inorganic - acids, alkalis, titrations
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
acid colour | basic/alkali colour | |
|---|---|---|
litmus | ||
phenolphthalein | ||
methyl orange |

why is litmus not good for titrations
colour change is not sharp (goes through a purple transition colour) in neutral solutions making it
difficult to determine an endpoint
ph scale acidic → alkali
universal indicator colorus
weakly/strongly acidic/alkaline sections
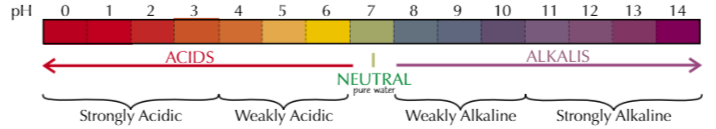
what kind of indicator is needed for titration
sharp colour change
when acids are added to water, they form ______ charged _______ ions (__). This presence makes a solution ______
when acids are added to water, they form positively charged hydrogen ions (H+). This presence makes a solution acidic
when alkalis are added to water, they form ______ charged _______ ions (__). This presence makes a solution ______
When alkalis are added to water, they form negative hydroxide ions (OH–)
The presence of the OH– ions is what makes the aqueous solution an alkali
acids are p_____ ______
proton donors
alkalis are p______ _______
proton acceptors
what is a neutralization reaction
what reacts with what to produce what
A neutralisation reaction occurs when an acid reacts with an alkali
When these substances react together in a neutralisation reaction, the H+ ions react with the OH– ions to produce water
neutralisation reaction hcl and naoh
- write out individual reactions taking place
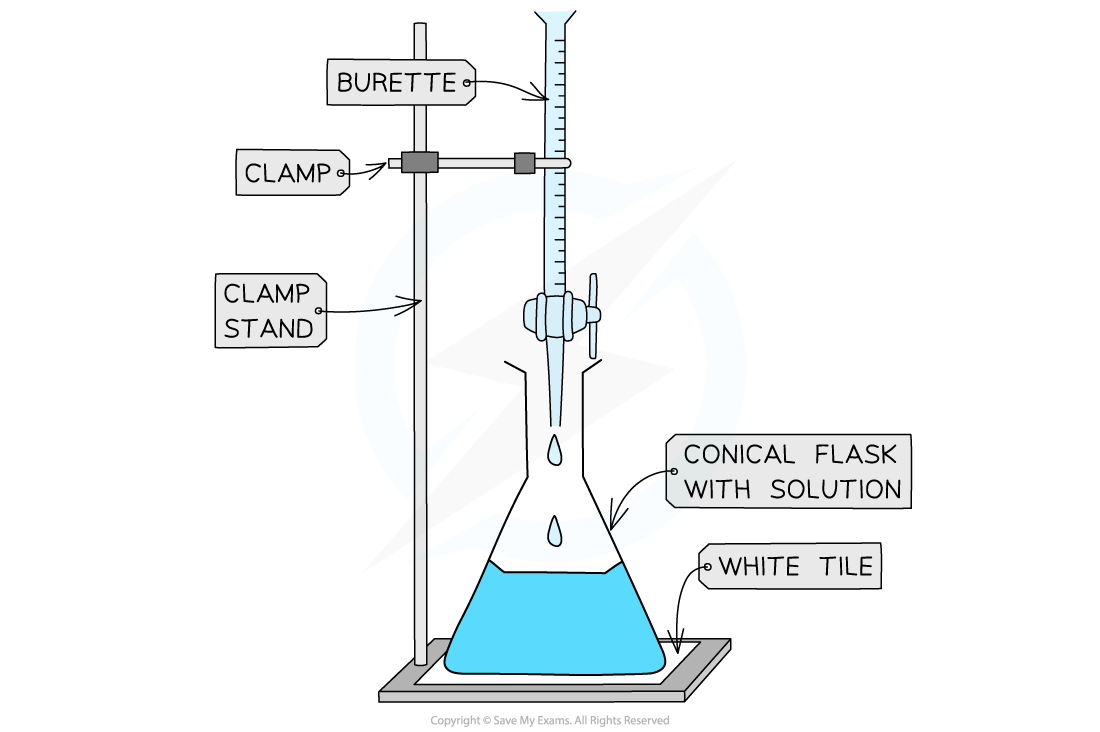
titration equipment labelled
6 labels
+a pipette
acid + metal oxide →
acid + metal oxide → salt + water
acid + metal hydroxide →
acid + metal hydroxide → salt + water
acid + ammonia →
acid + ammonia → ammonium salt
titration steps
use pipette and pipette filler to add (25cm3) of ALKALI to a conical flask, with some drops of sharp-change indicator (e.g. phenolpthalein)
fill burette with acid
place conical flask on white tile so tip of burette is inside with flask
use burette to add acid to alkali a little at a time, swirling the conical flask. add the acid drop-wise near the end-point.
indicator changes colour when all alkali has been neutralised (e.g. phenolphtalein turns colourless)
record volume of acid - eye level with the meniscus, repeat multiple times
what is a rough titration
to estimate rough point at which neutralisation occurs
to reduce ______ don’t add ______ at the start after having done the titration a couple times before
to reduce contamination don’t add indicator at the start
the burette must be ____ to measure the volume of acid added
the burette must be GRADUATED to measure the volume of acid added