EXAM 4: Chapter 11 Study Guide
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
IN PROGRESS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is the difference between the Out of Africa model versus the multi-regional hypothesis?
Both:
Human origins from Africa
200,000 years ago
Out of Africa (Eve Hypothesis):
H. erectus is from Africa → rise to H. heidelbergensis → H. sapiens
Authors: Chris Stinger (NIM) and Peter Andrews (UCL)
Global Dispersal/Regional Continuity Model
Human origins from Africa, AS WELL AS Europe and Asia
H. erectus dispersed and thrived globally
Authors: Milford Wolfpoff (MILF) et all.
Who is the Old man of Shanidar? What is his genus and species?
Shanidar, Iraq (Western Asia)
45,000 years old
Old male (40s)
Heavy wear on teeth
Large brain
Eye injury, arm amputation, foot with arthritis
Bulging bones = sign of arthritis
purposefully laid down in a flexed position
H. neanderthalensis
What is Homo heidelbergensis?
Archaic relatives of homo sapiens
Evolved from them
Large face with large browridge = sign of living through the cold (glaciation)
large, heavily worn out teeth = tools
~700 kya - 200 kya
1st heidelbergensis fossil = Mauer, Germany
Early = Acheulean
Late = Mousterian
What site did we get the sample to sequence the entire Neandertal genome?
Croatian sites
Krapina Rock Shelter, Croatia
Who studied the La-Chapelle-Aux Saints specimen? What was its genus and species?
M. Boule
Homo neanderthalensis
Became the caricature for neanderthalensis
Arthritic, cold adapted, elderly male
Arthritic = adapted to the cold
NO FUCKING CHIN
Very large nose = cold adaptation
Humidifier
Infraorbital foramen: large holes in their nose for more blood flow
Intelligent
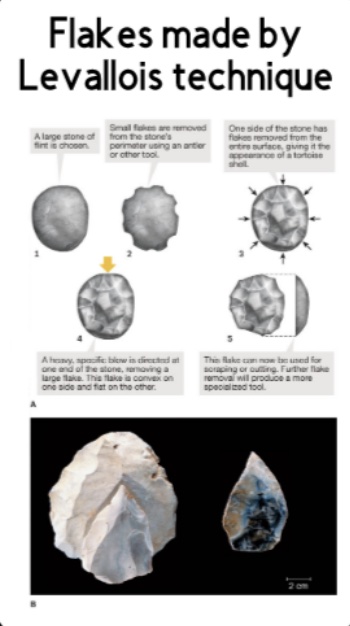
What is the Levallois technique?
~300,000 years ago
Used by Neanderthals and LATER Heidelbergensis
Stone napping technique
Levallois-Perret suburb of Paris, France
“requires removing all edges of the cortex, or outside surface of the raw material, in a circle before removing the lid. The flakes, which will eventually be turned into the individual tools, can then be removed from the core” (Textbook)
PART OF MOUSTERIAN COMPLEX
TURTLE SHAPEDD
Did Neandertals talk? How and with what evidence from the fossil record?
Yes
FOXP2 gene harvested from Croatian cave
gene that lets us talk was found in them too
By Svante Paabo
Where can we find Cro-Magnon?
France
Known for their angular eye sockets/orbits
Homo sapien
Cro-magnon = “large cliffs”
Who is Kennewick man? What is its genus and species?
The first american; homo sapien
Kennewick River, Washington (1996)
Mental eminence (chins) ← only homo sapiens have pointy chins
Was shot by an an atlatl (spear thrower) /arrow? on pelvis
Got kicked in the ribs
Robust bones
Lifestyle similar to coastal migrants
What is Homo floresiensis? What is its nickname/common name? Where can we find it?
Nickname = “hobbits”
Island dwarfism: when large animals move away to smaller environments/islands and they get smaller
Island of Flores, Indonesia; 100-16 kya
What tools can you find in the Upper Paleolithic? What is an atlatl?
Elongated forms = BLADES
Made them with objects other than stone
40-10kya
upper stone age
Solutrean (knife-like blades)
Magdalenian (atlatl = spear thrower)
Where are the Lascaux and Altamira caves? Why are they unique?
Altamira Cave, Spain
Discovred in 1880
Know it’s from stone age because of Solutrean and Magdalean lithics found in cave
Chacoal, ochre, and hematite -> used to create the art
Date: 20,000-15,000 ya
Lascaux Cave, France
HULL OF THE BULLS!!!!! ART HISTORY YAYY
Discovered in 1940
A dog named Robot ran into the cave the owner ran after him
Who are the Denisovans?
Closely related to Neanderthals than humans
Diverged from 700 kya
Migrated to Melanesia (Oceania) and China
Separate species from sapiens and neanderthals
Found by Svante Pääblo
What is the cranial capacity of Neandertals in comparison to Homo sapiens?
They had larger cranial capacity but idk the number ask about thisss
Which institute sequenced the entire Neandertal genome?
Max Planck Institution
How are Neandertals adapted for the cold (understand Bergmann and Allen’s rules)? Nasal aperture, large infraorbital foramina
Bergman’s Rule: Body shape!
Neandertal = stocky; why?
Cold adapted animals = large
less surface area relative to body size = less heat loss
Allen’s Rule: Limbs!
Neanderthal = short; why?
Cold-adapted animals = have short limbs
= reduce surface area = less heat escapes
Aka shorter you are = less heat lost
To reduce surface area which means less heat lost
EX: Inuit and Neanderthal bodies = similar -> live in cold areas
Nasal apertures:
Large; acted as a humidifier
Large infraorbital foramina (blood flow to the face)
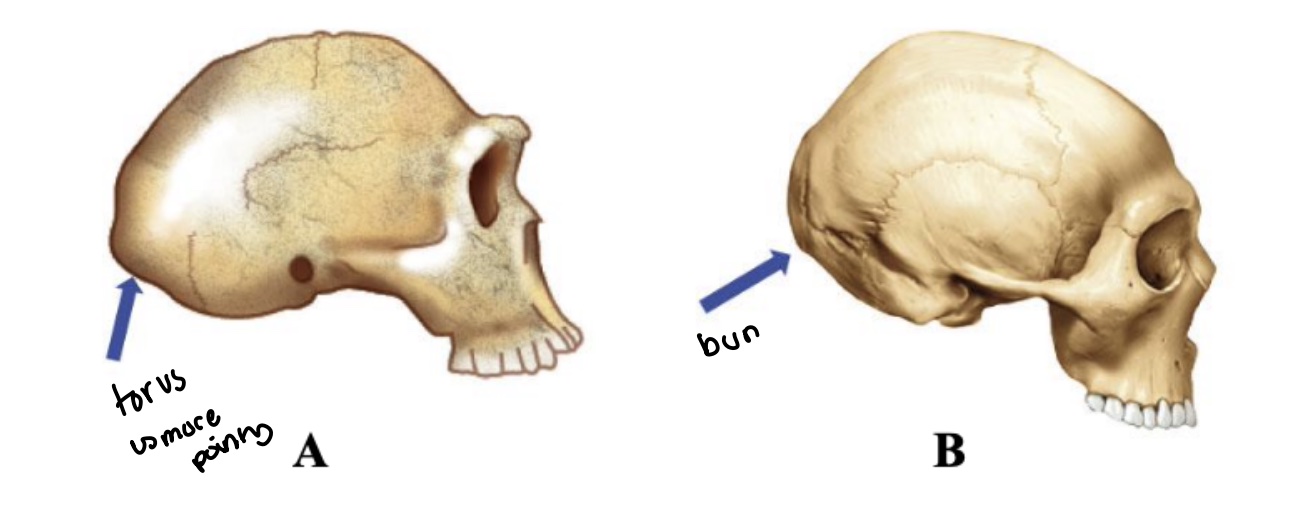
Occipital bun
FOUND ONLY IN NEANDERTHALS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ONLY THEM
prominent bulge or projection of the occipital bone at the back of the skull (wiki)
Upper paleolithic
the early phase of the Stone Age, lasting about 2.5 million years, when primitive stone implements were used
Clovis points
Arrowheads from paleoindians