BIOL 307 Human Physiology Chapter 9,10,11
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Ventricles
hollow tubes that connect within the brain. within the tubes fluid can flow and act as a cushion
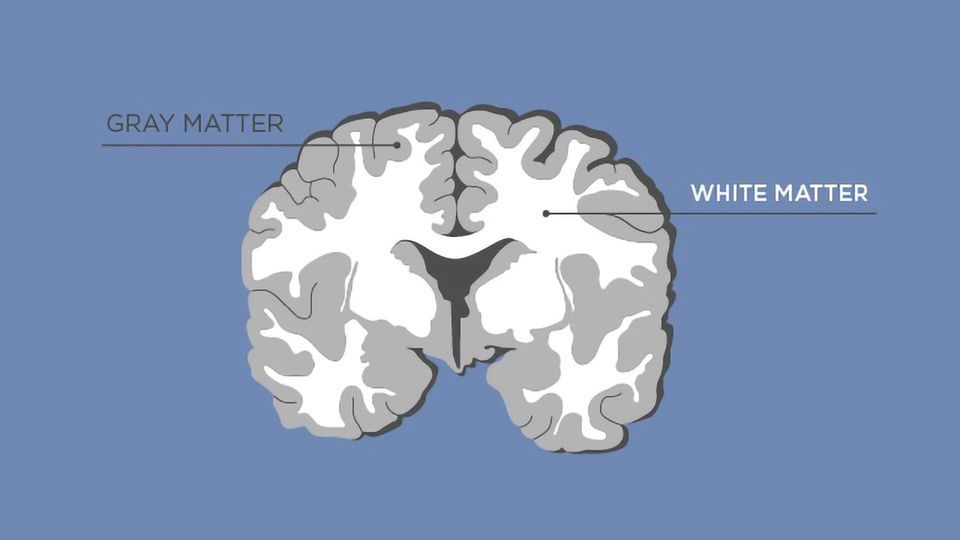
What is the difference between white matter and gray matter? Define the two
White Matter is mostly myelinated axons and contain very few neural cell bodies. While grey matter consist of unmyelinated nerve cell bodies, dendrites, and axons
Tract
Bundles of axons that connect different regions of the central nervous system
Meninges
Three layers of membrane that lie between the bones and tissues of the central nervous system
Cerebrospinal Fluid
A salty solution that is continuously secreted by the choroid plexus
Choroid Plexus
A specialized region on the walls of the ventricles
Spinal Nerve
Mixed nerves that interact directly with the spinal chord
What is the difference between the ascending tract and descending tract? Define them
The ascending tract takes sensory information to the brain.
The ascending tract is within the dorsal and external lateral portion of the brain.
The descending tract carry mostly motor signals from the brain to the chord.
Cranial Nerve
12 pairs of peripheral nerves that originate primarily from the brain stem
Recognize that most physiological variables have a…
circadian rhythm
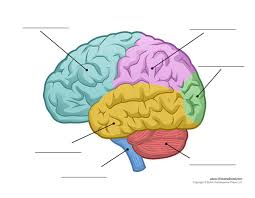
What is the blue part?
Frontal lobe
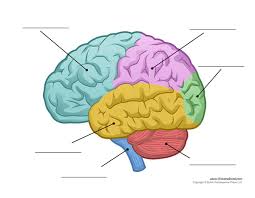
What is the pink part?
Parietal Lobe
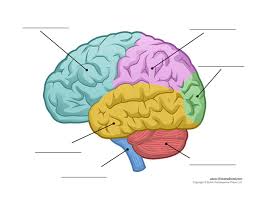
What is the green part?
Occipital Lobe
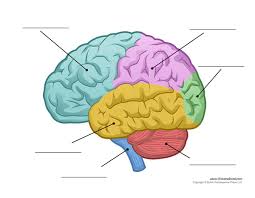
What is the yellow part?
Temporal Lobe
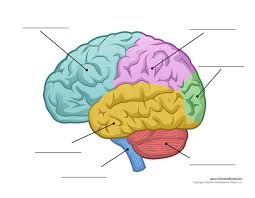
What is the blue stem?
Medulla
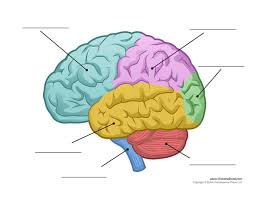
What is the red part?
Cerebellum
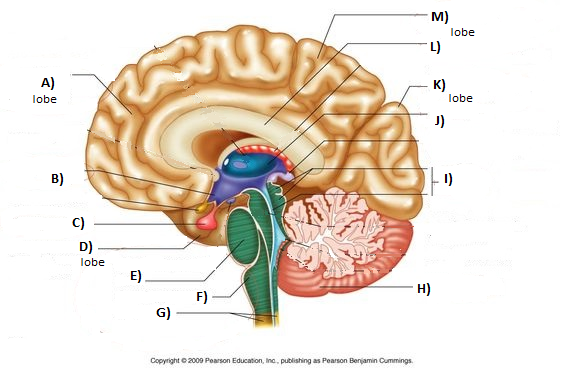
What is letter J (Blue circular organ)
Thalamus
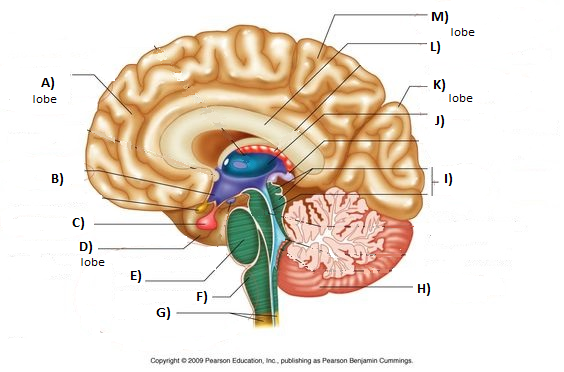
What is letter B (Purple Space)
Hypothalamus
Transduction/ Transducer
The conversion of stimulus energy into information that can be processed by the nervous system.
An example of a transducer can be a receptor/ sensor that can convert a stimulus into an intracellular signal.
Proprioception
Awareness of body position in space and the relative location of body parts
Chemoreceptor
Chemical ligands that bind to a receptor
Mechanoreceptor
Response from various forms of mechanical energy. An example can be vibrations or pressure
Thermoreceptors
Respond to temperatures
Photoreceptors
Vision to respond to light
Olfaction
Sense of smell
Gustation
Sense of taste
Pupil
Opening where light can pass ( black part)
Iris
Colored ring of pigment
Lens
Focuses light upon the retina
Cornea
Transparent disk of tissue connected to the sclera ( white part)
Retina
Layers that contain photoreceptors
Recognize that the function of all sensory receptors is transduction of…
Environmental signals/energy into an electrical signal
What is the difference between somatic senses and special senses? Give examples for each.
Somatic senses deal with senses around the body. For example: Touch, Temperature, Itch, Pain.
Special senses deal with sense detected by the head region.
For example: Taste, Sight, Equilibrium, Smell, Hearing
For a given receptor cell…
Increased stimulus intensity is always coded as increased action potential frequency no matter what the sense
What are our 5 taste senses?
Sweet, Salty, Sour, Bitter, Umami
What changes in the eye to maintain and keep focus on objects?
The eye lens will change shape to keep focus on objects. This is also known as accommodation
What is the difference between rods and cones?
Rods are responsible for night vision when objects are seen in black and white. Rods focus when light levels are low.
Cones are responsible for vision during the day when there are multiple colors. Cones focus when light levels are high.
Somatic Motor Pathway
A neuron from the central nervous system that secretes acetylcholine at a nicotine receptor on the target skeletal muscle.
Autonomic
Self governing; Automatic; Involuntary
Sympathetic Branch
Division of the autonomic nervous system that deals with fight or flight responses
Parasympathetic Branch
Division of autonomic nervous system that deals with daily activities
Ganglion
A cluster of nerve cell bodies that lie outside of the central nervous system
What are the differences between the actions of the somatic motor and the autonomic systems?
The somatic motor system includes a singular neuron that projects it’s axons towards a skeletal muscle. The somatic pathways are always excitatory
The autonomic systems always involve two neurons, with two divisions, that act on multiple organs. The autonomic systems can be either excitatory or inhibitory.
Evey autonomic circuit is a chain of
Two neurons ending at a target tissue with the two neurons synapsing at a ganglion
Many different
receptor subtypes exist for autonomic neurotransmitters allowing to target specific tissues
Somatic Motor Pathways
are single neuron, exclusively excitatory pathways
Dorsal Root
Specialized to carry incoming sensory information
Ventral Root
Carries information from the CNS to muscles and glands
Dorsal Horn
Region of spinal cord that contains sensory nuclei
Ventral Horn
Regions of spinal cord that contain efferent nuclei
What is the difference between the sensory, motor, and association areas of the brain
Sensory areas receive sensory input and translate it into perception(awareness)
Motor areas direct skeletal muscle movement
Association areas integrate information from sensory and motor information and can direct voluntary behaviors
What are the three layers of the brain or meninges
Dura Mater- Thickest part of the membrane
Arachnoid Membrane- loosely tied to the inner membrane
Pia Mater- Inner membrane that adheres to the surface of the brain
The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater is called…
the subarachnoid space where cerebrospinal fluid circulates
How does CSF provide protection to the brain?
CSF provides physical protection to the brain by reducing the weight of the brain through buoyancy. This results in the brain putting immensely less pressure on blood vessels and nerves attached to the CNS
What is the blood brain barrier
Capillary and endothelial cells held together by tight junctions. Tight junctions have low permeability resulting in only hydrophobic or small uncharged polar molecules.
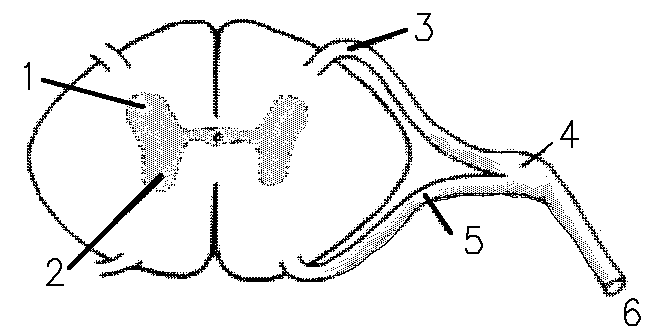
1 refers to
Dorsal Horn
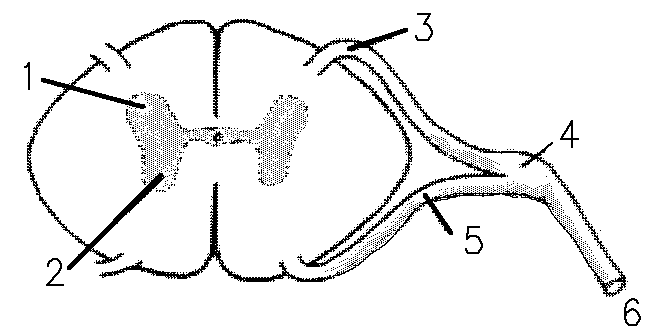
2 refers to
Ventral Horn
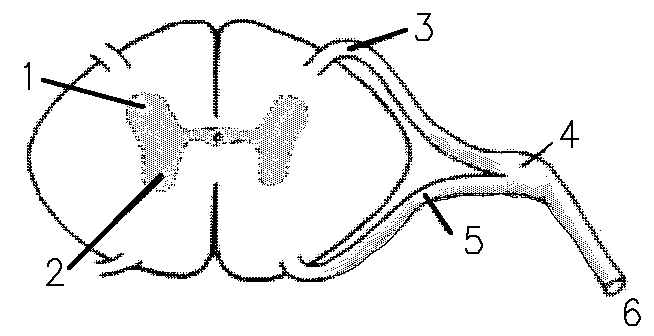
3 refers to
Dorsal Root
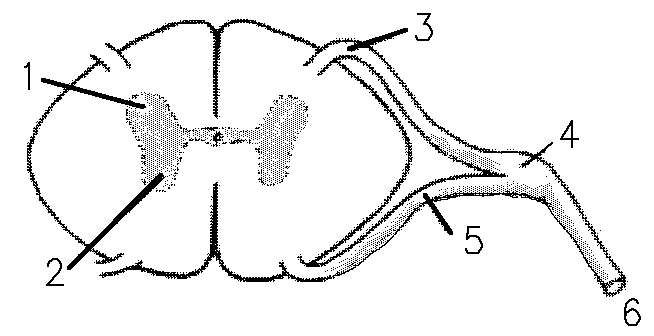
4 refers to
Dorsal Root Ganglion
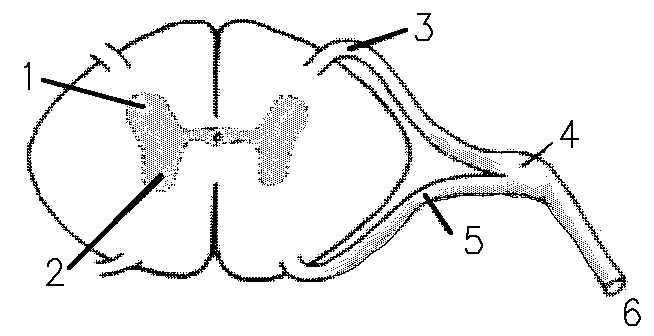
5 refers to
Ventral Root
Medulla Oblongata
Portion of the brain stem that controls involuntary functions such as breathing
Pons
Acts as a relay station for information transfer between the cerebellum and the cerebrum
Thalamus
Relays information going to and from higher brain centers
Hypothalamus
Contains centers for behavioral drive and plays a key role in body regulation
Corpus Callosum
Ensures the two hemispheres of the brain and communicating and cooperating
Basal Ganglia/nuclei
Nuclei surrounding the thalamus that help with planning movement
Primary Motor Cortex
Regions of the frontal lobe that coordinate skeletal movement
Limbic System
Serves as a link between primitive emotional responses and higher cognitive function