2A- Exchange of substances
1/10
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Why is having a large surface area to volume ratio good?
Organisms that have a small surface area to v ratio require a further distance for gases to move and require a specialised system in order to provide adequate gas exchange
Name 3 features of an effective gas exchange surfaces
Large surface area (folded membranes in mitochondria)
Thin walls (capillary walls)
Steep concentration gradient (a good blood supply provides a constant flow of oxygen)
What is ficks law

What is the structure of a cell membrane?
Phospholipid bilayer
Glycoproteins and glycolipids
Channel and carrier proteins
Cholesterol
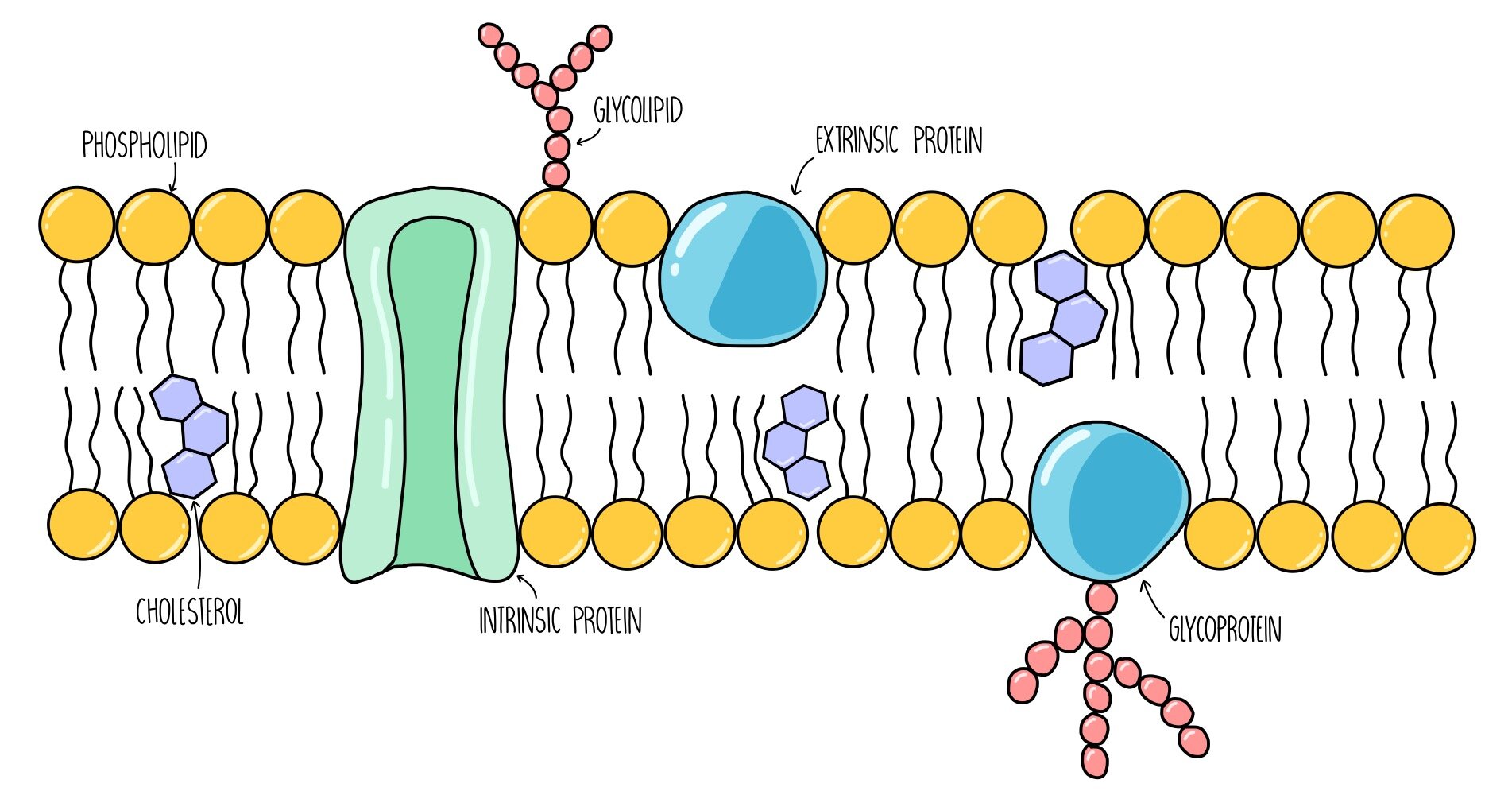
What is meant by the fluid mosaic model?
Fluid: the phospholipids can easily move around and embed new proteins
Mosaic: the random association of proteins within the membrane
Describe freeze-fracture
Freezing the cell membrane and then breaking it apart →fracturing it down the middle → results show smooth mosaic on inside.
Describe plant protein
Lectins are labelled with ferritin (visible under electron microscope) → showed membranes are asymmetrical
Describe mouse cells
Fusing mouse cells with human cells, specific membranes were labelled
1 min after - protein in the same position
40 min - complete intermixing
showed proteins diffuse through membranes and proved they’re fluid
What is facilitated diffusion
The movement of polar, particles from a high to lower concentration through a channel or carrier protein
Define active transport
The movement of particles from low to higher concentration which requires energy in the form of ATP, also requires a carrier protein.
What is endo/exocytosis?
Endocytosis: Cell membrane forms a vesicle and engulfs the molecule (proteins + lipids etc)
Exocytosis: Vesicle fuses with the cell membrane releasing the molecules (Enzymes + hormones)