General principles of neuroanatomy
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANHB2217
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms


Ipsilateral
Contralateral
Afferent
Efferent
Tract/column
Decussation
Ramus/rami plural
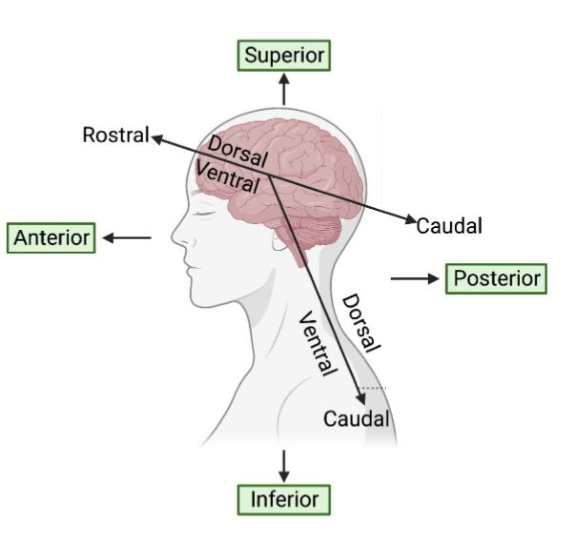
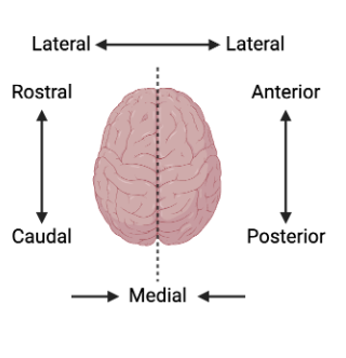
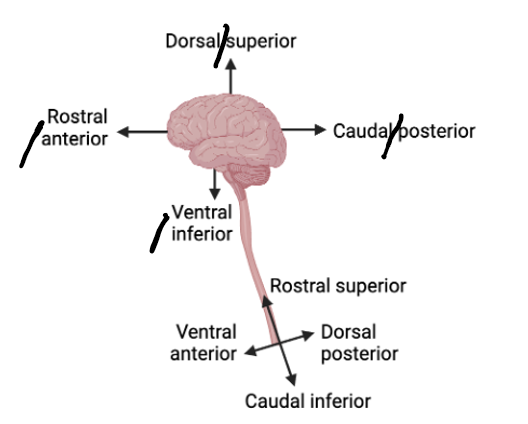
Ipsilateral – same side of the body
Contralateral – opposite side of the body
Afferent – inward or towards (the brain)
Efferent – outward or away from (the brain)
Funiculus=fasciculus=lemniscus (bundle) (refer to white matter tracts)
Chiasm (X shaped structure)
Branch
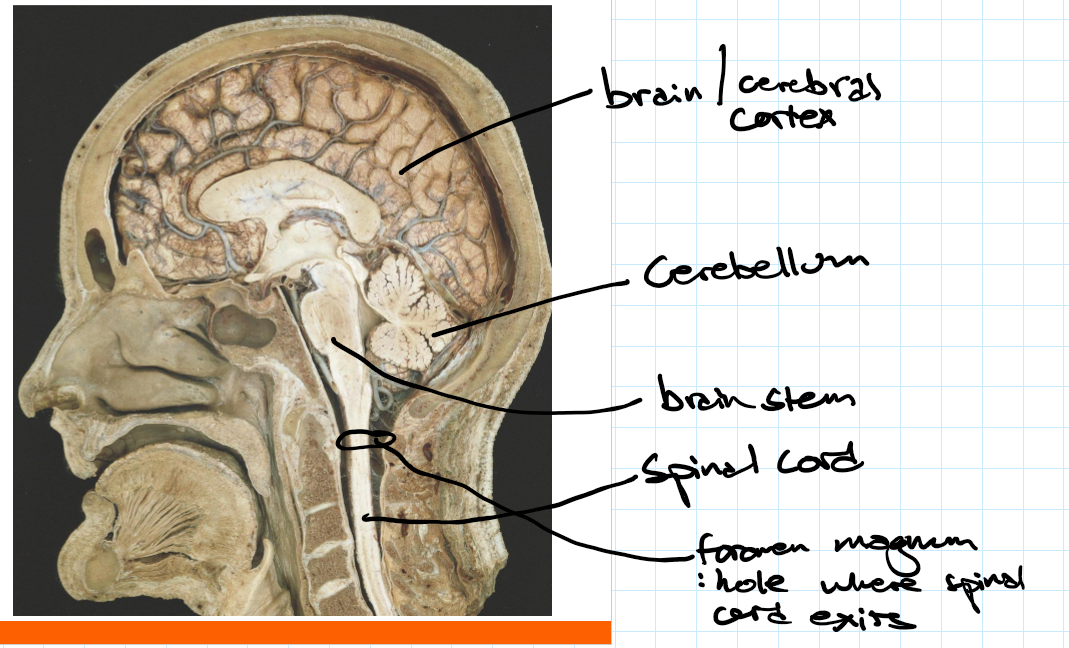
Central nervous system CNS
BS, contained within what
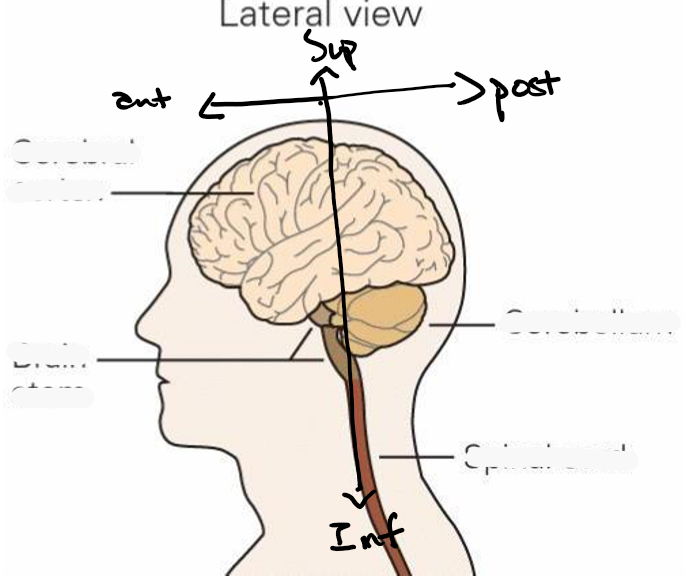
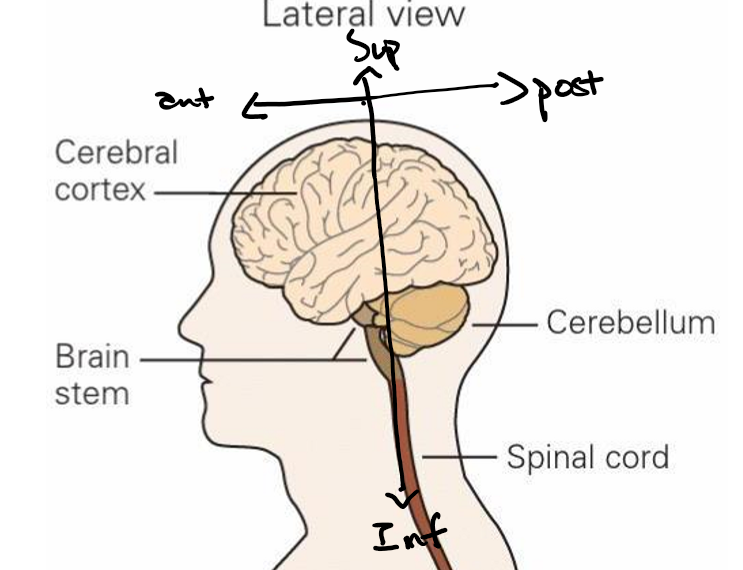
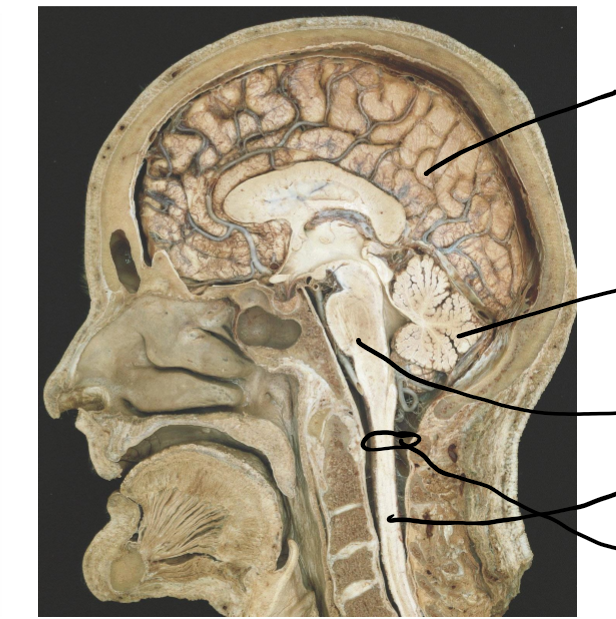
Brain -cortex, cerebellum and brainstem
Spinal cord
Contained within the skull and vertebral column
Peripheral nervous systems PNS
CBS
Cranial, spinal and peripheral nerves
Brachial, lumbar plexus, peripheral ganglia
Somatic, autonomic and enteric divisions
Lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
FPOT IC
Frontal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
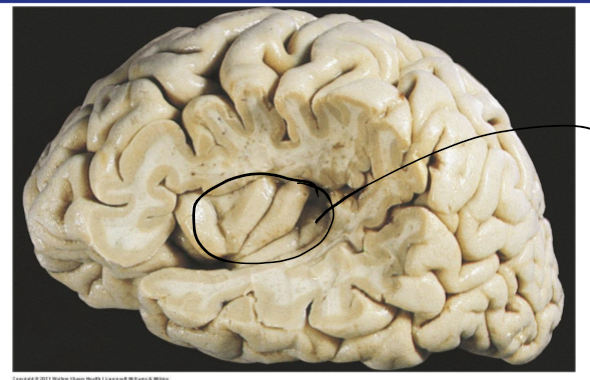
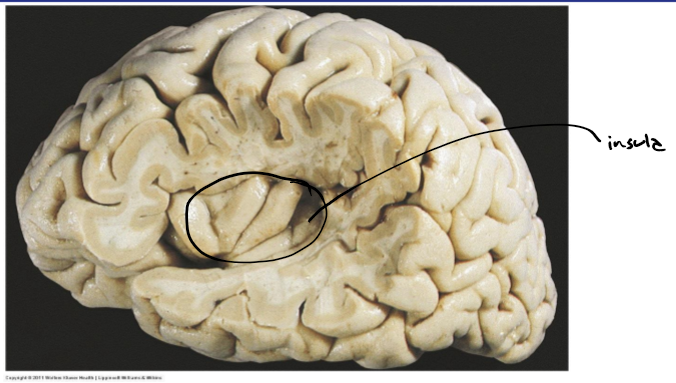
Insula
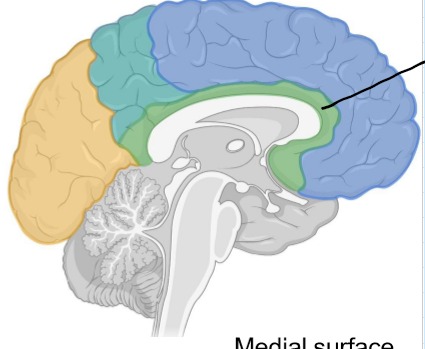
Cingulate
Frontal lobe
HMLH
Higher processing, memory, language, houses primary motor cortex for motor control
Parietal lobe
SPI
Houses somatosensory cortex which receives all sensory info, involved in sensory perception and integration
Occipital lobe
VSOM
Visual input, visual spatial processing, object recognition, memory
Temporal lobe
LALVE
Location of temporal bones, auditory processing, language, visual memory, emotion
Insula
RA(PS)
Risk reward behaviors, autonomic functions eg regulation of parasympathetic nervous system and sympathetic nervous system
Cingulate
L
Involved in limbic systems so emotional response to things
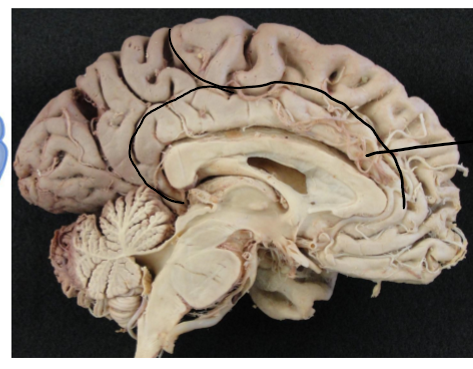
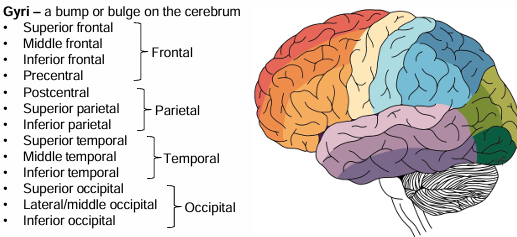
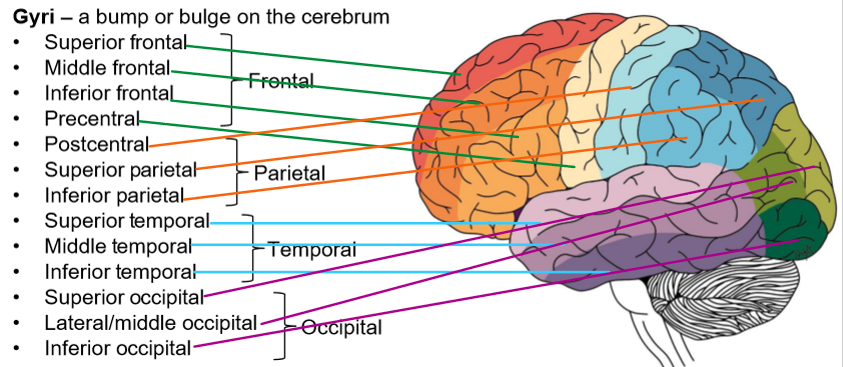
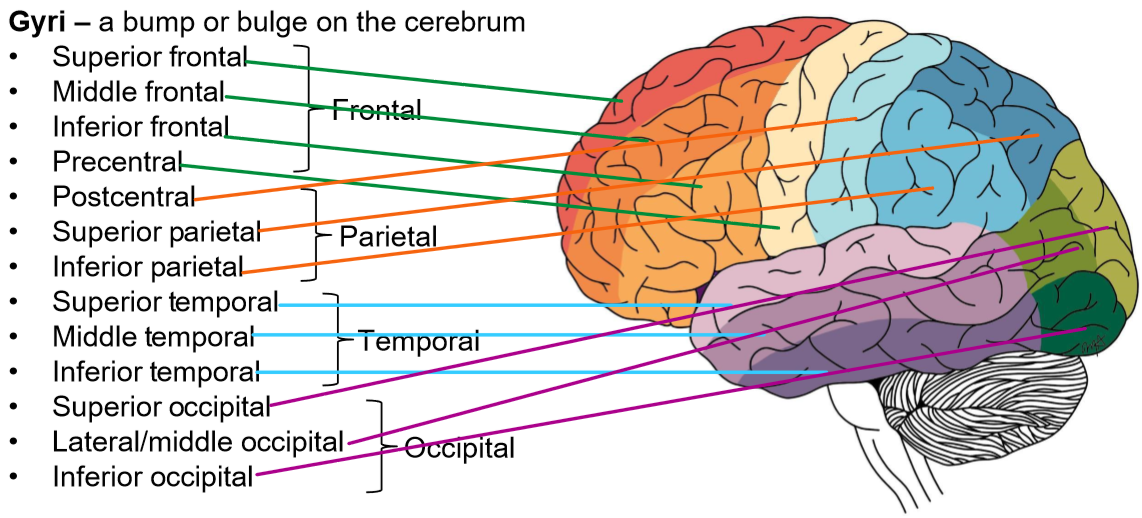
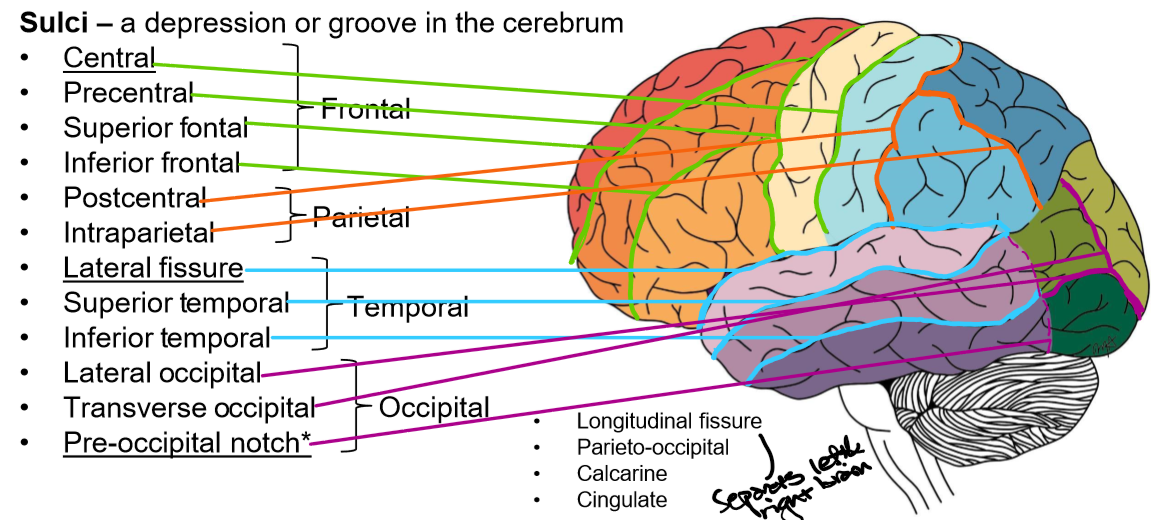
Gyri and Sulci definition
A bump or bulge on the cerebrum
A depression or groove in the cerebrum
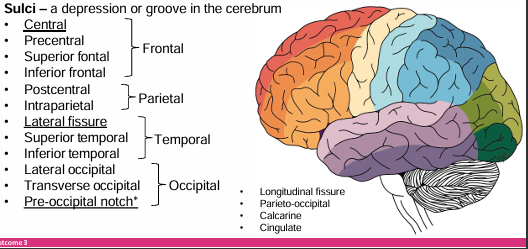
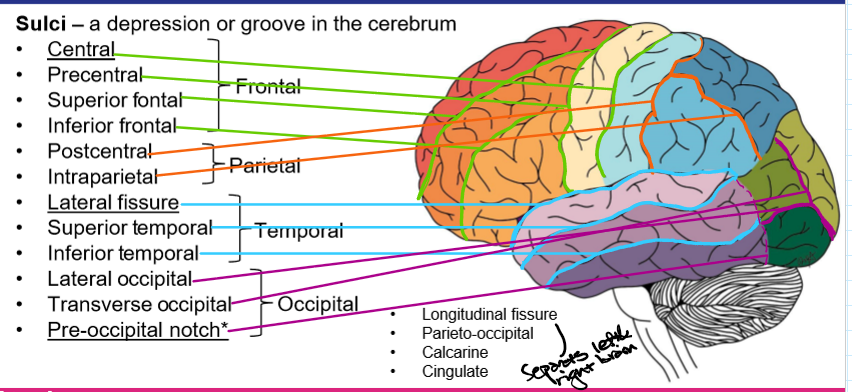
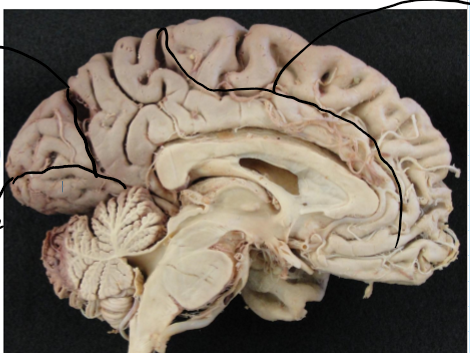
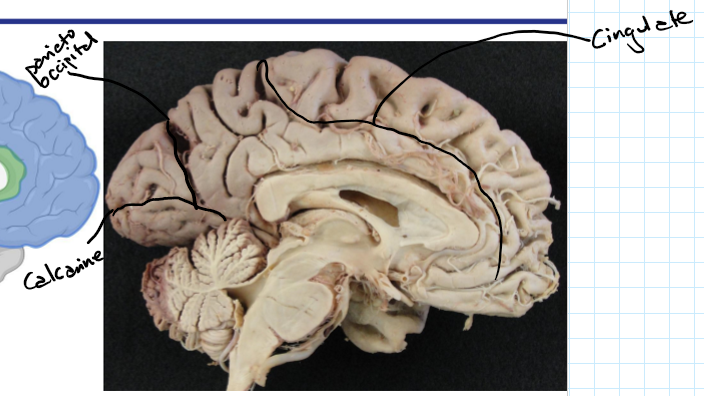
Longitudinal fissure
Separates left and right hemispheres
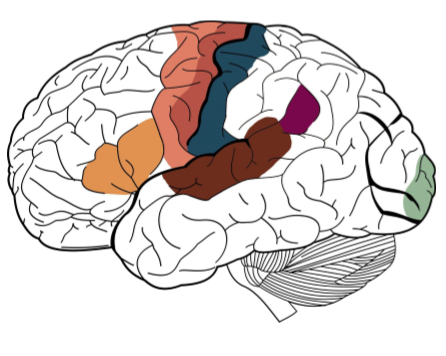
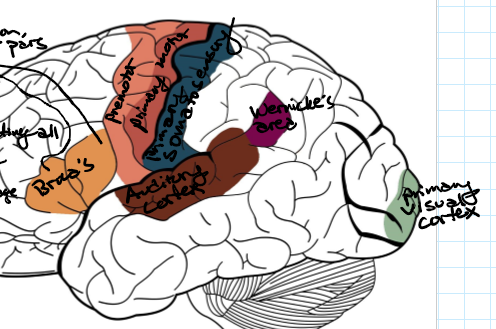
Broca’s area- Function, located where and made up of what 2 things
Premotor- function
Primary motor- function
Primary somatosensory- function
Auditory cortex- function
Wernicke’s area- function, found where
Primary visual cortex- function
Speech production and articulation, Found left side of the brain, Made up of pars traingularis and pars opercularis
Planning and organization of movements
Initiation of movement
Recieving and directing all sensory input
Hearing and hearing processing
Speech comprehension and language, left side of brain
Vision
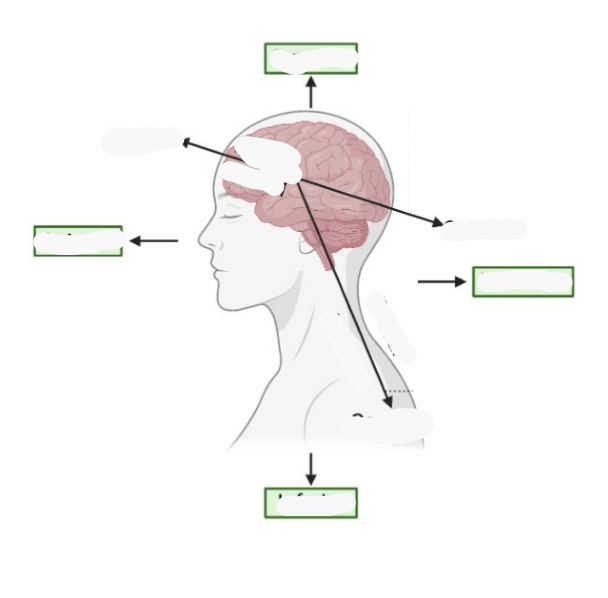
Identify the 7 main functional areas of the brain
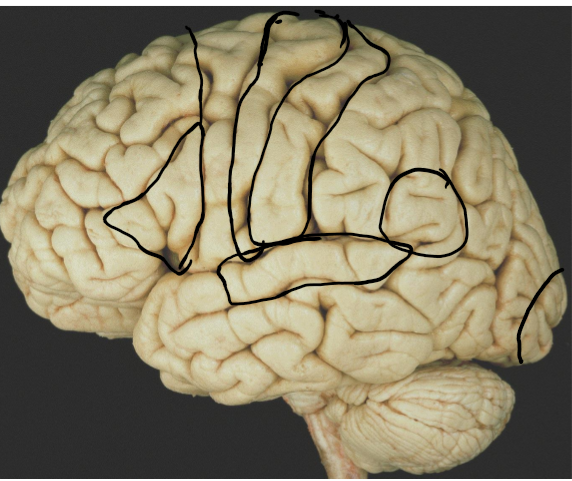
Identify the Gyri in the brain
Identify the sulci in the brain
What are the 6 layers of the cerebral cortex, cell types of each layer
which cortex doesn’t have all layers
1.Molecular layer- horizontal cells
2.External granule cell layer- cellate cells/star shape
3.Externa pyramidal cell layer- Pyramidal cells
4.Internal granule cell layer-Cellate cells
5.Internal pyramidal layer-pyramidal cells
6.Multiform layer- fusiform layer
Olfactory cortex doesn’t have 6 layers
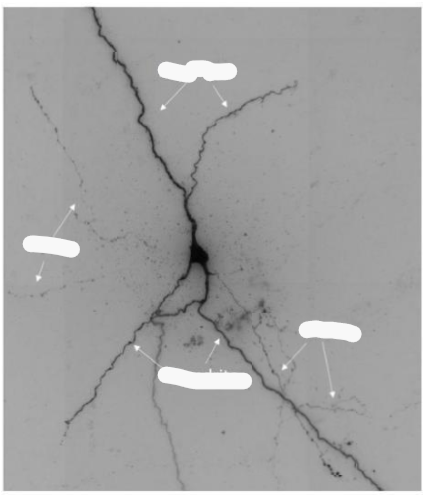
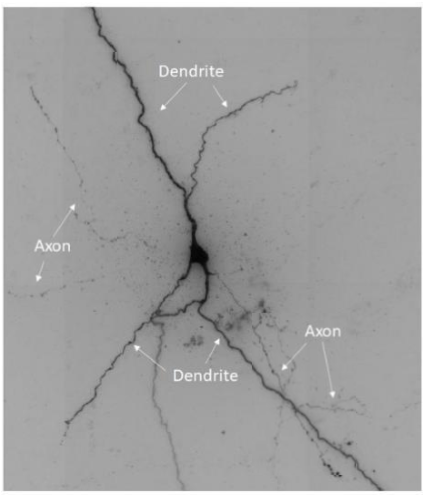
How can neurons be classified
The number of processes that come off the cell body and or the general neuronal shape eg pyramidal and Purkinje cell
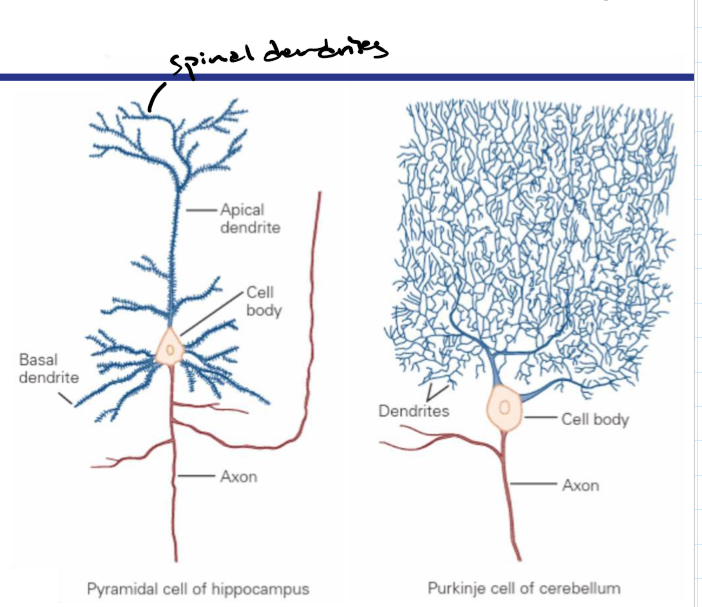
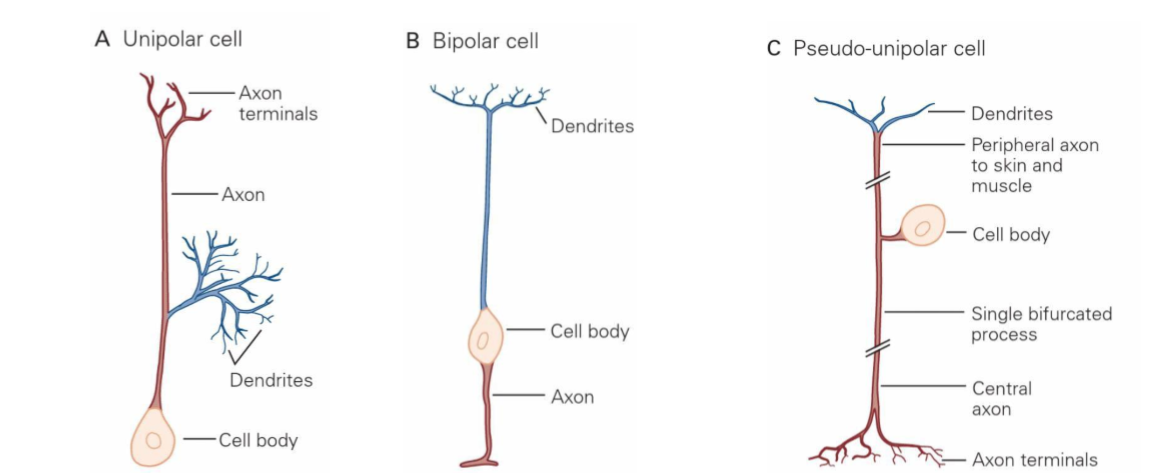
The 3 neuron structures
unipolar ,bipolar, pseudo-unipolar
Draw the structures
Unipolar cell- one process extending out of the cell body
Bipolar cell- 2 process extending out of cell body
Pseudo-unipolar cell- one process extending but axon splits into 2
Glial cells of CNS
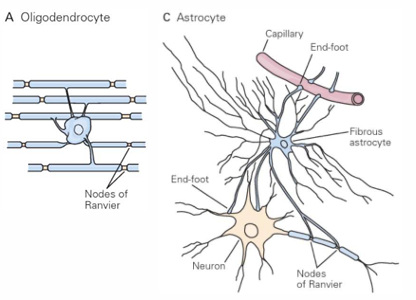
OAMER and their roles
Oligodendrocytes- major myelinating cells for faster axonal conduction
Astrocytes- support cells, maintain blood brain barrier and prevents things crossing in blood from external body for brain and spinal cord
Microglia- immune cells, invoke immune response and cell maintenance and survival
Ependymal cells- CSF production
Radial glia- guiding neurons in developing brain and nervous system, immune response, produce more neurons or more glial cells
Glial cells of PNS
NSE and their roles
Neurolemmocytes- myelinating cells for faster axon conduction (Schwann cells)
Satellite cells- immune cells
Enteric glia cells- associated with enteric neurons in gastrointestinal and digestive system, involved in gut tissue homeostasis
Grey matter
CSBC
Cell bodies, soma
Surface of the cerebral hemisphere
Brainstem nuclei
Center of the spinal cord
White matter
CCI
Cell processes, axons (myelinated)
Corpus callosum
Internal capsule
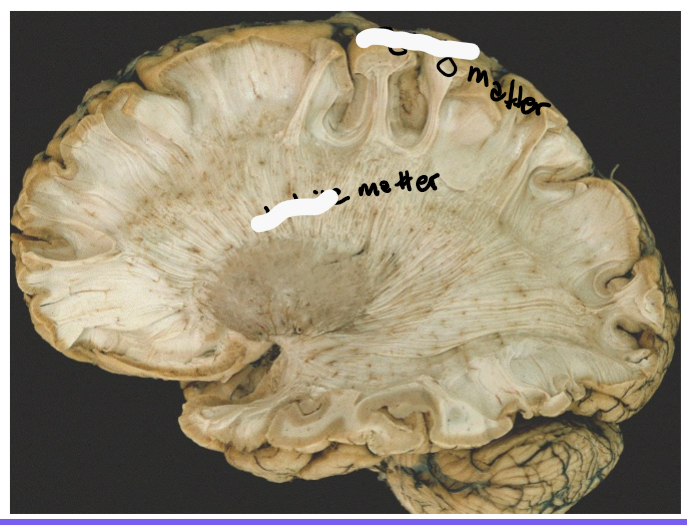
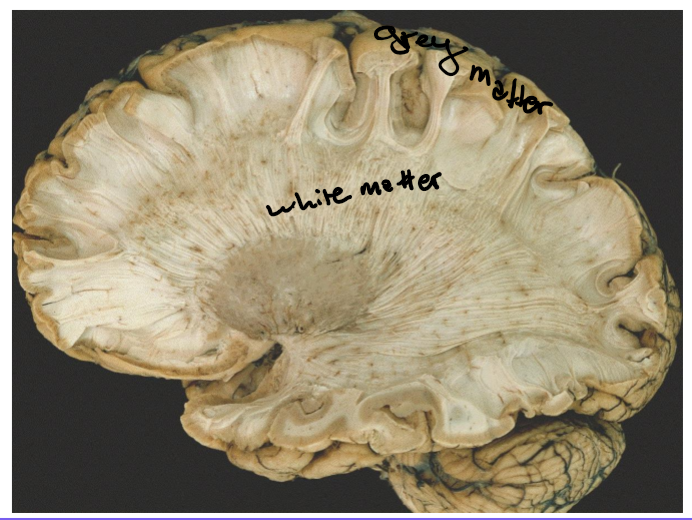
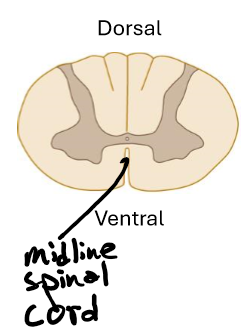
In the spinal cord what is the orientation of the white and grey matter
White on out and grey on inside
Neural pathways are formed by what
Formed by axons synapsing onto neurons in another location enabling a signal to be sent from one region of the nervous system to another
How are neurons connected
A single axon or a bundle of axons known as a nerve tract or fasciculus
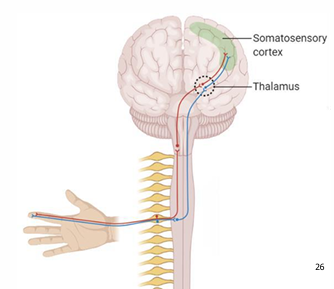
Ascending afferent sensory pathway
SST
Draw out the pathway
Stimulus receptor cel to spinal cord/brainstem (1st order neuron)
Spinal cord/brainstem to thalamus (2nd order neuron)
Thalamus to cortex (3rd order neuron)
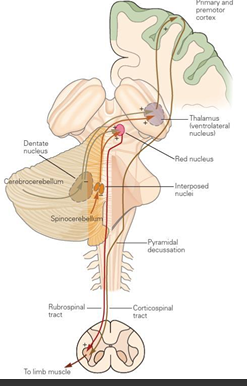
Descending efferent motor pathway
MS
Draw out the pathway
Motor cortex to the spinal cord (upper motor neuron)
Spinal cord to limb (lower motor neuron)