Ortho E2 random questions
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
a runner presents with pain in the anterolateral knee. They report the pain is worse when running downhill. what is the likely dx?
IT band syndrome → rubbing on lateral femoral epicondyle
which compartment is MC affected by compartment syndrome?
anterior
tx is emergency fasciotomy in acute! know there can be chronic
38 y/o pt presents with diffuse swelling and tenderness of the left calf. on PE, they have left lower leg ecchymosis and difficulty with dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the left calf. what is the most likely dx?
gastrocnemius tear
what is the hallmark of patellar/quad tendonitis?
anterior knee pain → after exercise, prolonged sitting, squatting, kneeling
tendonitis of which tendon is located on the superior pole of the patella?
quadriceps
patellar = inferior pole
pt presents with swelling of the left posteromedial knee with mild pain. you diagnose them with a popliteal cyst (aka baker cyst or synovial cyst). what is the most likely cause?
secondary to degenerative meniscus tears and OA
28 year old athlete presents with pain in the anteromedial distal 1/3 of their right leg. on PE, there is pain to palpation on the posterior tibialis. what imaging should you order? what do you expect it to show?
Shin splints (medial tibial stress syndrome) →MRI shows associated stress fractures
plain films would be normal
what causes shin splints?
commonly develops as result to increased exercise → inflam of the tibial periosteum d/t repetitive muscle contractions
which imaging study confirms dx of stress fractures?
MRI
which stress fracture has the worst prognosis and may need surgery?
anterior tibial
which amputation has the greatest patient outcome?
Below the knee (BKA) with prosthetic
what are common causes of amputations?
diabetes
severe infection
PVD
trauma
which drug should be given as prophylaxis for DVT?
enoxaparin (lovenox)
pt presents with unilateral left calf erythema and swelling. on PE, their left calf is significantly warmer than the right. Homan's sign is positive on the left. what is the gold standard study to confirm diagnosis?
DVT → venography
what is neurogenic claudication assoc. with?
spinal stenosis
what is vascular claudication assoc. with?
PVD and compromised blood flow with walking activities
neurogenic or vascular claudication: pain worsens with down incline walking d/t increased lordotic pressure?
neurogenic → pain doesn't resolve immediately when pt stops walking
neurogenic or vascular claudication: pain progresses from distal to proximal?
vascular
neurogenic progresses from proximal to distal
neurogenic or vascular claudication: diminished or absent pulses below the waist and pallor changes with elevation on PE
vascular
neurogenic has no abnormal PE findings at rest
lateral knee xray
know this
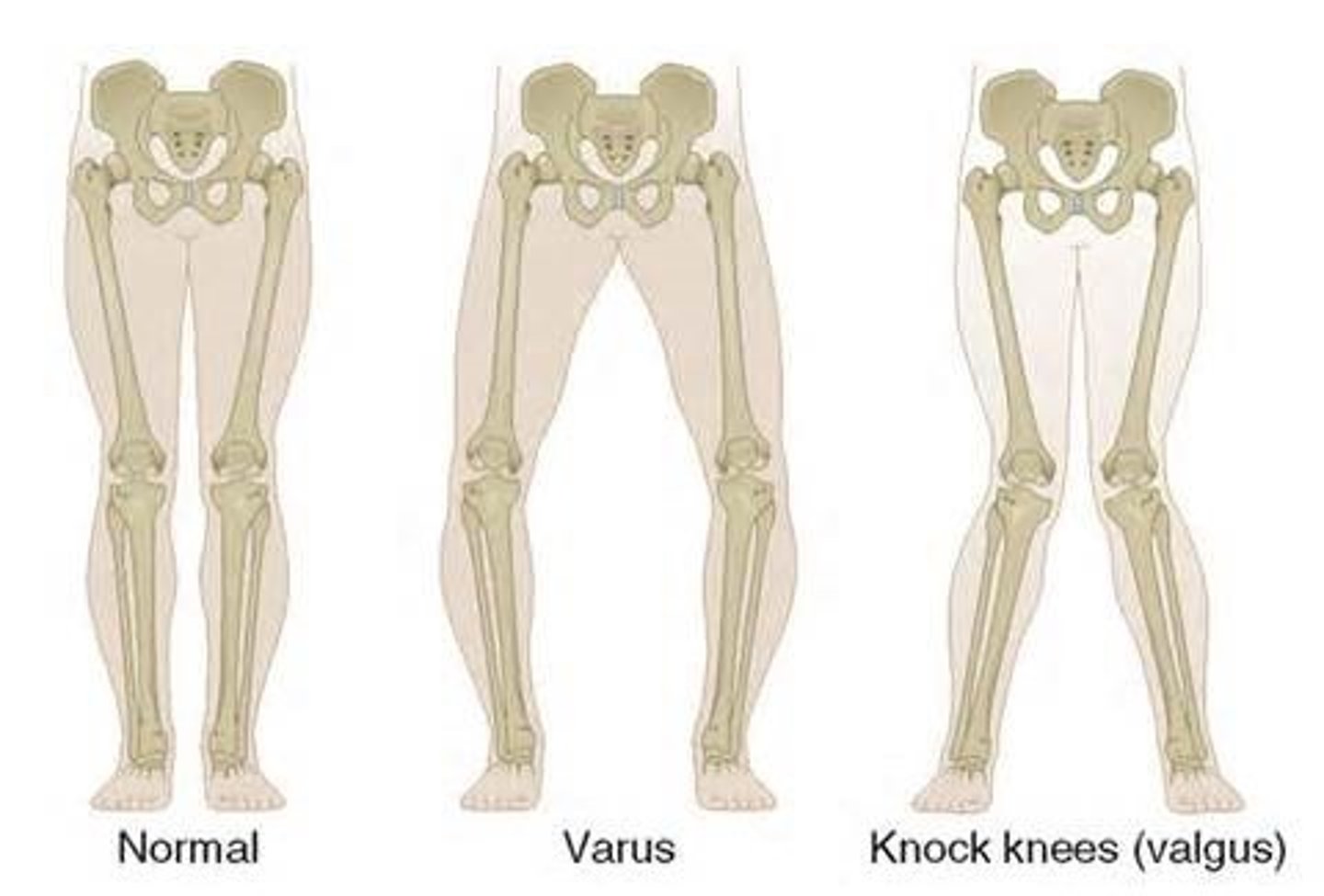
valgus vs. varus: bowed leg
varus → R like riding a horse
valgus is knock knee
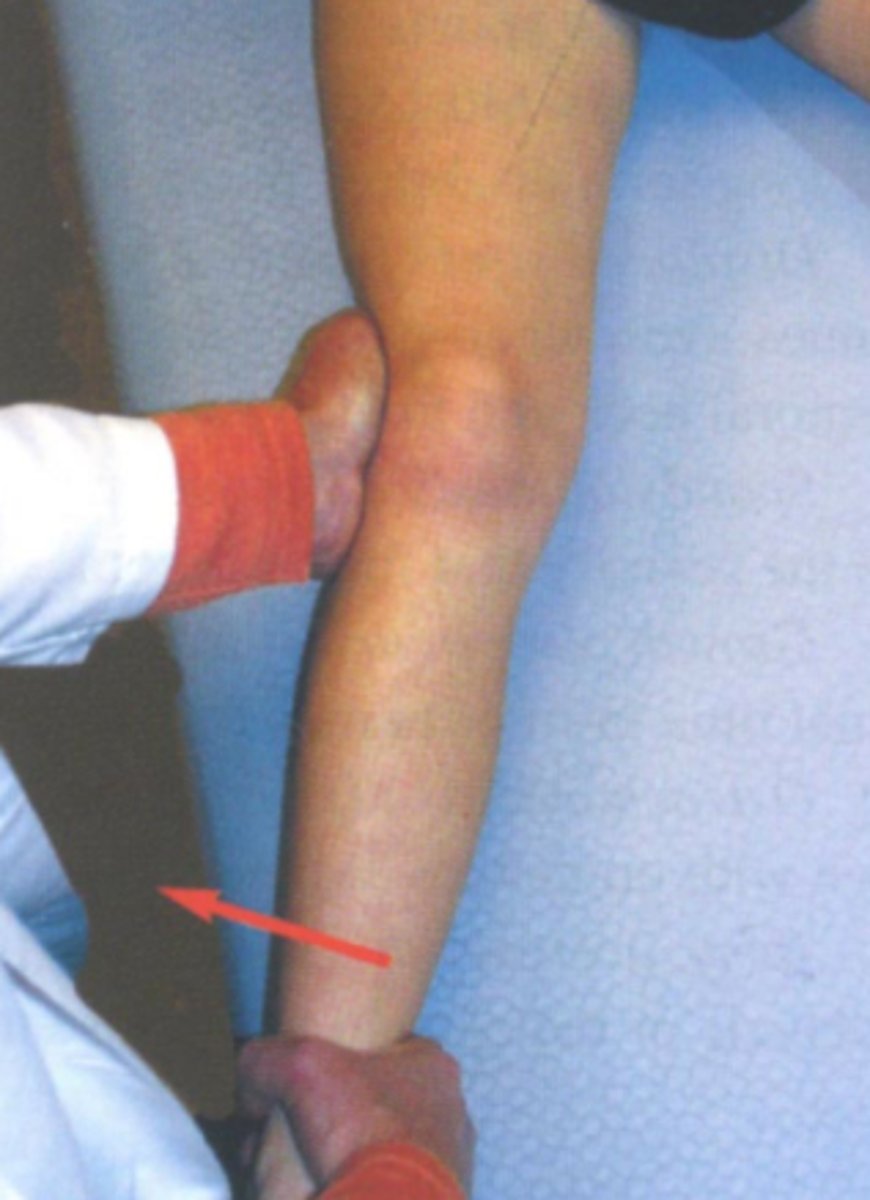
what does a positive valgus test indicate?
MCL injury
what does a positive varus test indicate?
LCL injury
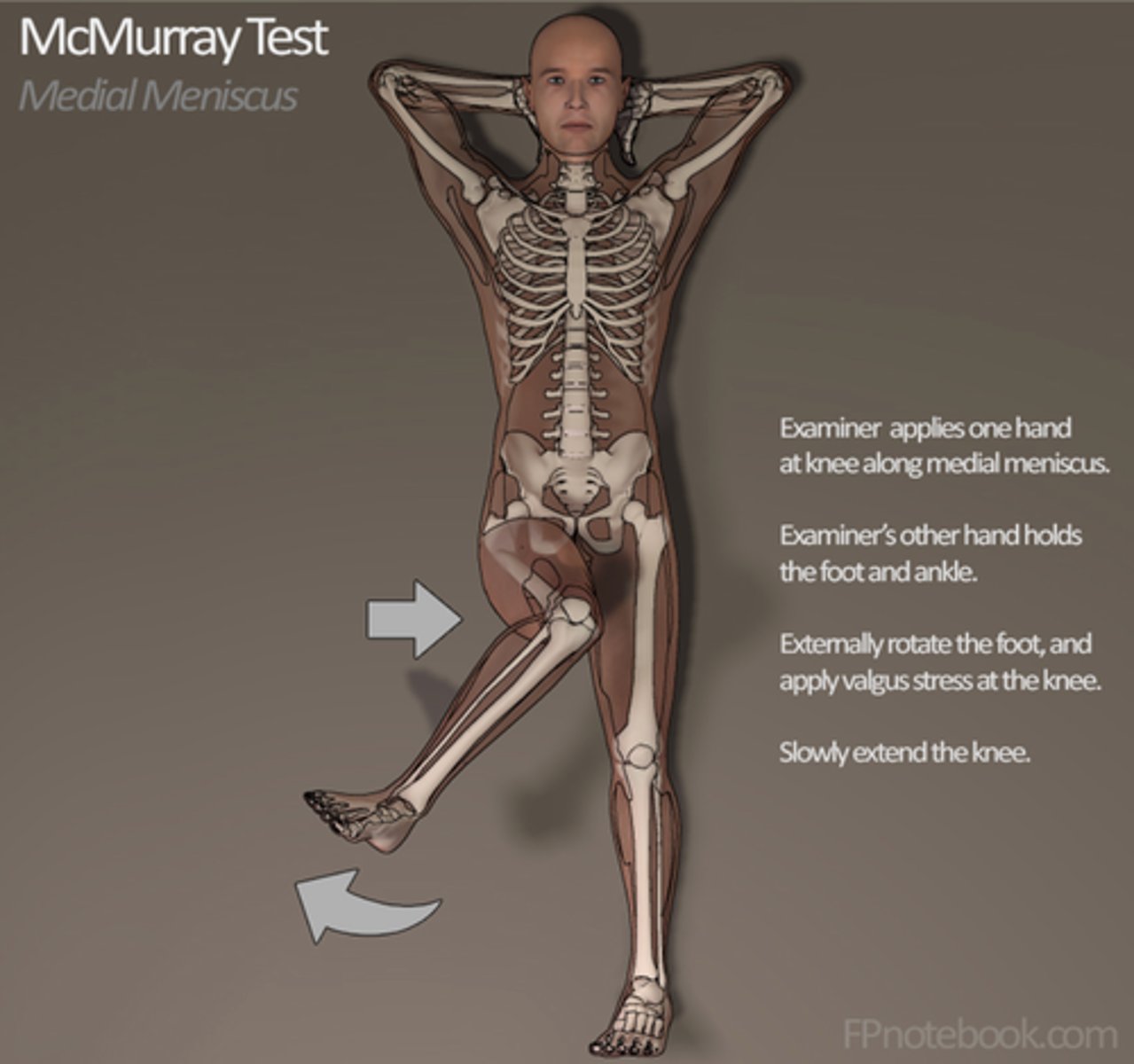
if the examiner internally rotates during the McMurray's test, what are they testing for?
lateral meniscus
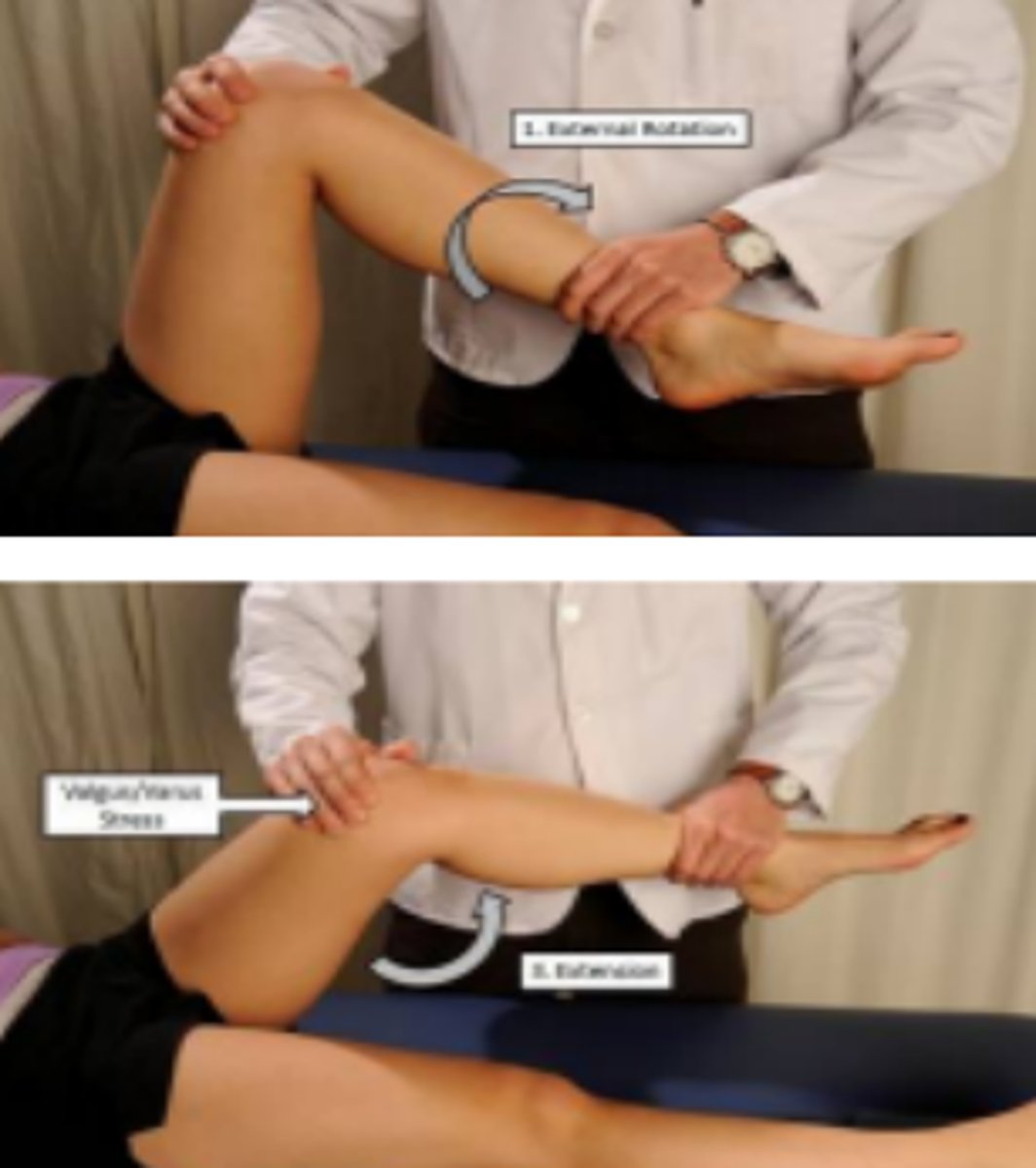
if the examiner externally rotates during the McMurray's test, what are they testing for?
medial meniscus
which special tests asses for ACL injury?
lachman (more sensitive!)
anterior drawer
PCL is posterior drawer
a high school wrestler presents with knee pain and swelling. he reports he was in a match when his opponent forcefully pushed him down at the level of his knee. How should you treat?
PCL injury → knee immobilizer, crutches, RICE< NSAIDs, PT
isolated PCL injuries are often treated nonoperatively
if you suspect a meniscal tear/injury, which imaging study would be best to order?
MRI → most accurate
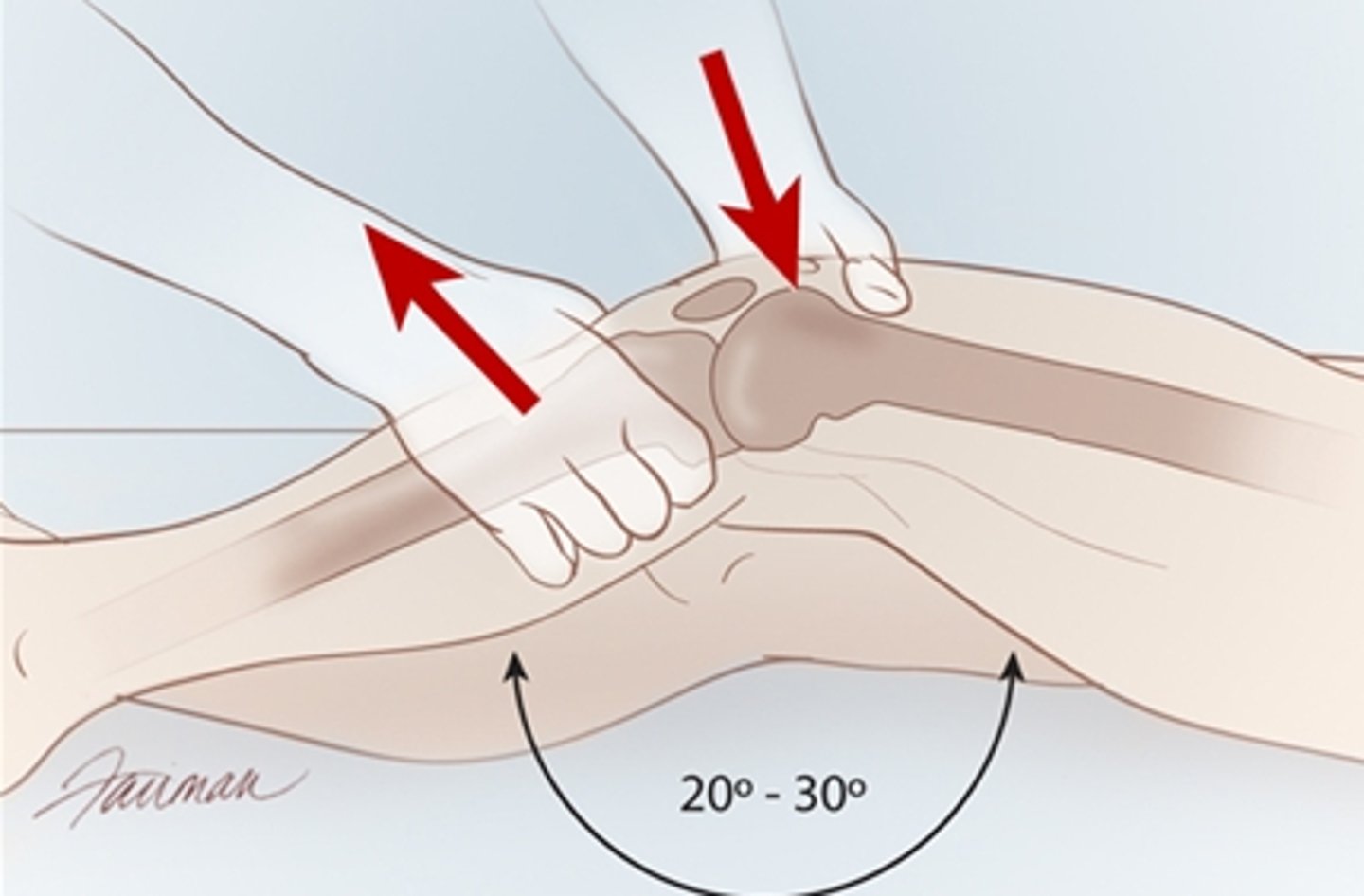
58-year-old male presents with complaints of swelling, pain, and locking of his left knee. he reports he was playing basketball and felt pain after pivoting his left leg quickly. what special test would help to confirm this dx?
meniscal tear → McMurray or Apley's compression
MOI is pivoting/rotating
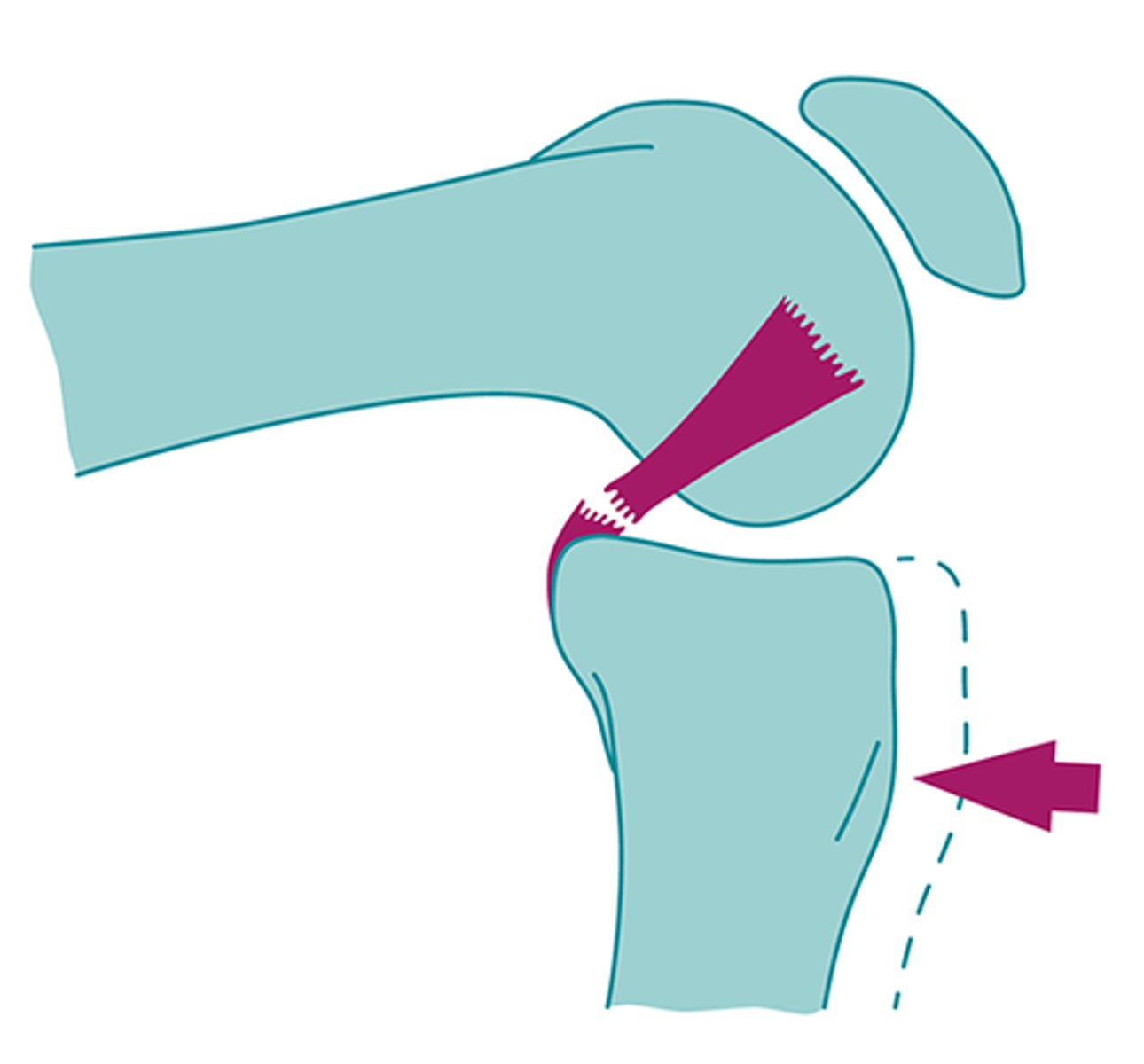
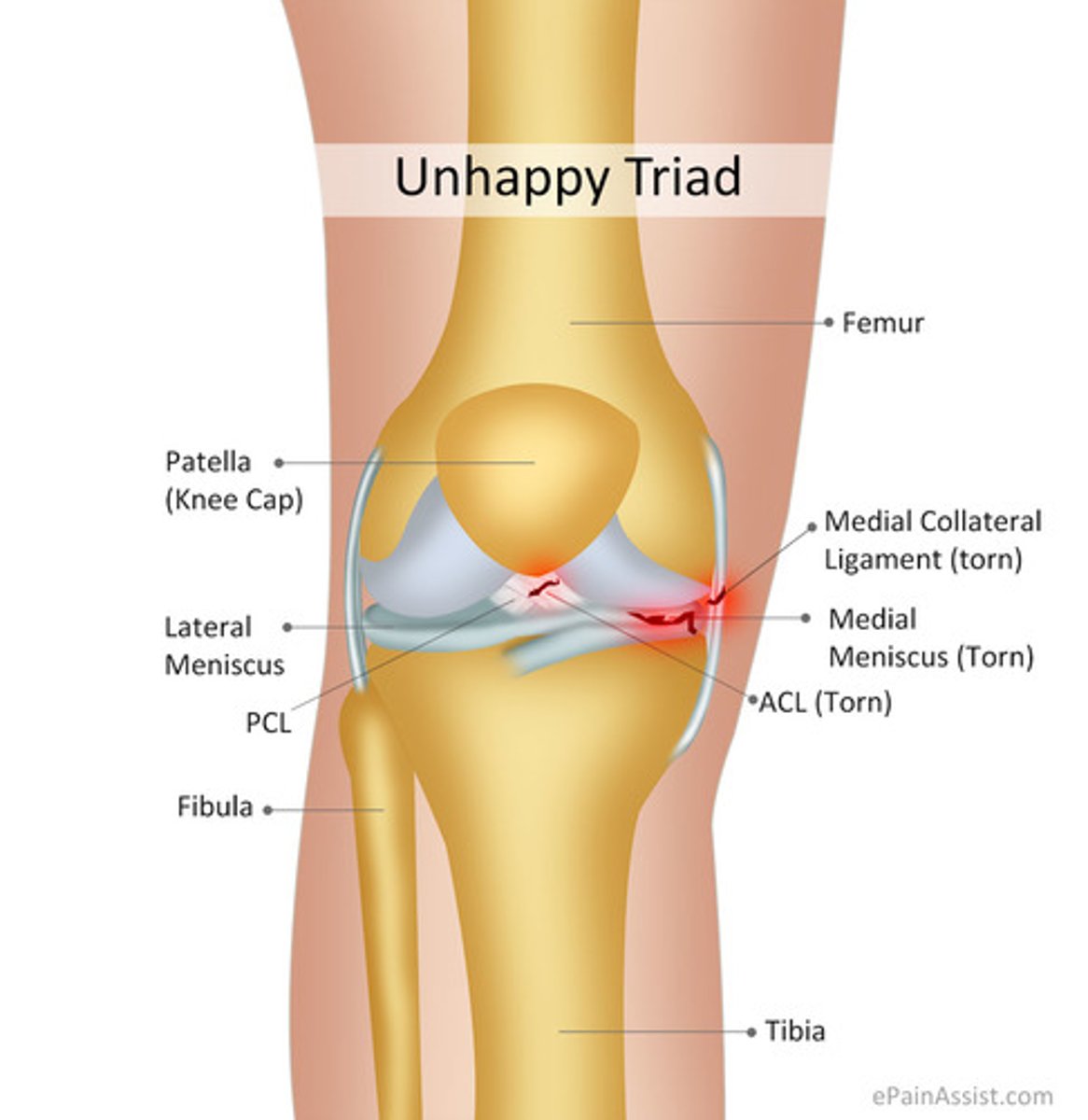
what is the unhappy triad?
ACL, MCL, meniscus tear
what is the gold standard for dx of ACL tear?
MRI
which knee (patellar) dislocation is most common?
lateral dislocation
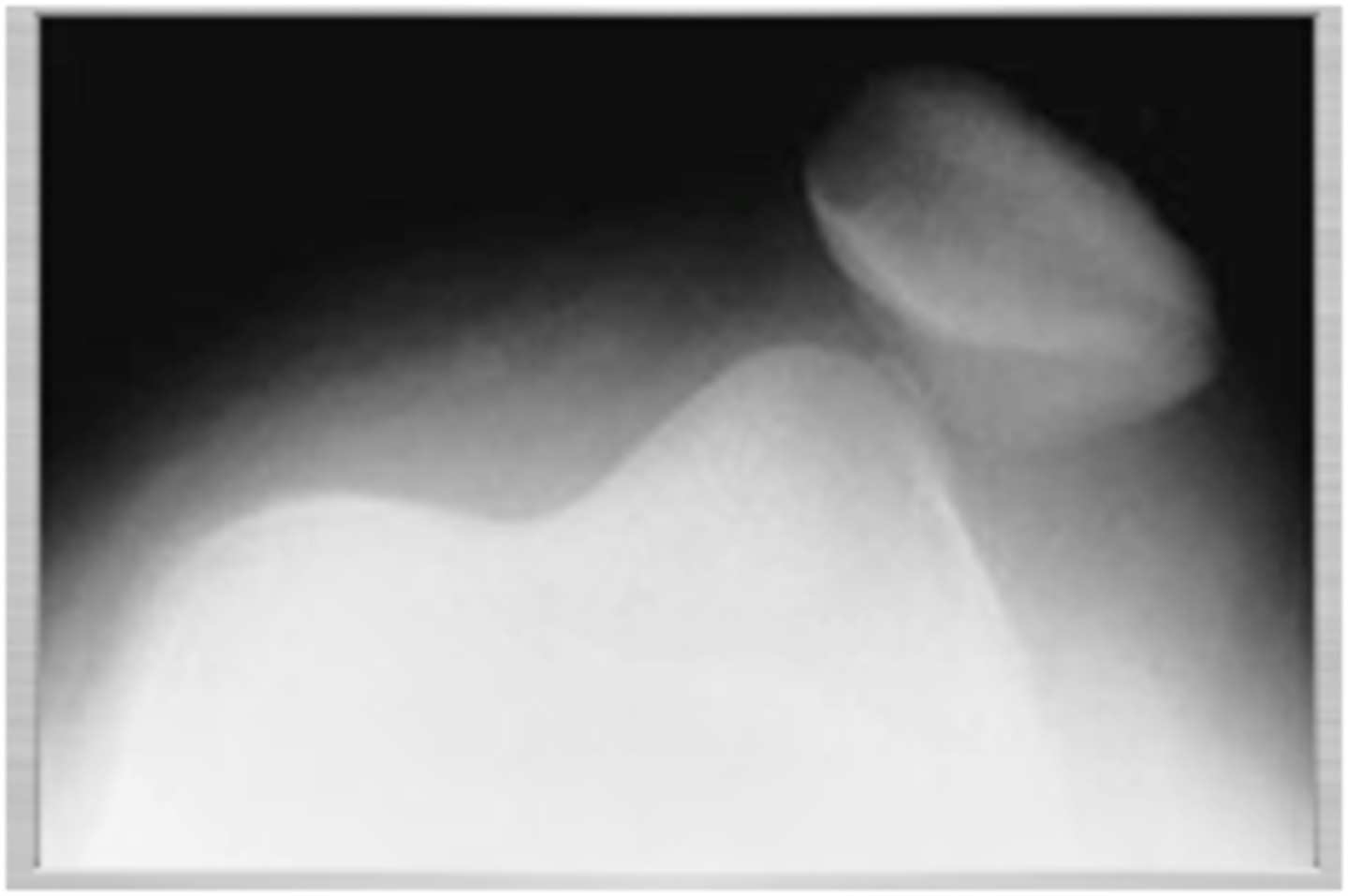
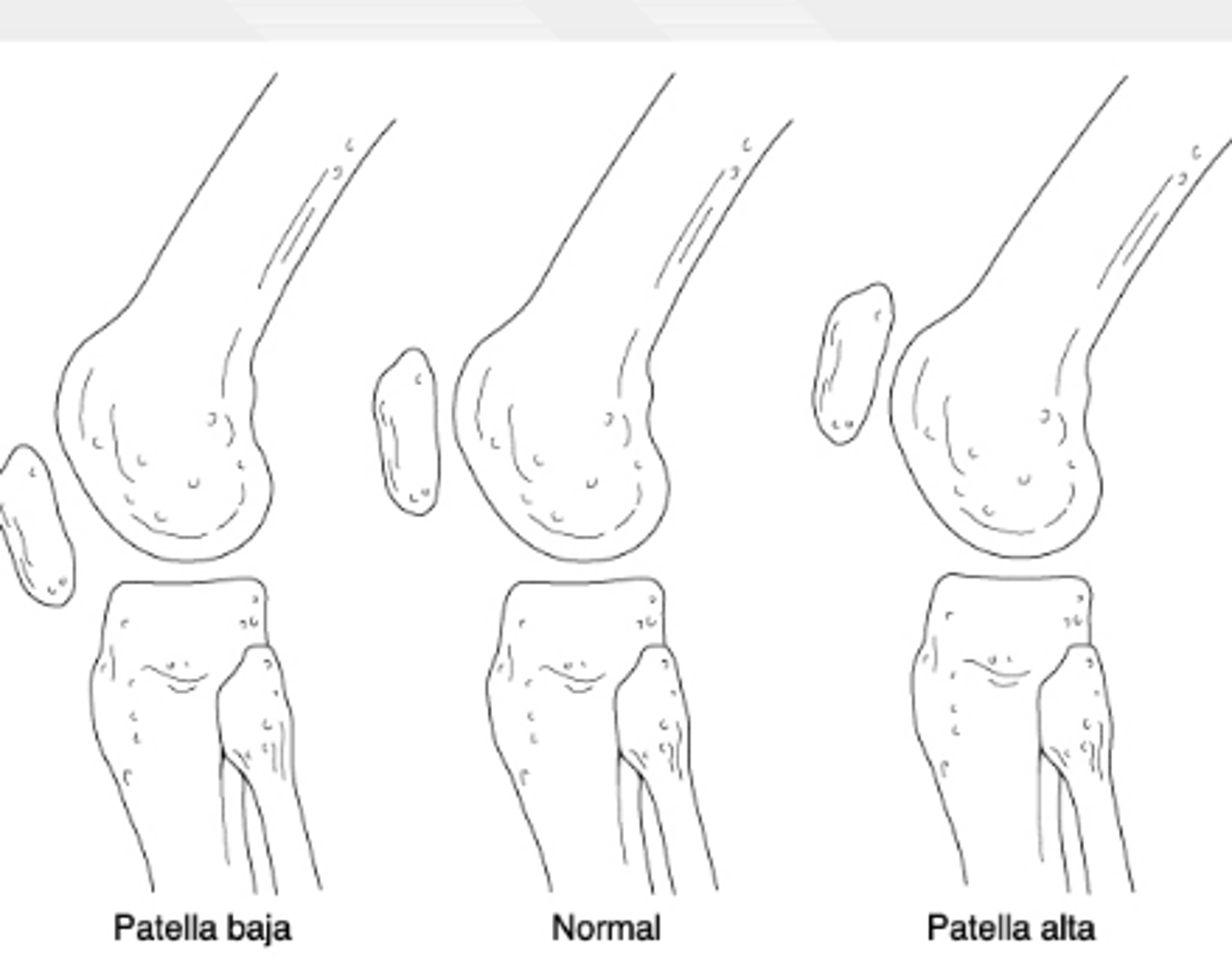
if a pt cannot actively extend their knee and they have a palpable defect inferior to the patella, what dx is most likely?
patellar tendon rupture → patella alta on XR
what is the most dangerous complication following tibiofemoral dislocation?
popliteal artery injury (and compartment syndrome)
any vascular compromise = stat vascular sx consult
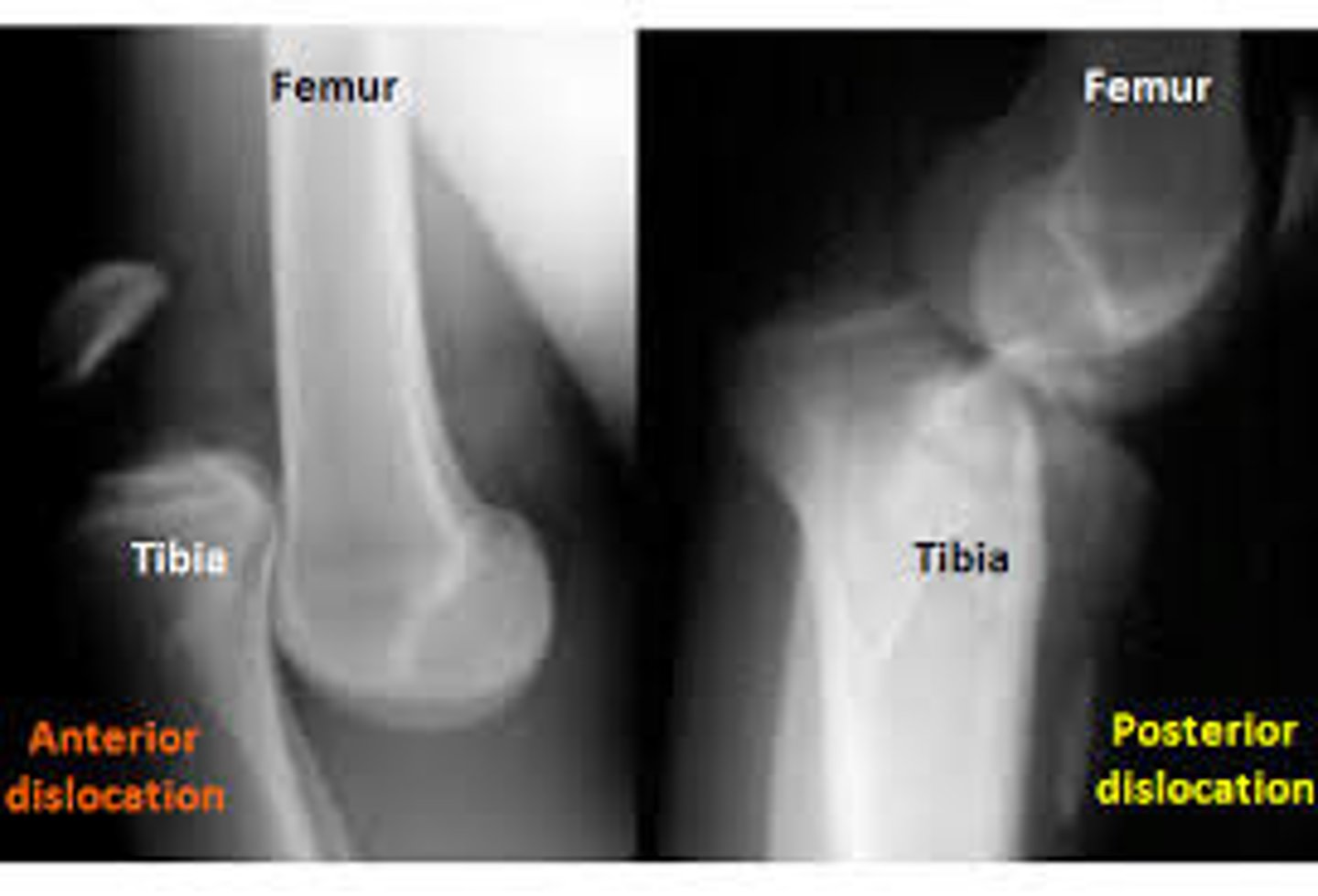
a pt is brought into the ER s/p MVA. they are unable to bear weight on their right leg and there is an obvious deformity in their right lower leg. what would you expect to see on XR?
tibiofemoral dislocation → + dislocation on XR
caused by high energy trauma
which population is Osgood-Schlatter disease MC in?
adolescent male athletes
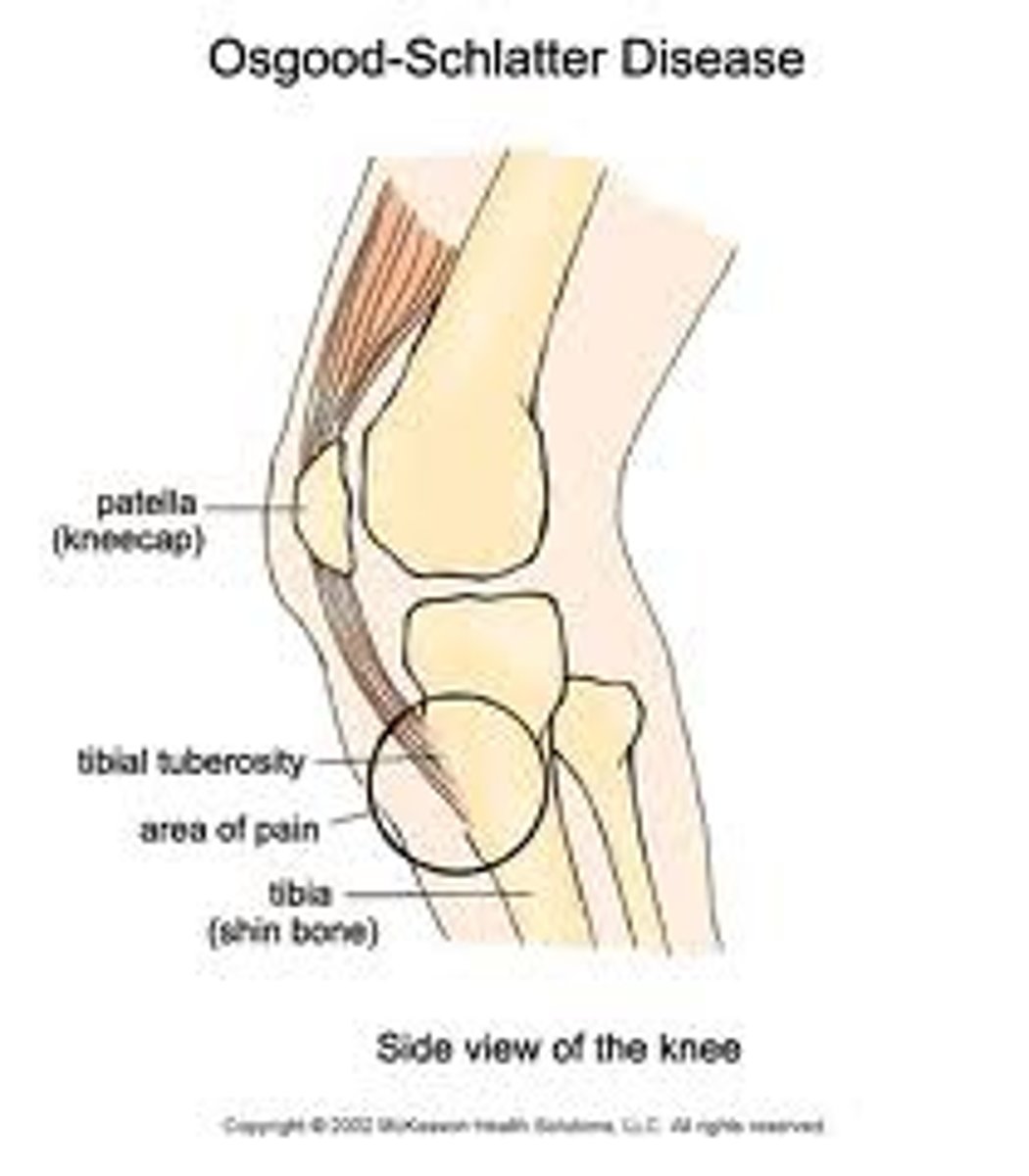
15 y/o male athlete presents with pain and swelling in his anterior left knee over the tibial tuberosity. how should you treat?
Osgood Schlatter →RICE, NSAIDS, ortho consult
but r/o fx on plain film XR
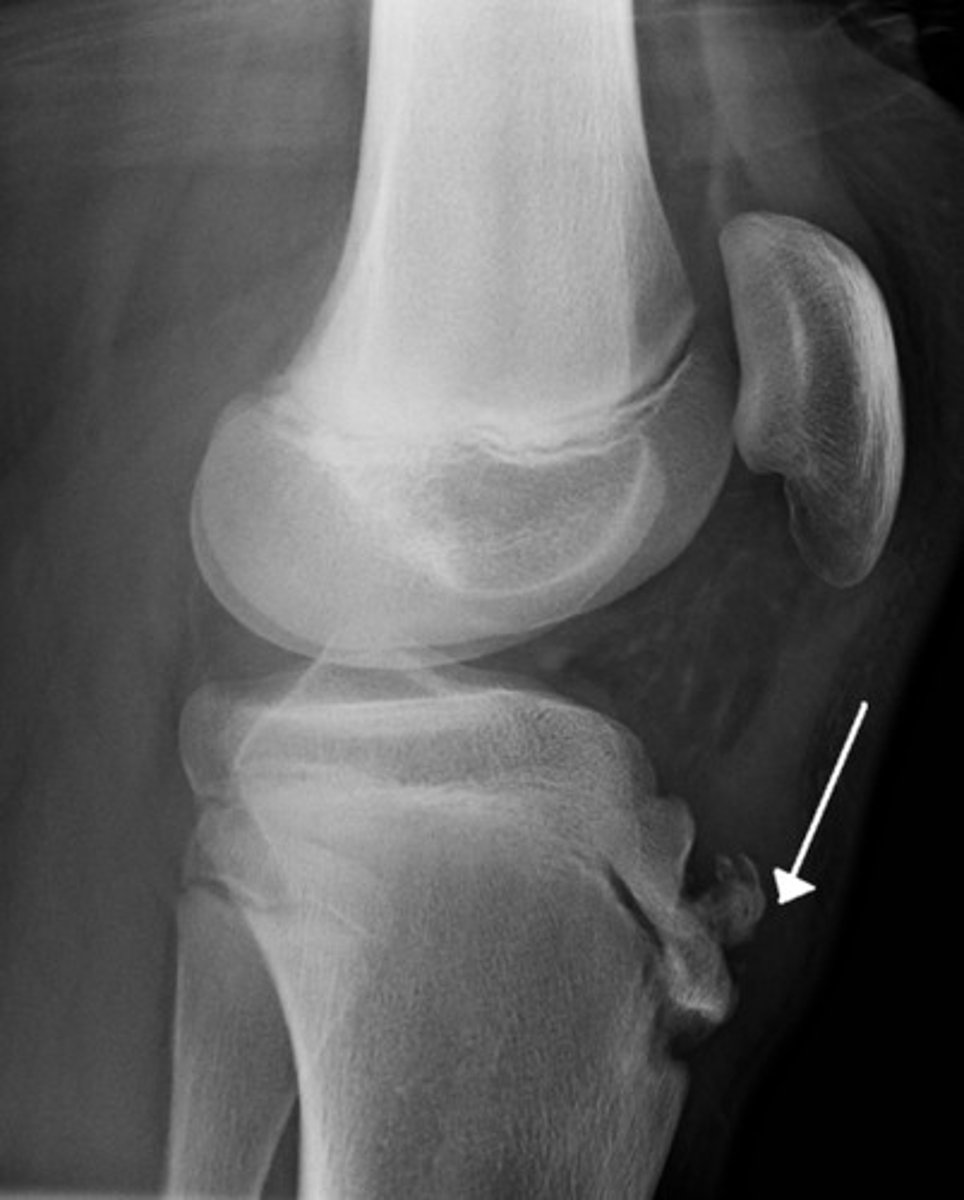
if you see a prominent area over the tibial tubercle on XR from an adolescent pt complaining of pain, what dx should you suspect?
osgood-schlatter
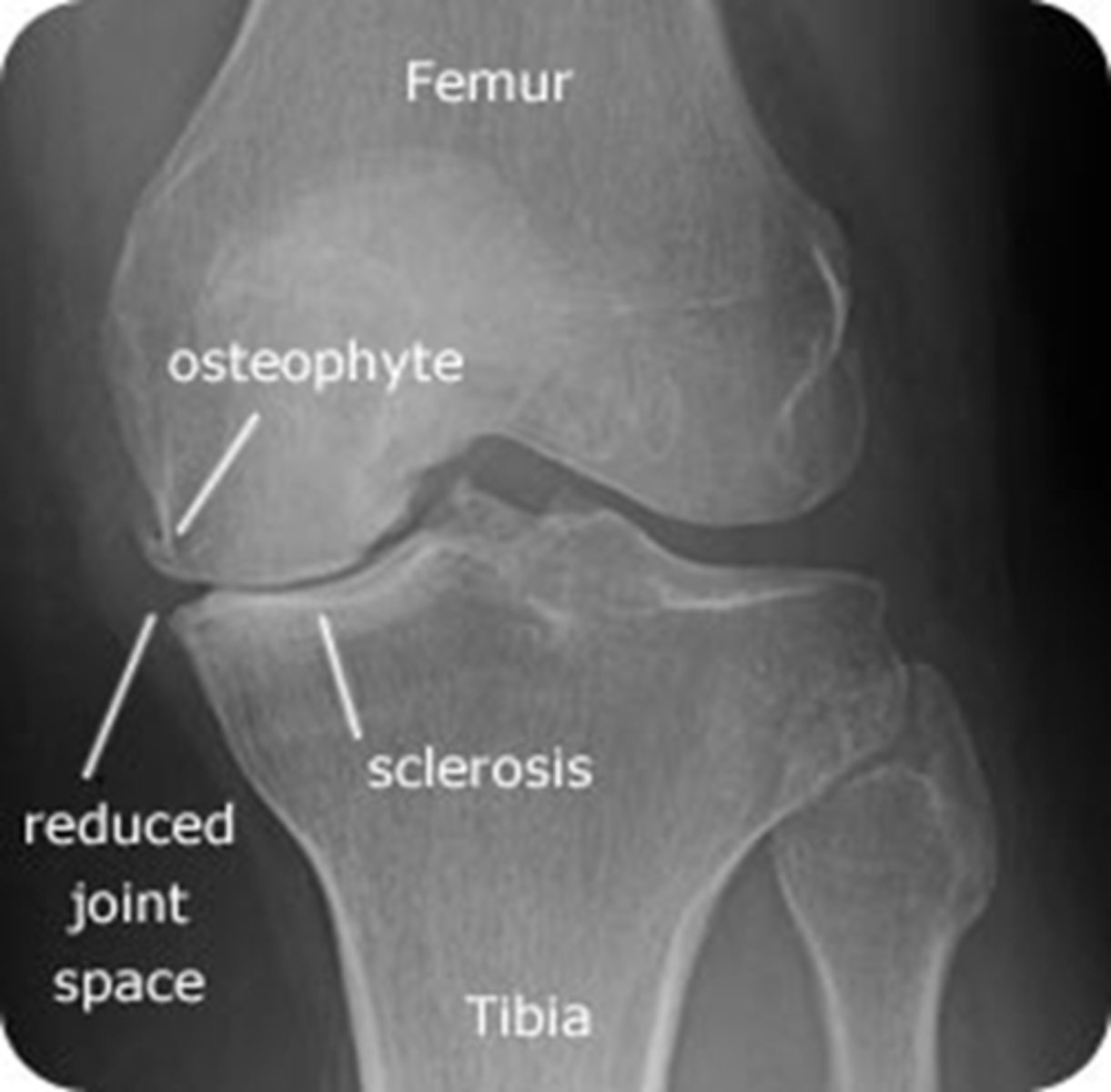
what would you expect to see on XR in a pt with osteoarthritis of the knee?
weight-bearing AP films → shows narrowing of the joint space, bone sclerosis, periarticular (Baker's cyst) and osteophytes
XR is most important for diagnosis!
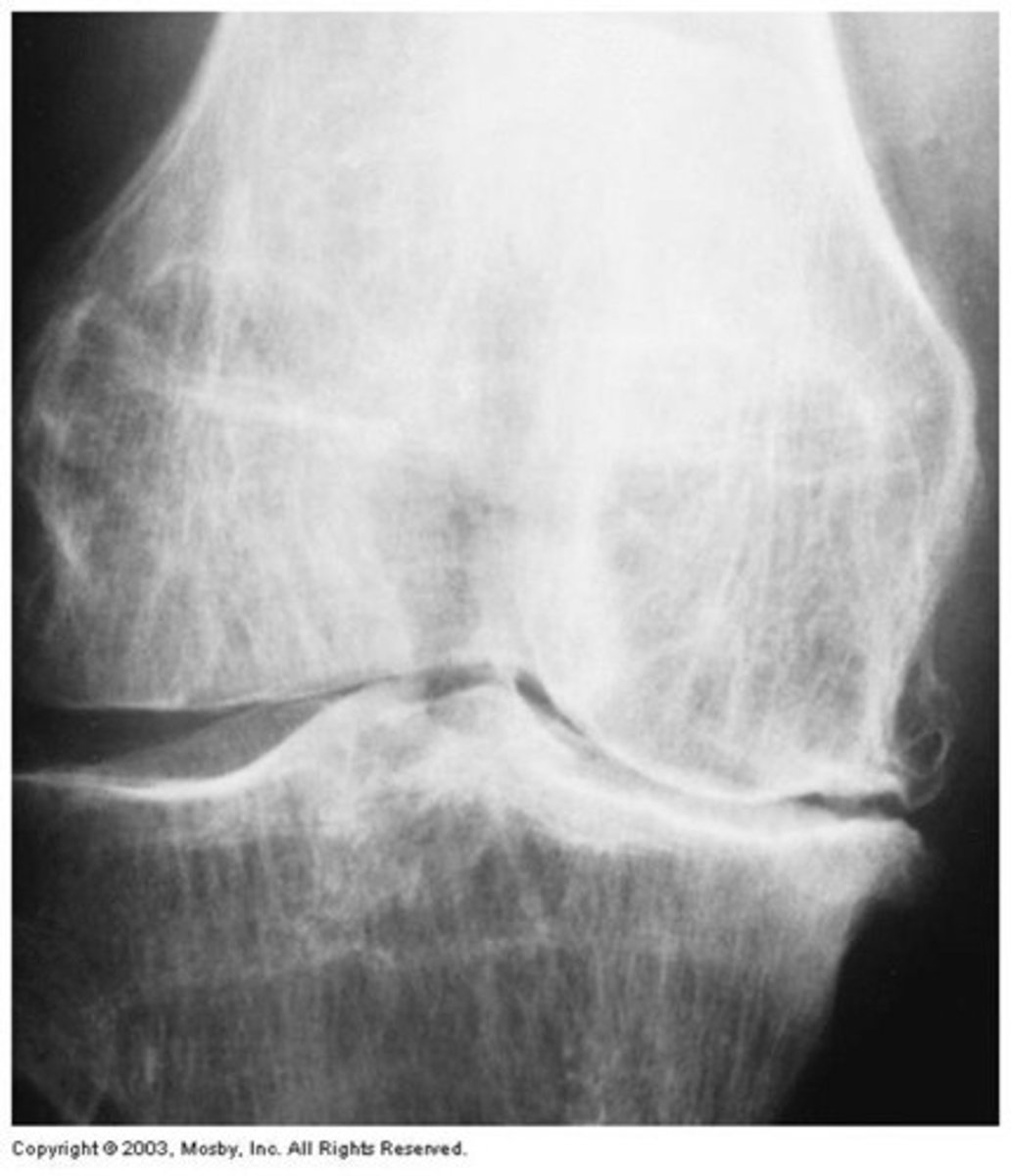
61 year old male presents with pain and stiffness in his knees. He reports buckling, and decreased ROM. on PE, he appears to have windswept deformities. what is the dx?
osteoarthritis of knee
medial compartment (medial tibial plateau and medial femoral condyle) is more commonly involved!
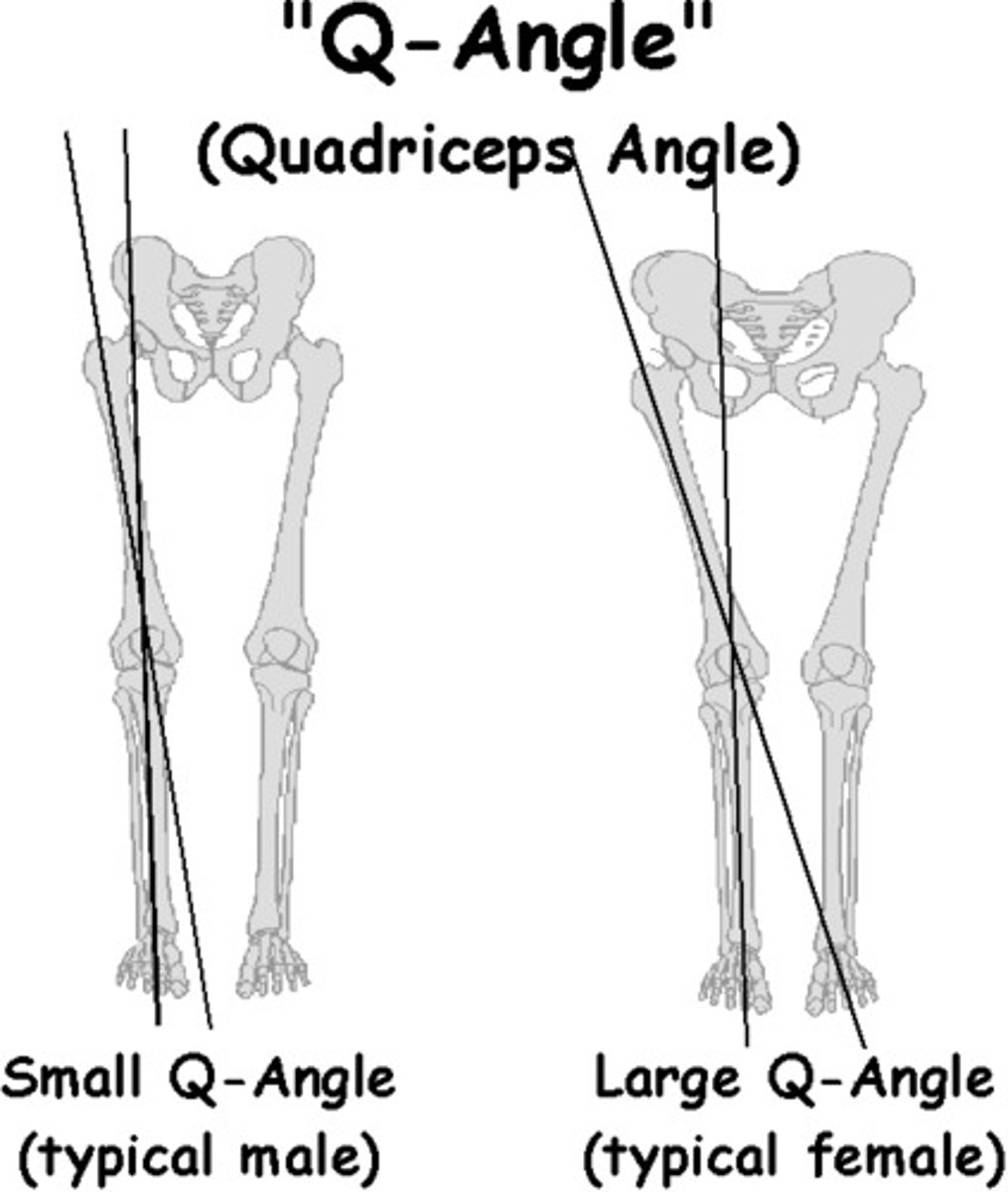
39-year-old female runner presents with complaints of dull, aching pain behind her kneecap with associated swelling. what special tests would you expect to be positive?
patellofemoral syndrome →
+ apprehensive and + Ober test
common in women bc of Q angle
what organism MC causes septic arthritis?
staph aureus
N. gonnorrhea in sexually active young adults
pt presents with edema, warmth, pain, and limited ROM in their left knee. they are unable to bear weight on their left leg. you dx them with septic arthritis. what would you expect to see on arthrocentesis?
WBC >50,000
17 year old volleyball player presents with tenderness along the patellar tendon. what is the dx?
patellar tendonitis -- key word volleyball bc its called "jumper's knee"
ankle/foot bones
review!
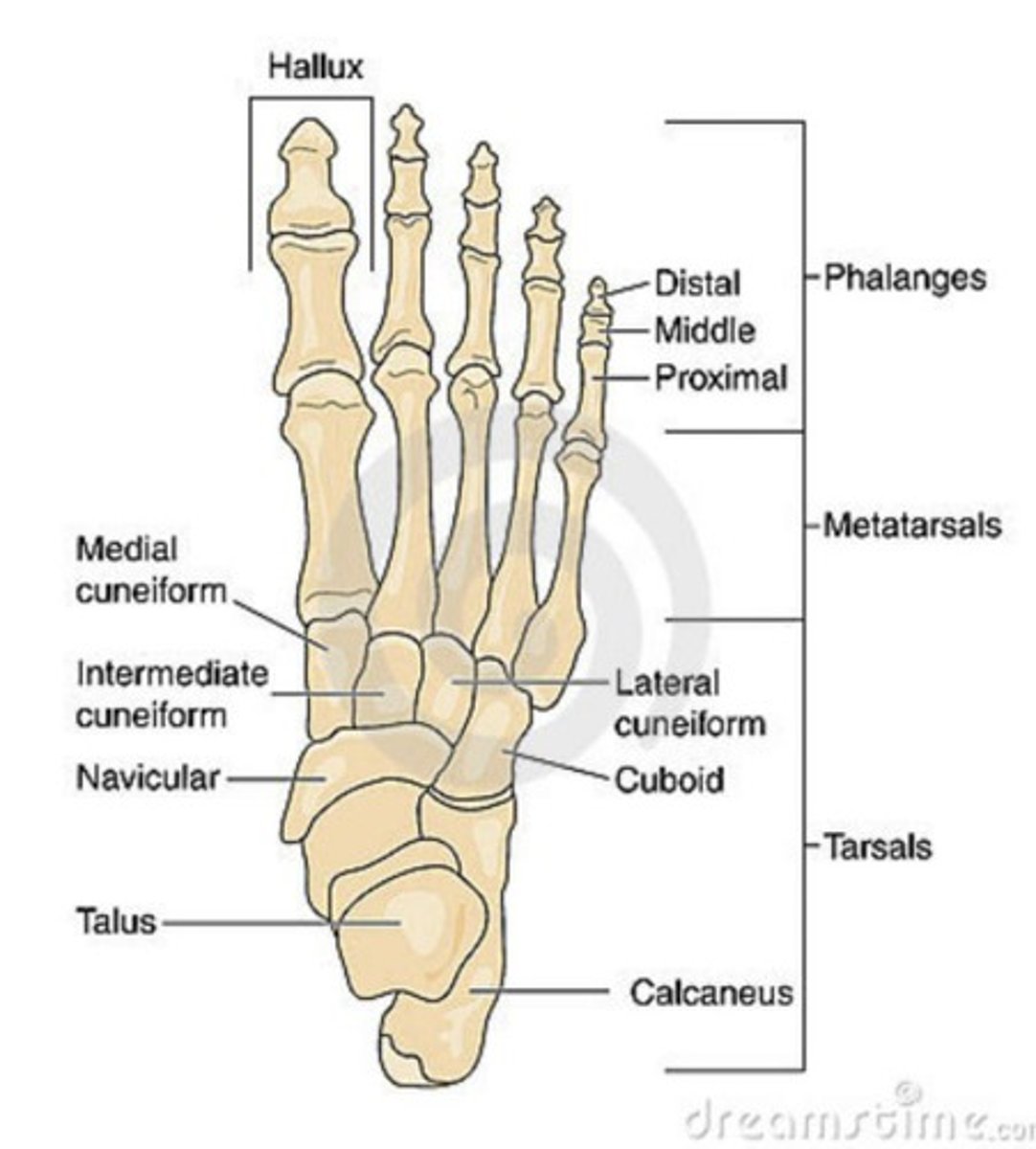
which ligament connects the distal end of the tibia to fibula anteriorly?
Anterior TIBIOfibular ligament
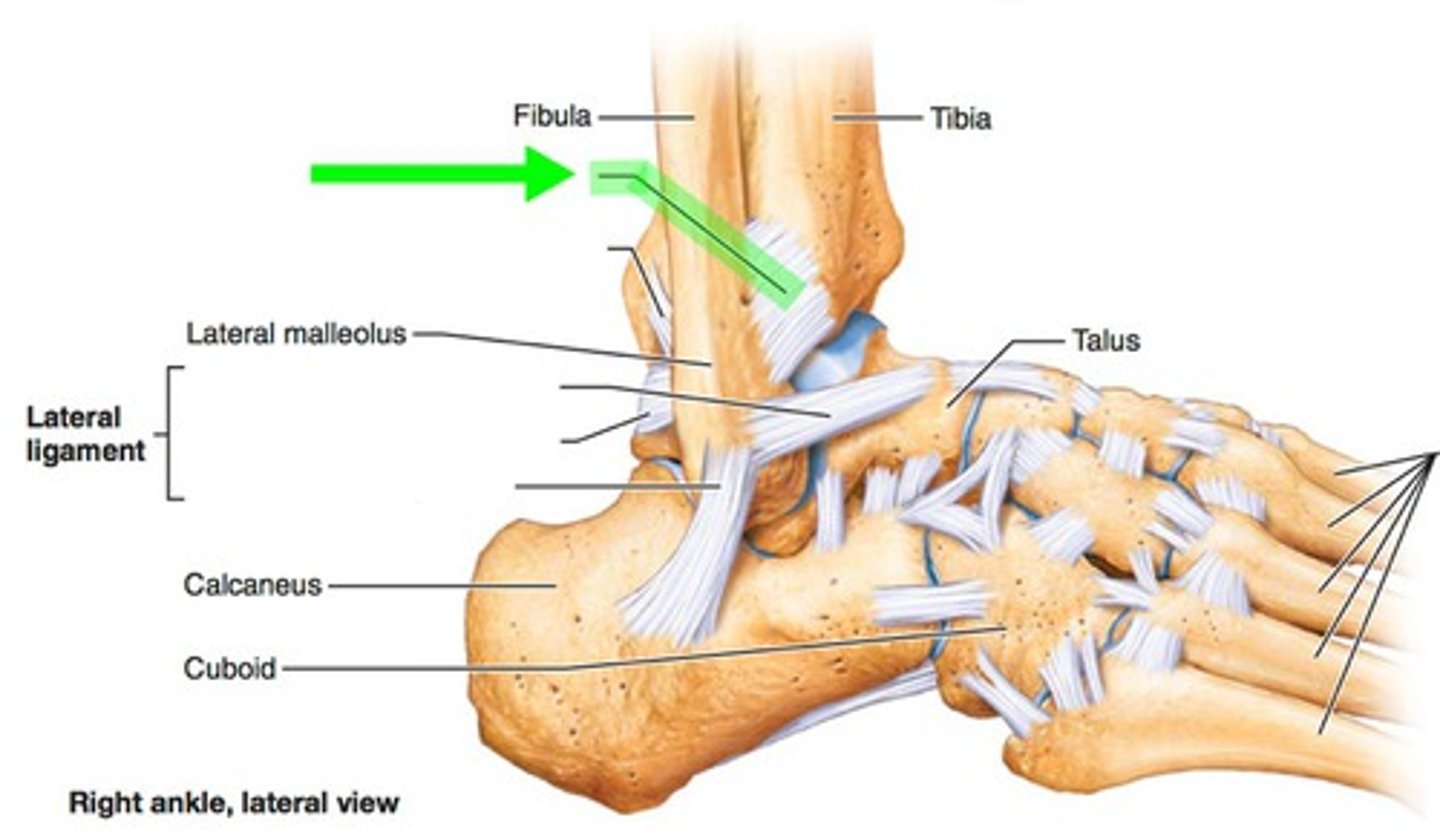
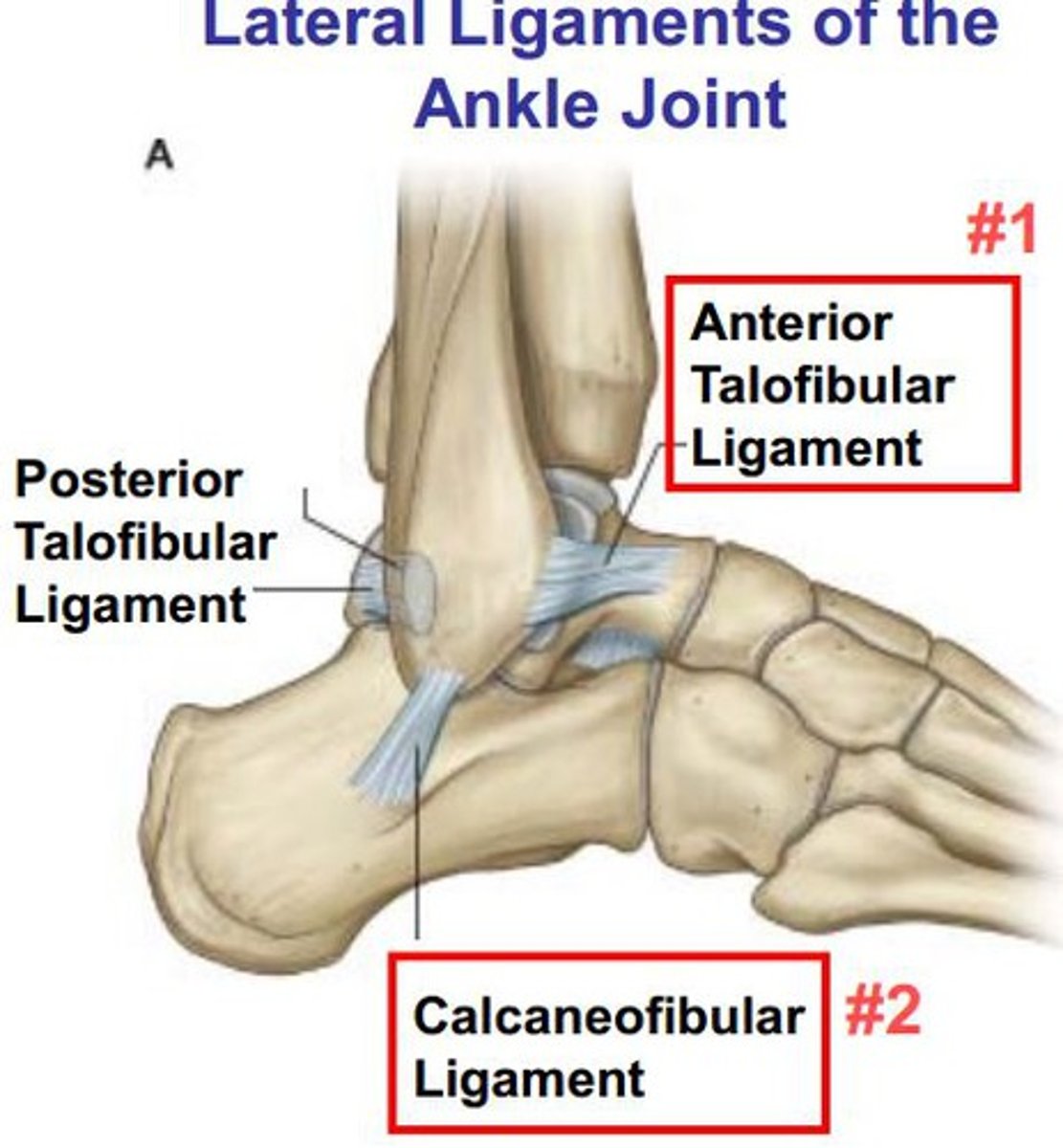
which special test tests for instability of anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL)
anterior drawer
ATFL is MC injured in ankle sprain
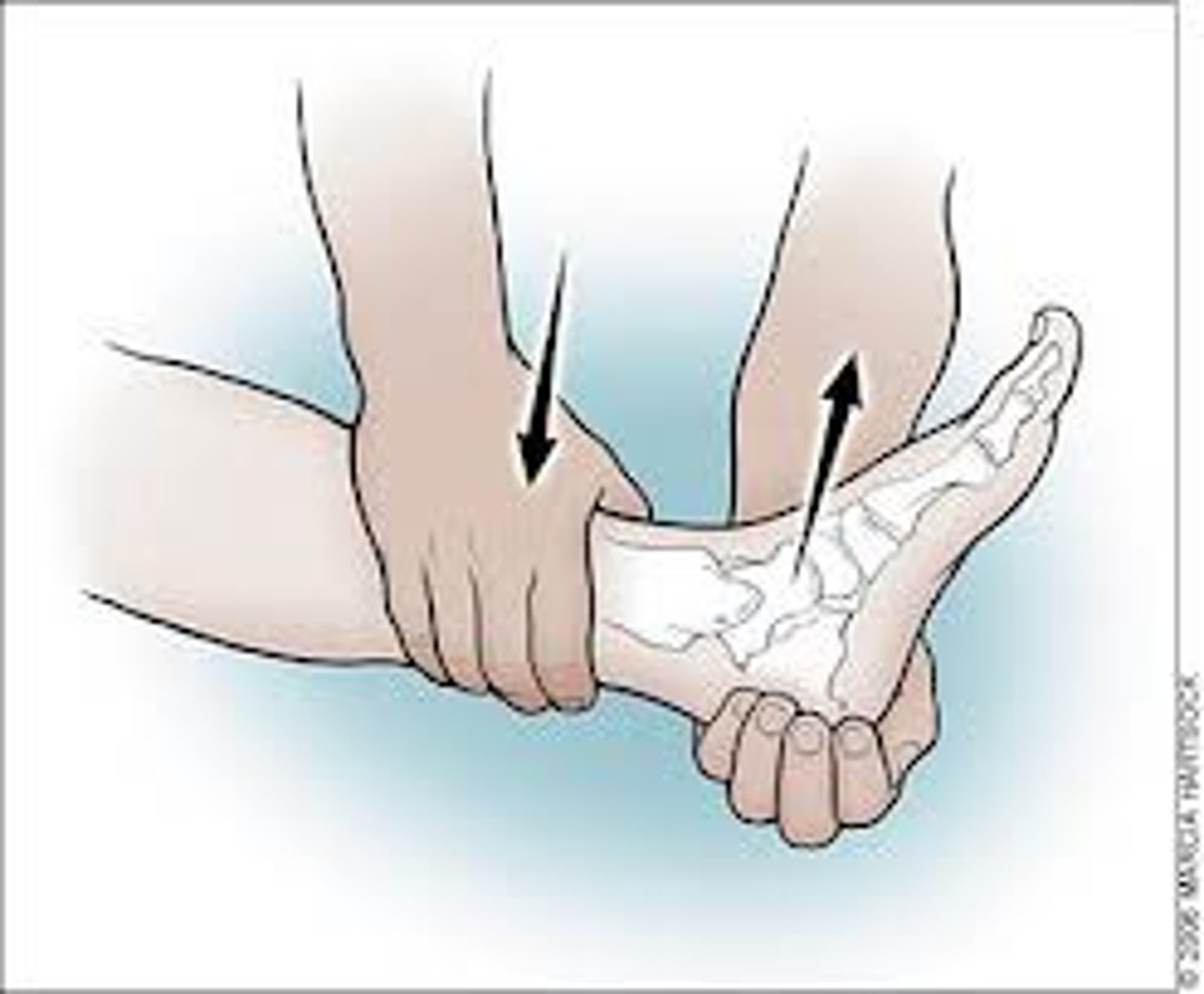
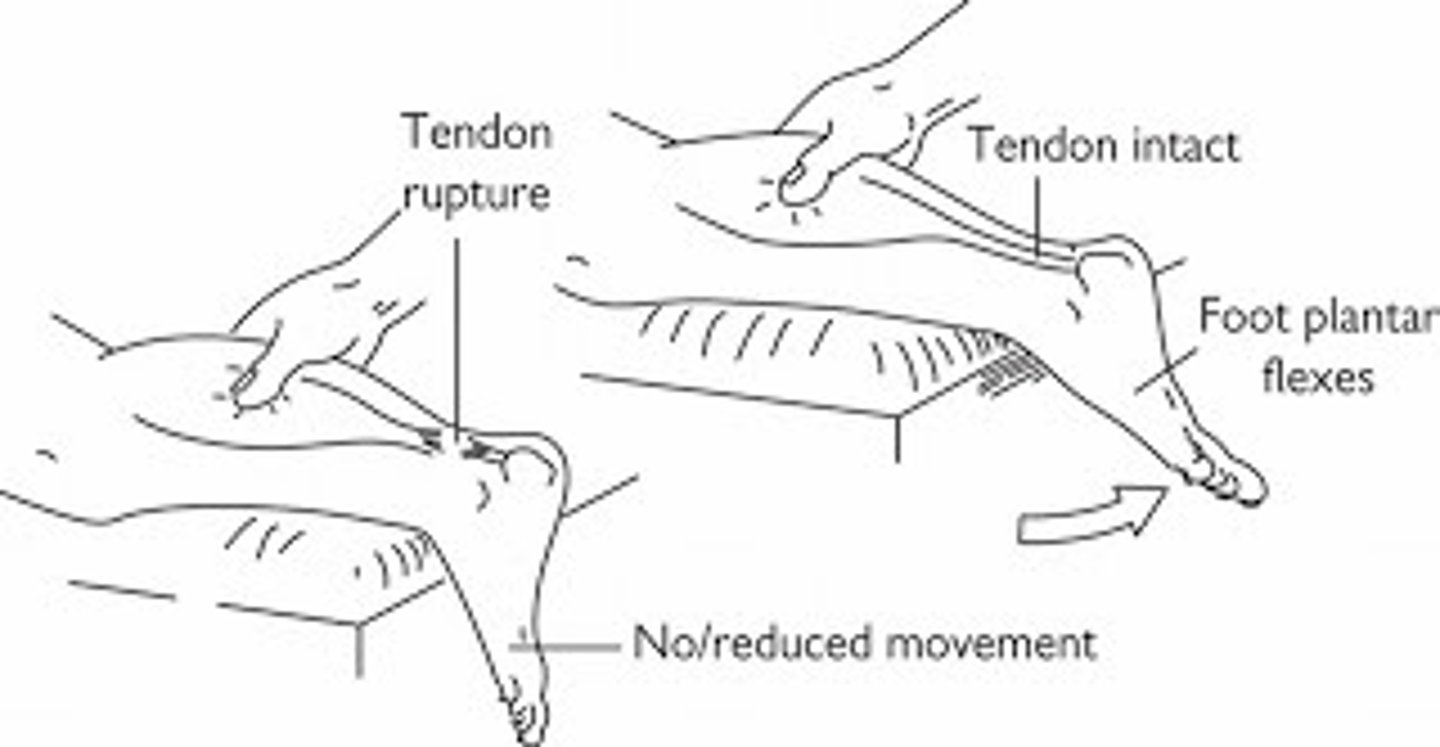
if you suspect an Achille's tendon rupture, which special test should you perform?
thompson's test → positive = absence of plantar flexion of foot
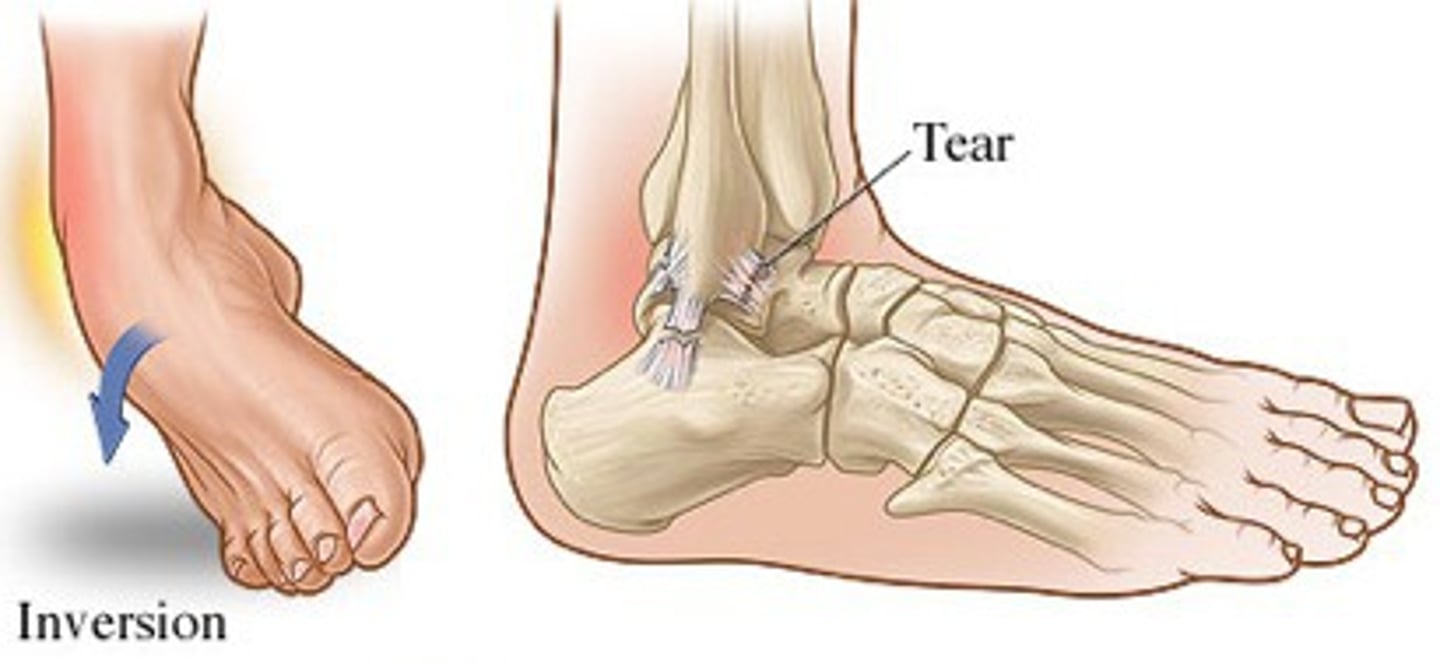
what is a common cause of ankle sprain?
inversion injury (90%)!
MC sport injury!
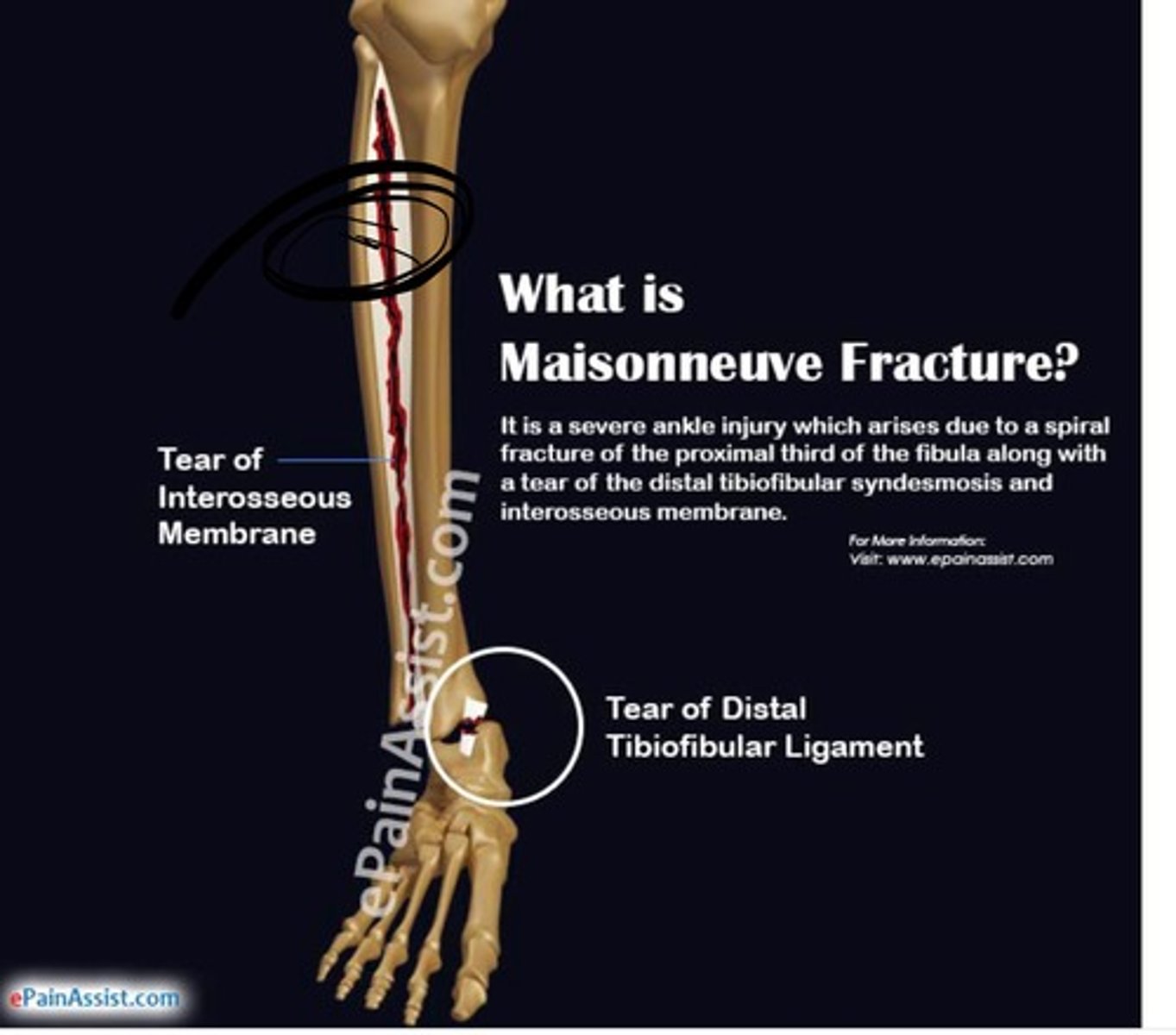
if an XR report shows ankle syndesmosis (widening of the ankle mortise medially), what is the dx?
Maisonneuve fracture → fracture of medial malleolus and spiral fx of proximal fibula
d/t pronation and external rotation
what bones are included in the forefoot?
5 phalanges
metatarsals
great toe
what bones are included in the midfoot?
navicular, cuboid, and 3 cuneiform bones
connects forefoot to rearfoot
what bones are included in the hindfoot?
talus and calcaneus
connects midfoot and ankle
which joint aids in eversion and inversion of the foot?
subtalar joint
56 year old female presents with complaints of heel pain. she reports the pain is worse in the AM, especially with her first steps out of bed. on PE, she has tenderness to palpation. how should you treat?
plantar fasciitis → NSAIDs, ice, stretching (PT), steroid injections
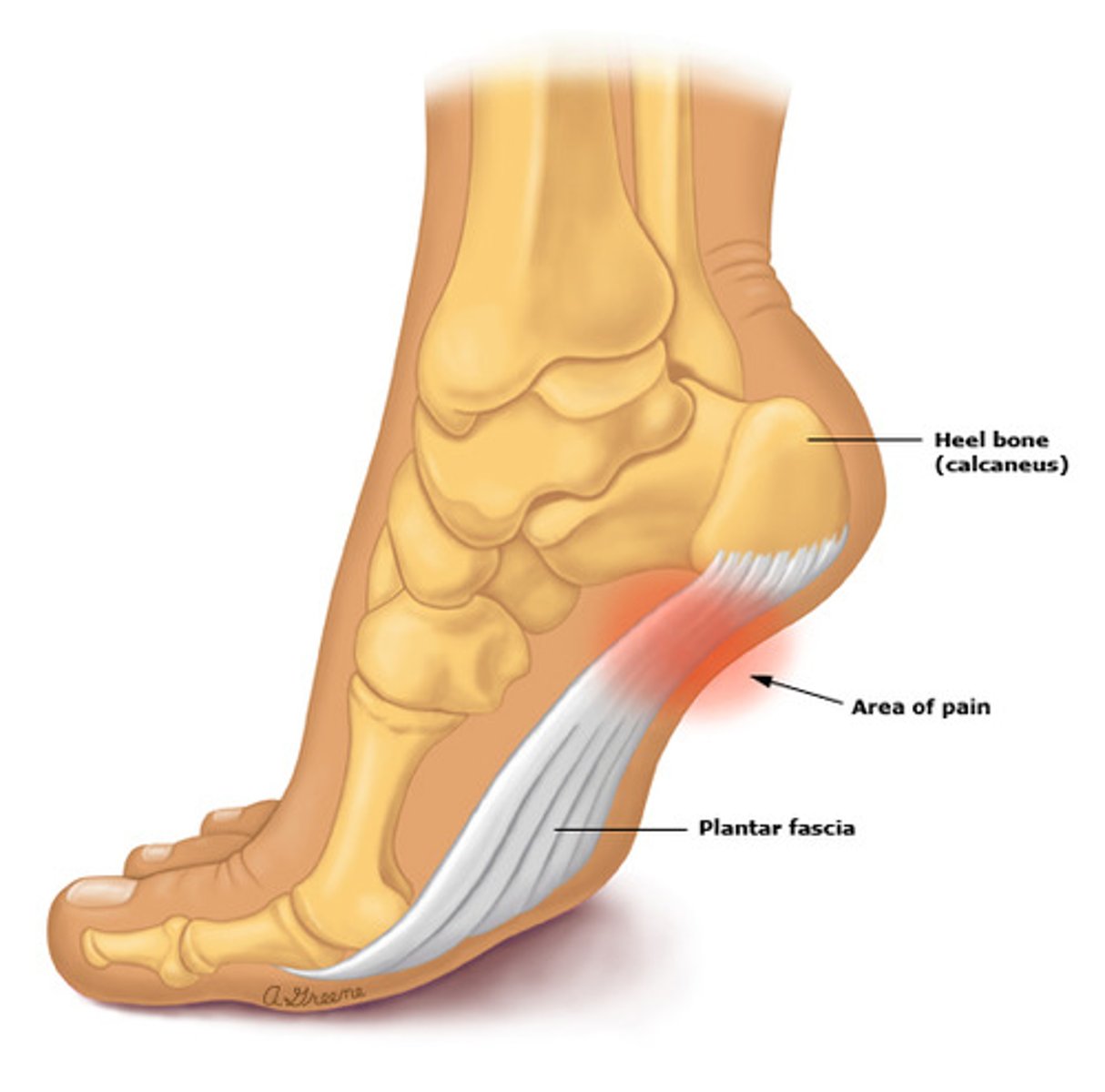
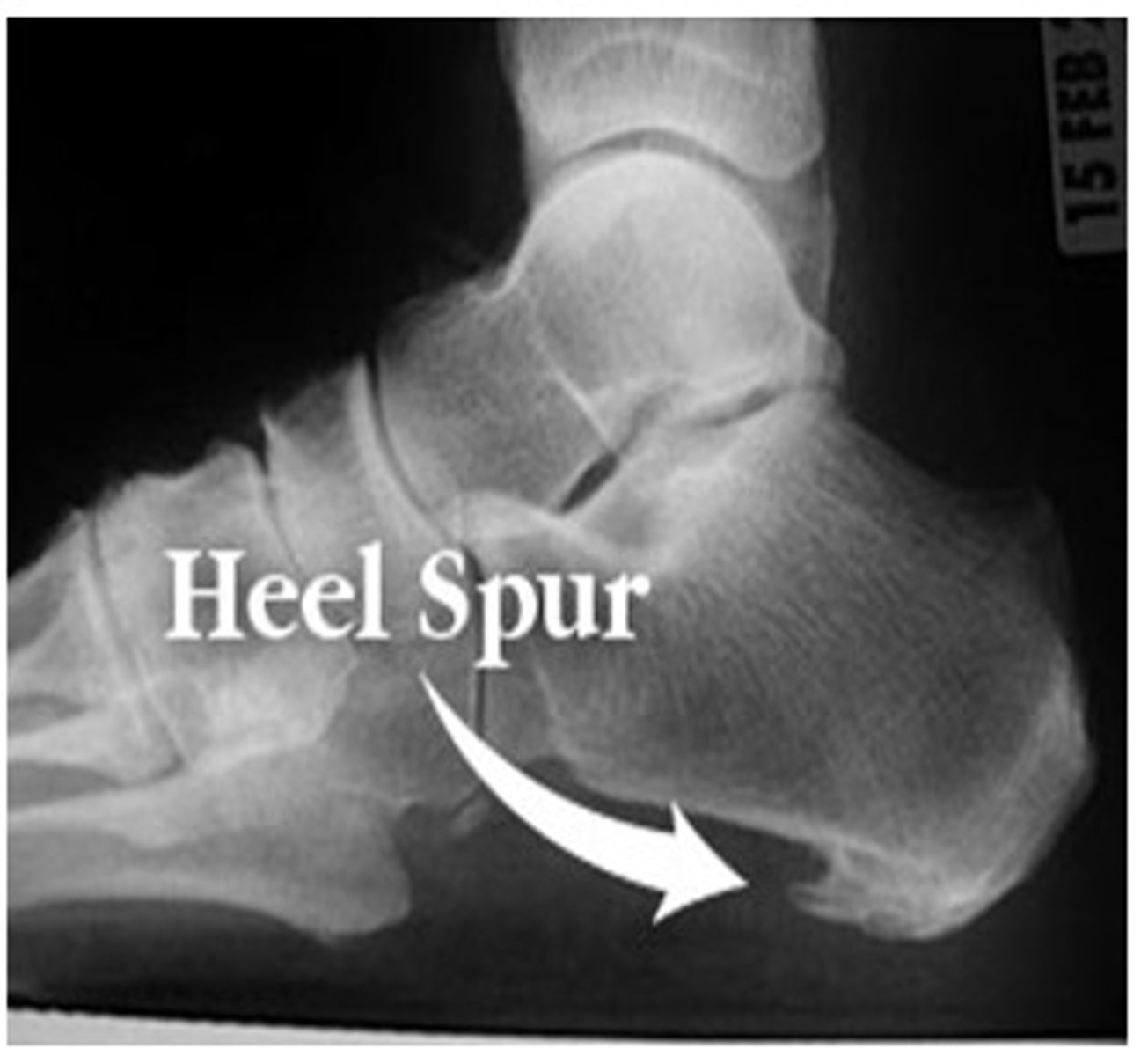
if a patient says they "feel like they're walking on a stone", what is the likely dx?
heel spur
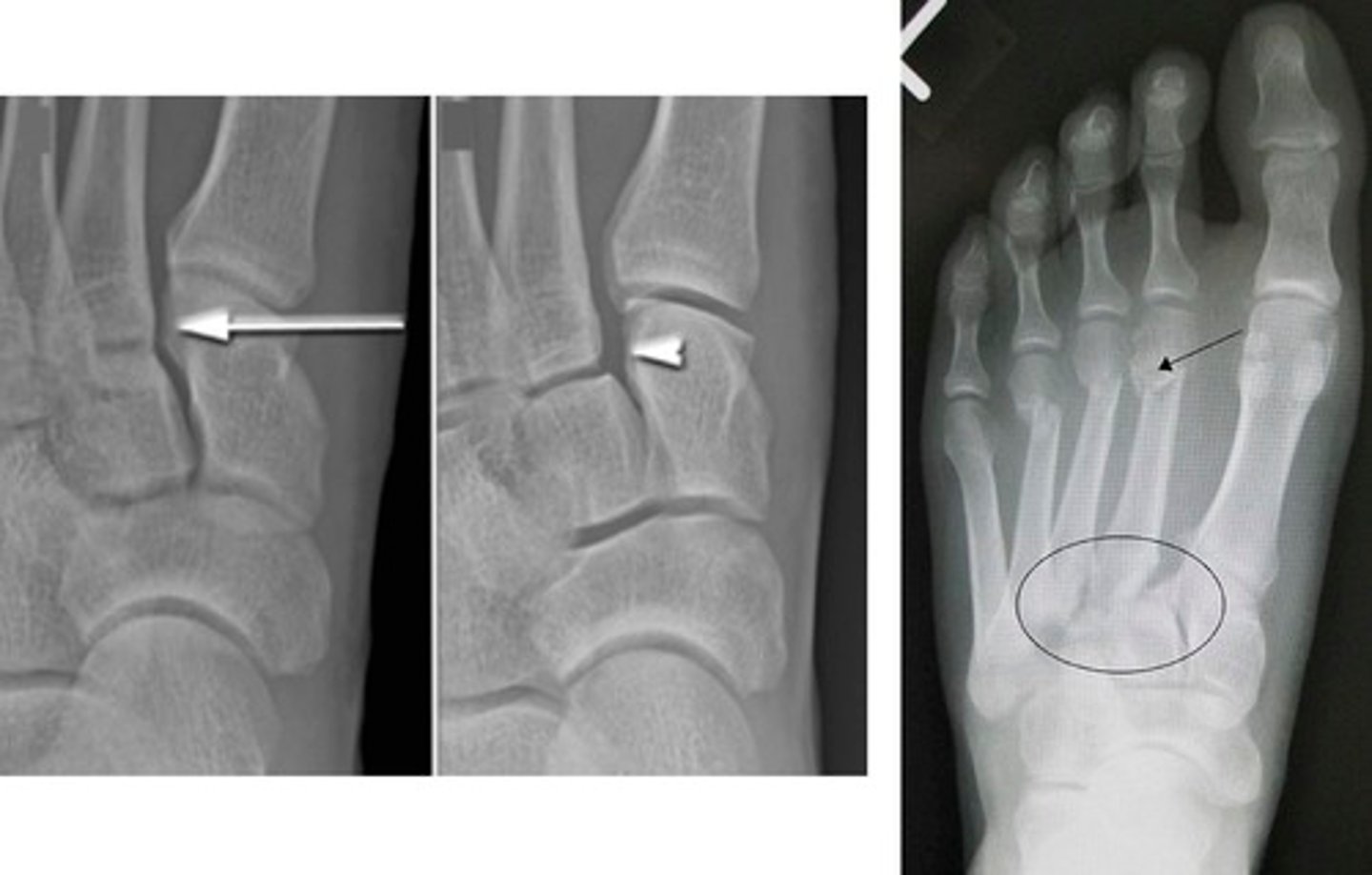
which dx is caused by a twisting injury of the midfoot, eliciting pain between the metatarsal and tarsal bones?
lisfranc injury → tarsometatarsal (TMT) fx dislocation
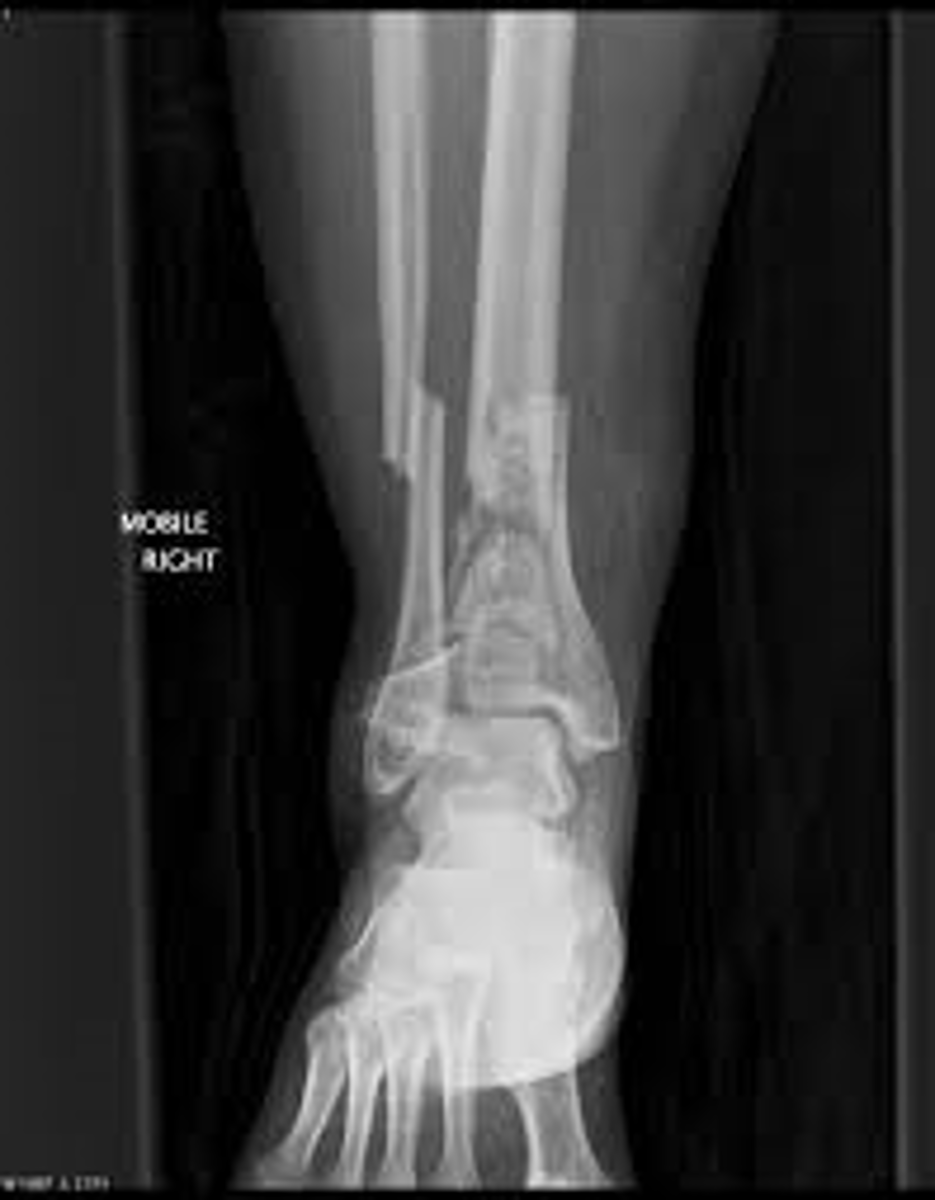
what is an oblique, comminuted fx of the distal tibia that extends through the tibiotalar articular surface?
pilon fracture → s/p trauma → 75% also have fibula fx
ortho referral!!!
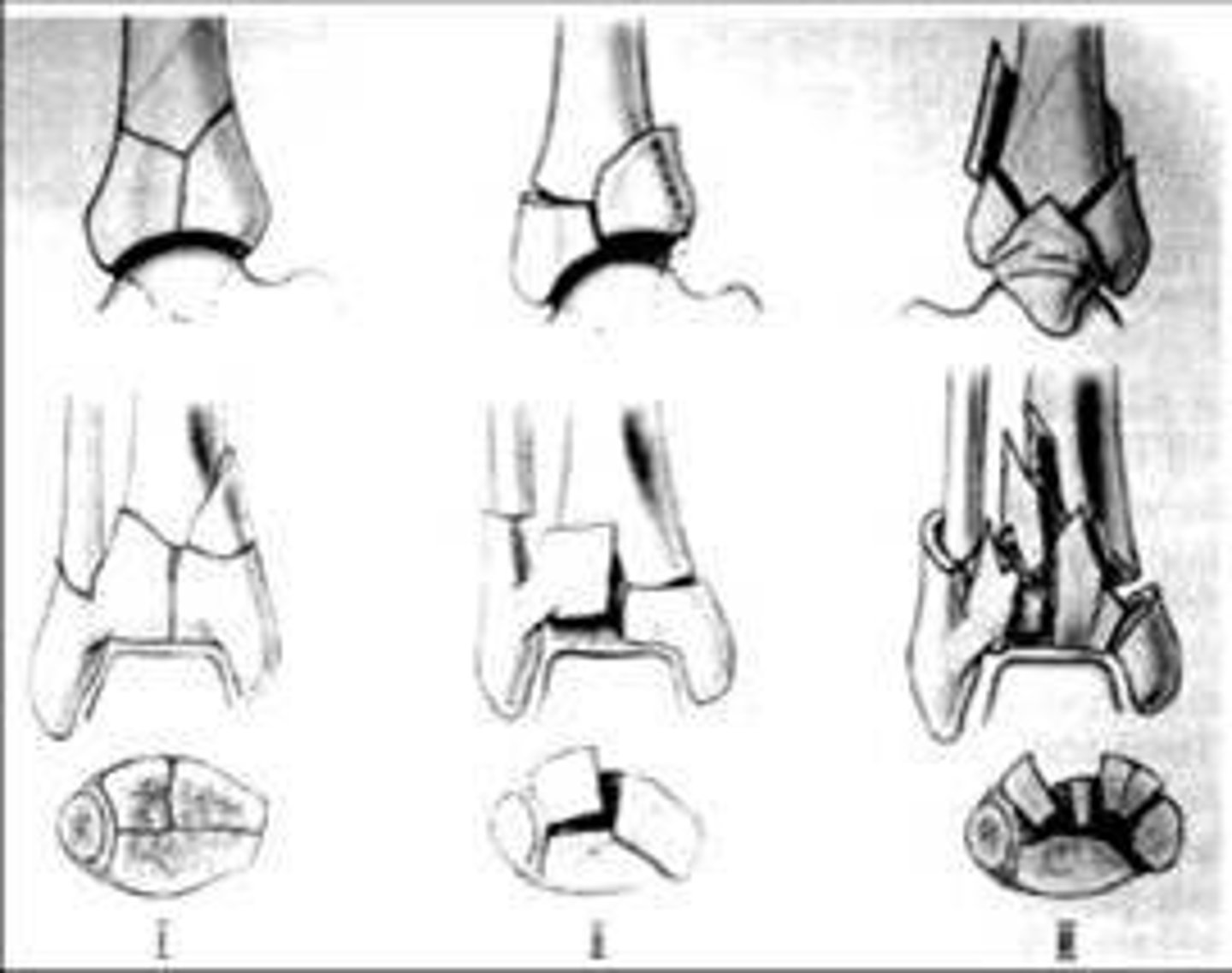
what is a complication of a pilon fracture?
arthritis
what is the cause of Jones' fracture?
trauma → inversion injury shows up as avulsion fx on XR
pain and tenderness over base of 5th metatarsal
patient complains of burning foot pain that worsens with activity. the pain is relieved upon removal of tight shoes. what test would you expect to be positive?
morton's neuroma → positive morton's test → tx with steroid injection
pain between 2nd/3rd or 3rd/4th metatarsal
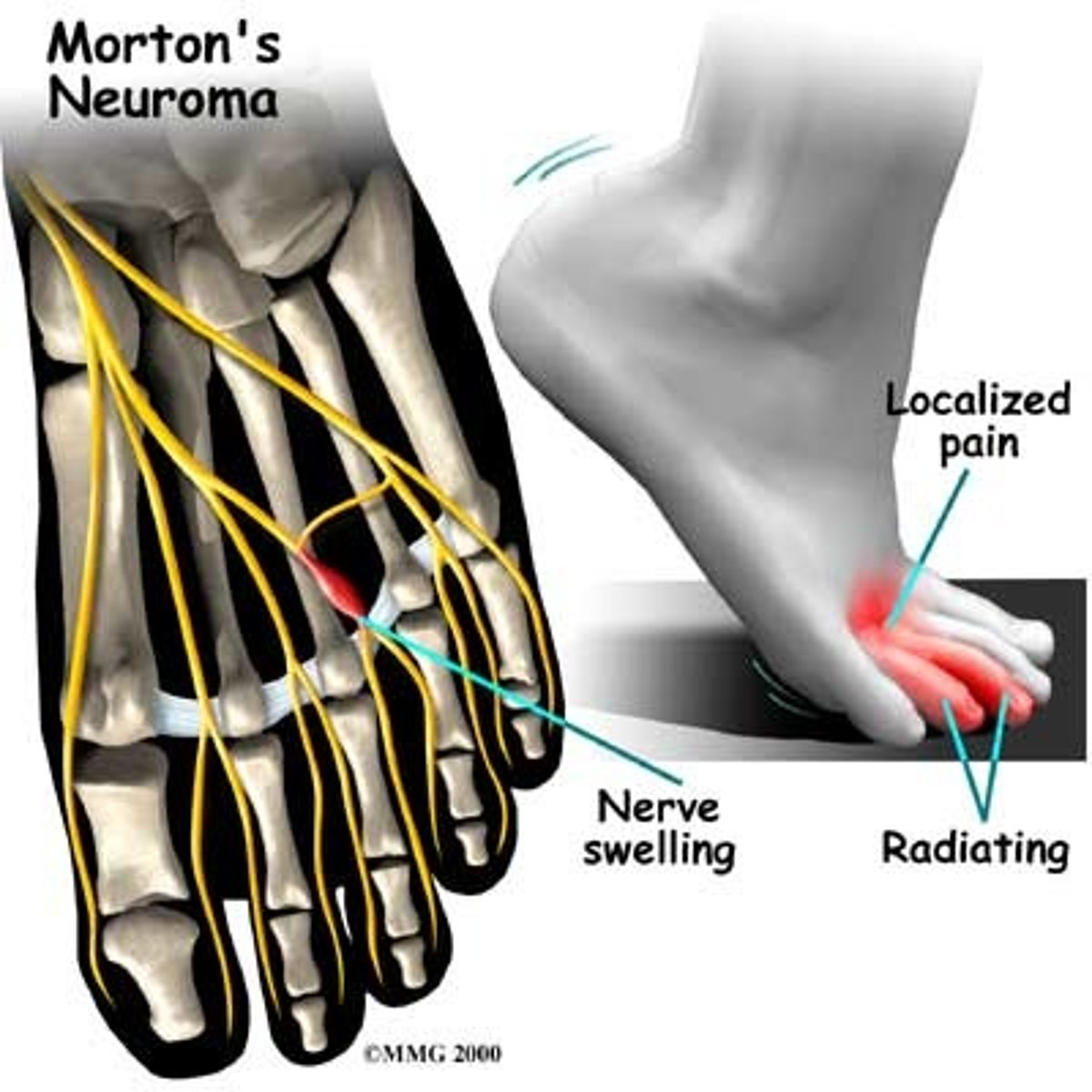
if a pt has damage to a nerve, what should you check on PE?
pulses
sensation
ROM
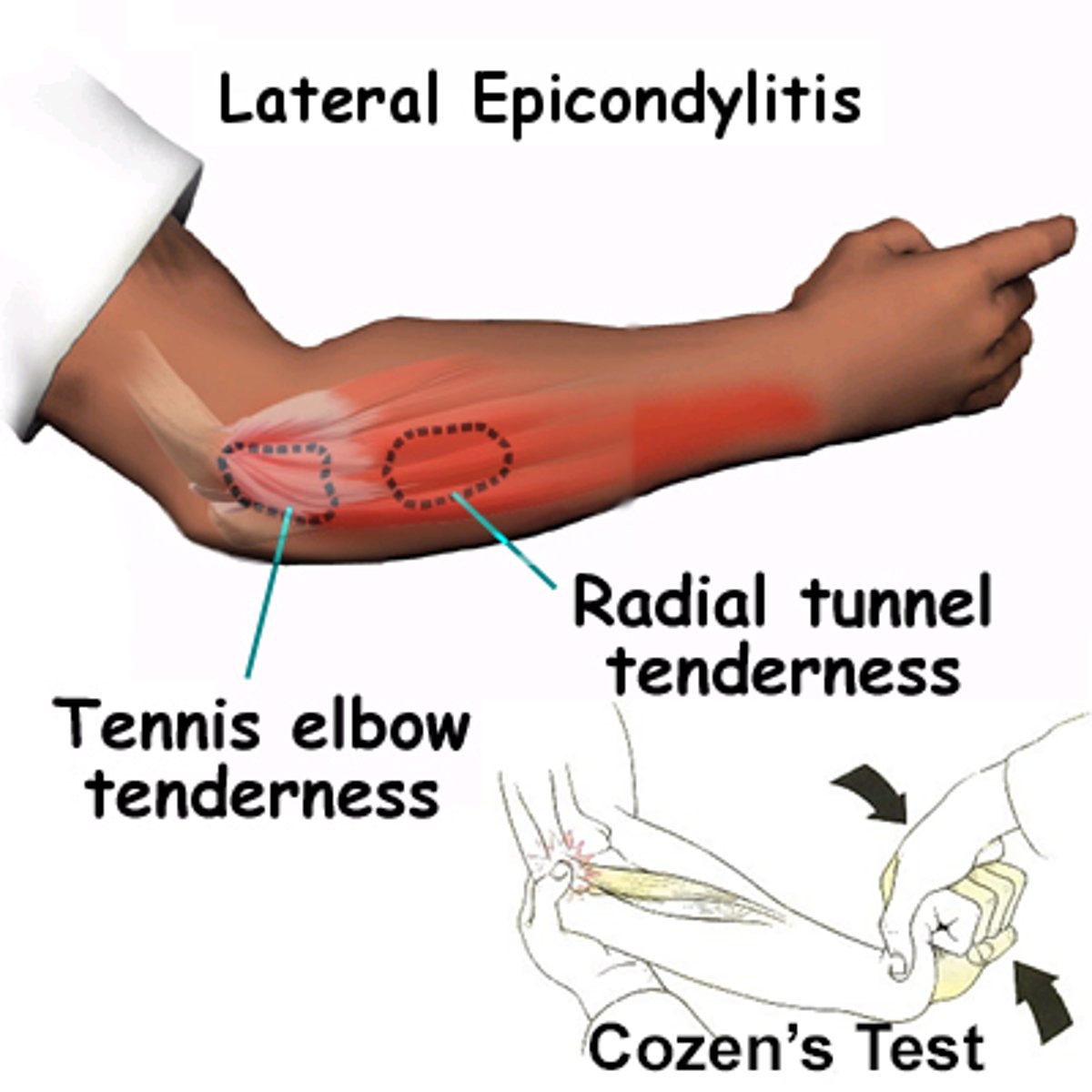
which special tests assess for lateral epicondylitis?
cozen
mill
what sign on XR indicates joint effusion?
fat pad sign
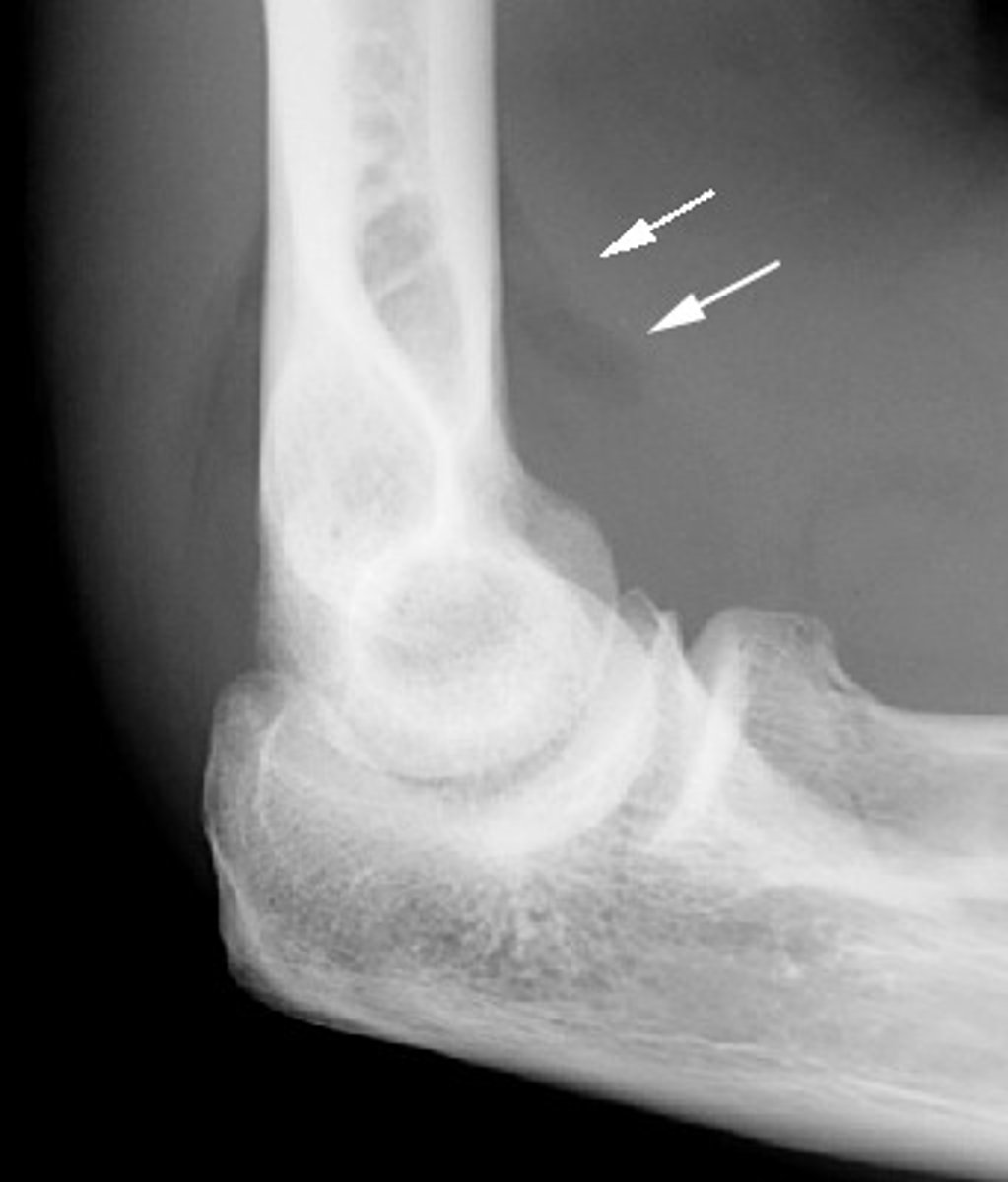
if you see fat pad/sail sign on XR, which fracture would you suspect?
occult fx or intra-articular fx
- subtle radial head fx in adults
- supracondylar fx of humerus in children
what dx is caused by annular ligament entrapment and radial head subluxation?
Nursemaid's elbow AKA pulled elbow → tx by closed reduction (feel a "pop")
not a dislocation!!!
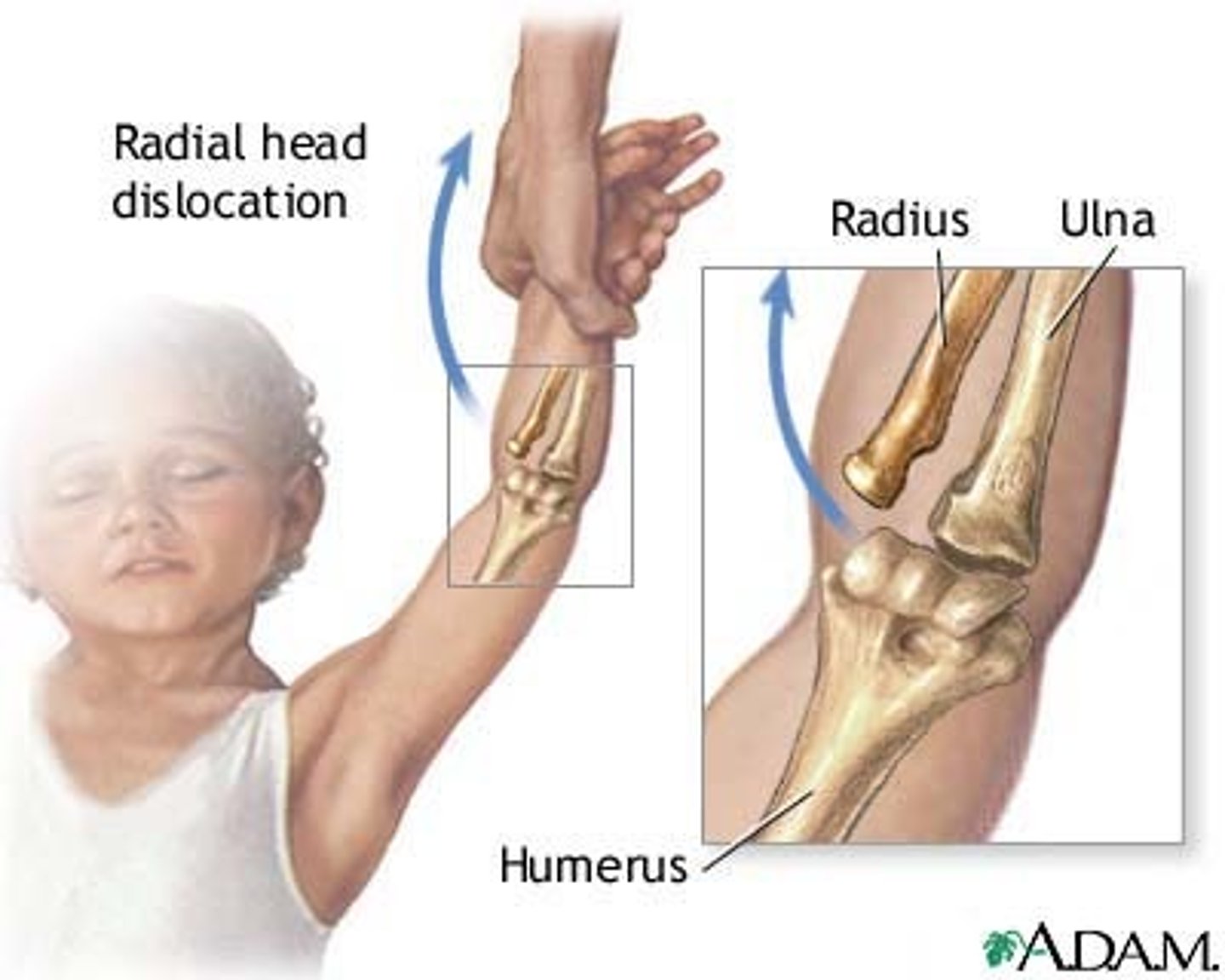
what fracture is Mc associated with elbow dislocations?
radial head/neck`
what is the terrible triad?
LCL rupture, radial head fracture, coronoid fracture
what is a dangerous complication of an elbow dislocation?
entrapment of median nerve and trauma to brachialis
what nerve is MC injured d/t distal humeral fx?
ulnar nerve
what is the MC cause of radial head/neck fracture?
FOOSH
pt reports with pain and swelling to their right elbow and numbness in their 4th and 5th right fingers s/p FOOSH. their pain is decreased with elbow flexion. what is the dx?
olecranon fracture → ulnar nerve compression causes the 4/5th finger numbness
must check pulses and cap refill!!
is a displaced or nondisplaced olecranon fx more common?
displaced → surgery treatment
splint the non-displaced
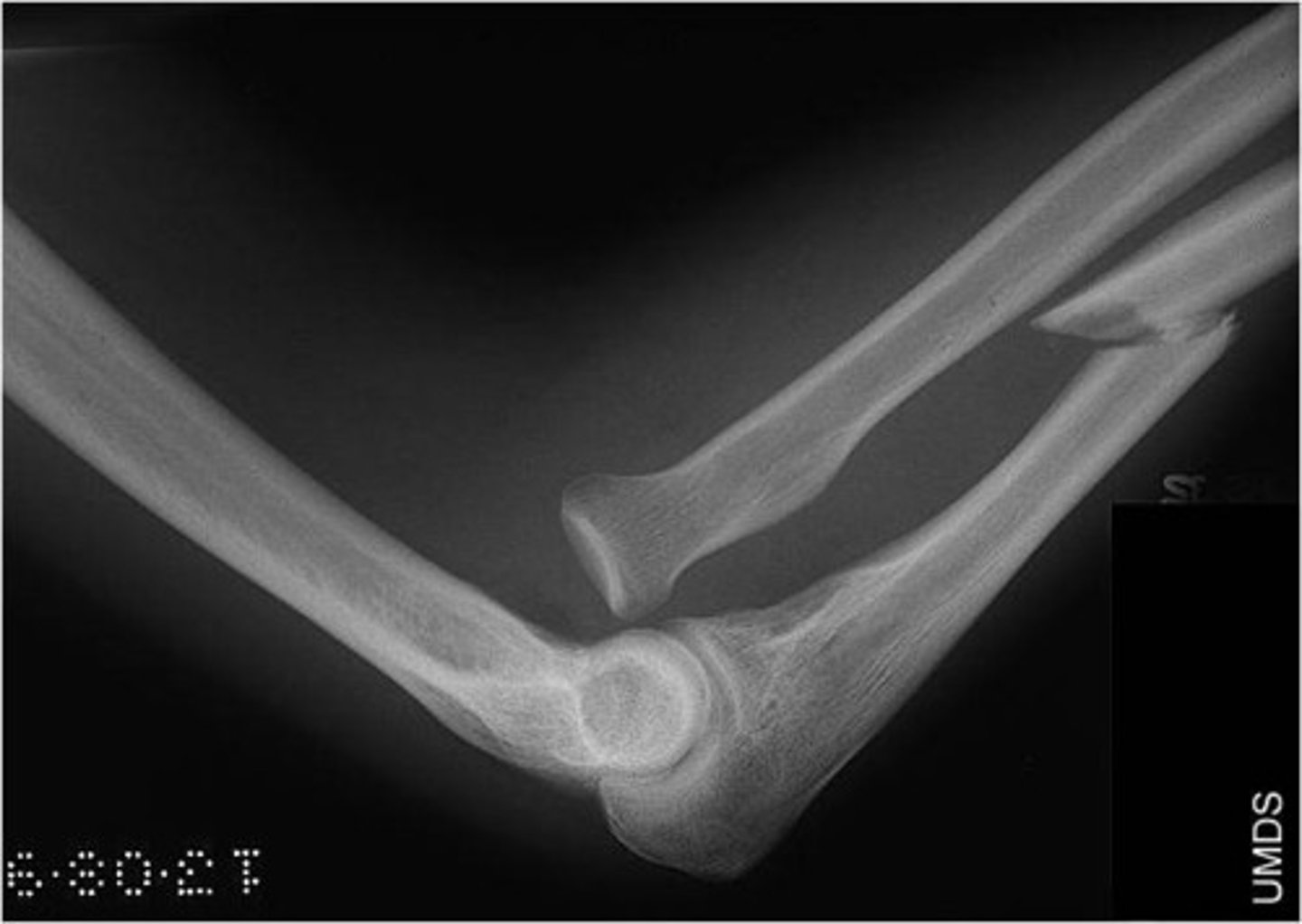
what is dislocation of the proximal radioulnar joint in association with forearm fracture?
monteggia fracture → fx to proximal 1/3 of ulna and radial head dislocation
MOI = FOOSH on hyperpronated forearm or blunt trauma
what is a radial shaft fracture with dislocation of distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ)?
galeazzi fracture
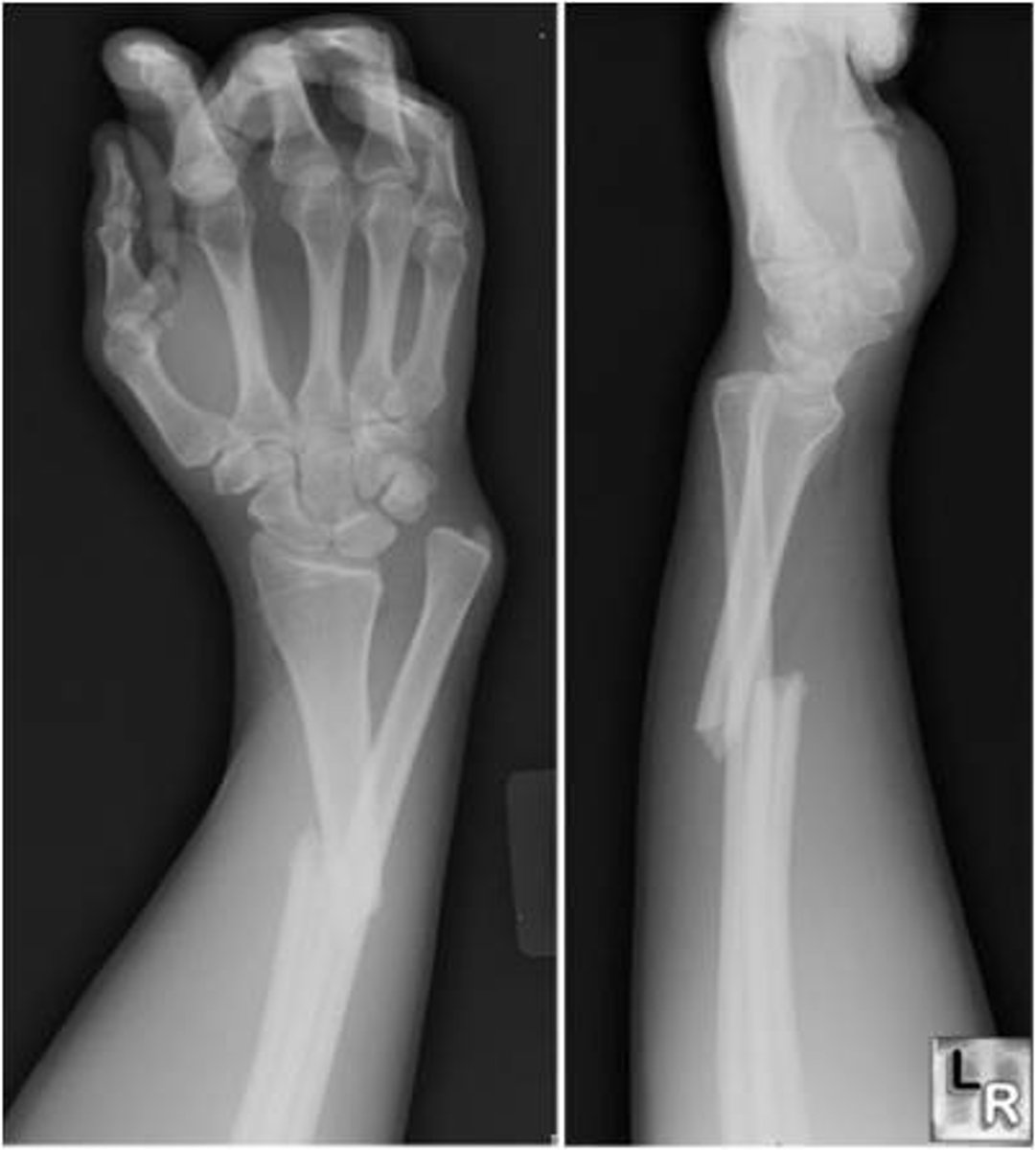
what is the MOI for a galeazzi fracture?
fall that causes an axial load to be placed on a hyperpronated forearm
which ligament connects lateral malleolus with the talus anteriorly
Anterior TALOfibular ligament (ATFL)
which dx causes pain over the ECRB muscle at lateral epicondyle of the humerus?
lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow)
38 year old female presents with burning pain along her lateral elbow when working on her computer. the pain resolves when she is not working. what is the most likely dx?
lateral epicondylitis → caused by repeated extension
what is the most important treatment for lateral epicondylitis?
eliminating or modifying activities
when does pain occur with medial epicondylitis?
flexor/pronator movement → distal to medial epicondyle
what is the drug of choice for treatment of lateral/medial epicondylitis?
NSAIDs
which dx is caused by muscular compression of the median nerve?
pronator syndrome → reproduction of pain to direct pressure over the proximal pronator teres
how does cubital tunnel present? what is the cause?
paresthesia of 4th-5th digits →caused by ulnar nerve compression
would have positive tinel's
which fracture caused by FOOSH is a distal radius fx with dorsal angulation?
colles fracture → extension fracture
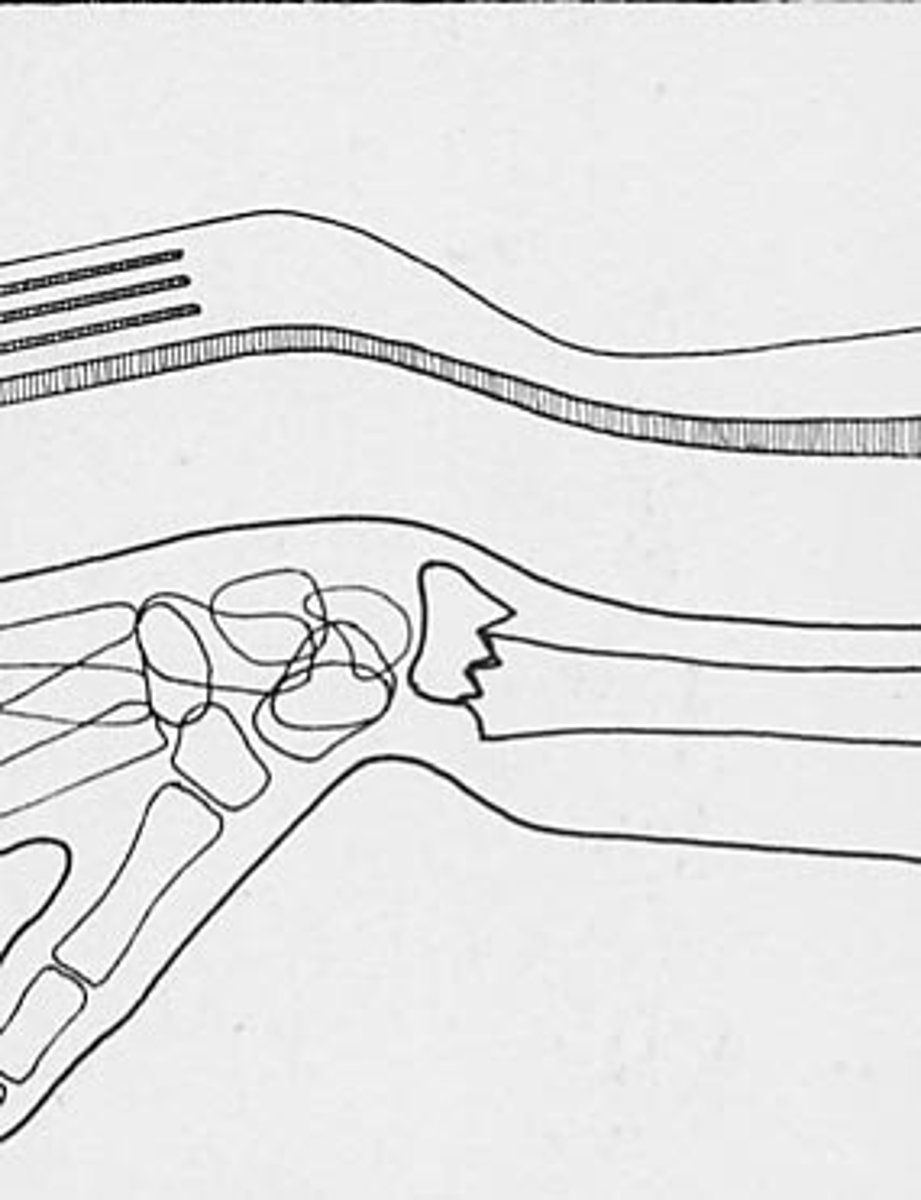
which fracture caused by FOOSH is a distal radius fracture with volar angulation?
smith fracture → flexion fracture
which dx is caused by inflammation of the sheath surrounding the ABL and EPV tendons in the wrist? which test would you expect to be positive?
DeQuervain's tenosynovitis →positive finklestein's
what are the risk factors for DeQuervain's?
middle-aged woman
repetitive use
43 year old female presents with pain and swelling over the radial aspect of the wrist. how would you treat?
DeQuervain's → thumb spica, NSAIDs, RICE, steroids are last resort
what is the gold standard for confirmation of carpal tunnel syndrome?
EMG/NCV
pt presents with complaints of decreased grip strength in their right hand along with paresthesias in their long and index fingers. what is the treatment of choice?
carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) →night time brace (volar splint in neutral position)
in what case would a patient with carpal tunnel require carpal tunnel release surgery?
if a pt has sensory loss, weakness, atrophy, or intolerable sx despite conservative measures
what are the risk factors for CTS?
pregnancy
thyroid disorders
DM
repetitive hand work
which dx presents as hypothenar atrophy and weakness?
ulnar tunnel syndrome
what is a complication of a scaphoid fx?
high incidence of nonunion and avasc. necrosis
a 23 year old male presents with tenderness on his anatomical snuff box following FOOSH. what is the dx?
scaphoid fx → most commonly fractured carpal
scaphoid view XR is most important view
what is a boxer's fracture?
fracture of the distal 5th metacarpal → caused by punching something
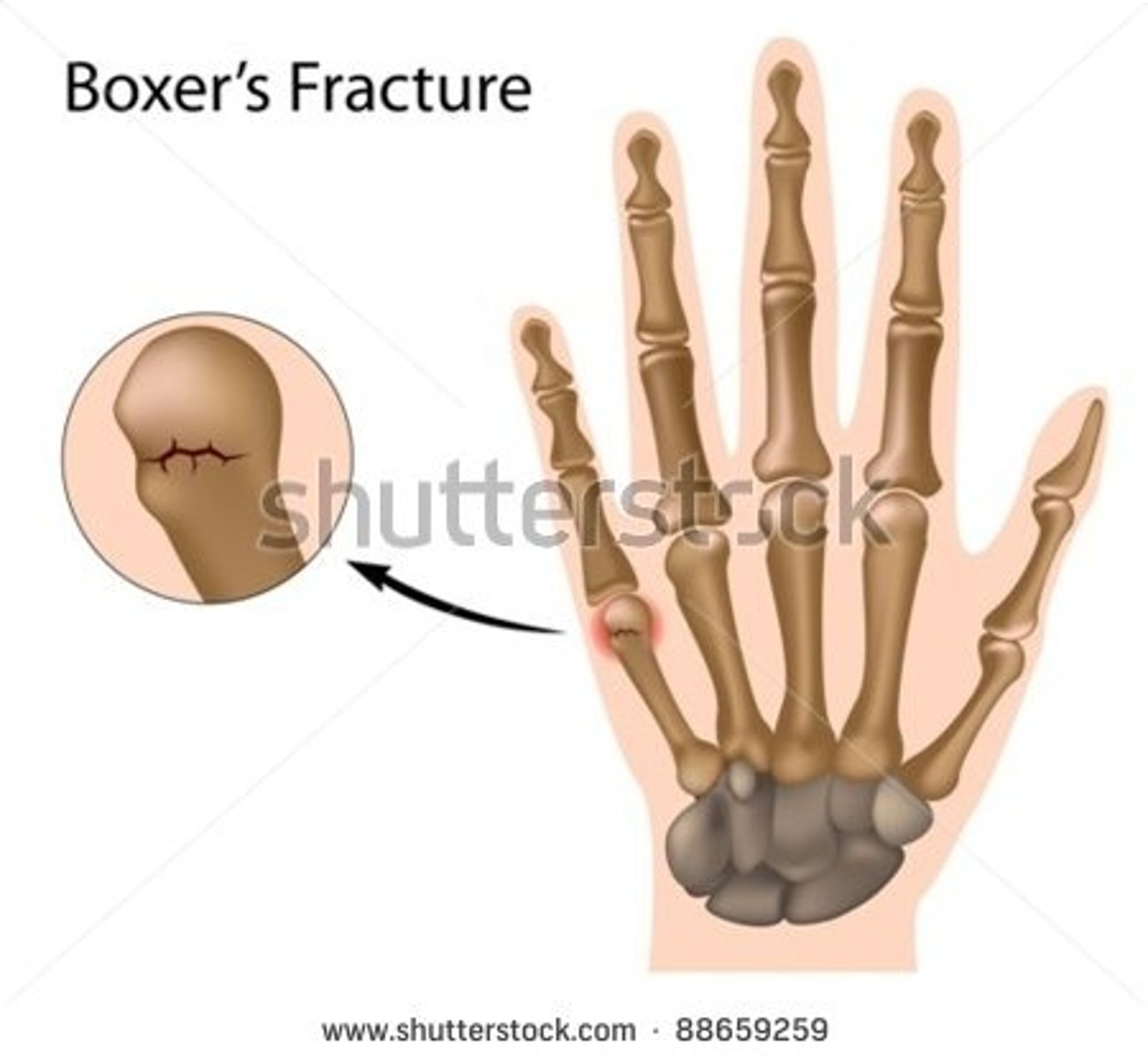
what is the treatment for a boxer's fracture?
ulnar gutter splint
if there is angulation of the pinky on PE → surgery
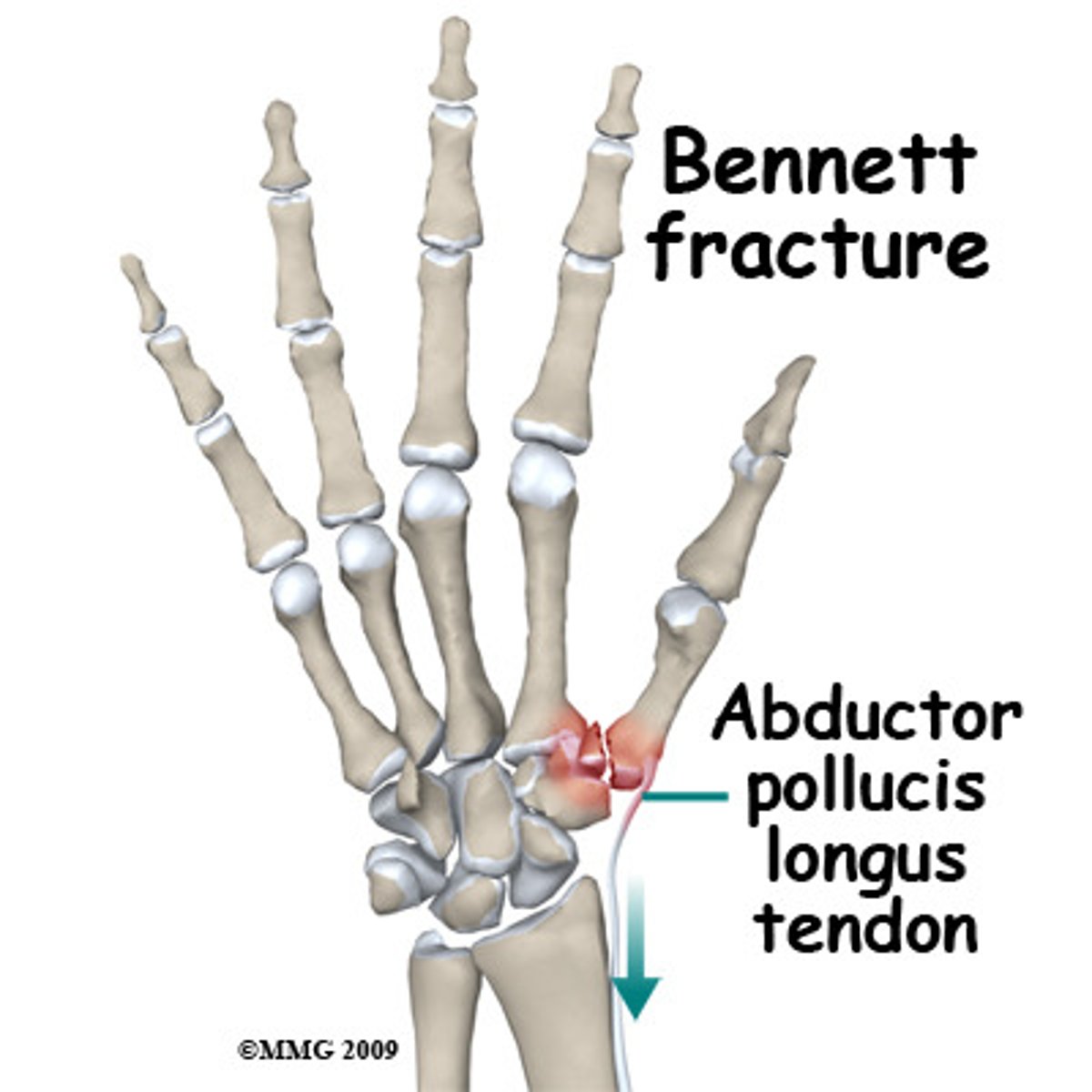
what is fracture of the base of the 1st metacarpal?
bennett's fracture → causes swelling and pain at the thumb base (CMC)
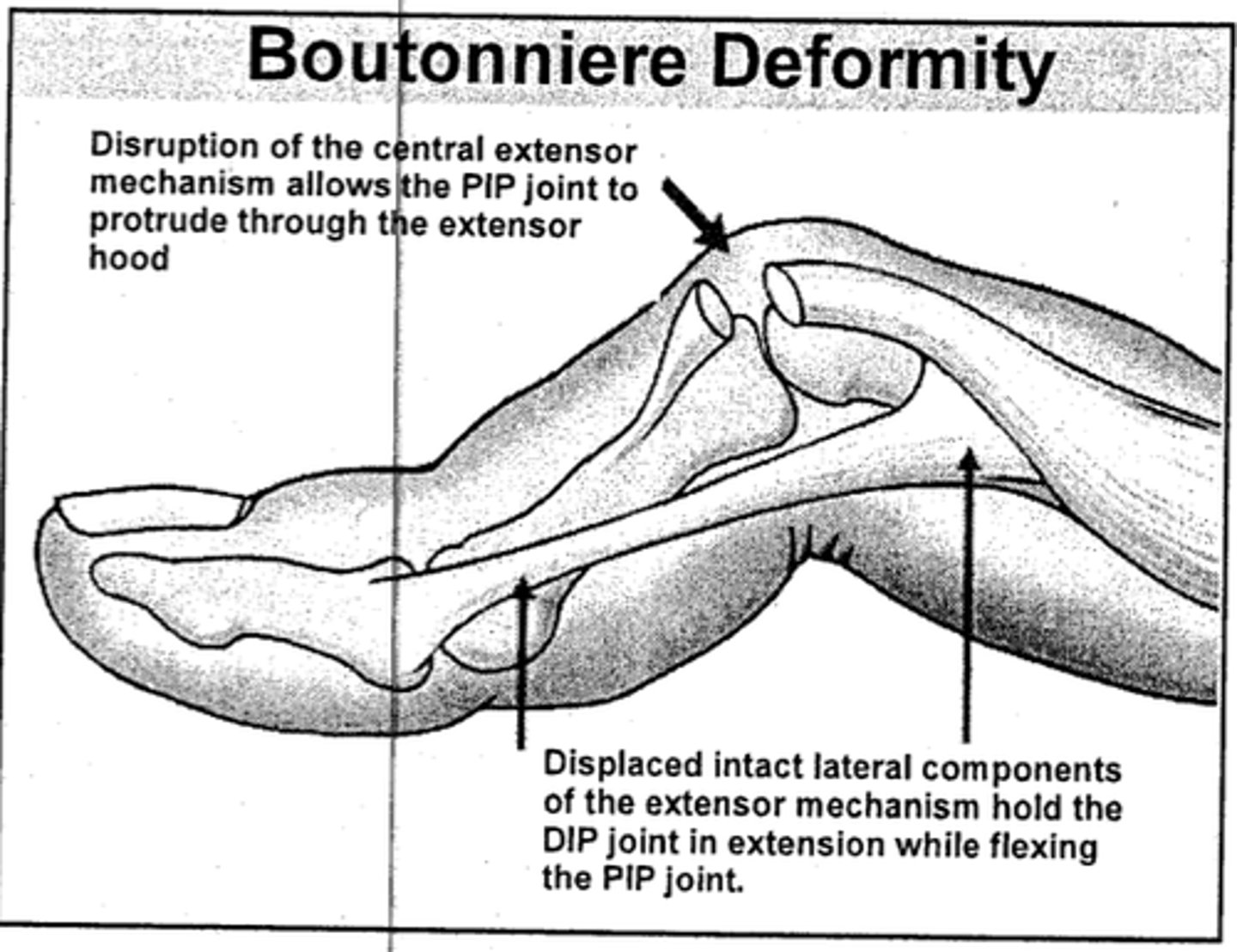
which deformity involves a flexed PIP and extended DIP?
boutonniere deformity →central extensor ruptures at insertion to middle phalanx
tx with PIP splint in extension