Ch. 15 The Autonomic Nervous System
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
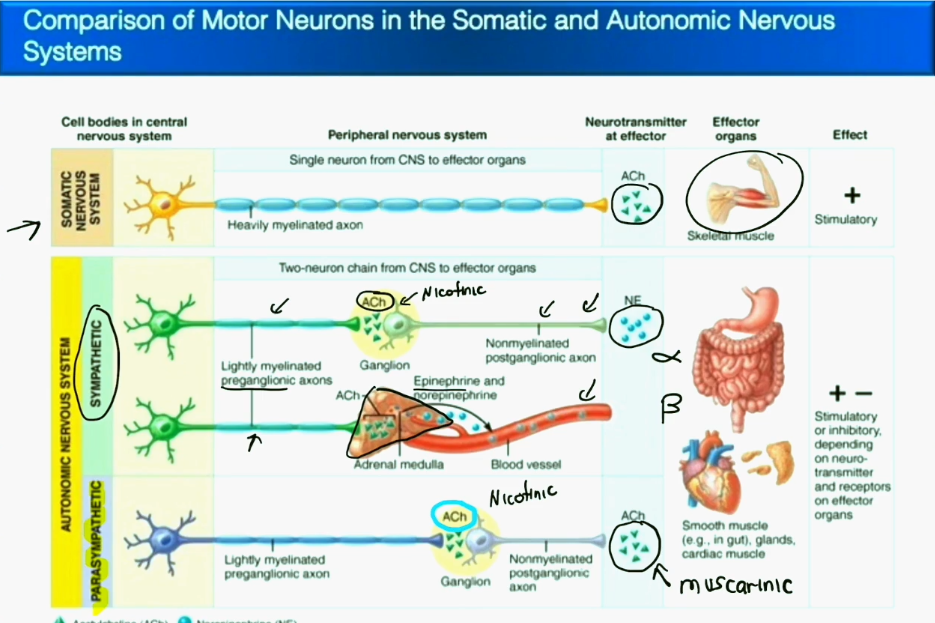
Autonomic Nervous System vs Somatic Nervous System
The ANS controls subconscious processes, such as maintaining our heart rate, body temperature, and performing digestion.
The SNS allows us to consciously control our body, particularly through the movement of skeletal muscle.

The ANS consists of motor neurons that:
Innervate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glandular tissue.
Make adjustments to ensure optimal body functionality.
Operate via subconscious control.

Autonomic vs Somatic:
Autonomic organs include cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands. Somatic effectors primarily include skeletal muscle.
Autonomic neurotransmitters include acetylcholine and norepinephrine. Somatic neurotransmitters only include acetylcholine.
Autonomic efferent pathway involves two seperate neurons, a preganglionic and post ganglionic neuron. Somatic efferent pathway only involes on neuron.

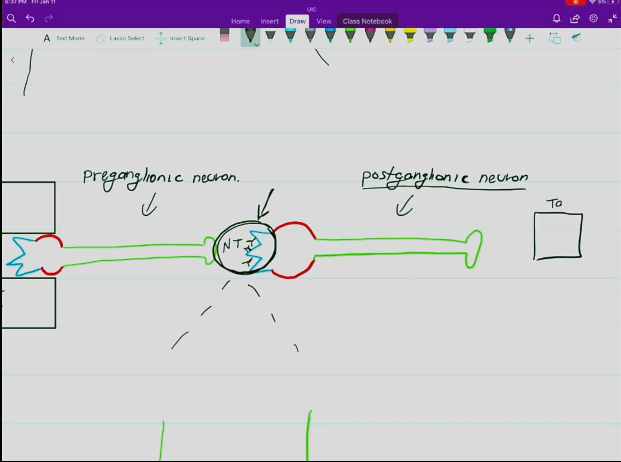
Preganglionic Neuron
Located in the CNS
Releases acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter.
Synaptic cleft located between the preganglionic neuron and the postganglionic neuron at the site of the ganglion.
Has a thin, lightly myelinated axon leading to the ganglion.
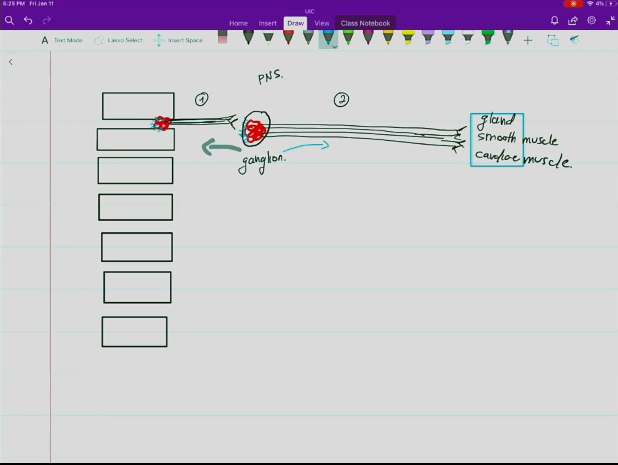
Postganglionic Neuron
Located in the PNS
Releases either acetylcholine or norepinephrine as its neurotransmitter, as either could have a stimulatory or inhibitory effect, depending on the target organ.
Synaptic cleft located between the postganglionic neuron and the target organ.
Has a nonmyelinated axon leading away from the ganglion that extends towards the effector organ.
Autonomic Nervous System Divisons:
Parasympathetic (chill tf out)
Sympathetic (tweaking)

Parasympathetic Role: + da secret name
Promote maintenance activities such as digestion, diuresis, and defecation. “Rest and digest”
Lowers blood preasure, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
Increases activity in the gastrointestinal tract.
Constricts pupils for close vision.
Thoracolumbar

Parasympathetic Anatomy:
Preganglionic fibers originate from the brainstem or from the sacrum. Including CN 3, 7, 9, and 10. S2, S4.
Preganglionic fibers are much longer than the postganglionic fibers, nearly reaching the target organ with the synapse.
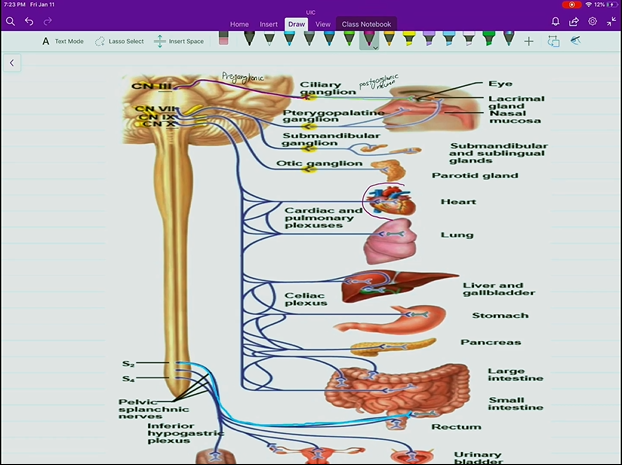
Sympathetic Role:
Mobilizes body during activity; “Fight or flight” system
Exercise, Excitement, emergency, embaraessment
Heart rate up, mouth dry, cold, sweating, dilating pupils.
During intense physical activity it can shunt blood to skeletal muscles and heart, dilate bronchioles, force the liver to release glucose.

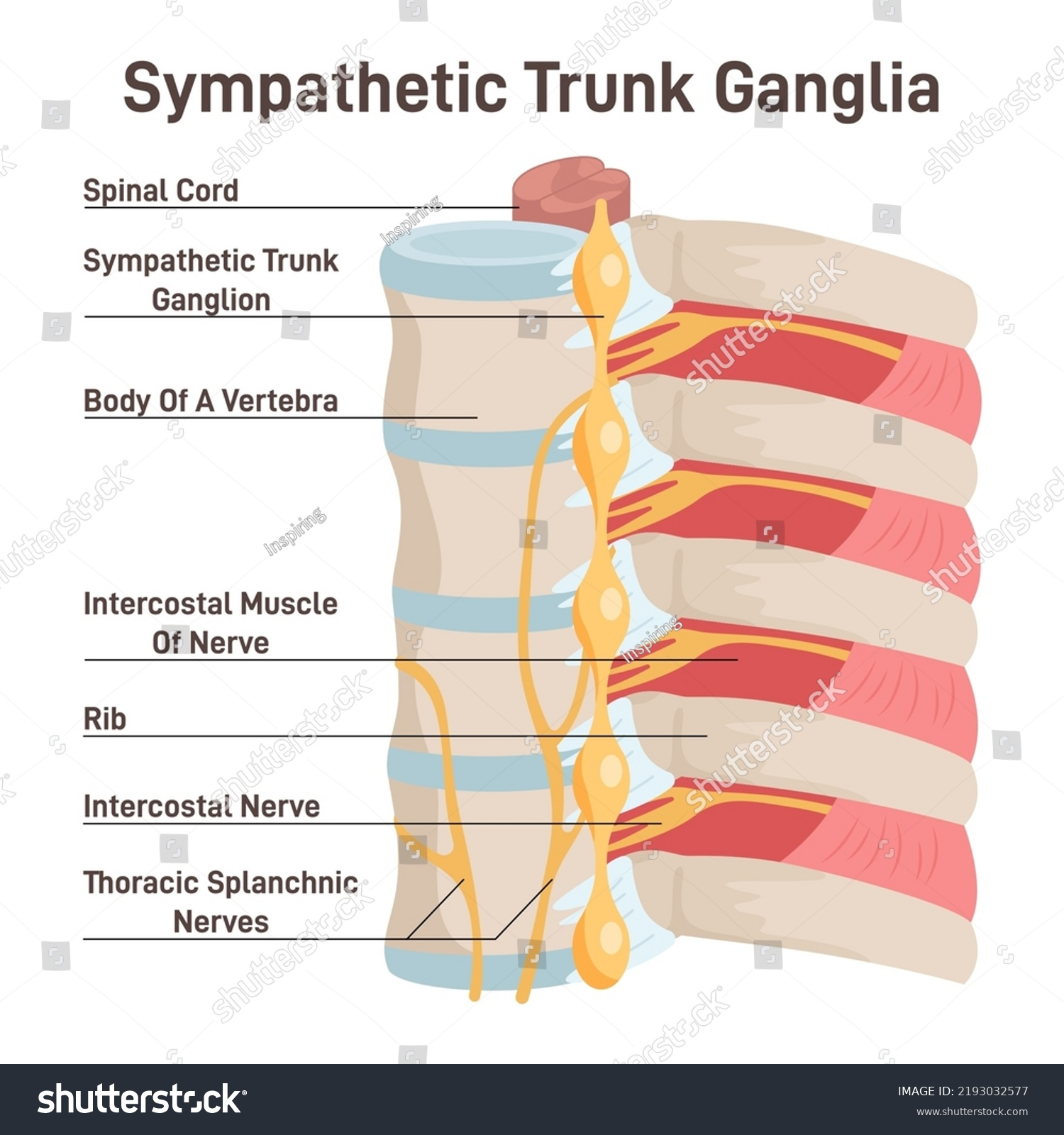
Sympathetic Anatomy
Originiates between T1 - L2, from the lateral horns of the vertebrae.
Preganglionic fibers pass through white rami communicantes and enter the sympathetic trunk/chain/paravertebral ganglia.
This time post is the big one and pre is the small one
oh yeah and the celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric ganglion kinda just f off to wherever they wan go
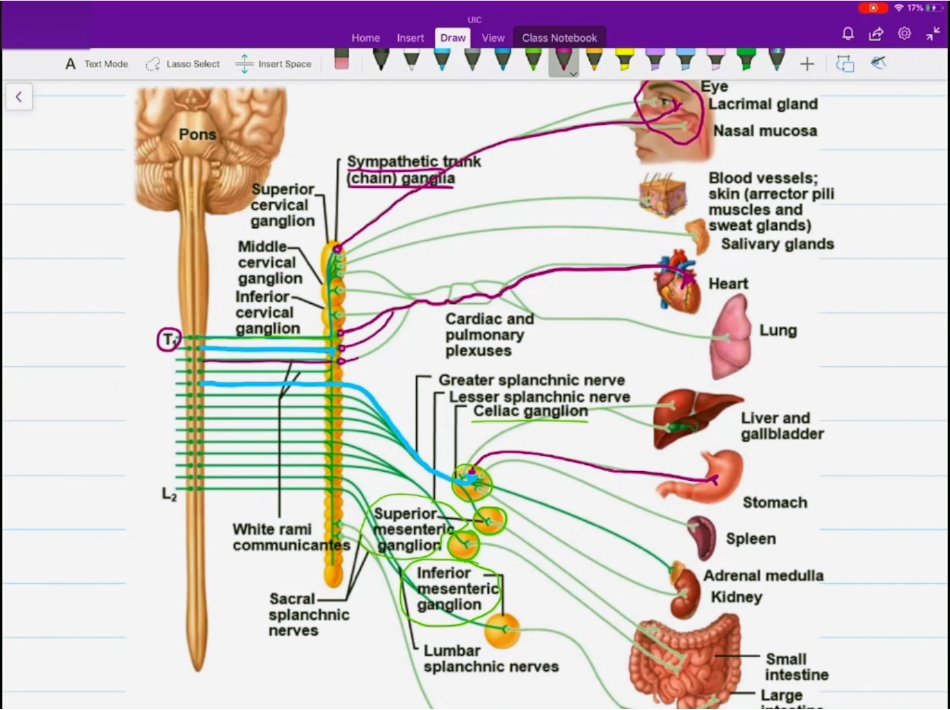
sympathetic trunk paravertebral ganglia
Where the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers meet in the sympathetic division.
Neurotransmitters and Receptors of the Parasympathetic Nervous System:
Preganglionic body begins in the CNS, the preganglionic axon releases acetylcholine (ach) from its terminal end into the nicotinic receptors of the postganglionic body. The postganglionic axon will then release acetylcholine (ach) into the muscarinic receptors of the gland/smooth muscle/cardiac muscle.

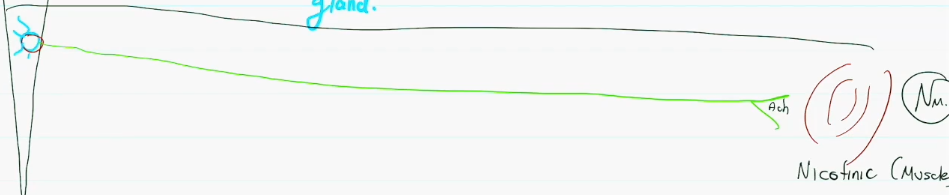
Neurotransmitters and Receptors of the Sympathetic Nervous System:
Preganglionic body begins in the CNS, the preganglionic axon releases acetylcholine (ach) from its terminal end into the nicotinic receptors of the postganglionic body. The postganglionic axon will then release norepinephrine (NE) into the alpha or beta receptors of the gland/smooth muscle/cardiac muscle. UNLESS the postganglionic axon is releasing into a sweat gland, in that case it will release acetylcholine (ach) into the muscarinic receptors of the sweat gland.

Neurotransmitters and Receptors of the Sympathetic Nervous System: (the special one)
Preganglionic body begins in the CNS, the preganglionic axon releases acetylcholine (ach) from its terminal end into the nicotinic receptors of the adrenal gland (it counts as a neuron and an organ). The adrenal gland will then secrete adrenaline.

Neurotransmitters and Receptors of the Somatic Nervous System:
Preganglionic body begins in the CNS, the preganglionic axon releases acetylcholine (ach) from its terminal end straight into the mf muscle via Nicotinic Muscle receptors.
Neurotrannsmittersss and receptors picture
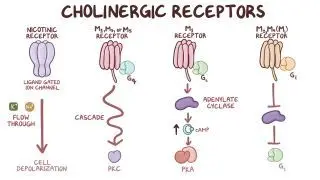
Muscarinic Receptors
They are found on all cells that are stimulated by postganglionic cholinergic fibers (Synaptic knobs).
Effect of ach on the receptor varries greatly depending on the organ.
Effect on Eyes:
Constricts the pupil so you see less.
Ur chilling, u dont need to see predators bruz

Effect on Heart:
Decreases the heart rate and by extension blood preasure
Again ur chilling bruz, ur body doesnt need a ton of oxygenated blood.

Effect on lungs
Decreases the rate of respiration,
ur chilling, u dont need oxygen for atp

Effect on Digestive System
Increase activity
Now that your chilling we can stock up on macro and micro nutrients for when ur not chilling

Bladder
U finna be pissing hella
Ur in a safe place, u can pee now no predator gonna catch u lacking

Glands
Secreate a lot of salavia (for eating), tears (for emotional release), etc.

Andrenergic Receptors
Two major classes: Alpha and Beta
Both are involved in the sympathetic nervous system, affected by norepinephrine
Effects depend on if an Alpha or Beta receptor is receiving.
Alpha 1
Eye, increases dilation
Arteries and veins, increases constriction
Urinary bladder, retains urine.

Alpha 2
Prejunctional Nerve:
Basically, alpha 2 detects if there is too much norepinephrine being sent and will restrict its release.

Beta 1
Heart, increase heart rate and therefore increases blood pressure.
Kidney, stimulates the release of adrenaline and increases blood pressure
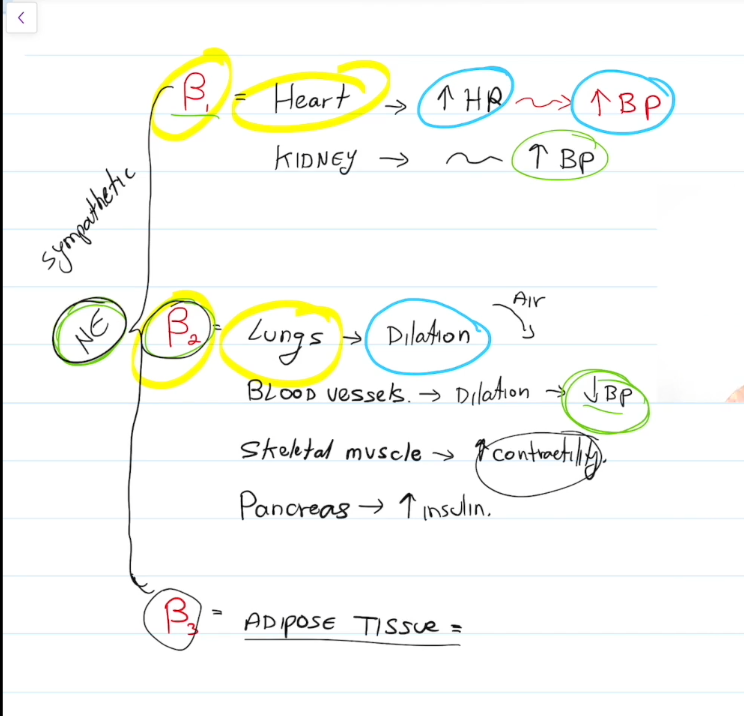
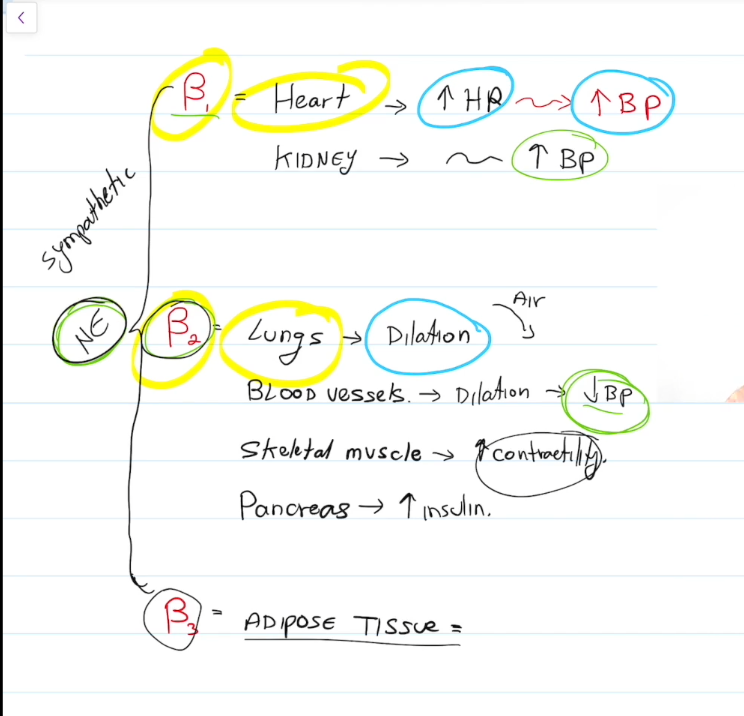
Beta 2
Lungs, dilate and increase air intake.
Blood Vessels, dilate and decrease blood pressure
Skeletal muscle, contract em
Pancrease, increase insulin
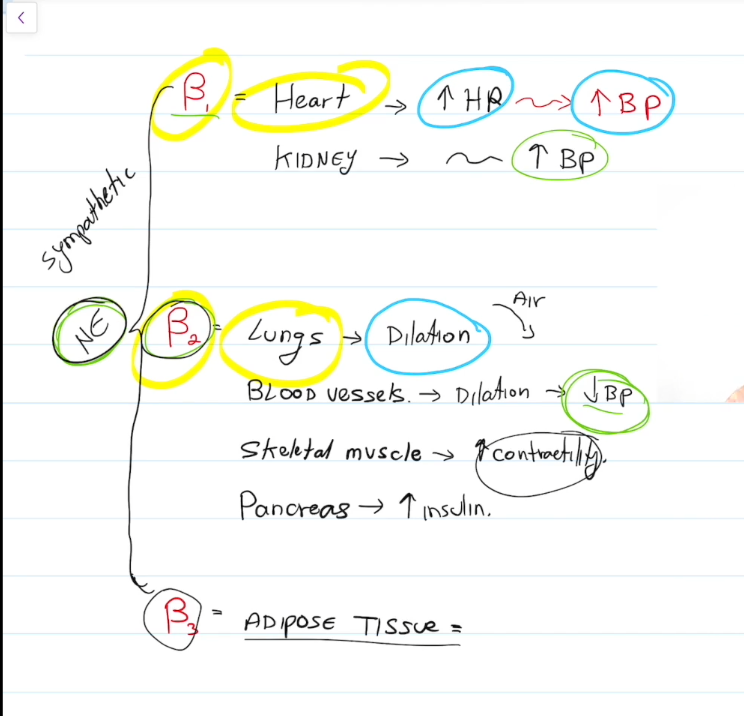
Beta 3
Break down fat in adipose tissue
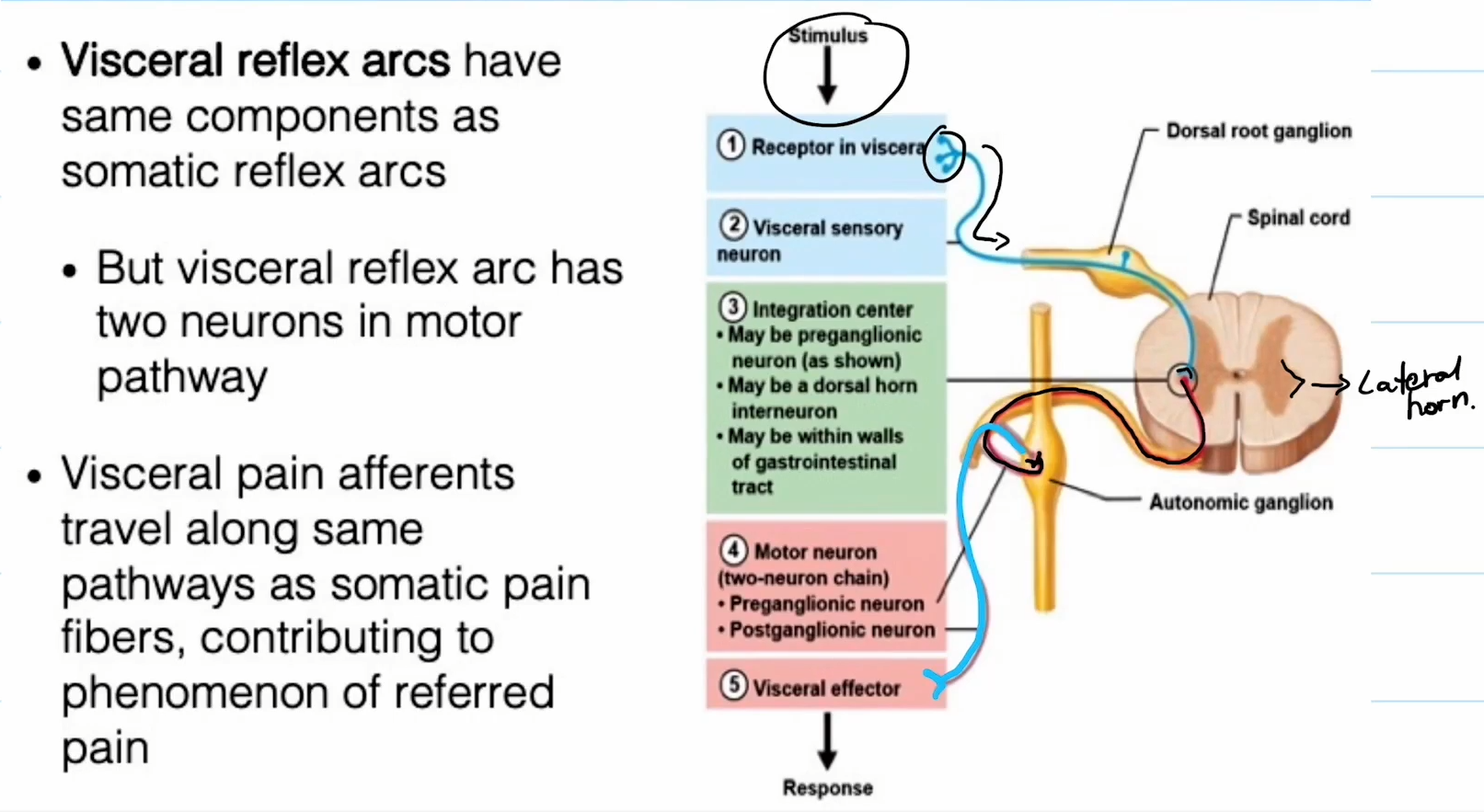
Visceral Reflexs
Visceral reflex arcs pretty much have the exact same components of somatic reflex arcs. The only difference is that it has two neurons in the motor pathway.
Receptor in viscera.
Travels to the visceral sensory neuron.
Integration center analyzes the information.
Motor neuron delivers response.
Visceral effecter kicks in.
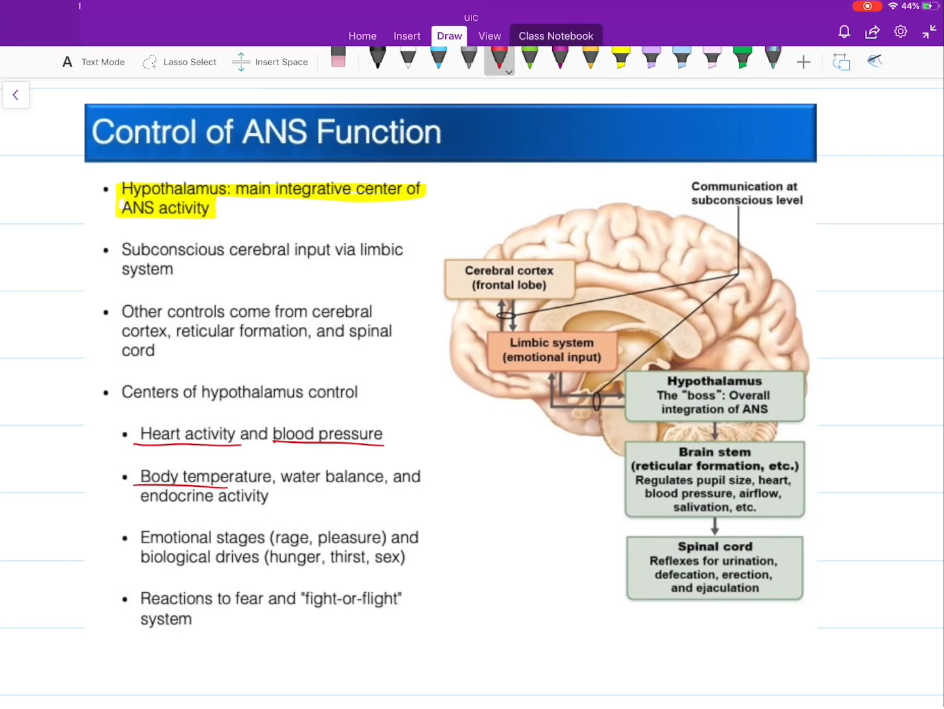
What controls the ANS?
Hypothalamus
How does parasympathetic and sympathetic work together?
Basically one opposes the other and allows for precise control of visceral activity.
