NERVOUS SYSTEM TEST
1/229
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
230 Terms
Dendrite Description
short and branched
Receives signals from other neurons
Carries messages towards cell body
Axon Description
Long and single
Sends signals to other neurons or muscles
Carries messages away from the cell body
CNS parts
Brain and Spinal Cord
PNS parts
Cranial and Spinal Nerves
Schwann Cells
Cells in the PNS that wrap around axons to form the myelin sheath
What are the 4 types of CNS neuroglia cells
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal
Astrocytes Functions
support neurons
maintain the blood brain barrier
regulate nutrients and ions
Oligodendrocytes Functions
form the myelin sheath
insulate axons
speed up signal transmission
Microglia Function
Remove debris and pathogens by phagocytosis
Ependymal Functions
line the ventricles of the brain and spinal cord
produce and circulate CSF
Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary actions
Moves skeletal muscles
Conscious control
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary actions
Controls organs, glands, and smooth and cardiac muscles
Unconscious control
What does the Sympathetic Nervous System do for us?
Fight or Flight
What does the Parasympathetic Nervous System do for us?
Rest and Relax
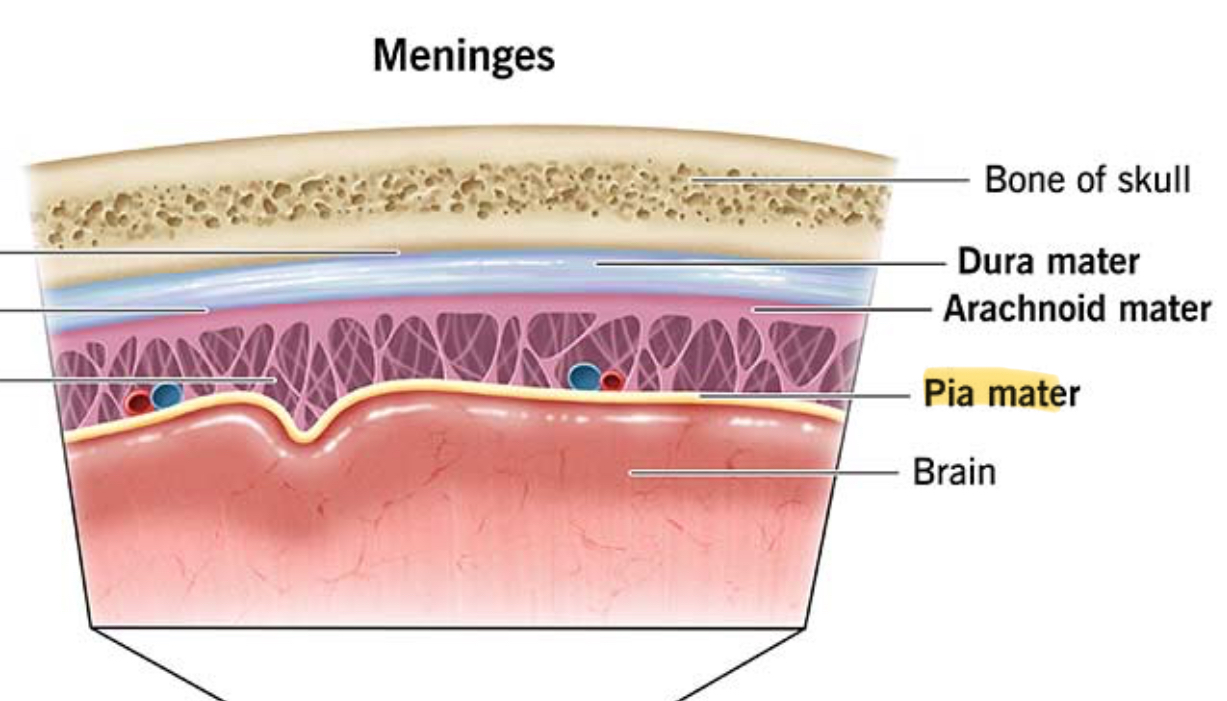
What are the 3 layers of the meninges?
Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
Dura Mater function
Protects brain and spinal cord from injury
Arachnoid Mater function
Cushions brain by holding CSF
Pia Mater function
Sticks tightly to the brain and spinal cord, supplying nutrients and O2
What is the corpus callosum?
A thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right sides of the brain
What are the four main lobes of the cerebrum?
Frontal
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
Frontal lobe functions
thinking
Decision making
Personality
Parietal Lobe function
Sensations like touch, temperature, and pain
Temporal lobe function
Hearing
Occipital lobe function
Vision
What does Broca’s area do?
Help you produce speech
Precentral Gyrus function
Controls voluntary movement of body
Postcentral Gyrus function
Processes touch, pressure, pain, and temperature
Where is the Thalamus located
Deep inside the brain, just above the brain stem, in the center of the brain
Thalamus function
Sends sensory signals to the right part of the brain
Hypothalamus location
Just below the Thalamus in the brain, near the base of the brain
Hypothalamus function
Controls body functions like:
hunger
thirst
body temperature
sleep
hormones
What are the parts of the brainstem?
Midbrain
Pins
Medulla Oblongota
Medulla Oblongota functions
Heart Rate and Breathing
Limbic System
A group of brain structures that control emotions, memory, and behavior
Reticular Formation
A network of nerves in the brainstem that controls alertness and attention
What is the functional unit of the nervous system?
The Neuron
Dendrite
Short, branchlike parts of a neuron that recieves signals from other nerve cells and carry those signals toward the cell body.
Their main function is to collect info so the neuron can process it
Axon
Long, thin part of a neuron that carries electrical signals away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands
Axon Hillcock
Cone shaped area where the cell body of a neuron connects to the axon. It starts the action potential if the incoming signals are strong enough.
Nodes of Ranvier
Small gaps between the myelin sheath along an axon that speeds up nerve signal transmission by allowing the electrical signal to jump from one node to the next.
Nissl Bodies
Small, grainy structures found in the neuron’s cell body and dendrites. It makes proteins that the neurons need for growth, repair, and normal function.
Schwann Cells
Cells in the PNS that wrap around axons to form the myelin sheath. They insulate the axon and speed up nerve signal transmission.
Neurilemma
The outermost layer of a Schwann cell that surrounds a nerve fiber in the PNS. It protects the axon and help in nerve regeneration post injury.
Myelin Sheath
The fatty, insulating layer that wraps around an axon. It speeds up the transmission of nerve signals along the neuron.
Synaptic Knob (Axon Terminal)
The small, rounded end of an axon. It releases NT’s that carry the signal across the synapse to the next cell.
What are the parts of the central nervous system (CNS)?
brain
spinal cord
What are the parts of the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
cranial
spinal nerves
What are the 2 functional parts of the PNS?
Sensory (Afferent)
Motor (Efferent)
What does the Sensory unit do?
Bring information towards the CNS
What does the Motor unit do?
Carry information away from the CNS
What are the 2 divisions of the Motor unit?
Somatic
Autonomic
What type of control is the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) of the Motor Unit?
Conscious
What type of control is the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) of the Motor Unit?
Unconscious
Somatic Nervous System (SNS) effectors
Skeletal Muscle
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) effectors
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Glands
What are the 2 divisions of the Autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
What is the Parasympathetic Nervous System?
“Rest and Digest”
Homeostasis
What is the Sympathetic Nervous System?
“Fight or Flight”
Energy Expending
Sympathetic Nervous System neurotransmitter
Acetylcholine (Ach)
Parasympathetic Nervous System neurotransmitter
Norepinepherine
Neuroglial cells function
Produce growth factors that nourish the neurons and remove ions and neurotransmitters between neurons to continue info transfer.
What do neuroglial cells do in embryo?
Guide neurons to position and may stimulate to specialize
What cells are in the PNS?
Schwann Cells
Satellite Cells
What cells are in the CNS?
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal
What do Astrocytes look like?
Star-shaped
Where are astrocytes found?
Between neurons and blood vessels to provide support
What are the 7 functions of Astrocyte cells?
Plays important role in blood barrier
Most abundant / versatile
Aids metabolism
Mop up leaked sodium
Recapture and recycle neurotransmitters
Responds to injury in the brain tissue to form a special type of scar
Participate in informational processes in the brain
What do Oligodendrocytes look like?
They resemble astrocytes with fewer processes
What do Oligodendrocytes do?
Form myelin in brain and spinal cord, which speeds up impulses
What can Oligodendrocytes do regarding myelin?
A single Oligodendrocyte can provide myelin for multiple neuron axons
What do Microglia look like?
Small with fewer processes
Microglia functions (2)
Help support neurons
Phagocytic against bacteria to cellular debris
Where are Microglia located?
They are scattered in the CNS
When do Microglia increase in number?
When brain or spinal cord is inflammed
Why are Microglia important?
Because cells of our immune system are denied access to the CNS
What do Ependymal cells look like?
Columnar or cuboidal with cilia
Where are Ependymal cells found?
They form the inner lining of central canal and cover inside spaces in the brain called ventricles
What do Ependymal cells do?
Help ventricles regulate composition of cerebralspinofluid (CFS)
What is step 1 of the transmission of nerve impulses?
Resting Potential
What is step 2 of the transmission of nerve impulses?
Threshold Reached
What is step 3 of the transmission of nerve impulses?
Depolarization
What is step 4 of the transmission of nerve impulses?
Repolarization
What is step 5 of the transmission of nerve impulses?
Hyperpolarizzation
What is step 6 of the transmission of nerve impulses?
Return to Resting Potential
Resting Potential
Neuron is at –70 mV
Inside is negative, outside positive
Sodium–potassium pump maintains this
Threshold Reached
A stimulus brings the neuron to about –55 mV
This is the minimum needed to trigger an impulse
Depolarization
Sodium (Na⁺) channels open
Na⁺ rushes in
Inside becomes positive
Membrane potential rises to about +30 mV
Repolarization
Sodium channels close
Potassium (K⁺) channels open
K⁺ flows out
Membrane potential drops back toward –70 mV
Hyperpolarization
K⁺ keeps leaving briefly
The neuron becomes more negative than resting
Return to resting potential?
Sodium–potassium pump restores balance
Neuron returns to –70 mV
Ready for the next impulse
Where are Meninges located?
Between bone and soft tissue of brain and spinal cord
What are the 3 layers of the Meninges
Dura mater
Arachnoid Mater
Pia Mater
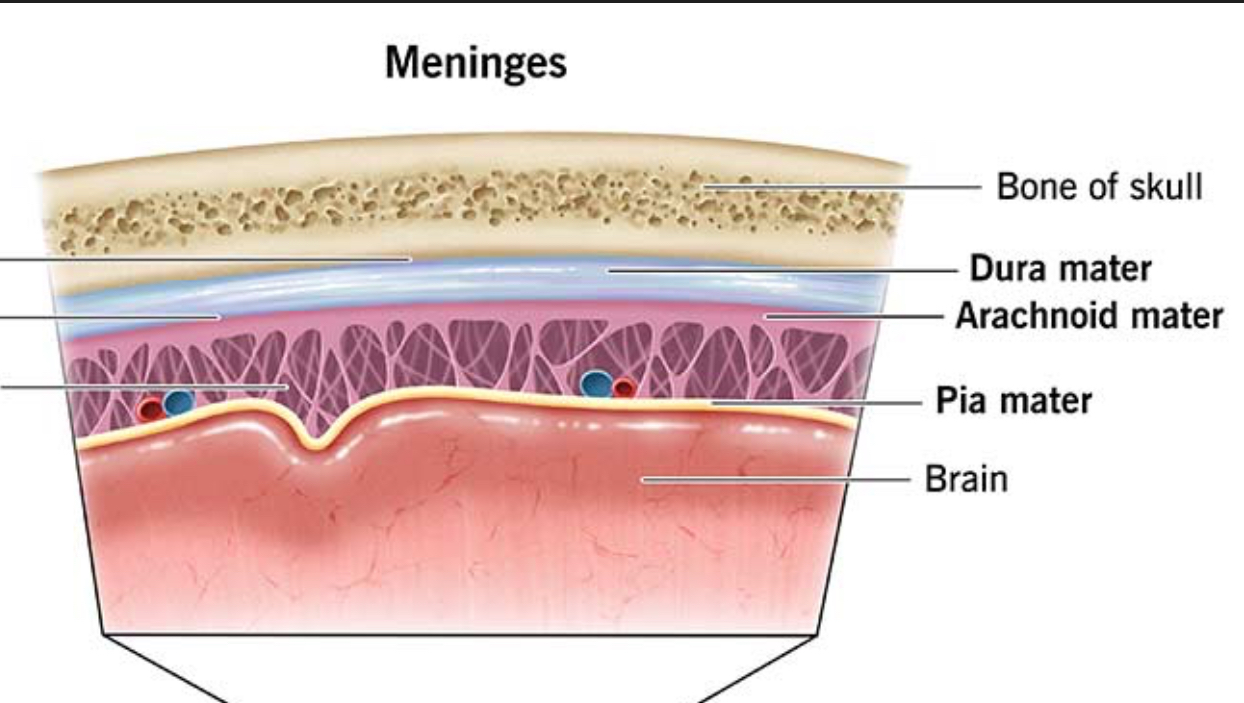
Dura Mater location
Outermost layer
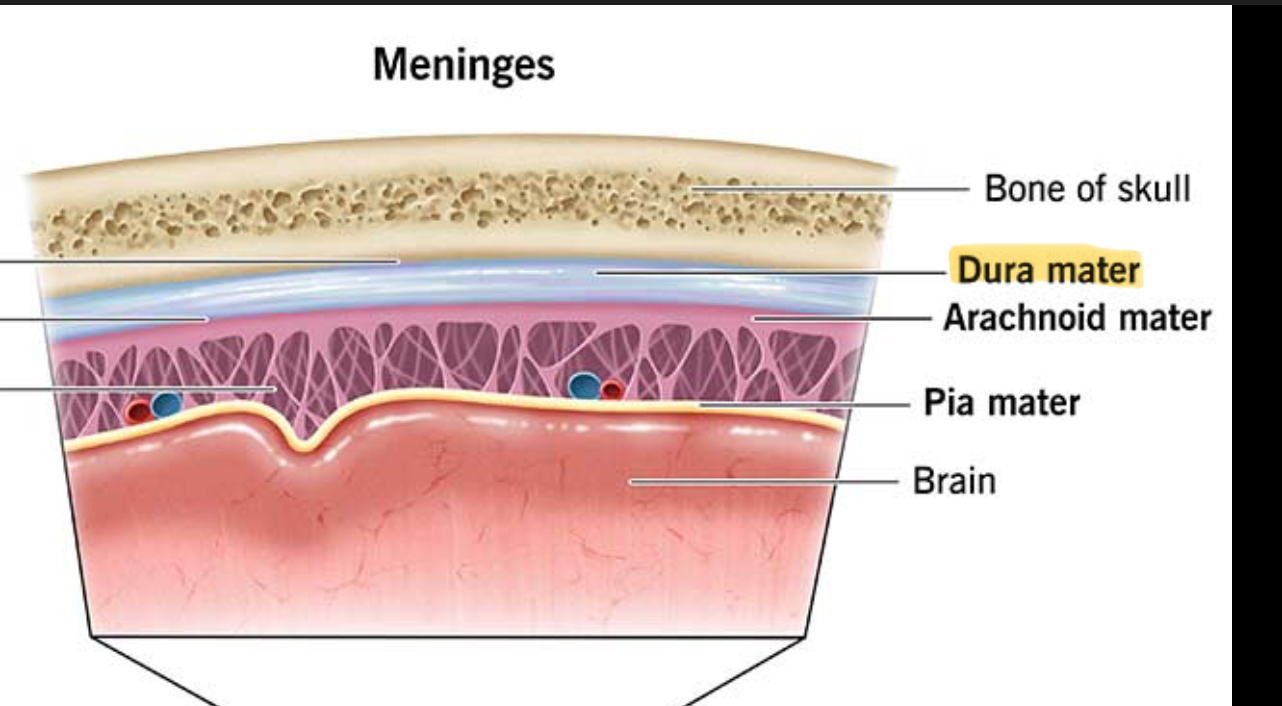
What is Dura Mater made of?
Tough, white dense CT
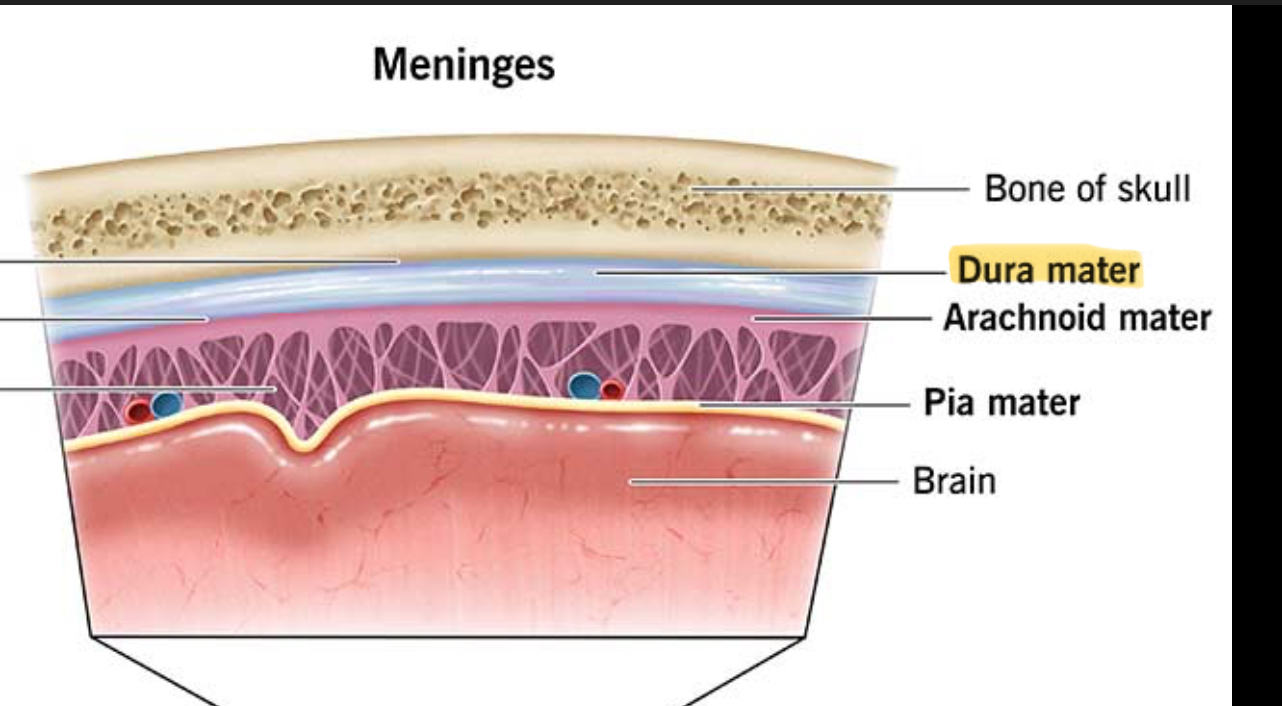
What are Dura Mater channels?
Dural Sinuses
Arachnoid Mater (Middle Layer) description
Thin, web-like membrane that lacks blood vessels
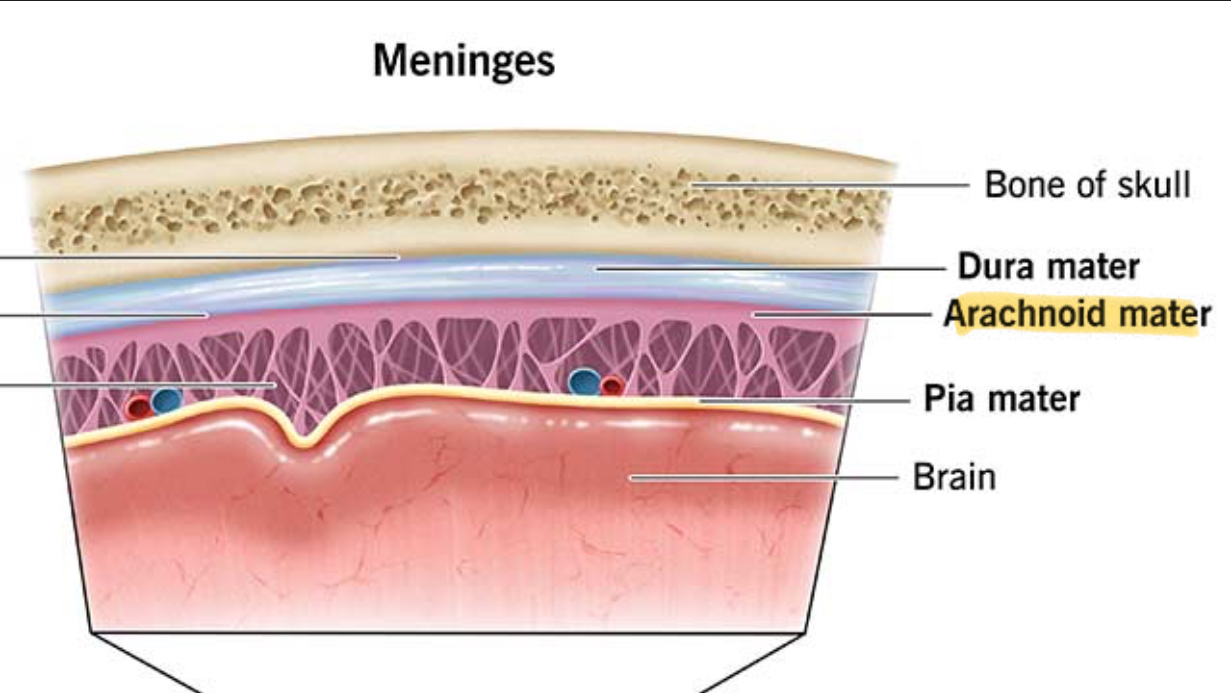
What does the Subarachnoid Space do?
Absorb forces before they reach the brain
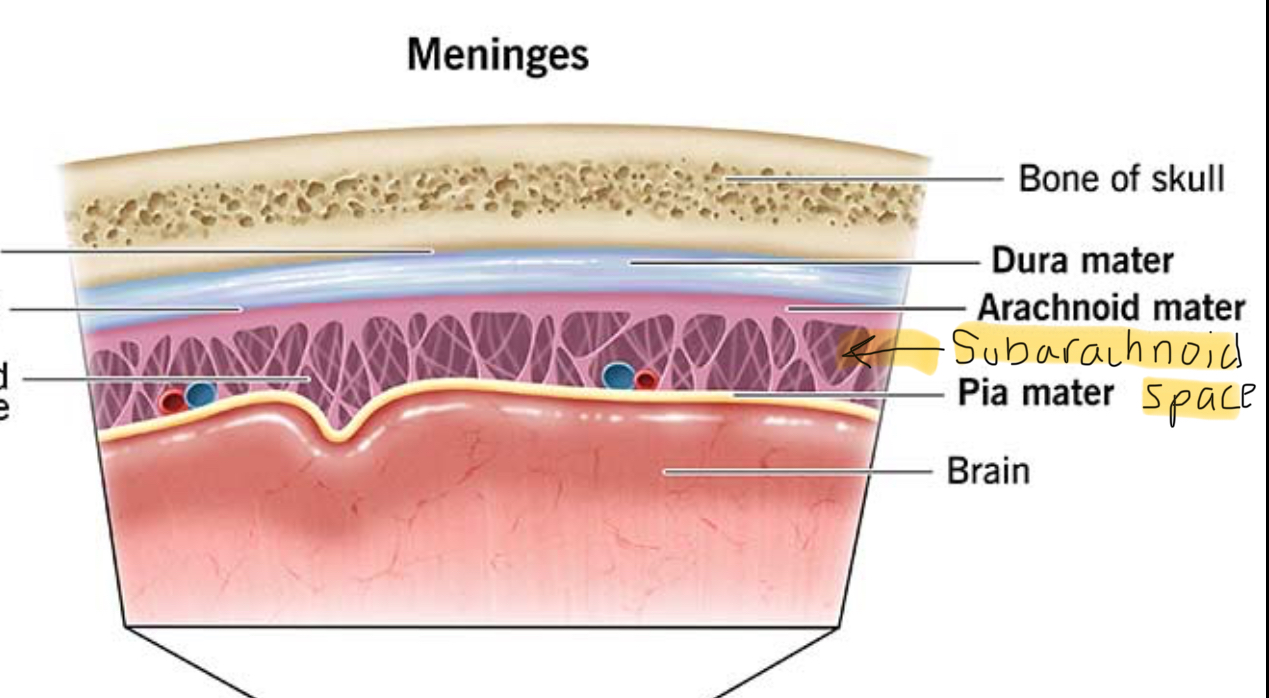
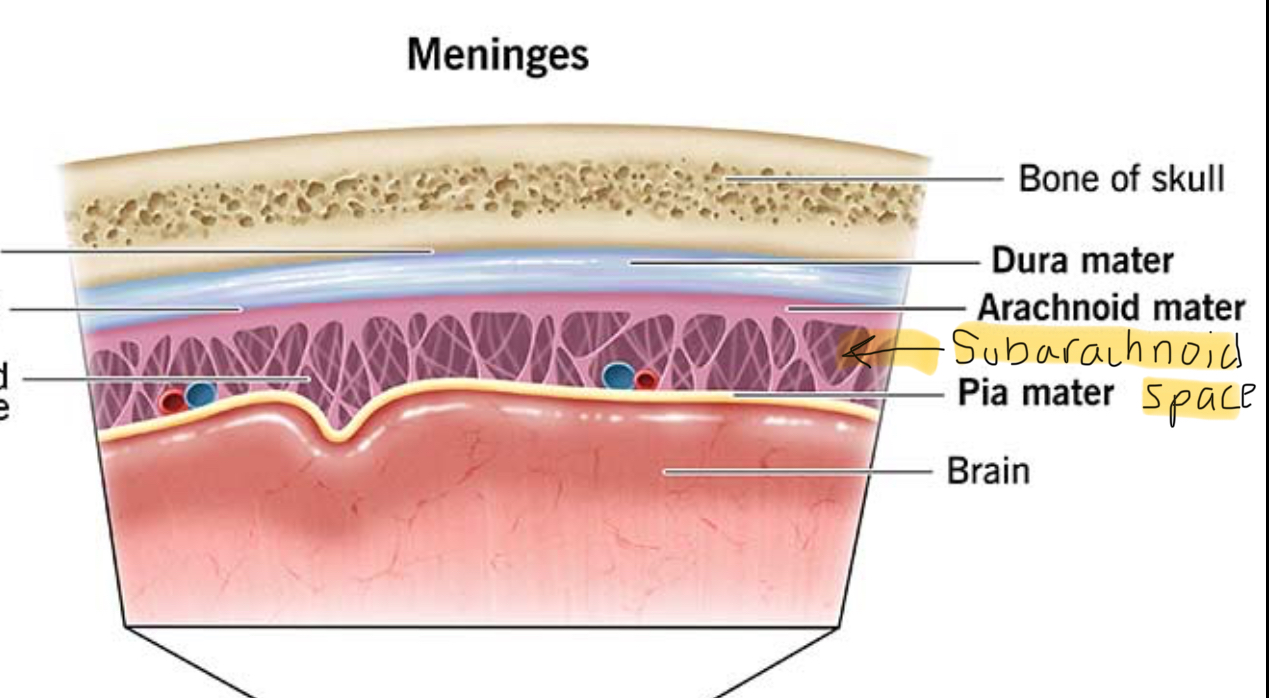
Subarachnoid Space description
located below Arachnoid Mater
contains CSF
Pia Mater description
Thin, contains many nerves and blood vessels
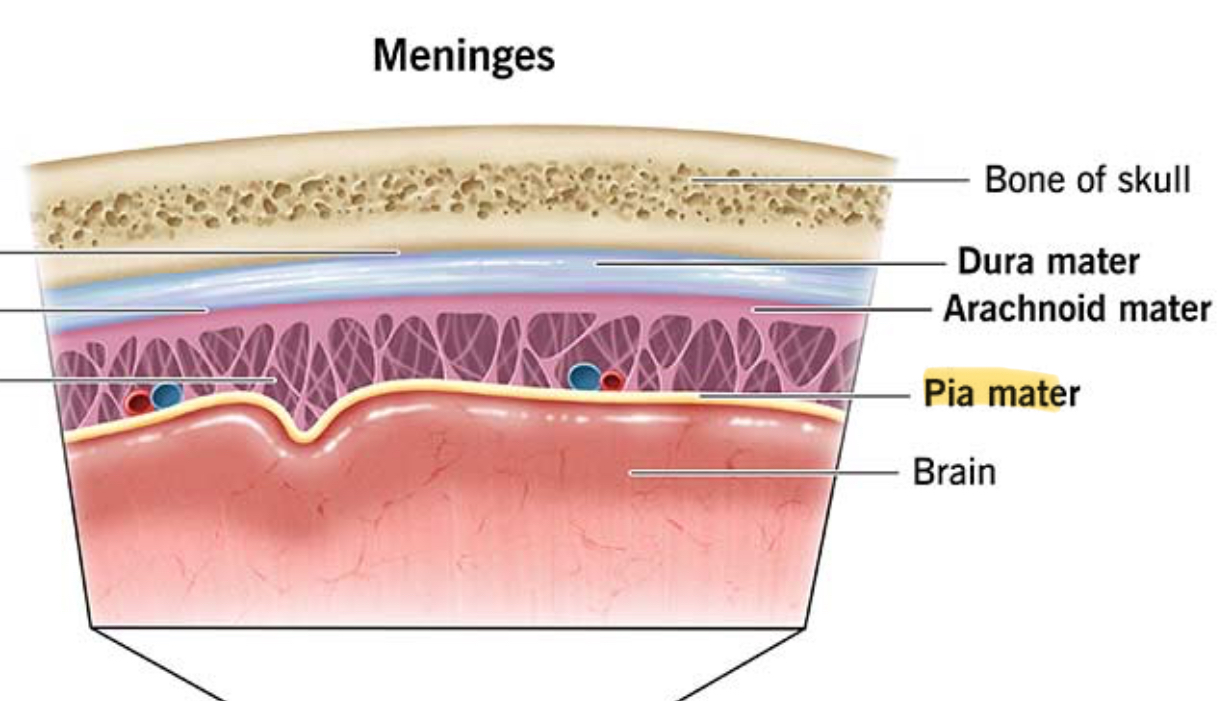
Pia Mater function
Helps nourish brain cells and spinal cord