AH Chemistry - Inorganic Chemistry - (b) - Atomic Orbitals, Electronic Configurations, and the Periodic Table
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
How can the discrete lines observed in atomic spectra be explained?
The discrete lines observed in atomic spectra can be explained if electrons, like photons, also display the properties of both particles and waves.
How do electrons behave in an atom?
Electrons behave as standing (stationary) waves in an atom. These are waves that vibrate in time but do not move in space.
What are the different sizes and shapes of standing wave possible around the nucleus known as?
The different sizes and shapes of standing wave possible around the nucleus are known as orbitals.
What is the maximum number of electrons an orbital can hold?
Orbitals can hold a maximum of two electrons.
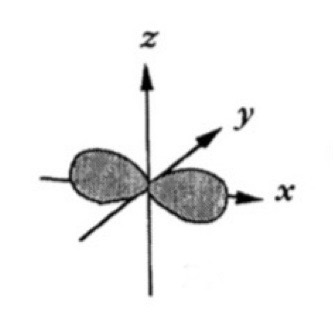
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is Px
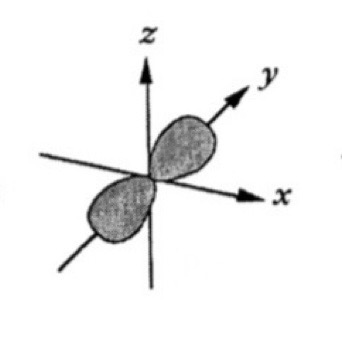
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is Py
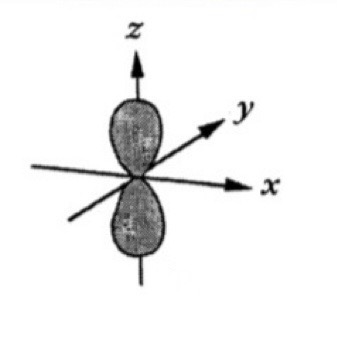
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is Pz
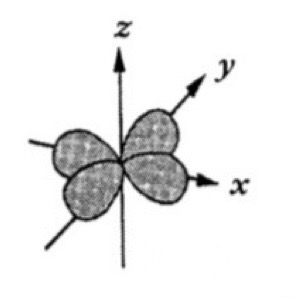
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is dx2-y2
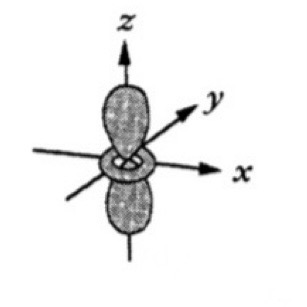
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is dx2
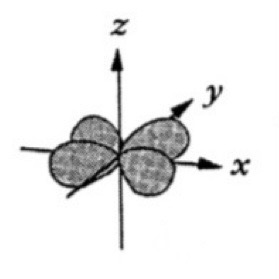
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is dxy
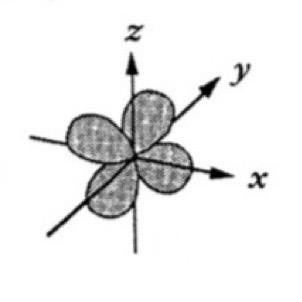
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is dyz
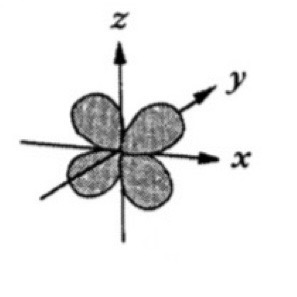
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is dxz
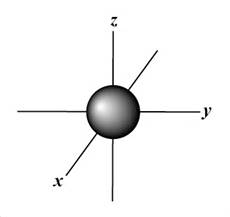
Which atomic orbital is this?
That is s
What do electrons within atoms have?
Electrons within atoms have fixed amounts of energy called quanta.
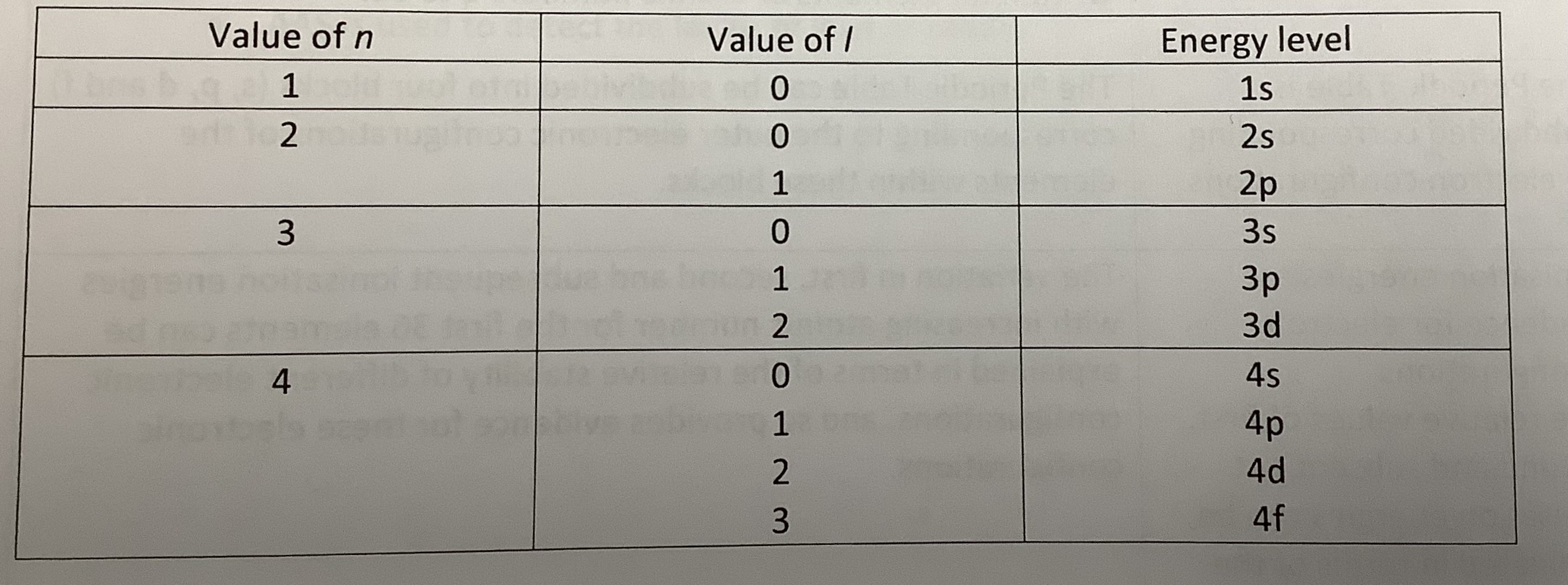
What are the four atomic numbers?
The four atomic numbers are:
n - Principal quantum number
l - Angular momentum quantum number
ml - Magnetic quantum number
ms - Spin magnetic quantum number
What is the principal quantum number?
The principal quantum number, n, is the quantum number that indicates the main energy level for an electron and is related to the size of the orbital.
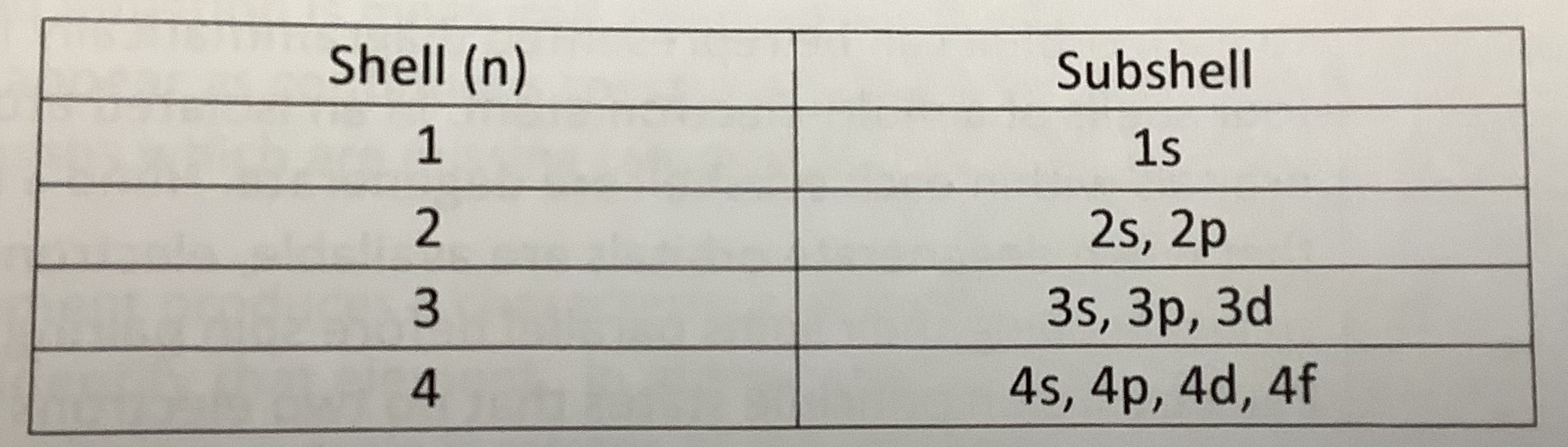

What is the angular momentum quantum number?
The angular momentum quantum number, l, is the quantum number that determines the shape of the subshell and can have values from zero to n-1
What is the magnetic quantum number?
The magnetic quantum number, ml, is the quantum number that determines the orientation of the orbital and can have values between -l and +l
What is the spin magnetic quantum number?
The spin magnetic quantum number, ms, is the quantum number that determines the direction of spin and can have values of +1/2 or -1/2.
What is the value of l for s orbitals?
The value of l for s orbitals is 0.
What is the value of l for p orbitals?
The value of l for p orbitals is 1.
What is the value of l for d orbitals?
The value of l for d orbitals is 2.
What is the l value for f orbitals?
The l value for f orbitals is 3.
What is the value of ml for s orbitals?
The value of ml for s orbitals is 0.
What is the value of ml for p orbitals?
The value of ml for p orbitals is -1,0, or +1
What is the value of ml for d orbitals?
The value of ml for d orbitals is -2, -1, 0, +1, or +2.
What is the value of ml for f orbitals?
The value of ml for f orbitals is -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, or +3.
What are electrons within atoms arranged according to?
Electrons within atoms are arranged according to:
The aufbau principle
Hund’s rule
The Pauli exclusion principle
What is the aufbau principle?
The aufbau principle is a principle that states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. Aufbau means building up in German.
What is Hund’s rule?
Hund’s rule is a rule that states that when degenerate orbitals are available, electrons fill each singly, keeping their spins parallel before spin pairing starts.
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
The Pauli exclusion principle is a principle that states that no two electrons can have the same set of four quantum numbers. Therefore, no orbital can hold more than two electrons and these two electrons must have opposite spins.
In an isolated atom, what are the orbitals within each subshell?
In an isolated atom, the orbitals within each subshell are degenerate.
What does degenerate mean?
Degenerate means of equal energy.
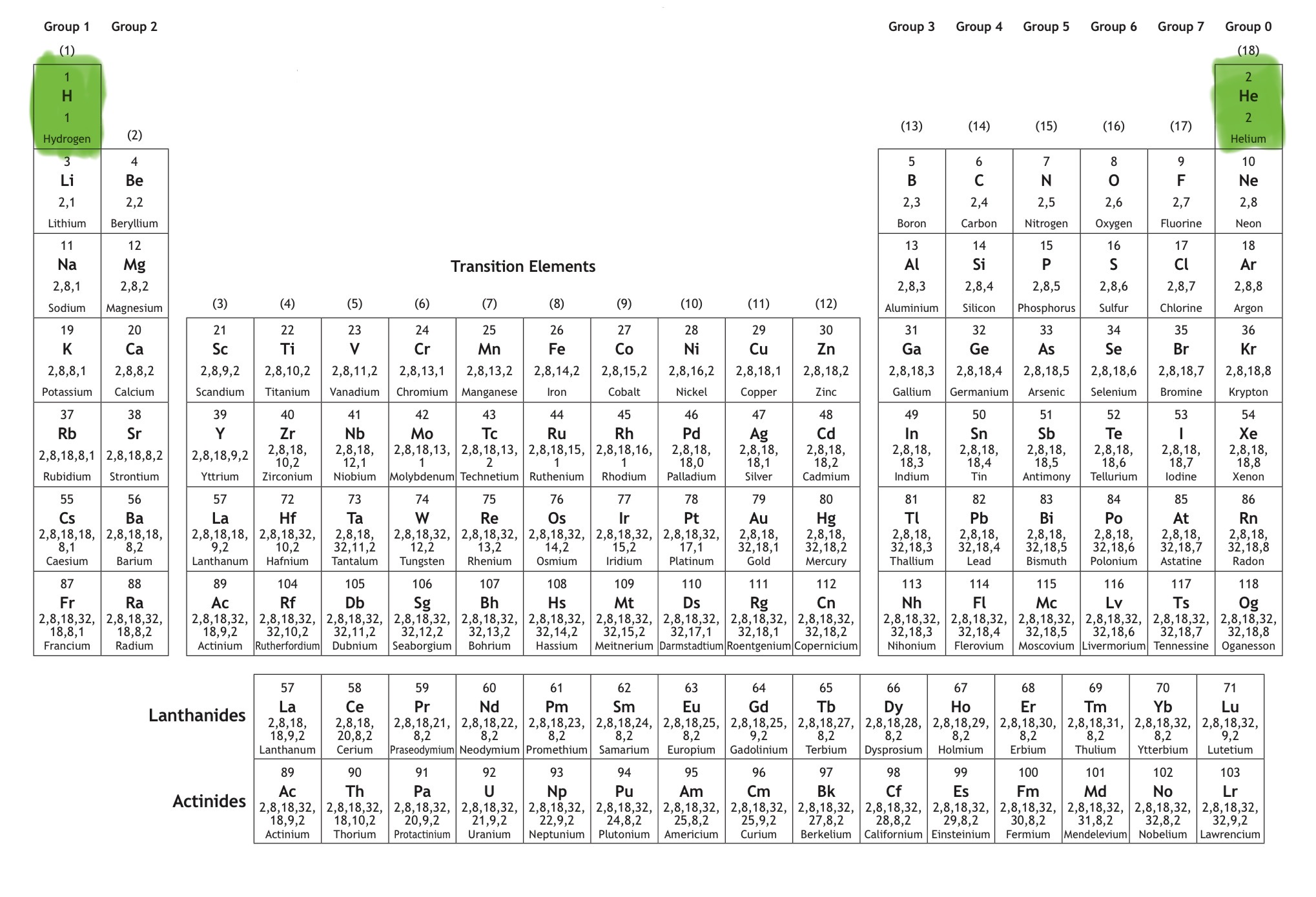
Which block is this?
That is s block
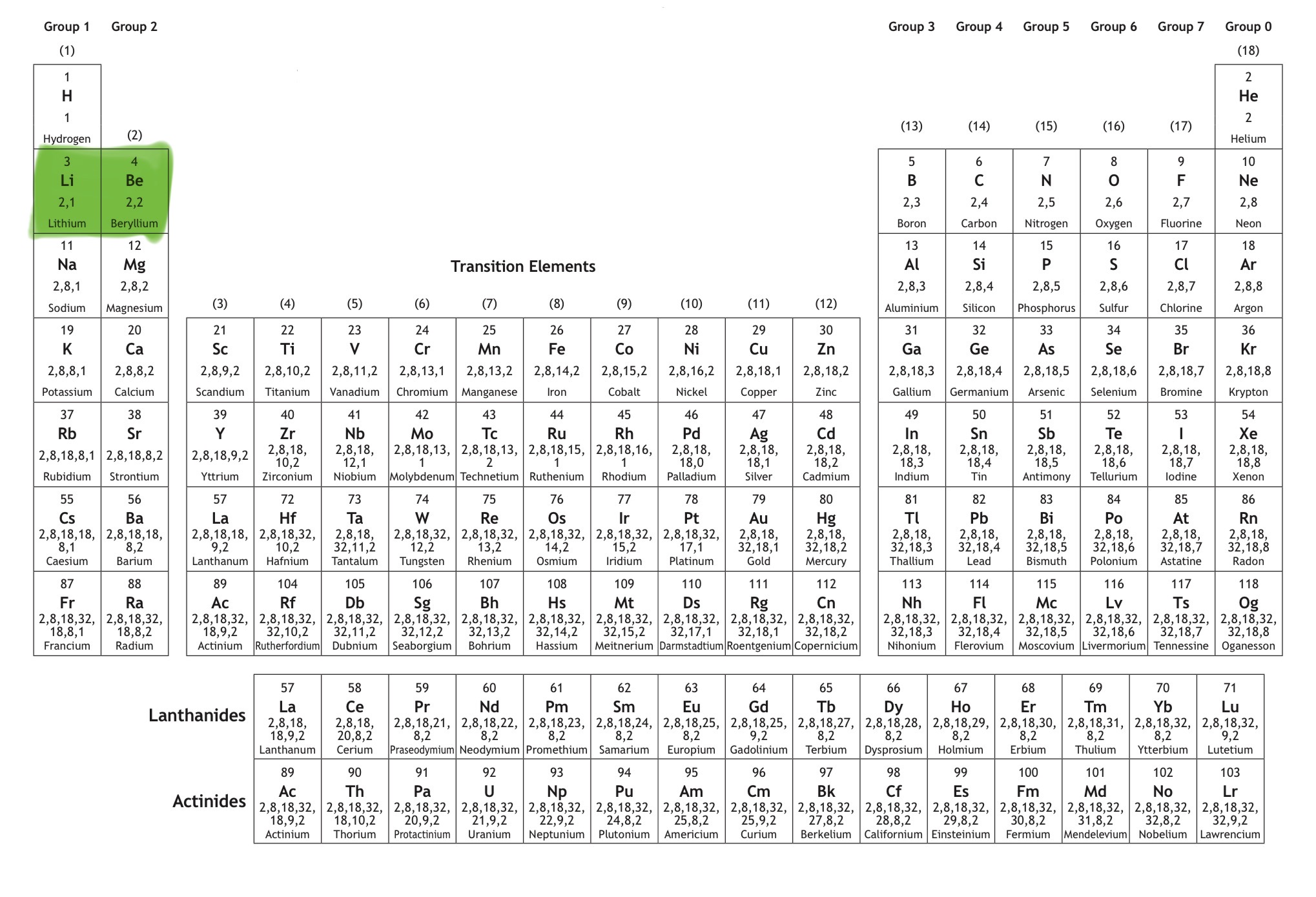
Which block is this?
That is p block.
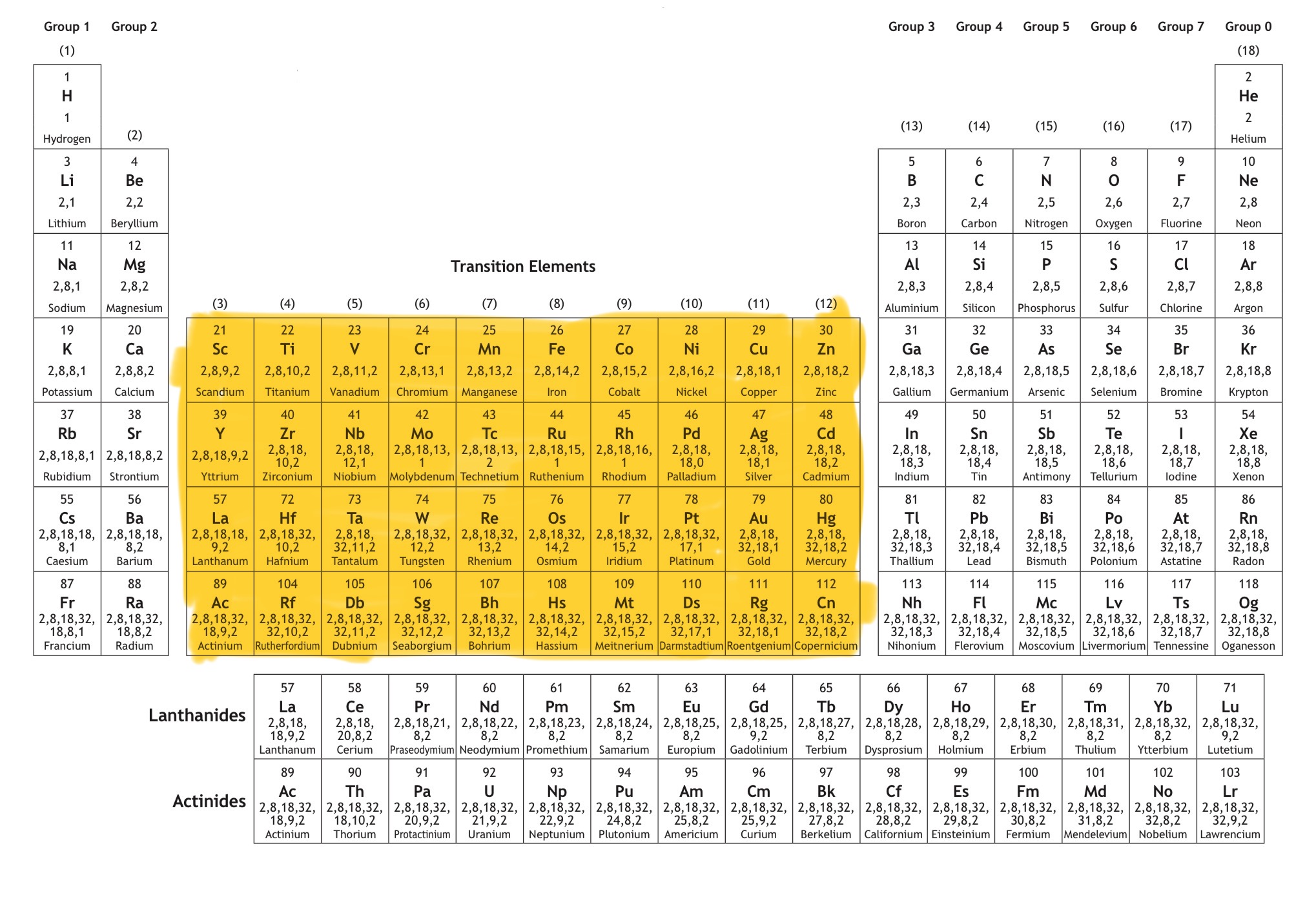
Which block is this?
That is d block.
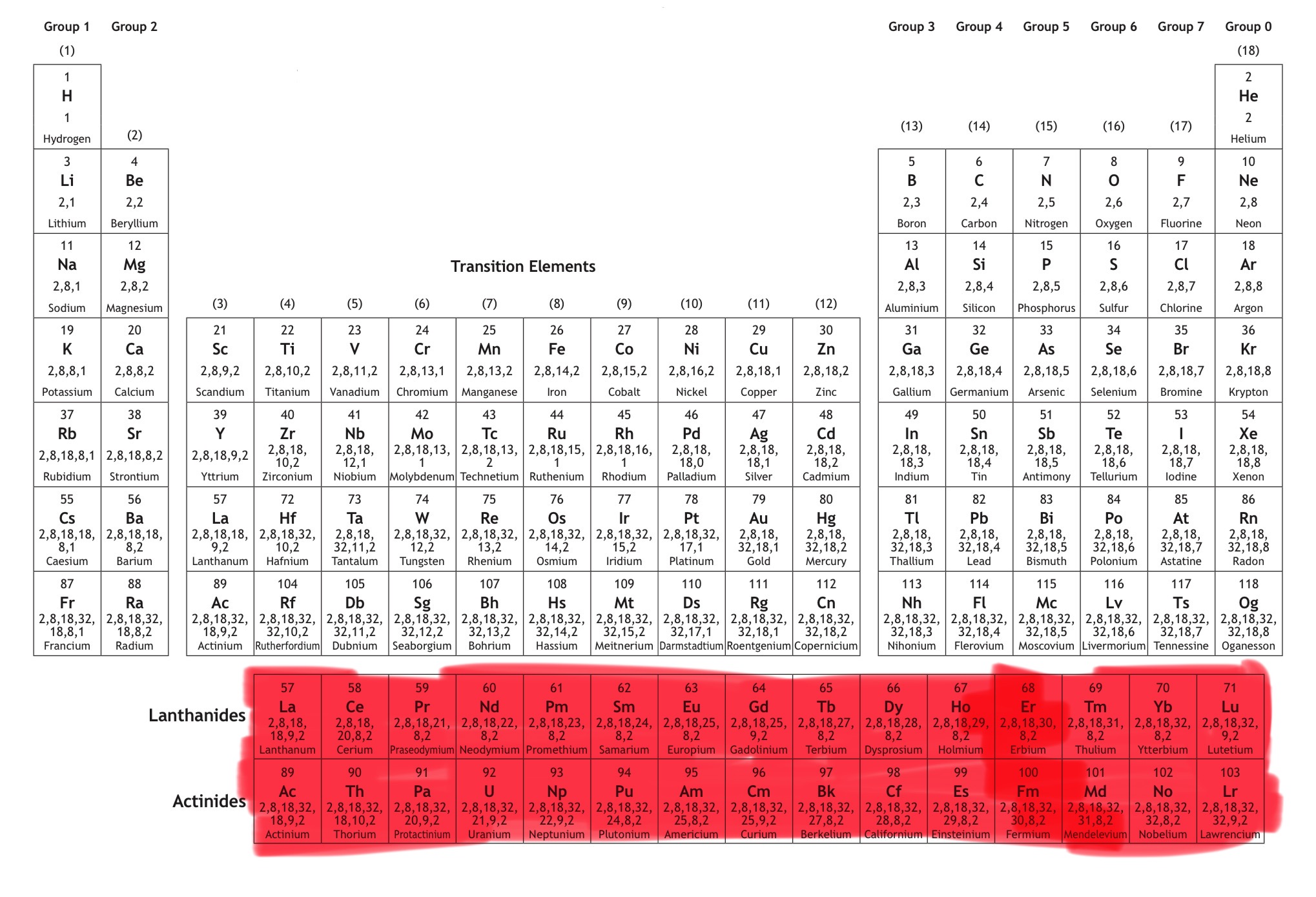
Which block is this?
That is f block.
Which orbital is this?
That is 1s
Which orbital is this?
That is 2s
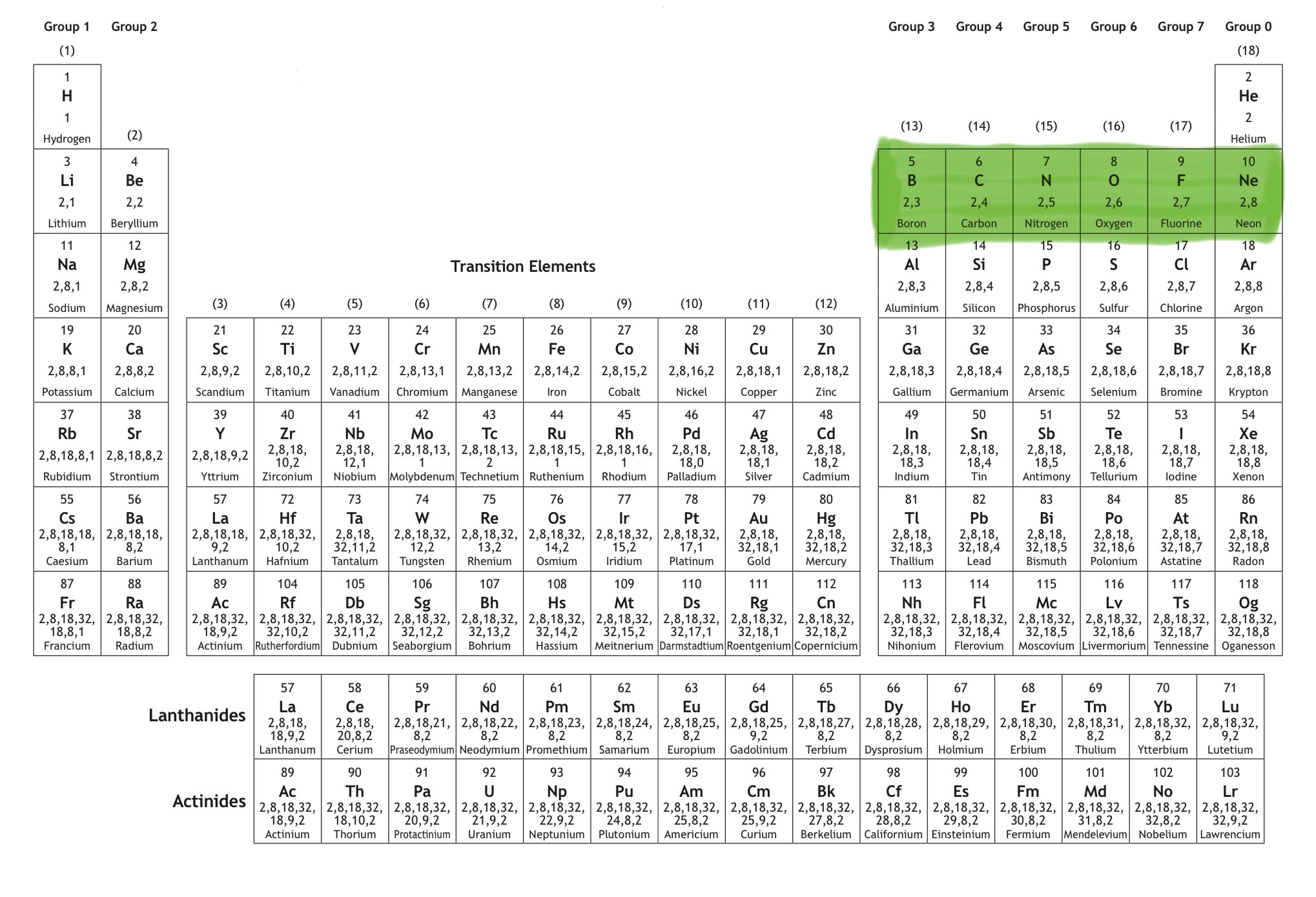
Which orbital is this?
That is 2p
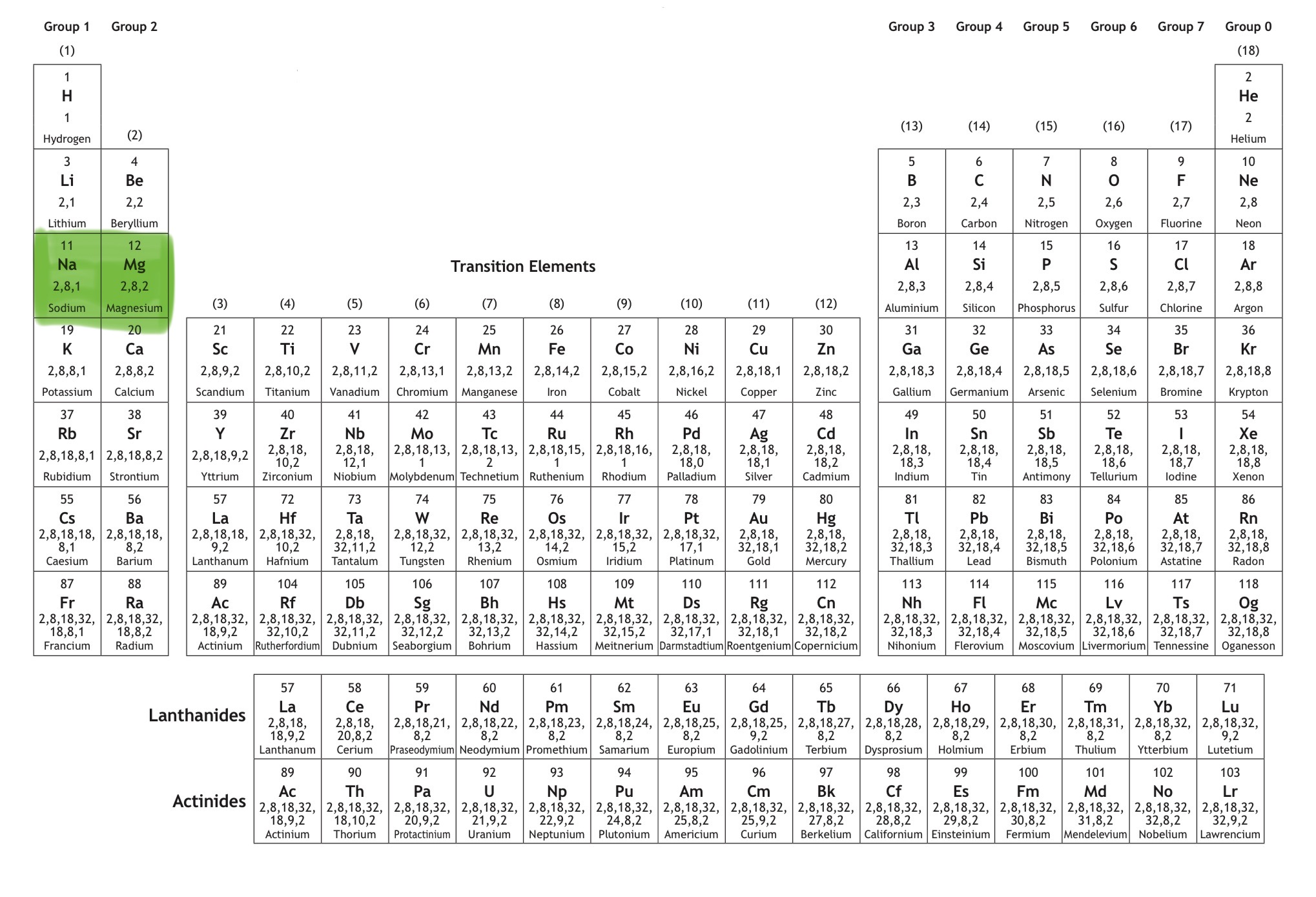
Which orbital is this?
That is 3s
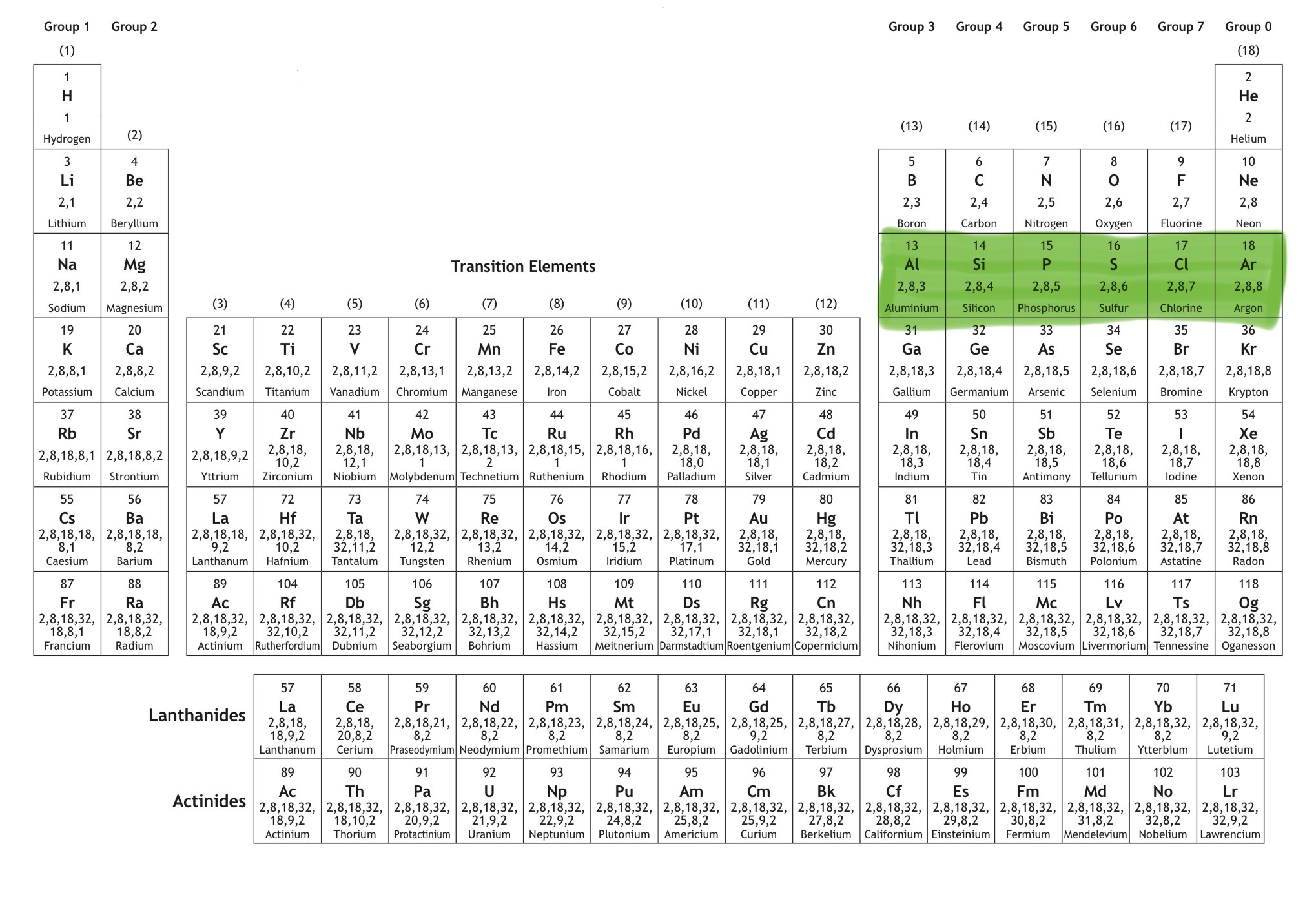
Which orbital is this?
That is 3p
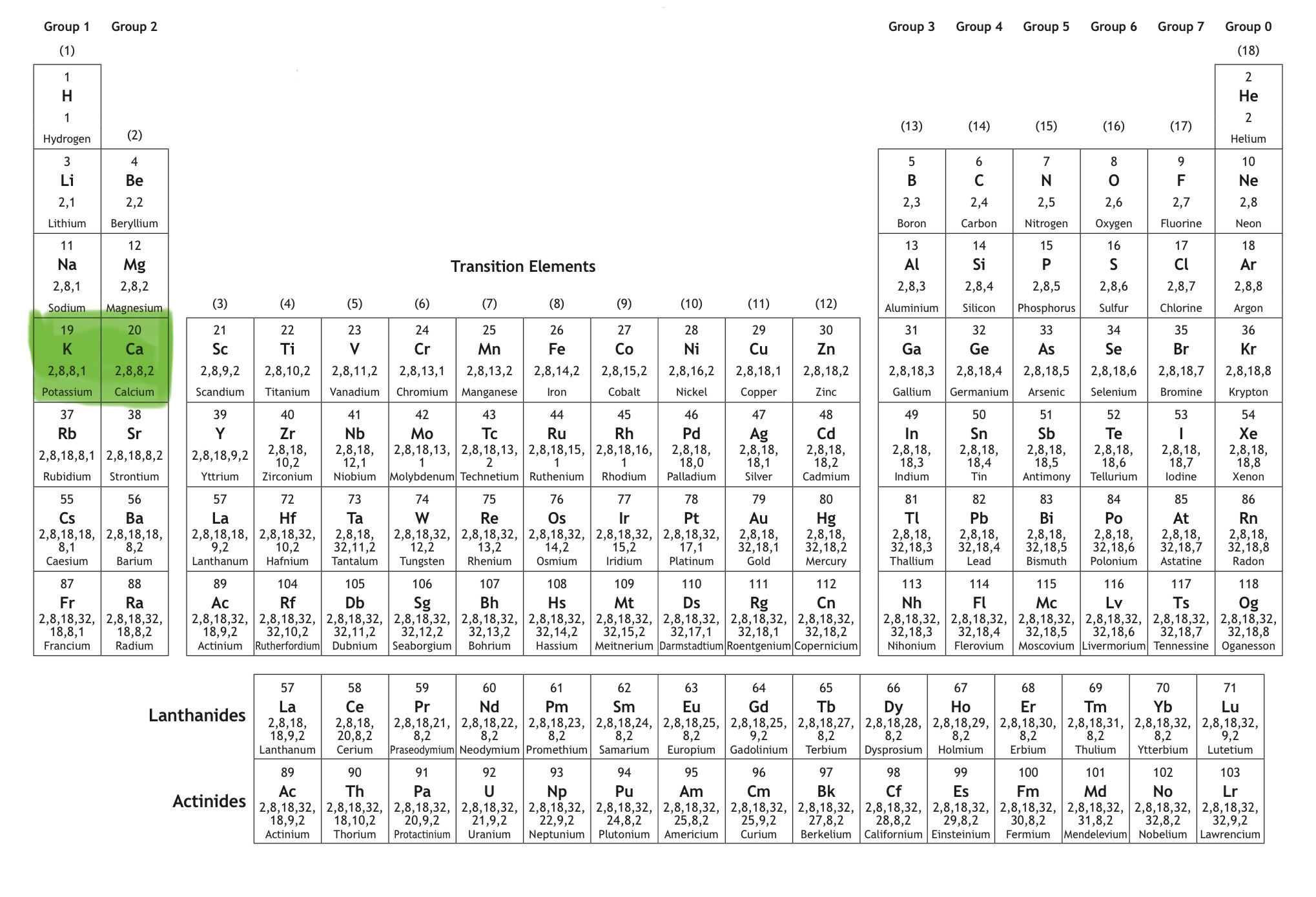
Which orbital is this?
That is 4s
Which orbital is this?
That is 3d.
Which orbital is this?
That is 4p.
What order do orbitals normally fill in from 1s to 4p.
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p
How can the variation in the first, second, and subsequent ionisation energies with increasing atomic number for the first 36 elements be explained by?
The variation in the first, second, and subsequent ionisation energies with increasing atomic number for the first 36 elements can be explained in terms of relative stability of different electron configurations. This provides evidence for these electronic configurations.
How can anomalies in trends of ionisation energy be explained?
Anomalies in the trends of ionisation energies can be explained by considering the electronic configurations.
What is there a special stability associated with?
There is a special stability associated with half-filled and full subshells. The more stable the electronic configuration, the higher the ionisation energy.
What can be used to predict the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions?
VSEPR, Valence Shell Electron Pair Replusion, theory can be used to predict the shapes of molecules and polyatomic ions.
How can the number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom be found?
The number of electron pairs surrounding a central atom can be found using the equation:
In a polyatomic atom, an electron must be added for each negative charge or removed for each positive charge.
CHECK IF DIFF EQUATION IS NEEDED FOR DIFF ATOMS or molecules
What characteristic do electron pairs have and what do they do as a result of this?
Electron pairs are negatively charged and repel eachother.
How are electron pairs arranged?
Electron pairs are arranged to minimise repulsion and maximise separation.
What is the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom if the central atom has two electron pairs?
The arrangement of electrons pairs around a central atom if the central atom has two electron pairs is linear.
What is the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom if the central atom has three electron pairs?
The arrangement of electrons pairs around a central atom if the central atom has three electron pairs is trigonal planar.
What is the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom if the central atom has four electron pairs?
The arrangement of electrons pairs around a central atom if the central atom has four electron pairs is tetrahedral.
What is the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom if the central atom has five electron pairs?
The arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom of the central atom has five electron pairs is trigonal bipyramidal.
What is the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom if the central atom has six electron pairs?
The arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom if the central atom has six electron pairs is octahedral.
What are shapes of molecules or polyatomic ions determined by?
Shapes of molecules or polyatomic ions are determined by the shapes adopted by the atoms present based on the arrangement of electron pairs.
What is the strength of electron pair repulsions in order of decreasing strength?
The strength of electron pair repulsions in order of decreasing strength is:
Non-bonding pair/non-bonding pair > non-bonding pair/bonding pair > bonding pair/bonding pair.
What do different strengths of electron pair repulsion account for?
Different strengths of electron pair repulsion account for slight deviations from expected bond angles in molecules such as NH3 and H2O.