Unit 7 Van More PCMS Final Exam Civil War
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Agrarian
related to farming, economic and cultural society based on farming and crops
-South economy
cotton gin
-separates seeds from cotton plants
-revolutionized cotton growth in the U.S, made it the number 1 crop
-1794
-Eli Whitney
-Increased cotton production, which increased demand for enslavement
plantation
Large acre of farmed land
abolitionist
someone who wants to end enslavement
Harriet Tubman & Underground Railroad
-Harriet Tubman: escaped enslaved person who went back to help others, used Underground RR
-Underground RR: secret network of safe houses + routes used by enslaved to escape
popular sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.
-allow voters in territory to decide whether they want to ban/allow slavery
Tallmadge Amendment (1819)
-Rep. Tallmadge of NY proposes amendment asking to join MO as a free state
-The South opposed, wanted enslavement
-Approved in the House, lost by the Senate
-1819 Congressional Session: issue remains combative
Missouri Compromise (1820)
-1820: Resumes issue of MO being free or enslaved state
-ME (Maine) also wants to join as a free state
-Congress first hears talk about South seceding
-Solution: MO enters as an enslaved state, ME as a free state
-Drew a line at 36'30 line, N of it = slavery abolished with exception of Missouri, S of it = slavery allowed
Nat Turner rebellion & Fugitive Slaves (1831)
-Slave revolt in 1831 in Virginia
-Killed around ~ 55 white ppl in 2 days
-Resulted in more small rebellions
-Enslaved attempt to escape and flee to North
Gag Rule (1836)
-1836: response to MO compromise
-North = flooding Congress w/ petitions --> get rid of slavery
-Response: Congress puts a halt on all talk about abolitionism and getting rid of slavery, South agrees, North angry
Wilmot Proviso (1846)
-PA Rep David Wilmot = proposed an amendment in 1846 seeking funds for MX-AM war
-no slavery allowed in Mexican Cession/any territory added to the U.S
-passed in the House, rejected in the Senate
-Sectionalism increased over the issue of slavery
Compromise of 1850
1. Cali enters as a free state
2. Mexican Cession = left up to the people to decide whether enslavement is allowed or not
3. End slave trade to Washington D.C. (not end slavery)
4. Fugitive Slave law is strengthened = becomes easier to catch fugitives
-Passed in 1850
Fugitive Slave Act (1850)
-1850: Federal crime to help runaway slaves
-Allowed gov. to arrest runaways where slavery was NO
-Slaves could not testify on their own at trial
-1st 10 years: 343 fugitive slave cases, 11 won
-Thousands of slaves escaped to Canada
-Northerners began to resist/rebel against the act
Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852)
Plays that sold millions, spread word of the abolitionist movement
-1852
-Harriet Beecher Stowe
Kansas Nebraska Act (1854)
-Proposed by Stephen Douglas of IL in 1854
-Divided the LA purchase into two: KS, NE
-Each territory uses pop sovereignty to decide enslavement or not
-Gets rid of MO compromise
-North = upset MO compromise gone, protested
-Bloodshed in Kansas
Bleeding Kansas (1854) & Pottawatomie Massacre (1856)
-Both sides fighting to win KS- enslavement or not? (1854)
-Fight in Lawrence: Pottawatomie Massacre (1856)
--> John Brown-abolitionist, fought back
--> He and 7 others killed 5 pro-slavery men
--> More fighting, eventually 200 died
--> Became a hot topic across the country
Brookes v Sumner (1856)
-Preston Brookes attacked Charles Sumner with a cane because Sumner gave an anti-slavery speech before
-Brookes (pro-slavery) Sumner (anti)
-Summer = severely injured
-Massachusetts 1856, senate floor
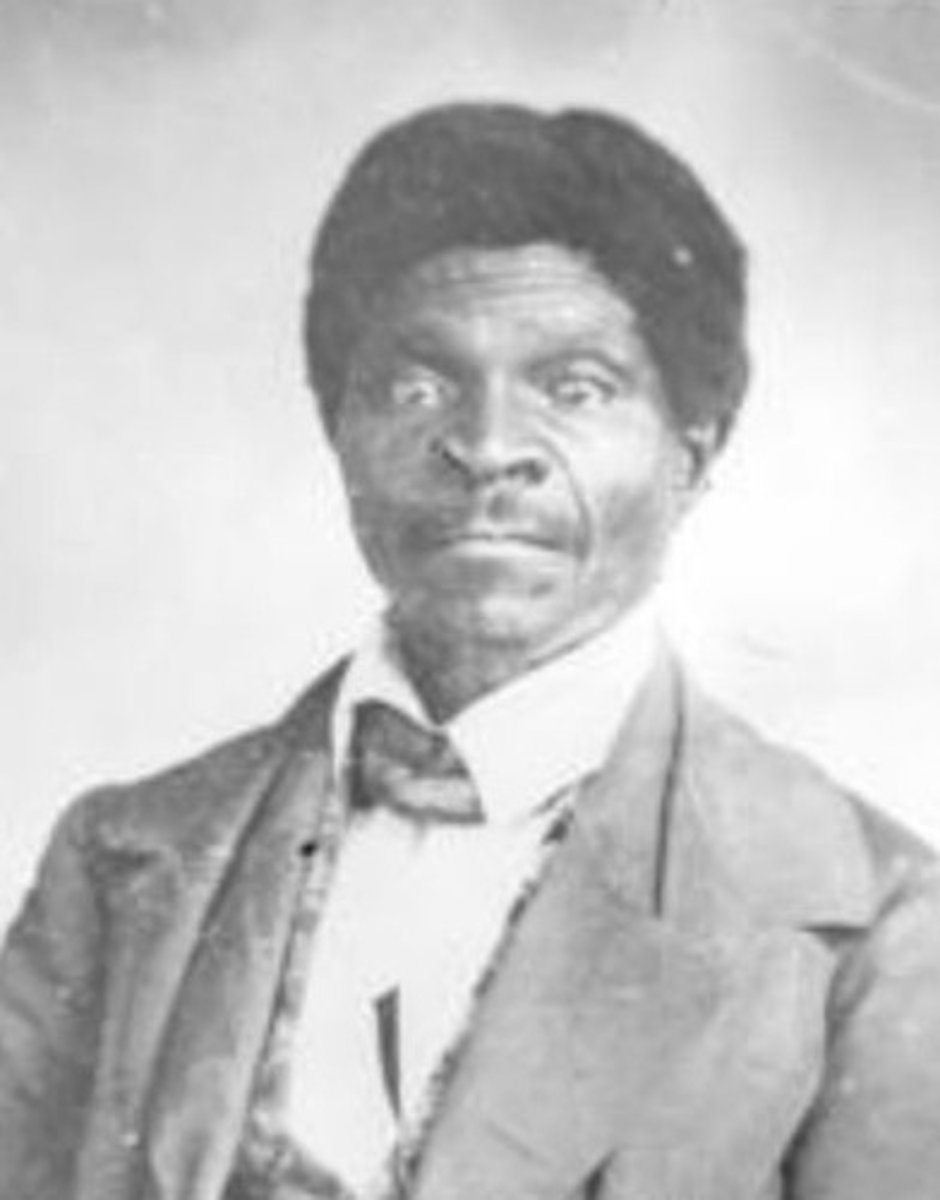
Dred Scott Case (1857)
-1857 Dred Scott: slave from St. Louis, MO
-Worked with his owner in free part of LA purchase
-Scott argued that he should be free when return to MO, since he worked in free territory
--> Scott even a citizen? (Could he go to court or no?)
--> Time spent on free land = he was free?
--> Ban on slavery constitutional in LA purchase?
Ruling of Dred Scott Case (1857)
-Justice Taney: Scott, not a citizen = no right to come to court
-Living on free land does not equal he is free
-Found ban on slavery in new territory unconstitutional
-This stunned North, angered Republicans, Lincoln enters

Republicans and Democrats
R: Abolition party, Northerners
S: Southerners, hated Abolition party
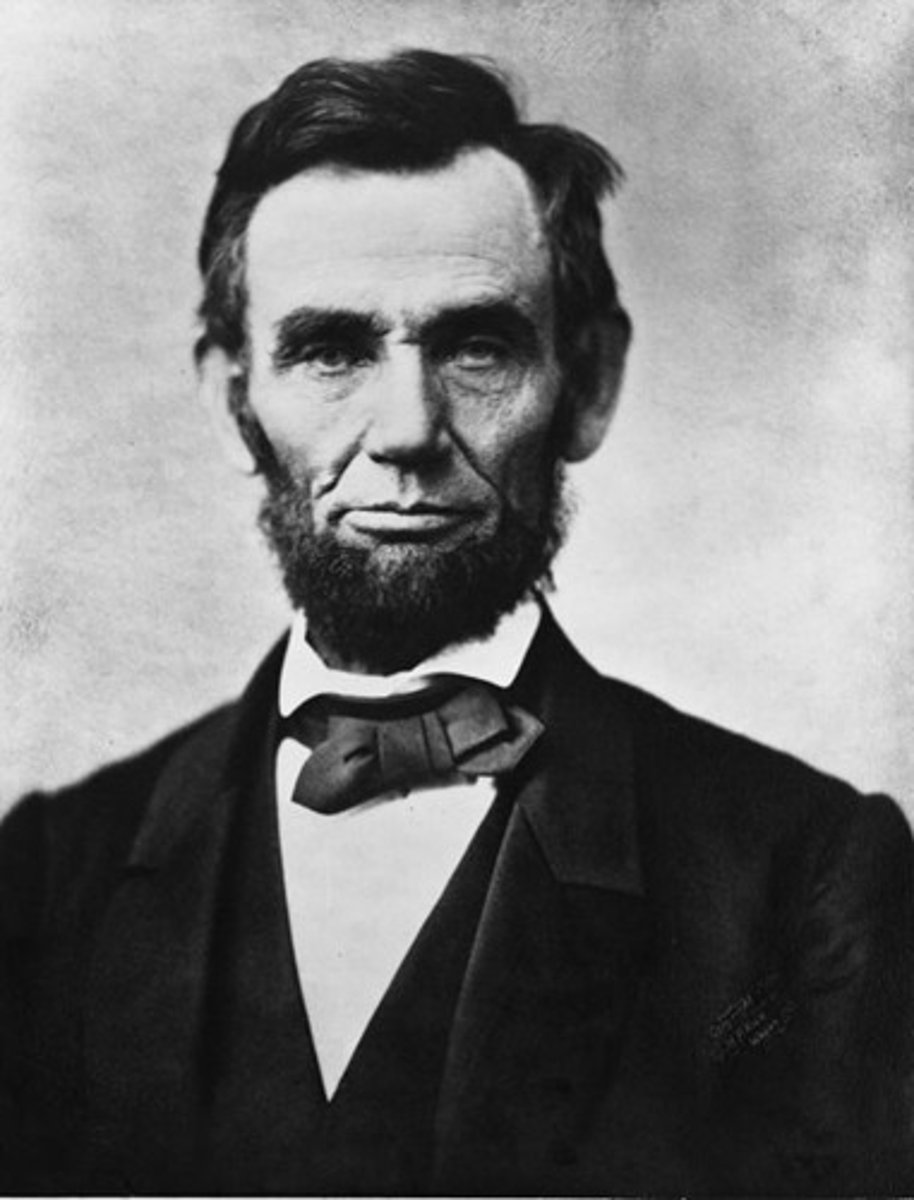
Abraham Lincoln
-From KY, moved to mid west in 1816
-4 terms in IL Congress
-Joined Republicans in 1856
-Fought to abolish enslavement
-Debated against Stephen Douglass in 1858
-President during Civil War, was reelected

Effects of the L-D Debate (1858)
-Douglass= country cannot be half slaved and half free
--> Continued to push for free union = warfare in North/South
--> Ppl, not Congress, determine to enslave or not
--> This helped Douglass win more votes, earns a seat in the Senate over Lincoln
-Lincoln: viewed it as a moral issue
-1858
John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry (1859)
-Harpers Ferry, VA
-Armed slaves and captured arsenal
-Abolition revolt
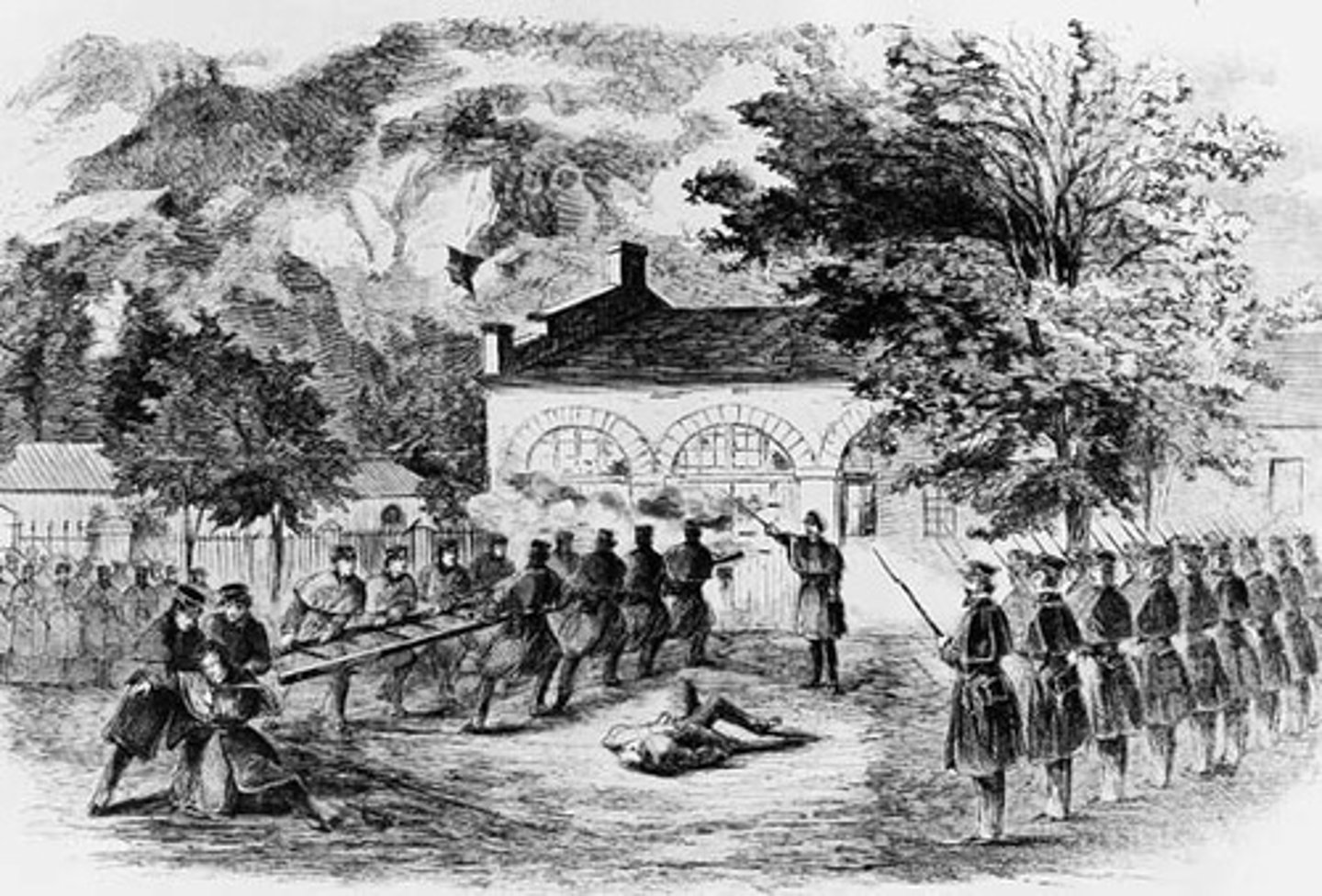
Election of 1860
-Country is divided over slavery. N vs S
-Lincoln won (~40% of votes, won the electoral vote, Southern states didn't even have his name on the ballot)
Secession of Southern States (1861)
-South = angry, saw this as a threat to their way of life
-Result: Southern states begin to leave, starting with SC, 10 that follow = 11 states in total
-Helped trigger the Civil War in 1861
-Southern states that left = Confederate States of America
Fort Sumter (1861)
-Military fort in Charleston, South Carolina, 1861
-Confederates attacked fort
-Union troops surrender
-First battle of Civil War, both sides began preparing for full-scale war
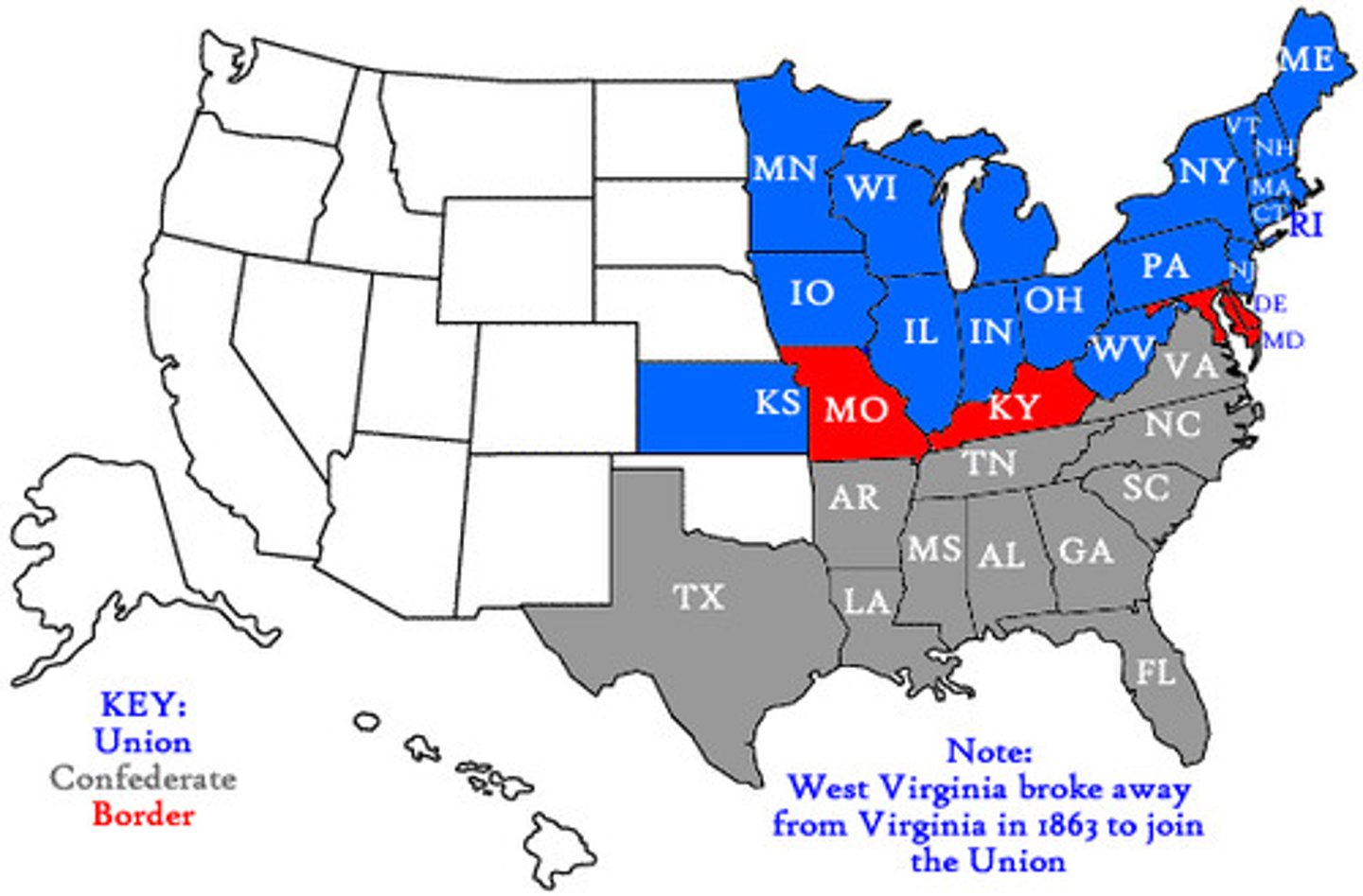
Theaters of war & border states
-Trans-Mississippi
-Western Theater: AL, GA, FL, MS, NC, SC, KY, TN=had MS river
-Eastern Theater: PA, MD, DE, VA=had Richmond
-Border states:
Delaware, Maryland, Kentucky Missouri. They were slave states, but did not secede.
Copperheads
-Northern democrats = felt that saving the Union and making peace was more important than ending slavery (Copperheads)
-Northern republicans saw this as a betrayal
Strengths/Weaknesses of the North
-Large army, established navy
-Larger population for enlistment
-Industrialization = more factories to produce what military needs
-(w) limited military leadership
-Would be the ones to go to the battle front
Strengths/Weaknesses of the South
-Military leadership
-Home field advantage (only needed to defend itself)
-Most battles were fought on Southern soil
-Strong identity and motivation for independence
-(w) lacked industrialization to produce goods and materials
Anaconda Plan
-Destroyed Southern economy by using naval blockade, blocked ports, cut off trade
-Control MS River to divide Confederacy = limit their trade and communication
-Capture Richmond, VA- confederate capital
War strategies for South
-Defend territory
-Wear down Union's will to fight
-Take WA, DC (Union capital)
-Win foreign allies
-Needed to sell cotton to GB and France for $ for war
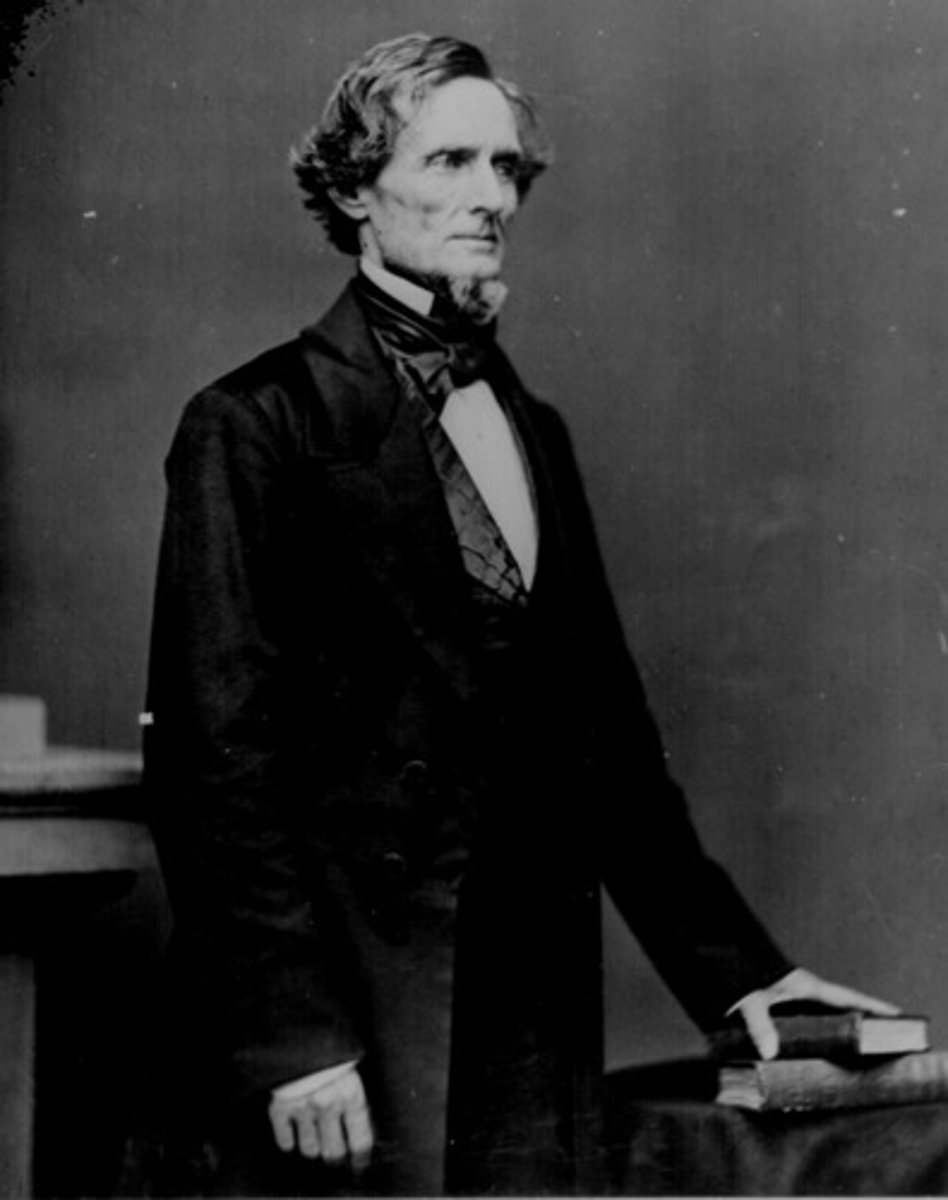
Jefferson Davis
President of the Confederate States of America
-1st president
-1861

Women in the war
-Ran farms + businesses
-Worked in factories
-Nurses, teachers, govt., employment
Military Involvement
-Messengers, guides, smugglers, spies
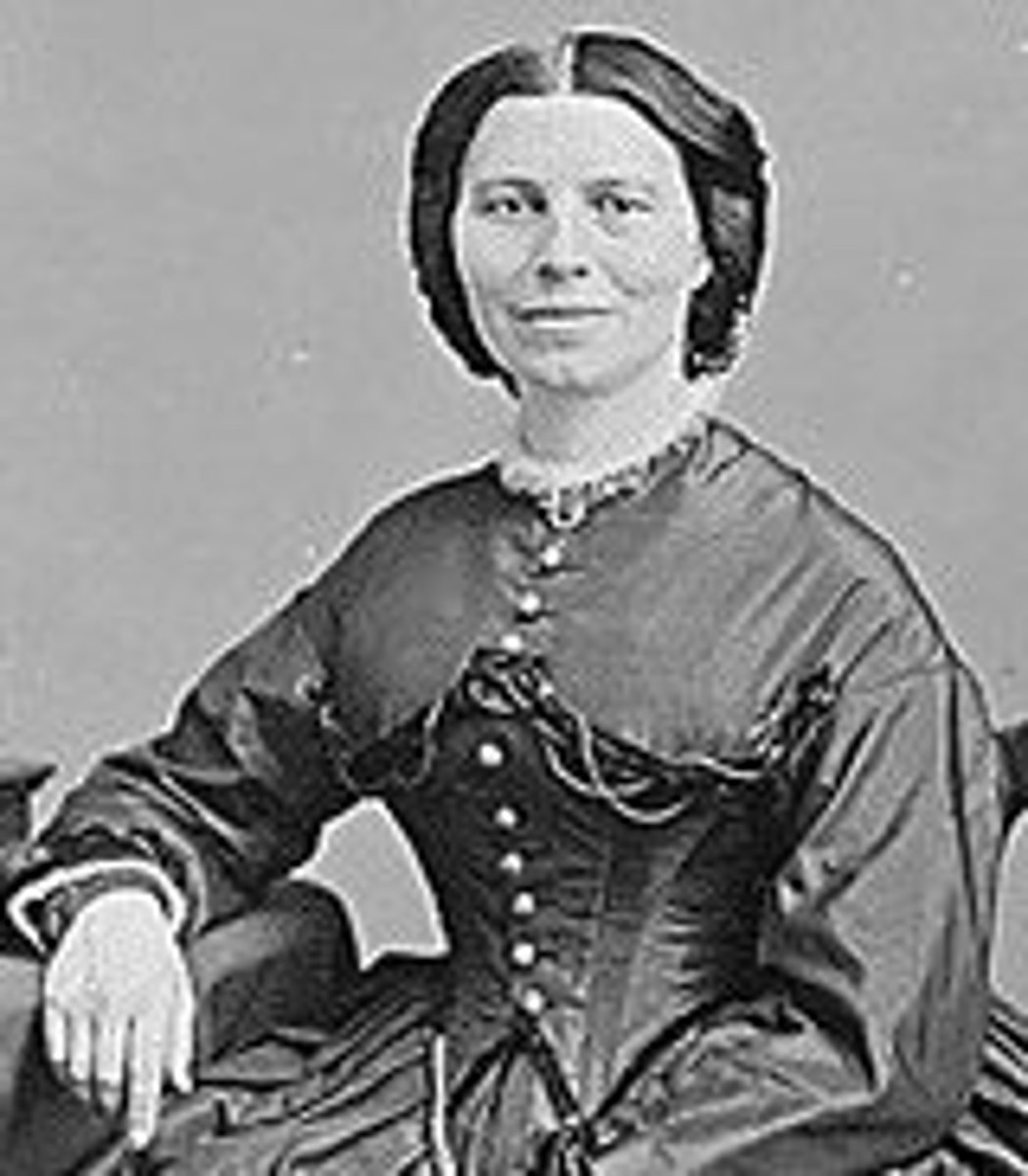
-Nursed injured soldiers: Dorthea Dix, Clara Barton
Clara Burton
-Founded American Red Cross in 1881
-Nursed injured soldiers during the war

General George McClellan
-Union, North
-Was one of the first to try and capture Richmond
-Antietam

General Robert E. Lee
-CSA
-Lead General of CSA
-Bull Run 2nd Battle, Antietam, Gettysburg, Chancellorsville, Petersburg, Appomattox Courthouse

General William Sherman
-Union, North
-Total War
-March to Sea (GA)
-Ending the war with his battles in the South

Stonewall Jackson
-Thomas Jackson
-Took home a CSA win that showed the North that battle would not be easy
-Bull Run 1st and 2nd, Antietam, wounded at Chancellorsville

General Ulysses S. Grant
-Union
-Lead general of U.S.
-18th president
-Vicksburg, Shiloh, Appomattox Courthouse

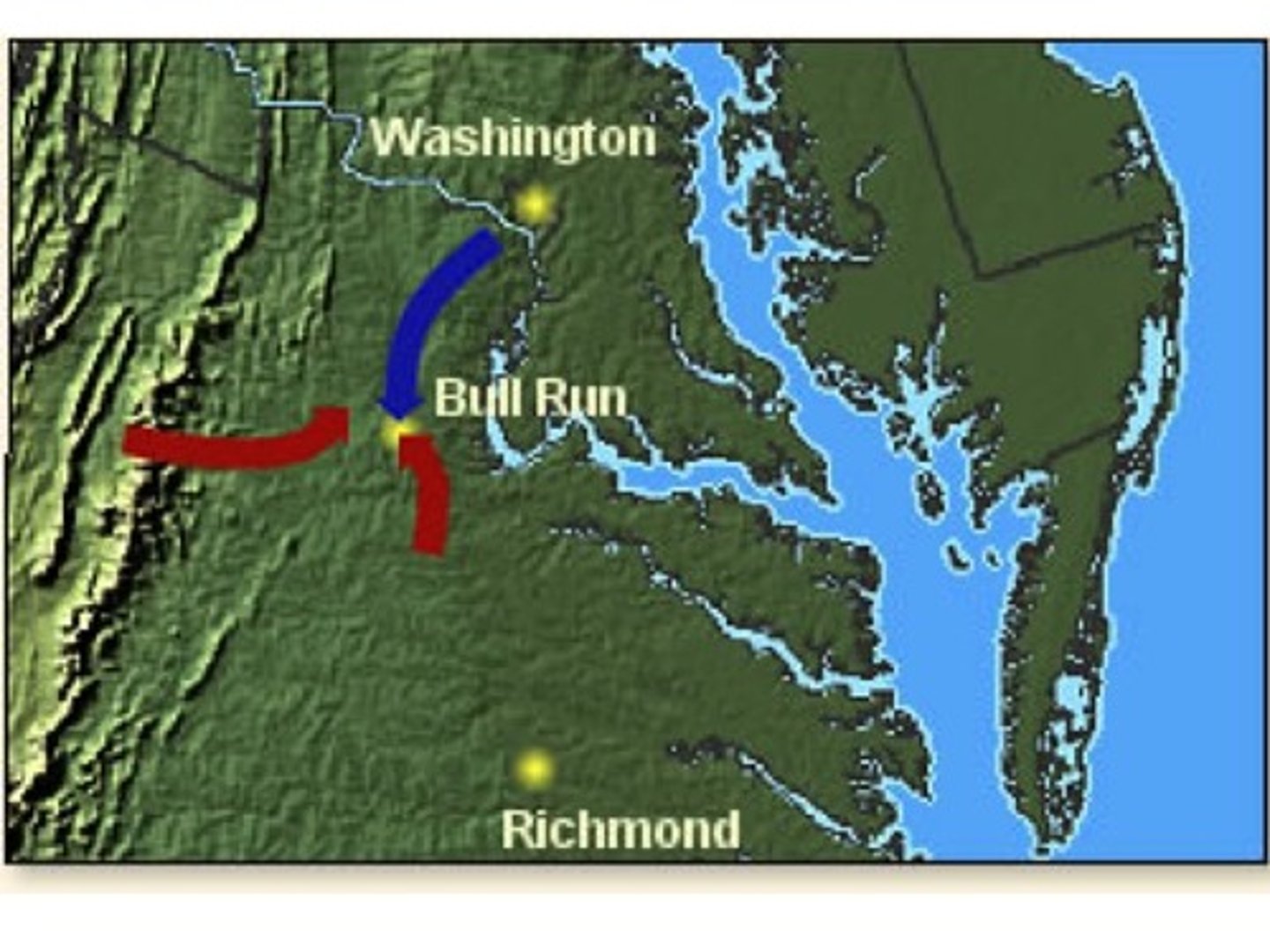
Bull Run (1861 1st Battle)
-When: 1861
-Who: McDowell's union army vs Stonewall's CSA army
-Where: Manassas, VA in Bull Run Creek
-North = wanted better positioning in border states for future battles
-Stonewall's determination broke Union lines, North retreated back to WA, DC
-Confederates won
-When North realized and accepted war would be longer and bloodier than expected
Shiloh, 1862
-When: 1862
-Where: Shiloh, TN, West Theater
-Who: Grant (U) vs CSA
-Confederates get the upper hand & looks like an easy victory
-US Grant proving his worth in western theater
-Union reinforcements on 2nd day turn tide in Union favor
-13,000 Union casualties
-10,000 Confederate casualties
Bull Run 2nd Battle (1862)
-When: 1862
-Who: CSA Stonewall & Lee vs Union army
-Where: Manassas, VA
-Confederacy under Stonewall and Lee; Union under General John Pops
-Lee had Jackson and men flank Union
-Union retreats to D.C
-Another win for confederacy
-Gave Lee confidence to invade the North, leading to Battle of Antietam
Battle of Antietam (1862)
-When: 1862
-Who: Union McClellan vs Lee & Jackson
-Where: MD, between PA and VA
-North wants to capture capital
-South wants MD to join them
-Lee invades territory in MD
-Confederacy forced to retreat back
-Bloodiest one day battle in U.S history
-Over 22,000 soldiers killed, wounded or missing in one day
-More ppl. died here than the War of 1813 & Mexican War combined
-Union claims victory; big cost on both sides
Merrimac vs. The Monitor 1862
-When: 1862
-Who: Merrimac (CSA) vs Monitor (Union)
-Where: Chesapeake Bay in VA
-Merrimac: Confederates take Union ship left in VA, cover with iron, and rename it the Virginia
-Monitor: Union iron clad navy vessel built in less than 100 days
-Merrimac: enters Chesapeake bay, destroys Union's wooden ships
-Union responds with Monitor the next day, neither sides win, Union begins using iron clad ships in next battles
-Naval technology = never the same, rise of iron clad ships
Emancipation Proclamation 1863
-Finalized in 1863
-Lincoln issued it due to the Union's performance at Antietam
-All enslaved in Confederate states (not Union or border states) were free
-Changed purpose from just saving Union to ending slavery as well
-South = cotton to export to FR & GB = Eman. Proc outlawed slavery = FR & GB didnt want to support a nation fighting for slavery
Battle of Gettysburg (1863)
-When: 1863
-Who: CSA Lee against Union army
-Where: Gettysburg, PA
-Lee invades North after winning many battles on Southern soil
-North wanted to capture Richmond, Virginia
-South wanted MD to join CSA, get foreign allies on their side
-Lee forced to retreat back to VA
-Bloodiest battle in war, turning point
-After Lee lost 1/3 of his men, he decided he would only fight on Southern soil
Gettysburg Address 1863
-1863
-Lincoln gave a speech at battlefield site
-In memory of Union soldiers who died trying to protect their country and its freedoms
-Both Union and Confederate need to be remembered, for they all fought under the premise of democracy & THAT is the goal
Vicksburg (1863)
-When: 1863
-Who: Farragut secured N. Orleans on MS river, now Grant is taking Vicksburg
-Where: Vicksburg, MS in MS River
--Grant uses gunboats for 6 weeks to shell the city from the river
-Army bombarded it from land
-Low on supplies and food, people of Vicksburg surrendered since they couldn't be protected
-UNION NOW CONTROLLS ALL OF MS RIVER IN 1863
MA 54th Regiment (1862)
-When: 1862
-Began allowing AA to fight in Union army
-200,000+ former slaves and AA join
-Often undertrained, undersupplied
-Massachusetts 54th: Colonel Robert Gould Shaw
—> 1,000 AA soldiers
—> Congress agrees AA = same pay as whites
—> Sent to Ft. Wagner, SC to fight
Total War
-complete obstruction of resources, people, everything in its path
-Northern strategy
-Unconditional Surrender- Union's General Grant's nickname
-Grant = on path to Richmond, invaded VA, doesn't give up, lots of casualties
Shermans March to Sea (1864)
-Atlanta GA 1864: Troops capture Atlanta, burned destroyed it and much of GA
-Went on to N.C and S.C
-Savannah, GA 1864: "Christmas present to Lincoln, siege of GA and then Carolinas set the stage to attack Richmond
-At this point: taken MS river, closed ports, no trade for South
-Final step for A. Plan
Petersburg, 1865
-When: 1865
-Where: Petersburg, VA
-Lee's last stand, Union wins
-Richmond = taken
-Fires & looting breaks out
Appomattox Courthouse 1865
-General Lee meets with General Grant to end the war in the A. Court house
-Small town outside of Richmond
Terms:
-Confed troops = go home with supplies, no more fighting
-Grant supplied Lee's troops with much needed food
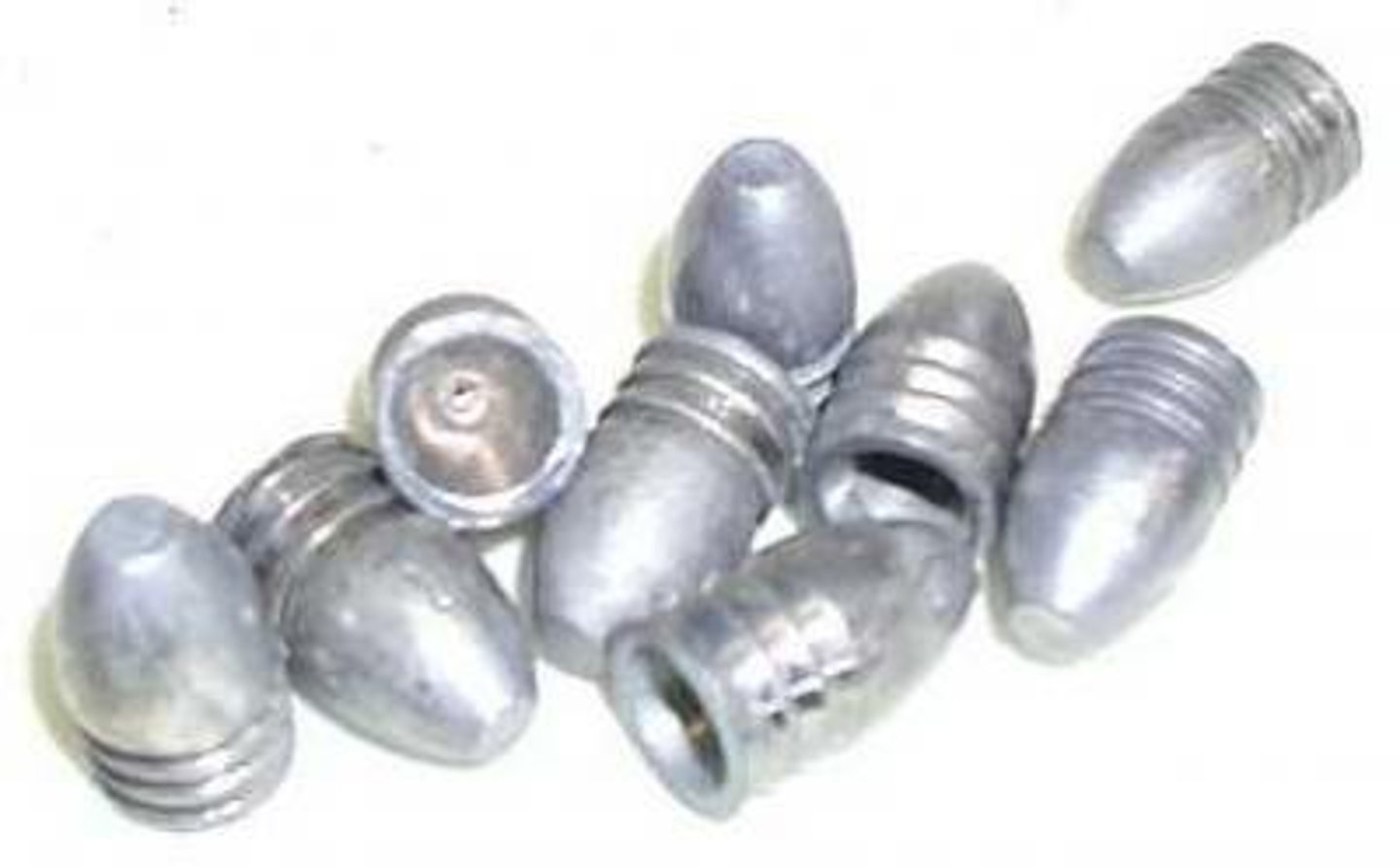
Minnie Ball 1849
-1849
-Increased accuracy and range
-Changed warfare; made Civil War deadliest conflict in American history

Telegraph, railroad, Lincolns war room
-Telegraph: enabled quick communication and coordination, Lincoln used it a lot in offices = CSA would destroy telegraph lines
-Railroad: advantage to North, transportation of troops, supplies. U had way more than C
-War rooms: Lincoln worked in his office A LOT, telegraphed a lot, fell asleep, space for reflection
Lincoln's Assassination 1865
-1865
-Fords Theater
-John Wilkes Booth
-Andrew Johnson - VP becomes prez., southern sympathizer
-Reconstruction: 1865-1877
Johnson's reconstruction plan
-Former confederate states = rejoin USA if:
-Write new state constitution
-Elect new state government
-Repeal acts of secession
-Cancelled war debts
-Had to ratify 13th amendment 1865

Tenure of Office Act (1867)
-Banned prez. from firing certain federal officials w/o Senate's consent
-Johnson fired an official regardless
-Impeached
-Won by 1 vote, but lost power
13th amendment (1865)
-Abolished enslavement and involuntary servitude in the U.S. and its territories
-First reconstruction amendment adopted after Civil War
Freedman's Bureau, 1865
-agency established by Congress at the end of war to help newly freed black Americans
-Food, medical care, land, job assistance to free AA
-Education: public schools for AA
-"40 acres and a mule", Shermans promise never fully fulfilled
-South saw this as northern disturbance
Ku Klux Klan (Formed in 1865)
-1865, Tennessee
-White supremacist terrorist group
-Violence & intimidation to suppress black people
-Racial hatred
-Hanged & lynched
Black Codes (1865-1866)
-laws passed through former CSA states to limit rights of AA
Limit rights of freedmen legally
-no citizenship/voting rights
Help planters find workers to replace slaves
-2nd round of subversive slavery
-limited jobs, no job = arrested/hired to planters
Keep freedmen at bottom of social order
-During reconstruction
Radical Republicans
-Led by Charles Sumner & Thaddeus Stevens
-Thought reconstruction was not over until freedmen got full rights of citizenship
Military Reconstruction Act of 1867
-Divides south into 5 district governments w/ generals supported by troops
-Both black and white government
-Southerners supported CSA = denied the right to vote
-Johnson vetoed; Congress overruled
14th amendment (1868)
-citizenship, due process, equal protection to everyone in U.S. except for Natives
-"all people born or naturalized in U.S."
Sharecropping
-Former slave owners needed labor, former slaves wanted land
-Planters divided lands into plots- rented plots to tenant farmers
-A few paid rent in cash; most paid in portion of crops raised usually about a third or half
-Most sharecroppers = borrow $$$ for tools, seed, supplies
-Few earned enough to payback what owed
-Not independence but debtor system
Scalawags
-Term used to describe white southerners who supported Republican party & agreed with Reconstruction policies
-White southern democrats viewed them as traitors
Carpetbaggers
Term used to describe a northerner who moved to the south after the war to get political advantages through the disorganization of the south
-Wanted money and power
15th Amendment (1870)
Guaranteed every male citizen right to vote, regardless of race
African Americans
- ~¼ elected officials @ Constitutional
Conventions
- 1/5 A.A. reps. & served in state
governments
- Progressive message: public education
(although only for whites), free from
debtors prison, voting rights to all
-Rebuild roads, bridges, railroads
-tax increased ~40% between 1860-1870 in
South
What was happening towards the end of reconstruction?
• Southerners blamed "Yankees" for interference & higher taxes but took
aggressions out on A.A.
• Ku Klux Klan - used violence to intimidate & control A.A. power & freedom in South
• Enforcement Acts: illegal to prevent another person from voting by bribery, force or
intimidation
• President Grant sent federal troops to enforce but fizzled b/c A.A. would not testify
against aggressors
Amnesty Act of 1872
-Forgive and move on feeling
-Allowed most former confederates to vote again
-1876: Democrats regained control of all but 3 states (SC, LA, FL)
Compromise of 1877
Election of 1876
• Samuel J. Tilden (D) vs. Rutherford B. Hayes (R)
-Tilden majority of popular votes & 184 electoral (one short of victory)
- Hayes won 165 electoral votes
- 20 electoral votes from four states = disputed
• Congressional committee (Rep. majority)
- voted to give all 20 to Hayes, outrage
• Democrats accepted electoral commission's decision, while Hayes agreed to withdraw federal troops from S.
• FL, LA, SC became Democrat controlled
• end of the Reconstruction era
• Law making bodies in south move to enforce whites in power & marginalize blacks
Reconstruction Reversal
-Lost education: S. Democrats cut fundings for schools
-Lost voting rights: Laws required high poll taxes & to pass literacy tests designed for AA to fail
-Whites = excused because of "grandfather clause" - (man whose father/grandfather could vote before Jan 1st, 1867)
-Upheld by Supreme Court, did not deny vote to color
Jim Crow Laws 1877-1950s
-1877-1950s
-enforced racial segregation
-Some states mandated it of schools, places, transportation, restrooms, restaurants, drinking fountains
-Post reconstruction
Plessy vs. Ferguson (1896)
-AA argued violation of 14th amendment
-Homer Plessy = arrested for refusing JC laws
-Supreme court declared no violation
-Separate but equal
-AA always inferior, no one enforced equal
Buffalo soldiers
AA who served in the US army on the war of the Western frontier following the Civil War

Civil Rights Act (1964)
-outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin
-outlawed segregation