PDA III - Exam 4: Alzheimers Disease - RW
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
What is meant by the term dementia?
Description of a collection of symptoms
Loss of memory, language skills, perception, reasoning, and judgment
What 2 conditions is dementia distinguished from?
Normal age related cognitive decline
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
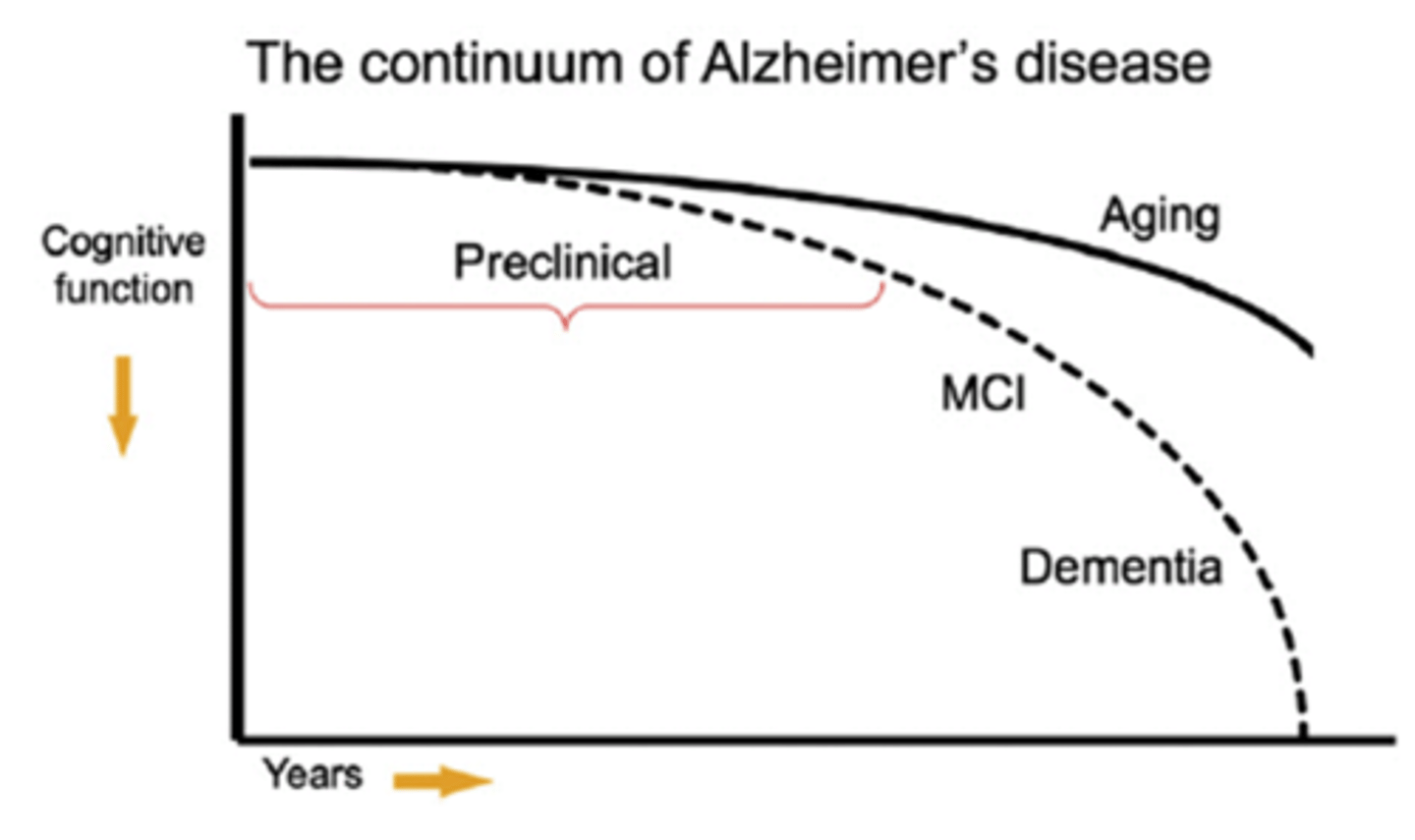
What is the most common cause of dementia in people over the age of 65?
Alzheimer's disease (AD)
At what age do most cases of AD occur?
Usually after age 60 (late onset)
What type of disease is AD?
progressive neurodegenerative disease
What is the main behavioral feature of AD?
Gradual decline in cognition over many years
Cognition - learning, memory, attention
What is often the 1st symptoms of AD to manifest?
Difficulty retaining new information (short-term memory)
What AD symptoms usually occur 2nd, after AD progresses?
Tendency to get lost (spatial memory)
And, loss of more remote memory (long-term memory)
What AD symptoms usually occur 3rd, after AD further progresses?
Inability to perform daily tasks of self-care
(dressing, hygiene, meal prep, etc.)
As cognitive decline in AD progresses, what other symptoms to patients exhibit?
Behavioral problems can occur
Aggression
Depression
irritability
Paranoia
Hallucinations
Delusions
How did AD used to be diagnosed?
By process of elimination
Using brain scans, electroencephalograms, lab tests and psych evals.
Confirmed at autopsy
What is currently used to diagnose and stage AD?
Biomarkers
PET scans of amyloid
Fluid (plasma/CSF) biomarkers of amyloid and p-tau
What are biomarkers used to diagnose AD?
PET scans of amyloid
Fluid (plasma/CSF) biomarkers of amyloid and p-tau
What was included in the old AD diagnostic criteria?
Memory impairment at at least 1 of:
-Aphasia
-Apraxia
-Agnosia
-Disturbed executive functioning
Cognitive deficits impair functioning
Deficits are a decline from previous higher fxn.
What is aphasia?
Loss of ability to speak with fluency and relevance
What is apraxia?
Inability to carry out a learned, purposeful movement
Even though there is no motor or sensory impairment
There is a deficit in motor planning
What is agnosia?
Failure to recognize sensory stimuli
Cannot recognize objects or people by sight
What are the stages of AD?
Mild
Moderate
Severe
What symptoms are present in mild AD?
Uncharacteristic forgetfulness
Impaired acquisition and retrieval of new info.
Geographic disorientation
Difficulty in proper word selection
Hesitancy in speech
Socially passive, disintersted
What is the MMSE score in mild AD?
21-24
What symptoms are present in moderate AD?
Inaccuracies in long-term memories
Confusion over relationships and identities of friends/relatives
Small tasks require supervision
Disruptive behaviors and psychiatric symptoms
What disruptive behaviors are seen in moderate AD?
Agitation
Restlessness
Sleep disturbances
Agression
What psychiatric symptoms are seen in moderate AD?
Paranoia
Delusions
Hallucinations
What is the MMSE score in moderate AD?
10-20
What symptoms are present in severe AD?
Nearly complete dependence on caregivers
Severe impairment of verbal output and comprehension
Personality disappears
Urinary/fecal incontinence is common
Weight loss is common
What is the MMSE score in severe AD?
<10
What are the 2 defining pathological features of AD?
Amyloid plaques
Neurofibrillary tangles
What are pathological features of AD?
Amyloid plaques
Neurofibrillary tangles
Degeneration of BFCS
Other neuronal degeneration
Brain is shrunken and cerebral BF is reduced
What are amyloid (senile) plaques?
Extracellular deposits of B-amyloid peptide
What are the 2 types of B-amyloid?
40 or 42 amino acid forms
Both can form plaques
42 more likely to
Which form of B-amyloid is more likely to form fibrils and clumps?
42
Where to plaques preferentially develop in the early stages of AD?
Hippocampus
Temporal and Frontal Lobes
Association cortex
(all areas impt. for cognitive fxn.)
What are diffuse plaques?
Consist mainly of the 40-aa form of B-amyloid
What are neuritic plaques?
Consist of both 40- and 42-aa forms of B-amyloid,
Dystrophic dendrites,
And, Glia
Contain filamentous AB (more toxic)
Are B-amyloid oligomers toxic?
Oligomers may be toxic
Or, at least interfere with signaling involved in learning/memory
What are neurofibrillary tangles?
Consist of hyperphosphorylated tau
What type of protein is tau?
Microtubule associated protein
(provides structure to neuron)
What is the basal forebrain cholinergic system (BFCS)?
Major cholinergic neurons in brain
ACh they release regulates cognitive fxn.
What are the parts of the BFCS?
Ch1-CH4
Septum (Ch1)
Diagonal band (Ch2+3)
Nucleus basalis of Meynert (Ch4)
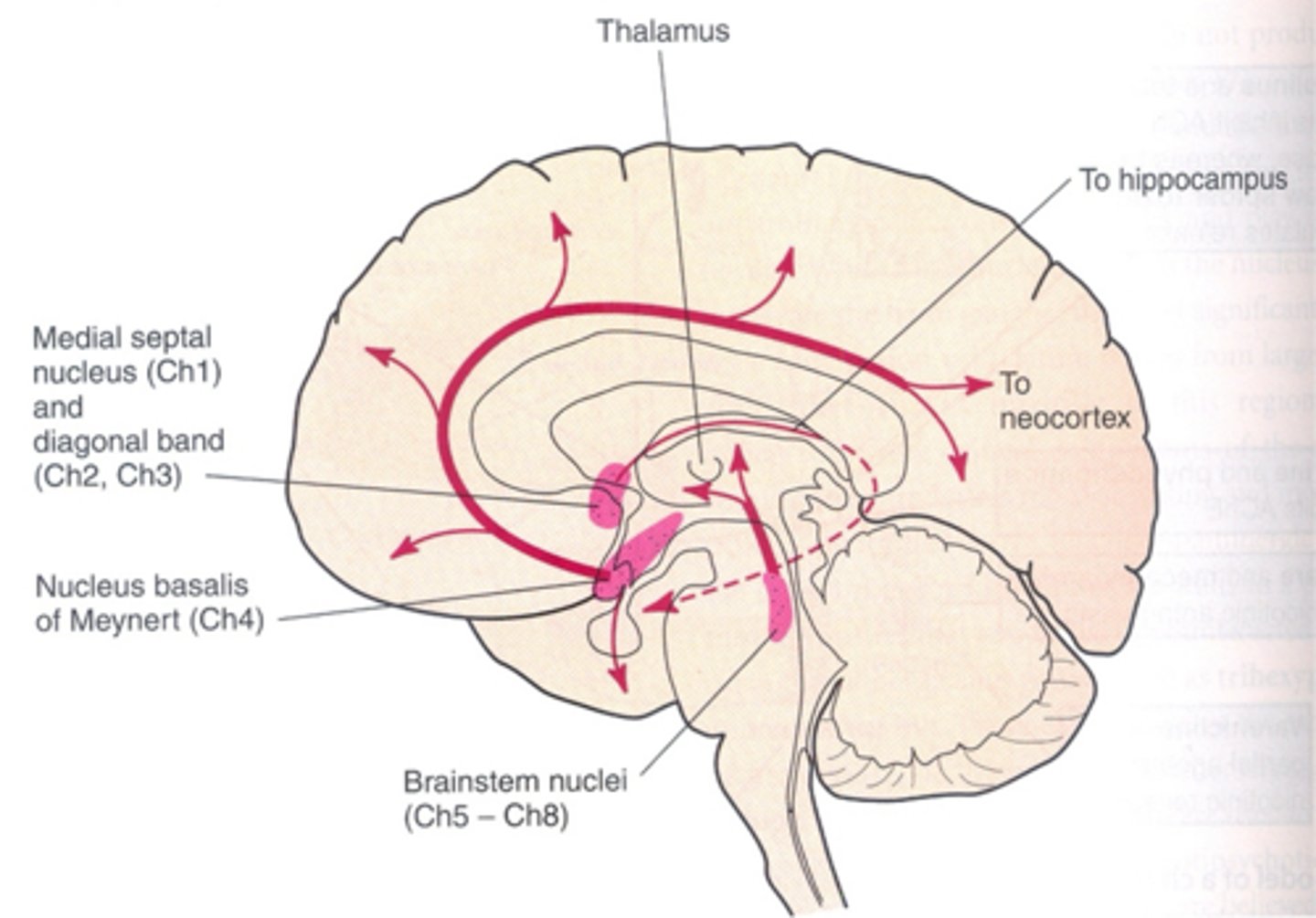
What happens to the BFCS in AD?
BFCS degenerates in AD
Degree of degeneration correlates with the degree of dementia
What are other neuronal populations that degenerate in AD?
Monoamine systems
Hippocampal neurons (CA1)
Cortical neurons
Amygdala neurons
What are characteristics of the brain in AD?
Brain is generally shrunken (ventricles are larger)
And, cerebral blood flow is reduced
What is the role of genetics in late-onset AD?
Late onset (>60) do not have a single genetic cause
Do have some risk factors
Arise from gene-enviroment interactions
Most cases
What is the major gene that influences the risk of late-onset AD?
ApoE
What is the role of genetics in early-onset AD?
Early onset (≤50s) are genetically caused
By autosomal dominant mutations
1-10% of cases
What type of mutations cause early onset AD?
Mutations that change amyloid processing
What molecule is amyloid derived from?
APP
What is APP processing?
APP undergoing post-translational processing
Mutations can be either non-amyloidogenic or amyloidogenic
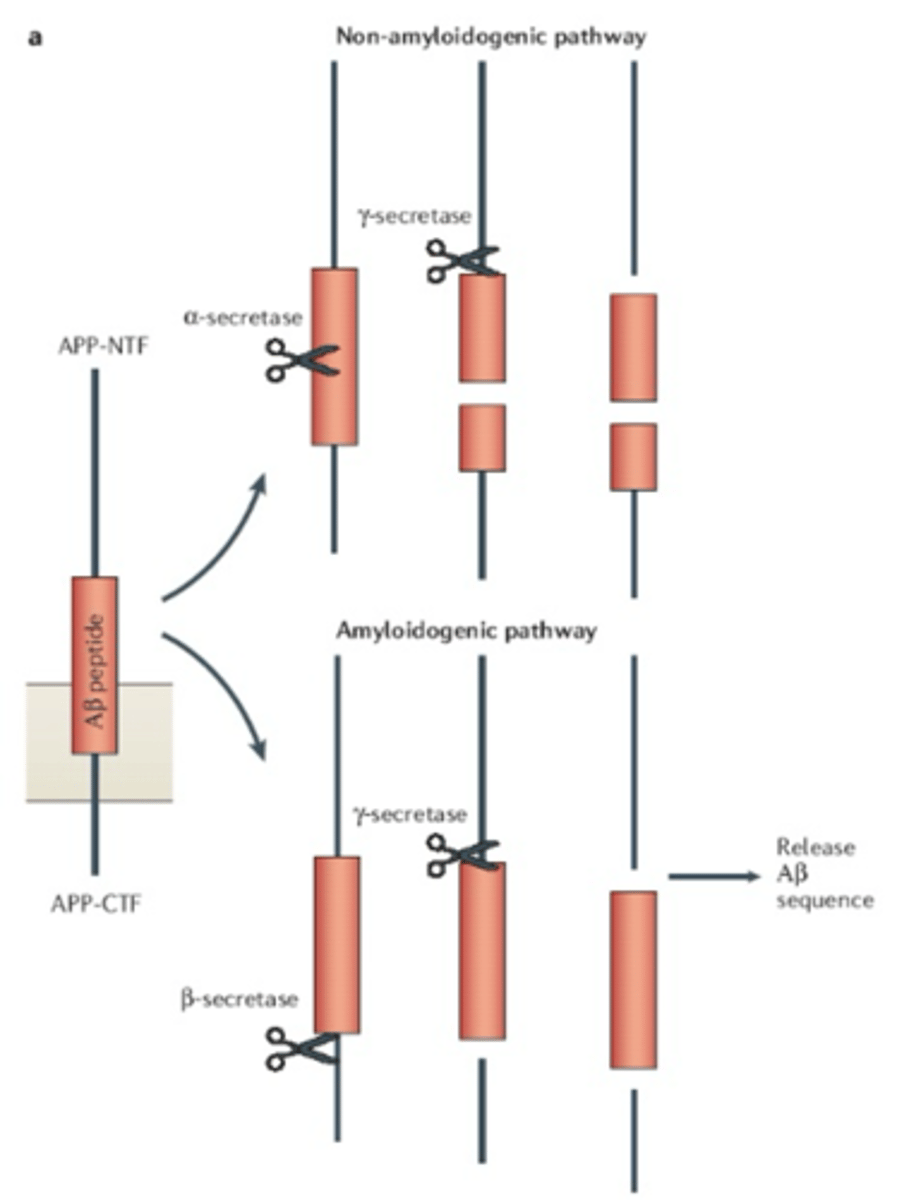
What are the 2 pathways of APP processing?
Non-amyloidogenic (non-pathogenic)
Amyloidogenic (pathogenic)
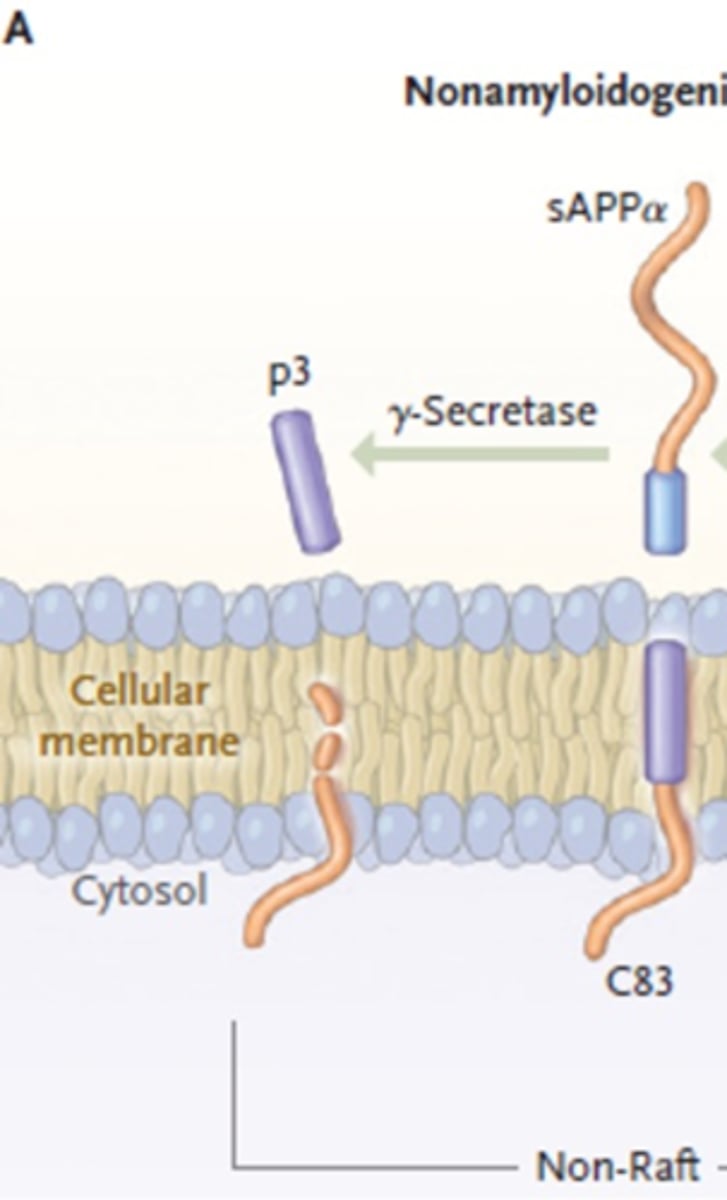
What is involved in non-amyloidogenic APP processing?
a-secretase produces C83
y-secretase produces p3
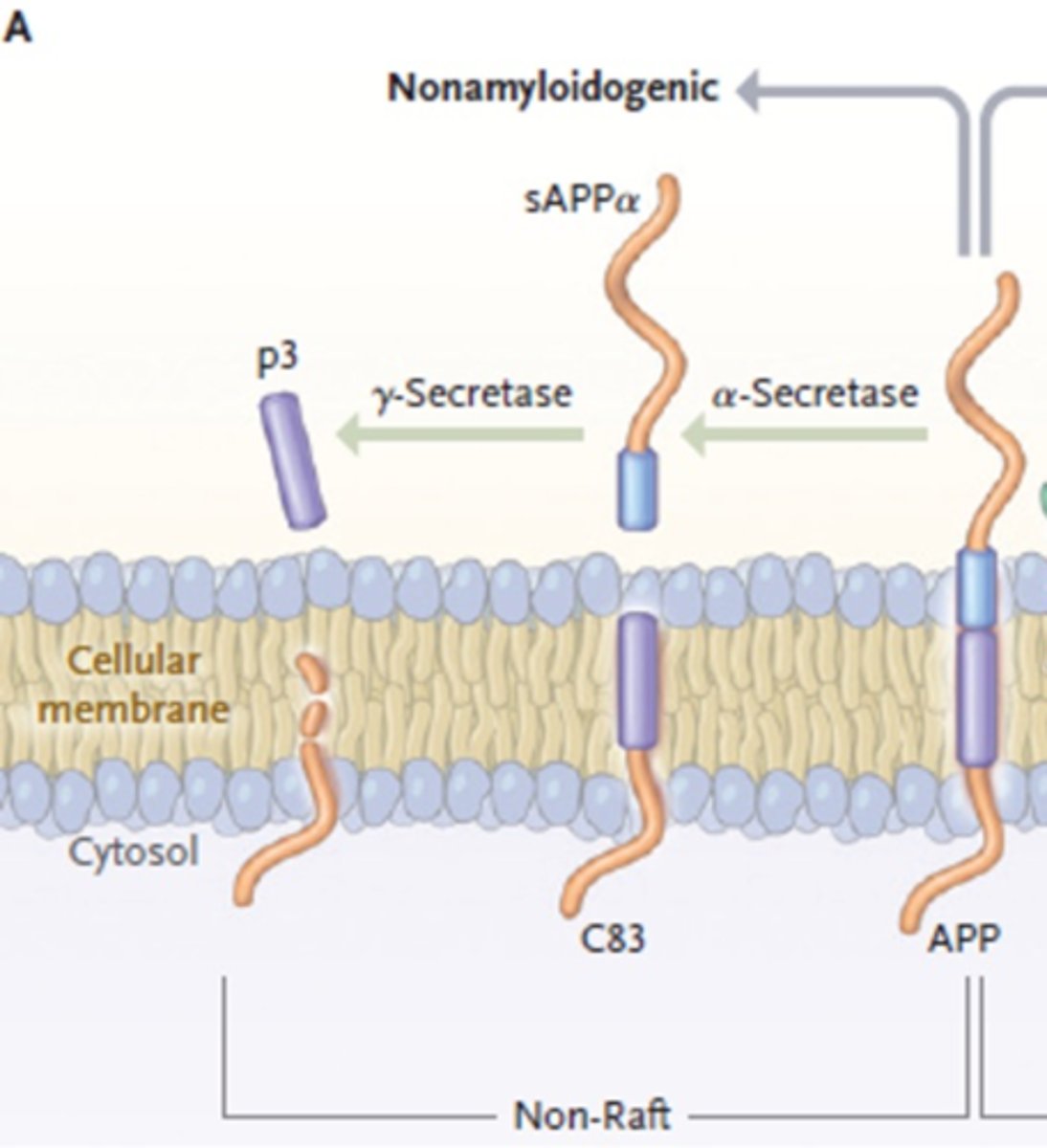
What is the first step in non-amyloidogenic APP processing?
a-secretase cleaves APP
Creating C83 and sAPPa
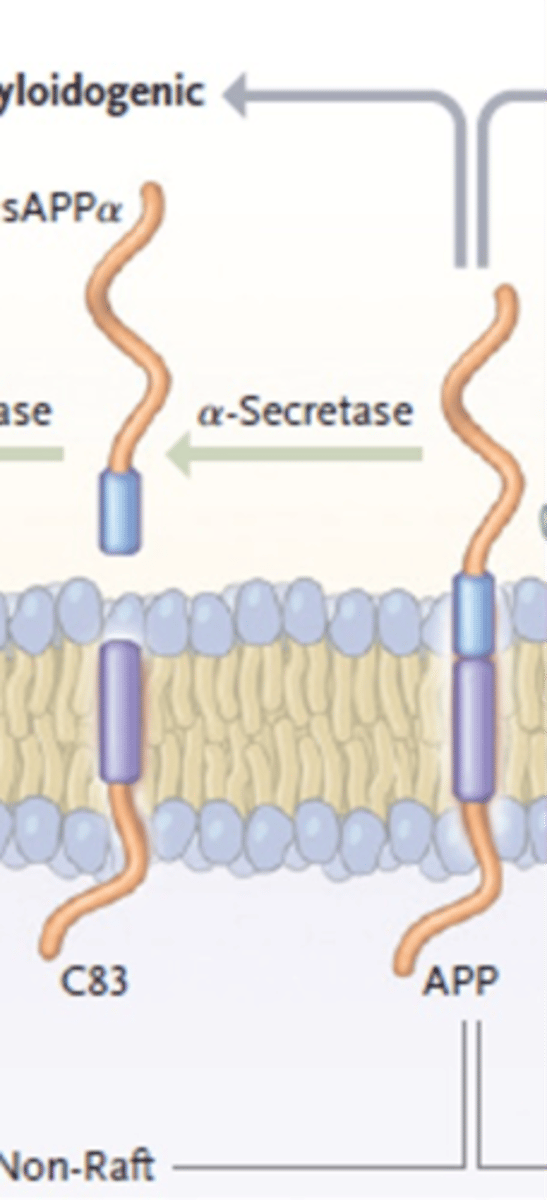
What is the second step in non-amyloidogenic APP processing?
y-secretase cleaves C83
Produces p3 (no effects)
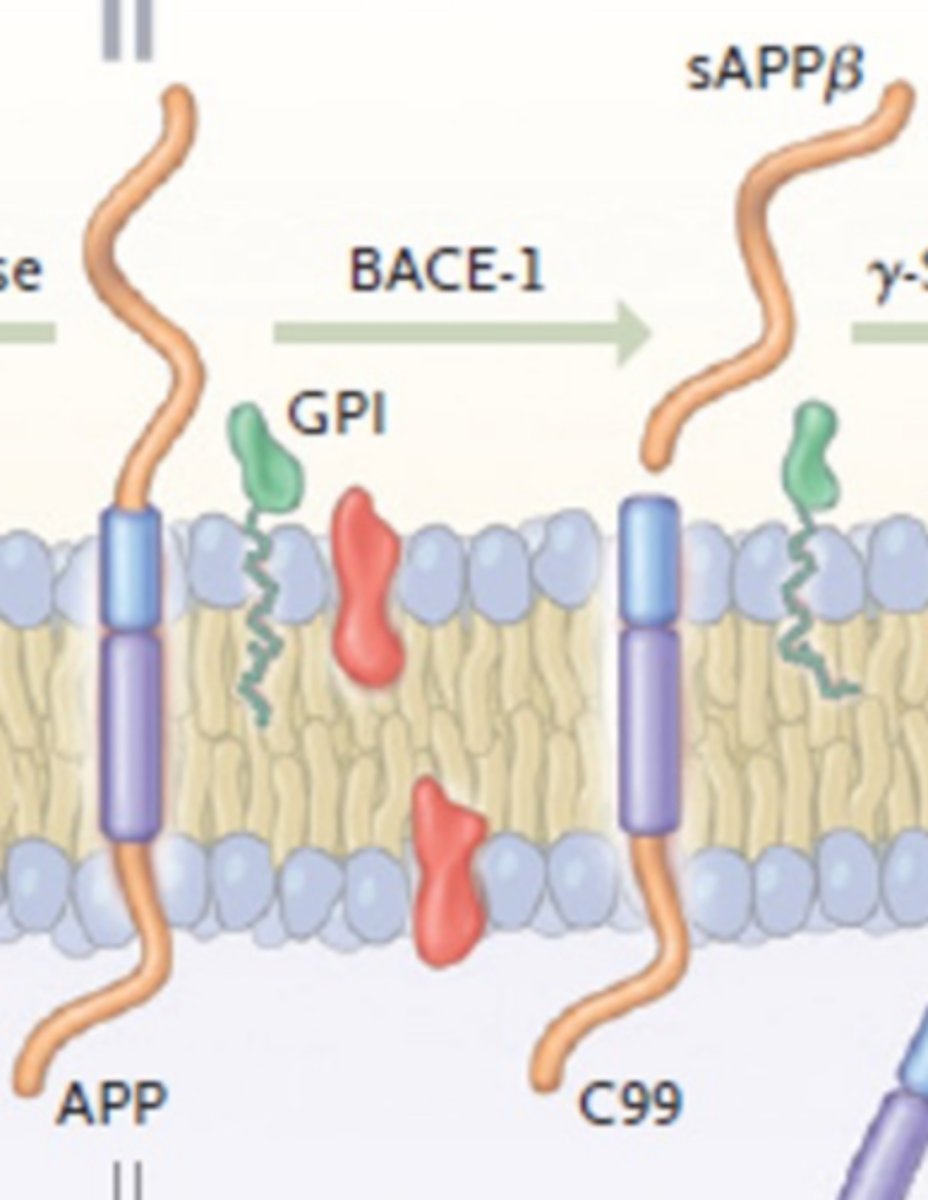
What is involved in amyloidogenic APP processing?
B-secreates (BACE-1) creates C99
y-secretase creates B-amyloid
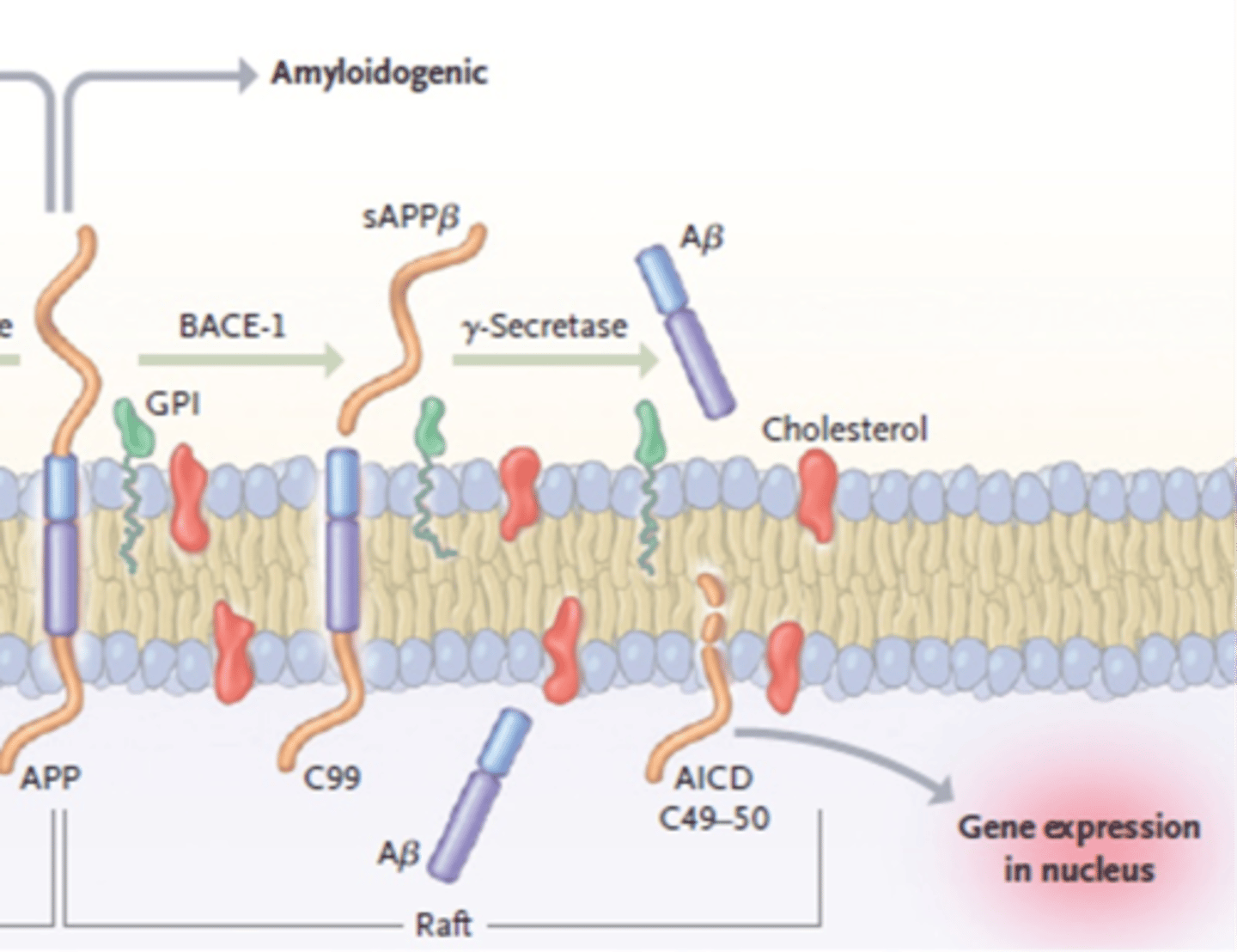
What is the first step in amyloidogenic APP processing?
B-secretase cleaves APP
Creating C99 and sAPPB
What is the second step in amyloidogenic APP processing?
y-secretase cleaves C99
Produces B-Amyloid
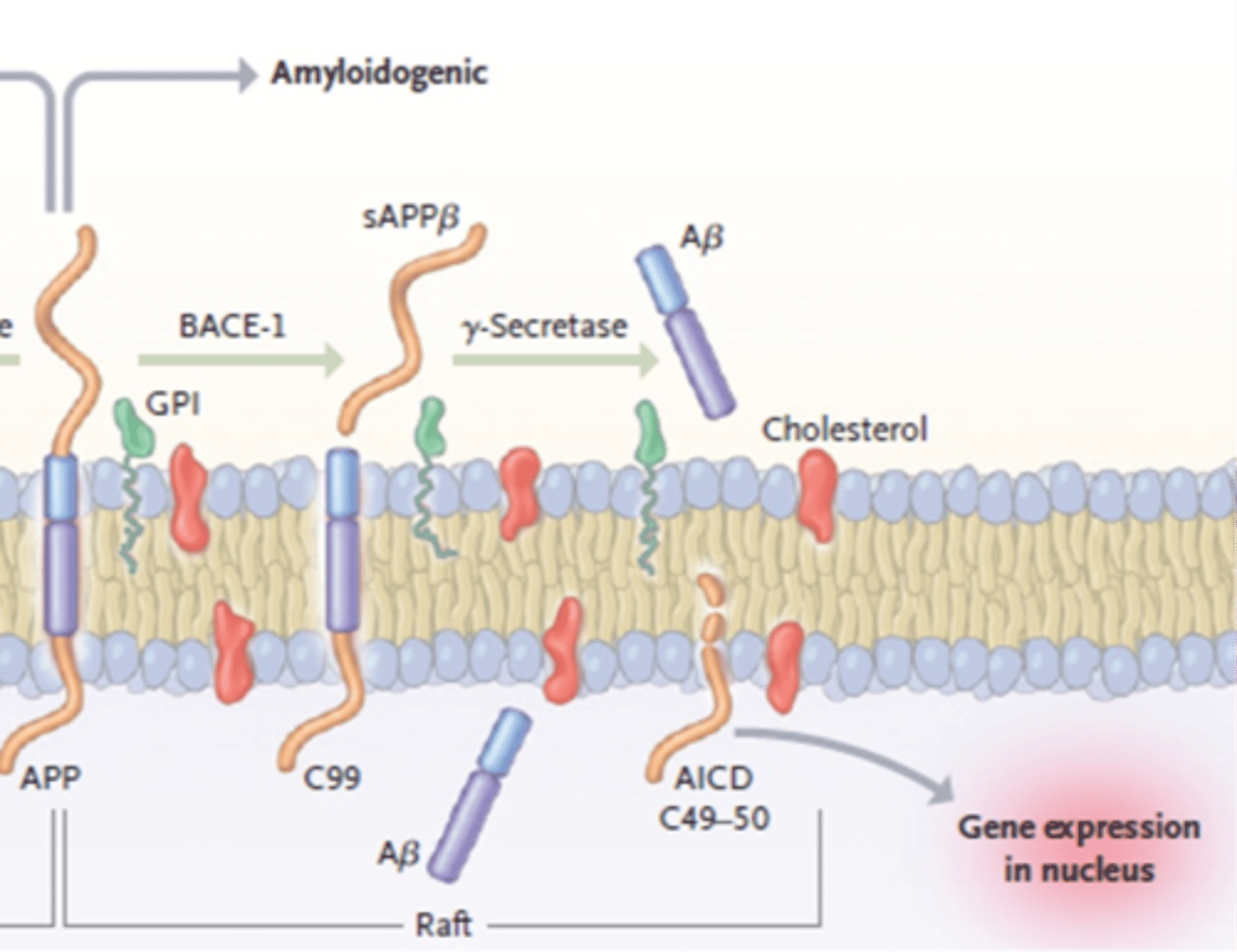
What happens to B-amyloid after it is created by amyloidogenic APP processing?
B-amyloid released extracellularly after cleaved
Can form oligomers/fibrils/clumps
And, eventually become a plaque
What type of protease is y-secretase?
A complex of proteins
Made up of:
-Presenilin 1 or 2
-Nicastrin
-PEN2
-APH-1
What proteins make up y-secretase?
Presenilin 1 or 2
Nicastrin
PEN2
APH-1
Which protein is the catalytic core of y-secretase?
Presenilin 1 or 2
(performs the actual cleavage)
Which proteins are the regulatory proteins of y-secretase?
Nicastrin
PEN2
APH-1
(surround the catalytic core)
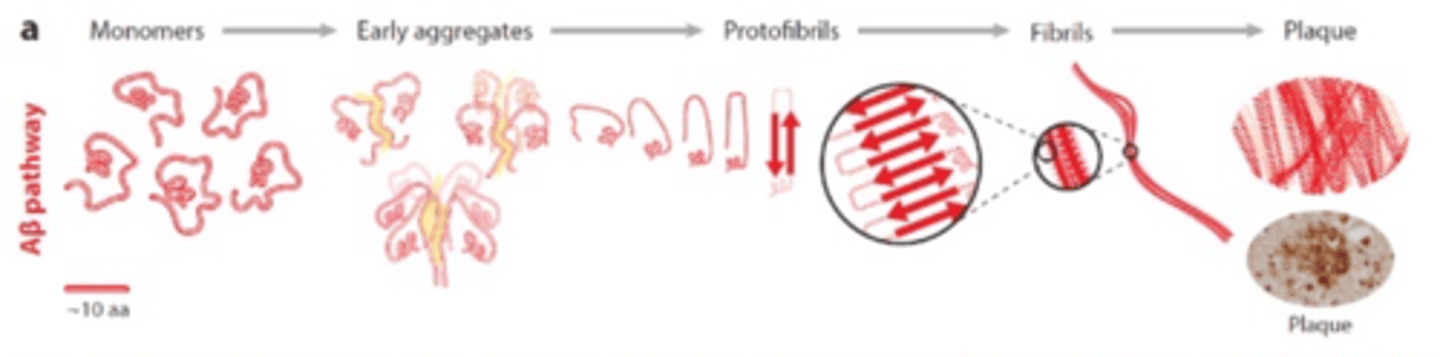
What are the steps to form a plaque after B-amyloid is released?
AB released as monomers ->
Early aggregates->
Protofibrils->
Fibrils->
Plaque
How are mutations named?
1st letter: original aa
#: where in protein sequence aa is
2nd letter: what the aa becomes in the mutated gene
What letter indicates the aa glutamate?
E
What letter indicates the aa aspartate?
D
What letter indicates the aa lysine?
K
What letter indicates the aa asparagine?
N
What letter indicates the aa methionine?
M
What letter indicates the aa leucine?
L
What letter indicates the aa alanine?
A
What letter indicates the aa threonine?
T
What letter indicates the aa histidine?
H
What letter indicates the aa arginine?
R
What letter indicates the aa glycine?
G
What letter indicates the aa glutamine?
Q
What letter indicates the aa valine?
V
What letter indicates the aa isoleucine?
I
What 3 genes can be mutated to cause early-onset AD?
APP
PSEN1
PSEN2
What is the effect of a mutation that favors B-secretase activity (cutting)?
Favors the pathogenic pathway
Inc. AB production
What is the effect of a mutation that inhibits B-secretase activity (cutting)?
Favors non-pathogenic pathway
What is the effect of a mutation that favors y-secretase activity (cutting)?
Favors the pathogenic pathway
Inc. AB production
What is the effect of a mutation that favors a-secretase activity (cutting)?
Favors non-pathogenic pathway
What is the effect of a mutation that inhibits a-secretase activity (cutting)?
Favors the pathogenic pathway
Dec. non-amyloidogenic processing by a-secretase
Shunts processing to amyloidogenic pathway
Inc. AB production
What can be mutated in y-secretase to increase activity (inc. AB formation)?
Catalytic core - PSEN1 or 2
What is a commonality of all mutations that cause early-onset AD?
All effect APP processing
All mutations result in inc. production of the long form (42) of AB
(more amyloidogenic form)
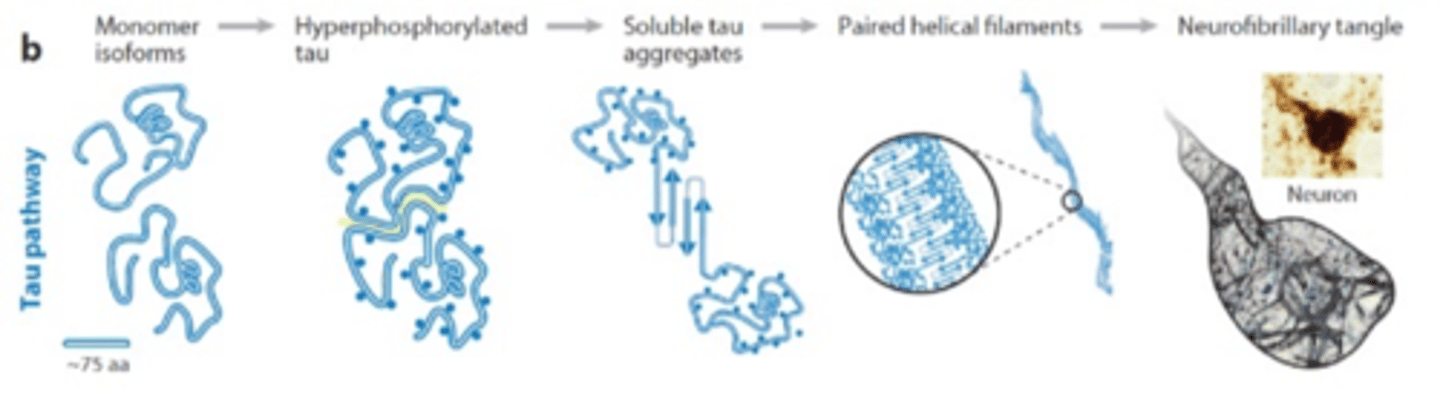
How are neurofibrillary tangles formed?
Formed by highly phosphorylated tau protein
This causes it to disassociated from microtubule. This makes the microtubule unstable as well as promotes association of multiple phosphorylated tau proteins
Aggregated tau proteins results in fibrils which can lead to tangles which causes the neuron to die
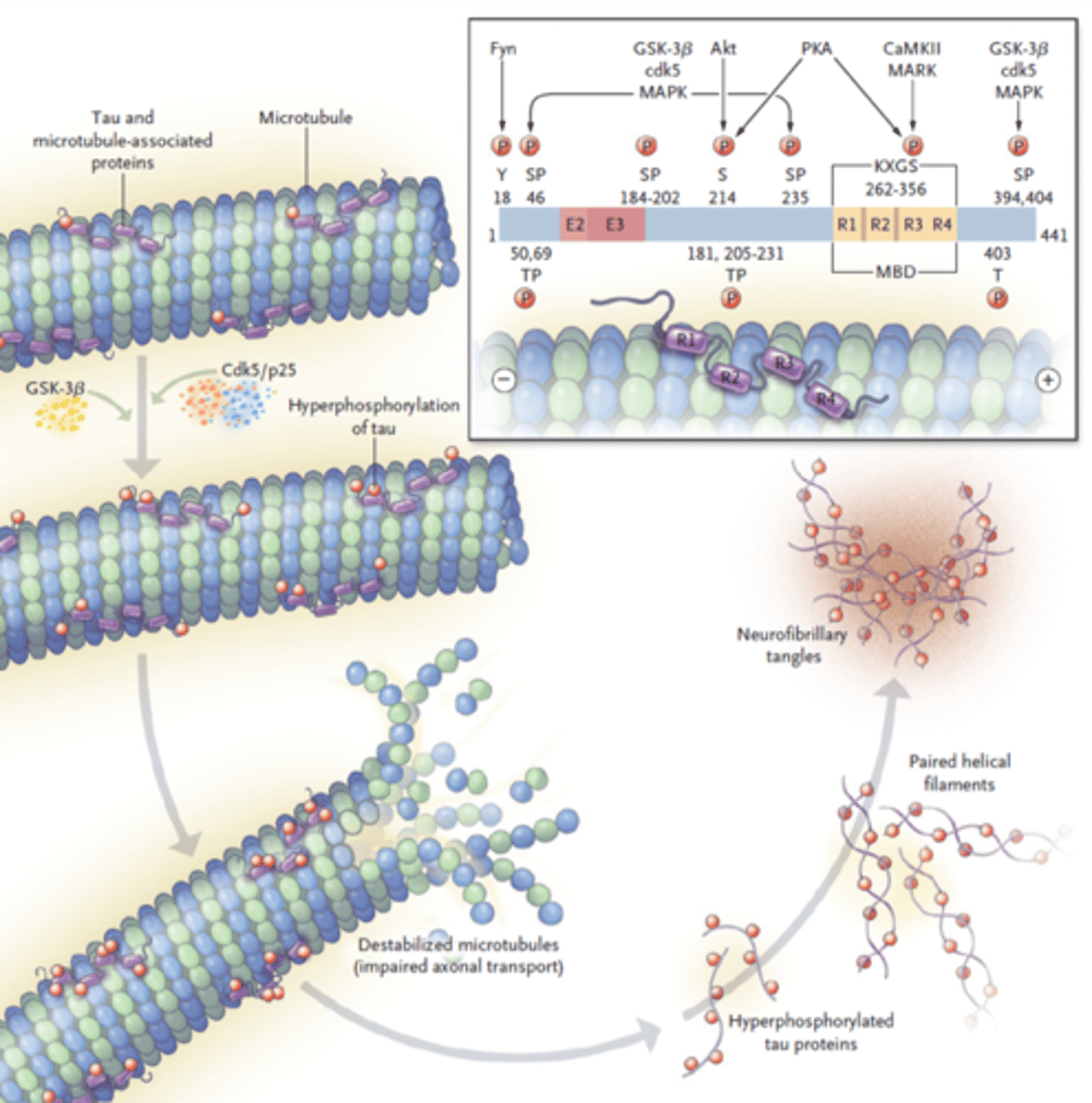
What enzymes phosphorylate Tau?
Kinases
What happens to Tau once it is hyperphosphorylated?
Loses affinity for microtubule
Released to form tangles
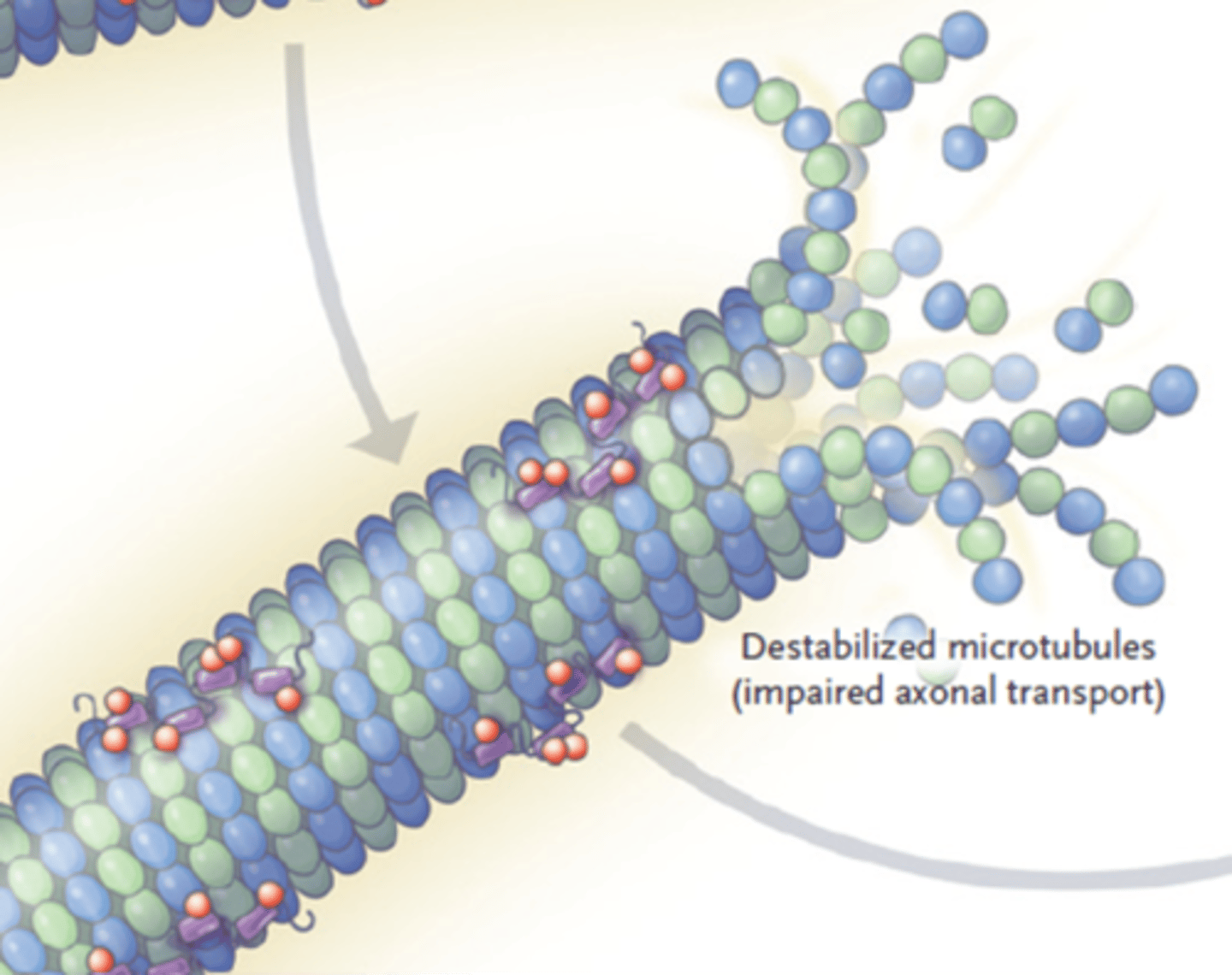
What happens to the microtubule once tau dissasociates?
Microtubule is destabilized
Neuron dies
What are the steps to form a neurofibrillary tangle after p-Tau is released?
Monomer ->
P-Tau ->
Soluble Tau aggregates ->
Paired helical filaments ->
Neurofibrillary tangle
What is ApoE?
Apolipoprotein E
Involved in cholesterol transport
May be involved in binding and removing AB from the brain
What is the relationship between ApoE and late-onset AD?
ApoE(4) is a major risk factor for AD
What are the 3 types of ApoE?
E2
E3
E4
Which type of ApoE increases the risk for AD?
E4 may promote formation of plaques
Why is it believed that ApoE4 increases AD risk?
E4 allele may not be good at removing AB from the brain
Allowing more AB to stay in the brain and form plaques
Which type of ApoE decreases the risk for AD?
E2 is protective
(E3 may also be)
What is the correlation between number of ApoE4 alleles and AD risk?
More E4 alleles means an increased risk of developing AD
What is the amyloid cascade hypothesis?
States that AB is the cause of AD
Supported by genetic evidence
What evidence contradicts the amyloid cascade hypothesis?
Can find AB plaques at high levels in people without dementia
Can see cognitive deficits before plaque formation
Can see cognitive deficits when no plaques are present
Can have plaques but no cognitive deficits
What are the 3 categories of treatments?
Symptomatic
Disease modifying
Curative
What are disease modifying therapies?
Slow or stop pathological process responsible for a disease