Week 12: Anatomical changes during pregnancy
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What changes happen during early pregnancy?
Symptoms similar to secretory phase of menstrual cycle, but no menstrual period
How do pregnancy tests work?
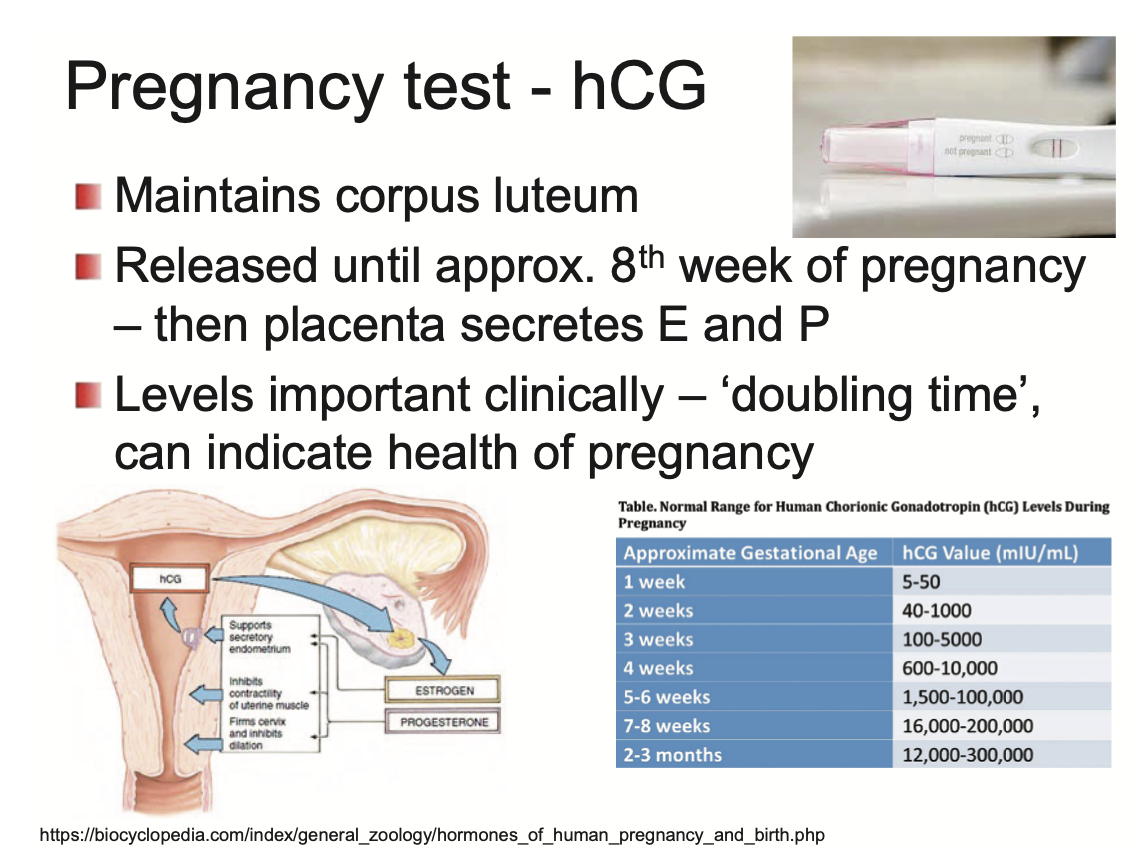
After 2 weeks, pregnancy can be detected by hCG secretion
cells outside blastocyst secrete hCG
hCG goes to ovary and maintains the corpus luteum
released until approx. Week 8 of pregnancy, then placenta secretes E and P
hCG levels can indicate health of pregnancy
What are the symptoms of the first trimester?
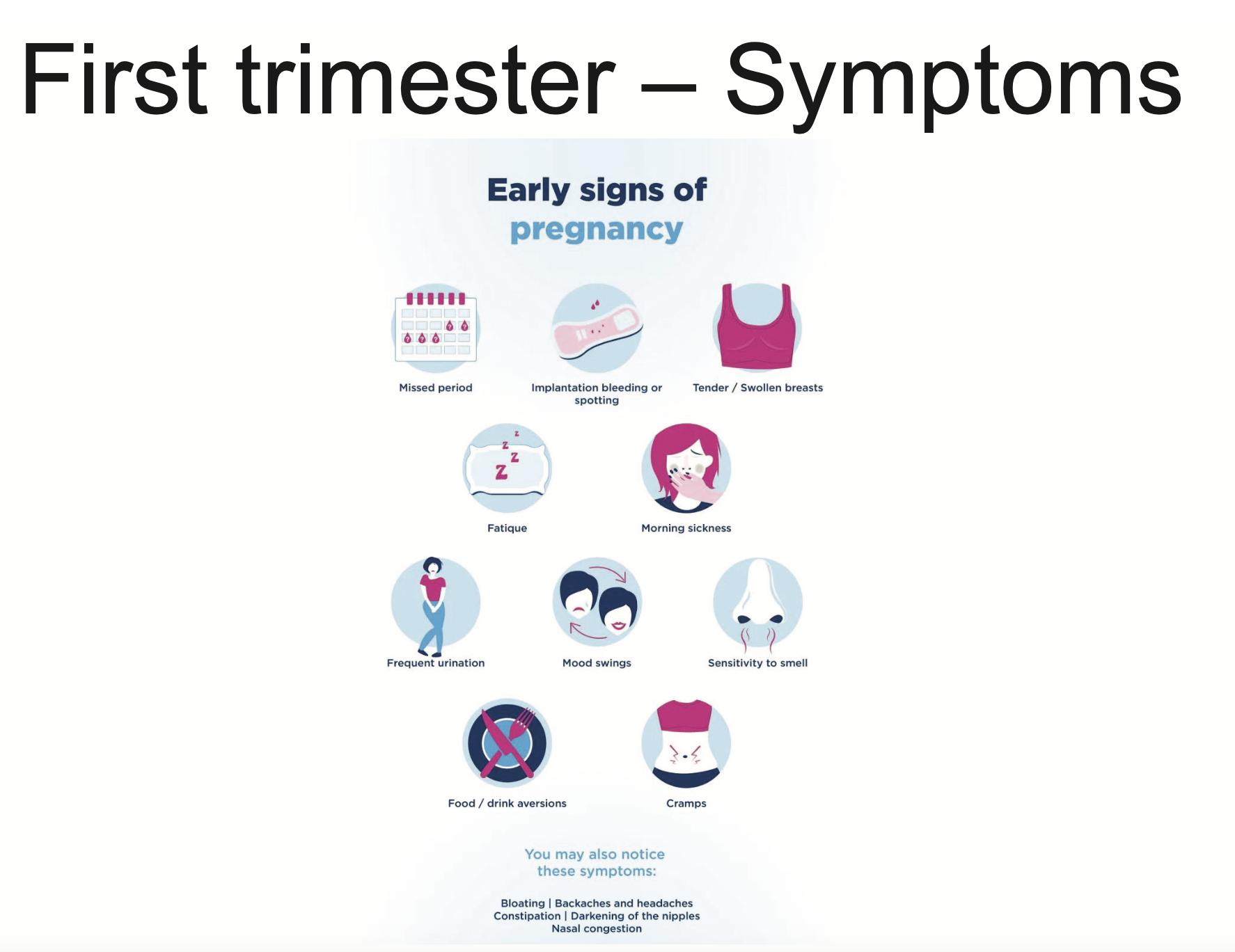
Mainly due to increases hormones - oestrogen, progesterone, hCG
missed period
swollen breasts
fatigue
morning sickness
increased blood flow to pelvic viscera
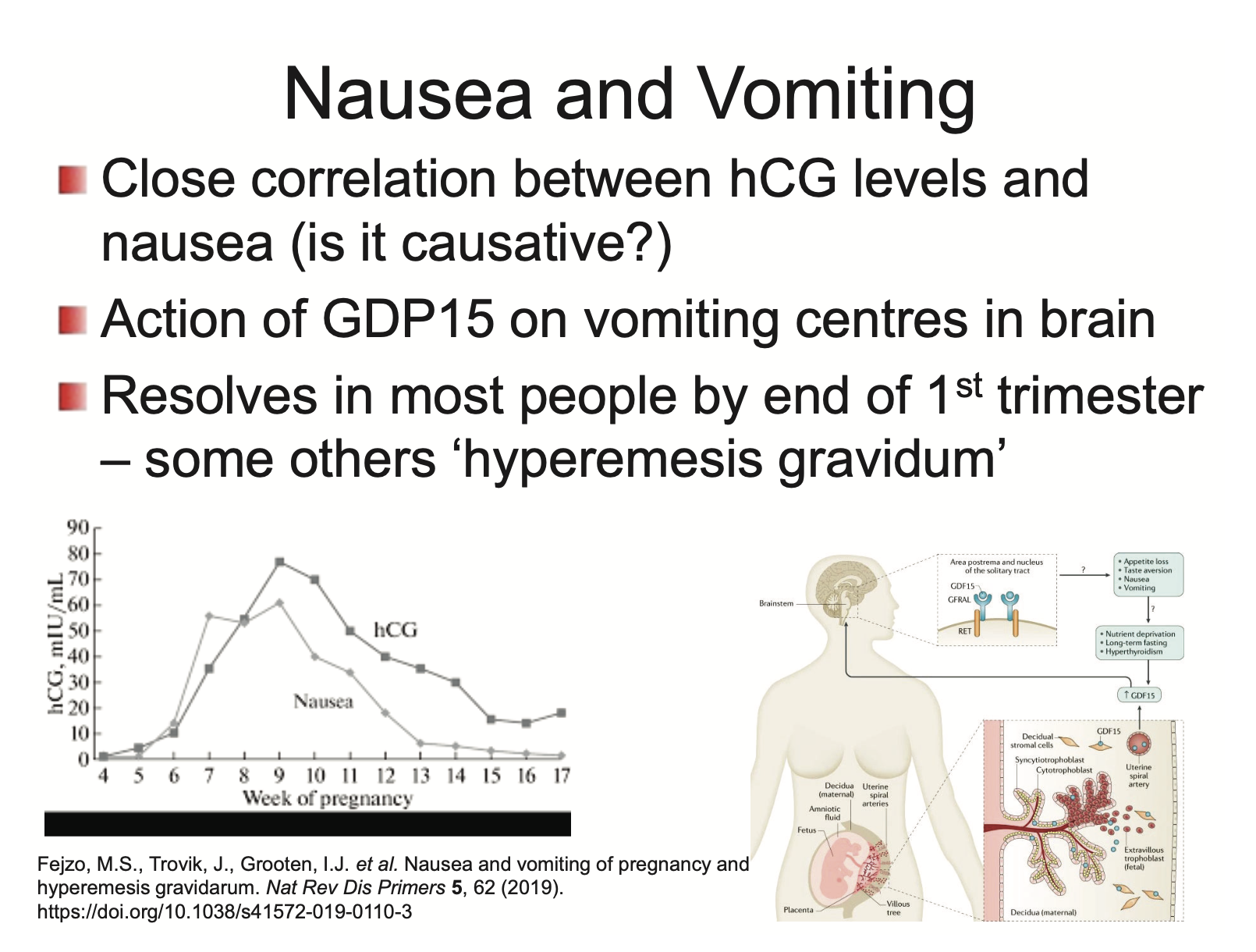
What causes nausea and vomiting in pregnancy?
Action of GDF15 on vomiting centres in brain
resolves in most people by end of 1st trimester
some others have ‘hyperemesis gravidum’
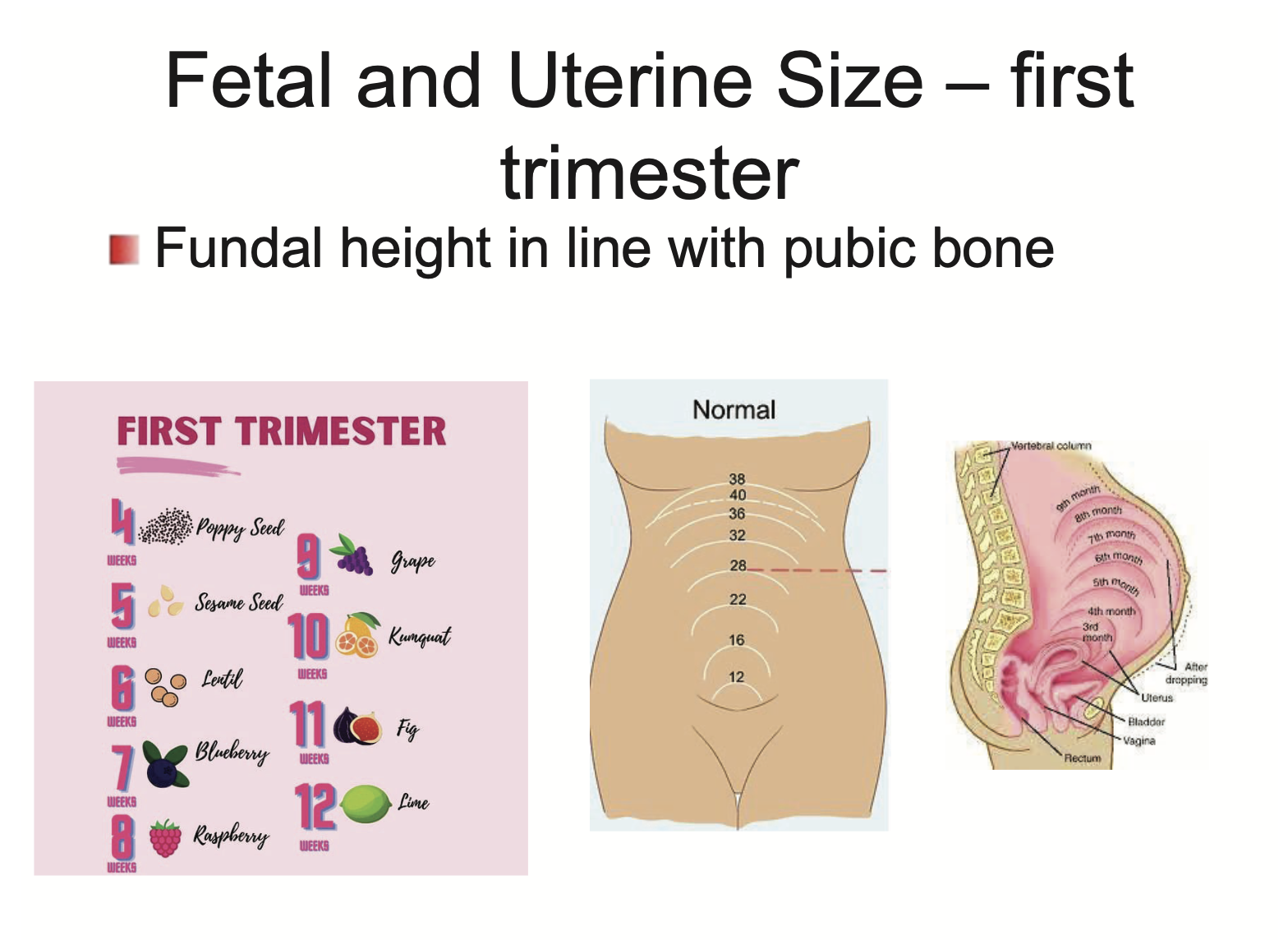
What does foetal and uterine size look like in the first trimester?
Fundal height will be in line with pubic bone
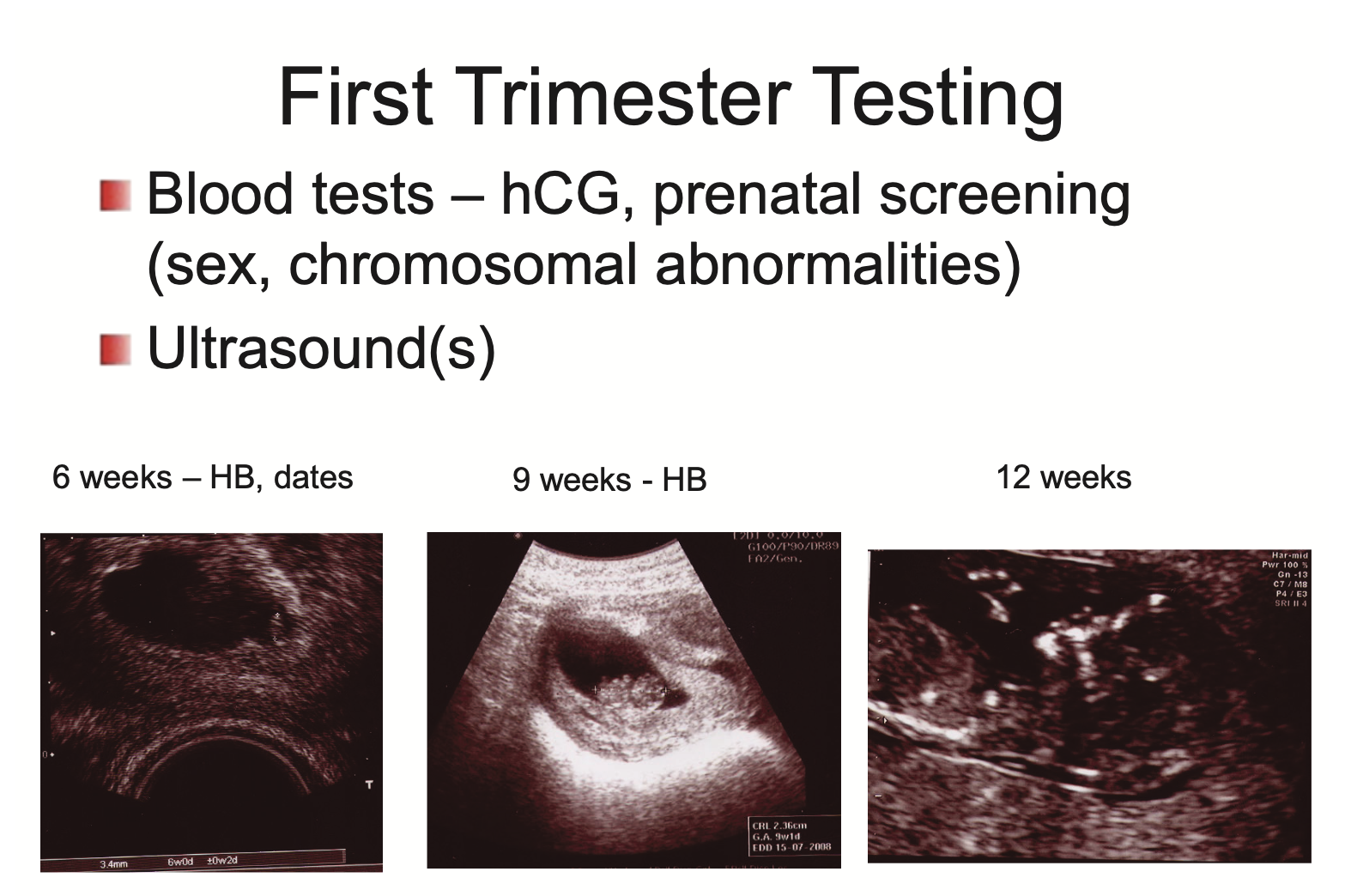
What types of testings can be done in the first trimester (2)?
Blood tests - hCG, prenatal screening (sex, chromosomal abnormalities)
Ultrasound(s)
What happens in the second trimester (5)?
‘Fun trimester’
usually fatigue and morning sickness disappears
growth of foetus and uterus - particularly lower portion
breast development
skin changes: stretching, pigmentation
changes in uterine ligaments (growing): round ligament and uterosacral ligament
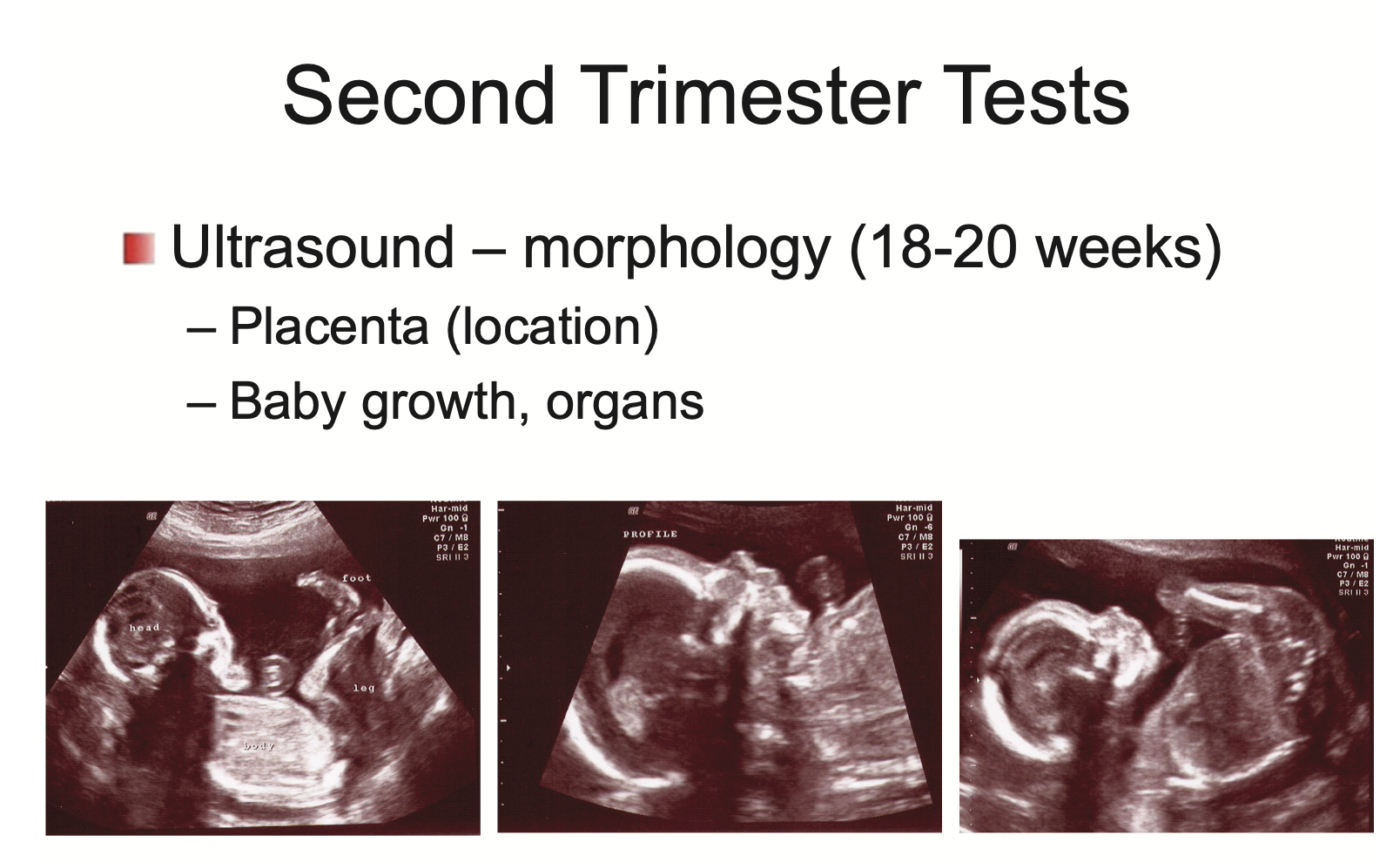
What test(s) are conducted in the second trimester?
Ultrasound - morphology (18-20 weeks)
placenta (location) - not bottom part of placenta grows last
baby growth, organs
What happens in the third trimester (4)?
Rapid growth of foetus (accelerates at 20 weeks, max growth at 28 weeks)
uterus stretches, wall thins
from 70g - 1.1kg
volume from 10mL to 5L
breast development → increase in glandular mass and secretions
production of colostrum
uterus - Braxton hicks ‘practice’ contractions
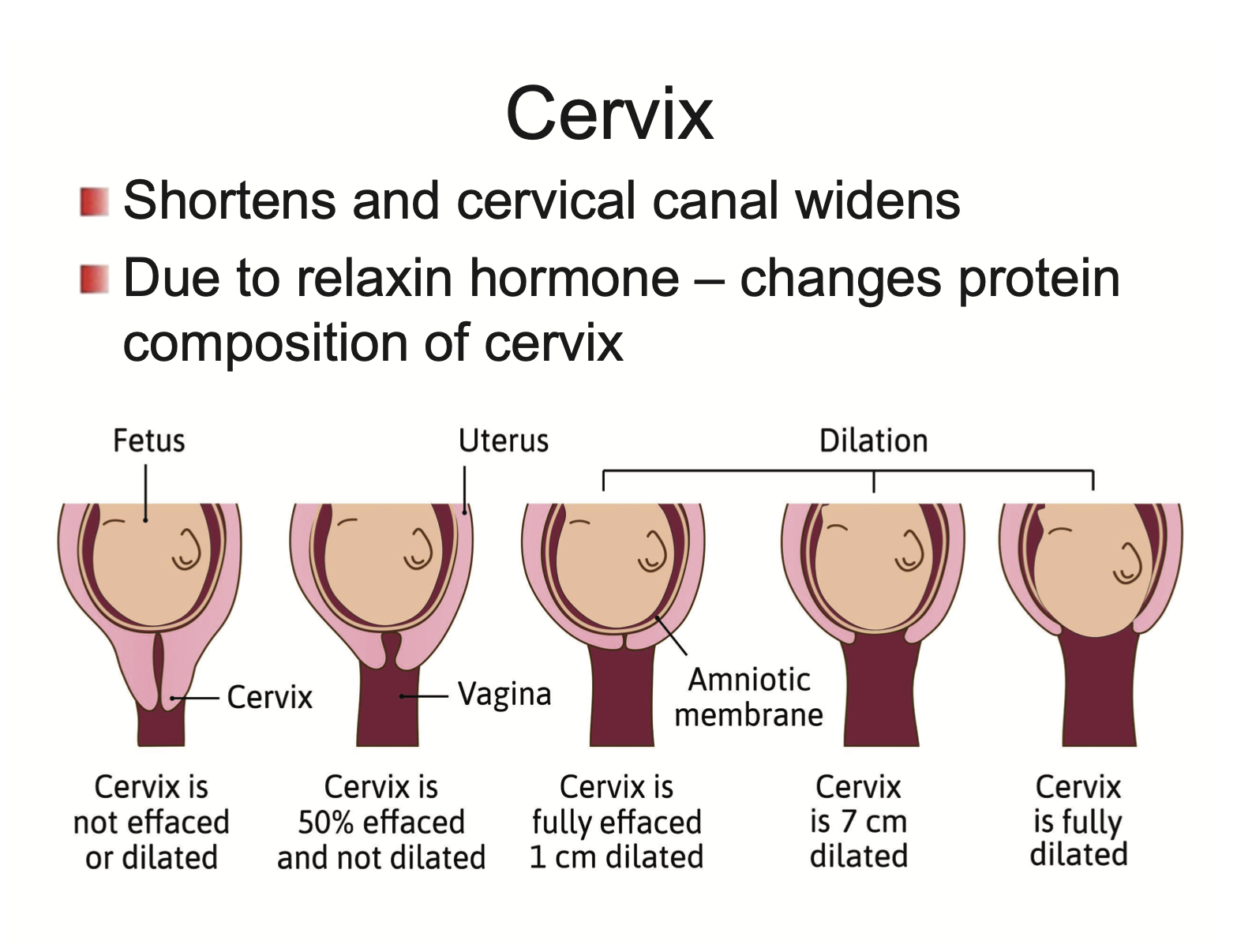
What happens to the cervix during pregancy?
Shortens and cervical canal widens
due to relaxin hormone → changes protein composition of cervix
What does relaxin do?
Relaxes smooth muscle in cervix → shortens cervix and widens cervical canal
has additional effects on muscle and ligaments
symphysis pubis dysfunction: pain during pregnancy
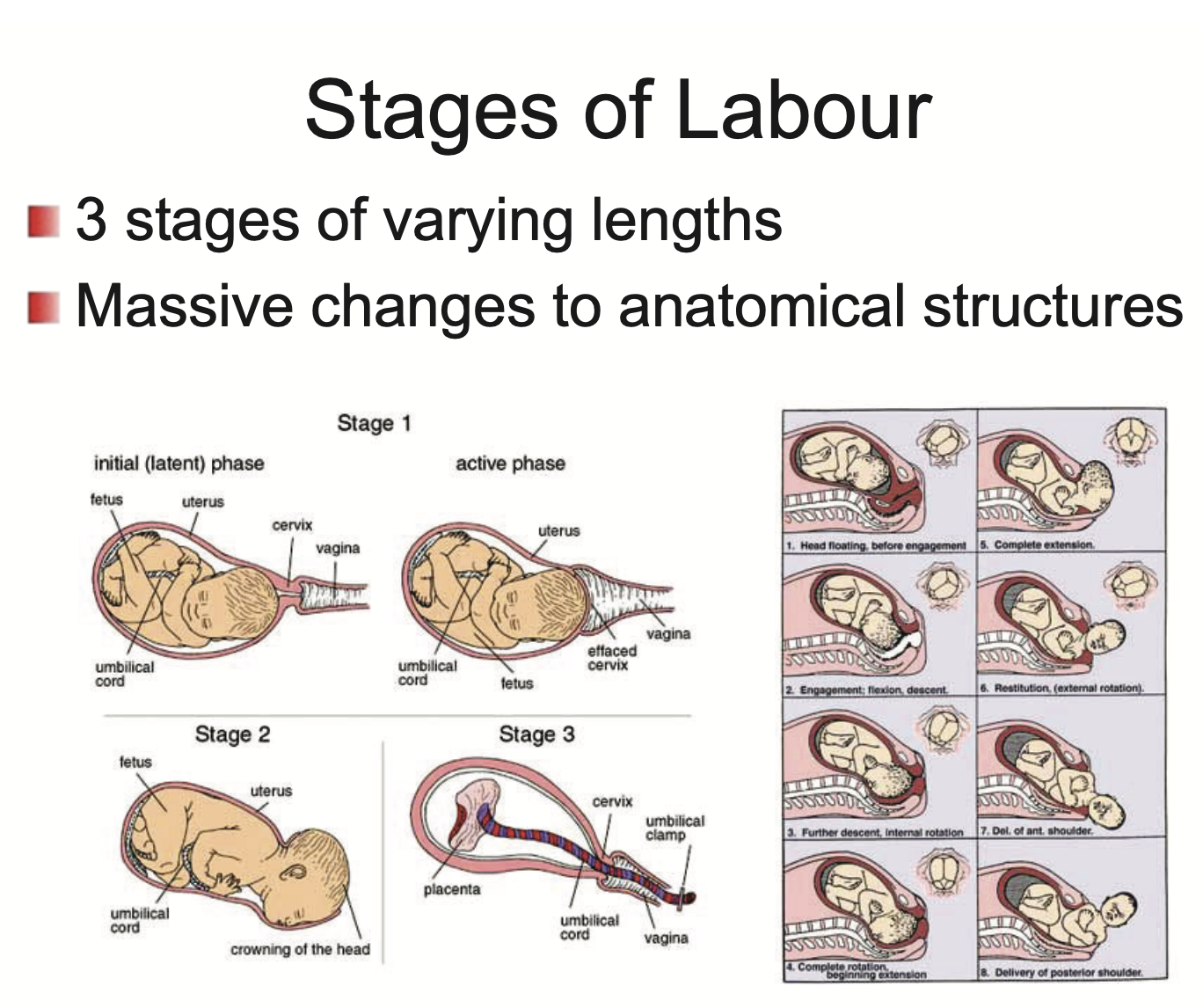
What are the 3 stages of labour?
Cervix dilation
Baby is born
Placenta is born
Describe the hormonal control of labour
Hormonal signals: oestrogen, progesterone, prostaglandins, oxytocin, relaxin
PGs and oxytocin can be used to induce labour
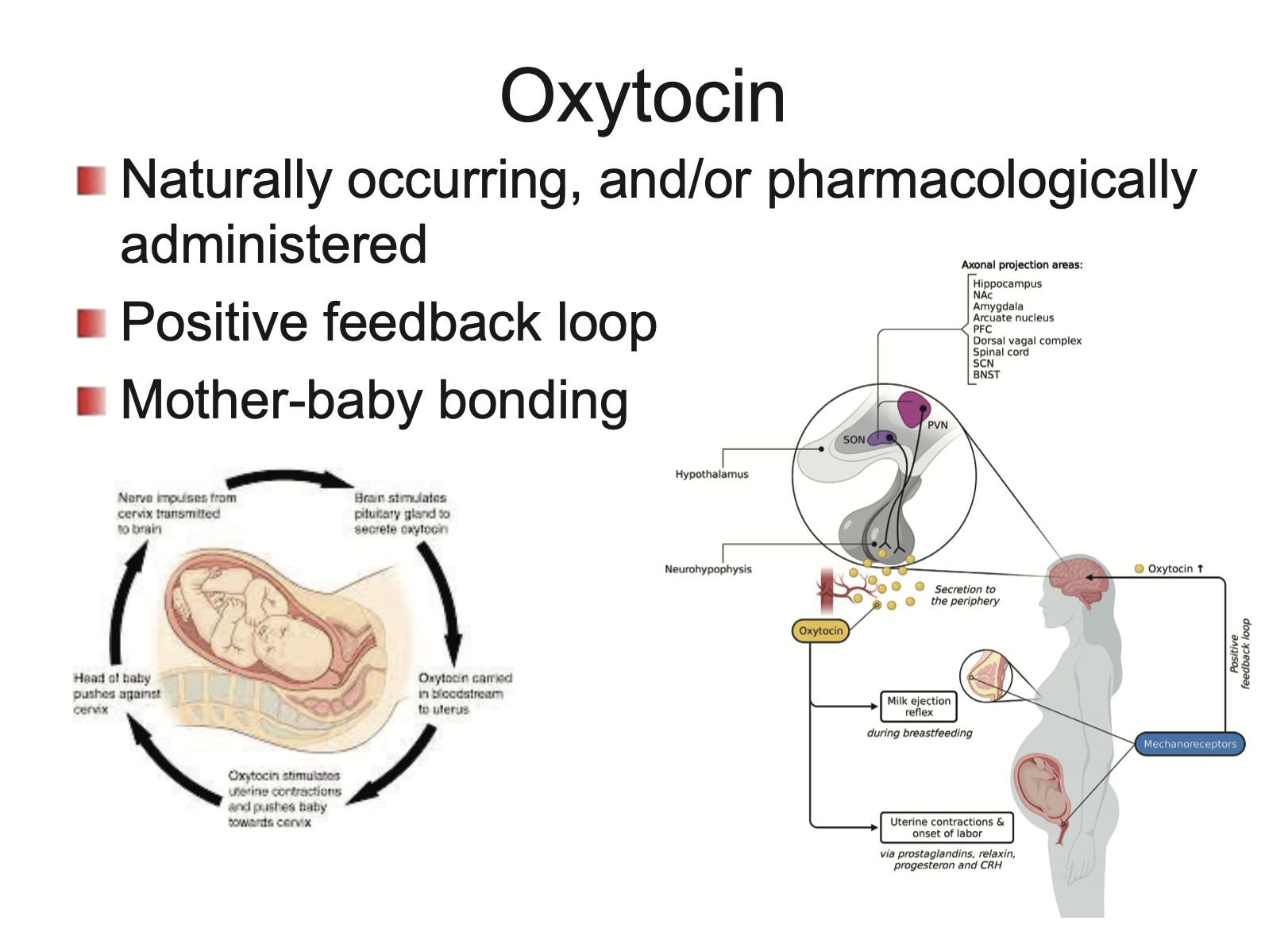
What is oxytocin?
Oxytocin is a hormone
naturally occurring, and/or pharmacologically administered
released through a positive feedback loop
leads to mother-baby bonding
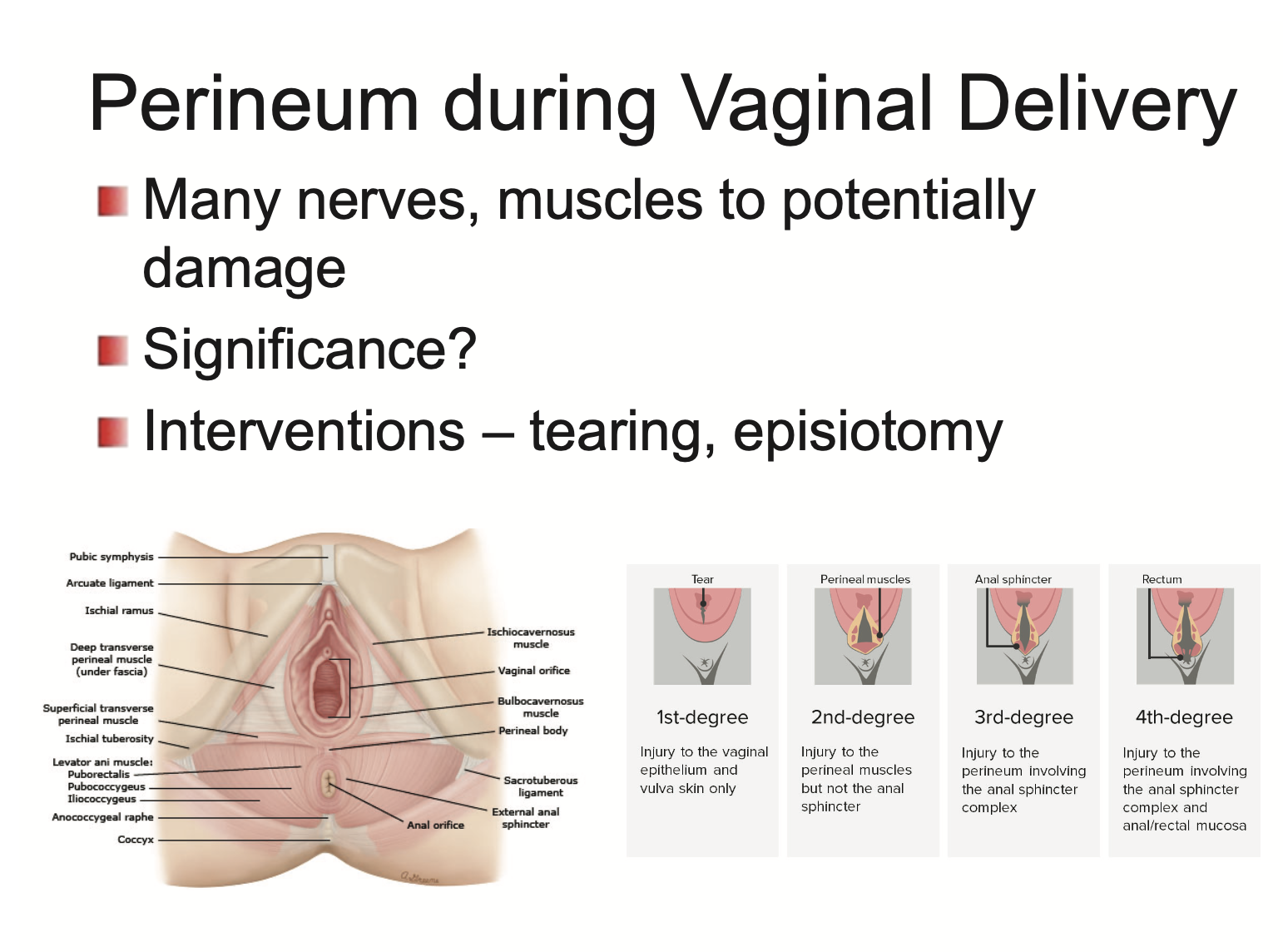
What happens to the perineum during vaginal delivery?
Many nerves and muscles are vulnerable to damage
interventions for tearing → episiotomy (cut sideways)
How is breastfeeding initiated?
Prolactin is suppressed during pregnancy (by oestrogen and progesterone)
After birth, the delivery of the placenta causes a sudden drop in progesterone and oestrogen, removing the inhibition on prolactin.
removal of progesterone → delivery of placenta
prolactin → milk production
oxytocin is released in response to suckling → contraction of cells around glands to expel milk
What happens to the uterus and cervix post-partum?
Uterine involution - but remains larger than pre-pregnancy
Cervical opening is less rounded