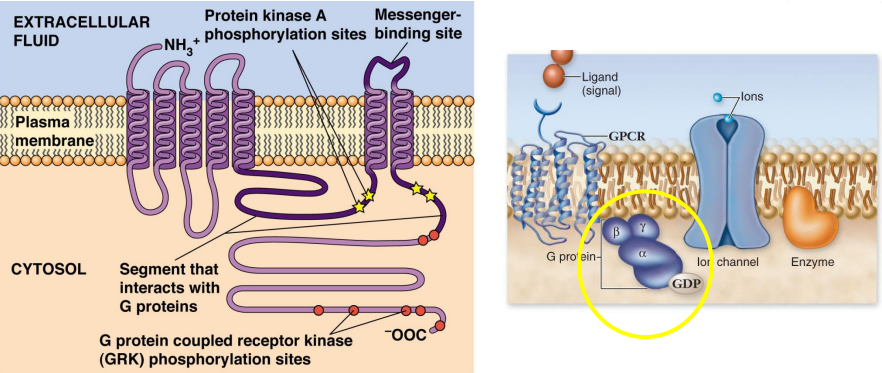
Guanine-nucleotide binding proteins, GTP, GDP, GEF, GAP, heterotrimeric, 40-45, alpha, beta, gamma, monomeric, 20-25, Ras, Rho, Rap, Rac
G Proteins:
Also called ___-___ ___ ___
Cycle between active state bound to ___ and inactive state bound to ___
___ exchange GDP for GTP
___ convert GTP to GDP
2 Types:
Large ___ G proteins of ___-___ (#) KDa with ___, ___, ___ subunits
Small ___ G proteins of ___-___ (#) KDa like ___, ___, ___, ___
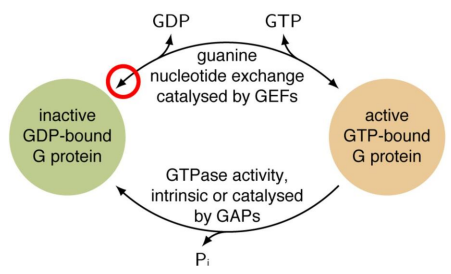
Gs, as, adenylyl cyclase, cAMP, Gi, ai, adenylyl cyclase, cAMP, Gq, aq, phospholipase C, calcium, protein kinase C, PKC
Classes of Heterotrimeric G-Proteins:
___ that has the ___ subunit and stimulates ___ ___ which increases ___
___ that has the ___ subunit and inhibits ___ ___ which decreases ___
___ that has the ___ subunit that mediates ___ ___ activation (which makes DAG and IP3), increases ___, and DAG activates ___ ___ ___ (___)
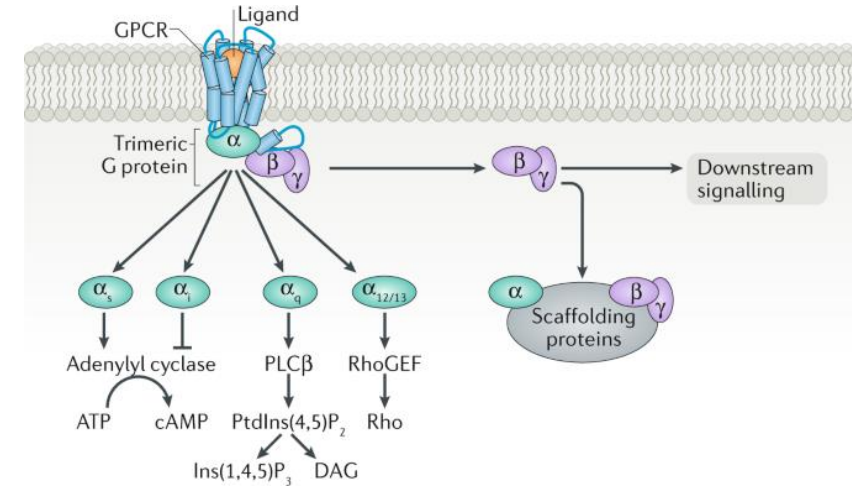
Resting, not, GDP, ligand, is, GTP, Ga, Gby, activate, inhibit, target proteins, transduction, GTP, GDP, inactivates, recombine, inactive G protein
Activity of Heterotrimeric G Proteins:
___ state where GPCR isn’t bound to a ligand and G protein ___ bound, alpha subunit is bound to ___
___ binds to GPCR and ___ bound to G protein, alpha subunit is bound to ___
___ and ___ separate
Subunits ___ or ___ the ___ ___ and start signal ___
Subunit hydrolyses ___ to make ___ which ___ the subunit
Subunits ___ to make an ___ ___ ___
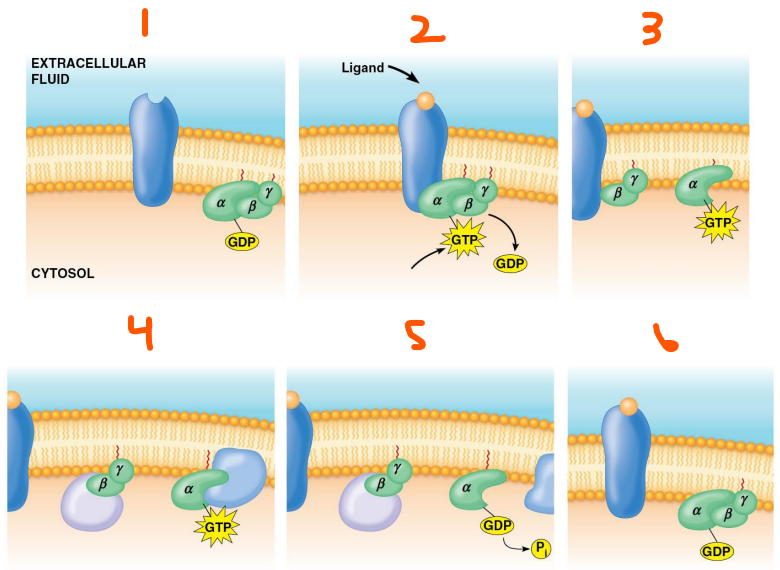
G-protein coupled receptor kinase, GRK, beta-arrestin, occupied, allosterically, GRK, phosphorylation, beta-arrestin, endocytosis
GPCR Regulation:
Can be desensitized by ___-___ ___ ___ ___ (___) and ___-___
___ GPCR is ___ activated by ___ through a ___ rxn
This recruits ___-___ to cause a rapid desensitization which leads to ___
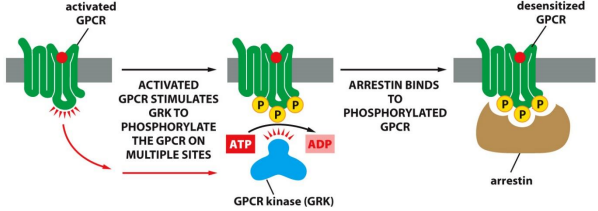
Activates, adenylyl cyclase, ATP, cAMP, inactivates, adenylyl cyclase, protein kinase A, PKA, serine/threonine kinase, exchange-protein-directly-activated-by-cAMP, Epac
G Protein Regulation:
When GTP-Gas binds, it ___ the enzyme ___ ___ that converts ___ to ___
When GTP-Gai binds, it ___ the enzyme ___ ___
Then cAMP activates ___ ___ ___ (___) (a ___/___ (AA) ___) and ___-___-___-___-___-___ (___)
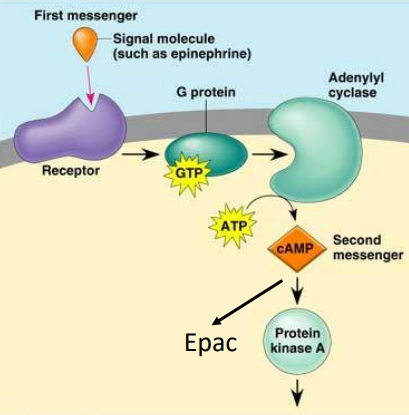
Adenylyl cyclase, ATP, cAMP phosphodiesterase, 5’AMP, degrade glycogen, produce FA, HR, BP, reabsorb water, bone resorption
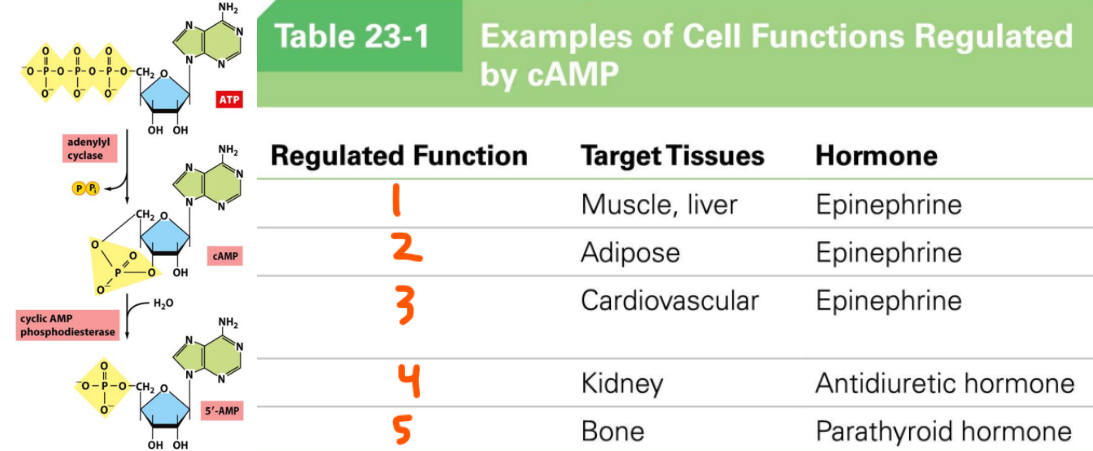
cAMP:
Made by ___ ___ from ___
Degraded by ___ ___ into ___
Functions:
Epinephrine stimulates muscles and liver to ___ ___
Epinephrine stimulates adipose to ___ ___
Epinephrine stimulates cardiovascular tissues to increase ___ and ___
Antidiuretic hormone stimulates the kidney to ___ ___
Parathyroid hormone stimulates bone tissue to cause ___ ___
2 regulatory, 2 catalytic, phosphorylate, ion channels, cytoplasmic targets, gene expression
cAMP Activates PKA:
cAMP activates PKA by binding to the ___ (#) ___ subunits to dissociate from the ___ (#) ___ subunits which then can ___ target proteins
PKA can regulate cellular functions by modulating ___ ___, ___ ___ like enzymes, and ___ ___
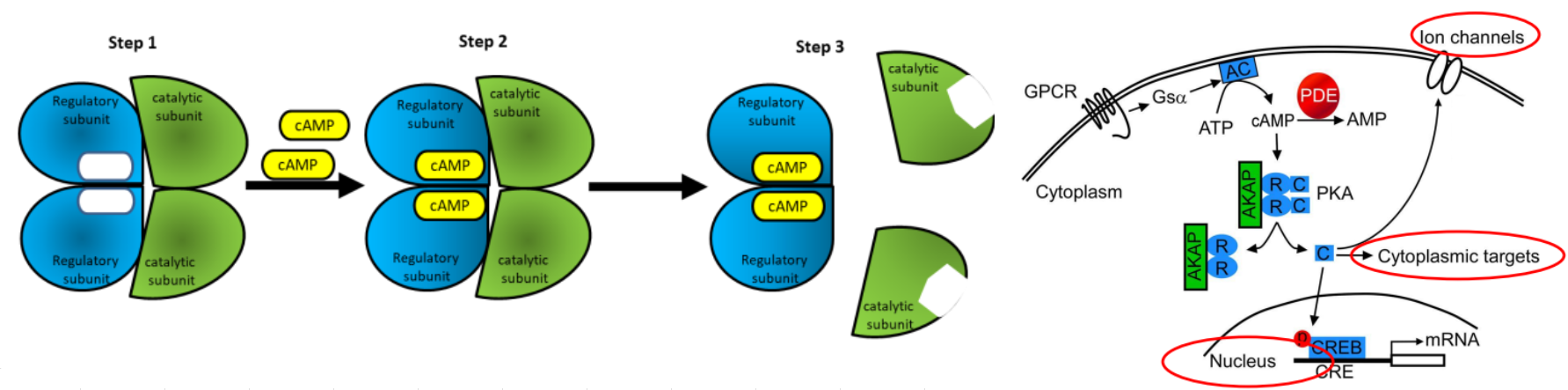
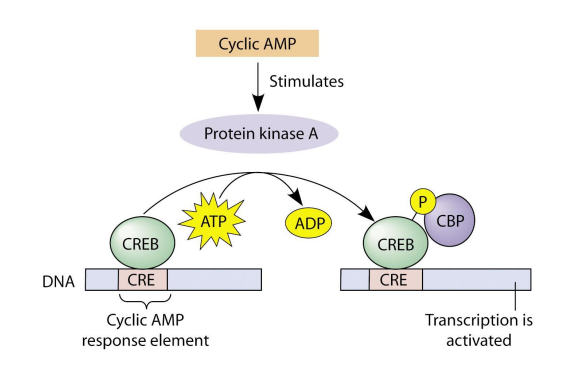
Phosphofructokinase 2/fructose bisphosphatase-2, fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein, CREB, cAMP response element, CRE, TGACGTCA
EX of cAMP Activating PKA:
EX: target protein: ___ ___/___ ___-___ which then regulates ___-___,___-___ levels
EX: gene expression: binds and activates ___ ___ ___ ___ ___-___ ___ (___) which binds to the gene ___ ___ ___ (___) with the code ___ (8)
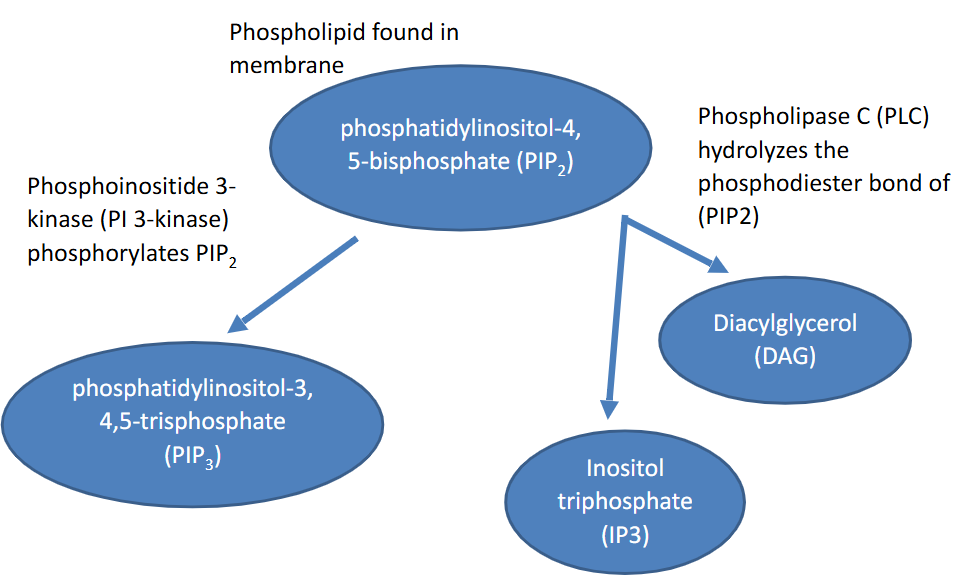
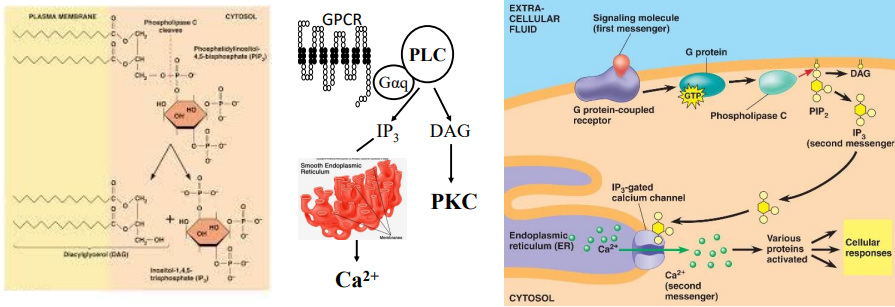
G proteins, Gaq, phospholipase Cb, PLCB, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, PIP2, inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate, diacylglycerol, Ca2+ channels, ER, protein kinase C, PKC, phosphorylates, ser, thr
IP3 and DAG:
Ultimately regulated by ___ ___ subunit ___ which stimulates the enzyme ___ ___ (___) which cleaves ___-___,___-___ (___) into ___-___,___,___-___ (IP3) and ___ (DAG)
IP3 binds to and opens ___ ___ in the ___ for physiological effects
DAG activates ___ ___ ___ (___) which then will ___ specific AA ___ and ___
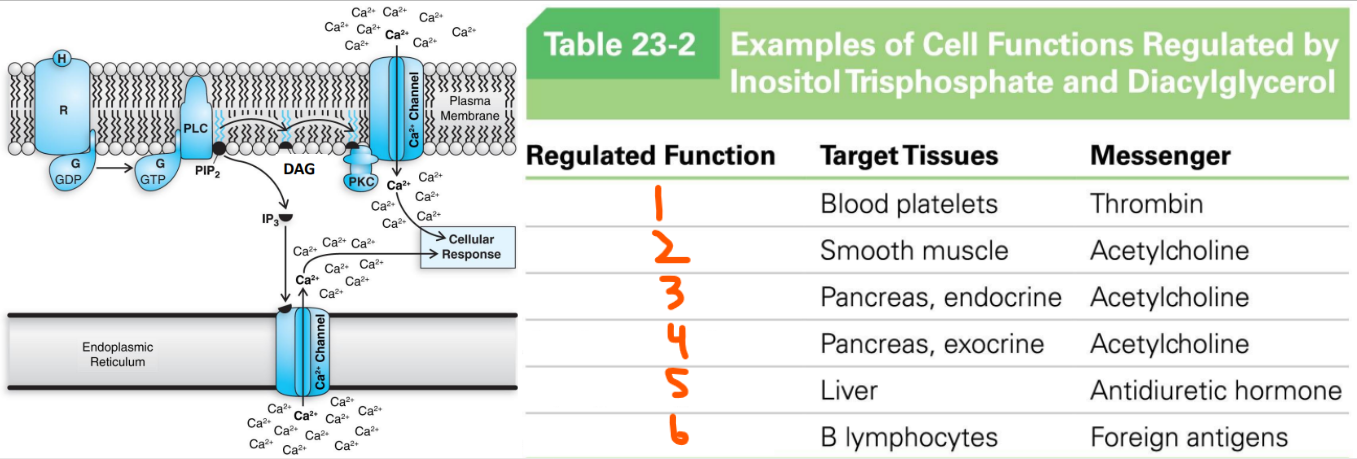
Activate platelets, contract muscles, secrete insulin, secrete amylase, degrade glycogen, antibodies
Functions of IP3 and DAG:
Thrombin stimulates blood platelets to ___ ___
Acetylcholine stimulates smooth muscle to ___ ___
Acetylcholine stimulates the pancreas (endocrine) to ___ ___
Acetylcholine stimulates the pancreas (exocrine) to ___ ___
Antidiuretic hormone stimulates the liver to ___ ___
Foreign antigens stimulate B lymphocytes to make ___
Epinephrine, a1-andrenergic, smooth muscles, blood vessels, contraction, inhibition, glycogen, GPCR, Gaq, phospholipase Cb, Ca2+, calmodulin, kinase, phosphorylate, glycogen synthase
Main IP3 Pathway:
___ hormone binds to ___-___ receptors found on ___ ___ and ___ ___ for ___ and ___ of ___ synthesis
The receptor is a type of ___ which activates the ___ subunit to then activate ___ ___
Resulting IP3 releases ___ which binds to ___ and activates a ___ to ___ and inactivate ___ ___
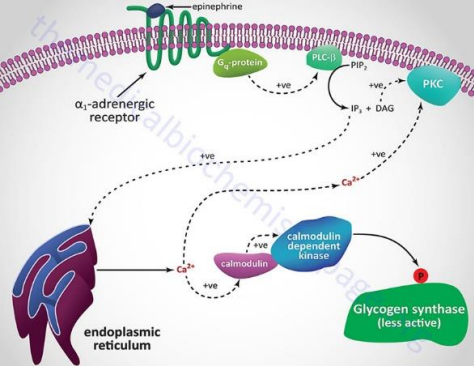
<0.1, Ca ATPases, plasma membrane, Ca ATPases, smooth ER membrane, Na+/Ca2+ exchangers, plasma membrane, mitochondria, IP3 receptors, smooth ER, ryanodine receptors, smooth ER, Ca induced-Ca release
Ca2+ Regulation:
Maintaining [] (red):
[] in cytosol kept at ___ (#) uM
___ ___ in the ___ ___ to keep Ca out
___ ___ in the ___ ___ ___ to take cytosolic Ca to the lumen
___/___ ___ in the ___ ___ keep cytosolic Ca out
___ transport Ca in
Increase Cytosolic [Ca2+] (blue):
___ ___ release Ca from ___ ___
___ ___ release Ca from ___ ___ (is a ___ ___-___ ___ mechanism)
![<p>Ca<sup>2+</sup> Regulation:</p><p>Maintaining [] (red):</p><ul><li><p>[] in cytosol kept at ___ (#) uM</p></li></ul><ol><li><p>___ ___ in the ___ ___ to keep Ca out</p></li><li><p>___ ___ in the ___ ___ ___ to take cytosolic Ca to the lumen</p></li><li><p>___/___ ___ in the ___ ___ keep cytosolic Ca out</p></li><li><p>___ transport Ca in</p></li></ol><p>Increase Cytosolic [Ca<sup>2+</sup>] (blue):</p><ol start="5"><li><p>___ ___ release Ca from ___ ___</p></li><li><p>___ ___ release Ca from ___ ___ (is a ___ ___-___ ___ mechanism)</p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0dcc1dc0-0783-4c85-8ce1-a2923659ecd0.png)
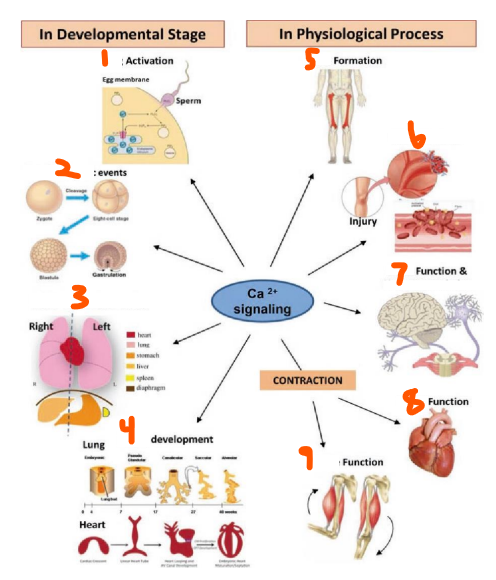
Calmodulin, calcineurin, phosphatase, synaptotagmin, egg, early embryonic, right-left axis patterning, organ, bone, blood clotting, brain, neurotransmission, heart, muscle
Ca2+ Effectors and Functions:
Effectors:
___
___ which is a ___
___ in neurons
Functions in Body:
___ activation
___ ___ events
___-___ ___ ___
___ development
___ formation
___ ___
___ function and ___
___ function
___ function
Neurotransmitters, synaptic vesicles, t-SNARE, v-SNARE, synaptotagmin
Ca2+ and Neurons:
Stimulates secretion of ___ from the ___ ___
Docking and fusion is mediated by ___-___ and ___-___ proteins that are allowed to interact by ___ which is a Ca sensor in the vesicle
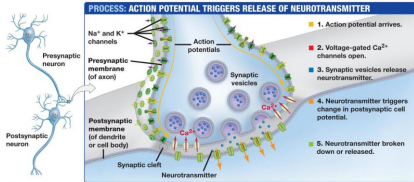
Ca binding protein, intracellular Ca receptor, 4, affinity binding sites, enzymatic
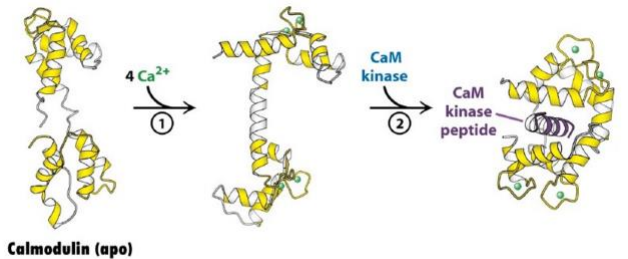
Calmodulin:
Is an important ___ ___ ___ / ___ ___ ___
Has ___ (#) high ___ ___ ___
No ___ activity
Activates other cellular molecules
Protein kinase-associated receptors, receptor, protein kinase, tyrosine, serine/threonine, growth factor, insulin, IGF-1, cycle, migration, metabolism, proliferation
Receptor Kinase:
Also called ___ ___-___ ___
Work as a ___ and ___ ___
2 Types:
___ kinase
___/___ kinase
Subtypes:
___ ___ receptors
___ receptors
___-___ receptors
Functions:
Mediate cell ___, ___, ___, and ___
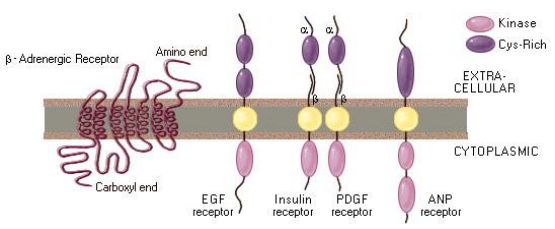
Epidermal, EGF, transforming, alpha, TGFa, platelet-derived, PDGF, transforming, beta, TGFb, fibroblast, FGF, interleukin-2, IL-2, colony-stimulating factor-1, CSF-1, Wnts, hedgehogs, neuronal, NGF
Growth Factor (GF) Families That Bind to Receptor Kinases:
Tyr kinase receptors on epithelial and mesenchymal cells with ___ GF (___)
Tyr kinase receptors on epithelial and mesenchymal cells with ___ GF ___ (___)
Tyr kinase receptors on mesenchyme, smooth muscle, and trophoblast cells with ___-___ GF (___)
Ser/thr kinase receptors on fibroblastic cells with ___ GF ___ (___)
Tyr kinase receptors on mesenchyme, fibroblast, etc cells with ___ GF (___)
3 subunit complex receptors on cytotoxic T lymphocytes with ___-___ (___)
Tyr kinase receptors on macrophage precursors with ___-___ ___-___ (___)
Frizzled (7-pass protein) receptors on embryonic cells with ___
Patched (7-pass protein) receptors on embryonic cells and melanocytes with ___
Also ___ GF (___)
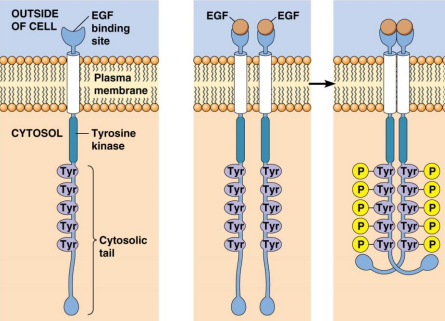
1 polypeptide chain, transmembrane, domains, extracellular, domain, cytosolic, tyr kinase, dimerization, 2, autophosphorylation
Receptor Tyr Kinase: Structure and Activation:
Structure:
Is a ___ ___ ___ with a ___ segment
Have distinct ___
The ___ portion has the ligand-binding ___
The ___ portion has the ___ (AA) ___
Activation:
___ of ___ (#) tyr kinase(s) join when a ligand binds
They undergo ___ from each other
Cascades, autophosphorylation, cytosolic proteins, phosphotyrosine, SH2 domain, Ras signaling, PI3-kinase, phospholipase Cy signaling
Receptor Tyr Kinase: Signal Transduction:
Start ___
___ step causes recruitment of specific ___ ___ that must have a sequence of AA that recognize ___ residue
Sequence of AA called ___ ___
Those proteins can activate different signal transduction pathways at the same time
EX of pathways: ___ ___, ___-___, ___ ___ ___
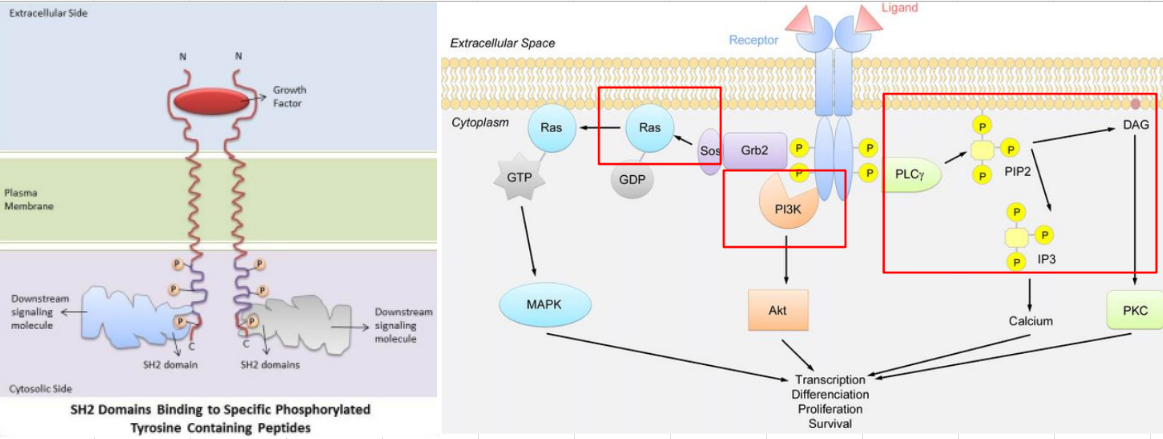
Monomeric G, GRB2, Sos, GEF, GDP, GTP, phosphorylation, transcription factors, gene expression, GTP, GAP
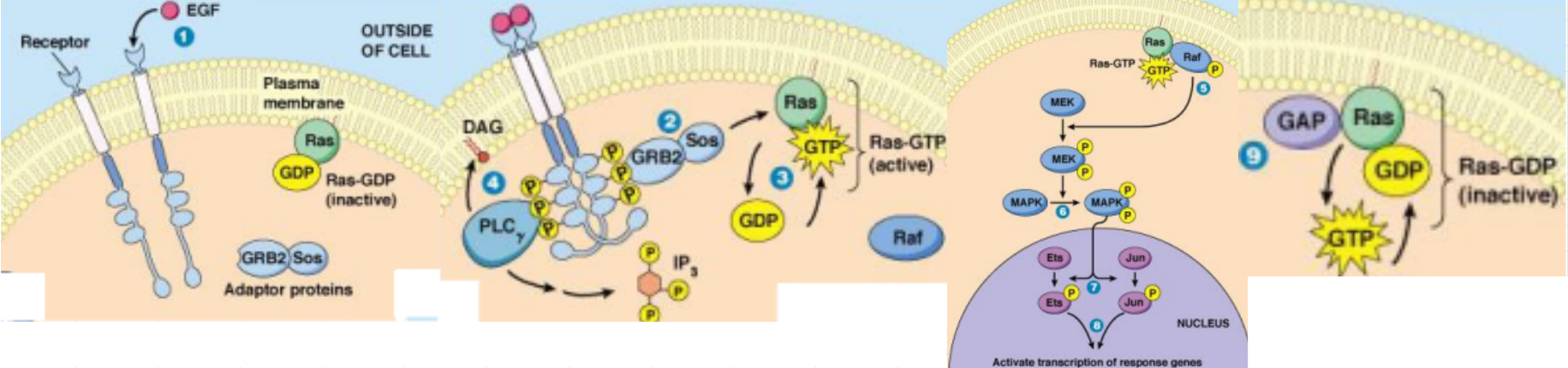
Receptor Tyr Kinase: Ras Signaling Pathway:
Ras is a ___ ___ protein
The protein bound to the phosphorylated tyr has a ___ (SH2 domain) and ___ (a ___ of Ras) that replaces ___ with ___
GTP-Ras causes ___ rxns towards ___ ___ for ___ ___
GTP-Ras is inactivated by hydrolysis of ___ by ___
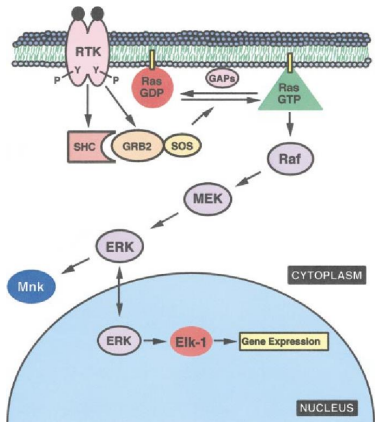
GTP-Ras, Raf, p-Raf, mitogen activated protein kinase kinase, MEK, ser/thr, p-MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinases, MAPK, tyr/thr, MAPK, transcription factors, cell growth, division
Receptor Tyr Kinase: Ras Signaling Phosphorylation Rxns:
___-___ phosphorylates ___
___-___ phosphorylates ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ (___) at ___/___ residues
___-___ phospohorylates ___-___ ___ ___ (___) at ___/___ residues
___ phosphorylates ___ ___ for ___ ___ and ___
Alpha, beta, b, insulin receptor substrate I, IRS-1, Ras, GRB2, PI3-kinase
Receptor Tyr Kinase: Insulin Signaling:
Receptor Tyr Kinase has 2 subunits: ___ and ___
The ___ subunit phosphorylates ___ ___ ___ ___ (___-___) which is the SH2 domain which can then stimulate 2 pathways:
___ pathway by recruiting ___
___-___ pathway
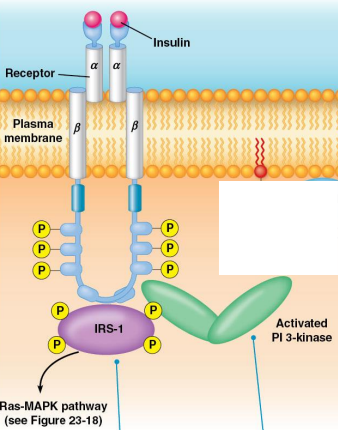
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, PIP2, phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate, PIP3, protein kinase B, PKB, Akt, PTEN, phosphatase
Receptor Tyr Kinase: PI3-Kinase:
___ ___-___ (PI3-Kinase) will phosphorylate ___-___,___-___ (___) to become ___-___,___,___-___ (___)
Then that will bind to ___ ___ ___ (___) or (___) that will then phosphorylate other kinases
PIP3 is converted back to PIP2 by ___ which is a ___
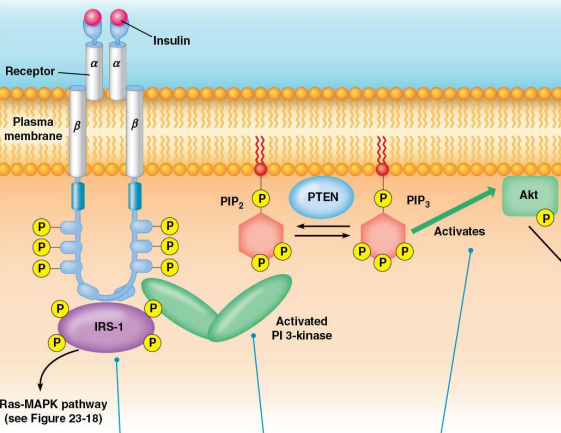
Glucose uptake, GLUT4, vesicles, membrane, glycogen synthase, glycogen synthase kinase 3, GSK3
Receptor Tyr Kinase: Akt Function:
Causes ___ ___ by moving ___ from ___ to ___
Causes activation of ___ ___ by phosphorylation and reducing the activity of ___ ___ ___ ___ (___)
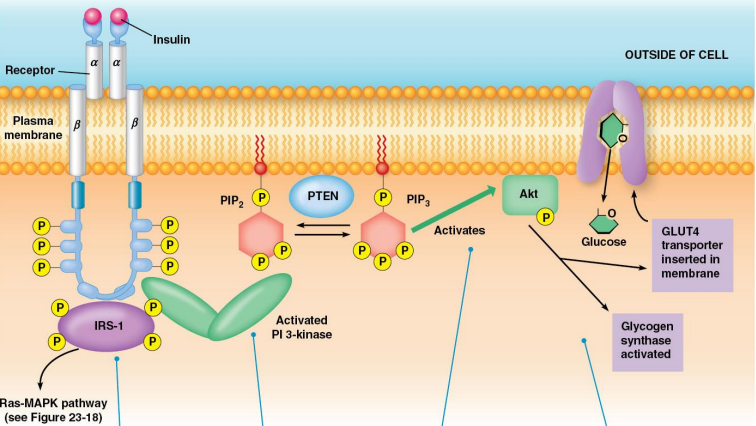
Endocrine, circulatory, [], specific receptors, intracellular, nuclear, gene expression, proteins, ion channels, polypeptides, AA, steroids
Hormones Basics and Types:
Are chemical signals from the ___ system that are secreted into the ___ system
Small ___
Act on ___ ___
Usually involved in ___ or ___ receptors
Functions:
Changing ___ ___
Activate/inactivate ___ or ___ ___
3 Types:
___
___ derivatives
___
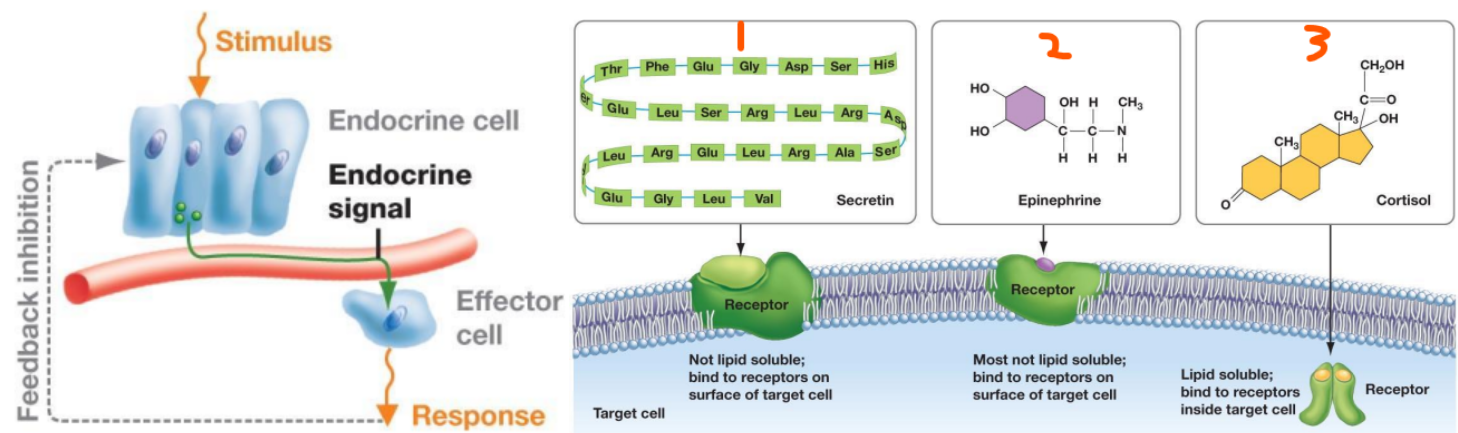
AA, peptides, proteins, steroids, AA, arachidonic acid
EX of Hormones:
___
___
___
___
___
___ ___
Steroid hormones, gene expression, steroid hormone, hormone binding, DNA binding, regulatory
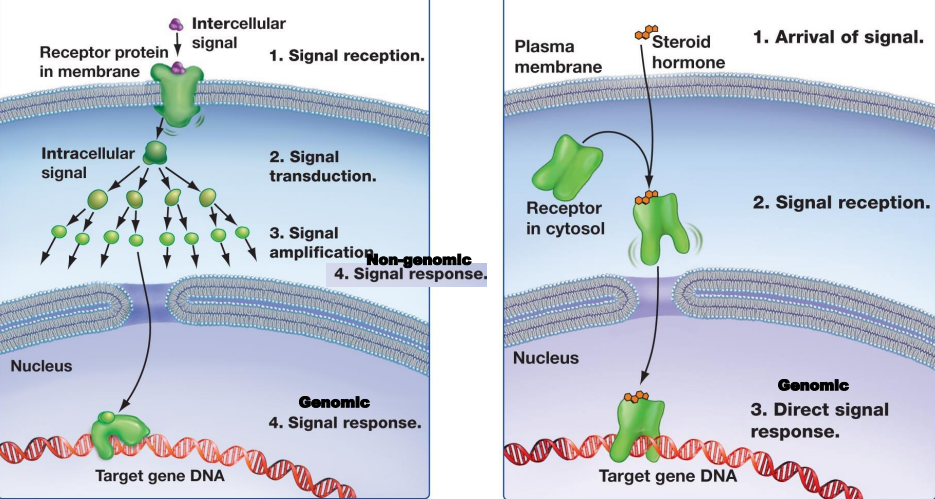
Nuclear Receptors:
Usually involve ___ ___ as ligands that usually regulate ___ ___
Receptors are ___ ___ receptors
3 Domains:
___ ___ domain
___ ___ domain with high homology
___ domain
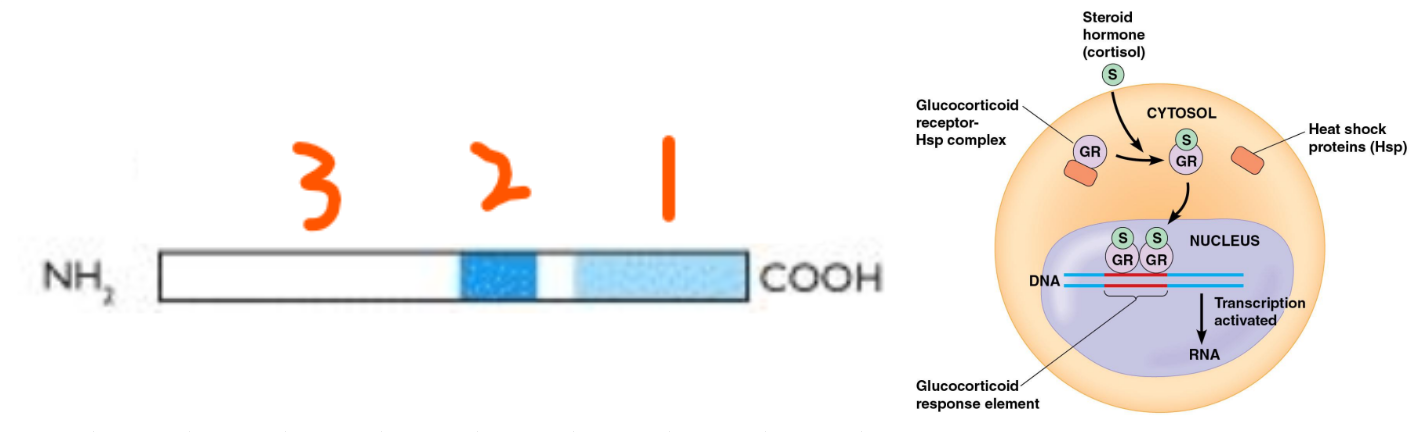
Monomers, heat shock proteins, HSP, dimerized, steroid-response elements, SRE, co-regulators, genomic ER, membrane-bound ER, GPER
Steroid Hormone Receptors:
Cytoplasmic receptors are usually ___ that are bound to ___ ___ ___ (___) which then go to the nucleus
Nucleus receptors become ___ when the hormone binds
Then the receptors bind to ___-___ ___ (___) and interact with ___-___ to modulate gene expression
Steroid Receptors can activate 3 Main Pathways:
___ ___ pathway
___-___ ___ pathway
___ pathway
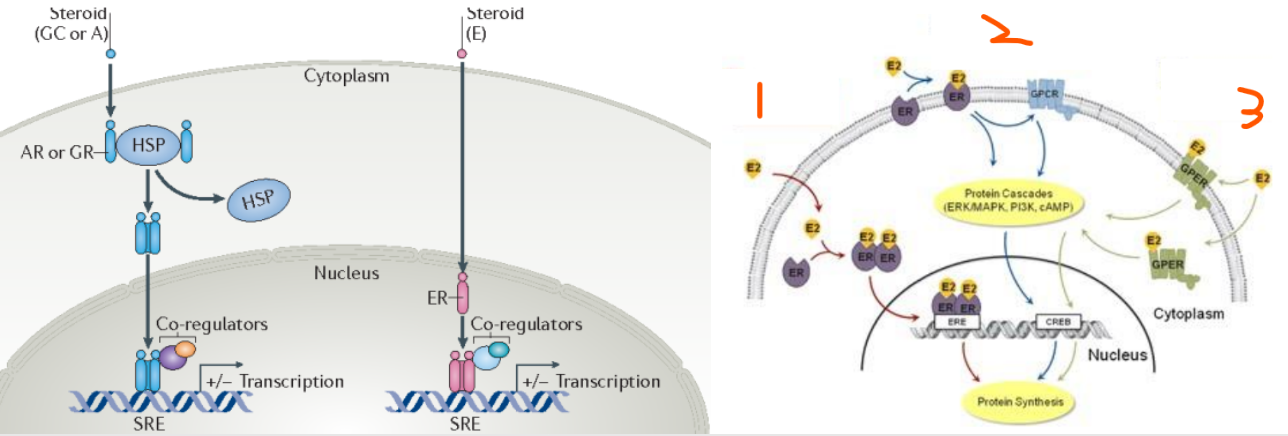
Crosstalk, many, many, same
Integration of Different Signaling Pathways:
Through ___
Cells integrate different signals for the right response
1 receptor can activate ___ pathway(s) or ___ pathway(s) can converge to make the ___ molecule(s)
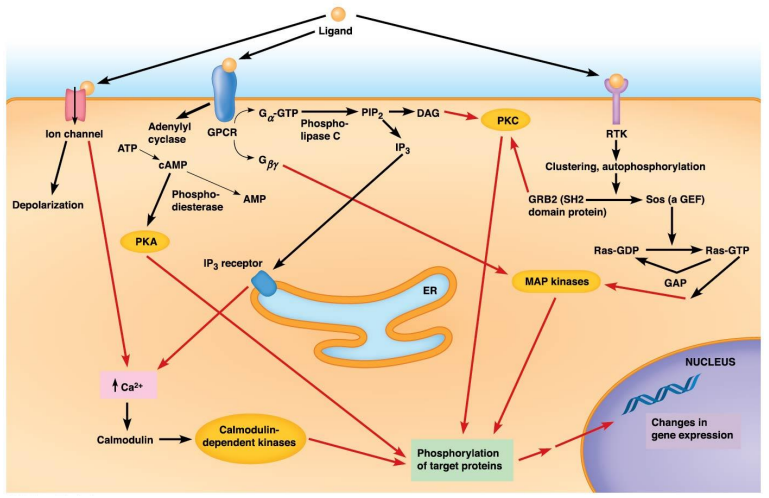
2
Overall, what is the point of chemical signal transduction?
to internalize proteins that can then be degraded in the lysosomes
to sense and respond to the environment outside the cell
to adjust a cell’s energy needs to the local environment
to detect when a cell needs to move, and then move
3
Why is the consequence of epinephrine so different for heart cells and liver cells?
The epinephrine receptors on the surface of their target cells are different.
The epinephrine receptors are more abundant on the surface of heart cells.
The proteins stimulated by the bound epinephrine receptor are different in heart cells and liver cells.
Different amounts of epinephrine reach each different type of target cell.
1, 4, 3, 2
Place the following steps of signal transduction in order
A messenger (ligand or signal) binds to its receptors
The signal and transduction pathway is turned off.
There is a change cellular function or gene expression
The ligand-receptor interaction initiates the signaling process.
1
Which is an example of a hormone in action?
A peptide made in the liver promotes uptake of AA from the blood throughout the body.
A steroid causes nearby cells to become pigmented.
A derivative of tryptophan causes a tissue, next to the one in which it is produced, to show signs of inflammation.
a and b
b and c
4
Which of the following mechanisms would you associate with an antagonist drug action?
a drug that binds postsynaptic receptors and mimics the effect of the endogenous neurotransmitter.
a drug that prevents the normal reuptake of neurotransmitters inside presynaptic terminals.
a drug that increases the enzymatic synthesis of neurotransmitters.
a drug that binds postsynapatic receptors and blocks the normal action of the endogenous neurotransmitter.
3
Which of the following hormones could have an intracellular receptor? (select all that apply)
Insulin (hydrophilic hormone)
Epinephrine
Cortisol
Angiotensin II (lipid-insoluble peptide hormone)
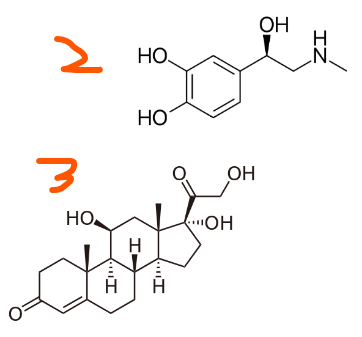
4
Which of the following is true regarding G-proteins
GAPS activate G-proteins exchanging GDP for GTP
GAPS activate G-proteins exchanging GTP for GDP
GEFs activate G-proteins exchanging GTP for GDP
GEFs activate G-proteins exchanging GDP for GTP
1
When luteinizing hormone binds to its receptor (LHR) on ovarian granulosa cells, there is an increase in the gene expression of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (HSD). This increases progesterone production from these cells. LHR is a G-protein coupled receptor that when activated, increases intracellular cAMP.
What type of G protein binds to the LHR?
Gαs
Gαi
Gαq
Ras
56?!
58?!
3
Consider a mutant liver cell isolated from a liver cancer patient. This cell contains about 104 molecules of active protein kinase A, even in the absence of epinephrine. What is a reasonable genetic explanation?
The cell’s phosphorylase kinase gene has a mutation that makes the kinase active all of the time.
The cell’s glycogen phosphorylase gene has a mutation that makes the phosphorylase active all of the time.
The cell’s adenylate cyclase gene has a mutation that makes the cyclase active all of the time.
The cell’s adenylate cyclase gene has a mutation that makes the cyclase inactive all of the time.
4
Which of the following proteins has SH2 domains?
guanylyl cyclase
inactive large heterotrimeric G protein
the EGF receptor, a tyrosine kinase receptor
PLCγ
3
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in males and the second most deadly. One area of investigation for understanding the development and progression of this cancer involves fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling. What type of receptor does FGF binds to?
GPCR
Intracellular steroid receptor
Tyrosine Kinase Receptor
Ionotropic Receptor
4
Prostate cancer is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in males and the second most deadly. One area of investigation for understanding the development and progression of this cancer involves fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling.
The FGF receptor is a tyrosine kinase receptor that activates the Ras signaling pathway. Which of the following is NOT important in this signaling pathway
Sos
Ras
MAPK
Ca 2+ second messenger
Transcription factors
3
Which of the following is true regarding the comparison between GPCRs and RTKs
GPCRs have cytosolic sites for phosphorylation kinases, RTKs have an extracellular component that acts as the tyrosine kinase
GPCRs have multiple (3-5) transmembrane segments, RTKs have 2 transmembrane segment
Ligand binding of GPCRs results in activation of G-proteins and exchange of GDP for GTP, Ligand binding of RTKs results in dimerization and autophosphorylation
2
Which of the following is important for phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) phosphorylation
Inositol triphosphate (IP3)
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase)
Phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3)
Diacylglycerol
PLC
Add
Review?!