Biology exam
1/34
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle is a series of stages that a cell goes through to grow and divide, ensuring proper replication and distribution of genetic material.
Cells produce through controlled growth and division that consists of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
Definition and stages of Mitosis
Mitosis is when the cell’s nucleus and genetic material divide (DNA). Mitosis allows for accurate separation of cell’s replicated DNA and enables the cell’s DNA to pass into the daughter cells intact.
The 4 stages of mitosis are…
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
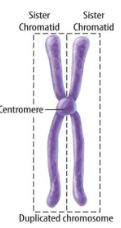
In this phase, each chromosome exist as 2 copies on one chromosome, due to DNA synthesis
Sister chromatids are held together by the centromere.
The nuclear membrane breaks down
Spindle fibres form from the centrosome
The 2 chromosome “arms” are sister chromatids
Metaphase
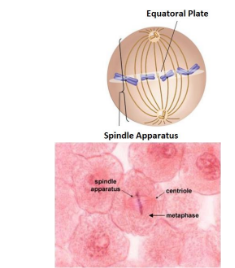
Chromosomes line up in the middle of cell
The spindle fibres stretch from centrosomes on opposite sides of the cell
The spindle fibres attach to the centrosome of each chromosome and guides them to the equator of the cell
Anaphase
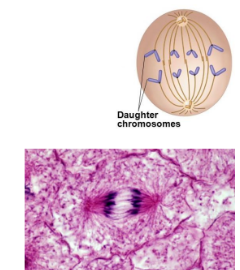
Sister chromatids are pulled apart
Each of the centromere splits apart and the sister chromatids are no longer joined
Separated sister chromatids are now known as daughter chromosomes
The spindle fibres are now shorter, causing the daughter chromosomes to be pulled towards opposite ends ( to the poles)
Telophase
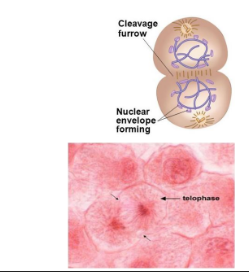
The daughter chromosomes have both reaches opposite ends
The chromosomes unwind into less visible chromatin
The spindle fibres break down
Nuclear membranes form around the new sets of chromosomes.
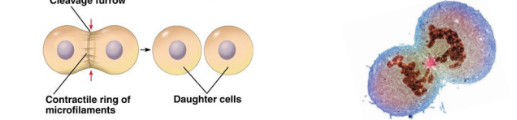
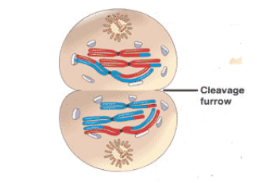
Cytokinesis
Membrane pinches off to form 2 new cells
Somatic cells
Body cells of animals and plants.
Autosomes
The other 22 pairs of chromosome, excluding the sex cells.
Nucleotides
A subunit that makes up the DNA. Nucleotides are made up of…
A phosphate group
A pentose sugar
A nitrogenous base (A, T, G, C)
The phosphate and sugar forms the rails
The base protrude inward, which forms the rungs
Purine bases include, Adenine and Guanine
Pyramid bases include, Thymine and Cytosine
Genome
A complete DNA sequence of an organism
Genetic mutation
A change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA
Semi-Conservative Replication
During the process of DNA replication, the double helix unwinds and each strand is a template for a new strand. Each new double helix contains one original strand and one new strand.
Sex Chromosomes
Out of all 23 pairs of chromosome, 1 pair is the sex chromosomes
Can be either X or Y, these determine the genetic sex of an organism
Karyotypes
karyotypes are a person’s particular set of chromosomes
In metaphase, the chromosomes are collected and stained, so they can appear as sister chromatid X’s
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes that are paired together but can carry different forms of the same genes. Example: Brown Hair versus Blonde Hair
Asexual Reproduction
Requires only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring.
Sexual Reproduction
Requires 2 parents and produces genetically distinct offspring.
Requires the fusion of 2 gametes (sperm + egg)
Zygote
A cell formed by the fusion (combining) of 2 gametes. The zygote must have the same number of chromosomes as a somatic cell.
Fertilization
The joining of male (23) and female (23) gametes. Gametes must contain half of the number of chromosomes.
Haploid and Diploid cells
Gamete cell’s are haploids (half of the OG chromosome, 46, 23 chromosomes)
Zygote cell’s are diploid (the OG amount of chromosomes 46)
Meiosis
A cellular process that produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cells. The outcomes of this process is to, have the haploid cells produced (Genetic reduction) and ensure offspring are genetically different from one another and their parents, which increases genetic variation (Genetic recombination).
This process involves 2 types of cell division, Meiosis I and Meiosis II.
Meiosis I
Aims to separate the double pair. The cycle of meiosis I are…
Prophase 1
Metaphase 1
Anaphase 1
Telophase 1
Prophase I
Just like mitosis…
The chromatin condenses into chromosomes
The nuclear membrane disappears
New process
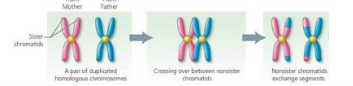
Each pair of homologous chromosomes pair up side by side, forming a tetrad
Crossing over happens, where the paternal and maternal chromatids connect at one or more points and exchange their segment of DNA
Centrosomes move towards opposite ends
Metaphase I
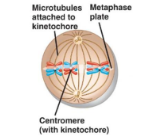
The tetrad from prophase I, line up along the middle of the cell in a random way, this is called independent assortment, of maternal and paternal chromosomes.
Spindle fibres attach to the centromere of each homologous chromosome.
Anaphase I
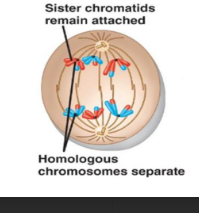
The homologous chromosomes separate from each other (but the sister chromatids are still together in this phase.
The chromosome numbers are reduced from 2n to n.
Telophase I
The homologous chromosomes uncoil into chromatin. Then cytokinesis takes place to produce 2 cells.
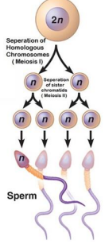
What happens in Meiosis II
After Meiosis I is completed, each chromosome will still have 2 chromatids, which is 2x the amount of DNA a cell needs to have.
Meiosis II, reduces the amount of DNA back to normal
Splits up the chromosomes, so each daughter cell has only one chromatid per chromosome.
This process is completed with Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II.
Prophase II
New spindle fibres form and chromosomes begin to move
Metaphase II
Chromosomes align at equator of cell
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibres
Telophase II
Chromosomes uncoil, and the nuclear membrane reforms
4 haploid cells have been produced.
Spermatogenesis
This is the process of producing male gametes (sperm) in the testes
Its starts off with diploid cell, which is called spermatogonia, and it reproduces by mitosis at the start of puberty
After undergoing mitosis, the cells go through meiosis to form 4 haploid cells (23 of 46 chromosomes)
The head of the sperm, carries the DNA, the mitochondria is in the midsection, and the flagella (tail) is for locomotion.
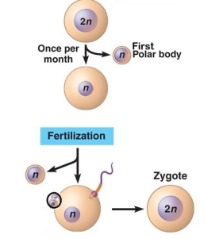
Oogenesis
This is the process, when female gametes (eggs/ova) are produced in the ovaries
Usually begins with diploid cell oogonia
The oogonia begins before birth, through mitosis. They begin meiosis but stops at prophase I.
There is an unequal division of cytoplasm
The cell that receives most cytoplasm continues to go through meiosis I and meiosis II to form viable egg
Smaller cells are formed, and these are the cells that did not get a lot of cytoplasm and are called polar bodies, and will eventually disintegrate
Meiosis II will not be completed unless the egg is fertilized
Sperm Vs Egg
Similarities
The Egg and the Sperm, both starts with diploid cells
They both reproduce by mitosis
Differences
The production of sperm is done in the testes but the production of egg is done in the ovaries
The egg