1 - protein function
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
sections
function of protein
Molecular forms of proteins (hetero-, iso- and aloproteins)
Oligopeptides, polypeptides and proteins.
Amino acids - types and classification. Levels of organization of the protein molecule.
levels of organisation of protein molecule and structure and properties
function of protein
Some Cats Take Really Dumb Mice to Eat
Structural – Form cell and tissue structures (e.g., collagen, actin).
Catalytic – Act as enzymes to speed up reactions.
Transport – Carry gases (hemoglobin), ions (transferrin, ceruloplasmin), and lipids (albumin, retinol-binding protein).
Regulatory – Include hormones (TSH, GH), growth factors, and cytokines.
Defense – Involved in immunity (antibodies, complement) and clotting.
Motor – Enable movement (muscle proteins like actin, myosin).
Energy – Electron transport proteins help make ATP.
Some Cats Take Really Dumb Mice to Eat
Molecular forms of proteins (hetero-, iso- and aloproteins)
Heteroproteins: Same function, different species.
Isoproteins: Same function, same species, different tissues or properties (e.g. structure, stability).
Alloproteins: Same function, different individuals of the same species; due to genetic variation (alleles).
Oligopeptides, polypeptides and proteins.
Peptides: 2–50 amino acids (AA)
Oligopeptides: 2–20 AA (e.g., Vasopressin & Oxytocin – 9 AA)
Polypeptides: 20–100 AA (e.g., Insulin – 51 AA)
Proteins: >100 AA
Made of one or more polypeptides
Example: Cytochrome – 104 AA
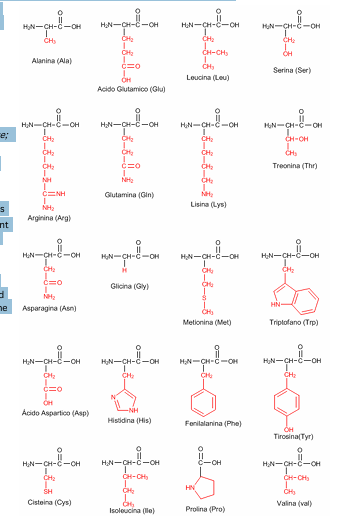
Amino acids - types and classification. Levels of organization of the protein molecule.
There are 20 AAs involved in protein synthesis and 9 are essential which must be provided by human body through diet. Some of proteogenic AAs have other function other than peptide formation such as tyrosine and thyroid hormones. Other AAs are found in body in free state performing special functions.
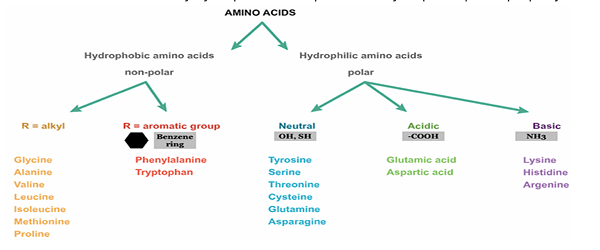
Classifications:
nonpolar aromatic R groups - phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine
nonpolar aliphatic R groups - alanine, valine, methionine, proline, leucine, isoleucine
polar uncharged R groups - cysteine, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, glycine
polar charged R groups - negative charge - aspartic acid, glutamic acid
polar charged R groups - positive charge - lysine, histidine, arginine
levels of organisation of protein molecule and structure and properties
Primary structure
number and type of AAs composing protein. This structure is maintained by peptide bonds. Sequence of AAs is important and determine the protein
Secondary structure
stable arrangements of AAs rise to repeating structural patterns. Maintained by hydrogen bonds. Forms alpha helix and beta sheets conformations
Tertiary structure
describes all aspects of 3-dimensional folding pf polypeptide. The AAs are more spaced
Quaternary structure
2 or more polypeptides joined together it becomes quaternary. Weak non-covalent bonds are present