Davies - Pulse-Echo Instrumentation
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
180 Terms
In these images, what technique is used to fill in the empty data between the scan lines?
A. apodization
B. Interpolation
C. dynamic receive
D. subdicing
E. dynamic damping
Interpolation
You have decreased the image sector width. Which of the following will most likely change as a result of this adjustment?
A. frame rate
B. axial resolution
C. elevational resolution
D. dynamic range
E. bandwidth
Frame rate
An M-mode display is most commonly used for what type of ultrasound image?
A. small parts
B. abdominal
C. cardiac
D. vascular
E. opthalmologic
Cardiac
When you adjust the output power control, you affect the following system component:
A: Pulser
B: Beam former
C: Scan converter
D: Memory
E: Receiver
Pulser
When you select compound imaging, which artifact is less likely to be observed?
A: Refraction
B: Shadowing
C: Enhancement
D: Acoustic speckle
E: All of the above
All of the above
While scanning a curved structure, you notice shadowing at the lateral edges of the structure. What is required for this artifact to occur?
A. different media propagation speeds
B. perpendicular incidence
C. transmit frequency exceeding 5MHz
D. fluid-filled structure in the path of the beam
E. phased array transducer
Different media propagation speeds
What system control do you adjust to equalize the differences in echo amplitudes received from similar structures situated at different depths?
A. dynamic range or compression
B. rectification
C. TGC
D. PRF
E. rejection
TGC
In this image of an artery there is a calcification with a dark vertical band extending beyond it. Which explanation best describes the etiology of the dark bend?
A. propagation speed error at the vessel wall interface
B. reduction in signal amplitude in tissue distal to a highly attenuating or reflecting object
C. refraction due to oblique incidence at the plaque interface
D. range ambiguity due to high PRF setting
E. comet tail artifact due to calcification in plaque
Reduction in signal amplitude in tissue distal to a highly attenuating or reflecting object
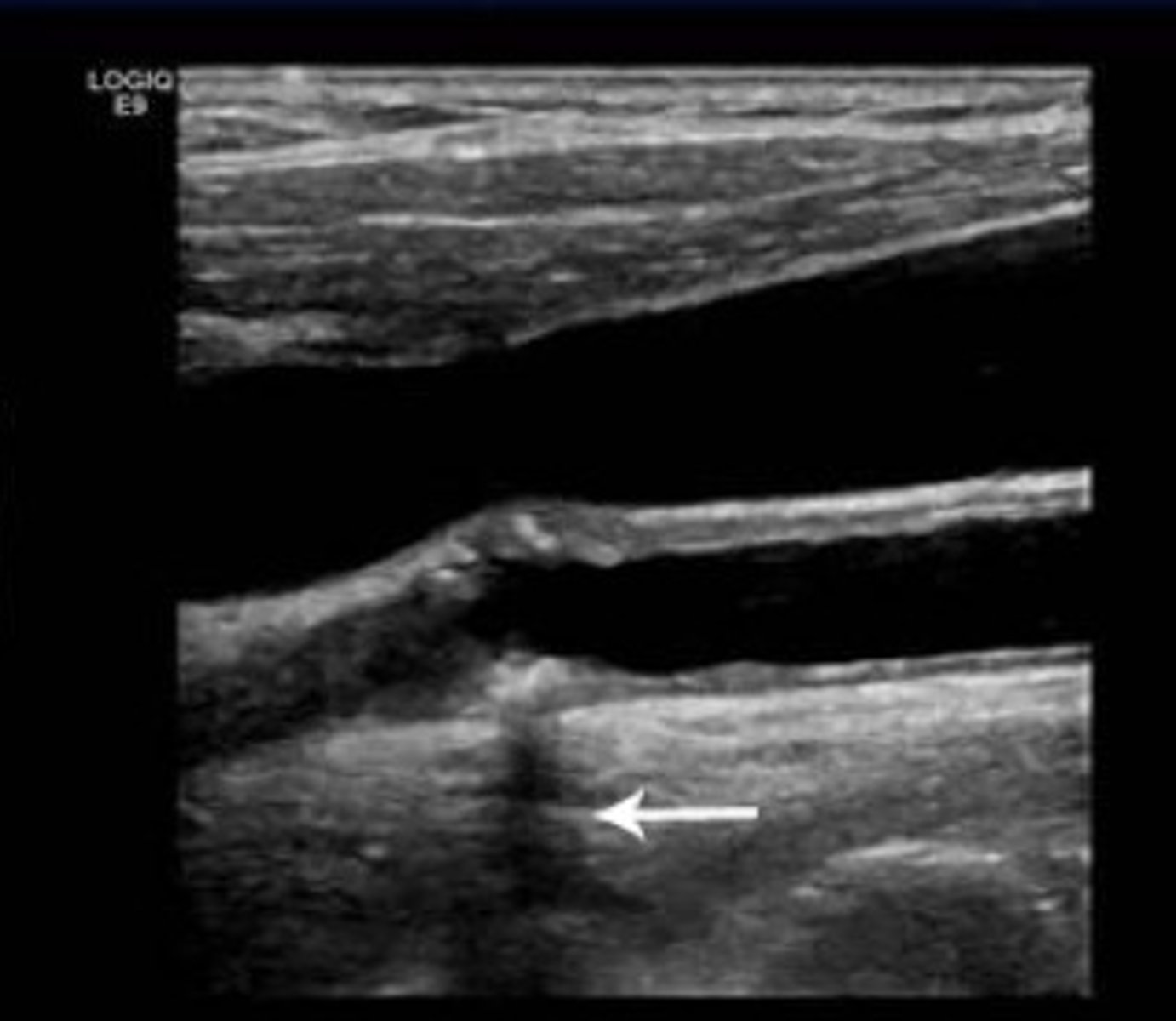
Which of the following does NOT affect the time required to create one image frame?
A. # of transmit focal zones
B. # of acoustic scan lines
C. image depth setting
D. speed of sound in tissue
E. transducer aperture
transducer aperture
What control should you adjust to better compensate for the attenuation of sound as it propagates through tissue?
A. dynamic range
B. TGC
C. acoustic power output
D. rejection
E. focusing
TGC
This image was displayed with a linear array transducer that employs phasing to steer the beam. What artifact do the arrows point to?
A. grating lobes
B. reverberation
C. mirror-imaging
D. slice-thickness
E. multipath reflections
grating lobes
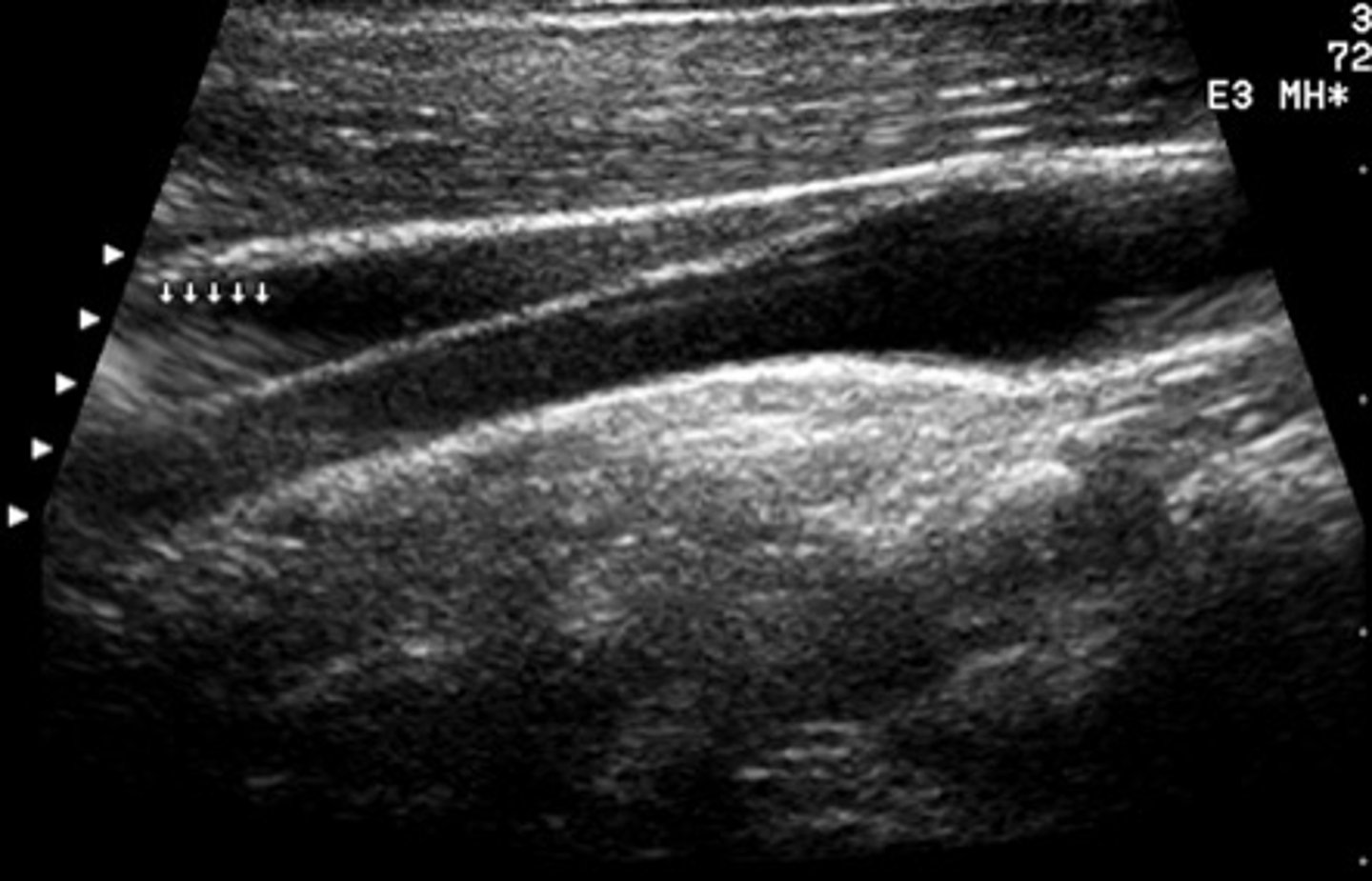
Which is an assumption of sonographic imaging that determines how detected echoes are mapped in the image?
A: Sound waves travel along curved paths
B: Velocity is a constant 333 m/s
C: Echoes originate from the most recently transmitted pulse
D: Large structures yield a high brightness level on the display
E: Media with varying propagation speeds alter the travel time of the sound pulse
Echoes originate from the most recently transmitted pulse
In ultrasound systems, the range equation is used to determine which of the following?
A. reflector amplitude
B. reflector frequency
C. reflector direction
D. reflector depth
E. reflector size
reflector depth (d=1/2ct)
The term duty factor is defined as:
A. the fraction of time the transducer is actively transmitting sound
B. the fraction of time the transducer is actively receiving sound
C. the fraction of time between the transmitted and received sound pulse
D. the fraction of time between transmitted sound pulses
E. the fraction of time required for round-trip travel of a sound pulse to one cm in tissue
the fraction of time the transducer is actively transmitting sound
In order for distance measurements to be accurate in an US tissue phantom, the phantom sound propagation speed must be
A. 13 ms/cm
B. 1.54 m/s
C. 1540 m/s
D. half the speed of sound in tissue
E. twice the speed of sound in soft tissue
1540 m/s
What three colors are used on a color monitor to produce the range of available colors?
A. red, purple, yellow
B. yellow, green, blue
C. blue, yellow, red
D. red, green, blue
E. blue, white, red
red, green, blue
What system component is responsible for transmit focusing?
A. receiver
B. monitor
C. beam former
D. preprocessing
E. system clock
beam former
All of the following are limitations of M-mode scanning EXCEPT?
A. information is obtained along only one line of sight
B. motion lateral to the transducer is not displayed
C. motion axial to the transducer is not displayed
D. the two-dimensional shape of a structure is not shown
E. all of the above are limitations of M-mode
Motion axial to the transducer is not displayed
Where are the images stored in the ultrasound system?
A. pulser
B. receiver
C. beam former
D. display
E. scan converter
scan converter
a digital scan converter is another name for what system component?
A. pulser
B. receiver
C. image memory
D. analog-to-digital converter
E. beam former
image memory
while performing an obstetric exam, you wish to increase the frame rate to evaluate the fetal heart. What should you do?
A. increase scan line denisty
B. increase the number of focal zones
C. decrease sector width
D. decrease the system PRF
E. all of the above
decrease the sector width
Which display mode may be used to calculate distance measurements?
A. A-mode
B. B-mode
C. M-mode
D. B and C only
E. A, B, and C
A, B, and C
In the scan converter, interpolation is performed to:
A: Amplify the reflected signal in comparison to the background noise
B: Decrease the dynamic range to a level that can be handled by the monitor
C: Amplify weak echo signals from deep structures to compensate for beam attenuation
D: Fill in the empty pixels that occur between scan lines
E: Increase the number of shades of gray in the resultant image
fill in the empty pixels that occur between the acoustic scan lines
When you select one focal zone, how many pulse/listen cycles are required for each acoustic scan line in one image frame?
A: One
B: Two
C: Four
D: Eight
E: Sixteen
one
Which technology would be most helpful to obtain accurate anatomic volume measurements?
A. 2D imaging
B. 3D imaging
C. Color Doppler imaging
D. harmonic imaging
E. compound imaging
3D imaging
What system function is limited by the speed of sound in tissue?
A. demodulation
B. PRF
C. voltage amplitude
D. rectification
E. TGC
PRF
The elapsed time between the transmitted pulse and the detected echo is 26 ms. How far is the interface from the transducer?
A. 1 cm
B. 2 cm
C. 3 cm
D. 4 cm
E. 5 cm
2 cm
Which of the following artifacts commonly results in echoes filling the lumina of small vessels?
A. refraction
B. partial volume
C. mirror image
D. range ambiguity
E. multipath reflections
partial volume
What is the purpose of the pre-amplification of the incoming signal that occurs in the transducer assembly?
A. to decrease the dynamic range of the signal
B. to increase echo voltages before noise is induced through the cable
C. to reduce sensitivity to side lobes
D. to reduce acoustic impedance mismatch between the tissue and the transducer
E. to compensate for attenuation of the beam with depth
to increase echo voltages before noise is induced through the cable
Which control would you adjust to alter the dynamic range of the displayed echo
A. compression
B. transmit power
C. scanning depth
D. TGC
E. focusing
compression
Which of the following will result in aliasing of the Doppler frequency shift using CW Doppler?
A. PRF 10 kHz, frequency shift 4 kHz
B. PRF 12 kHz, frequency shift 8 kHz
C. PRF 5 kHz, frequency shift 2.3 kHz
D. PRF 8 kHz, frequency shift 5 kHz
E. none of the above
none of the above
What is the advantage of using write-zoom instead of read-zoom magnification?
A. write zoom provides a higher frame rate than read zoom
B. write zoom allows you to select a location in the image, whereas read zoom must be applied to only the center of the image
C. write zoom reduced the display of electronic noise and side lobes because it is performed in the memory component of the instrument
D. write zoom provides greater dynamic range than read zoom
E. write zoom provides better spatial resolution than read zoom
write zoom provides a better spatial resolution than read zoom
What receiver function is responsible for decreasing the difference between the smallest and largest received signal amplitudes?
A. amplification
B. compensation
C. compression
D. demodulation
E. rejection
compression
A group of 8 bits is called?
A. binary
B. kilobyte
C. pixel
D. byte
E. matrix
byte
Which function of the receiver converts electric signals from radiofrequency to video form?
A. amplifiication
B. compensation
C. compression
D. demodulation
E. rejection
demodulation
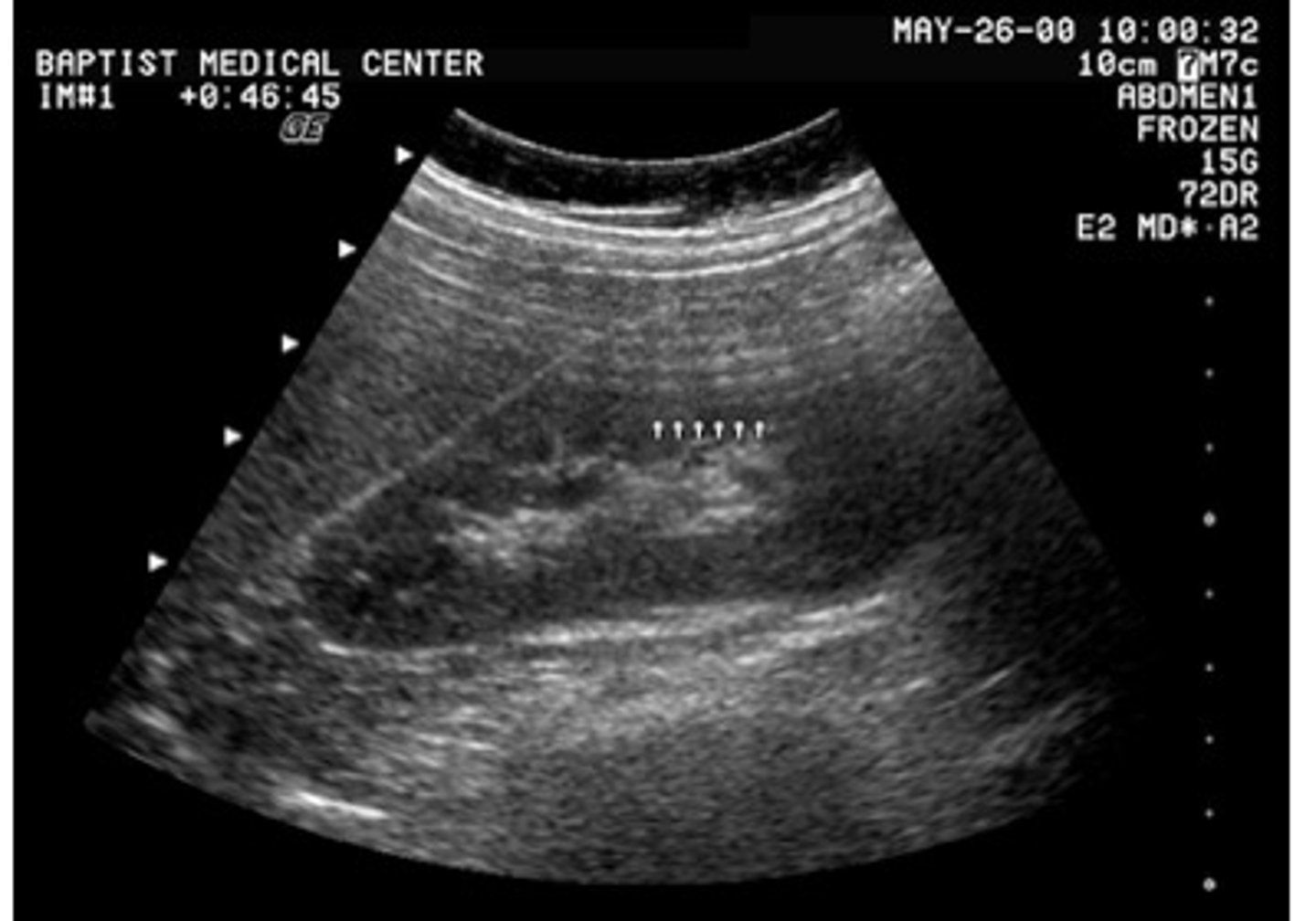
What is the source of the echoes depicted in the image of the kidney?
A. side lobes
B. grating lobes
C. refraction
D. reverberation
E. multipath reflections
reverberation
Which term below most correctly describes this Doppler waveform?
A. aliasing
B. spectral mirroring
C. spectral broadening due to sample volume size
D. reverberation
E. bidirectional flow
spectral mirroring
Using the modality worksheet has the advantage of
A. avoiding the need to type patient information
B. reducing patient information error
C. speeding up patient preparation time
D. easily confirming patient information
E. all of the above
all of the above
What effect will you detect in the image if you increase the threshold control?
A: Increased image brightness
B: Decreased image brightness
C: Decreased appearance of weak echo signals
D: Increased appearance of strong echo signals
E: Decreased appearance of strong echo signals
decreased appearance of weak echo signals (threshold is another name for reject control - reduces the display of weak echoes)
You may observe a mirror-image artifact with which imaging mode?
A. B-mode
B. spectral doppler
C. color doppler
D. power doppler
E. all of the above
all of the above
What system component determines the PRF?
A. pulser
B. receiver
C. memory
D. display
E. scan converter
pulser
The M in M-mode stands for?
A. motion
B. magnetic
C. megahertz
D. manual
E. maximum
motion
Which of the following helps to improve the elevational resolution in a B-mode image?
A. increased transmit power
B. increased bandwidth
C. focusing with an acoustic lens
D. increased dynamic range
E. beam steering
focusing with an acoustic lens
How many lines of sight are sampled and displayed on the monitor in A-mode?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 10
D. 256
E. 525
1
Which of the following would be most helpful to enhance the contrast difference between tissues having subtle variations in echogenicity?
A. decreasing the acoustic power output
B. decreasing the scan line density
C. performing a read-zoom over the area of interest
D. changing the gray-scale map assignment
E. increasing the overall receiver gain
changing the gray-scale map assignment
electronic noise is reduced in the ultrasound system by this method
A. demodulation
B. compensation
C. rectification
D. amplification
E. rejection
rejection
Which of the following best described M-mode
A. presentation of reflector amplitudes along multiple lines of sight
B. two-dimensional gray-scale image
C. movement of a single structure along multiple lines of sight
D. depth of reflectors along a single line of sight vs. time
E. frequency shift of moving reflectors along a single line of sight
depth of reflectors along a single line of sight vs. time
While scanning a curved structure, you notice at the lateral edges of the structure. What artifact is this?
A. grating lobes
B. comet-tail
C. acoustic speckle
D. ring-down
E. refraction
refraction
What is meant by thee term 4D imaging in sonography?
A. 3D imaging with the addition of time
B. 3D imaging with rendering
C. 3D imaging with transparent views
D. 3D imaging with tomographic views
E. 3D imaging with rotational movie
3D imaging with the addition of time
What artifact might you see with an array transducer due to energy that propagates from the transducer in a direction different from the primary beam?
A: Grating lobe
B: Mirror image
C: Reverberation
D: Range ambiguity
E: Acoustic enhancement
grating lobes
which of the following ultrasound examinations would require the highest frame rate?
A. small parts
B. abdominal
C. pelvic
D. vascular
E. cardiac
cardiac
the number of images displayed per second in real-time imaging is termed the
A. PRF
B. PRP
C. frame rate
D. pulse duration
E. pulse length
frame rate
a type of sonographic imaging that transmits two pulses of opposite phase in rapid succession so they can be cancelled out upon reception is termed?
A. pulse inversion harmonics
B. compound imaging
C. speckle reduction imaging
D. tomographic imaging
E. panoramic imaging
pulse inversion harmonics
digital-to-analog conversion of the US signal must occur at what part of the imaging process?
A. between the transducer and the receiver
B. between the beam former and the transducer
C. between the receiver and the scan converter
D. between the scan converter and the display
E. digital-to-analog conversion does not occur in the US system
between the scan converter and the display
What component of the US system converts the electric energy provided by the pulser into acoustic pulses transmitted into the patient?
A. receiver
B. scan converter
C. memory
D. display
E. transducer
transducer
You have increased the output power by 10 dB. The signal intensity has:
A: Doubled
B: Tripled
C: Quadrupled
D: Increased by a factor of 10
E: Increased by a factor of 100
increased by a factor of 10
You made changes to the following controls during a sonogram. Which adjustment increased the duty factor?
A. increasing receiver gain
B. increasing output power
C. increasing PRF
D. increasing scanning time
E. increasing TGC
PRF (duty factor is the percentage of time that the US is being transmitted)
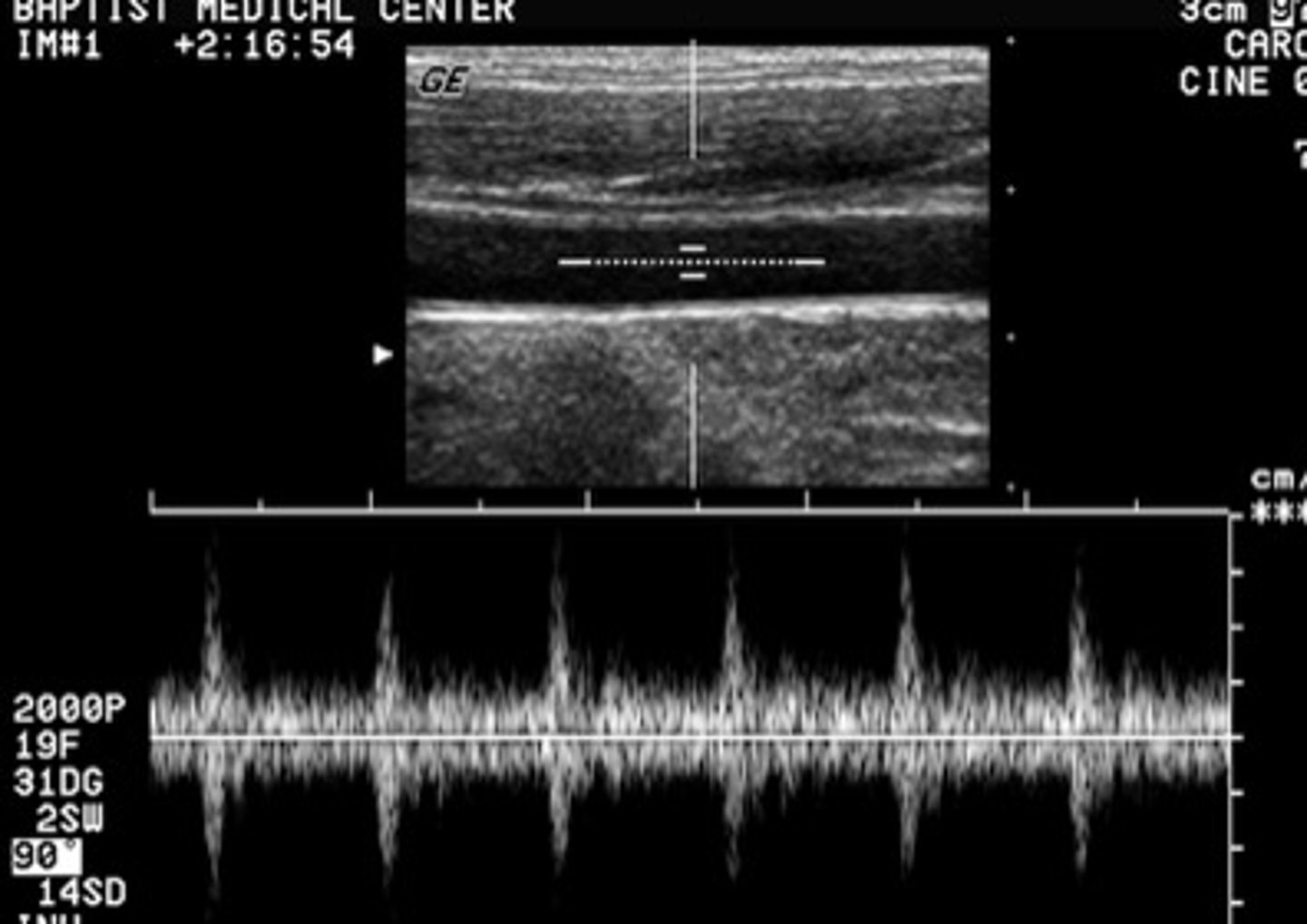
In this image, the letter B is demonstrating what type of resolution?
A. axial
B. lateral
C. elevational
D. contrast
E. temporal
elevational
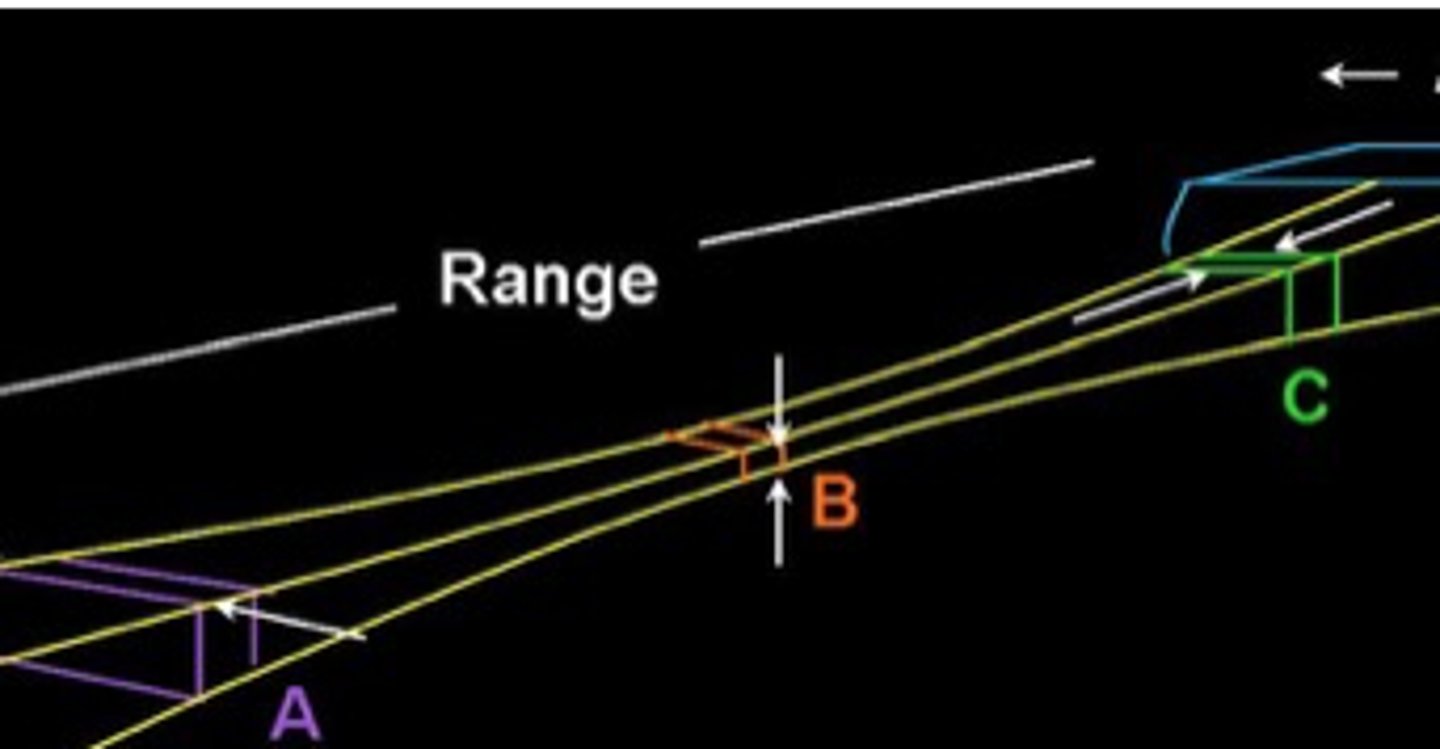
How many levels of information can a single bit represent?
A. one
B. two
C. four
D. eight
E. sixteen
two (on and off)
What part of the sonographic instrument is responsible for apodization, beam steering, focusing, and aperture control?
A. beam former
B. receiver
C. memory
D. pulser
E. scan converter
beam former
What can you improve by changing gray-scale map?
A: Axial resolution
B: Lateral resolution
C: Contrast resolution
D: Elevational resolution
E: Temporal resolution
contrast resolution
You are imaging a 3D dataset that has ansioptropic resolution. What does this mean?
A. spatial resolution is better than temporal resolution
B. spatial resolution is equal in all dimensions
C. contrast resolution is superior to spatial resolution
D. unequal resolution is present between imaging planes
E. elevational resolution and contrast resolution are the same
unequal resolution is present between imaging planes
You obtained a 3D sweep in an axial plane and are viewing it in a multiplanar display. What orthogonal planes will be displayed?
A. coronal and sagittal
B. transverse and coronal
C. transverse and sagittal
D. oblique planes at 90 degrees
E. oblique planes at 60 degrees
coronal and sagittal
if sound did not attenuate with increasing depth, what system control would you no longer need?
A. dynamic range
B. reject
C. frame averaging
D. TGC
E. master gain
TGC
What is the disadvantage of a water-path scanner?
A. it reduces axial resolution
B. the beam width is perpendicular to the image plane is increased, resulting in poor elevational resolution
C. bubbles in the fluid can inhibit sound transmission into the body
D. it is useful only with very low frequencies
E. the fluid path increases the mechanical index
bubbles in the fluid can inhibit sound transmission into the body
What information is present in M-mode display?
A. time, motion, pattern, and amplitude
B. amplitude, frequency, and time
C. motion pattern and frequency
D. time, motion pattern, and frequency
E. bandwidth, amplitude, frequency, time, and motion pattern
time, motion pattern, and amplitude
you are imaging a fluid-filled structure that has equidistant horizontal bands appearing in the near field. The bands have decreasing brightness with depth. What artifact are you seeing?
A. slice-thickness
B. side lobes
C. reverberation
D. comet-tail
E. ring-down
reverberation
a typical value for the duty factor in diagnostic sonographic imaging is?
A. 80-100%
B. 50-75%
C. 25-45%
D. 5-20%
E. 0.1-1%
0.1-1%
the range equation describes the relationship between
A. acoustic impedance of the two media
B. side-lobe intensity between two crystals
C. round-trip pulse travel time and distance to the transducer
D. bandwidth and transducer frequency
E. all of the above
round-trip pulse travel time and distance to the reflector
What information is present in the A-mode display?
A. frequency bandwidth, amplitude, and reflector distance
B. time, amplitude, and motion pattern
C. amplitude and reflector distance
D. time, motion pattern, reflector distance, and frequency bandwidth
E. frequency shift, amplitude, and reflector distance
amplitude and reflector distance
What type of imaging results in selective reception of frequencies that are two times that of the transmitted frequency?
A. color doppler imaging
B. pulsed doppler imaging
C. tissue doppler imaging
D. M-mode imaging
E. tissue harmonic imaging
tissue harmonic imaging
What technique would be most likely to produce grating lobes in your image?
A. beam steering
B. tomographic US imaging
C. 3D imaging
D. speckle reduction imaging
E. tissue harmonic imaging
beam steering
you are performing a sonographic examination and select the tissue harmonics operating mode. What advantage will you obtain over conventional imaging?
A. improved contrast resolution
B. improved penetration
C. improved temporal resolution
D. improved signal-to-noise ratio
E. increased bandwidth
improved contrast resolution (contrast resolution is always improved with increasing frequency)
what term below describes the rate at which the transducer applies electronic voltage pulses to the transducer
A. period
B. PRF
C. depth gain compensation
D. demodulation
E. apodization
PRF
what affect will you see in the image if you increase the reject level?
A. increased numbers of shades of gray
B. decreased low-level echoes
C. decreased frame rate
D. decreased scanning depth
E. decreased amplitude of the brightness of gray
decreased low-level echoes
you are using a transducer that produces a beam with a very wide slice thickness. Which of the following problems are you most likely to encounter as a result?
A. increased near-field reverberations in fluid-filled structures
B. increased side lobes
C. decreased penetration
D. partial volume artifact
E. decreased frame rate
partial volume artifact (occurs when slice thickness is wider than the structure being imaged)
What is the main advantage you will have by choosing a transducer that produces a thin slice over the image plane
A. improved frame rate
B. decreased volume averaging
C. better axial resolution
D. larger field of view
E. greater penetration
decreased volume averaging
What receiver function listed below is NOT operator-adjustable?
A: Amplification
B: Compensation
C: Demodulation
D: Rejection
E: A and D
demodulation
what is an advantage of a water-path scale
A. near-field reverberations are reduced
B. penetration is increased
C. temporal resolution is improved
D. axial resolution is improved
E. slice thickness is reduced
near-field reverberations are reduced
of the following, which is the best choice to help you demonstrate tissue boundaries that are not perpendicular to the sound beam?
A. speckle-reducing algorithm
B. spatial compounding
C. persistence
D. panoramic imaging
E. TGC
spatial compounding (when the sound beam is steered in multiple directions by employing time delays, then images are averaged)
The picture elements in a scan converter matrix are termed
A. decimals
B. binary numerals
C. bits
D. pixels
E. bytes
pixels
What control should you adjust to modify the image if the attenuation coefficient of the tissue is very high?
A: Dynamic range
B: Rejection
C: Threshold
D: Compensation
E: Compression
compensation
What is another name for the hyperechoic artifact distal to a fluid-filled structure
A. refraction
B. shadowing
C. speckle
D. grating lobe
E. enhancement
enhancement
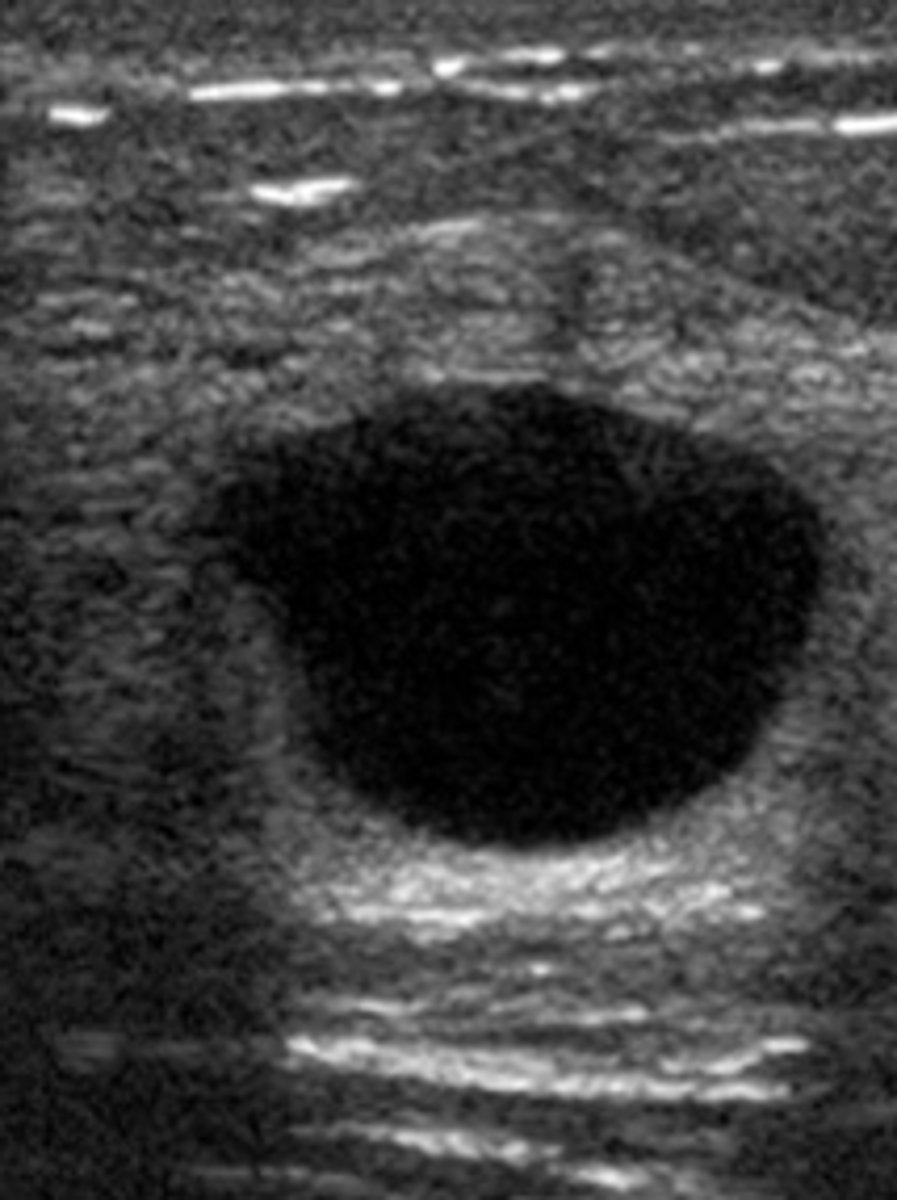
What is the maximum number of shades of gray in an 8-bit digital scan converter?
A. 16
B. 32
C. 64
D. 128
E. 256
256 (2^8)
With an A-mode display, the internal contents of a simple cyst will appear as
A. an area with very dark shades of gray
B. an area with rapidly moving spikes
C. an area with tall spikes surrounded on each end with areas absent of spikes
D. an area with no spikes
E. an area with multiple tiny spikes
an area with no spikes
Propagation speed error results in which sonographic appearance?
A. improper lateral position of an echo
B. improper axial position of an echo
C. shadowing behind an echo
D. enhancement behind an echo
E. none of the above
improper axial position of an echo
You are observing a sonographic artifact based on the interference patterns of scattered echoes. Which of the following will decrease the presence of the artifact you are seeing?
A. using frame averaging (persistence)
B. using compound imaging
C. reducing the output power
D. increasing the overall gain
E. A and B
A and B
What type of focusing is performed by delay circuitry reception?
A. dynamic receive focusing
B. elevational focusing
C. transmit focus
D. multizone transmit
E. mechanical focusing
Dynamic receive focusing
Pulsing of the transmitted sound wave is necessary for real-time imaging because
A. the transducer becomes too hot to handle if continuous sound waves are emitted
B. the crystal in the transducer will break under the stress of continuous emissions
C. the depth of the interface from which the echo originated can be determined
D. lateral resolution is improved by pulsed transmission
E. temporal resolution is improved by pulsed transmission
the depth of the interface from which the echo originated can be determined
What component is necessary for a real-time B-mode scanner but is not present in an A-mode scanner
A. clock
B. transmitter
C. transducer
D. scan converter
E. receiver
scan converter
When you adjust the TGC, what component of the US system implements the changes?
A. pulser
B. receiver
C. monitor
D. scan converter
E. clock
receiver
Which scanning mode not NOT rely on the principal of echo ranging to determine interface location
A. M-mode
B. PW Doppler
C. Static B-mode
D. Transmission
E. A-mode
transmission
With A-mode, the strength of the echo signal is represented by:
A: The brightness of the dot
B: The brightness of the spike
C: The distance between two spikes
D: The distance between two dots
E: The height of the spike
the height of the spike
What type of transducer will improve the artifact demonstrated in this image?
A. linear array
B. 1.5D or multirow array
C. mechanical 3D
D. phased array
E. mechanical sector
1.5D or multirow array
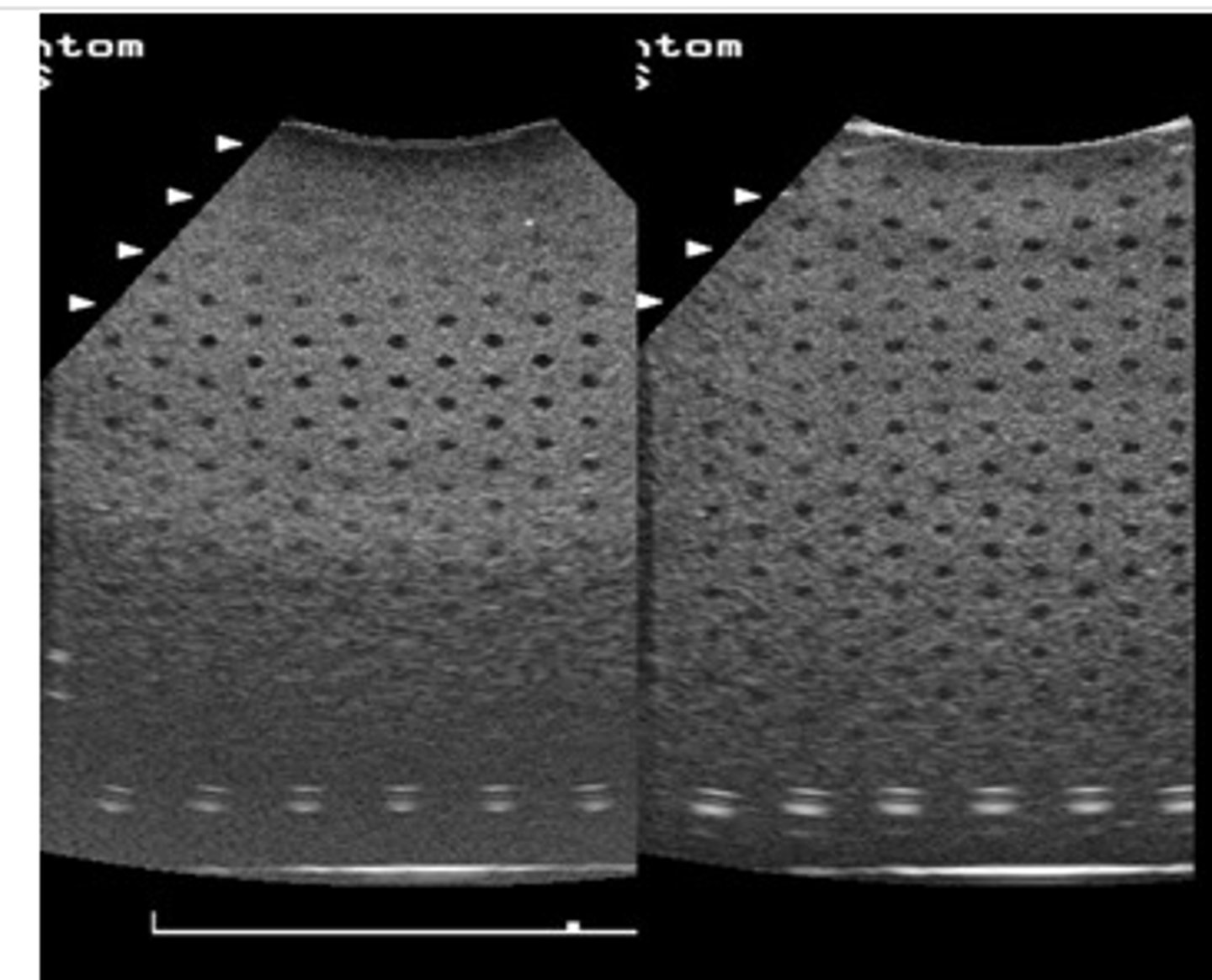
You are manipulating a volume data set that was previously obtained on your patient. What is the maximum number of imaging planes that can be obtained from this data set?
A: One
B: Ten
C: One hundred
D: One thousand
E: There is no limit
there is no limit
which imaging technique may increase visualization of the reflections from blood flow on the real-time US image
A. compound imaging
B. tissue harmonic imaging
C. 3D imaging
D. tomographic imaging
E. speckle reduction imaging
tissue harmonic imaging (harmonics has reduce clutter, improved contrast resolution, and higher frequency)
Sonographic images are usually compressed before sending to PACS in order to
A. reduce the time to transmit the image
B. increase the spatial resolution of the image
C. preserve measurements with the image data
D. reduce costs by lowering image quality
E. increase the real-time image frame rates
reduce the time to transmit the image
While performing a sonographic examination, you have performed both preprocessing and postprocessing functions. Which of the following functions is postprocessing
A. write-zoom magnification
B. frequency change
C. gray-scale map assignment
D. scan line density
E. acoustic power output
gray-scale map assignment
What technique would be most helpful in reducing grating lobes in your image?
A. beam steering
B. compound imaging
C. 3D imaging
D. speckle reduction imaging
E. tissue harmonic imaging
tissue harmonic imaging
What artifact is related to the sound beam traveling through a structure with low attenuation
A. comet-tail
B. aliasing
C. enhancement
D. reverberation
E. side-lobe
enhancement