xylem part 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What physical properties does the shape of water molecules give
Excellent solvent
High specific heat capacity and latent heat of vaporization
Surface tension - adhesion and cohesion
Tensile strength
What bonds do water molecules make
H bonds and can form up to 4 with other water molecules
Water contact angle
The angle between a water droplet and surface to measure if the surface is hydrophilic (less than 90) or hydrophobic (greater than 90)
Diffusion
Spontaneous movement of solutes from regions of higher to lower concentration
Spontaneous processes occur towards
More entropy (disorder)/ less free energy
The time required for diffusion across a certain distance is proportional to
The square of the distance
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable barrier
What is osmosis limited by
The volume of the cell wall. The cell wall resists deformation and creates an inward force increasing hydrostatic pressure within cell but not volume.
what does free energy drive into the plant
Biochemical rxns, solute concentration, and long distance transport
Free energy
The potential for performing work
G = force * distance
Chemical potential
Relative quantitative expression of free energy associated with a substance
Water potential
Chemical potential of water divided by the volume of 1 mol of water.
Free energy of water per unit volume
Unit for water potential
Pascal (Pa)
How does water move
From high to low water potential
What factors influence water potential
Concentration, pressure, gravity
Does gravity play a part in water potential on the cellular level
No
Water potential formula
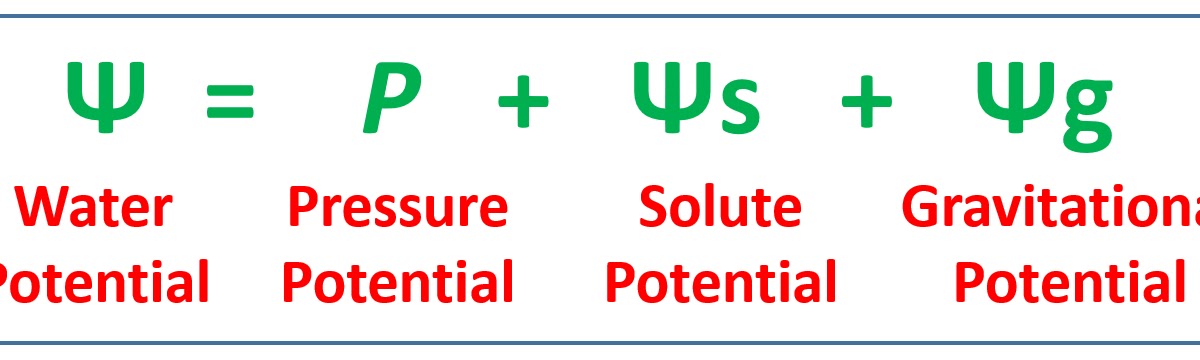
Solute potential
Reduce free energy of water by diluting the water. Lowers water potential
What is solute potential independent of
The nature of the solute
Solute potential formula
S = -RTc
The more solute the more -ve solute potential
What do solutes lower
Water potential in the -ve range
Pressure potential
Positive hydrostatic pressure raises water potential – turgor
Negative hydrostatic pressure lowers water potential – tension
How is hydrostatic pressure measured?
As the deviation from standard atmospheric pressure
When does pressure potential equal zero for water
Add atmospheric pressure
Gravity potential
= pgh
pgh has a constant value of
0.01 MPa m-1
Gravity potential in cells
Typically omitted
What part of the tree has more water potential?
The roots because water moves from high to low water potential
When does wilting occur?
When turgor pressure reaches zero
For water to move up the tree, which part should have a lower water potential
The leaves
What do rigid cell walls allow
Plant cells to accommodate changes in water potential with large changes and pressure potential
Aquaporins
Water specific channels to facilitate water movement across membranes. Can be reversibly gated based on cellular stimuli