le3 - sq6 cvs respi Embryology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
tracheoesophageal Fistula, 4th
(1) dz due to abnormal PARTITION by the tracheoesophageal SEPTUM. trachea & esophagus r connected pa.
(2) wc occurs at the __th week.
Pleuroperitoneal membrane, dorsal mesentery of esophagus, somites c3-5, ingrowths from lateral body wall
DIAPHRAGM FORMATION (oriigin:future)
x: central tendon, ct
X: crura
x: ms parts
x: peripheral rim
Eventration of diaphragm
Due to total or defective muscular development: myoblasts from cervical 3-5 somites. Weak diaphragm part.
congenital diaphragmatic hernia
dz There is a posterolateral defect in the diaphragm.
Thus, the contents of the abdomen would herniate into the
thoracic cavity
● Usually occurs in the left side
● Contents that could possibly herniate into the thoracic cavity and
compress the developing lung: → Intestine
→ Spleen
→ Stomach
→ Liver
→ Or all of the contents
● All of this happens in utero (in the womb) and the lungs are still
developing
● If herniation occurs during development, the lungs (one lung or
both lungs) will not be able to grow normally and form
hypoplastic compressed lung or a small undeveloped lung
hyaline membrane disease, respiratory distress syndrome
1) dz due to baby born before lung fully matures, thus lacking in surfactant
2) other name
20, canalicular, 28, saccular, 34,
at __ weeks, surfactant is synthesized during the __ phase. Formation of alveoli.
at __ weeks, sig. Amt of detectable surfactant, can survive, during the __ phase. Alveolarization initiated.
at __ weeks, increased amt of surfactant is synthesized w/ better chance of survival.
Embryonic, Pseudoglandular, simple COLUMNAR, Canalicular, simple CUBOIDAL, Saccular, simple squamous, Alveolar
FORMATION OF TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TREE:
__ devt of PROXIMAL (malayo) airways such as trachea & bronchi
__ devt of LOWER CONDUCTING airways + VASCULAR SUPPLY.
Epithelium ⬆
__ formation of GAS EXCHANGING UNITS
Epithelium ⬆
__ initiation of ALVEOLARIZATION
Epithelium ⬆
__ continued alveoli devt & proliferation
septum Primum, atrium septum, septum secundum & foramen secundum
PARTITION OF PRIMORDIAL ATRIUM (origin:future)
__ : atrium septum & valve of f. ovale
__ : (L & R) atrium
__ & _ : foramen ovale
RIGHT HORN sinus venosus, left horn sinus venosus. Primitive Atrium, Primitive PULMONARY VEIN
sinus venosus (origin:future)
__ sinus venarum, crista terminalis
__ coronary sinus
__ pectinate ms, (l) auricle, right atrium r = rough,
__ left atrium
Truncus arteriosus, Transposition of Great Arteries, Tetralogy of Fallot
ABNORMALITIES IN THE FORMATION OF THE SPIRAL SEPTUM
Results from failure of truncal ridges and aorticopulmonary septum to develop normally, thus mix O2 & Deox blood.
Most common cause of cyanotic heart disease in newborn
infants. Conotruncal/aorticopulmonary/spiral septum fails to follow its spiral course and runs straight down
Most common beyond infant.Due to unequal division of the conus resulting from anterior displacement of the conotruncal/spiral septum
Maxillary, hyoid stapes, cca ica, aortic arch right subcla, pulmonary a, ductus arteriosus
Course of Laryngeal Nerve
1st
2nd
3rd
4th
6th
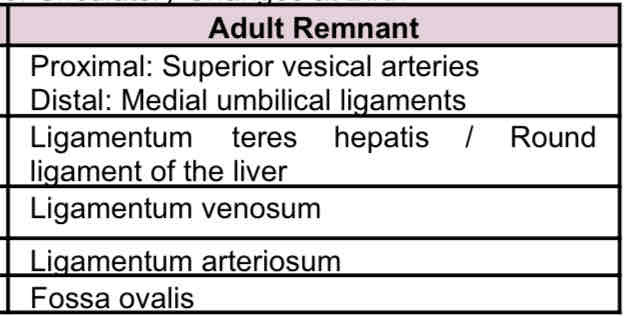
Umbilical a, left umbilical v, ductus venosus, ductos arteriosus, foramen ovale
CIRC CHANGES AT BIRTH (origin:future)