AP Psych Brain Anatomy and Function
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Brainstem
central trunk of the brain connecting to the spinal cord; consists of the medulla, pons, and midbrains, controlling mostly automatic function
medulla
contains cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure
thalamus
large mass of gray matter with several functions such as relaying sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, and the regulation of consciousness, sleep and alertness
Hypothalamus
controls body temp, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep and circadian rhymes
limbic system
a set of brain structures that includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and amygdala
hippocampus
important roles in the consolidation of information from short term memory to long term memory and in spatial memory that enables navigation
olfactory bulbs
perceive information deal with olfaction (smell)
amygdala
primary role in the processing of memory, decision making and emotional reactions, the amygdalae are considered a part of the limbic system
cerebral cortex
two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callous. plays key role in memory, attention, perception, awareness, though, language, and consciousness
reticular formation
a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem polling a crucial role in maintaining behavioral arousal and consciousness
pons
deals primarily with sleep, respiration, swallowing, bladder control, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movement, facial expressions, facial sensation, posture
cerebellum
plays important role in motor control and it may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language as well as in regulating fear and pleasure repossess, but its movement-related functions are most solidly established
motor cortex
the region of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements
somatosensory cortex
middle of parietal lobe, deals with sensory information (soft, hot, cold, etc)
corpus callosum
white matter at the center of the brain connecting the two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex
frontal lobe
speaking, planning, logic, personality, abstract thinking, problem solving
parietal lobe
sensory; touch and body position
occipital lobe
vision
temporal lobe
audition (hearing)
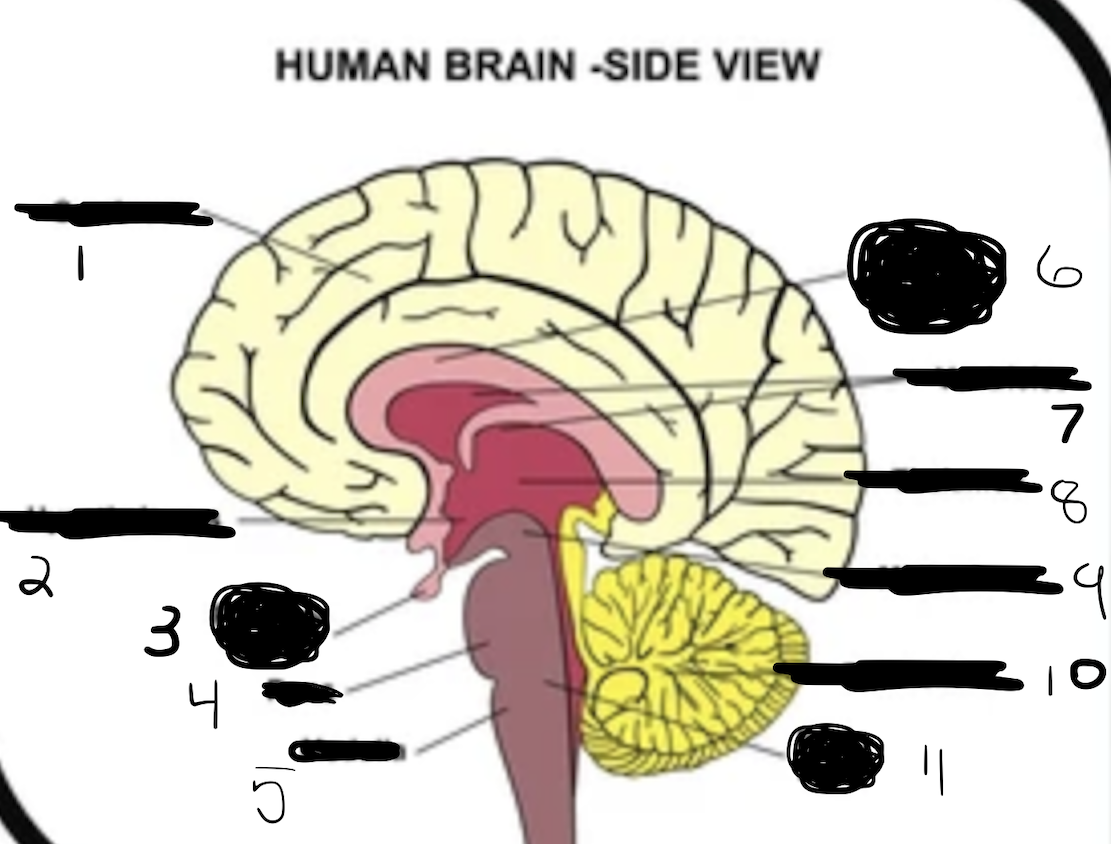
1
cerebrum
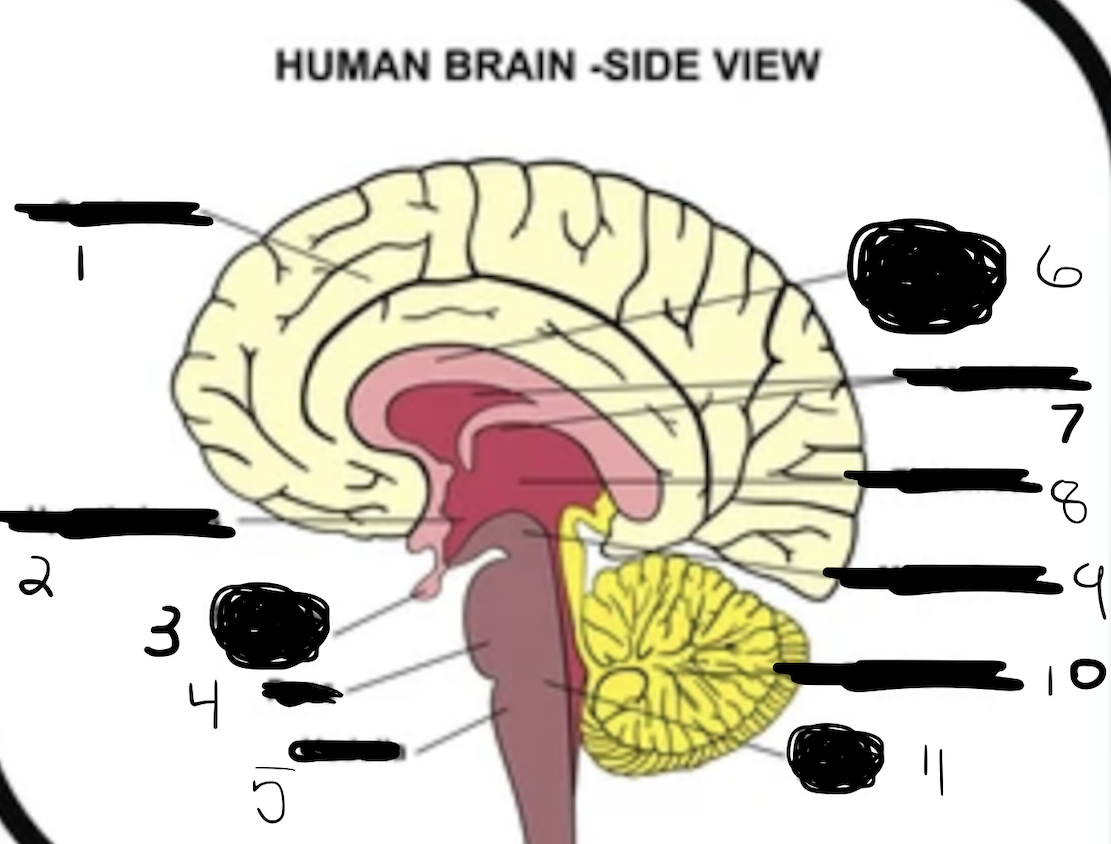
2
hypothalamus
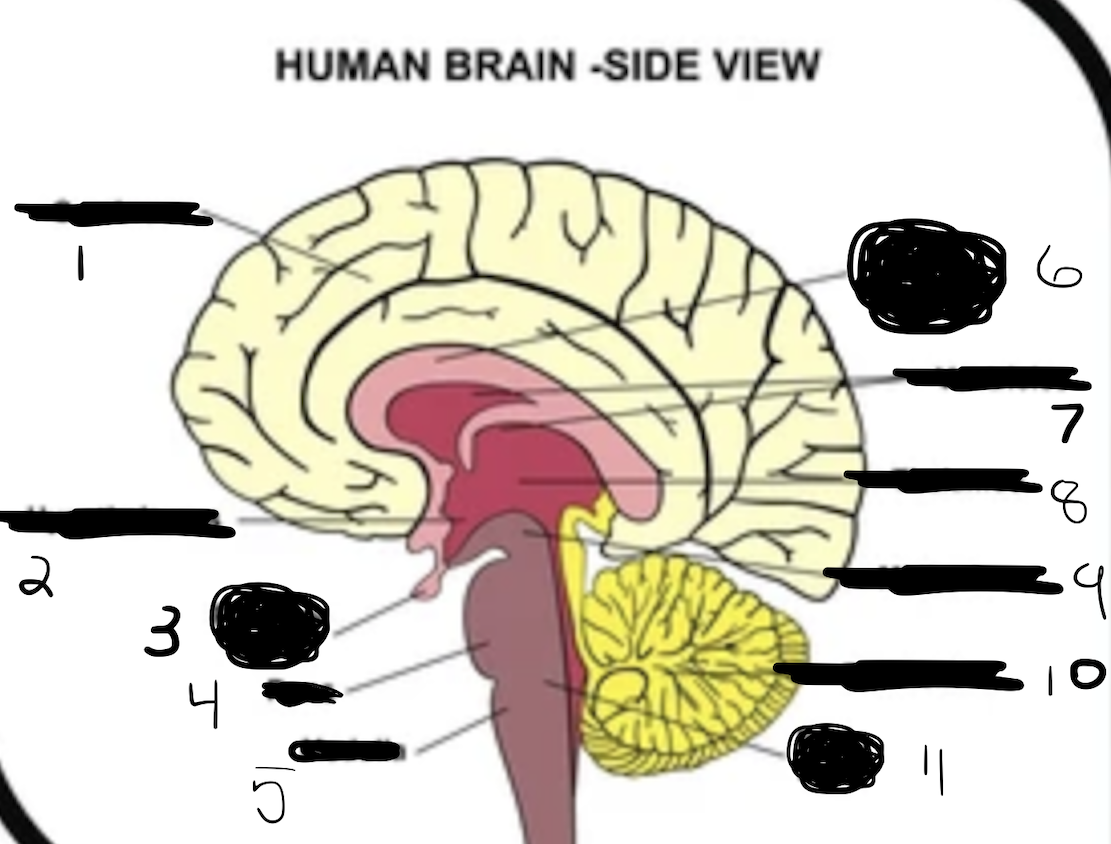
3
pituitary gland
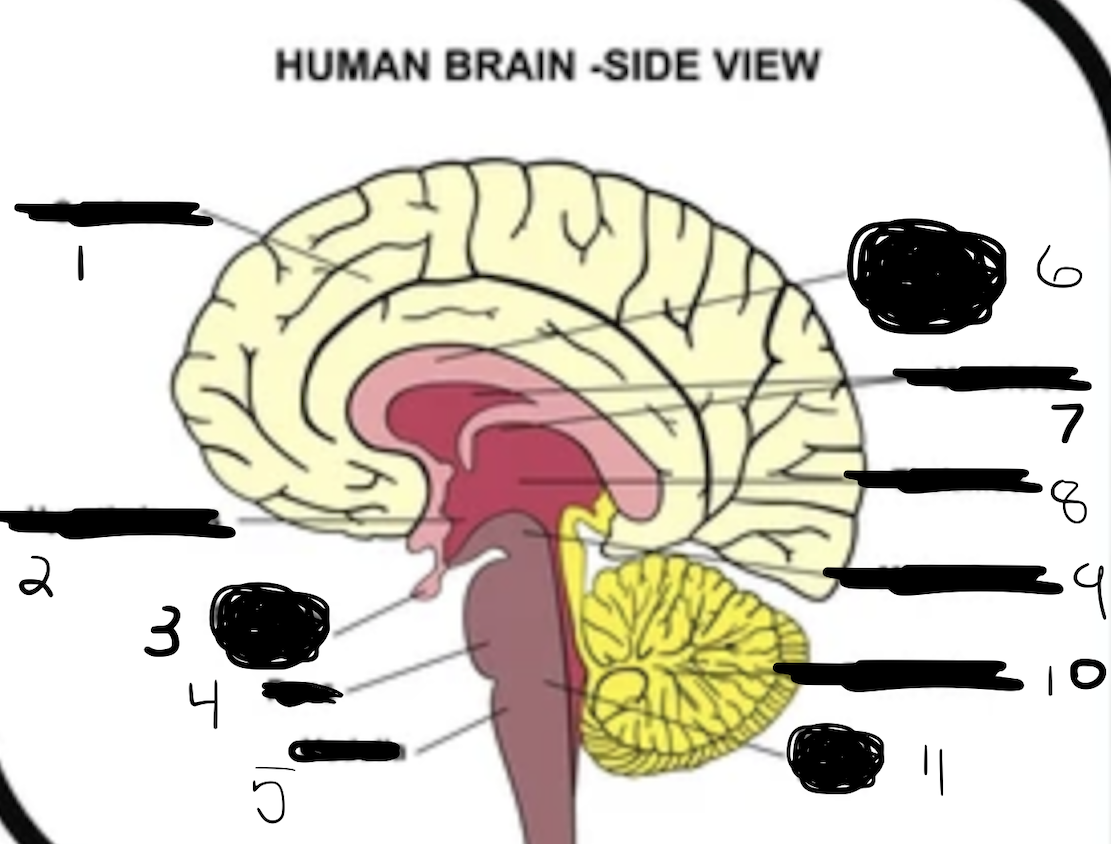
4
pons
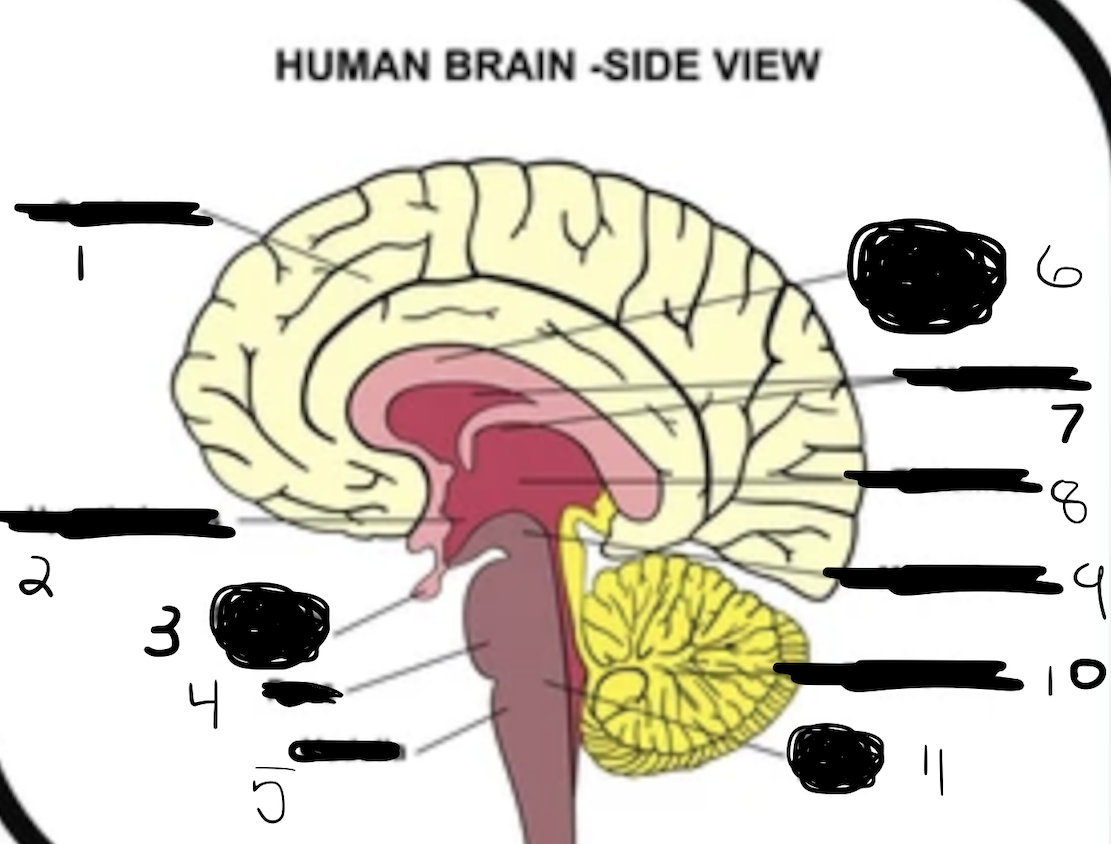
5
medulla
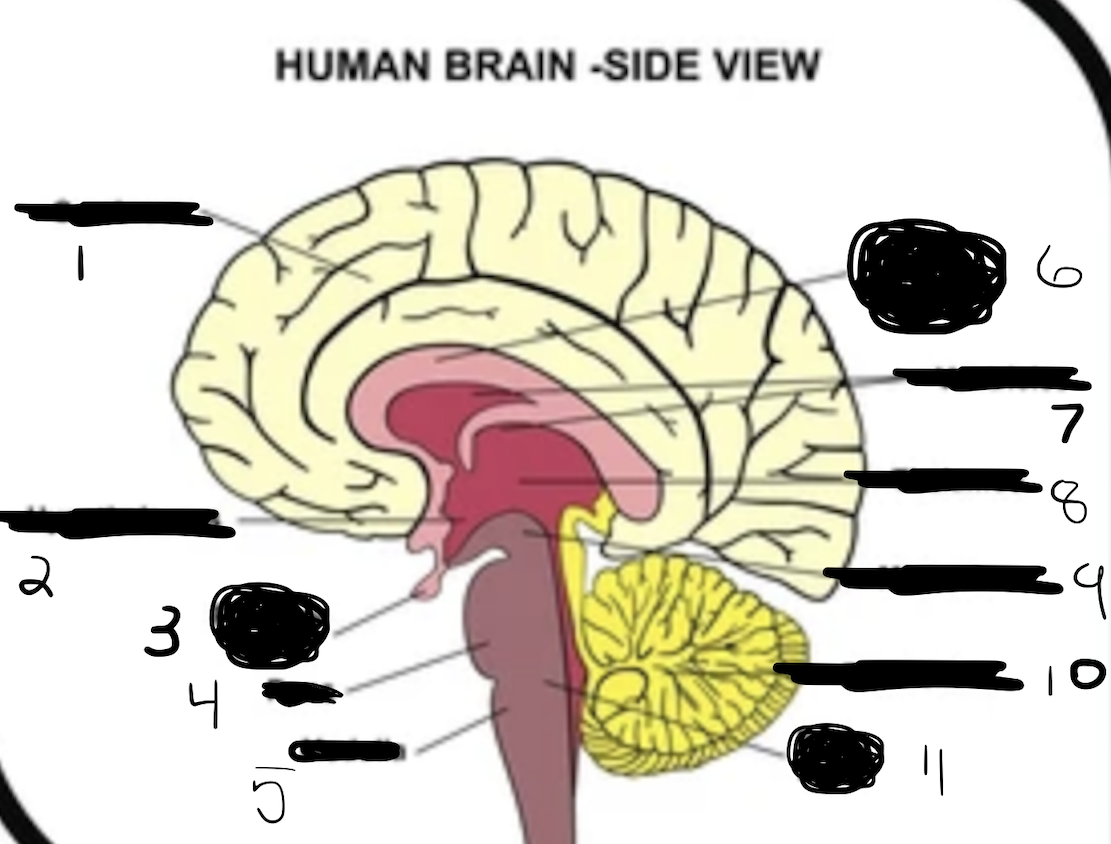
6
corpus callosum
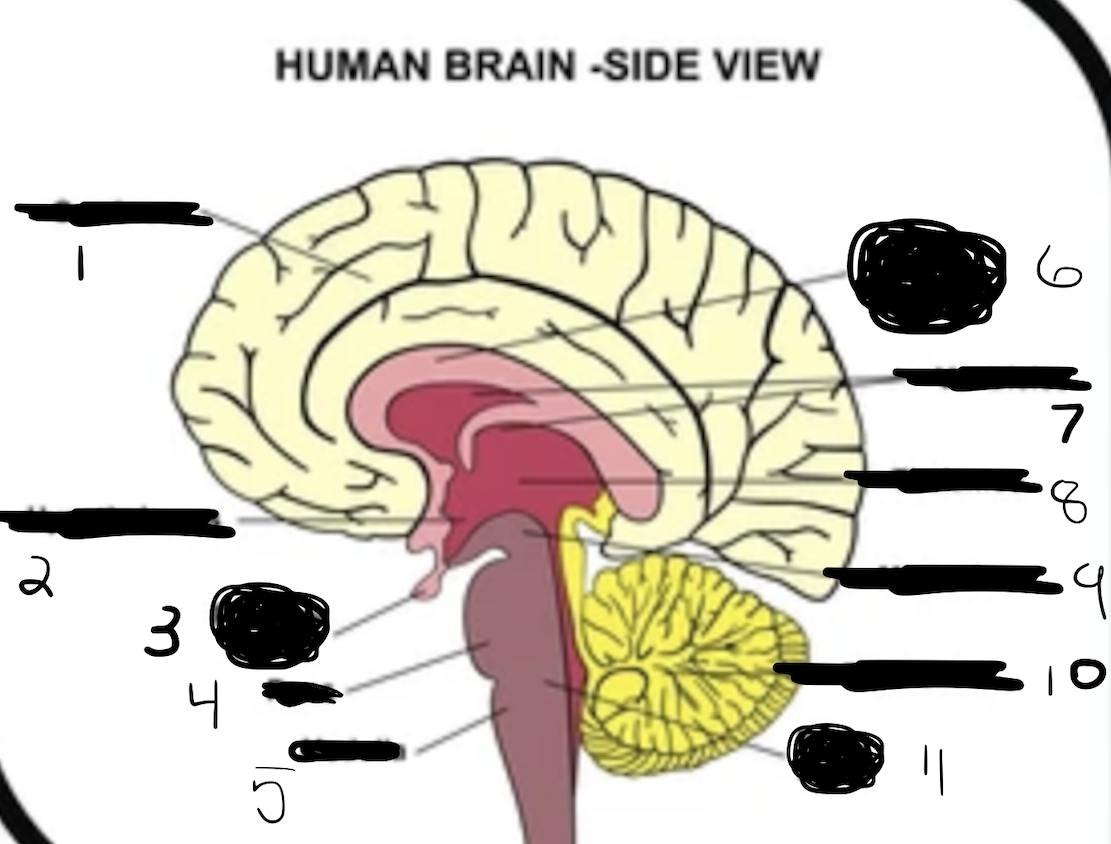
7
ventricles
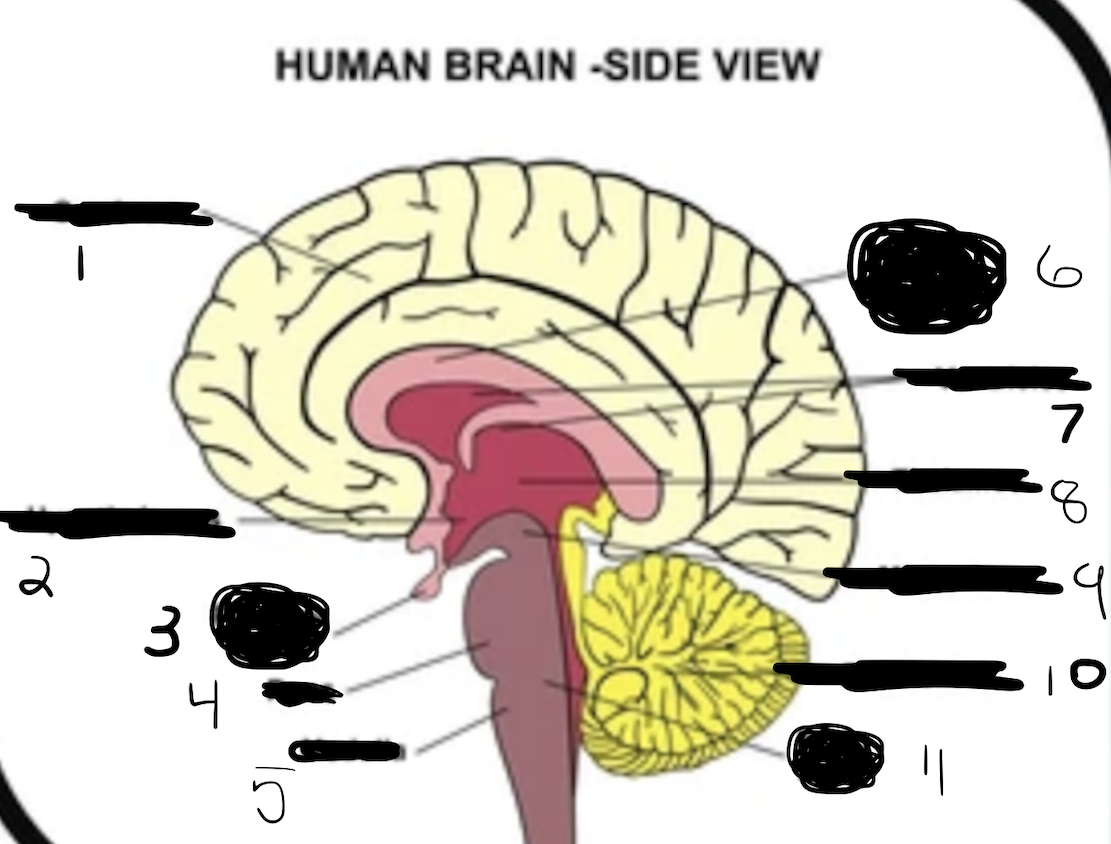
8
thalamus
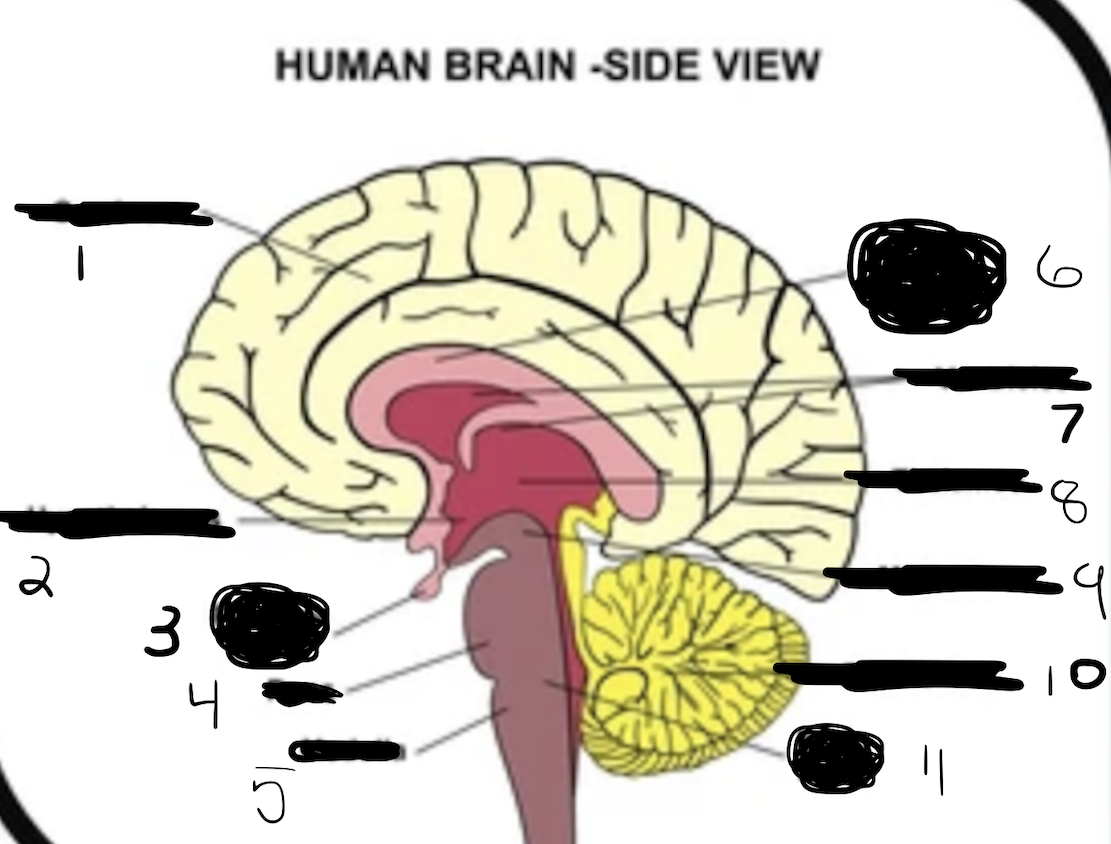
9
midbrain
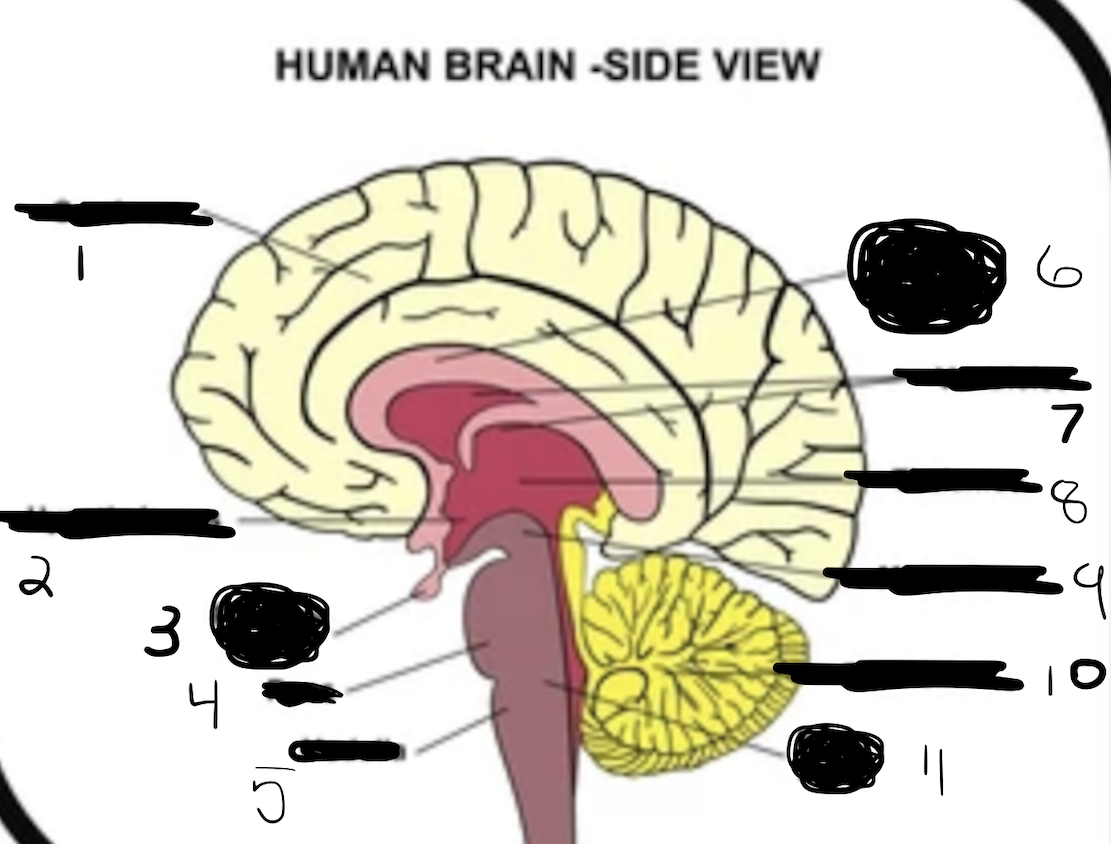
10
cerebellum
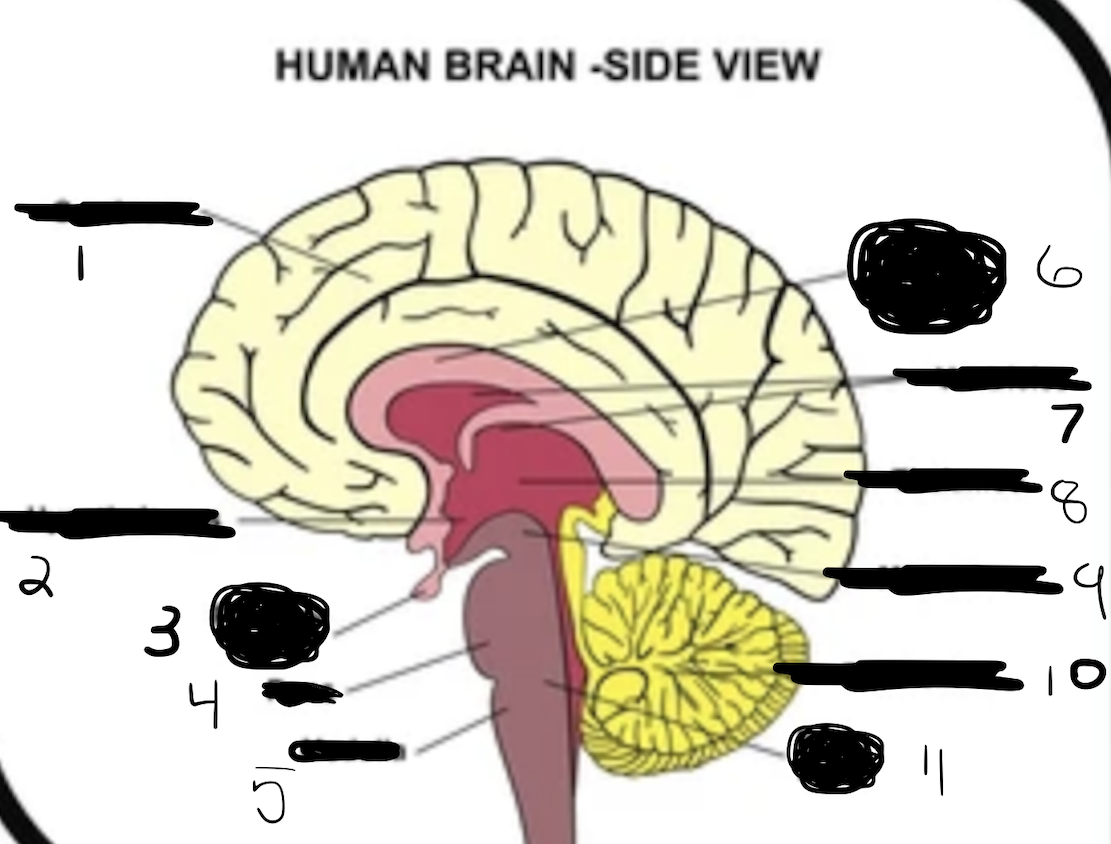
11
brain stem
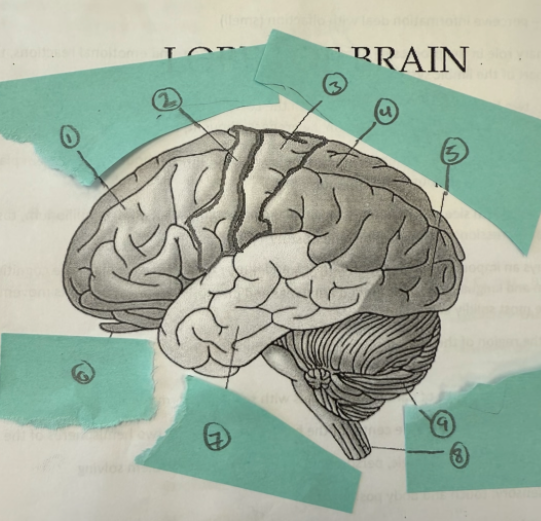
1
frontal lobe
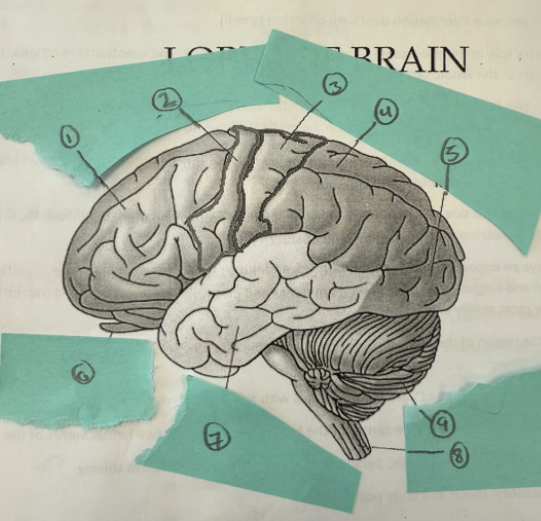
2
motor complex
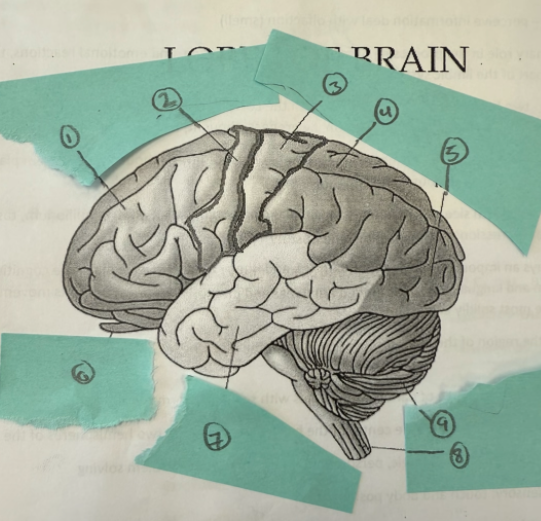
3
soma sensory cortex
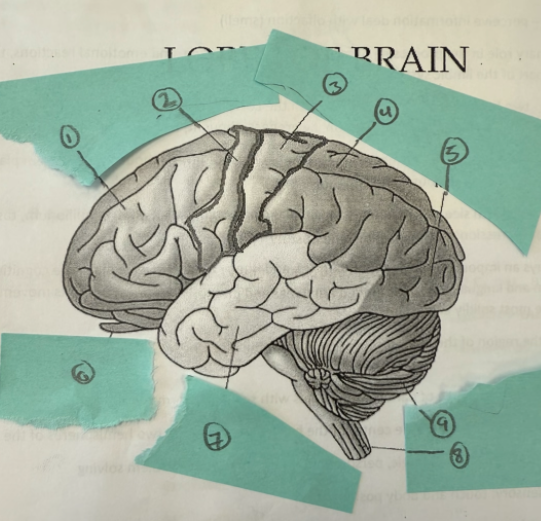
4
parietal lobe
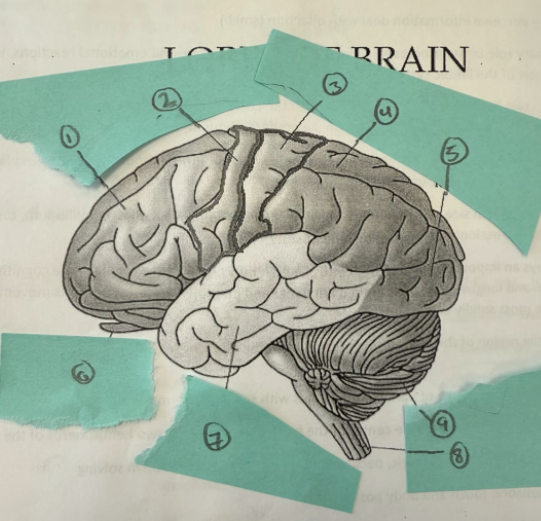
5
occipicial lobe
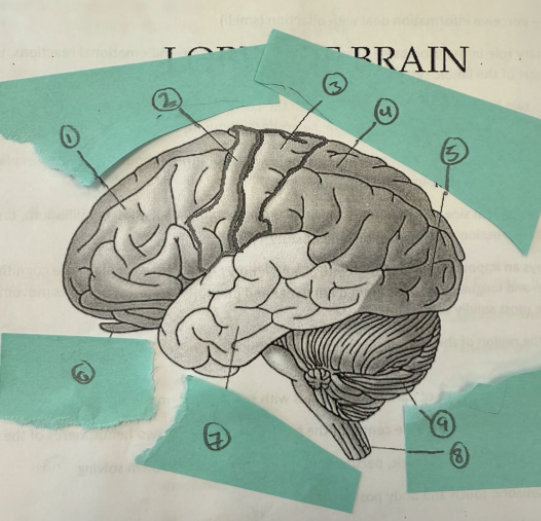
6
olfactory lobe
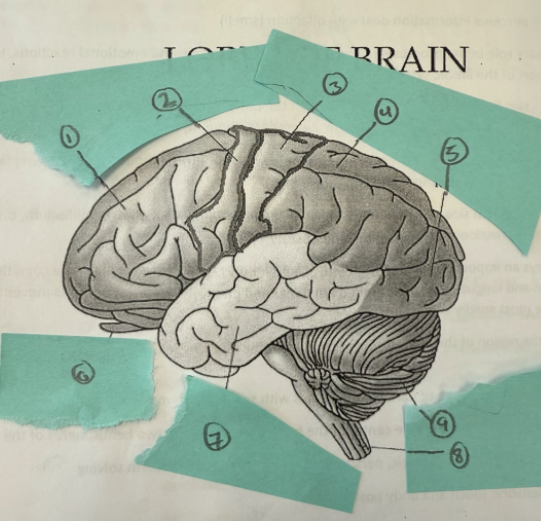
7
temporal lobe
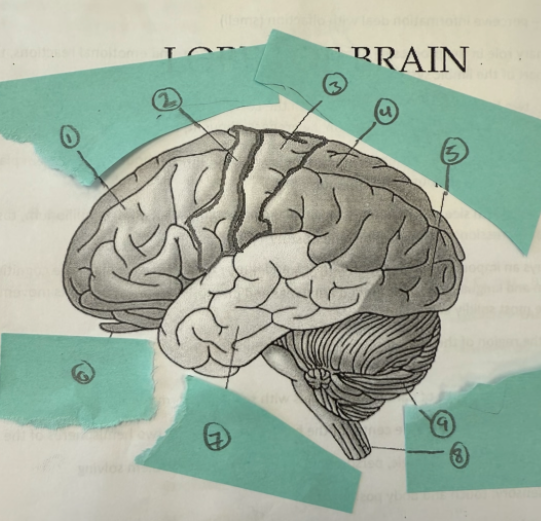
8
spinal cord
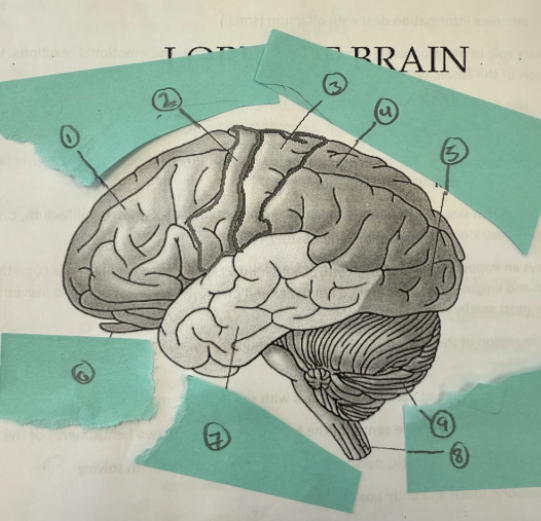
9
cerebellum
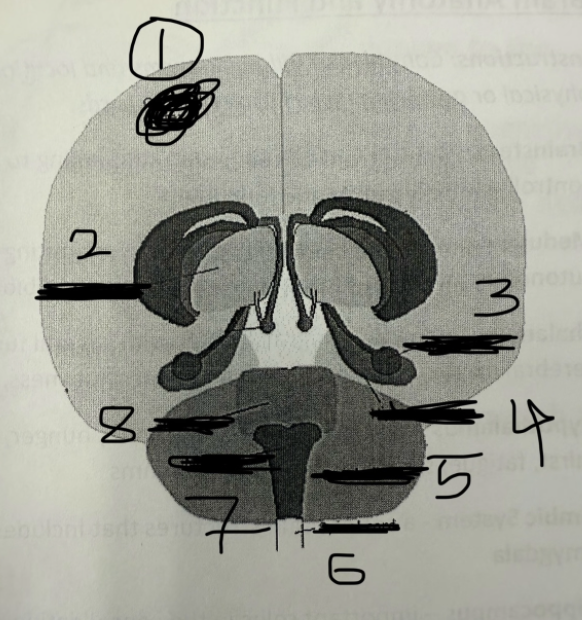
1
cerebral cortex
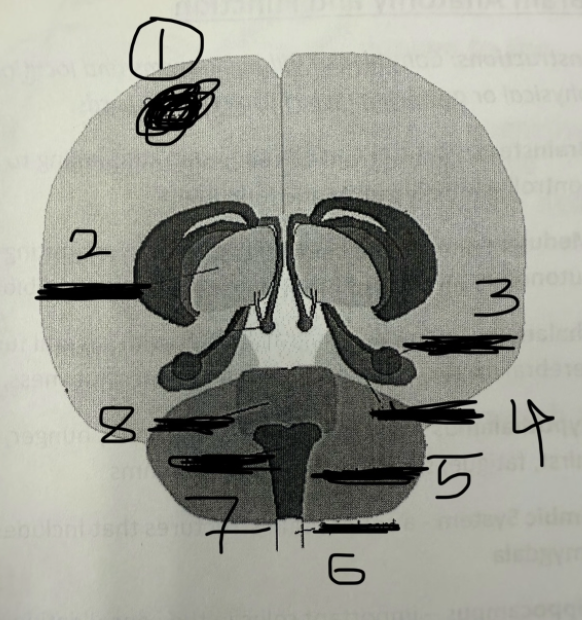
2
thalamus
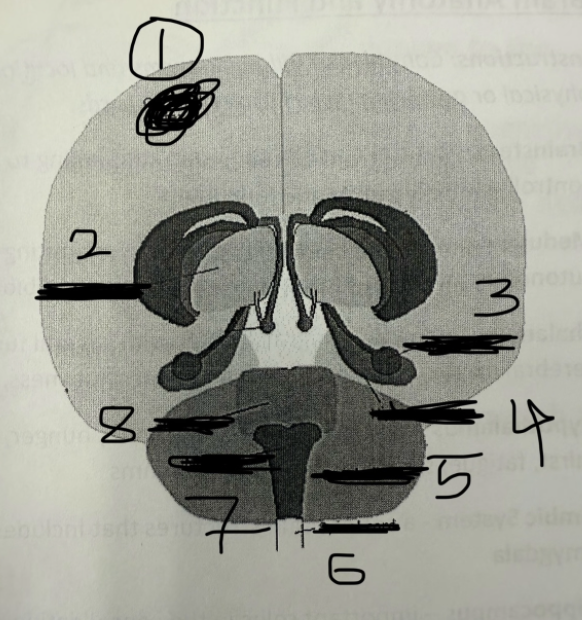
3
amygdala
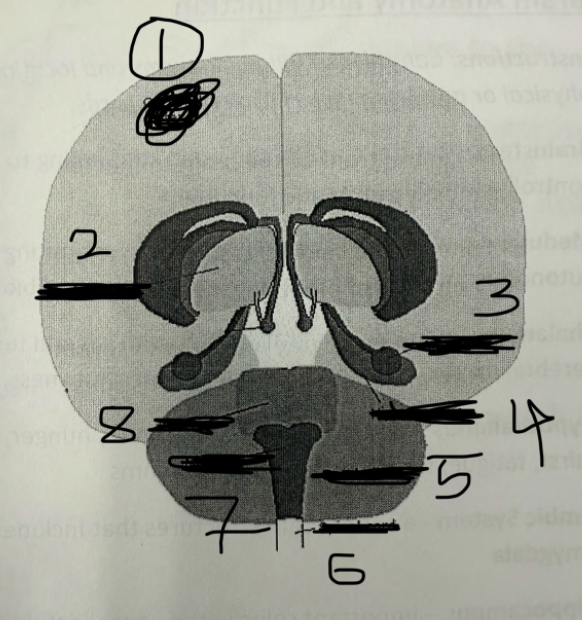
4
hippocampus
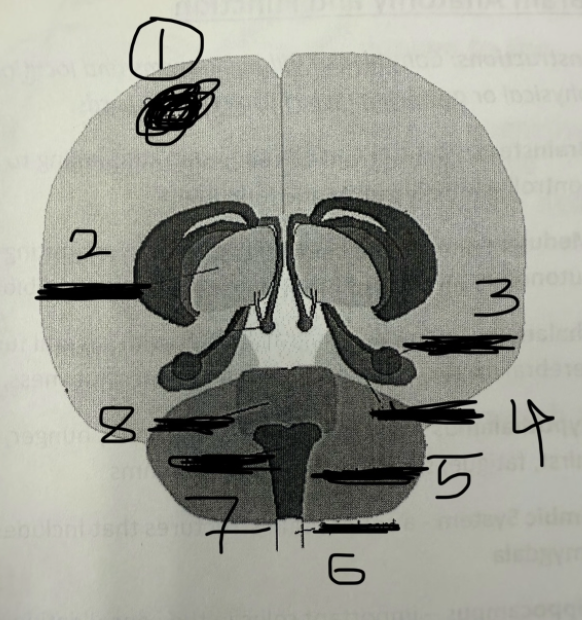
5
cerebellum
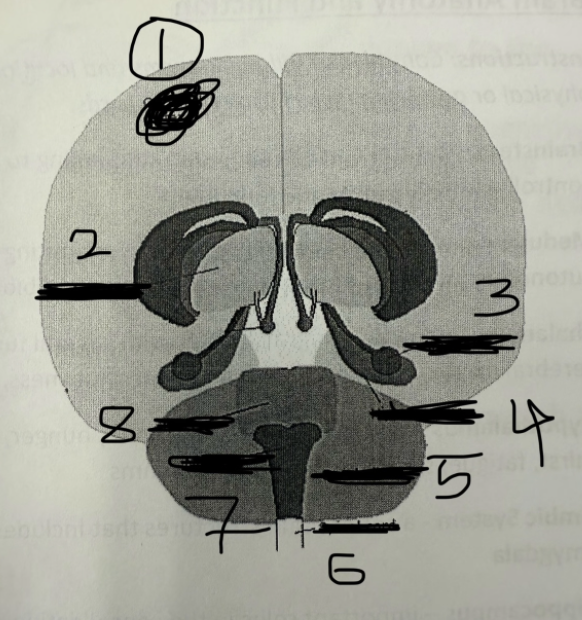
6
spinal cord
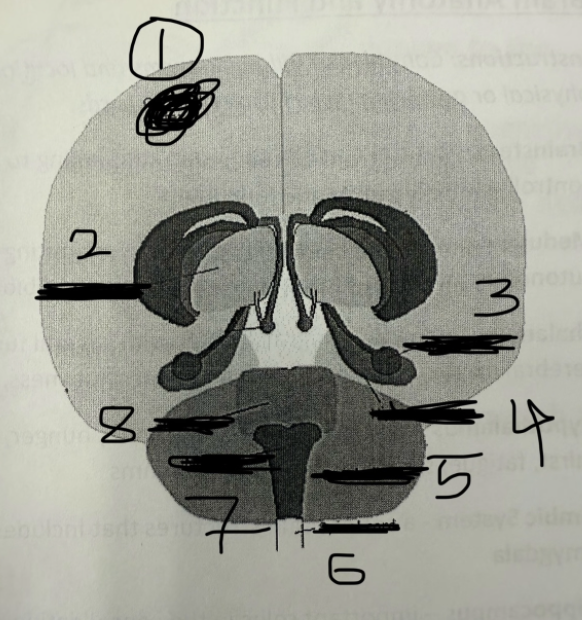
7
medulla
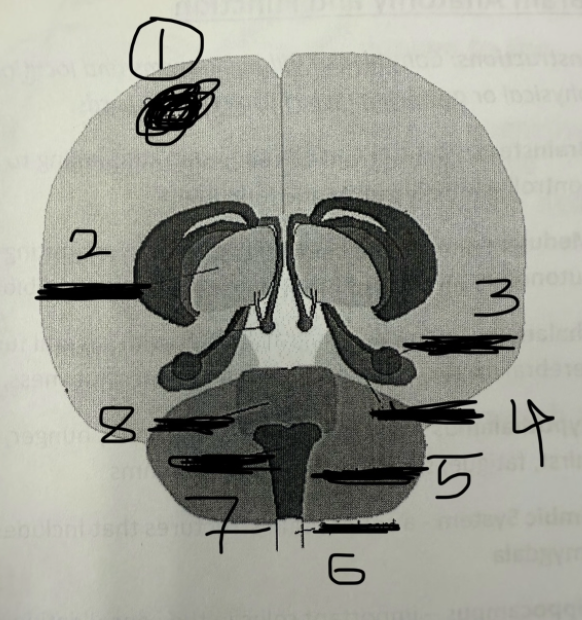
8
pons