P4 - Electric circuits
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
What is static electricity?
Materials rubbing against each other and charging up
What is an ion?
Charged atom
How are electrons transferred?
When materials rub each other
How are electrons transferred between rubbing a cloth and a rod
It transfers the electron from the cloth to the rod, meaning the rod is negative while the cloth is positive
How do two objects start attracting each other?
Two charge objects create a magnetic field, which increases the force pulling objects together
What do the lines on an electric field represent?
The movement of charge
What way do lines point in a charge?
Positive charge point away from an object while negative lines points towards
What way do oppositely charged objects go?
Towards the positive charge
Why does sparks happen?
The field is very strong and pull electrons from air molecules, which hit other air molecules and knock electrons from them, creating the flow of electrons
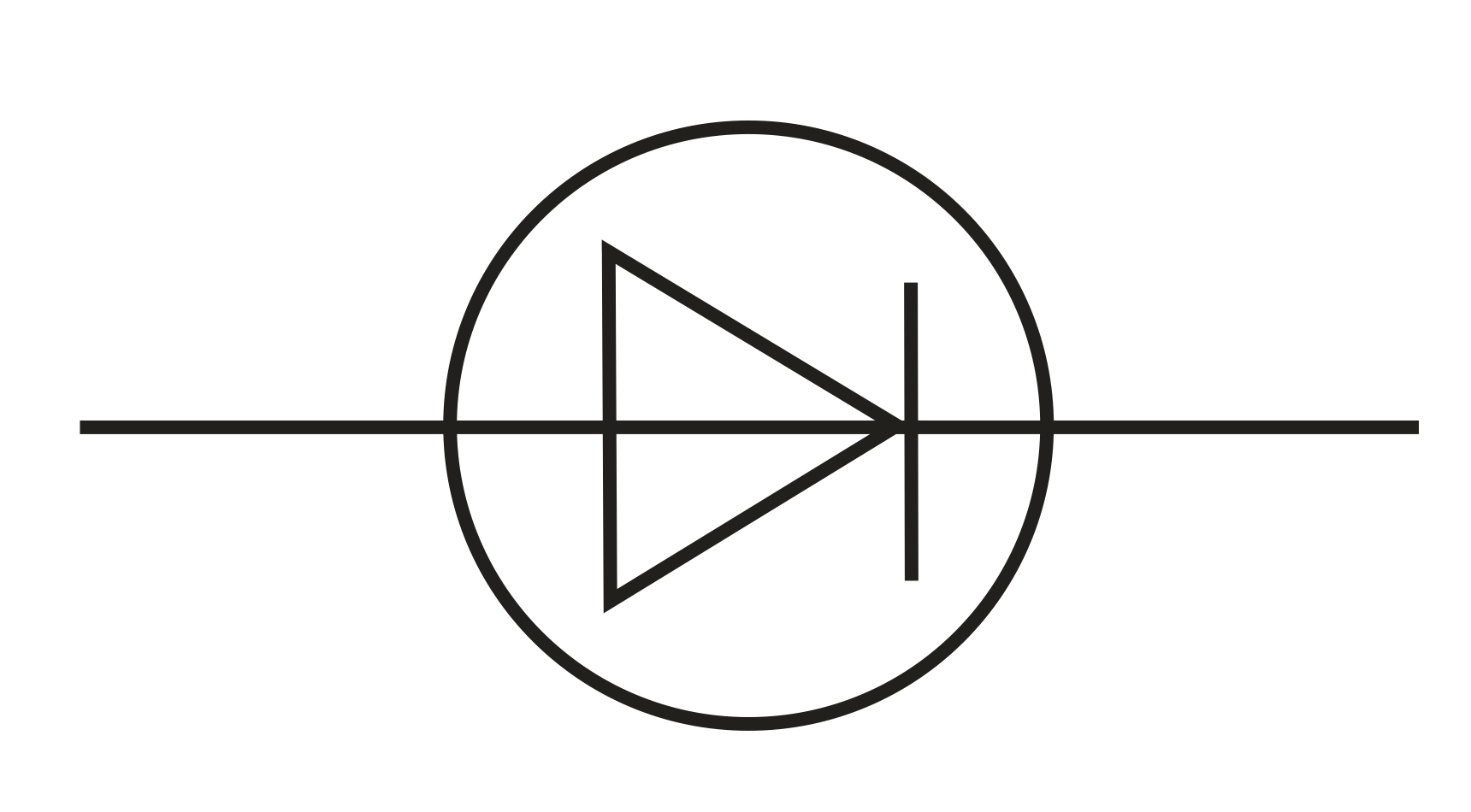
What is a diode?
Allows current through only one way
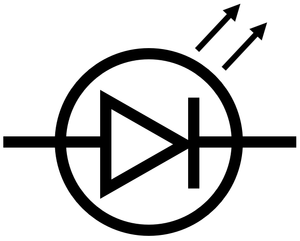
What is a Light emitting Diode (LED)?
Emits light when current passes through it
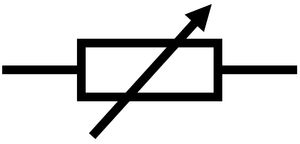
What is a variable resistor?
Allows current to vary
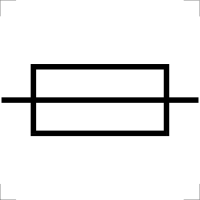
What is a fuse?
Melts and breaks the circuit if too much current goes through
What is a heater?
Transfers energy from electric current to heat the surroundings
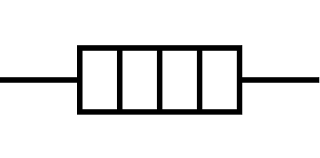
What is a current?
Flow of charge
Why do metals conduct electricity?
Electrons in metals stop positive ions from moving apart
How does current change?
The bigger or smaller the amount of electrons flowing through a charge, the bigger or smaller the current
How does current change in a single-looped circuit?
Current does not change in a single loop current
What is the equation to find charge with current and time?
Charge flow (Q) = Current (I) x time (T)
Coulomb (C) = Amperes (A) x seconds (s)
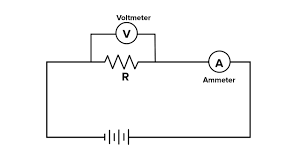
What is an ammeter?
Measures current going through the bulb
Where is the ammeter connected in the circuit?
In series to the component so the current remains the same as the bulb
What does 1 milliamperes (mA) equal to in Amps (A)?
0.001 amps (A)
What does the voltmeter mean?
Measures the potential different (p.d.) across the bulb
What does voltage mean?
Energy transferred to the bulb or work done by each coulomb of charge, measured in V
Where is the voltmeter connected in the circuit?
Parallel to the torch to measure the potential difference across it
What is the diagram of how ammeter and voltmeter should be connected?
What is the formula for potential difference with energy and charge?
P.d = energy transferred/charge
V = E (J)/Q (C, coulombs)
What is resistance?
When electrons have to push past vibrating atoms
What is the formula for resistance?
Resistance = pd/current
R (ohms) = V/I (A)
What happens to current as resistance increases?
The current decreases
What happens to current as pd increases?
Current also increases as they are directly proportional
What is another name for a wire and why?
A wire is also called an ohmic conductor as resistance is constant as current change
What happens to resistance if the current and p.d were negative?
The resistance stays the same
What happens to the line of an IV graph as resistance increases?
The larger the resistance, and steeper the IV graph
Wy do most circuit fails happen?
Too much current flows through the wires
What is an non-ohmic conductor?
When the line curves away from the y-axis, so the current is not directly proportional to p.d and bulb is a non-ohmic conductor
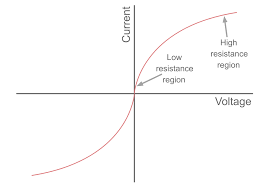
What happens to resistance when temperature increases and why?
Resistance increases as the atoms vibrate more
What is a diode?
Allows current to flow in one direction
What type of conductor is a diode and why?
A diode is a non-ohmic conductor as the line curves towards the y-axis, so current is not proportional to p.d
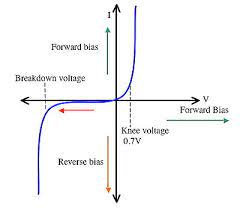
What happens to current and p.d in a diode in the forwards direction in an IV graph?
The line curves to the y-axis, so the current is not directly proportional to p.d
What happens to current in a diode in the reverse direction and what does this mean in terms of resistance?
The current is 0 meaning resistance is higher in reverse direction than forwards direction
What is a Light Emitting diode (LED)?
Diode that emits light when current passes through the forwards direction
What is a thermistor?
Temperature-dependant resistor, where resistance decreases as temperature increases
What is a light dependant resistor (LDR)
Resistance decreases when light increases
What happens to current in a series circuit in general?
The current remains the same across all components as the number of electrons passed per second is the same
What happens to p.d in a series circuit in general?
The p.d, or energy, is shared across the components, meaning the p.d change when the position of the voltmeter changes, and the components have different p.d. However, the sum of p.d remains the same for all components
How is potenetial difference calculated when knowing the p.d of different components?
It would be the sum of all components
What does adding more components/resistors do to p.d in a series circuit?
The p.d is shared meaning the p.d of different components are different
How is the total current calculated in a parallel circuit?
It is the current of the individual resistors
How is the potential difference across a parallel circuit?
It is the same across all components
How do charges flow in a parallel circuit?
Through different branches
What happens to resistance as you add more resistors to a parallel circuit?
Resistance decreases as you add more resistors since the battery supplies the same amount of current to the new path, meaning the current increases. Using the formula we see that the resistance decreases
How do you test resistors in series and parallel circuits?
Test the two resistors in individual circuit
Add them to a series or parallel circuit
In series - the sum for the resistance of the individual circuits should be same as the series circuit
In parallel - the sum for the resistance of the individual circuits should be higher than the parallel circuit
What is the frequency of UK mains supply?
50 Hz
What is the equation of power with resistance and current?
P = I2 * R
A student took the readings: 15.3, 15.8 and 16.
When he took another reading, it ended up being 16.2
Why is this reading more inaccurate?
The fourth reading is a lot further away than others, while the other readings are closer together.
Why is there a shock when a charged person touches metal?
There is a potential difference between the person and the metal
Why are you less likely to build up shock when rubbing against a conductor than an insulator
A conductor allows charge to flow through it easily, meaning when it gains electrons, they simply pass through it and they don’t have a build up of charge so you are less likely to collect electrons. Insulators, on the other hand, cannot let electrons flow through very easily, meaning when they gain electrons it just stays in that spot or you are more likely to gain electrons
How do you know a graph is inversely proportional?
If you get two coordinates and put into an equation y = k/x, k should be the same for both. Get another coordinate to verify that it is true
How would you describe a force of attraction/repulsion?
As a non-contact/electrostatic force
Why can metal wires sometimes not be used to earth an insulator?
The electrons may not flow off the insulators as well
How does a diode not allow current to go the other way?
The diode has high resistance when it flows the other way
A student investigated how the current in a filament lamp varies with the potential difference across the filament lamp.
ammeter in series with filament lamp
• current measured with an ammeter
• voltmeter in parallel with filament lamp
• p.d. measured with a voltmeter
• variable resistor (or variable power pack or variable number of cells) used to vary current in and p.d. across filament lamp
• range of p.d. of 0 to 6 V
• interval of p.d. of 1 V
• reverse connections to power supply to obtain negative values
• take repeat readings and calculate a mean
• discard anomalies
What happens to resistance when the switches in a parallel circuit are closed?
The resistance decreases
What does direct potential difference mean?
The polarity does not change
How does the increase in temperature of resistors affect current and voltage?
The current potential difference would not be directly proportional as the resistor gains temperature
What is zero In an ameter
When the ammeter has not been connected to a circuit