Biochemistry II: Exam 1
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Roles of Lipids in the Body
Energy Storage, Hormone precursor
What is a TAG ?
Triacylglycerols; contain three fatty acids (may not be the same one)
What stimulates TAG synthesis ?
Insulin, results in TAG esterification
How do TAGs get transported ?
Emulsified by bile → Lipase cleavage → (across stomach membrane) → Fatty acid remade →TAGs packaged into chylomicrons → (across cell membrane) → exports and enters circulatory system
What does Albumin do ?
Transports Free Fatty Acids to adipose and muscle tissue
What does FATP1 do ?
It enhances the uptake of long-chain fatty acids
What do Chylomicrons do ?
A sort of vesicle for fatty acid transport
What do VLDLs do ?
Carries fats from the liver to tissues for energy
What do Lipases do ?
Breaks down fats
What does ApoC-II do ?
Acts as a co-factor in activating lipoprotein lipase
What does lipoprotein lipase do ?
Breaks down triglycerides in the blood
What is Heme derived from ?
Glycine and succinyl-CoA
What is Dopamine derived from ?
Tyrosine
What is Epinephrine derived from ?
Tyrosine
What is Histamine derived from ?
Histidine
What is GABA ( brain activity regulator ) derived from ?
Glutamate
What is Serotonin derived from ?
Tryptophan
What mutation can cause albinism ?
Tyrosine hydroxylase mutation
What amino acid can produce tyrosine ?
Phenylalanine
What steps stimulate nitric oxide synthesis ?
Acetylcholine release → GDP-GTP exchange → activation of phospholipase C → cleavage of PIP2 → IP3 mediated Ca2+ release from ER → activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase
What happens after the stimulation of nitric oxide synthesis ?
Arginine → NO + Citrulline → Diffusion of NO across cell membrane → Activation of soluble guanylate cyclase in smooth muscle cell → GTP → cGMP → GMP + cGMP → cGMP activates protein kinase G (PKG) → Phosphorylation of target proteins → muscle relaxxation and blood vessel dilation
Which Amino Acids are used in purine and pyrimidine biosynthesis ?
Glutamate, Glycine, Aspartate (Histidine shares several reactions with Purine biosynthesis)
Describe how the nitrogen cycle works to redistribute nitrogen in Earth's biosphere.
Atmospheric N2 → Biological Fixation by soil bacteria → NH4+ → Plants assimilate NH4+ into G and E → organic material → decomposition → NH4+
Bacterial glutamine synthetase is subject to complex regulation. Describe two types of regulation of this enzyme, and give specific examples of each.
Adenylation can be caused by an increase in Glutamine, resulting in the inactivation of GS. This prevents the creation of glutamine from glutamate.
Uridylation can be caused by an increase in alpha-ketoglutarate. This removes adenylation from the enzyme, resulting in the production of glutamine from glutamate as it activates GS.
Consider how disruption of Tyrosine synthesis (through phenylalanine hydroxylase) could exacerbate Parkinson’s symptoms.
This would prevent the creation of Dopamine from Tyrosine. This would cause a disruption in movement and balance, resulting in the major Parkinson’s symptoms of shaking as dopamine regulates these.
What is the carbon skeleton of Amino Acids recycled into ?
Citrate cycle, Pyruvate, Oxaloacetate, Acetyl-CoA
Glycerol-3-P’s role in TAG synthesis ?
It works as the base for TAGs. Acetyl groups are added to Glycerol-3-P using G3P-Acyltransferase
Where does G3P come from ?
Glycolysis
How are FA secreted from the liver ?
They are packed into VDLs in the endomembrane system, stored in adipose in lipid droplets and protected by perilipin
What are the five different reactions in FAS1 and which domains are they in ?
1) Transfer of the Malonyl Group ; MAT
2) Condensation ; KS
3) Reduction ; KR
4) Dehydration ; DH
5) Reduction ; ER
How many carbons are in Palmitate ?
16 Carbon (Saturated Fatty Acid)
Steps of TAG Synthesis & Their enzymes
DHAP → Glycerol 3-P (G3PD)
G3P + CoA → Lysophosphatidic acid (Glycerol-3-P-acyltransferase)
Lysophosphatidic acid + CoA → Phosphatidic Acid (Glycerol-3-P-acyltransferase)
Phosphatidic Acid → Diacylglycerol (Phosphatase)
Diacylglycerol → TAG (Diglyceride acyltransferase)
Steps of Carnintine Transport
1) Palmitoyl-CoA → Palmitoylcarnitine (Carnitine Acyltransferase)
2) Palmitoylcarnitine is transported through the membrane w/ Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase
3) Palmitoylcarnitine → Carnitine (Carnitine acyltransferase II)
4) Carnintine is transported into the intermembrane space w/ Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase
How does Carnintine Transport Cycle regulate cellular metabolism ?
controlls flux of fatty acids to degrade them or synthesize them
How does Malonyl-CoA regulate the Carnintine Transport Cycle ?
Inhibits carnitine acyltransferase, prevents transport of longchain fatty acids into mitochondria
Required reactions for Beta oxidation
Breakdown of acyl-CoA into acetyl-CoA
How is ACC (Acyl-CoA carboxylase) regulated ?
Insulin stimulates dephosphorylation and activation with citrate
Fates of Palmitate ?
Linoleate & alpha-Linolenate (essential fatty acids) , Arachidonate → integrated into phospholipids
Elongation, Desaturation
How are COX-1 and COX-2 different ?
COX-1 works against stomach ulcers and COX-2 works in joint inflammation; With Nonselective inhibitors, only COX-2 is partially inhibitied but COX-1 is fully inhibitited. With Selective COX-2, COX-1 is not inhibited but COX-2 is.
What do COX enzymes do ?
Regulate inflammation, pain, and fever
What does active ACC do ?
Turns Acetyl CoA to Malonyl
What happens if Fatty Acyl CoA is unable to be “tagged” with carnitine? What enzymes are involved in this process?
If it is not tagged, it will be unable to pass through the mitochondrial membrane in the carnitine transport cycle. The enzyme carnitine acyltransferase I and II and carnitine translocase are involved in this cycle.
What are the four enzymes involved in mitochondrial B-oxidation? What reaction does each catalyze?
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; Fatty acyl-CoA + FAD → trans-delta²-Enoyl-CoA + FADH2
Enoyl-CoA hydratase; trans-delta²-Enoyl-CoA + H2O → 3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA
3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase ; 3-L-Hydroxyacyl-CoA + NAD+ → Beta-Ketoacyl-CoA + NAD
Beta-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase ; Beta-Ketoacyl-CoA + CoA → Acyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA
What would happen if the ER subunit of Fatty acid synthase is not functional? What reactions would take place and what steps would not (include enzyme names and types of reactions) Big picture, what do you think would happen within the cell?
Should the ER subunit be not functional, the production of Palminate would be unable to occur as the subunit is vital in enoyl reduction during FAS1. The first half of FAS1 would still occur as MAT in the malonyl acyl transfer reaction, KS in the condensation reaction for the shift of the malonyl group to the acyl group, KR in the first reduction reaction, and DH in the dehydration reaction are still functioning. This would only create a 4-Carbon unsaturated chain as the double bond between the second and third carbon has not been saturated using the ER subunit.
For the rest of the cell, the ability to make essential fatty acids and lipids integrated within the phospholipid membrane wouldn’t be able to happen, likely causing cell death.
Compare and contrast the fatty acid degradation and fatty acid synthesis pathways in eukaryotic cells.
Degradation: CoA, FAD/NAD+ dependent ; Multiple Enzymes ; Limited by Carnitine Transport
Synthesis: ACP, NADPH dependent ; Two enzymes ; Limited by Malonyl-CoA synthesis
How does insulin stimulate fatty acid synthesis? What enzyme directly involved in fatty acid synthesis does it affect?
It activates ACC, which converts acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is vital in FAS1.
What is the importance of Isoprene ?
It is used in the formation of cholestoral in the form of IPP and DMAPP
How is Cholesterol used ?
It is the precursor for numerous important compounds like cortisol, testosterone, aldosterone. However, it can cause an atherosclerotic clot.
For liver cholesterol, it is stored in lipid droplets, packaged into lipoprotein, or converted into bile acids.
Stages of Cholesterol ?
1) Formation of Mevalonate and Acetyl CoA
2) Formation of isopentyl diphosphate
3) Formation of Squalene
4) Cyclization of Squalene
What are the three steps and their enzymes in Stage 1 of Cholesterol Synthesis ?
1) 2 x Acetyl-CoA → CoA-SH + acetoacyl-CoA (thiolase)
2) Acetoacyl-CoA + Acetyl-CoA → HMG-CoA + CoA-SH (HMG-CoA synthase)
3) HMG-CoA + 2NADPH + 2H+ → Mevalonate + 2NADP + CoA-SH (HMG-CoA reductase)
What regulates HMG CoA Reductase ? What effects do they cause ?
Insig: Senses level of sterols in membrane ; With high levels of sterols, it regulates the activation of E3 ligase and Ubc 7, resulting in the ubiquitination of HMGR.
UBIAD: Holds unto HMG to ensure it isn’t chopped up. If high in GGPP, it releases HMGR and VCP pulls it out of membrane to go to proteosome.
SREBP-SCAP: In low sterol conditions, they move to Golgi Body. There, SREBP is snipped by S1P and S2P. The N-terminus is secreted to nucleus to upregulate expression.
AMPK: Covalently modifies HMGR and deactivates it
What happens in Stage 2 of Cholesterol Synthesis ?
Three phosphates are transfered from ATP to mevalonate.
Decarboxylation and hydrolysis create a isoprene with a double bond.
Isomerization to a second isoprene (IPP and DMAPP)
What happens in Stage 3 of Cholesterol Synthesis ?
6 isoprenes are used to form Squalene
IPP + DMAPP head to tail= geranyl pyrophosphate (GP)
GP + IPP head to tail = Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FP)
FP + FP head to head = squalene
How many cyclization events occur to form Cholesterol ?
3 steps form Lanosterol and 19 more make Cholesterol.
What and where to do HDLs transport ?
Cholesterol from other cells to the liver to be metabolized
What and where to do LDLs transport ?
Cholesterol to Muscle and Adipose tissue
What does ApoC-II do to Chylomicrons ?
ApoC-II activates lipoprotein lipase to allow fatty acid release in adipose tissue, heart, and skeletal muscle.
What and where to do VLDLs transport ?
FFAs to the Liver in order to reconvert them to TAGs and store them in lipid droplets
What does ApoB-100 do to LDL ?
It binds to LDL receptors
What does Apo-A1 do to HDL ?
Activates LCAT (Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase)
What is Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase’s role in cholesterol transport ?
Esterification of Cholesterol in order to be taken up into HDL particle
How is the LDL receptor regulated, by what and how is it recycled ?
Under low cholesterol, SREBP induces transcription of the receptor. Lysosomal mediated release of the receptor and causes LDL to be broken down. The receptor is then recycles into PM.
What is the fate of Cholesterol when levels are high enough ?
What is the order of reactions for FA synthase?
A. priming, reduction, condensation, dehydration, reduction
B. priming, condensation, reduction, dehydration, reduction
C. priming, dehydration, reduction, condensation, reduction
D. priming, reduction, condensation, reduction, dehydration
E. reduction, condensation, priming, dehydration, reduction
B
What is the reaction for nitrogen fixation ?
N2 + 10 H + 8 e- + 16 ATP → NH4 + 16ADP + 16 P + H2
What enzyme is used in Nitrogen Fixation ?
Nitrogenase complex ( 3 subunits ; one being Dinitrogenase reductase )
What enzymes are used in Ammonia Assimilation into Glutamate and Glutamine ? Are they organism specific ?
Glutamine synthetase (found in all organisms)
Glutamate synthase (plants, bacteria and some insects)
Glutamate dehydrogenase (found in all organisms but functional in ammonia assimilation only when NH4+ levels are very high.
How is Glutamate assimilated into Glutamine ?
Glutamate + ATP → gamma-Glytamyl phosphate + NH4 → Glutamine + ADP + P
(Glutamine synthetase)
How do plants maintain levels of Glutamate ?
Glutamine + alpha-ketoglutarate → 2 x Glutamate
(Glutamate Synthase)
What is the difference between plants and animals in FA synthesis ?
Plants in the plastids where Animals do it in the cytosol
What is the difference between plants and animals in FA breakdown ?
Plants break it down in peroxisomes. Animals do it in the mitochondria.
What is the difference between plants and animals in FA storage ?
Plants tend to store unsaturated fats whereas animals store saturated
How does Citrate affect FAS ?
It works as a way to transport Acetyl CoA into the Cystol
What are the essential amino acids ?
Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Threonine, Valine
How can we utilize amino acid essentialness in lab studies ?
One can use this to control cell growth and investigate metabolic pathways
What are the function of transaminases ?
Transfer amine groups to generate glutamate
What pathway synthesizes essential amino acids ?
Shikimate Pathway: Aromatic AA (F, Y, W)
E. coli’s Oxaloacetate and Pyruvate Pathway: I, V, L, K, T, M
How does Glutamate contribute to the Urea Cycle ?
It can be deaminated so that it can be removed as urea
What is Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1’s first concerted step ?
HCO3 + NH4 + 2ATP → Carbamoyl phosphate + 2 ADP + P
What are the reactants and products of Ornithine transcarbamoylase ?
Ornithine + Carbamoyl phosphate → Citrulline + P
What are the reactants and products of Argininosuccinate synthetase ?
Citrulline + Aspartate + ATP → Arginosuccinate + AMP + 2P
Where does the ornithine-citrulline shuttle occur ?
Cytoplasm and mitochondria
What are the reactants and products of Argininosuccinase ?
Arginosuccinate → Arginine + Fumarate
How is Fumarate used ?
It is made into oxaloacetate
What happens to Dinitrogen reductase in Nitrogen Fixation ?
Reduced by ferredoxin e- transfer between Fe-S to Fe-S to FeMo release of Dinotrogenase reductase occurs after e- transfer between Fe-S to Fe-S(Pcluster)
What does Glutamine do for NH3 ?
It transports NH3 from peripheral tissues to the liver.
How is Glutamine Synthetase Regulated ?
It can be regulated via Glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase (GSA) or via Uridylyltransferase (UT).
GSA ( OH on Tyr 51) inactivates GS on Tyr397 by adding AMP onto the OH group. UT activates GS by adding UMP to Tyr 51, which results in a deadenylylating activity.
When does Uridylation occur ?
High energy conditions, presence of alpha-Ketoglutarate
When does Adenylation occur ?
Low energy conditions, presence of Glutamine
Why would Glutamine synthetase be a worthy cancer therapeutic target ?
It would stop de novo glutamine synthesis, stopping the further creation other Amino Acids and nucleotides
What is the importance of alpha-ketoglutarate ?
It is the precursor to multiple different pathways such as the TCA cycle, ROS Scavenger, Glutamate synthesis, Amino Acid metabolism, regulation of signaling molecules, and genetic modification
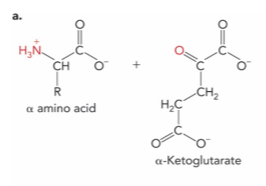
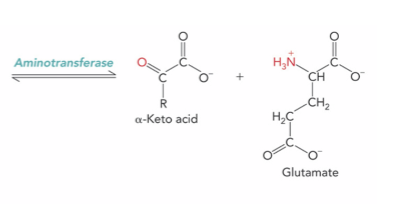
What is the enzyme and product ?
Aminotransferase ; alpha-keto acid and glutamate
What types of reactions are shared in both Nucleic acid and amino acid synthesis ?
transfer of 1 carbon groups ( biotin, THF, SAM)
transamination ( PLP )
N group transfer using amide of glutamine
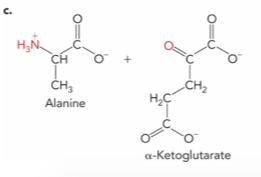
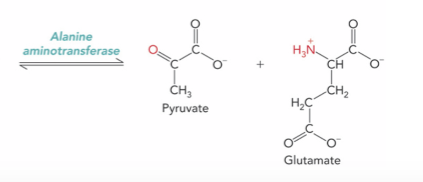
What is the enzyme and product ?
Alanine aminotransferase ; Pyruvate and Glutamate
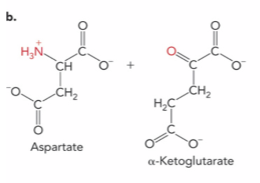
What is the enzyme and product ?
Aspartate aminotransferase ; Oxaloacetate and Glutamate
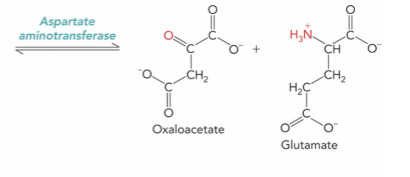
How do transaminases work ?
They rely on pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) to act as a carrier for the amino group during the transfer of the amide group.
What is Homocysteine synthesis ?
It is necessary for generation of Cys. Met is used for this. Homocysteine can be converted back to Met, but Met is still essential as it is a cyclical reaction.
What is Glutamine amidotransferase ?
Binds to Glutamine and removes NH3 group to the second active site of the enzyme to bind with an acceptor group with an OH or a double bonded O. It then produces Glutamate using H2O. Cysteine is necessary for this reaction as it uses the Sulfur to remove the amide.