Concept 7.5: Bulk transport across the plasma membrane occurs by exocytosis and endocytosis
1/5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
Vesicles
Separated sections of membrane for large molecules like polysaccharides and proteins to cross the lipid bilayer
Smaller molecules and water are transported through proteins or the layer itself instead
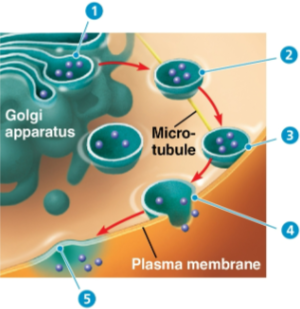
Exocytosis
Process where transport vesicles migrate to the membrane, fuse with it, and release their contents outside the cell
Secretory cells like the pancreas can export products like insulin via this
Endocytosis
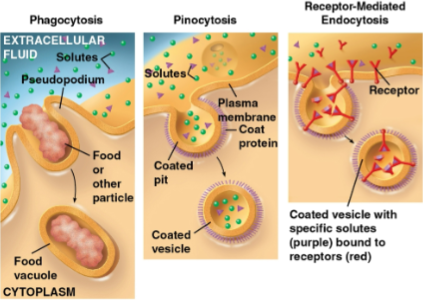
Process where macromolecules are taken into the cell in vescles through a pocket formed and deepened by the membrane that is eventually pinched off; includes
Phagocytosis (cellular eating)
Pinocytosis (cellular drinking)
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
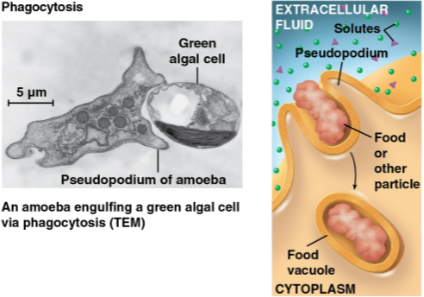
Phagocytosis
Form of endocytosis where a cell engulfs a particle by extending pseudopodia around it and packing it in a membranous sac called a food vacuole
This food vacuole then fuses with a lysosome for digestion
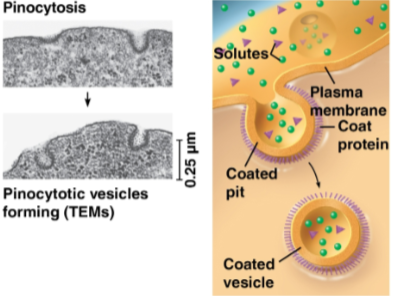
Pinocytosis
Form of endocytosis where a cell takes up extracellular fluid via small vesicles; this is nonspecific for substance transport and any solutes are taken into the cell
The inner side of vesicles formed from the plasma membrane are coated with coat proteins
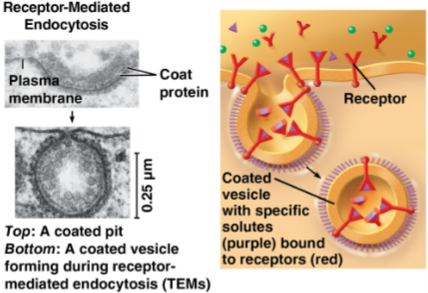
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Form of endocytosis where vesicle formation is triggered by a solute binding to a receptor
Receptors bound to specific solutes from the extracellular fluid are clustered in coated pits that form coated vesicles
Emptied receptors can be recycled into the plasma membrane by the same vesicle
Used to take in cholesterol within particles called low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) — lack of receptors can lead to hypercholesterolemia, building up in blood vessels