Chemical Changes (paper 1)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What happens when metals react with oxygen?
Metal oxides are produced.
Oxidation reaction
What is an oxidation reaction?
A reaction in which oxygen is gained
What is a reduction reaction?
When oxygen is lost.
How do we measure the reactivity of magnesium,zinc,iron and copper as they don’t react with water at room temperature ?
React them with dilute acids
Don’t react group 1 metals with dilute acids as it’ll react dangerously fast.
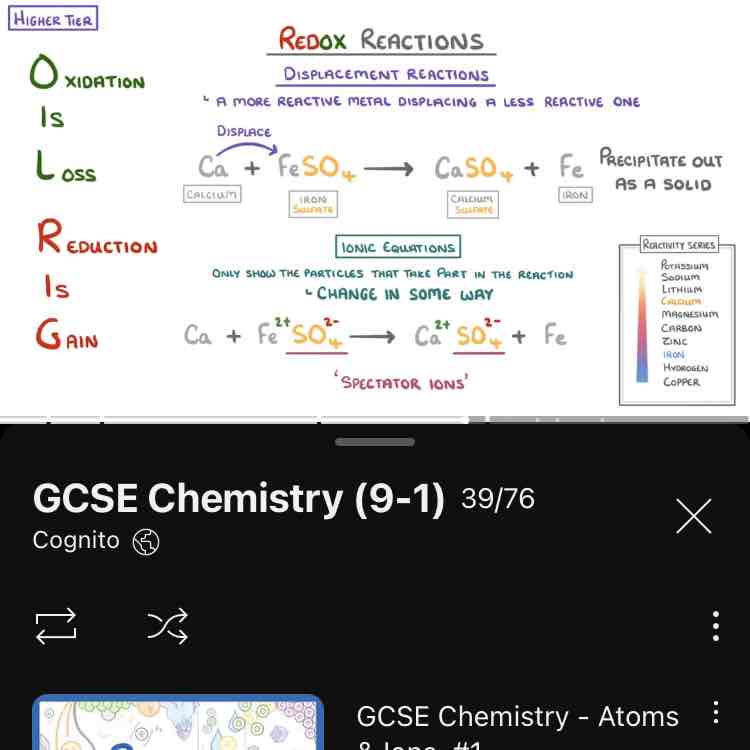
The reactivity series
Potassium
Sodium
Lithium
Calcium
Magnesium
Carbon
Zinc
Iron
Hydrogen
Copper
Silver
Gold
What determines how rapidly a metal reacts?
When metals react, they lose electrons and form a positive ion.
E.g. K→ K+ +e-
The reactivity of a metal depends on its ability to lose electrons and form a positive ions.
Metals at the top of the series can lose electrons and form a positive ion more easily than metals at the bottom.
How does potassium react with water?
burns with a lilac flame
effervescence because of production of hydrogen
production of salt
How does sodium react with water?
burns with a flame
effervescence because of production of hydrogen
production of salt
sodium disappears- dissolves
How does lithium react with water?
burns with a flame
effervescence because of production of hydrogen
production of salt
lithium eventually disappears
How does calcium react with water?
effervescence because of production of hydrogen
production of salt
reacts slower than g1 tho
How does magnesium react with water?
steam
some fizzing
quite slow
How does zinc react with water?
How does iron react with water?
How does copper react with water?
How does potassium react with dilute acid?
How does sodium react with dilute acid?
How does lithium react with dilute acid?
How does calcium react with dilute acid?
How does magnesium react with dilute acid?
How does zinc react with dilute acid?
How does iron react with dilute acid?
How does copper react with dilute acid?
(Room temp)
How are unreactive metals found?
As the metal (by) itself
An example of this is gold
Contrastingly, iron and copper react with oxygen to form compounds.
How can we extract the metal that we want in a metal compound?
Get a more reactive element in the reactivity series
However because most of these are expensive we mainly use carbon as it’s cheap.
Oxidation and reduction in terms of electrons
Oxidation is the loss of electrons
Reduction is the loss of electrons
OIL RIG
e.g. Mg→ Mg 2+ + 2e-
This is a half equation showing magnesium has been oxidised.
e.g. S+2e- → S2-
Sulfur has been reduced
Formula of hydrochloric acid
HCl (aq)
(aq) means aqueous solution- dissolved in water.
In aqueous solutions, acids produce H+ ions
Example:
H2SO4 (aq)→ 2H+ (aq) + SO4 2- (aq)
Formula of sulfuric acid
H2SO4 (aq)
Nitric acid
HNO3 (aq)
What is a base?
Chemicals which can neutralise acids, producing a salt and water.
Bases are usually metal oxides or metal hydroxide.
Examples of bases
Copper oxide
Iron (III) hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide is soluble in water, making it an alkali and a base whereas the other two are only bases because they aren’t soluble in water.
What are alkalis?
Bases which are soluble in water.
In aqueous solutions, alkalis produce hydroxide ions (OH-)
Example: NaOH (aq) → Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq)
What do acids have a pH between?
0-6
What are solutions with a pH of 7?
Neutral
What do alkaline solutions have a pH between?
8-14
How can we determine the pH of a solution?
Using a pH probe
Universal indicator
What does a pH probe do?
Determines the pH of a solution electronically.
What does universal indicator do?
Changes colour depending on whether a solution is acid alkali or neutral.
Deceive colours on the pH scale
Red= very acidic
Green= neutral
Very purple= alkaline
Neutralisation reaction between acid and alkali?
Acids produce H+
Alkalis produce OH-
H+(aq) +OH- (aq)→ H2O (l)
When we react an acid with an alkali the hydrogen ions react with the hydroxide ions to produce water (which is neutral).
What do all acids contain?
Hydrogen
Which metals can this place hydrogen from acids?
Potassium to iron
This is because they’re more reactive
What is produced when acids react with metals?
Salt and hydrogen gas
How do we know which salt we’ll produce?
Depends on the acid and metal
What’s the ending of the salt produced when hydrochloric acid reacts with a metal?
Chloride
What’s the ending of the salt produced when sulfuric acid reacts with a metal?
Sulphate
What do acids produce in aqueous solutions?
Hydrogen ions
H+
2HCl + Mg → MgCl2 + H2
Mg → Mg 2+ +2e-
It has been oxidised
2H+ +2e- → H2
It’s been reduced as it’s gaining electrons
This is a redox reaction
What is a redox reaction?
A reaction in which both oxidation and reduction is happening.
Redox reaction
Ca + FeSO4 → CaSO4 + Fe
Write with charges
Form ionic equation.
Get rid of spectator ion from ionic equation.
Form half equation and see what’s been oxidised and what’s been reduced
When an acid is reacted with either a base or an alkali, what is produced?
A salt and water
What do salts contain?
A positive ion which comes from the base or alkali
Salt also contains negative ion which comes from the acid.
Metal carbonates
Sodium carbonate Na2CO3
Calcium carbonate CaCO3
Potassium carbonate K2CO3
When acids react with a metal carbonate, what is made?
Salt, water and carbon dioxide
E.g.
Hydrochloric acid + Sodium Carbonate→ Sodium Chloride + water + carbon dioxide
Required practical: Making soluble salts
Get equipment: beaker, gauze, tripod, heatproof mat and Bunsen burner.
Gently heat up 20 cm³ of sulfuric acid until almost boiling.
Use a spatula to add small amounts of copper oxide to the acid and then stir the solution with a glass rod.
The copper oxide will react and dissolve in the acid to form a blue solution.
Then add excess copper oxide (until there’s remaining unreacted powder in the solution) to solution in order to ensure that all of the sulfuric acid has reacted (to prevent it from contaminating the salt).
Get filter funnel and filter paper so you can carry out filtration in order to remove the unreacted copper oxide.
Then to get the salt from the solution, put the solution into an evaporating dish and heat it gently till half of the water has evaporated from the salt.
Then leave for 24 hours in a cool place so it can crystalise to form crystals- if you evaporate all the water immediately then a white powdered salt will be formed.
What do acid molecules do in aqueous solutions?
They ionise and release H+
Strong and Weak acids
Strong acids fully ionise in aqueous solutions, most or all of the acid molecules release their H+ ions.
arrows go in one direction only showing that the acid has fully ionised
Weak acids partially ionise in aqueous solutions.
arrows go in both directions, showing it’s a reversible reaction so not all of the acid molecules have ionised (only some).
Examples of strong acids
HCl
H2SO4
HNO3
Examples of weak acids
Carbonic acid
Ethanoic acid- vinegar
Citric acid
The pH scale
Strong acids have a lower pH then weak acids for a given concentration.
As the pH scale decreases by one unit, the concentration of H+ ions increases by 10 times, meaning that it’s 10 times more acidic.
What do H+ ions determine?
How strong an acid is
Dilute and concentrated acids
This is different from the strength of the acid.
Dilute acid will have fewer acid molecules in a given volume than a concentrated acid even if the strength of the acid is the same.
Required Practical: Titrations
Use a volumetric pipette to transfer 25 cm³ of sodium hydroxide solution into a conical flask.
Transfer the alkali onto a white tile- this is so the colour change can be observed more clearly.
Add a few drops of indicator such as methyl orange or phenolphthalein to the conical flask.
Now fill a burette with sulfuric acid and record the starting volume.
Add acid to the alkali whilst swirling the conical flask to ensure that the acid and the alkali are mixing.
To do this accurately add the acid drop by drop when a colour change is seen.
Do this until the solution is neutral.
Read the volume of acid added from the burette at the bottom of the meniscus making sure your eyes is level with the surface of the liquid.
Repeat the process until you get at least two concordant results.
Use the concordant results to calculate an average titre.
Use the titre volume to calculate the unknown concentration of the acid.
This is for concentration of acid- switch the acid and alkali if you want concentration of alkali.
What are titrations used for?
To calculate the concentration of either an unknown alkali or acid when we know the volume and concentration of the other