Proteins
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Protein
Peptides with >100aa residues
Peptide Bond
Dehydration reaction between the N and C terminus of aa
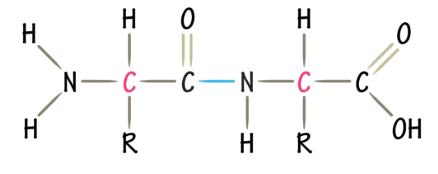
Primary Structure
Sequence of aa
Secondary Structure
Arrangements of backbone atoms
Tertiary Structure
3D structure of all atoms and prosthetic groups
Quaternary Structure
Spatial arrangement of multiple subunits
Subunit
Polypeptides that can chain together to form proteins
Prosthetic Group
Not made of aa or ribosomes
Part of function
Disulfide Bond
Covalent bond formed between two Cystine atoms
Salt Bridge
Electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged groups
Positive → lysine, arginine, histidine
Negative → aspartate, glutamate
Fibrous Protein
Structural proteins that contain stiff, elongated, fibrous regions
Globular Protein
Compact, highly-folded, globular structure
Sections of a-helix and B-sheet
Hydrophobic effect
a-helix
Right-handed helical coil
H-bond between carbonyl oxygen of one residue and N-H hydrogen 4 residues later
Core atoms in vdW
Peptides with oppositely charged R groups
B-sheet
H-bonded chains
Pleated appearance to maximize H-bonds
Peptides with bulky R groups
Antiparallel B-sheet
Strands run in opposite directions
More stable H-bonds
Parallel B-sheet
Strands run in same direction
Diagonal H-bonds
B-bend
Abrupt change in direction of backbone
Strong H-bond between carbonyl oxygen of one residue and N-H hydrogen 3 residues later, residue 2 is normally Proline
Coiled-Coil
Two or more a-helices coil around each other in leftward, counter clockwise direction
Native Structure
Tertiary structure naturally formed
Random Coil Structure
Non-specific arrangement of polymer chain
No fixed stucture
Cis-conformation
R-groups on same side
Sometimes proline
Trans-conformation
R-groups on opposite sides
More common
Denaturation
Heat, pH, detergents, chaotropic agents (increase hydrophobic)
Protein loses tertiary structure and function
Protein Conformation
Primary sequence determines interactions that form other sturtcures
Unimolecular Micelle
Hydrophobic tails face inwards while hydrophilic heads face outwards to maximize favorable interactions
Protein Stability
Hydrophobic effect, electrostatic interactions. disulfide bonds, metal ions
Hydrophobic Effect
The tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in aqueous solutions, minimizing their exposure to water and stabilizing protein structures
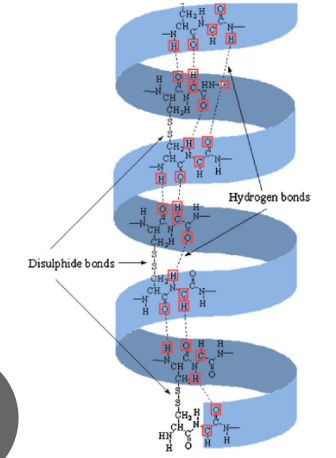
a-keratin
Tough, insoluble protein
Right-handed a-helical structure form left-handed coiled coil
Rich in cys → disulfide bonds to cross-link
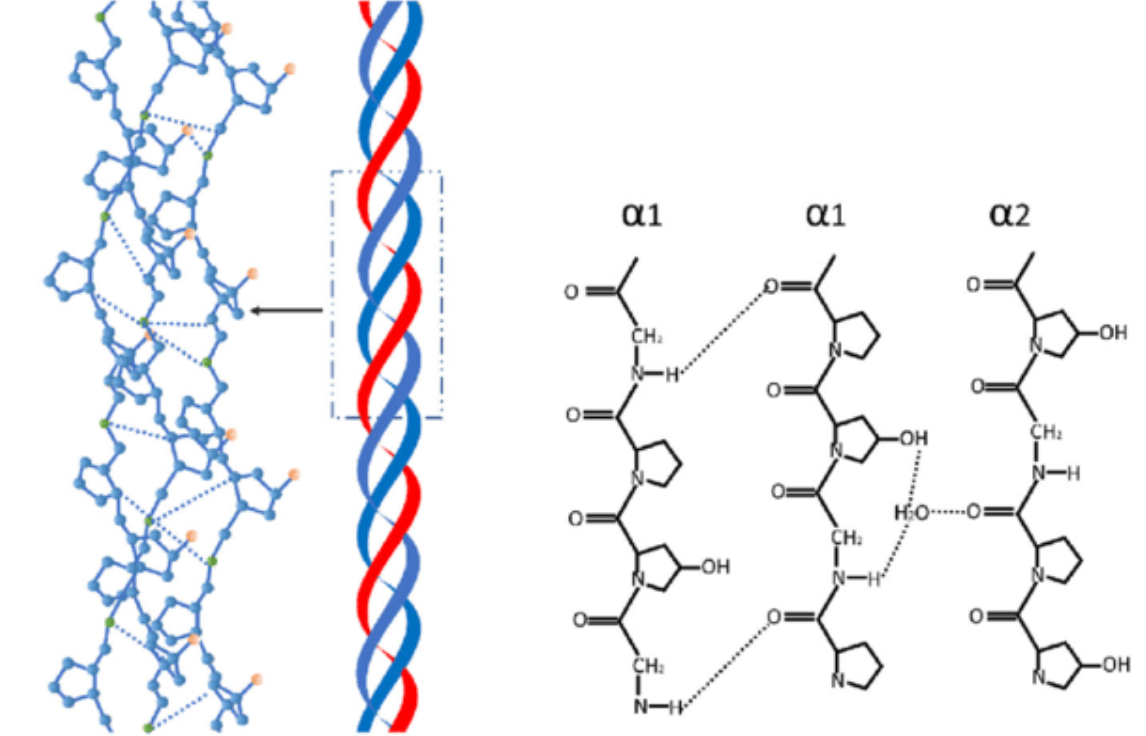
Collagen
Strong, insoluble, fibrous protein
Left-handed collagen helix structure, 3 residues per turn form right-handed super helical structure
Scurvy
Deficiency of vitamin C in diet → failure of prolyl hydroxylase to make Hyp | Skin lesions |
Lathyrism
Presence of ODAP in diet → failure of lysyl oxidase to covalently cross-link collagens | Abnormal bones, joints, and large blood vessels |
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Genetic mutations that change primary sequence of Type I collagen → structural distortions in collagen triple helix structure | Varies with nature and position of mutation |
Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes
Collagen deficiencies or abnormal activity of collagen-processing enzymes | Hyperextensible joints and skin |
Motif
Short, conserved sequence or pattern within protein
Domain
Independent unit of protein that can fold and function on it’s own