Carbohydrates
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Are carbohydrates polyfunctional molecules?
Yes (carbonyl and multiple alcohol groups)
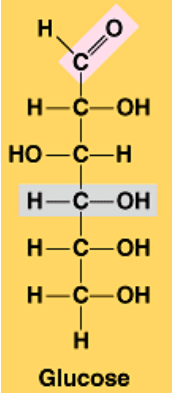
Classification of glucose
aldohexose
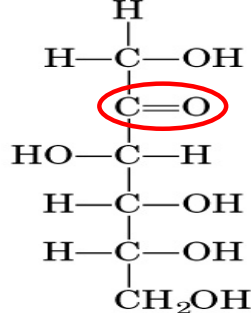
Classification of fructose
ketohexose
What kinds of monosaccharides are the most common in living cells?
pentoses and hexoses
General formula of monosaccharides
(CH2O)n
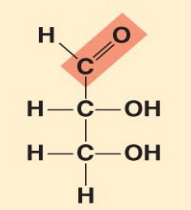
what monosaccharide is this?
Glyceraldehyde
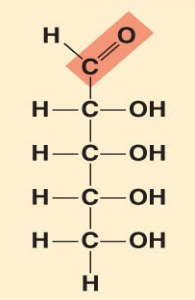
what monosaccharide is this?
Ribose
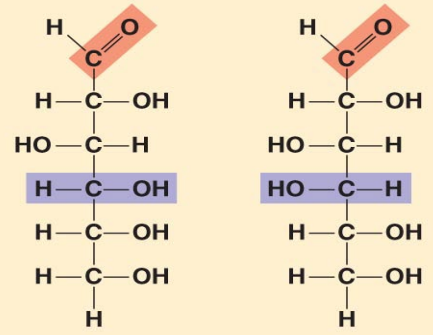
Aldohexoses
Glucose and galactose
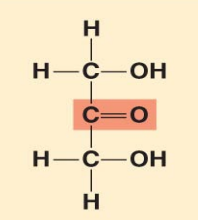
what monosaccharide is this?
Dihydroxyacetone
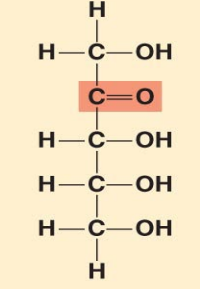
what monosaccharide is this?
Ribulose
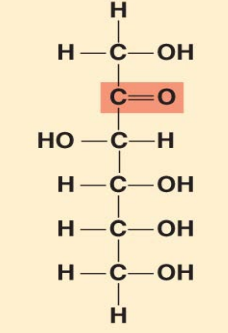
What monosaccharide is this?
fructose
Fructose facts
found in fruits, used by the food industry as a sweetening agent
Ribose facts
Component of RNA nucleotides
Glucose facts
most abundant monosaccharide in nature, used as primary fuel by living cells
Galactose facts
used to synthesize biomolecules (glycolipids, glycoproteins)
How is a disaccharide formed?
By a dehydration reaction between two monosaccharides, forming a glycosidic bond
Composition of maltose (doesn’t exist freely in nature)
2 glucose joined by a 1-4 glycosidic bond (hydrolysed by maltase)
Composition of sucrose
glucose and fructose joined by a 1-2 glycosidic bond (hydrolysed by sucrase)
Composition of lactose (found in milk)
glucose and galactose joined by a 1-4 glycosidic bond (hydrolysed by lactase)
Oligosaccharides
small polymers of 3-20 monosaccharide residues, don’t occur freely in nature
Glycolipid
Oligosaccharide covalently bonded to a lipid
Glycoprotein
Oligosaccharide covalently bonded to a protein
Kinds of covalent bonds in a glycoprotein
O-glycosidic linkage between an oligosaccharide and the O atom of serine or threonine
N-glycosidic linkage between an oligosaccharide and the N atom of asparagine
Functions of oligosaccharides
protect the cell surface from chemical and mechanical damage, cell-to-cell recognition and binding, cell lubrication, blood types
which glycoproteins enable the HIV virus to attach to T-cells?
gp120 (external) and gp41 (across the membrane)
which protein lines the inside of the HIV virus envelope?
p17
which proteins compose the HIV virus capsid?
p6 and p24
which protein is bound the RNA of the HIV virus?
p7
Which enzymes are associated with the viral genome of HIV?
RT, integrase and protease
HIV binding process
gp120 binds to CD4 receptors (on the target cell surface) and CCR5. it changes conformation exposing gp41 which inserts its hydrophobic terminus into the target cell membrane and folds on itself bringing the virus closer allowing fusion
Composition of A antigen
O Antigen + GalNac (N-Acetylgalactosamine) thanks to GalNac transferase
Composition of B antigen
O Antigen + Gal (Galactose) thanks to Gal transferase
Polysaccharides
Hundreds to thousands of monosaccharides residues linked by glycosidic bonds
Homopolysaccharides
Polysaccharides only composed by one type of monosaccharide
Heterosaccharides
Polysaccharides composed by 2 or more types of monosaccharides
Examples of storage polysaccharides
starch, glycogen
Starch
storage polysaccharide found in chloroplasts (plants), consists only of glucose monomers, hydrolysed by alpha-amylase
Amylose (starch)
20-30%, unbranched, 1000s of glucose residues, long tight helices
Amylopectin (starch)
70-80%, branching every 20-25 residues, no helix formation
Glycogen
storage polysaccharide found in vertebrates, mainly in liver and muscle cells, branching every 8-12 residues